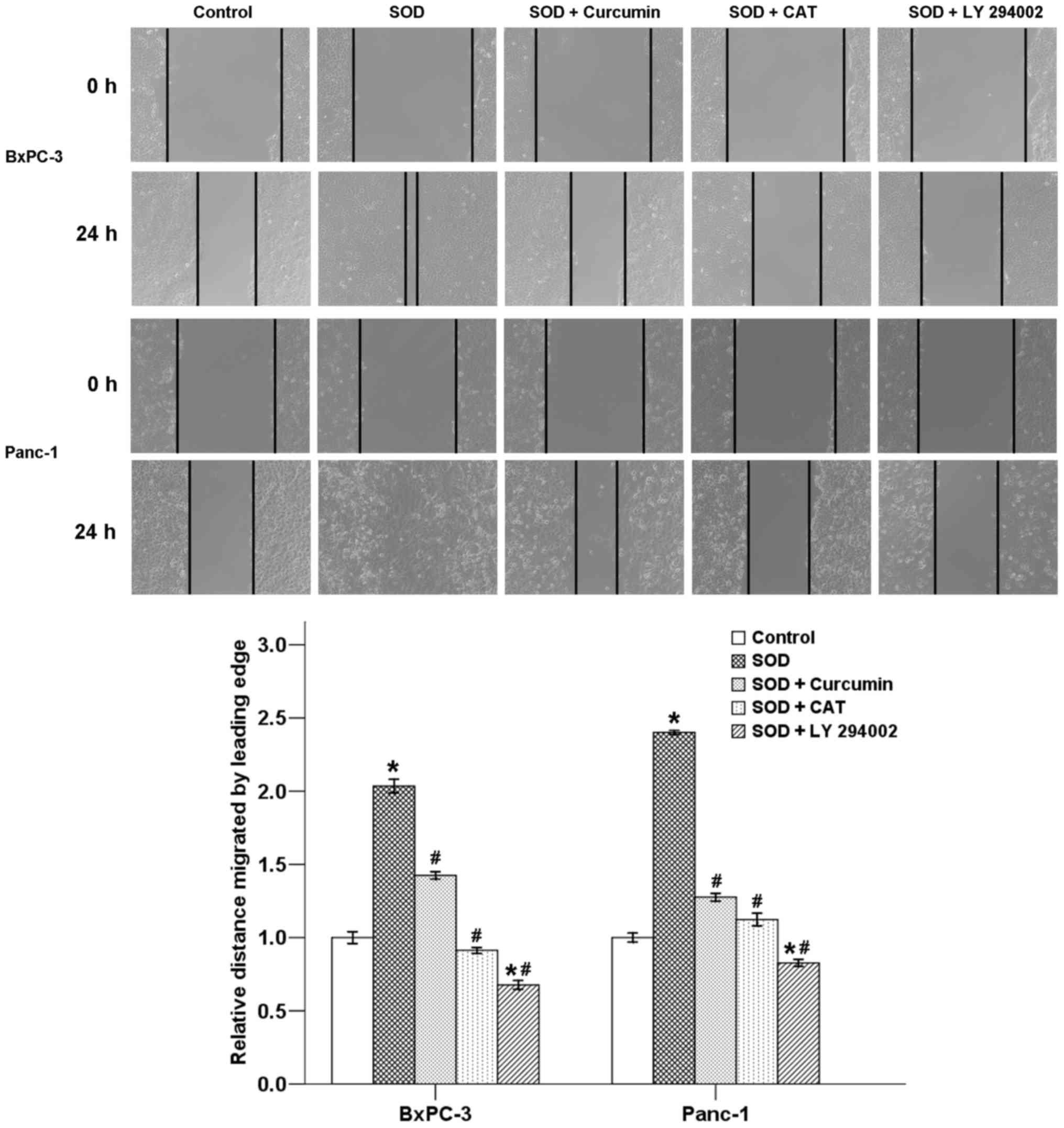
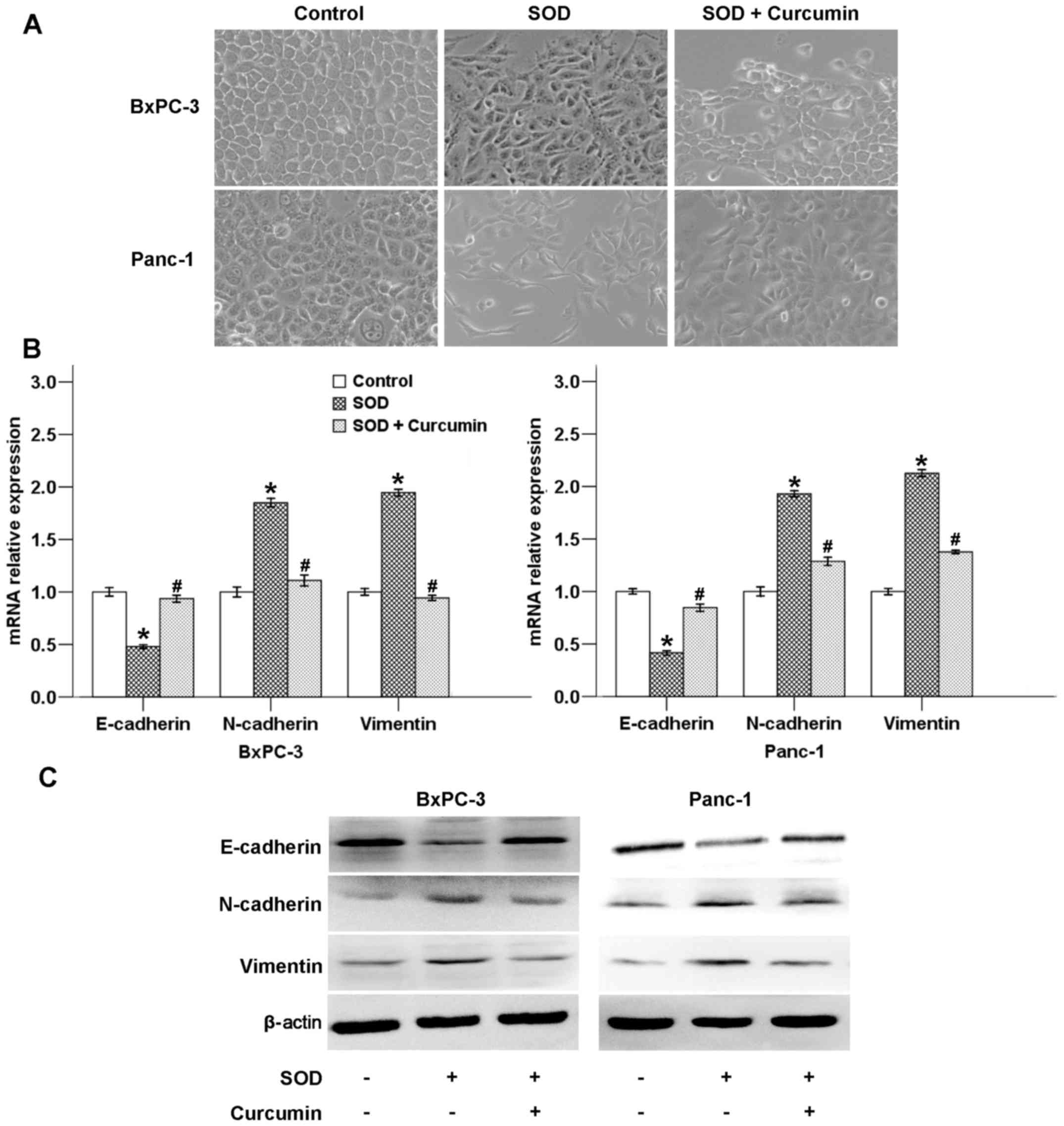
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin QJ, Yang F, Jin C and Fu DL: Current
status and progress of pancreatic cancer in China. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7988–8003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shanmugam MK, Rane G, Kanchi MM, Arfuso F,
Chinnathambi A, Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Tan BK, Kumar AP and Sethi G:
The multifaceted role of curcumin in cancer prevention and
treatment. Molecules. 20:2728–2769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang Z, Wu R, Xie W, Xie C, Wu J, Geng S,
Li X, Zhu M, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al: Effects of curcumin on tobacco
smoke-induced hepatic MAPK pathway activation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vivo. Phytother Res.
31:1230–1239. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu H, Wang C, Yang D, Wei Z, Xu J, Hu Z,
Zhang Y, Wang W, Yan R and Cai Q: Curcumin regulates proliferation,
autophagy, and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by affecting PI3K
and P53 signaling. J Cell Physiol. Sep 19–2017.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liang Z, Lu L, Mao J, Li X, Qian H and Xu
W: Curcumin reversed chronic tobacco smoke exposure induced
urocystic EMT and acquisition of cancer stem cells properties via
Wnt/β-catenin. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30662017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cao L, Xiao X, Lei J, Duan W, Ma Q and Li
W: Curcumin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial mesenchymal
transition in pancreatic cancer cells via suppression of the
hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:3728–3734. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhatia S, Monkman J, Toh AKL, Nagaraj SH
and Thompson EW: Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in
cancer: Clinical and preclinical advances in therapy and
monitoring. Biochem J. 474:3269–3306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Ma Q, Liu J, Han L, Ma G, Liu H,
Shan T, Xie K and Wu E: Hyperglycemia as a mechanism of pancreatic
cancer metastasis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:1761–1774. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li W, Zhang L, Chen X, Jiang Z, Zong L and
Ma Q: Hyperglycemia promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of pancreatic cancer via hydrogen peroxide. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:51903142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li W, Cao L, Han L, Xu Q and Ma Q:
Superoxide dismutase promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of the
H2O2/ERK/NF-κB axis. Int J Oncol.
46:2613–2620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Costa A, Scholer-Dahirel A and
Mechta-Grigoriou F: The role of reactive oxygen species and
metabolism on cancer cells and their microenvironment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 25:23–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo L, Tan K, Wang H and Zhang X:
Pterostilbene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through
p53/SOD2/ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Oncol Rep.
36:3233–3240. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Martinez-Useros J, Li W, Cabeza-Morales M
and Garcia-Foncillas J: Oxidative stress: A new target for
pancreatic cancer prognosis and treatment. J Clin Med. 6:E292017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mayer IA and Arteaga CL: The PI3K/AKT
pathway as a target for cancer treatment. Annu Rev Med. 67:11–28.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu X, Wu Q, Wang L, Zhao Y, Zhang Q, Meng
Q, Pawan and Wang S: Silencing of ST6GalNAc I suppresses the
proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocarcinoma cells
through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Tumour Biol. 37:12213–12221. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gaianigo N, Melisi D and Carbone C: EMT
and treatment resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel).
9:92017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Castellanos EH, Cardin DB and Berlin JD:
Treatment of early-stage pancreatic cancer. Oncology (Williston
Park). 25:182–189. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Claudia L, Jette R, Rudolf L, Ludger AW
and Barbara Sr: Hydrogen peroxide - production, fate and role in
redox signaling of tumor cells. Cell Commun Signal. 13:392015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li W, Wu Z, Ma Q, Liu J, Xu Q, Han L, Duan
W, Lv Y, Wang F, Reindl KM, et al: Hyperglycemia regulates
TXNIP/TRX/ROS axis via p38 MAPK and ERK pathways in pancreatic
cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 14:348–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li F, Wang H, Huang C, Lin J, Zhu G, Hu R
and Feng H: Hydrogen peroxide contributes to the manganese
superoxide dismutase promotion of migration and invasion in glioma
cells. Free Radic Res. 45:1154–1161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Damiano S, Petrozziello T, Ucci V, Amente
S, Santillo M and Mondola P: Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase activates
muscarinic acetylcholine M1 receptor pathway in neuroblastoma
cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 52:31–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cao L, Liu J, Zhang L, Xiao X and Li W:
Curcumin inhibits H2O2-induced invasion and
migration of human pancreatic cancer via suppression of the
ERK/NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep. 36:2245–2251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Griess B, Tom E, Domann F and
Teoh-Fitzgerald M: Extracellular superoxide dismutase and its role
in cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 112:464–479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hempel N, Carrico PM and Melendez JA:
Manganese superoxide dismutase (Sod2) and redox-control of
signaling events that drive metastasis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
11:191–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun GG, Wang YD, Lu YF and Hu WN:
Different association of manganese superoxide dismutase gene
polymorphisms with risk of prostate, esophageal, and lung cancers:
Evidence from a meta-analysis of 20,025 subjects. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:1937–1943. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kang SW: Superoxide dismutase 2 gene and
cancer risk: Evidence from an updated meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:14647–14655. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang H, Dong X, Day RS, Hassan MM and Li
D: Antioxidant genes, diabetes and dietary antioxidants in
association with risk of pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis.
31:607–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hart PC, Mao M, de Abreu AL,
Ansenberger-Fricano K, Ekoue DN, Ganini D, Kajdacsy-Balla A,
Diamond AM, Minshall RD, Consolaro ME, et al: MnSOD upregulation
sustains the Warburg effect via mitochondrial ROS and
AMPK-dependent signalling in cancer. Nat Commun. 6:60532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yi L, Shen H, Zhao M, Shao P, Liu C, Cui
J, Wang J, Wang C, Guo N, Kang L, et al: Inflammation-mediated
SOD-2 upregulation contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and migration of tumor cells in aflatoxin G1-induced lung
adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:79532017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Yang C, Su X, Liu A, Zhang L, Yu A, Xi Y
and Zhai G: Advances in clinical study of curcumin. Curr Pharm Des.
19:1966–1973. 2013.
|
|
36
|
Zhou X, Su J, Feng S, Wang L, Yin X, Yan J
and Wang Z: Antitumor activity of curcumin is involved in
down-regulation of YAP/TAZ expression in pancreatic cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:79076–79088. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Wang J, Xu J, Lu Y, Jiang J, Wang
L, Shen HM and Xia D: Curcumin targets the TFEB-lysosome pathway
for induction of autophagy. Oncotarget. 7:75659–75671.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Guha S, Krishnan S,
Diagaradjane P, Gelovani J and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin potentiates
antitumor activity of gemcitabine in an orthotopic model of
pancreatic cancer through suppression of proliferation,
angiogenesis, and inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated
gene products. Cancer Res. 67:3853–3861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang HH, Zhang Y, Cheng YN, Gong FL, Cao
ZQ, Yu LG and Guo XL: Metformin incombination with curcumin
inhibits the growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of hepatocellular
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Mol Carcinog. 57:44–56. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Su J, Zhou X, Yin X, Wang L, Zhao Z, Hou
Y, Zheng N, Xia J and Wang Z: The effects of curcumin on
proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and NEDD4 expression in
pancreatic cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 140:28–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li W, Ma J, Ma Q, Li B, Han L, Liu J, Xu
Q, Duan W, Yu S, Wang F, et al: Resveratrol inhibits the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells via
suppression of the PI-3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Curr Med Chem.
20:4185–4194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang Q, Chen X and Hay N: Akt as a target
for cancer therapy: More is not always better (lessons from studies
in mice). Br J Cancer. 117:159–163. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Baer R, Cintas C, Therville N and
Guillermet-Guibert J: Implication of PI3K/Akt pathway in pancreatic
cancer: When PI3K isoforms matter? Adv Biol Regul. 59:19–35. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|