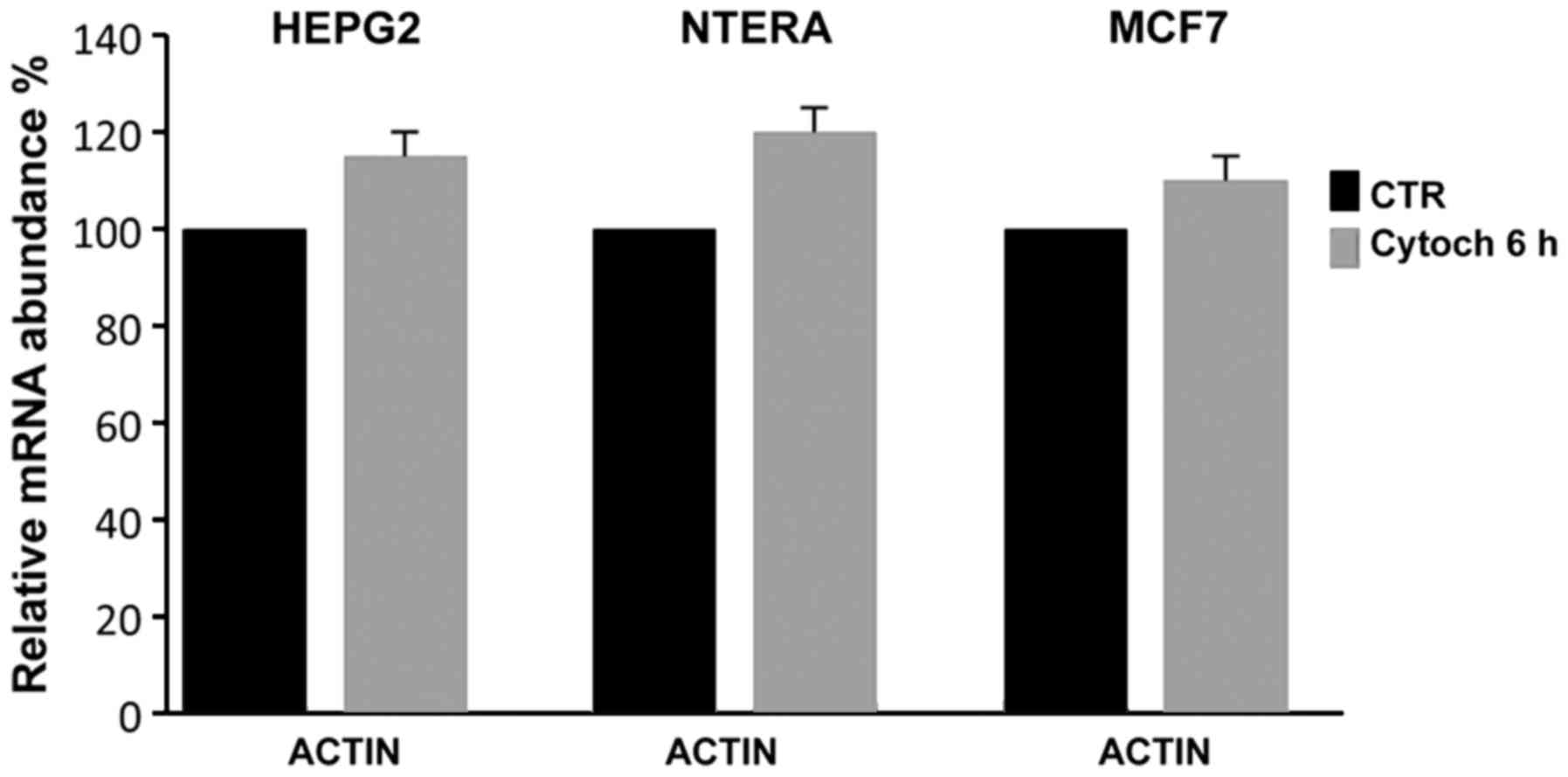
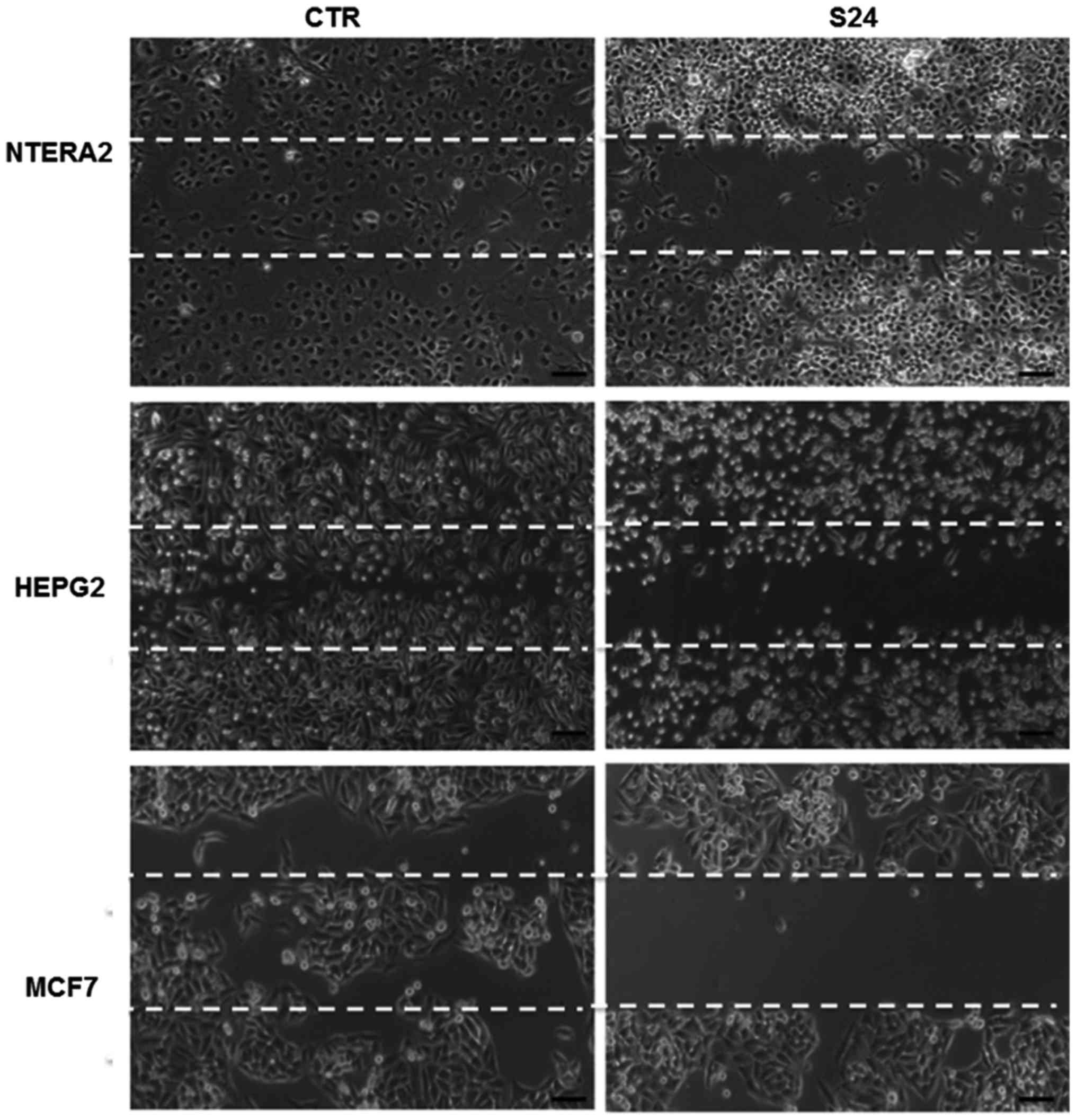
|
1
|
Spampanato C, De Maria S, Sarnataro M,
Giordano E, Zanfardino M, Baiano S, Cartenì M and Morelli F:
Simvastatin inhibits cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis
correlated to activation of Bax and down-regulation of BCL-2 gene
expression. Int J Oncol. 40:935–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zanfardino M, Spampanato C, De Cicco R,
Buommino E, De Filippis A, Baiano S, Barra A and Morelli F:
Simvastatin reduces melanoma progression in a murine model. Int J
Oncol. 43:1763–1770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liao JK and Laufs U: Pleiotropic effects
of statins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 45:89–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
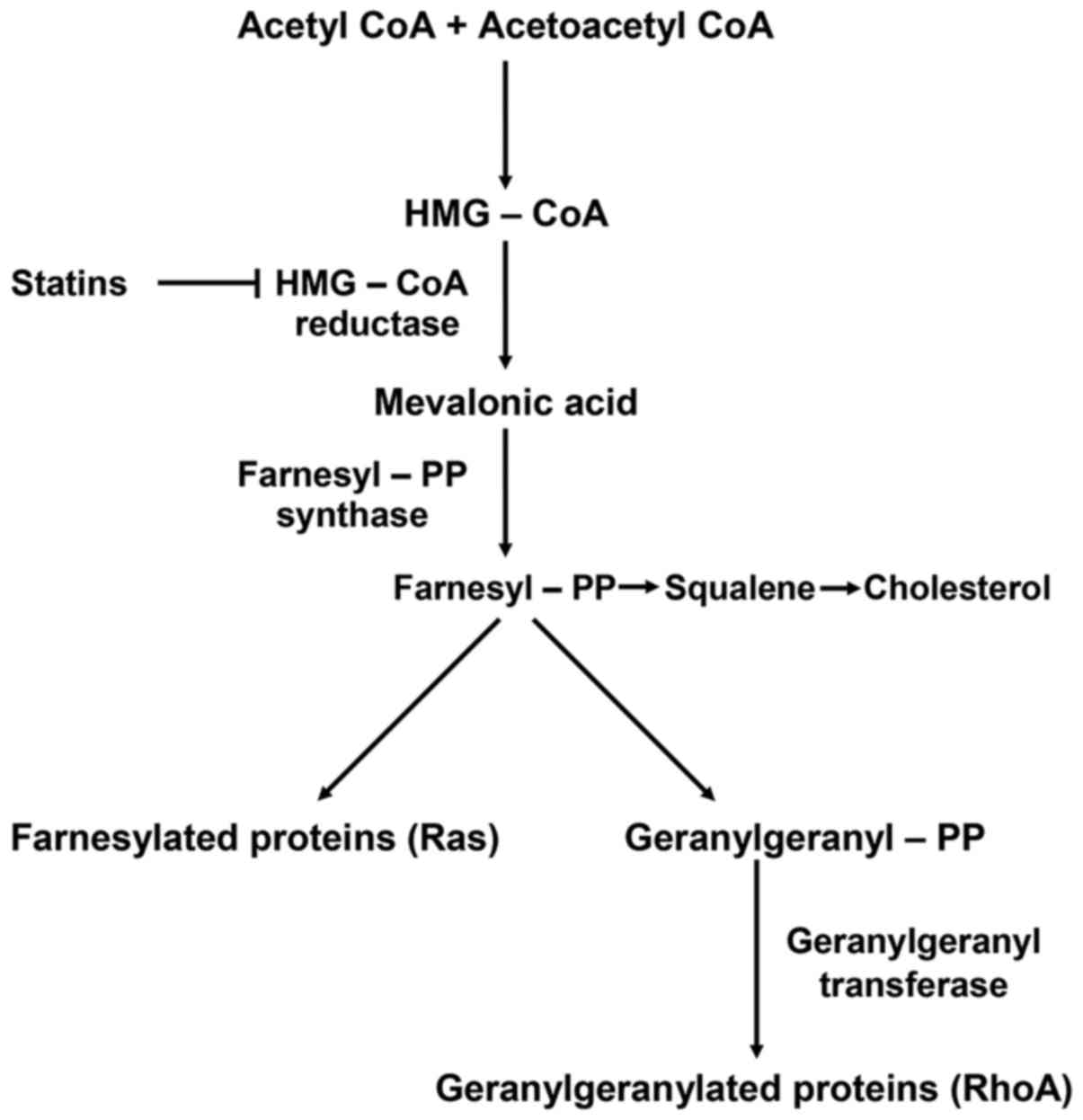
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Regulation of
the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343:425–430. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee MH, Cho YS and Han YM: Simvastatin
suppresses self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells by inhibiting
RhoA geranylgeranylation. Stem Cells. 25:1654–1663. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sorrentino G, Ruggeri N, Specchia V,
Cordenonsi M, Mano M, Dupont S, Manfrin A, Ingallina E, Sommaggio
R, Piazza S, et al: Metabolic control of YAP and TAZ by the
mevalonate pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 16:357–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang S and Cui W: Sox2, a key factor in
the regulation of pluripotency and neural differentiation. World J
Stem Cells. 6:305–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, Johnstone SE,
Levine SS, Zucker JP, Guenther MG, Kumar RM, Murray HL, Jenner RG,
et al: Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 122:947–956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega
VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, et al: Integration of
external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network
in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 133:1106–1117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loh KM and Lim B: A precarious balance:
Pluripotency factors as lineage specifiers. Cell Stem Cell.
8:363–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thomson M, Liu SJ, Zou LN, Smith Z,
Meissner A and Ramanathan S: Pluripotency factors in embryonic stem
cells regulate differentiation into germ layers. Cell. 145:875–889.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Askarian-Amiri ME, Seyfoddin V, Smart CE,
Wang J, Kim JE, Hansji H, Baguley BC, Finlay GJ and Leung EY:
Emerging role of long non-coding RNA SOX2OT in SOX2 regulation in
breast cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1021402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bowles J, Schepers G and Koopman P:
Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors
based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev Biol. 227:239–255.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilson M and Koopman P: Matching SOX:
Partner proteins and co-factors of the SOX family of
transcriptional regulators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 12:441–446. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kamachi Y, Uchikawa M and Kondoh H:
Pairing SOX off: With partners in the regulation of embryonic
development. Trends Genet. 16:182–187. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ambrosetti DC, Schöler HR, Dailey L and
Basilico C: Modulation of the activity of multiple transcriptional
activation domains by the DNA binding domains mediates the
synergistic action of Sox2 and Oct-3 on the fibroblast growth
factor-4 enhancer. J Biol Chem. 275:23387–23397. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, Vega VB, Zhang W,
Chen X, Bourque G, George J, Leong B, Liu J, et al: The Oct4 and
Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse
embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 38:431–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tomioka M, Nishimoto M, Miyagi S,
Katayanagi T, Fukui N, Niwa H, Muramatsu M and Okuda A:
Identification of Sox-2 regulatory region which is under the
control of Oct-3/4-Sox-2 complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:3202–3213.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jauch R, Aksoy I, Hutchins AP, Ng CK, Tian
XF, Chen J, Palasingam P, Robson P, Stanton LW and Kolatkar PR:
Conversion of Sox17 into a pluripotency reprogramming factor by
reengineering its association with Oct4 on DNA. Stem Cells.
29:940–951. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Loh KM and Lim B: A precarious balance:
Pluripotency factors as lineage specifiers. Cell Stem Cell.
8:363–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Oron E, Nelson B, Razis S and
Ivanova N: Distinct lineage specification roles for NANOG, OCT4,
and SOX2 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 10:440–454.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K,
Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Okita K, Mochiduki Y, Takizawa N
and Yamanaka S: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol.
26:101–106. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huangfu D, Osafune K, Maehr R, Guo W,
Eijkelenboom A, Chen S, Muhlestein W and Melton DA: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts with only
Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1269–1275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okita K, Ichisaka T and Yamanaka S:
Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells.
Nature. 448:313–317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alonso MM, Diez-Valle R, Manterola L,
Rubio A, Liu D, Cortes-Santiago N, Urquiza L, Jauregi P, Lopez de
Munain A, Sampron N, et al: Genetic and epigenetic modifications of
Sox2 contribute to the invasive phenotype of malignant gliomas.
PLoS One. 6:e267402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Basu-Roy U, Seo E, Ramanathapuram L, Rapp
TB, Perry JA, Orkin SH, Mansukhani A and Basilico C: Sox2 maintains
self renewal of tumor-initiating cells in osteosarcomas. Oncogene.
31:2270–2282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Shi L, Zhang L, Li R, Liang J, Yu
W, Sun L, Yang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al: The molecular mechanism
governing the oncogenic potential of SOX2 in breast cancer. J Biol
Chem. 283:17969–17978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cox JL, Wilder PJ, Desler M and Rizzino A:
Elevating SOX2 levels deleteriously affects the growth of
medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 7:e440872012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Girouard SD, Laga AC, Mihm MC, Scolyer RA,
Thompson JF, Zhan Q, Widlund HR, Lee CW and Murphy GF: SOX2
contributes to melanoma cell invasion. Lab Invest. 92:362–370.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Leis O, Eguiara A, Lopez-Arribillaga E,
Alberdi MJ, Hernandez-Garcia S, Elorriaga K, Pandiella A, Rezola R
and Martin AG: Sox2 expression in breast tumours and activation in
breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 31:1354–1365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, Neubauer H,
Scheble V, Müller F, Schneider F, Petersen K, Wallwiener D, Kanz L,
et al: Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in
early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:42–52. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li XL, Eishi Y, Bai YQ, Sakai H, Akiyama
Y, Tani M, Takizawa T, Koike M and Yuasa Y: Expression of the
SRY-related HMG box protein SOX2 in human gastric carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 24:257–263. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sanada Y, Yoshida K, Ohara M, Oeda M,
Konishi K and Tsutani Y: Histopathologic evaluation of stepwise
progression of pancreatic carcinoma with immunohistochemical
analysis of gastric epithelial transcription factor SOX2:
Comparison of expression patterns between invasive components and
cancerous or nonneoplastic intraductal components. Pancreas.
32:164–170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sattler HP, Lensch R, Rohde V, Zimmer E,
Meese E, Bonkhoff H, Retz M, Zwergel T, Bex A, Stoeckle M, et al:
Novel amplification unit at chromosome 3q25-q27 in human prostate
cancer. Prostate. 45:207–215. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Seo E, Basu-Roy U, Zavadil J, Basilico C
and Mansukhani A: Distinct functions of Sox2 control self-renewal
and differentiation in the osteoblast lineage. Mol Cell Biol.
31:4593–4608. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, Ge R,
Bell GW, Regev A and Weinberg RA: An embryonic stem cell-like gene
expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human
tumors. Nat Genet. 40:499–507. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Sarrio D,
Moreno-Bueno G, Rodriguez-Gil Y, Martinez MA, Hernandez L,
Hardisson D, Reis-Filho JS and Palacios J: Sox2: A possible driver
of the basal-like phenotype in sporadic breast cancer. Mod Pathol.
20:474–481. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, Neubauer H,
Scheble V, Müller F, Schneider F, Petersen K, Wallwiener D, Kanz L,
et al: Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in
early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:42–52. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Leis O, Eguiara A, Lopez-Arribillaga E,
Alberdi MJ, Hernandez-Garcia S, Elorriaga K, Pandiella A, Rezola R
and Martin AG: Sox2 expression in breast tumours and activation in
breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 31:1354–1365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Basu-Roy U, Bayin NS, Rattanakorn K, Han
E, Placantonakis DG, Mansukhani A and Basilico C: Sox2 antagonizes
the Hippo pathway to maintain stemness in cancer cells. Nat Commun.
6:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li X, Xu Y, Chen Y, Chen S, Jia X, Sun T,
Liu Y, Li X, Xiang R and Li N: SOX2 promotes tumor metastasis by
stimulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via regulation of
WNT/β-catenin signal network. Cancer Lett. 336:379–389. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen Y, Shi L, Zhang L, Li R, Liang J, Yu
W, Sun L, Yang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al: The molecular mechanism
governing the oncogenic potential of SOX2 in breast cancer. J Biol
Chem. 283:17969–17978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, Yokoe T,
Okugawa Y, Ioue Y, Miki C and Kusunoki M: Correlation of CD133,
OCT4, and SOX2 in rectal cancer and their association with distant
recurrence after chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3488–3498.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jia X, Li X, Xu Y, Zhang S, Mou W, Liu Y,
Liu Y, Lv D, Liu CH, Tan X, et al: SOX2 promotes tumorigenesis and
increases the anti-apoptotic property of human prostate cancer
cell. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:230–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bryant DM and Stow JL: The ins and outs of
E-cadherin trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 14:427–434. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ikenouchi J, Matsuda M, Furuse M and
Tsukita S: Regulation of tight junctions during the
epithelium-mesenchyme transition: Direct repression of the gene
expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J Cell Sci.
116:1959–1967. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Strauss R, Li ZY, Liu Y, Beyer I, Persson
J, Sova P, Möller T, Pesonen S, Hemminki A, Hamerlik P, et al:
Analysis of epithelial and mesenchymal markers in ovarian cancer
reveals phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity. PLoS One.
6:e161862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jiang YG, Luo Y, He DL, Li X, Zhang LL,
Peng T, Li MC and Lin YH: Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate
cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Int J Urol.
14:1034–1039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Beavon IR: The E-cadherin-catenin complex
in tumour metastasis: Structure, function and regulation. Eur J
Cancer. 36:1607–1620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Spaderna S, Hlubek F
and Kirchner T: Opinion: Migrating cancer stem cells - an
integrated concept of malignant tumor progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:744–749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Driscoll TP, Cosgrove BD, Heo SJ, Shurden
ZE and Mauck RL: Cytoskeletal to nuclear strain transfer regulates
YAP signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. Biophys J. 108:2783–2793.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Artman L, Dormoy-Raclet V, von Roretz C
and Gallouzi IE: Planning your every move: The role of β-actin and
its post-transcriptional regulation in cell motility. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 34:33–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Driscoll TP, Cosgrove BD, Heo SJ, Shurden
ZE and Mauck RL: Cytoskeletal to nuclear transfer regulate YAP
signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. Biophys J. 108:2783–2793.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|