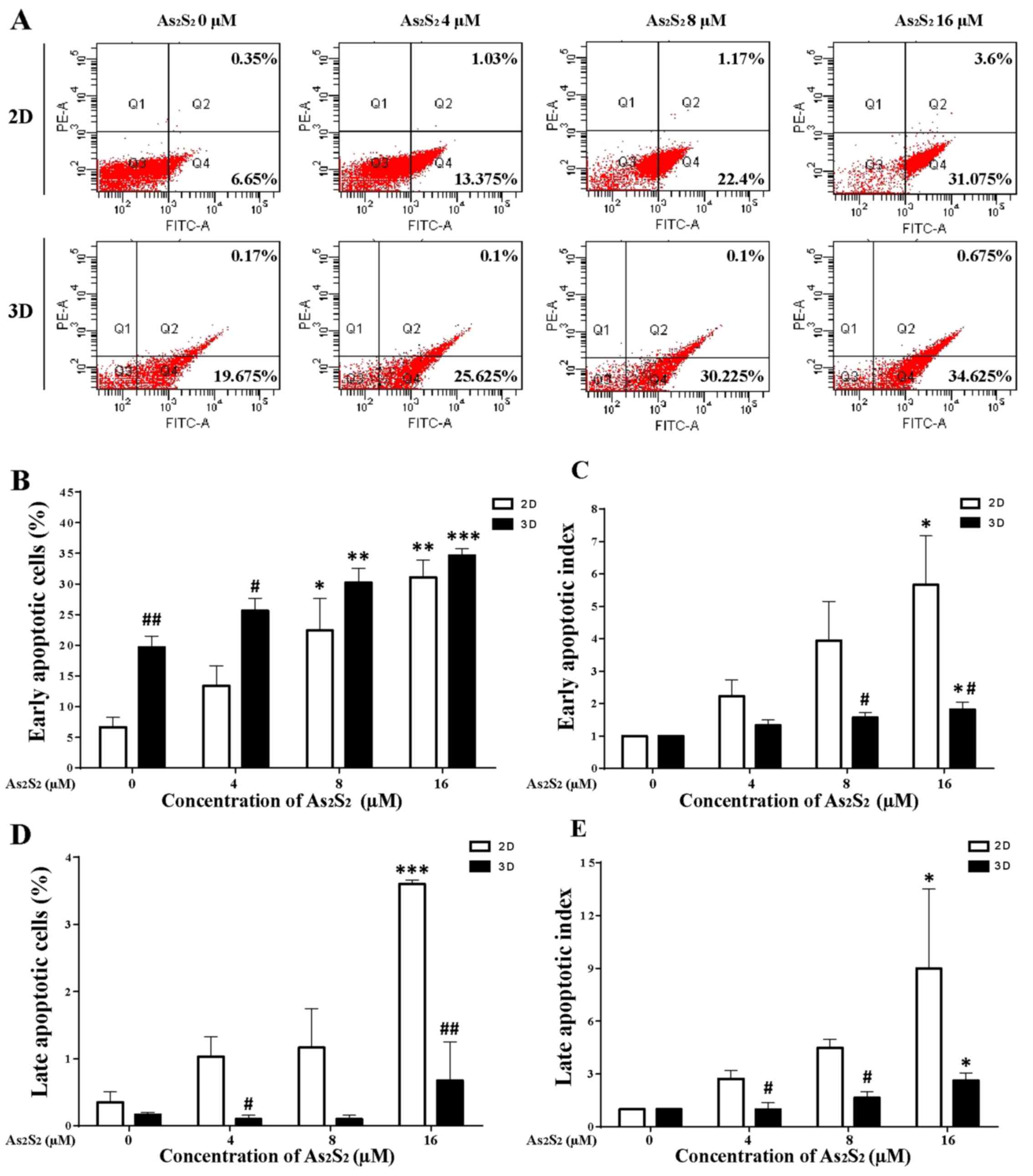
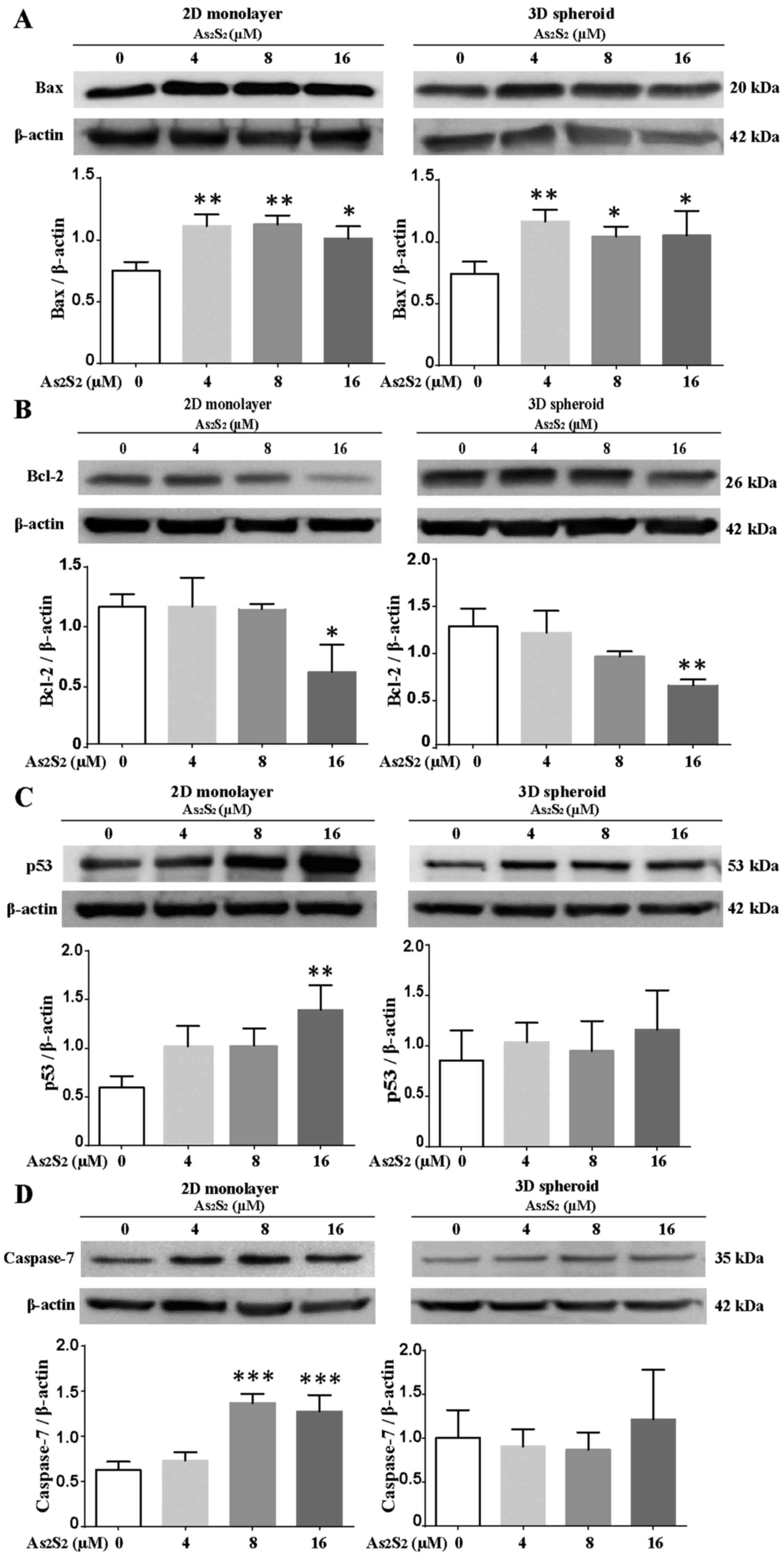
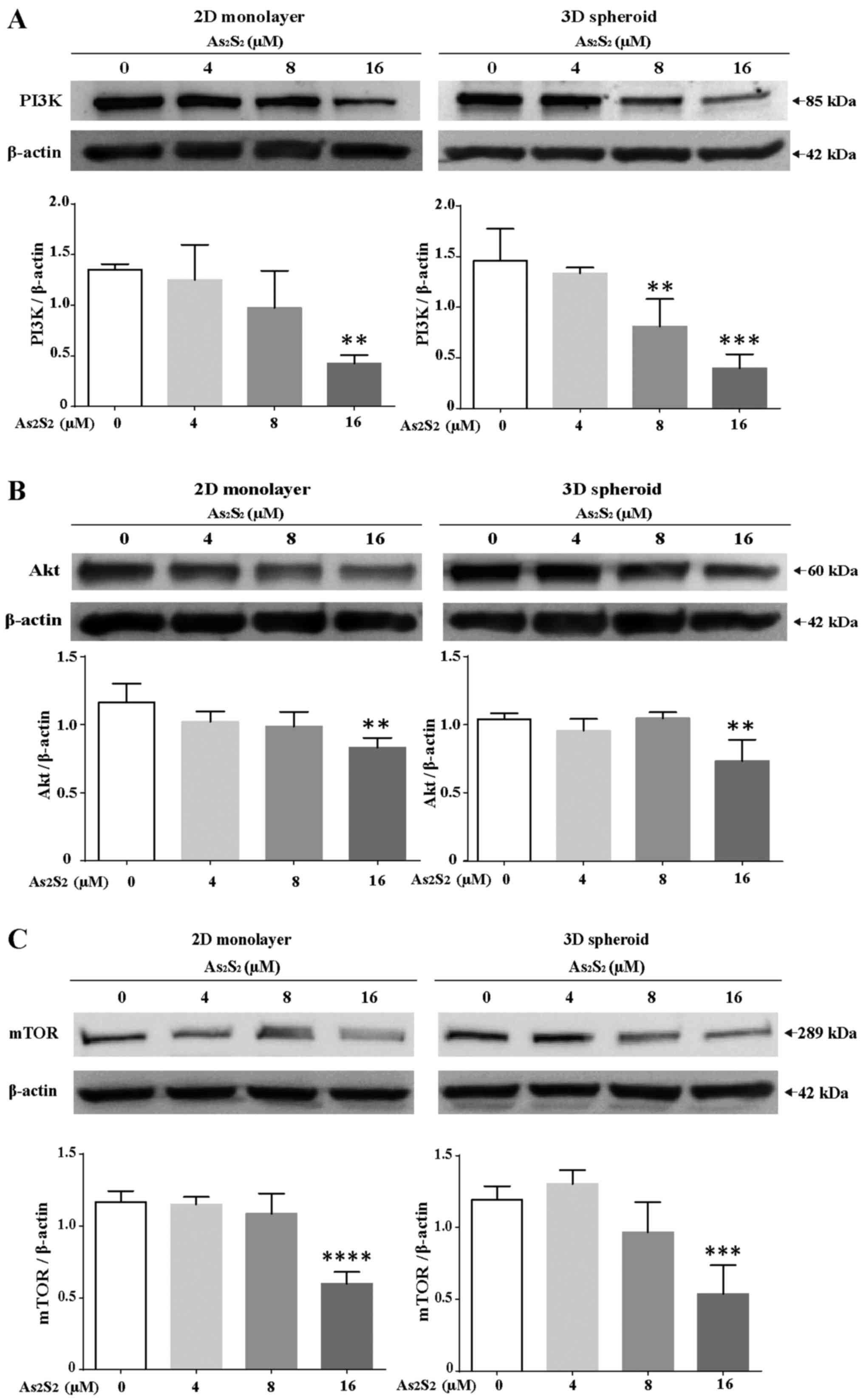
|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Recht A, Come SE, Henderson IC, Gelman RS,
Silver B, Hayes DF, Shulman LN and Harris JR: The sequencing of
chemotherapy and radiation therapy after conservative surgery for
early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 334:1356–1361. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rojewski MT, Körper S and Schrezenmeier H:
Arsenic trioxide therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia and
beyond: From bench to bedside. Leuk Lymphoma. 45:2387–2401. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cicconi L and Lo-Coco F: Current
management of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann
Oncol. 27:1474–1481. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer
J and Waxman S: Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer
Res. 62:3893–3903. 2002.
|
|
7
|
Chow SK, Chan JY and Fung KP: Suppression
of cell proliferation and regulation of estrogen receptor alpha
signaling pathway by arsenic trioxide on human breast cancer MCF-7
cells. J Endocrinol. 182:325–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yao M, Yuan B, Wang X, Sato A, Sakuma K,
Kaneko K, Komuro H, Okazaki A, Hayashi H, Toyoda H, et al:
Synergistic cytotoxic effects of arsenite and tetrandrine in human
breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Int J Oncol. 51:587–598. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Soria EA, Bongiovanni GA, Luján CD and
Eynard AR: Effect of arsenite on nitrosative stress in human breast
cancer cells and its modulation by flavonoids. Nutr Cancer.
67:659–663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu JZ and Ho PC: Comparing the relative
oxidative DNA damage caused by various arsenic species by
quantifying urinary levels of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine with
isotope-dilution liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Pharm
Res. 26:1525–1533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Horibe Y, Adachi S, Yasuda I, Yamauchi T,
Kawaguchi J, Kozawa O, Shimizu M and Moriwaki H: Anticancer effect
of arsenite on cell migration, cell cycle and apoptosis in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 12:177–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dangleben NL, Skibola CF and Smith MT:
Arsenic immunotoxicity: A review. Environ Health. 12:732013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lu DP, Qiu JY, Jiang B, Wang Q, Liu KY,
Liu YR and Chen SS: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide for the treatment
of acute promyelocytic leukemia: A pilot report. Blood.
99:3136–3143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lu YF, Yan JW, Wu Q, Shi JZ, Liu J and Shi
JS: Realgar- and cinnabar-containing an-gong-niu-huang wan (AGNH)
is much less acutely toxic than sodium arsenite and mercuric
chloride. Chem Biol Interact. 189:134–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Liang SX, Lu YF, Miao JW, Wu Q and
Shi JS: Realgar and realgar-containing Liu-Shen-Wan are less
acutely toxic than arsenite and arsenate. J Ethnopharmacol.
134:26–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y,
Yan XJ, Xu F, Wang BS, Mao JH, Shen ZX, et al: Dissection of
mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as
an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:4826–4831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang QY, Mao JH, Liu P, Huang QH, Lu J,
Xie YY, Weng L, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Chen SJ, et al: A systems biology
understanding of the synergistic effects of arsenic sulfide and
Imatinib in BCR/ABL-associated leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:3378–3383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, He P, Cheng X and Zhang M:
Long-term outcome of 31 cases of refractory acute promyelocytic
leukemia treated with compound realgar natural indigo tablets
administered alternately with chemotherapy. Oncol Lett.
10:1184–1190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu F, Wu D, Ren Y, Duan C, Chen S and Xu
A: Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing five contemporary
treatment strategies for newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic
leukaemia. Oncotarget. 7:47319–47331. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Liu X, Li X, Lv X, Lu K, Chen N,
Li P and Wang X: Arsenic disulfide induces apoptosis of human
diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells involving Bax cleavage. Oncol
Rep. 30:2427–2434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cheng YX, Liu R, Wang Q, Li BS, Xu XX, Hu
M, Chen L, Fu Q, Pu DM and Hong L: Realgar-induced apoptosis of
cervical cancer cell line Siha via cytochrome c release and
caspase-3 and caspase-9 activation. Chin J Integr Med. 18:359–365.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Song P, Chen P, Wang D, Wu Z, Gao Q, Wang
A, Zhu R, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhao L, et al: Realgar transforming
solution displays anticancer potential against human hepatocellular
carcinoma HepG2 cells by inducing ROS. Int J Oncol. 50:660–670.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang G, Zhang T, Sun W, Wang H, Yin F,
Wang Z, Zuo D, Sun M, Zhou Z, Lin B, et al: Arsenic sulfide induces
apoptosis and autophagy through the activation of ROS/JNK and
suppression of Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in osteosarcoma. Free
Radic Biol Med. 106:24–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tian Y, Wang X, Xi R, Pan W, Jiang S, Li
Z, Zhao Y, Gao G and Liu D: Enhanced antitumor activity of realgar
mediated by milling it to nanosize. Int J Nanomedicine. 9:745–757.
2014.
|
|
25
|
Breslin S and O’Driscoll L:
Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery.
Drug Discov Today. 18:240–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yamada KM and Cukierman E: Modeling tissue
morphogenesis and cancer in 3D. Cell. 130:601–610. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Weigelt B, Ghajar CM and Bissell MJ: The
need for complex 3D culture models to unravel novel pathways and
identify accurate biomarkers in breast cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
69–70:42–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rimann M and Graf-Hausner U: Synthetic 3D
multicellular systems for drug development. Curr Opin Biotechnol.
23:803–809. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kiyomi A, Makita M, Ozeki T, Li N,
Satomura A, Tanaka S, Onda K, Sugiyama K, Iwase T and Hirano T:
Characterization and clinical implication of Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokines
produced from three-dimensionally cultured tumor tissues resected
from breast cancer patients. Transl Oncol. 8:318–326. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dubois V, Jardé T, Delort L, Billard H,
Bernard-Gallon D, Berger E, Geloen A, Vasson MP and Caldefie-Chezet
F: Leptin induces a proliferative response in breast cancer cells
but not in normal breast cells. Nutr Cancer. 66:645–655. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Alcolea V, Plano D, Encío I, Palop JA,
Sharma AK and Sanmartín C: Chalcogen containing heterocyclic
scaffolds: New hybrids with antitumoral activity. Eur J Med Chem.
123:407–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ciruelos Gil EM: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:862–871. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yun SM, Woo SH, Oh ST, Hong SE, Choe TB,
Ye SK, Kim EK, Seong MK, Kim HA, Noh WC, et al: Melatonin enhances
arsenic trioxide-induced cell death via sustained upregulation of
Redd1 expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
422:64–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang S, Ma C, Pang H, Zeng F, Cheng L,
Fang B, Ma J, Shi Y, Hong H, Chen J, et al: Arsenic trioxide
suppresses cell growth and migration via inhibition of miR-27a in
breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:55–61. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang YF, Zhang M, Huang XL, Fu YJ, Jiang
YH, Bao LL, Maimaitiyiming Y, Zhang GJ, Wang QQ and Naranmandura H:
The combination of arsenic and cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis
through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-reactive oxygen
species in breast cancer cells. Metallomics. 7:165–173. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Honma Y
and Kumakura S: Cotylenin A and arsenic trioxide cooperatively
suppress cell proliferation and cell invasion activity in human
breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:841–848. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Luo XQ, Ke ZY, Huang LB, Guan XQ, Zhang YC
and Zhang XL: Improved outcome for Chinese children with acute
promyelocytic leukemia: A comparison of two protocols. Pediatr
Blood Cancer. 53:325–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhu HH, Wu DP, Jin J, Li JY, Ma J, Wang
JX, Jiang H, Chen SJ and Huang XJ: Oral tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide
formula versus intravenous arsenic trioxide as first-line treatment
of acute promyelocytic leukemia: A multicenter randomized
controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 31:4215–4221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Xiang-Xin L, Lu-Qun W, Hao L, Xiao-Peng H,
Fang-Lin L, Ling-Ling W, Xue-Liang C and Ming H: Clinical study on
prospective efficacy of all-trans Acid, realgar-indigo naturalis
formula combined with chemotherapy as maintenance treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:9875602014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu JZ and Ho PC: Evaluation of the in
vitro activity and in vivo bioavailability of realgar nanoparticles
prepared by cryogrinding. Eur J Pharm Sci. 29:35–44. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang H, Liu Z, Gou Y, Qin Y, Xu Y, Liu J
and Wu JZ: Apoptosis and necrosis induced by novel realgar quantum
dots in human endometrial cancer cells via endoplasmic reticulum
stress signaling pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:5505–5512. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ding W, Zhang L, Kim S, Tian W, Tong Y,
Liu J, Ma Y and Chen S: Arsenic sulfide as a potential anti cancer
drug. Mol Med Rep. 11:968–974. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tsukikawa S, Matsuoka H, Kurahashi Y,
Konno Y, Satoh K, Satoh R, Isogai A, Kimura K, Watanabe Y, Nakano
S, et al: A new method to prepare multicellular spheroids in cancer
cell lines using a thermo-reversible gelation polymer. Artif
Organs. 27:598–604. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Khaitan D, Chandna S, Arya MB and
Dwarakanath BS: Establishment and characterization of multicellular
spheroids from a human glioma cell line; Implications for tumor
therapy. J Transl Med. 4:122006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF and
Yang L: Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their
applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay
Drug Dev Technol. 12:207–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Biswas DK, Shi Q, Baily S, Strickland I,
Ghosh S, Pardee AB and Iglehart JD: NF-kappa B activation in human
breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10137–10142. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN and Van
Bockstaele DR: Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 36:165–175.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fischbach C, Chen R, Matsumoto T,
Schmelzle T, Brugge JS, Polverini PJ and Mooney DJ: Engineering
tumors with 3D scaffolds. Nat Methods. 4:855–860. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Debnath J and Brugge JS: Modelling
glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev
Cancer. 5:675–688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Breslin S and O’Driscoll L: The relevance
of using 3D cell cultures, in addition to 2D monolayer cultures,
when evaluating breast cancer drug sensitivity and resistance.
Oncotarget. 7:45745–45756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zeng H, Sun M, Zhou C, Yin F, Wang Z, Hua
Y and Cai Z: Hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether-mediated photodynamic
therapy selectively kills sarcomas by inducing apoptosis. PLoS One.
8:e777272013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Akeda K, Nishimura A, Satonaka H, Shintani
K, Kusuzaki K, Matsumine A, Kasai Y, Masuda K and Uchida A:
Three-dimensional alginate spheroid culture system of murine
osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 22:997–1003. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chandrasekaran S, Marshall JR, Messing JA,
Hsu JW and King MR: TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells
cultured as 3D spheroids. PLoS One. 9:e1114872014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sodek KL, Murphy KJ, Brown TJ and
Ringuette MJ: Cell-cell and cell-matrix dynamics in intraperitoneal
cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:397–414. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Daubriac J, Fleury-Feith J, Kheuang L,
Galipon J, Saint-Albin A, Renier A, Giovannini M, Galateau-Sallé F
and Jaurand MC: Malignant pleural mesothelioma cells resist anoikis
as quiescent pluricellular aggregates. Cell Death Differ.
16:1146–1155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Khairul I, Wang QQ, Jiang YH, Wang C and
Naranmandura H: Metabolism, toxicity and anticancer activities of
arsenic compounds. Oncotarget. 8:23905–23926. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Boehme KA, Nitsch J, Riester R,
Handgretinger R, Schleicher SB, Kluba T and Traub F: Arsenic
trioxide potentiates the effectiveness of etoposide in Ewing
sarcomas. Int J Oncol. 49:2135–2146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kadam CY and Abhang SA: Apoptosis markers
in breast cancer therapy. Adv Clin Chem. 74:143–193. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH:
Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:383–424. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kurokawa H, Nishio K, Fukumoto H, Tomonari
A, Suzuki T and Saijo N: Alteration of caspase-3
(CPP32/Yama/apopain) in wild-type MCF-7, breast cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 6:33–37. 1999.
|
|
62
|
Simstein R, Burow M, Parker A, Weldon C
and Beckman B: Apoptosis, chemoresistance, and breast cancer:
Insights from the MCF-7 cell model system. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
228:995–1003. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wang X, Simpson ER and Brown KA: p53:
Protection against tumor growth beyond effects on cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 75:5001–5007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Pietsch EC, Sykes SM, McMahon SB and
Murphy ME: The p53 family and programmed cell death. Oncogene.
27:6507–6521. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H and Zhao JJ: PI3K
in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and
therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:7–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Miller TW, Rexer BN, Garrett JT and
Arteaga CL: Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway:
Role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2242011. View Article : Google Scholar
|