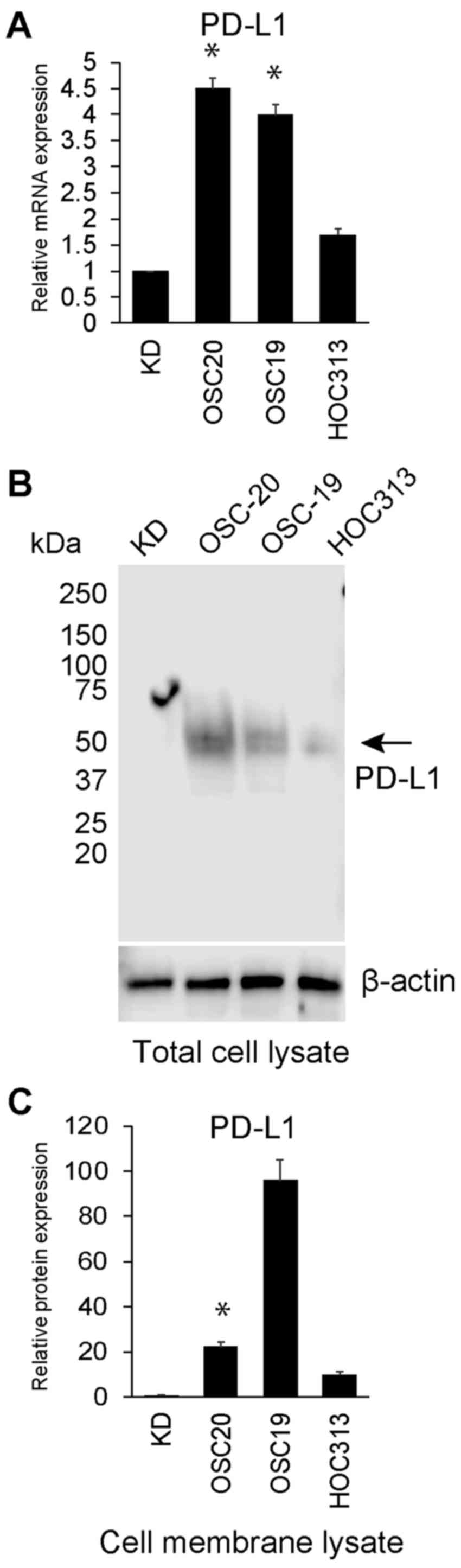
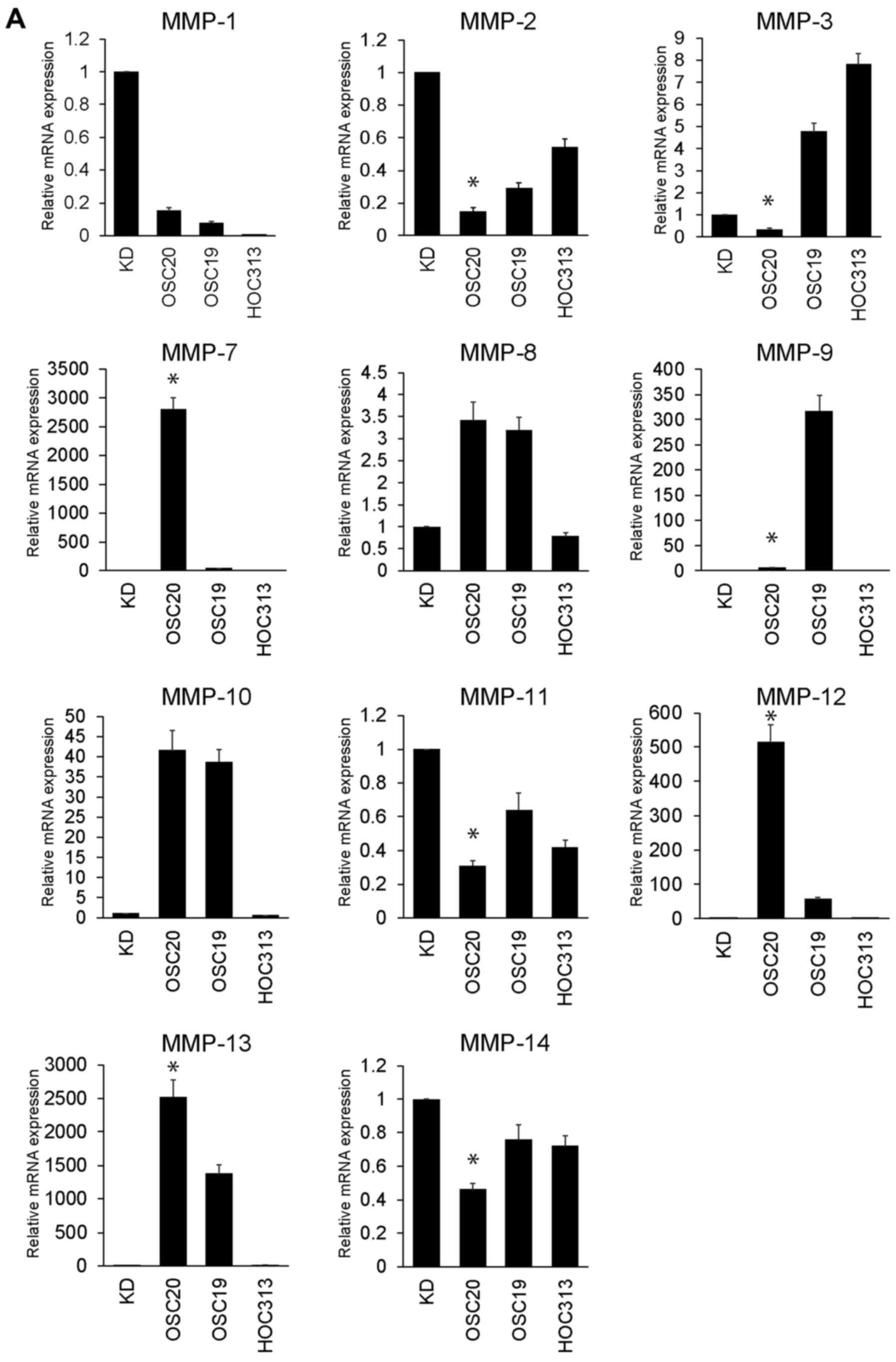
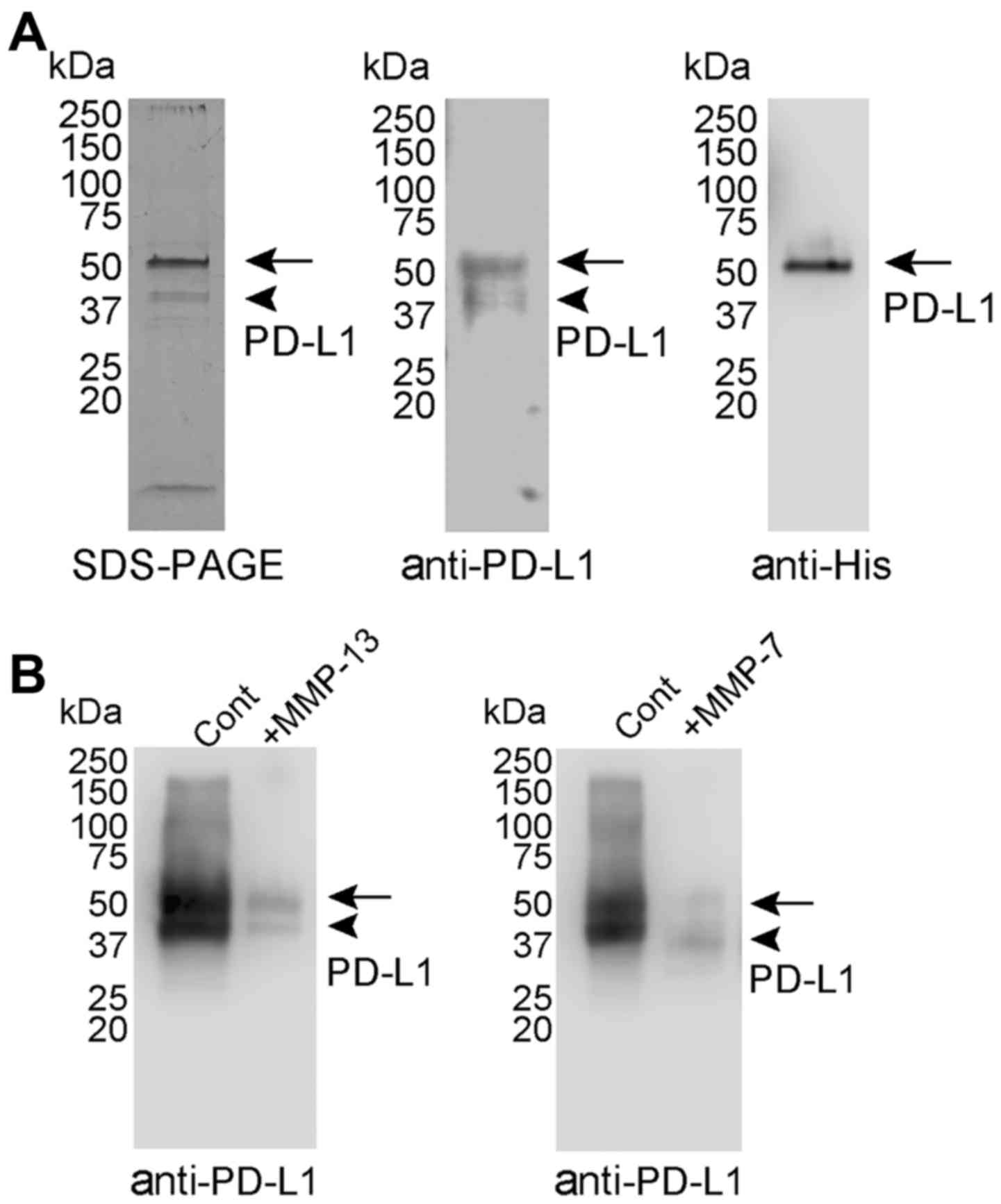
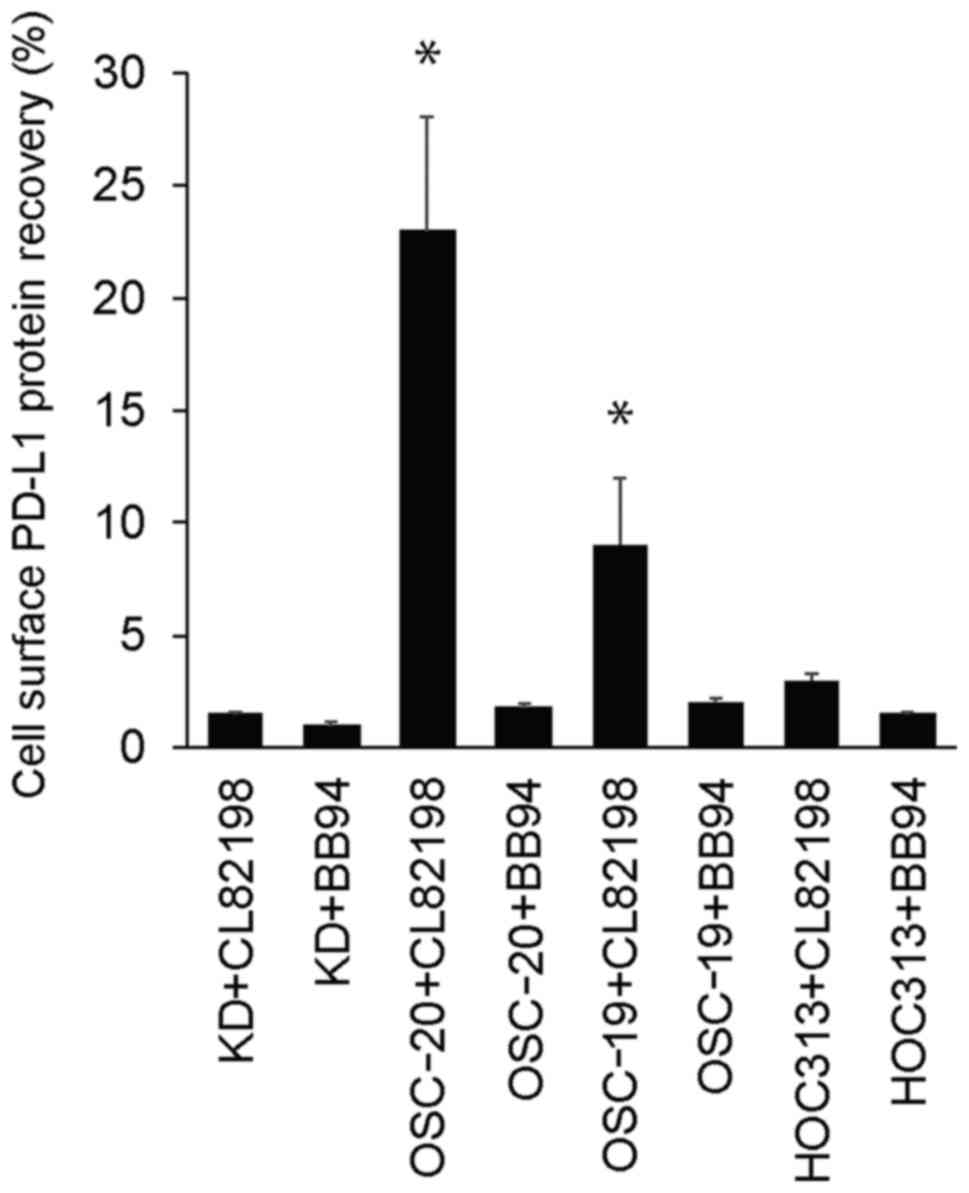
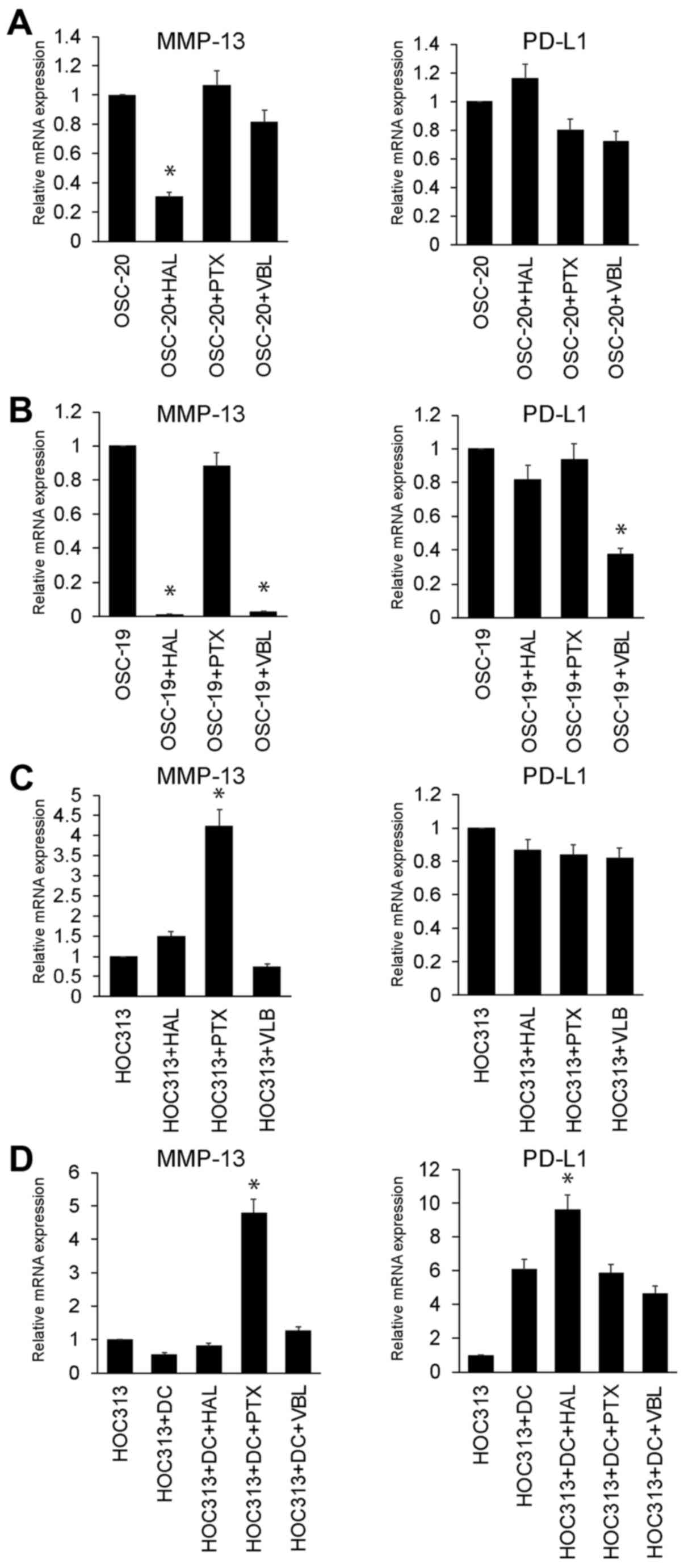
|
1
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor
immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 24:207–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oliveira-Neto HH, Gleber-Netto FO, de
Sousa SF, França CM, Aguiar MC, Silva TA and Batista AC: A
comparative study of microvessel density in squamous cell carcinoma
of the oral cavity and lip. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol. 113:391–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang X, Zhou H, Liu X, He Y, Tang Y, Zhu
G, Zheng M and Yang J: Effect of local hyperthermia on
lymphangiogenic factors VEGF-C and -D in a nude mouse xenograft
model of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 46:111–115.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Strome SE, Dong H, Tamura H, Voss SG,
Flies DB, Tamada K, Salomao D, Cheville J, Hirano F, Lin W, et al:
B7-H1 blockade augments adoptive T-cell immunotherapy for squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:6501–6505. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lyford-Pike S, Peng S, Young GD, Taube JM,
Westra WH, Akpeng B, Bruno TC, Richmon JD, Wang H, Bishop JA, et
al: Evidence for a role of the PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in immune
resistance of HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 73:1733–1741. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zandberg DP and Strome SE: The role of the
PD-L1:PD-1 pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Oral Oncol. 50:627–632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Butte MJ, Keir ME, Phamduy TB, Sharpe AH
and Freeman GJ: Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically
with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses.
Immunity. 27:111–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsushima F, Tanaka K, Otsuki N, Youngnak
P, Iwai H, Omura K and Azuma M: Predominant expression of B7-H1 and
its immunoregulatory roles in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral
Oncol. 42:268–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Iwai Y, Terawaki S and Honjo T: PD-1
blockade inhibits hema-togenous spread of poorly immunogenic tumor
cells by enhanced recruitment of effector T cells. Int Immunol.
17:133–144. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hirano F, Kaneko K, Tamura H, Dong H, Wang
S, Ichikawa M, Rietz C, Flies DB, Lau JS, Zhu G, et al: Blockade of
B7-H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer
therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res. 65:1089–1096. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirai M, Kitahara H, Kobayashi Y, Kato K,
Bou-Gharios G, Nakamura H and Kawashiri S: Regulation of PD-L1
expression in a high-grade invasive human oral squamous cell
carcinoma microenvironment. Int J Oncol. 50:41–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Durand I, Alberti L,
Bendriss-Vermare N, Valladeau-Guilemond J, Duc A, Magron A, Morel
AP, Sisirak V, Rodriguez C, et al: A novel regulation of PD-1
ligands on mesenchymal stromal cells through MMP-mediated
proteolytic cleavage. Oncoimmunology. 5:e10911462015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metal-loproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Overall CM and López-Otín C: Strategies
for MMP inhibition in cancer: Innovations for the post-trial era.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:657–672. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Milner JM and Cawston TE: Matrix
metalloproteinase knockout studies and the potential use of matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitors in the rheumatic diseases. Curr Drug
Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:363–375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Le NT, Xue M, Castelnoble LA and Jackson
CJ: The dual personalities of matrix metalloproteinases in
inflammation. Front Biosci. 12:1475–1487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yokoi T, Hirata S, Nishimura F, Miyakawa
A, Odajima T and Kohama G: Some properties of a newly established
human cell line derived from an oral squamous carcinoma. Tumor Res.
25:93-91–93. 1990.
|
|
23
|
Yokoi T, Homma H and Odajima T:
Establishment and characterization of OSC-19 cell line in serum and
protein free culture. Tumor Res. 24:1–17. 1988.
|
|
24
|
Ishisaki A, Oida S, Momose F, Amagasa T,
Rikimaru K, Ichijo H and Sasaki S: Identification and
characterization of autocrine-motility-factor-like activity in oral
squamous-cell-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 59:783–788. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arrighi JF, Hauser C, Chapuis B, Zubler RH
and Kindler V: Long-term culture of human CD34(+) progenitors with
FLT3-ligand, thrombopoietin, and stem cell factor induces extensive
amplification of a CD34(−)CD14(−) and a CD34(−) CD14(+) dendritic
cell precursor. Blood. 93:2244–2252. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang D, Chen Q, Le Y, Wang JM and
Oppenheim JJ: Differential regulation of formyl peptide
receptor-like 1 expression during the differentiation of monocytes
to dendritic cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 166:4092–4098. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nakamura H, Fujii Y, Ohuchi E, Yamamoto E
and Okada Y: Activation of the precursor of human stromelysin 2 and
its interactions with other matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J
Biochem. 253:67–75. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakamura H, Fujii Y, Inoki I, Sugimoto K,
Tanzawa K, Matsuki H, Miura R, Yamaguchi Y and Okada Y: Brevican is
degraded by matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS4)
at different sites. J Biol Chem. 275:38885–38890. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zou W and Chen L: Inhibitory B7-family
molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:467–477. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wintterle S, Schreiner B, Mitsdoerffer M,
Schneider D, Chen L, Meyermann R, Weller M and Wiendl H: Expression
of the B7-related molecule B7-H1 by glioma cells: A potential
mechanism of immune paralysis. Cancer Res. 63:7462–7467.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Azuma M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H and Nishimura M: B7-H1 expression on non-small
cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5094–5100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y,
Hamada K, Ikeda N, Mizuno T, Yoriki R, Kashizuka H, Yane K, et al:
Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed
death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2947–2953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Thompson RH and Kwon ED: Significance of
B7-H1 overexpression in kidney cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
5:206–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki
T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, Higuchi T, Yagi H, Takakura K, Minato N,
et al: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating
CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human
ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:3360–3365. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo
A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M, et al:
Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed
death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2151–2157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ghebeh H, Tulbah A, Mohammed S, Elkum N,
Bin Amer SM, Al-Tweigeri T and Dermime S: Expression of B7-H1 in
breast cancer patients is strongly associated with high
proliferative Ki-67-expressing tumor cells. Int J Cancer.
121:751–758. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yao Y, Tao R, Wang X, Wang Y, Mao Y and
Zhou LF: B7-H1 is correlated with malignancy-grade gliomas but is
not expressed exclusively on tumor stem-like cells. Neuro Oncol.
11:757–766. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liotta LA and Kohn EC: The
microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 411:375–379.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shiomi T and Okada Y: MT1-MMP and MMP-7 in
invasion and metastasis of human cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
22:145–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cornelius LA, Nehring LC, Harding E,
Bolanowski M, Welgus HG, Kobayashi DK, Pierce RA and Shapiro SD:
Matrix metalloproteinases generate angiostatin: Effects on
neovascularization. J Immunol. 161:6845–6852. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hamano Y, Zeisberg M, Sugimoto H, Lively
JC, Maeshima Y, Yang C, Hynes RO, Werb Z, Sudhakar A and Kalluri R:
Physiological levels of tumstatin, a fragment of collagen IV alpha3
chain, are generated by MMP-9 proteolysis and suppress angiogenesis
via alphaV beta3 integrin. Cancer Cell. 3:589–601. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fukuda H, Mochizuki S, Abe H, Okano HJ,
Hara-Miyauchi C, Okano H, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama M, D'Armiento J and
Okada Y: Host-derived MMP-13 exhibits a protective role in lung
metastasis of melanoma cells by local endostatin production. Br J
Cancer. 105:1615–1624. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Yoshida H, Yoshioka T,
Nishimoto H and Itohara S: Reduced angiogenesis and tumor
progression in gela-tinase A-deficient mice. Cancer Res.
58:1048–1051. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wilson CL, Heppner KJ, Labosky PA, Hogan
BL and Matrisian LM: Intestinal tumorigenesis is suppressed in mice
lacking the metalloproteinase matrilysin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:1402–1407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Matsuda H, Nishimoto H,
Yoshioka T, Suzuki R and Uehira M: Experimental metastasis is
suppressed in MMP-9-deficient mice. Clin Exp Metastasis.
17:177–181. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Acuff HB, Carter KJ, Fingleton B, Gorden
DL and Matrisian LM: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 from bone
marrow-derived cells contributes to survival but not growth of
tumor cells in the lung microenvironment. Cancer Res. 66:259–266.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
McCawley LJ, Crawford HC, King LE Jr,
Mudgett J and Matrisian LM: A protective role for matrix
metalloproteinase-3 in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
64:6965–6972. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Acuff HB, Sinnamon M, Fingleton B, Boone
B, Levy SE, Chen X, Pozzi A, Carbone DP, Schwartz DR, Moin K, et
al: Analysis of host- and tumor-derived proteinases using a custom
dual species microarray reveals a protective role for stromal
matrix metal-loproteinase-12 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Res. 66:7968–7975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Balbín M, Fueyo A, Tester AM, Pendás AM,
Pitiot AS, Astudillo A, Overall CM, Shapiro SD and López-Otín C:
Loss of collagenase-2 confers increased skin tumor susceptibility
to male mice. Nat Genet. 35:252–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kitahara H, Hirai M, Kato K, Bou-Gharios
G, Nakamura H and Kawashiri S: Eribulin sensitizes oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells to cetuximab via induction of
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. Oncol Rep. 36:3139–3144.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dezső Z, Oestreicher J, Weaver A, Santiago
S, Agoulnik S, Chow J, Oda Y and Funahashi Y: Gene expression
profiling reveals epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) genes can
selectively differentiate eribulin sensitive breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 9:e1061312014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kavallaris M: Microtubules and resistance
to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:194–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dong C, Li Z, Alvarez R Jr, Feng XH and
Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ: Microtubule binding to Smads may regulate
TGF-beta activity. Mol Cell. 5:27–34. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Leivonen SK, Ala-Aho R, Koli K, Grénman R,
Peltonen J and Kähäri VM: Activation of Smad signaling enhances
collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression and invasion of head and neck
squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 25:2588–2600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|