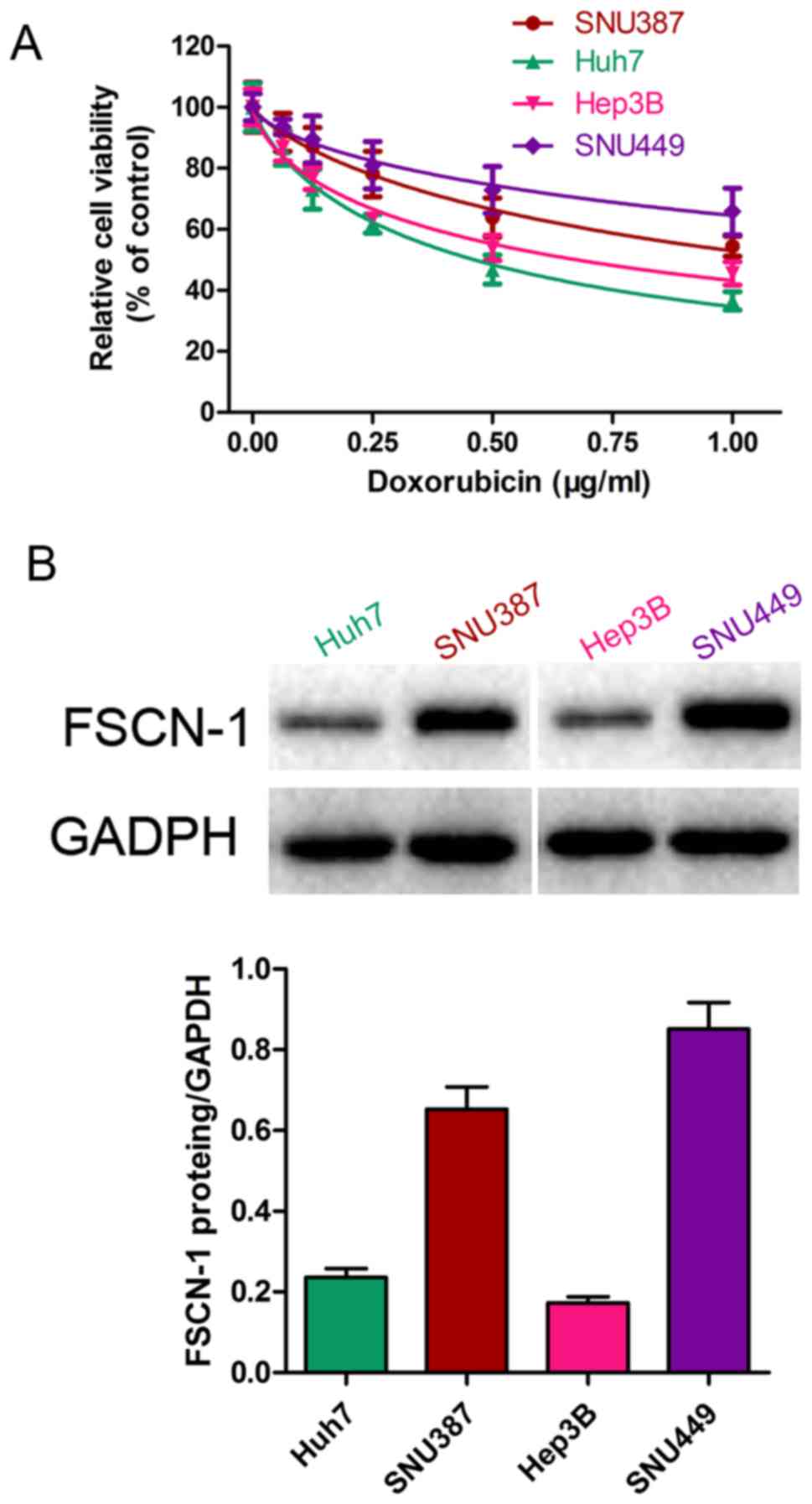
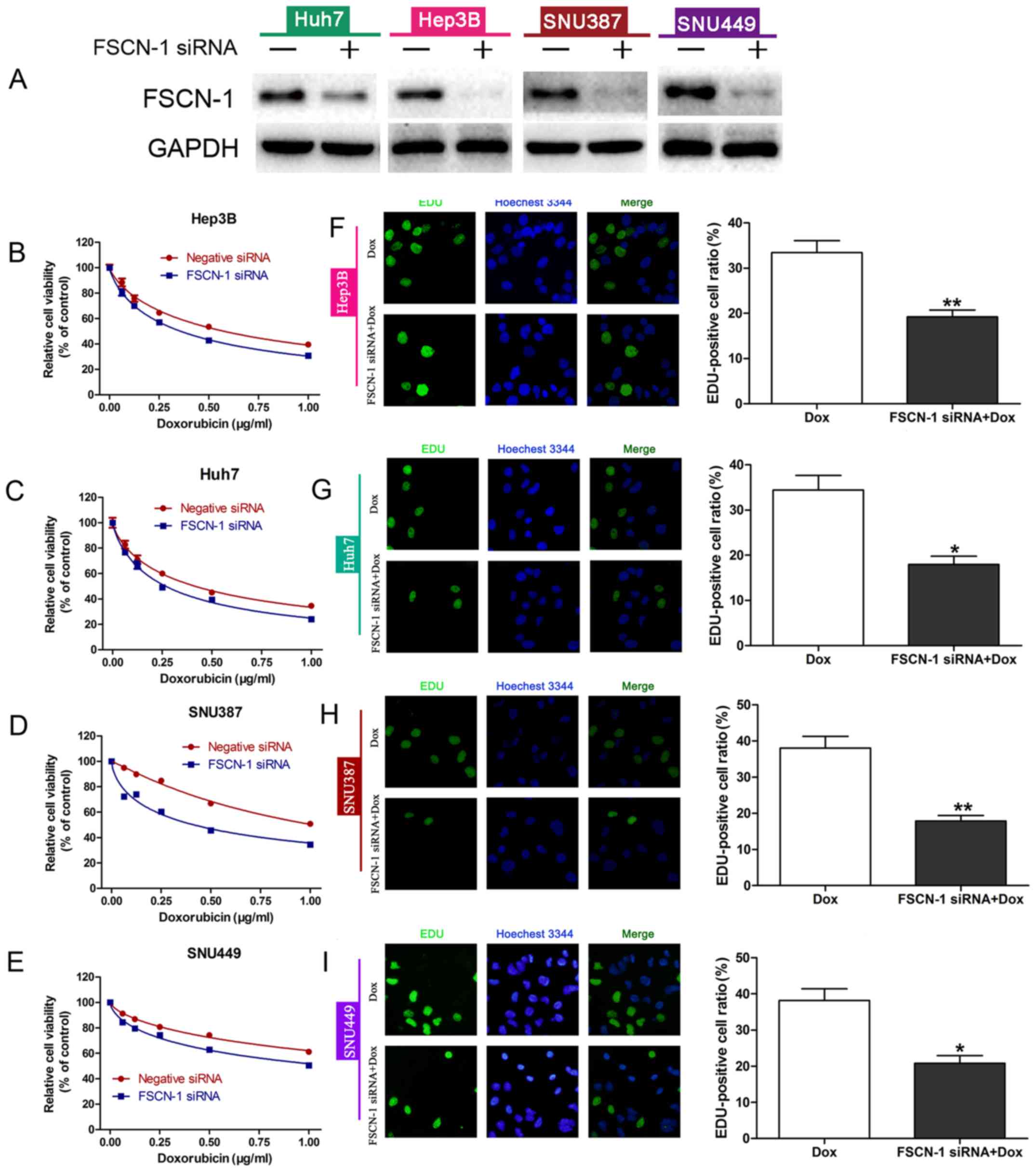
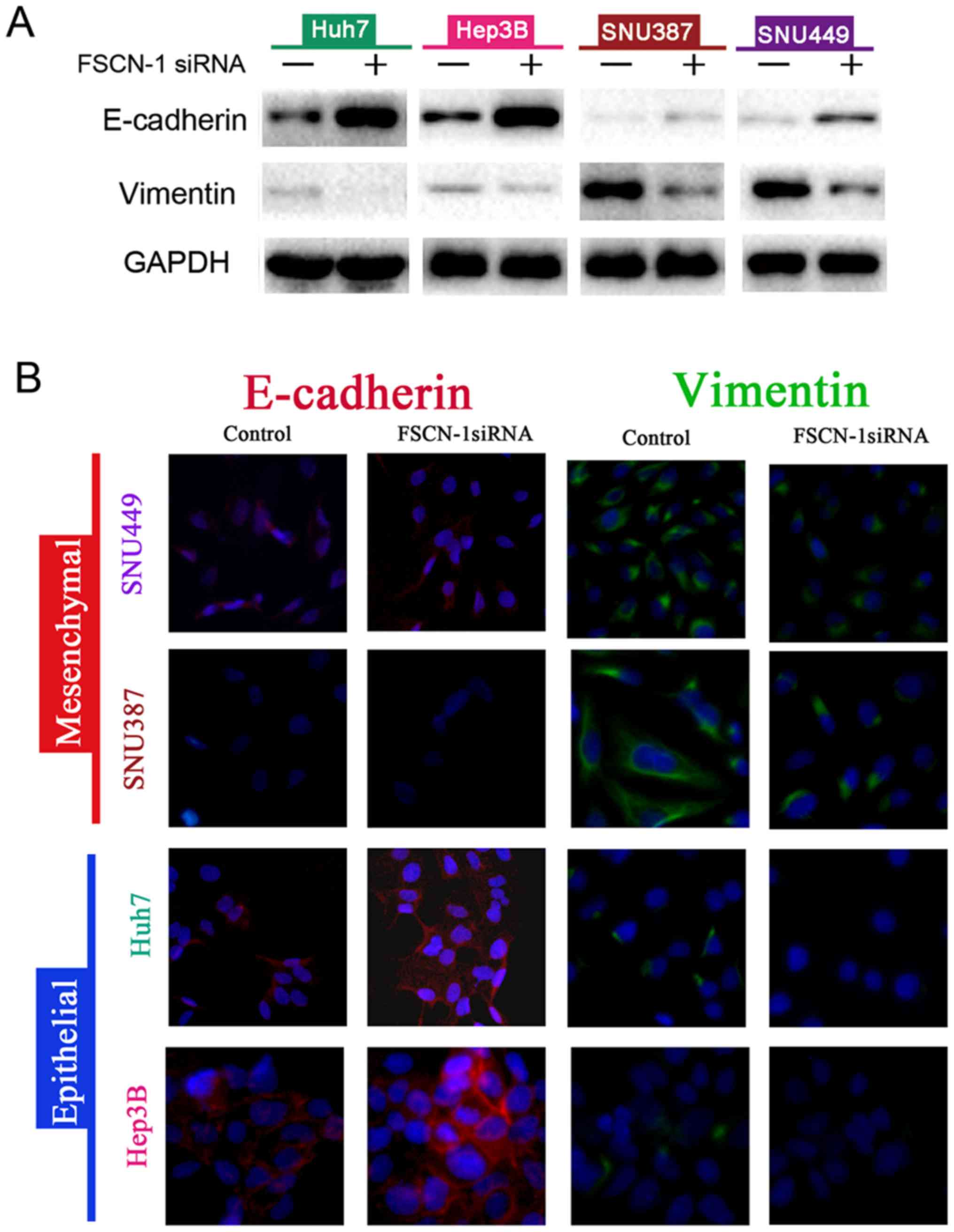
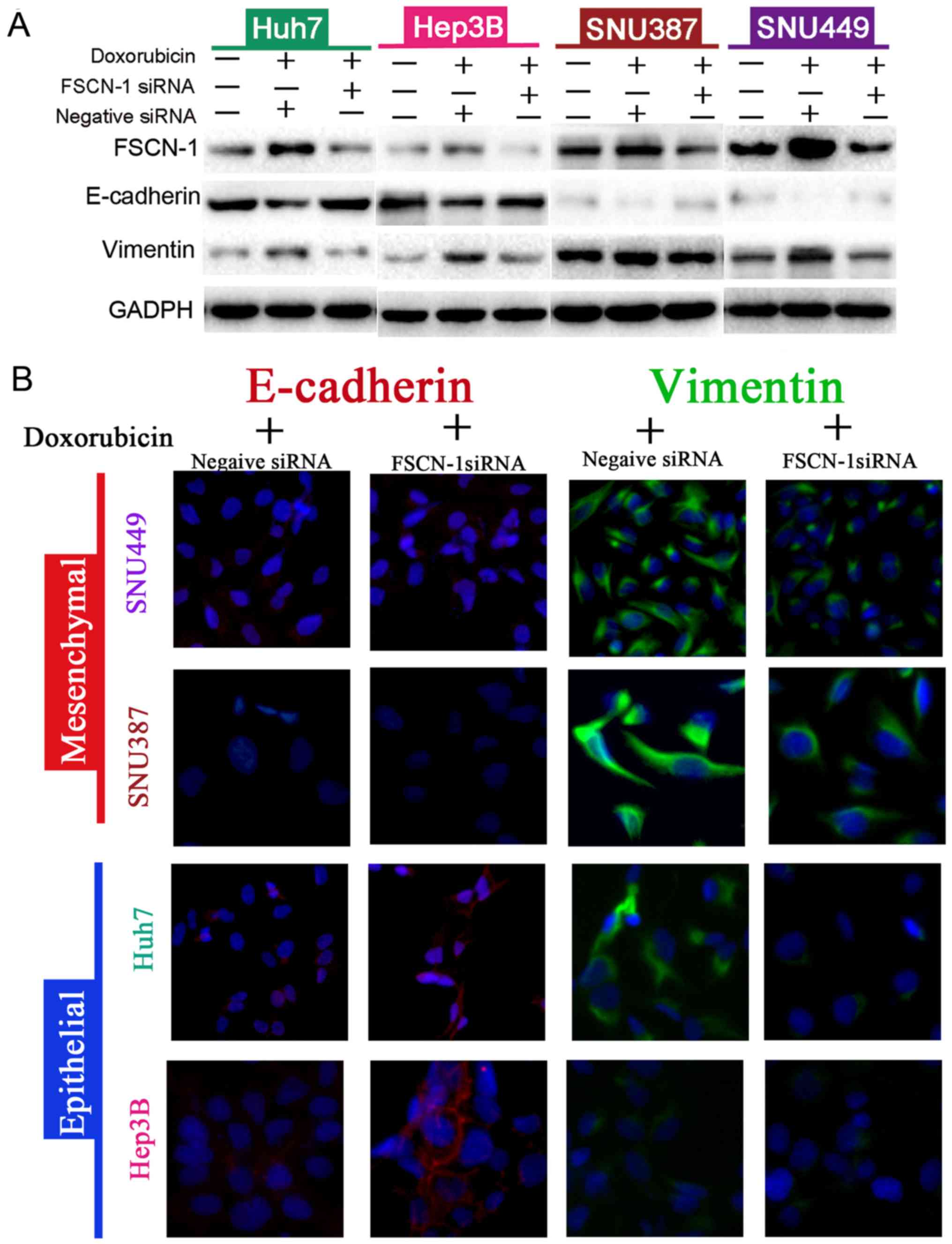
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl 1):
S27–S34. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Njei B, Rotman Y, Ditah I and Lim JK:
Emerging trends in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and
mortality. Hepatology. 61:191–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piska K, Koczurkiewicz P, Bucki A,
Wójcik-Pszczoła K, Kołaczkowski M and Pękala E: Metabolic carbonyl
reduction of anthracyclines - role in cardiotoxicity and cancer
resistance. Reducing enzymes as putative targets for novel
cardioprotective and chemosensitizing agents. Invest New Drugs.
35:375–385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo
G and Gianni L: Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and
pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and
cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 56:185–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Olweny CL, Toya T, Katongole-Mbidde E,
Mugerwa J, Kyalwazi SK and Cohen H: Treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma with adriamycin. Preliminary communication. Cancer.
36:1250–1257. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Asghar U and Meyer T: Are there
opportunities for chemotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular
cancer? J Hepatol. 56:686–695. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montaña X, Planas R,
Coll S, Aponte J, Ayuso C, Sala M, Muchart J, Solà R, et al
Barcelona Liver Cancer Group: Arterial embolisation or
chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 359:1734–1739. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Forner A, Ayuso C, Varela M, Rimola J,
Hessheimer AJ, de Lope CR, Reig M, Bianchi L, Llovet JM and Bruix
J: Evaluation of tumor response after locoregional therapies in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Are response evaluation criteria in solid
tumors reliable? Cancer. 115:616–623. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burrel M, Reig M, Forner A, Barrufet M, de
Lope CR, Tremosini S, Ayuso C, Llovet JM, Real MI and Bruix J:
Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by
transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) using Drug Eluting Beads.
Implications for clinical practice and trial design. J Hepatol.
56:1330–1335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J, García De and Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vignjevic D, Kojima S, Aratyn Y, Danciu O,
Svitkina T and Borisy GG: Role of fascin in filopodial protrusion.
J Cell Biol. 174:863–875. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoder BJ, Tso E, Skacel M, Pettay J, Tarr
S, Budd T, Tubbs RR, Adams JC and Hicks DG: The expression of
fascin, an actin-bundling motility protein, correlates with hormone
receptor-negative breast cancer and a more aggressive clinical
course. Clin Cancer Res. 11:186–192. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hashimoto Y, Skacel M, Lavery IC,
Mukherjee AL, Casey G and Adams JC: Prognostic significance of
fascin expression in advanced colorectal cancer: An
immunohistochemical study of colorectal adenomas and
adenocarcinomas. BMC Cancer. 6:2412006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin JS, Yu CP, Sun GH, Lin YF, Chiang H,
Chao TK, Tsai WC and Sheu LF: Increasing expression of fascin in
renal cell carcinoma associated with clinicopathological parameters
of aggressiveness. Histol Histopathol. 21:1287–1293.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai WC, Jin JS, Chang WK, Chan DC, Yeh
MK, Cherng SC, Lin LF, Sheu LF and Chao YC: Association of
cortactin and fascin-1 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma:
Correlation with clinicopathological parameters. J Histochem
Cytochem. 55:955–962. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zou J, Yang H, Chen F, Zhao H, Lin P,
Zhang J, Ye H, Wang L and Liu S: Prognostic significance of
fascin-1 and E-cadherin expression in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 19:11–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin CK, Su HY, Tsai WC, Sheu LF and Jin
JS: Association of cortactin, fascin-1 and epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGFR) expression in ovarian carcinomas: Correlation with
clinicopathological parameters. Dis Markers. 25:17–26. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Arcangelis A, Georges-Labouesse E and
Adams JC: Expression of fascin-1, the gene encoding the
actin-bundling protein fascin-1, during mouse embryogenesis. Gene
Expr Patterns. 4:637–643. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao H, Kang X, Xia X, Wo L, Gu X, Hu Y,
Xie X, Chang H, Lou L and Shen X: miR-145 suppresses breast cancer
cell migration by targeting FSCN-1 and inhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Transl Res. 8:3106–3114.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hayashi Y, Osanai M and Lee GH: Fascin-1
expression correlates with repression of E-cadherin expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells and augments their invasiveness in
combination with matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Sci.
102:1228–1235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim SJ, Choi IJ, Cheong TC, Lee SJ, Lotan
R, Park SH and Chun KH: Galectin-3 increases gastric cancer cell
motility by up-regulating fascin-1 expression. Gastroenterology.
138:1035–1045. e1031–1032. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fu H, Wen JF, Hu ZL, Luo GQ and Ren HZ:
Knockdown of fascin1 expression suppresses the proliferation and
metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Pathology. 41:655–660. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Onodera M, Zen Y, Harada K, Sato Y, Ikeda
H, Itatsu K, Sato H, Ohta T, Asaka M and Nakanuma Y: Fascin is
involved in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent production of
MMP9 in cholangiocarcinoma. Lab Invest. 89:1261–1274. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li QQ, Xu JD, Wang WJ, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Tang F, Chen ZQ, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Twist1-mediated
adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to
multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2657–2665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu H, Hu Z, Wen J, Wang K and Liu Y:
TGF-beta promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells
by increasing fascin1 expression via ERK and JNK signal pathways.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:648–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta
G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, Girardi L, Cillo U, Burra P, Giacomin A, et
al: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): The role of angiogenesis and
invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:914–921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sridharan S, Varghese R, Venkatraj V and
Datta A: Hypoxia stress response pathways: Modeling and targeted
therapy. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 21:875–885. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prasad P, Mittal SA, Chongtham J, Mohanty
S and Srivastava T: Hypoxia-mediated epigenetic regulation of
stemness in brain tumor cells. Stem Cells. 35:1468–1478. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Myung SJ and Yoon JH: Hypoxia in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 13:9–19. 2007.In
Korean. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lencioni R, Llovet JM, Han G, Tak WY, Yang
J, Guglielmi A, Paik SW, Reig M, Kim DY, Chau GY, et al: Sorafenib
or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for
intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J Hepatol. 64:1090–1098.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang P, Long M, Zhang S, Cheng Z, Zhao X,
He F, Liu H and Ming L: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α regulates
autophagy via the p27-E2F1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:2107–2112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tan Q, Joshua AM, Wang M, Bristow RG,
Wouters BG, Allen CJ and Tannock IF: Up-regulation of autophagy is
a mechanism of resistance to chemotherapy and can be inhibited by
pantoprazole to increase drug sensitivity. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 79:959–969. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun
J, Yang S and Hao J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating
transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res.
74:2455–2464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|