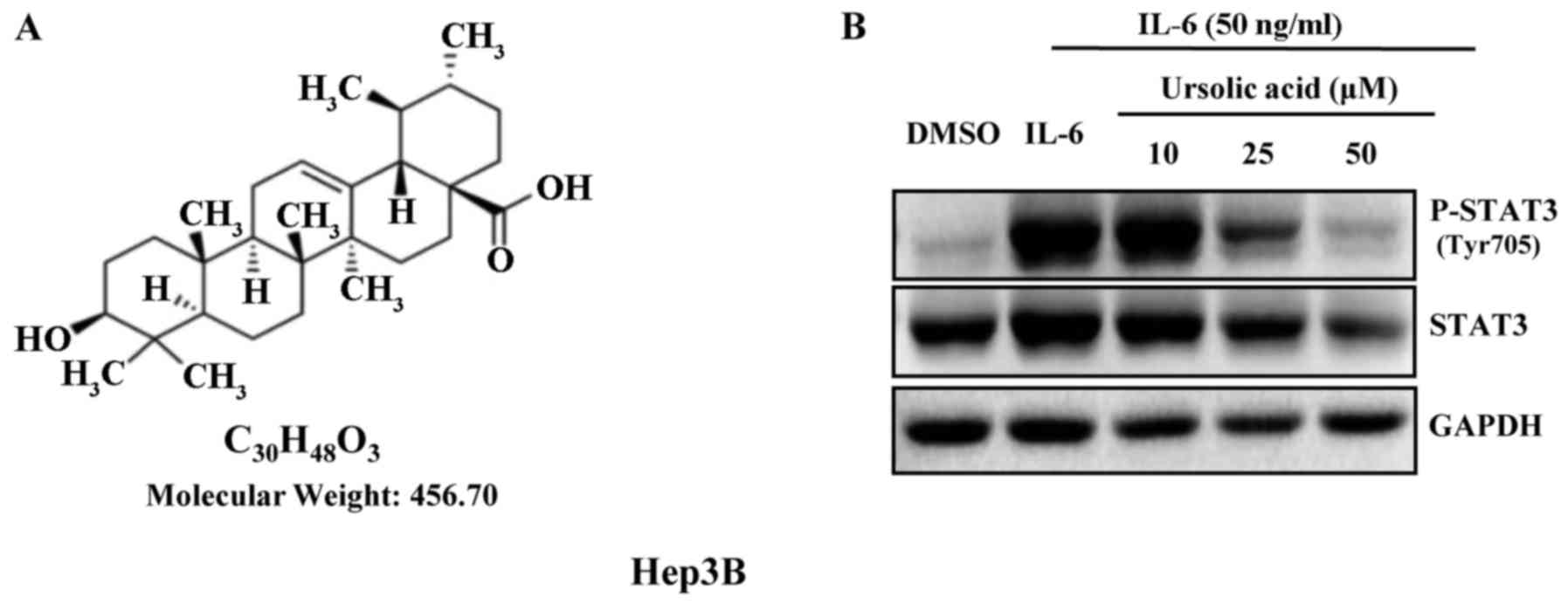
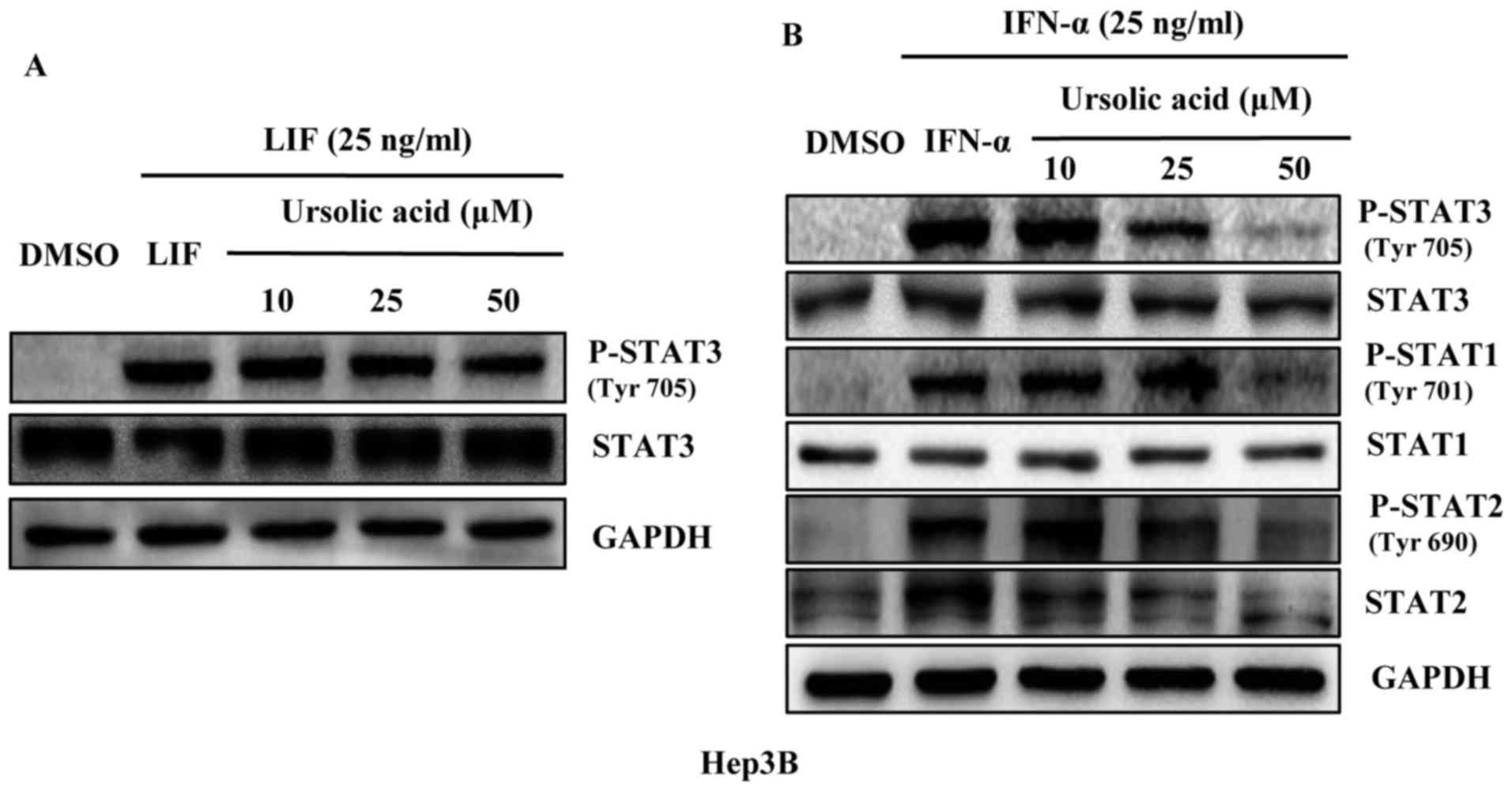
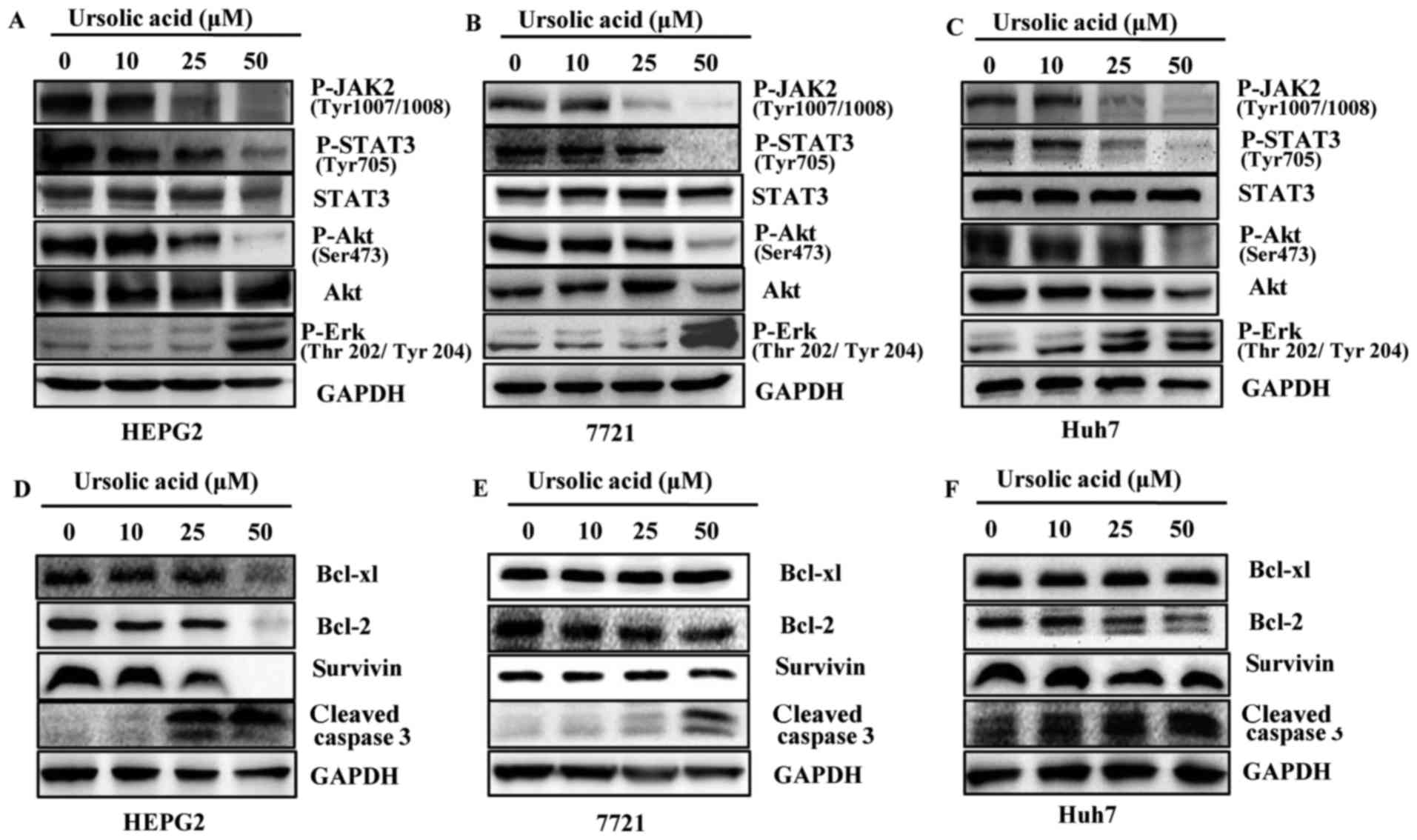
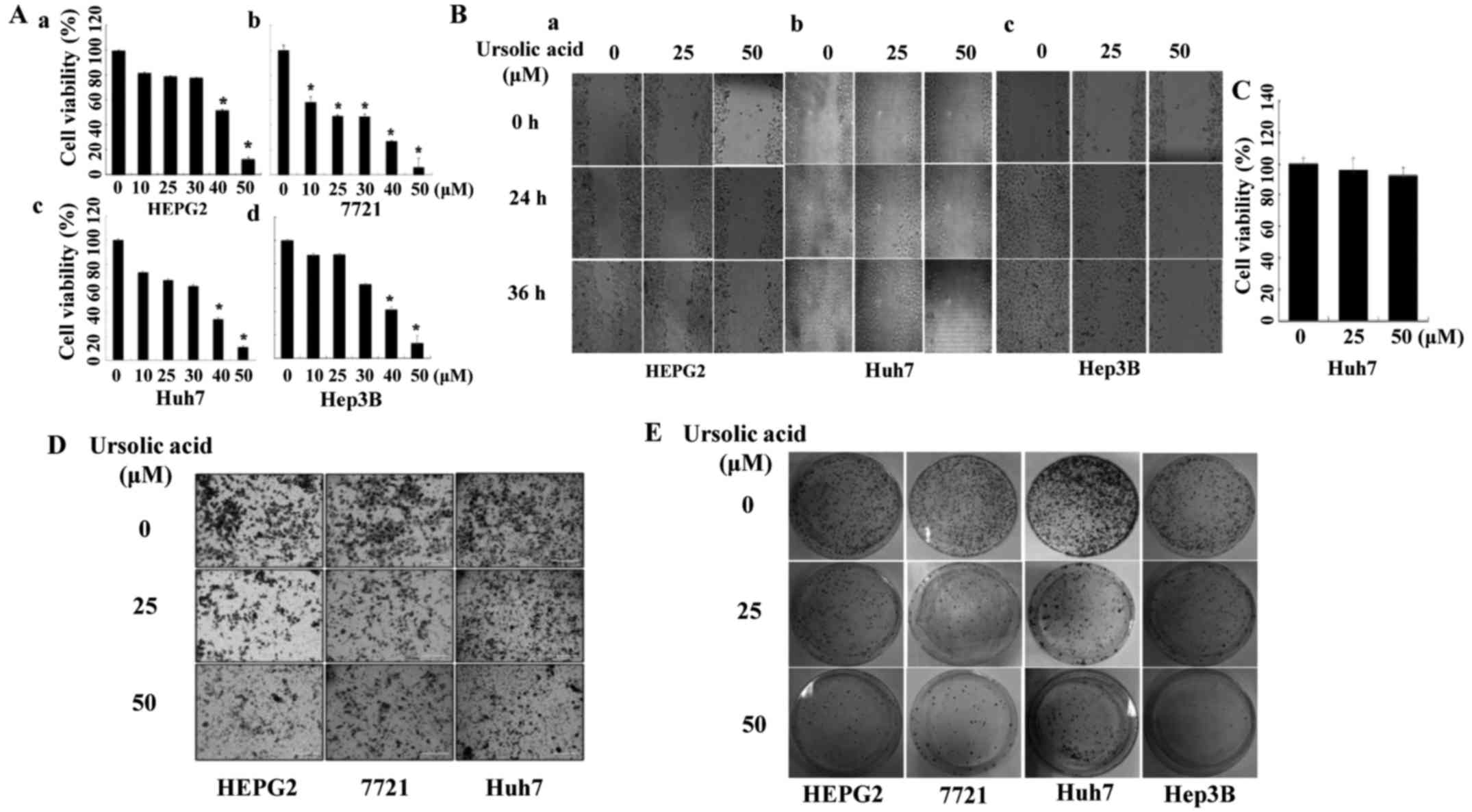
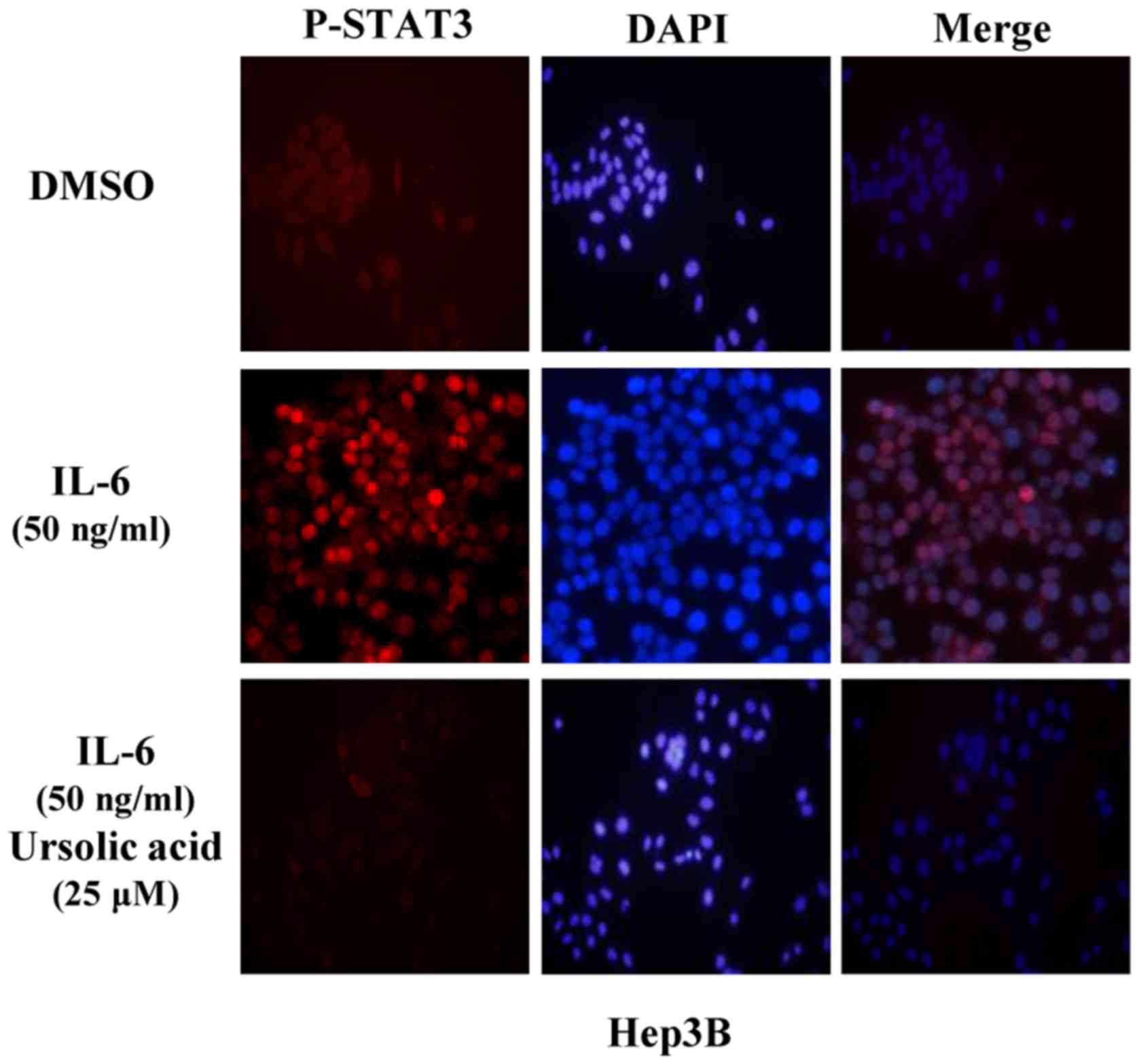
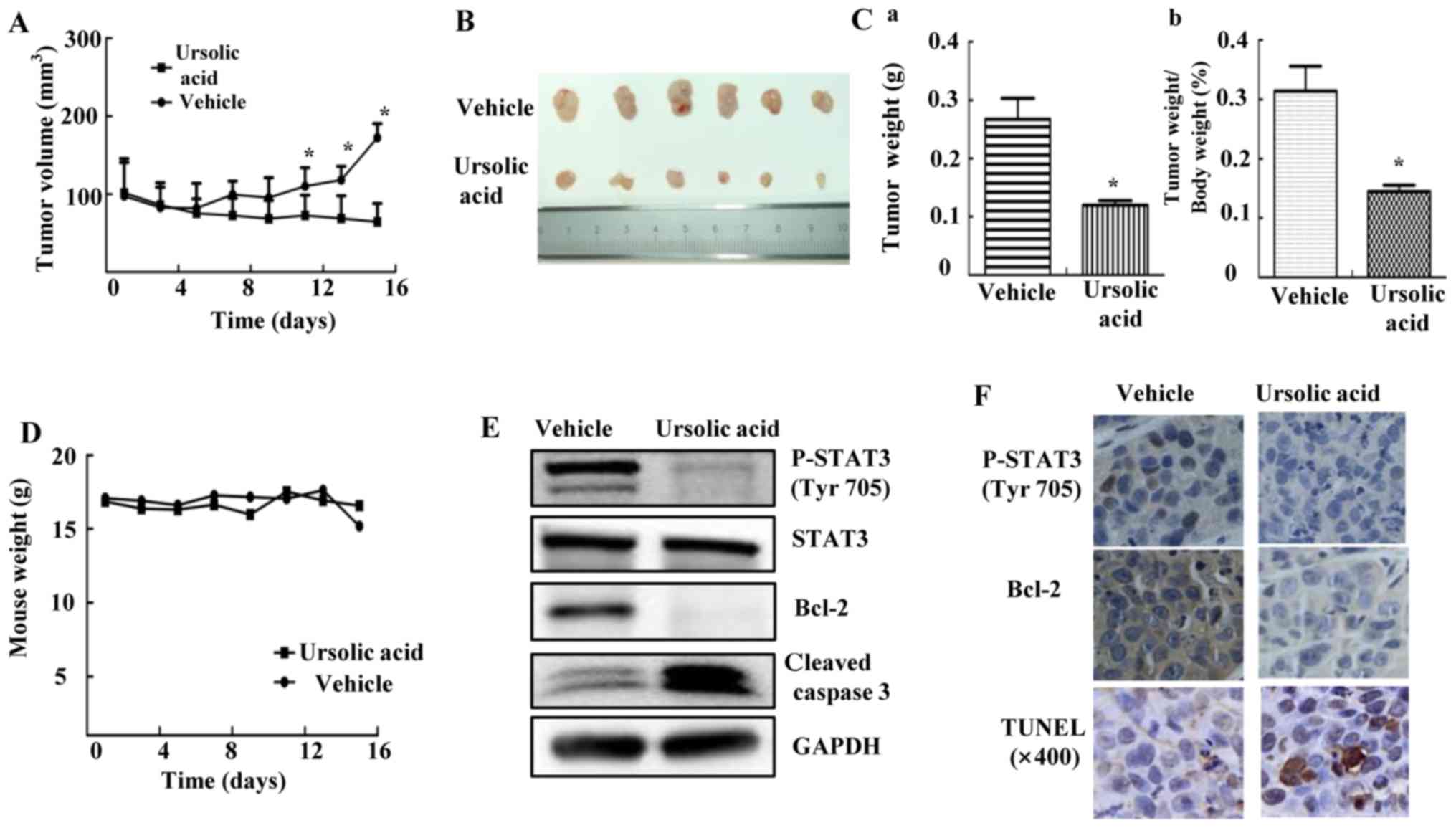
|
1
|
Wang R, Chen XZ, Zhang MG, Tang L and Wu
H: Incidence and mortality of liver cancer in mainland China:
Changes in first decade of 21st century. Hepatogastroenterology.
62:118–121. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buettner R, Mora LB and Jove R: Activated
STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for
therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 8:945–954.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, Li
F, Nachiyappan A, Dai X, Swamy SN, Ahn KS, Kumar AP, Tan BK, et al:
Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription
(STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1835:46–60. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Chevalier S, Fourcin M, Robledo O,
Wijdenes J, Pouplard-Barthelaix A and Gascan H: Interleukin-6
family of cytokines induced activation of different functional
sites expressed by gp130 transducing protein. J Biol Chem.
271:14764–14772. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hermanns HM, Radtke S, Haan C, Schmitz-Van
de Leur H, Tavernier J, Heinrich PC and Behrmann I: Contributions
of leukemia inhibitory factor receptor and oncostatin M receptor to
signal transduction in heterodimeric complexes with glycoprotein
130. J Immunol. 163:6651–6658. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Jia D, Duan F, Sun Z, Liu X, Zhou
L, Sun L, Ren S, Ruan Y and Gu J: Combined anti-tumor effects of
IFN-α and sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in
vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 422:687–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ataseven H, Bahcecioglu IH, Kuzu N, Yalniz
M, Celebi S, Erensoy A and Ustundag B: The levels of ghrelin,
leptin, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular
carcinoma due to HBV and HDV infection. Mediators Inflamm.
2006:783802006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song B, Zhan H, Bian Q and Gu J:
Piperlongumine inhibits gastric cancer cells via suppression of the
JAK1,2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:4475–4480.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Lai KB,
Lee CN and Hsieh CY: Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth
by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene.
22:1517–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin L, Hutzen B, Li PK, Ball S, Zuo M,
DeAngelis S, Foust E, Sobo M, Friedman L, Bhasin D, et al: A novel
small molecule, LLL12, inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and
activities and exhibits potent growth-suppressive activity in human
cancer cells. Neoplasia. 12:39–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mohan CD, Bharathkumar H, Bulusu KC,
Pandey V, Rangappa S, Fuchs JE, Shanmugam MK, Dai X, Li F,
Deivasigamani A, et al: Development of a novel azaspirane that
targets the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of
transcription (STAT) pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro
and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 289:34296–34307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pathak AK, Bhutani M, Nair AS, Ahn KS,
Chakraborty A, Kadara H, Guha S, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB: Ursolic
acid inhibits STAT3 activation pathway leading to suppression of
proliferation and chemosensitization of human multiple myeloma
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 5:943–955. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang W, Zhao C, Jou D, Lü J, Zhang C, Lin
L and Lin J: Ursolic acid inhibits the growth of colon
cancer-initiating cells by targeting STAT3. Anticancer Res.
33:4279–4284. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heo TH, Wahler J and Suh N: Potential
therapeutic implications of IL-6/IL-6R/gp130-targeting agents in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:15460–15473. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Gupta SC,
Tyagi AK and Aggarwal BB: Ursolic acid inhibits the growth of human
pancreatic cancer and enhances the antitumor potential of
gemcitabine in an orthotopic mouse model through suppression of the
inflammatory microenvironment. Oncotarget. 7:13182–13196.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F, Nema T,
Vali S, Abbasi T, Kapoor S, Sharma A, Kumar AP, Ho PC, et al:
Ursolic acid inhibits multiple cell survival pathways leading to
suppression of growth of prostate cancer xenograft in nude mice. J
Mol Med (Berl). 89:713–727. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kawano M, Hirano T, Matsuda T, Taga T,
Horii Y, Iwato K, Asaoku H, Tang B, Tanabe O, Tanaka H, et al:
Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human
multiple myelomas. Nature. 332:83–85. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang JF, He ML, Fu WM, Wang H, Chen LZ,
Zhu X, Chen Y, Xie D, Lai P, Chen G, et al: Primate-specific
microRNA-637 inhibits tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by
disrupting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
signaling. Hepatology. 54:2137–2148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li T, Dong ZR, Guo ZY, Wang CH, Tang ZY,
Qu SF, Chen ZT, Li XW and Zhi XT: Aspirin enhances IFN-α-induced
growth inhibition and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
JAK1/STAT1 pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 20:366–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Testoni B, Schinzari V, Guerrieri F,
Gerbal-Chaloin S, Blandino G and Levrero M: p53-paralog DNp73
oncogene is repressed by IFNα/STAT2 through the recruitment of the
Ezh2 polycomb group transcriptional repressor. Oncogene.
30:2670–2678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wan S, Zhao E, Kryczek I, Vatan L,
Sadovskaya A, Ludema G, Simeone DM, Zou W and Welling TH:
Tumor-associated macrophages produce interleukin 6 and signal via
STAT3 to promote expansion of human hepatocellular carcinoma stem
cells. Gastroenterology. 147:1393–1404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Liu K, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhang F, Yang H,
Liu J, Pan T, Chen J, Wu M, et al: Exosomes mediate the
cell-to-cell transmission of IFN-α-induced antiviral activity. Nat
Immunol. 14:793–803. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR and Cantley LC: PI3K:
Downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 88:435–437. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|