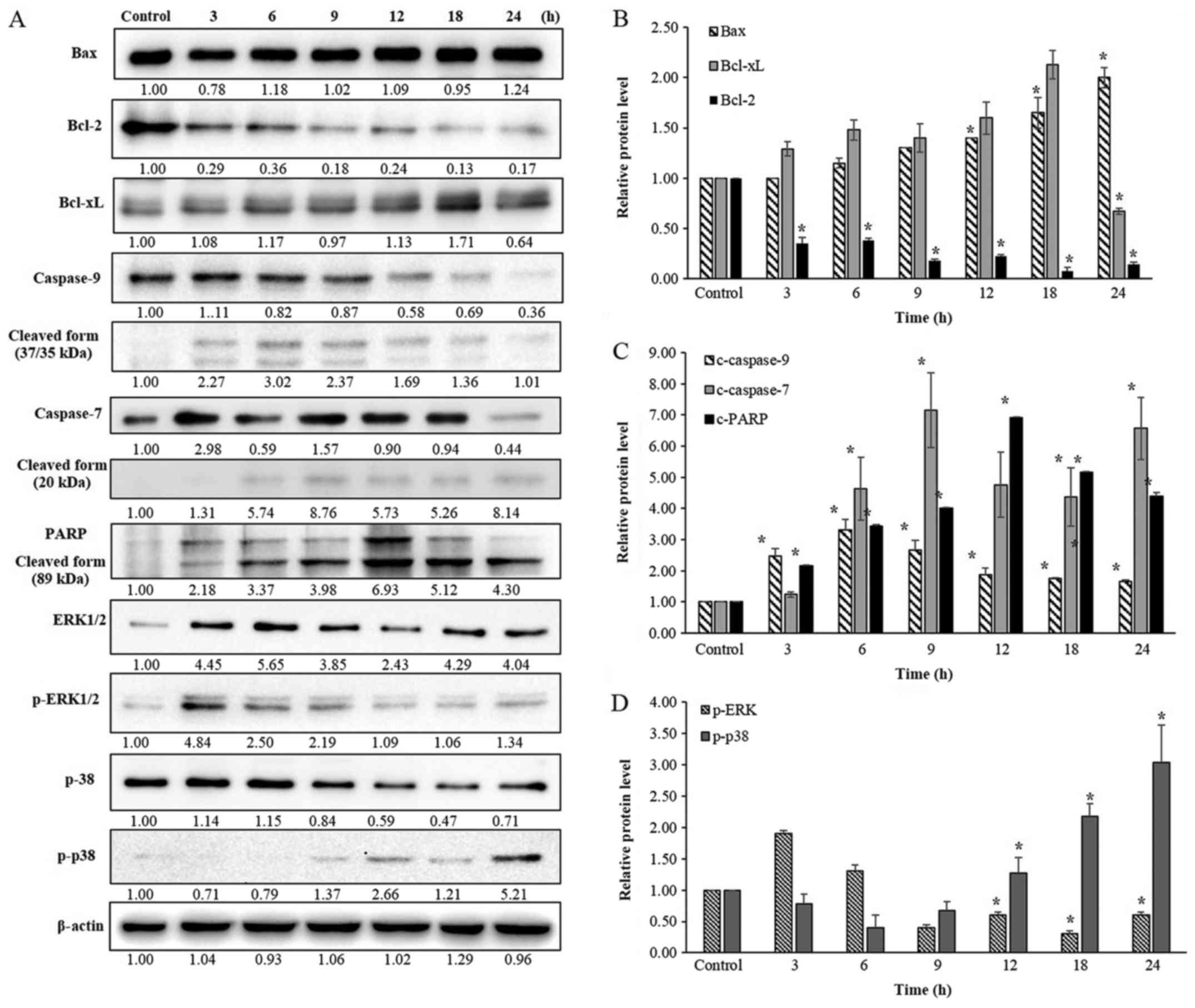
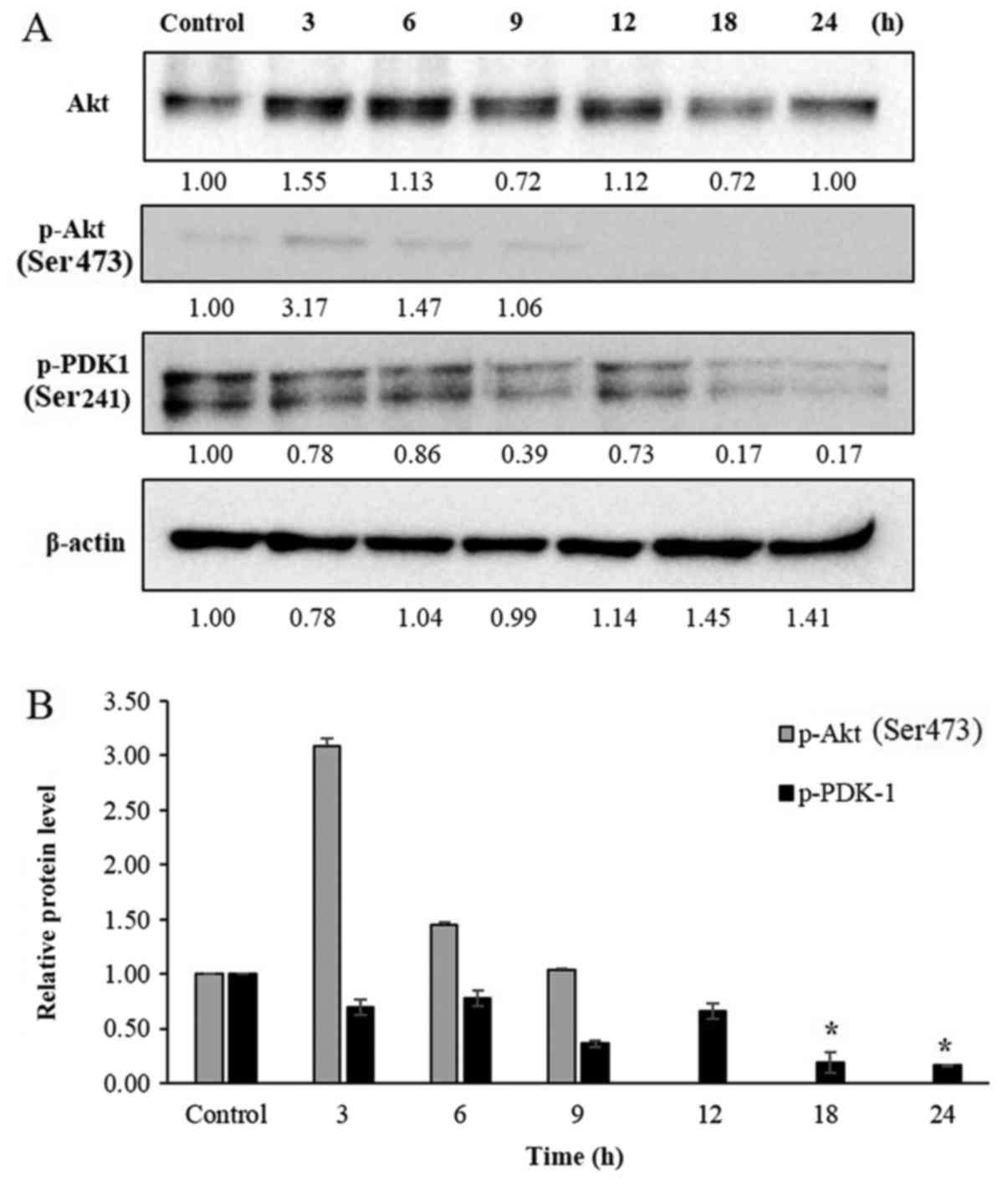
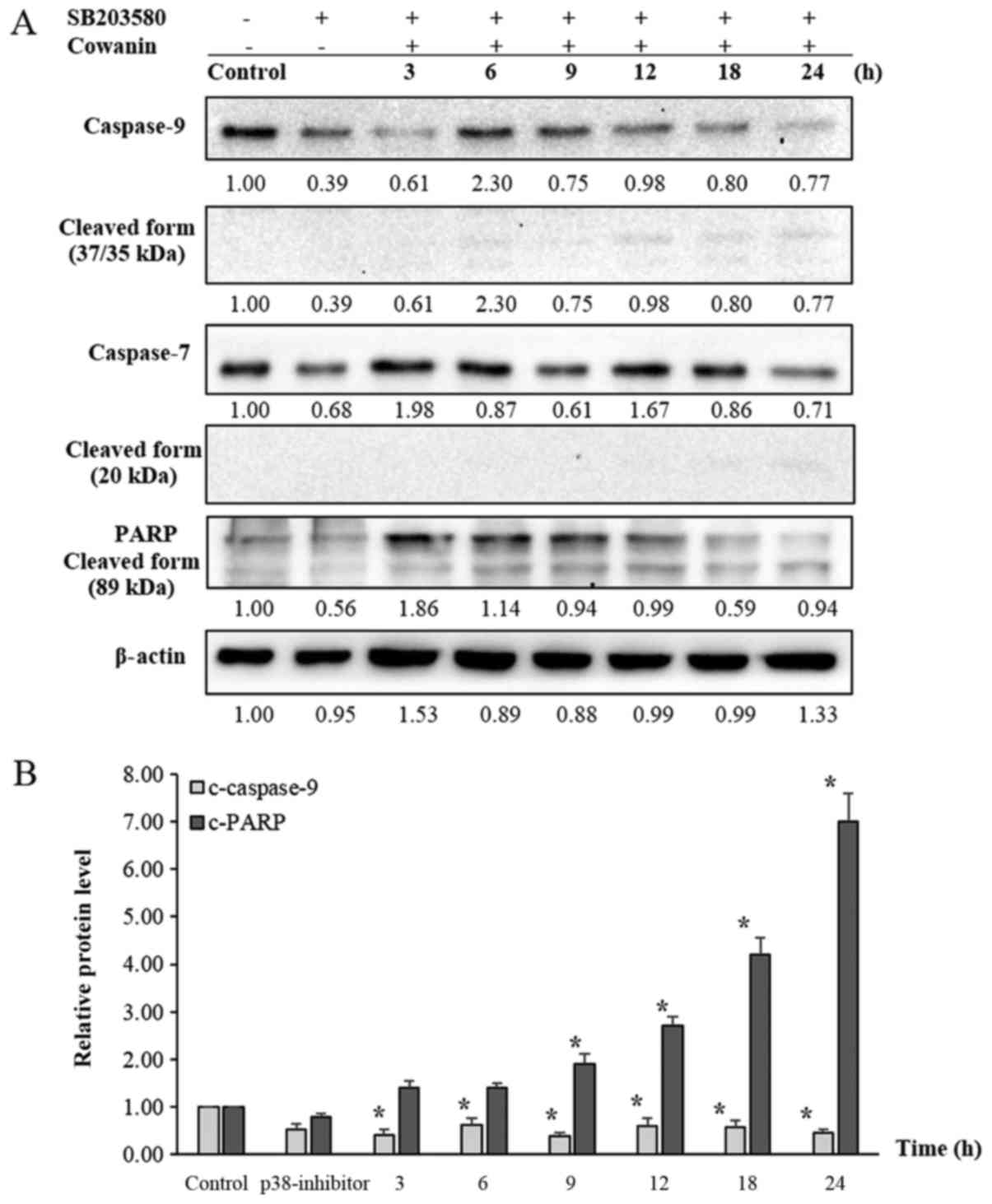
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lohsiriwat V, Lohsiriwat D and
Thavichaigarn P; Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Thailand:
Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: A survey among Thai
general surgeons. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 10:467–470. 2009.
|
|
4
|
Khuhaprema T and Srivatanakul P: Colon and
rectum cancer in Thailand: An overview. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
38:237–243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yaoxian W, Hui Y, Yunyan Z, Yanqin L, Xin
G and Xiaoke W: Emodin induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer
HeLa cells via intrinsic mitochondrial and extrinsic death receptor
pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 13:712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M
and Greenwood MT: Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: A review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:238–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sugino T, Nozaki K, Takagi Y, Hattori I,
Hashimoto N, Moriguchi T and Nishida E: Activation of
mitogen-activated protein kinases after transient forebrain
ischemia in gerbil hippocampus. J Neurosci. 20:4506–4514. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fang JY and Richardson BC: The MAPK
signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 6:322–327.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Porras A, Zuluaga S, Black E, Valladares
A, Alvarez AM, Ambrosino C, Benito M and Nebreda AR: P38 alpha
mitogen-activated protein kinase sensitizes cells to apoptosis
induced by different stimuli. Mol Biol Cell. 15:922–933. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Genovese MC: Inhibition of p38: Has the
fat lady sung? Arthritis Rheum. 60:317–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Panthong K, Pongcharoen W, Phongpaichit S
and Taylor WC: Tetraoxygenated xanthones from the fruits of
Garcinia cowa. Phytochemistry. 67:999–1004. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
na Pattalung P, Thongtheeraparp W,
Wiriyachitra P and Taylor WC: Xanthones of Garcinia cowa. Planta
Med. 60:365–368. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Poomipamorn S and Kumkong A: Edible
Multipurpose Tree Species: Cha-Muang. Agriculture Federative
Co-operation of Thailand Ltd. Printing; Bangkok: pp. 118–120. 1997,
In Thai.
|
|
18
|
Murakami A, Jiwajinda S, Koshimizu K and
Ohigashi H: Screening for in vitro anti-tumor promoting activities
of edible plants from Thailand. Cancer Lett. 95:139–146. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ilham M, Yaday M and Norhanom AW: Tumour
promoting activity of plants used in malaysian traditional
medicine. Nat Prod Sci. 1:31–42. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Likhitwitayawuid K, Phadungcharoen T,
Mahidol C and Ruchirawat S: 7-O-methylgarcinone e from Garcinia
cowa. Phytochemistry. 45:1299–1301. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Panthong K, Hutadilok-Towatana N and
Panthong A: Cowaxanthone F, a new tetraoxygenated xanthone, and
other anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds from Garcinia
cowa. Can J Chem. 87:1636–1640. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wahyuni FS, Shaari K, Stanslas J, Lajis NH
and Dachriyanus: Cytotoxic xanthones from the stem bark of Garcinia
cowa Roxb. J Chem Pharm Res. 7:227–236. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Mahabusarakam W, Chairerk P and Taylor WC:
Xanthones from Garcinia cowa Roxb. latex. Phytochemistry.
66:1148–1153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ritthiwigrom T, Laphookhieo S and Pyne SG:
Chemical constituents and biological activities of Garcinia cowa
Roxb. Maejo Int J Sci. 7:212–231. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nuñez G and Clarke MF: The Bcl-2 family of
proteins: Regulators of cell death and survival. Trends Cell Biol.
4:399–403. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gross A, MaDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nakagawa Y, Iinuma M, Naoe T, Nozawa Y and
Akao Y: Characterized mechanism of alpha-mangostin-induced cell
death: Caspase-independent apoptosis with release of endonuclease-G
from mitochondria and increased miR-143 expression in human
colorectal cancer DLD-1 cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:5620–5628. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Krajarng A, Nakamura Y, Suksamrarn S and
Watanapokasin R: α-Mangostin induces apoptosis in human
chondrosarcoma cells through downregulation of ERK/JNK and Akt
signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 59:5746–5754. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Innajak S, Mahabusrakum W and
Watanapokasin R: Goniothalamin induces apoptosis associated with
autophagy activation through MAPK signaling in SK-BR-3 cells. Oncol
Rep. 35:2851–2858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pan BS, Wang YK, Lai MS, Mu YF and Huang
BM: Cordycepin induced MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cell apoptosis by
regulating p38 MAPKs and PI3K/AKT sihnaling pathways. Sci Rep.
5:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hammond WA, Swaika A and Mody K:
Pharmacologic resistance in colorectal cancer: A review. Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 8:57–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Huang F, Bai Z, Chi B, Wu J and
Chen X: Curcumol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of
colorectal cancer LoVo cell line via IGF-1R and p38 MAPK pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:19851–19867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sophonnithiprasert T, Nilwarangkoon S,
Nakamura Y and Watanapokasin R: Goniothalamin enhances
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through DR5
upregulation and cFLIP downregulation. Int J Oncol. 47:2188–2196.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ji YB, Ji CF and Zhang H: Laminarin
induces apoptosis of human colon cancer LOVO cells through a
mitochondrial pathway. Molecules. 17:9947–9960. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Krishan A: Rapid flow cytofluorometric
analysis of mammalian cell cycle by propidium iodide staining. J
Cell Biol. 66:188–193. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rysavy NM, Shimoda LMN, Dixon AM, Speck M,
Stokes AJ, Turner H and Umemoto EY: Beyond apoptosis: The mechanism
and function of phosphatidylserine asymmetry in the membrane of
activating mast cells. Bioarchitecture. 4:127–137. 2014.
|
|
41
|
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C,
Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Poirier GG, Dawson TM and Dawson VL:
Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by
apoptosis-inducing factor. Science. 297:259–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wen X, Zhou J, Zhang D, Li J, Wang Q, Feng
N, Zhu H, Song Y, Li H and Bai C: Denatonium inhibits growth and
induces apoptosis of airway epithelial cells through mitochondrial
signaling pathways. Respir Res. 16:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, Gaffney
PR, Reese CB, Painter GF, Holmes AB, McCormick F and Hawkins PT:
Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the
activation of protein kinase B. Science. 277:567–570. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sabnis G, Schayowitz A, Goloubeva O,
Macedo L and Brodie A: Trastuzumab reverses letrozole resistance
and amplifies the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to estrogen.
Cancer Res. 69:1416–1428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Oskouian B, Sooriyakumaran P, Borowsky AD,
Crans A, Dillard-Telm L, Tam YY, Bandhuvula P and Saba JD:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase potentiates apoptosis via p53- and
p38-dependent pathways and is down-regulated in colon cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17384–17389. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cuenda A, Rouse J, Doza YN, Meier R, Cohen
P, Gallagher TF, Young PR and Lee JC: SB 203580 is a specific
inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular
stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 364:229–233. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lali FV, Hunt AE, Turner SJ and Foxwell
BMJ: The pyridinyl imidazole inhibitor SB203580 blocks
phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase activity, protein kinase
B phosphorylation, and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation in
interleukin-2-stimulated T cells independently of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 275:7395–7402. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Junn E and Mouradian MM: Apoptotic
signaling in dopamine-induced cell death: The role of oxidative
stress, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, cytochrome c and
caspases. J Neurochem. 78:374–383. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ma XL, Kumar S, Gao F, Louden CS, Lopez
BL, Christopher TA, Wang C, Lee JC, Feuerstein GZ and Yue TL:
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase decreases
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves cardiac function after
myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation. 99:1685–1691.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|