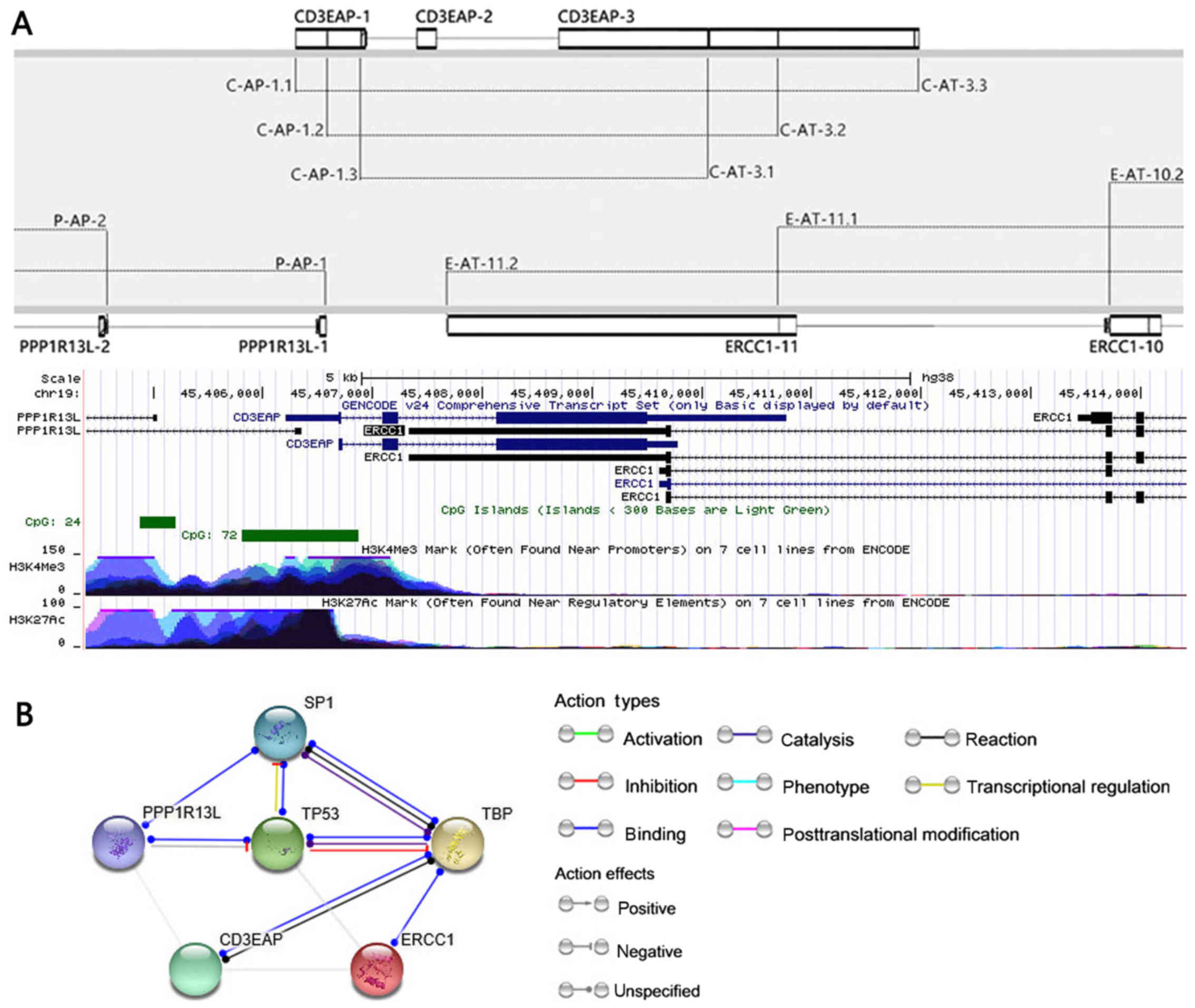
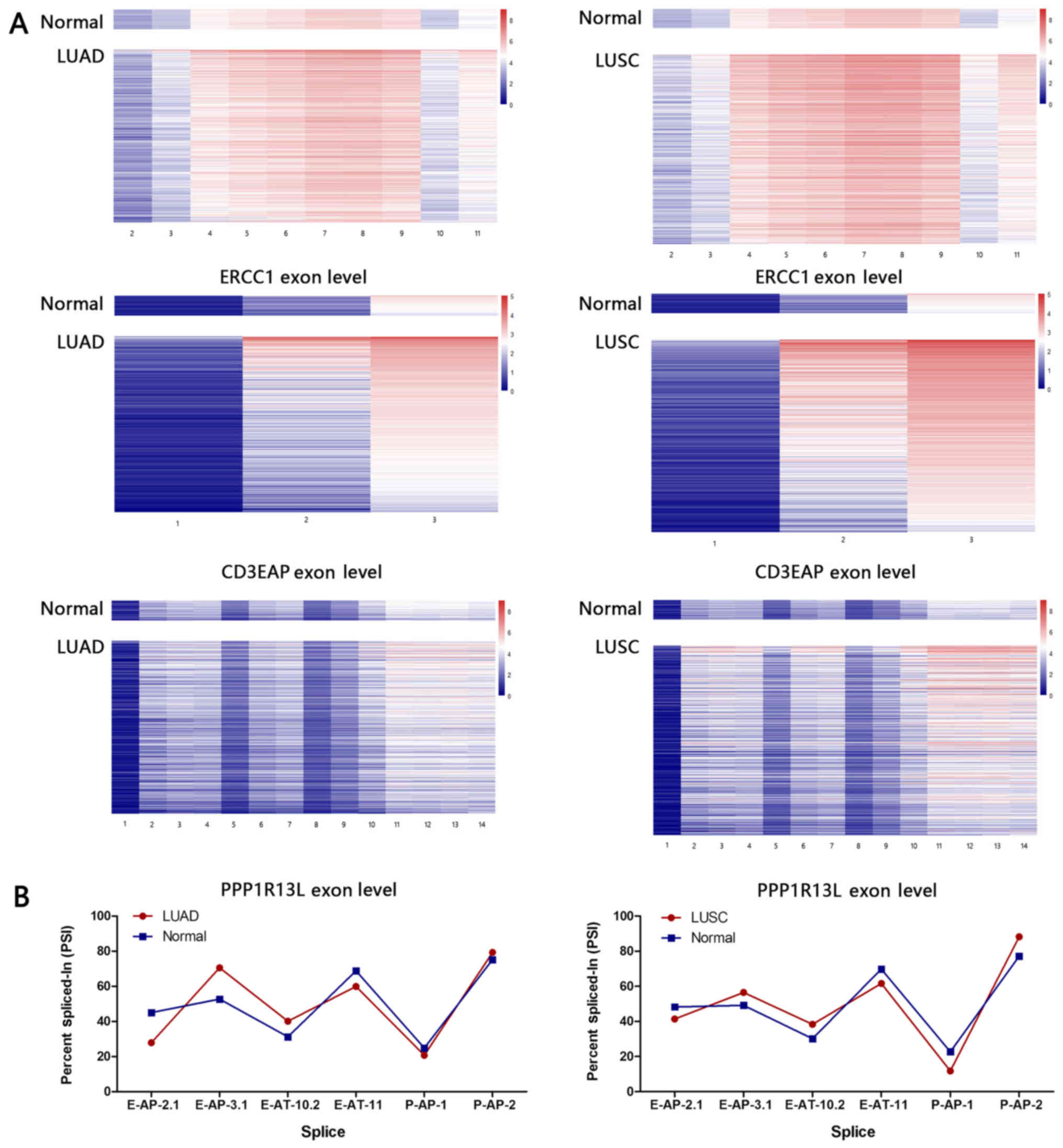
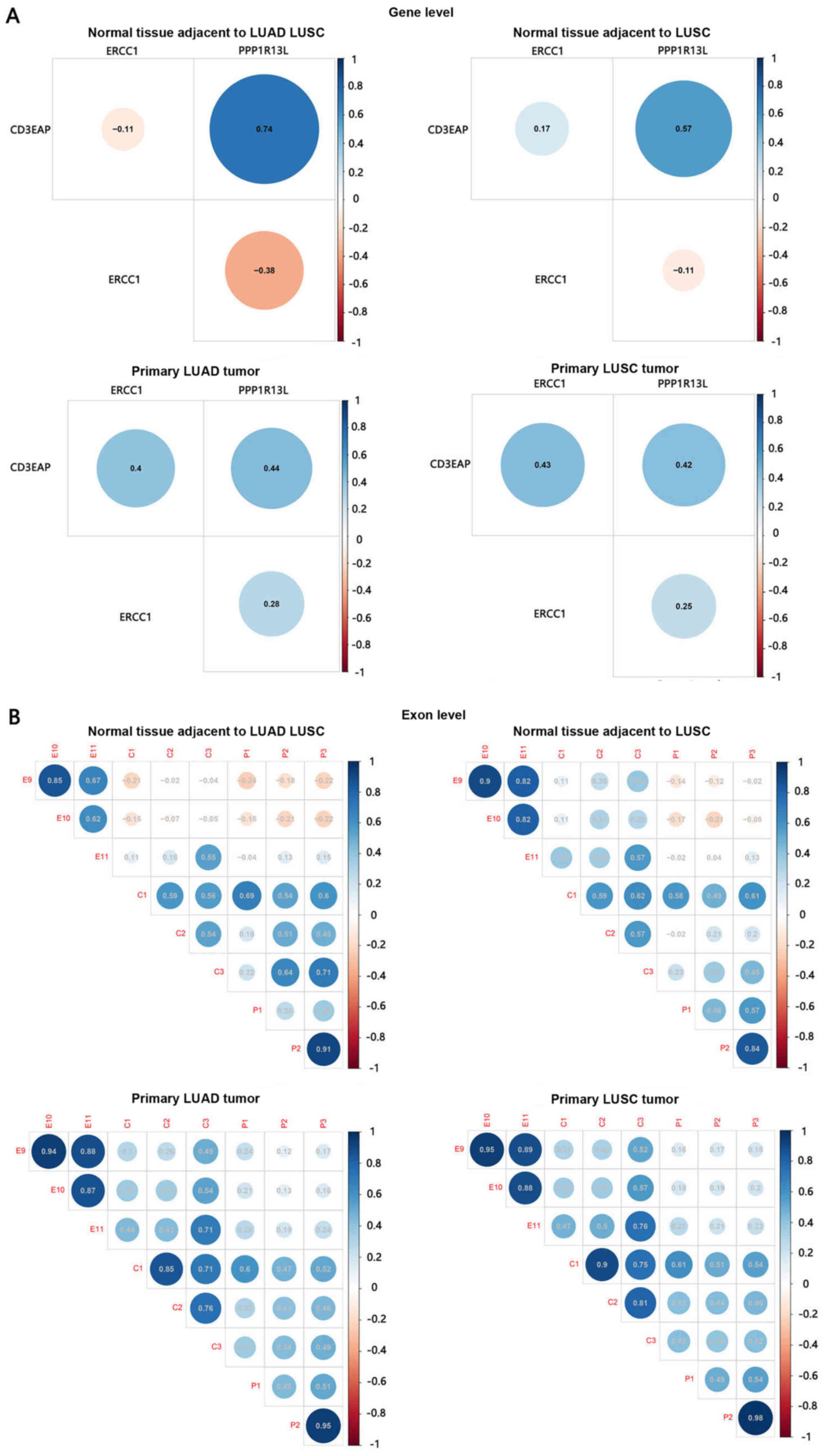
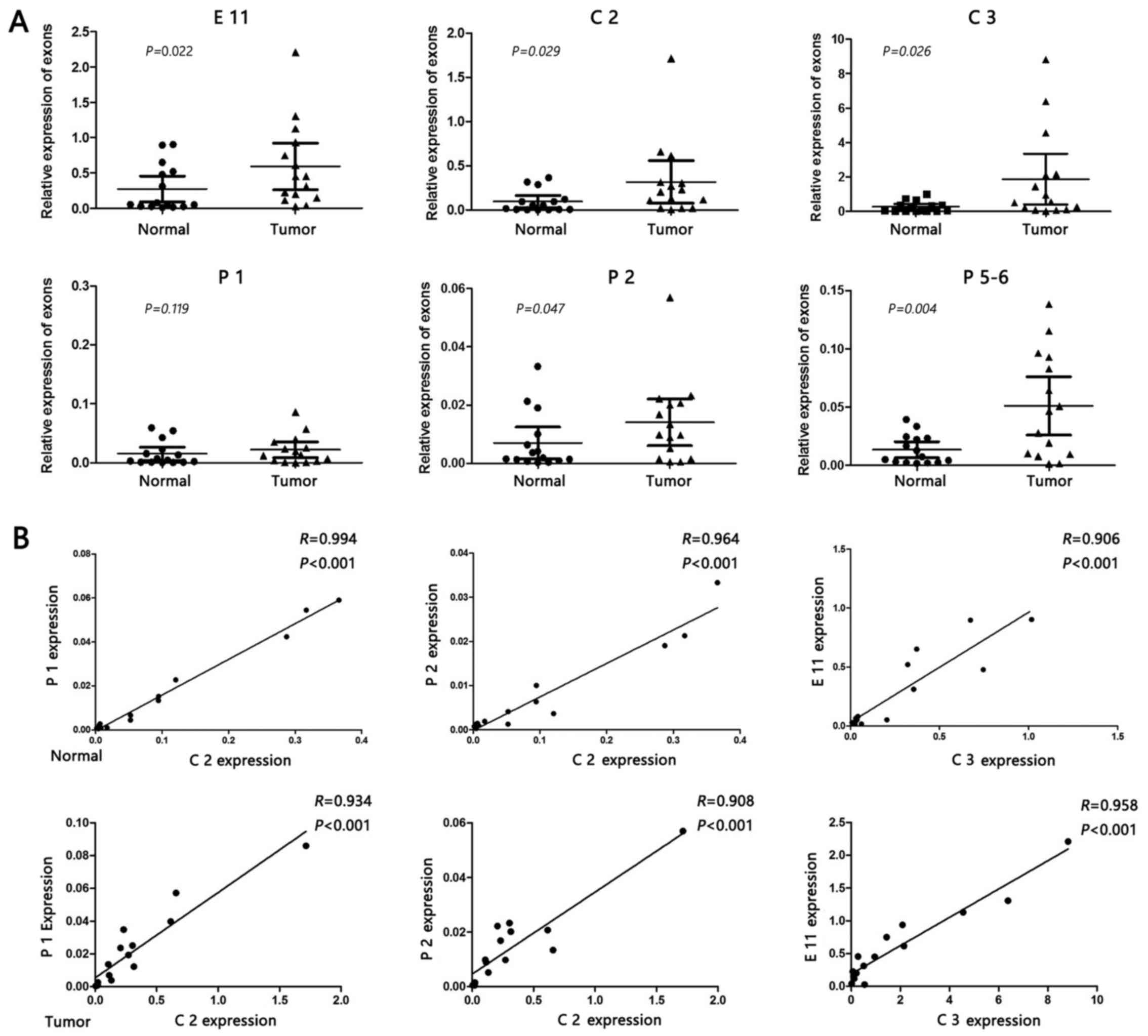
|
1
|
Oberg M, Jaakkola MS, Woodward A, Peruga A
and Prüss-Ustün A: Worldwide burden of disease from exposure to
second-hand smoke: A retrospective analysis of data from 192
countries. Lancet. 377:139–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H and Zhang S: The
incidence and mortality of major cancers in China, 2012. Chin J
Cancer. 35:732016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV,
Douillard JY, Shepherd FA, Stephens RJ, Dunant A, Torri V, Rosell
R, Seymour L, et al LACE Collaborative Group: Lung adjuvant
cisplatin evaluation: A pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative
Group. J Clin Oncol. 26:3552–3559. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Martin LP, Hamilton TC and Schilder RJ:
Platinum resistance: The role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:1291–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
de Boer J and Hoeijmakers JH: Nucleotide
excision repair and human syndromes. Carcinogenesis. 21:453–460.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
van Duin M, de Wit J, Odijk H, Westerveld
A, Yasui A, Koken MH, Hoeijmakers JH and Bootsma D: Molecular
characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA
cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene
RAD10. Cell. 44:913–923. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bergstralh DT and Sekelsky J: Interstrand
crosslink repair: Can XPF-ERCC1 be let off the hook? Trends Genet.
24:70–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang Z and Burge CB: Splicing regulation:
From a parts list of regulatory elements to an integrated splicing
code. RNA. 14:802–813. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I,
Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP and Burge CB: Alternative
isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature.
456:470–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Friboulet L, Olaussen KA, Pignon JP,
Shepherd FA, Tsao MS, Graziano S, Kratzke R, Douillard JY, Seymour
L, Pirker R, et al: ERCC1 isoform expression and DNA repair in
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:1101–1110. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mayr C and Bartel DP: Widespread
shortening of 3′UTRs by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation
activates oncogenes in cancer cells. Cell. 138:673–684. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Whitehead CM, Winkfein RJ, Fritzler MJ and
Rattner JB: ASE-1: A novel protein of the fibrillar centres of the
nucleolus and nucleolus organizer region of mitotic chromosomes.
Chromosoma. 106:493–502. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto K, Yamamoto M, Hanada K, Nogi Y,
Matsuyama T and Muramatsu M: Multiple protein-protein interactions
by RNA polymerase I-associated factor PAF49 and role of PAF49 in
rRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 24:6338–6349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ,
Trigiante G, Crook T, Hsieh JK, O’Connor DJ, Zhong S, Campargue I,
Tomlinson ML, et al: iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53
conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet. 33:162–167. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang JP, Hori M, Sanda T and Okamoto T:
Identification of a novel inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB,
RelA-associated inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 274:15662–15670. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mattick JS: RNA regulation: A new
genetics? Nat Rev Genet. 5:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Krystal GW, Armstrong BC and Battey JF:
N-myc mRNA forms an RNA-RNA duplex with endogenous antisense
transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 10:4180–4191. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen J, Sun M, Kent WJ, Huang X, Xie H,
Wang W, Zhou G, Shi RZ and Rowley JD: Over 20% of human transcripts
might form sense-antisense pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:4812–4820.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mihalich A, Reina M, Mangioni S, Ponti E,
Alberti L, Viganò P, Vignali M and Di Blasio AM: Different basic
fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-antisense
expression in eutopic endometrial stromal cells derived from women
with and without endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
88:2853–2859. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Annilo T, Kepp K and Laan M: Natural
antisense transcript of natriuretic peptide precursor A (NPPA):
Structural organization and modulation of NPPA expression. BMC Mol
Biol. 10:812009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Frith MC, Carninci P, Kai C, Kawai J,
Bailey TL, Hayashizaki Y and Mattick JS: Splicing bypasses 3′ end
formation signals to allow complex gene architectures. Gene.
403:188–193. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tufarelli C, Stanley JA, Garrick D, Sharpe
JA, Ayyub H, Wood WG and Higgs DR: Transcription of antisense RNA
leading to gene silencing and methylation as a novel cause of human
genetic disease. Nat Genet. 34:157–165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Proudfoot NJ, Furger A and Dye MJ:
Integrating mRNA processing with transcription. Cell. 108:501–512.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Karolchik D, Barber GP, Casper J, Clawson
H, Cline MS, Diekhans M, Dreszer TR, Fujita PA, Guruvadoo L,
Haeussler M, et al: The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2014 update.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D764–D770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ryan MC, Cleland J, Kim R, Wong WC and
Weinstein JN: SpliceSeq: A resource for analysis and visualization
of RNA-Seq data on alternative splicing and its functional impacts.
Bioinformatics. 28:2385–2387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBio-Portal. Sci Signal. 6:12013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chansky K, Detterbeck FC, Nicholson AG,
Rusch VW, Vallières E, Groome P, Kennedy C, Krasnik M, Peake M,
Shemanski L, et al IASLC Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee,
Advisory Boards, and Participating Institutions: The IASLC lung
cancer staging project: External validation of the revision of the
TNM stage groupings in the eighth edition of the TNM classification
of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1109–1121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kaelin WG Jr and McKnight SL: Influence of
metabolism on epigenetics and disease. Cell. 153:56–69. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Benayoun BA, Pollina EA, Ucar D, Mahmoudi
S, Karra K, Wong ED, Devarajan K, Daugherty AC, Kundaje AB, Mancini
E, et al: H3K4me3 breadth is linked to cell identity and
transcriptional consistency. Cell. 158:673–688. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ramakrishnan S, Pokhrel S, Palani S,
Pflueger C, Parnell TJ, Cairns BR, Bhaskara S and Chandrasekharan
MB: Counteracting H3K4 methylation modulators Set1 and Jhd2
co-regulate chromatin dynamics and gene transcription. Nat Commun.
7:119492016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Salton M and Misteli T: Small molecule
modulators of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med.
22:28–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson
G, Frank J, Burghardt R, Kim S and Safe S: HOTAIR is a negative
prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic
cancer. Oncogene. 32:1616–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Luo JH, Ren B, Keryanov S, Tseng GC, Rao
UN, Monga SP, Strom S, Demetris AJ, Nalesnik M, Yu YP, et al:
Transcriptomic and genomic analysis of human hepatocellular
carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Hepatology. 44:1012–1024. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|