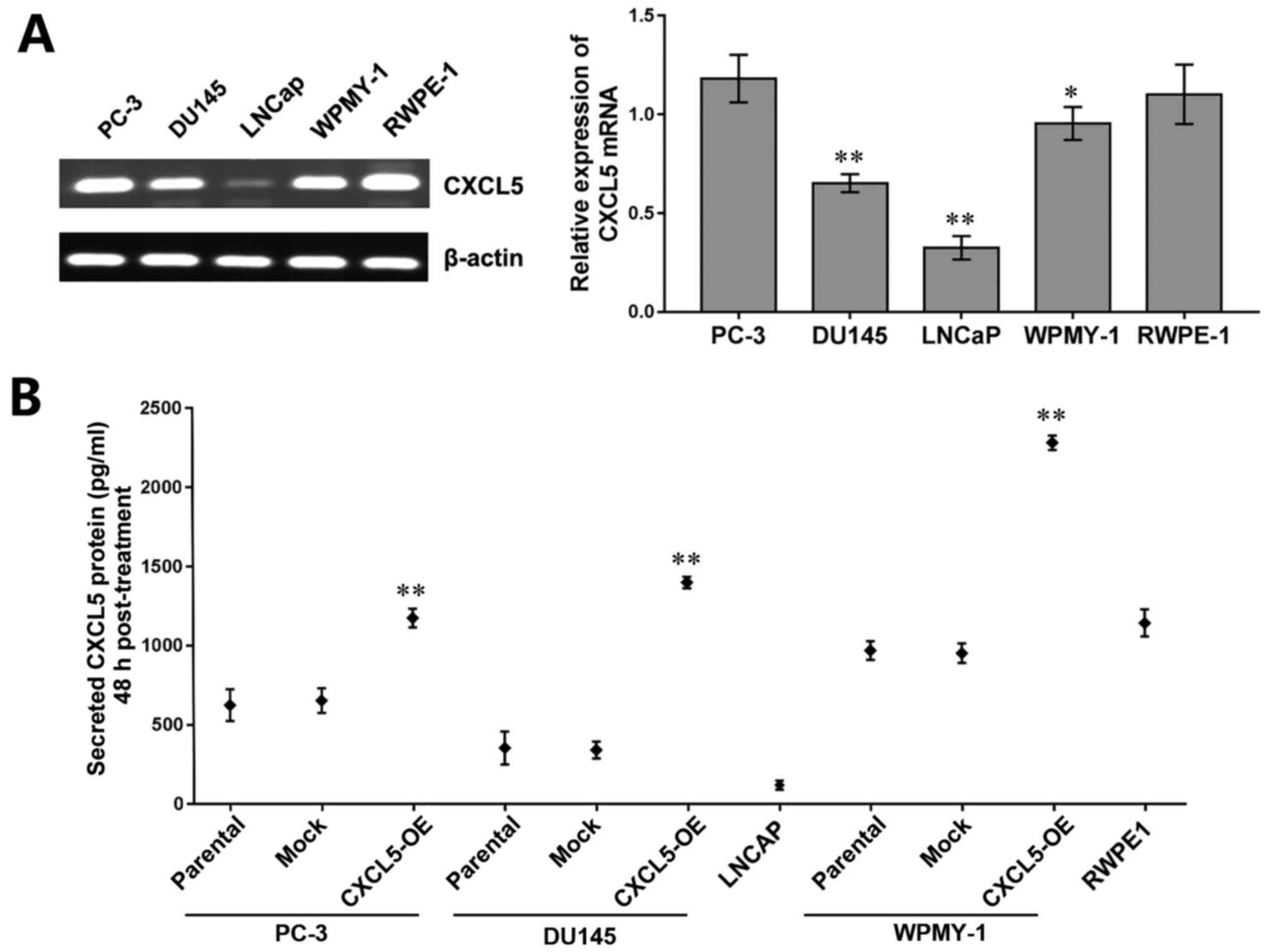
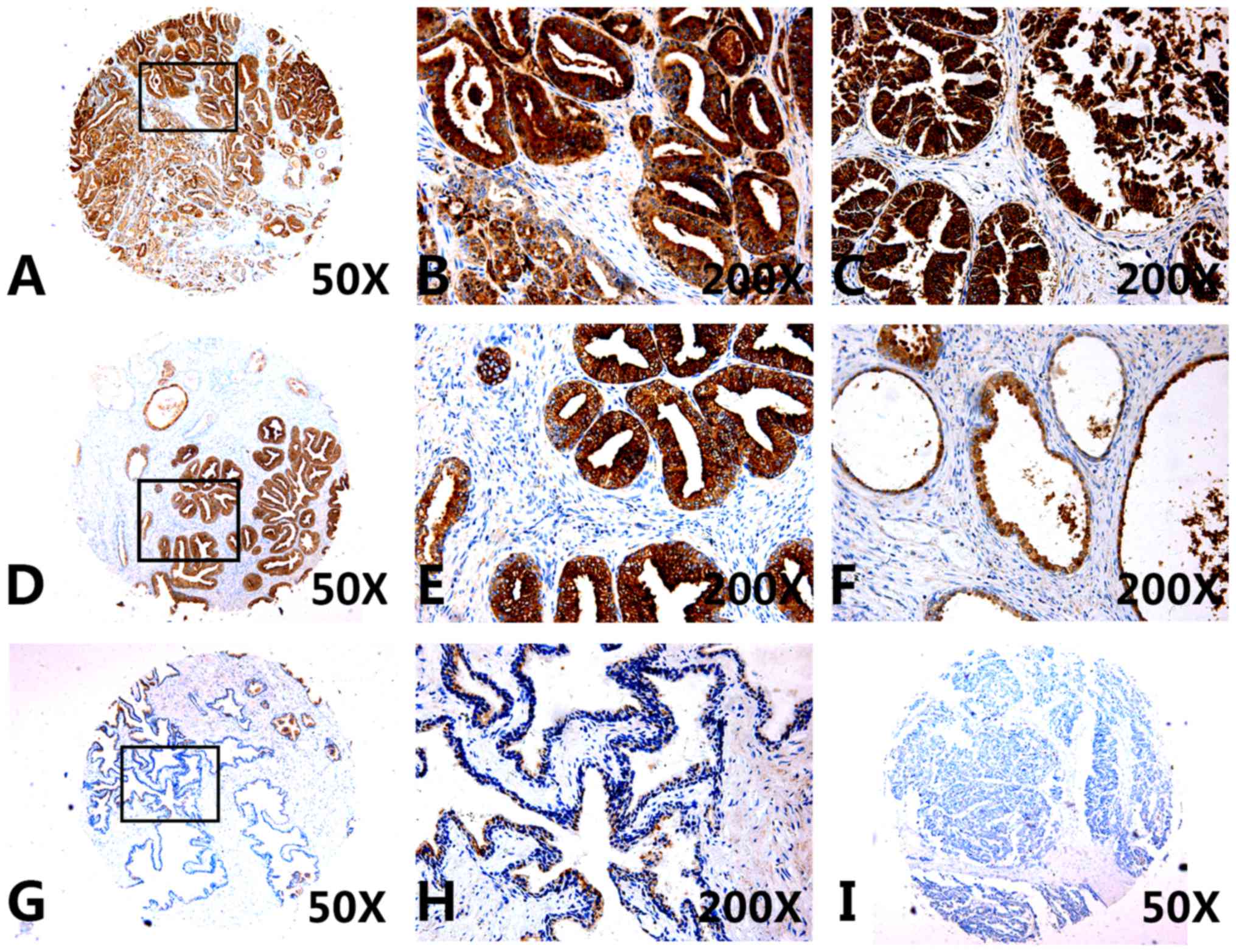
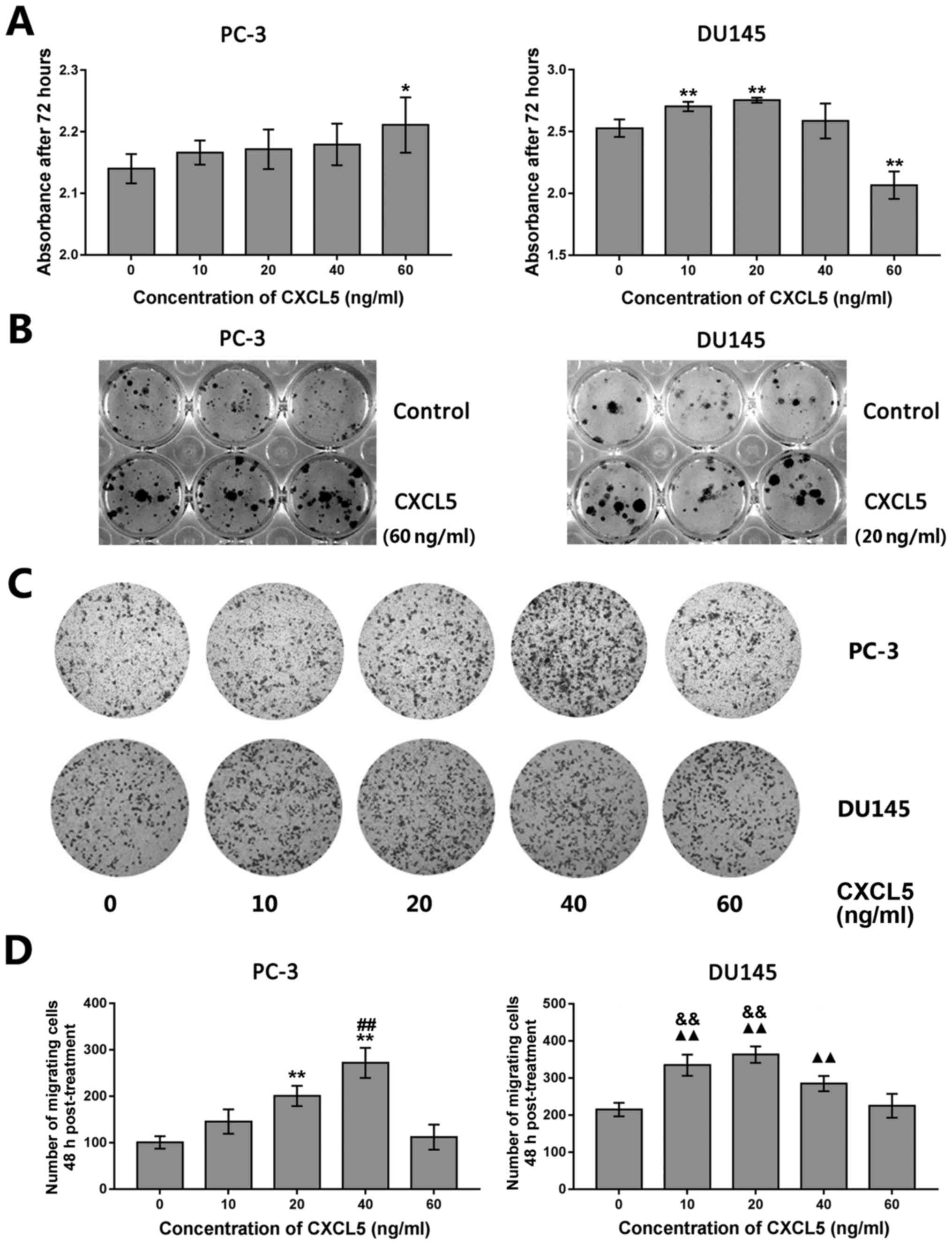
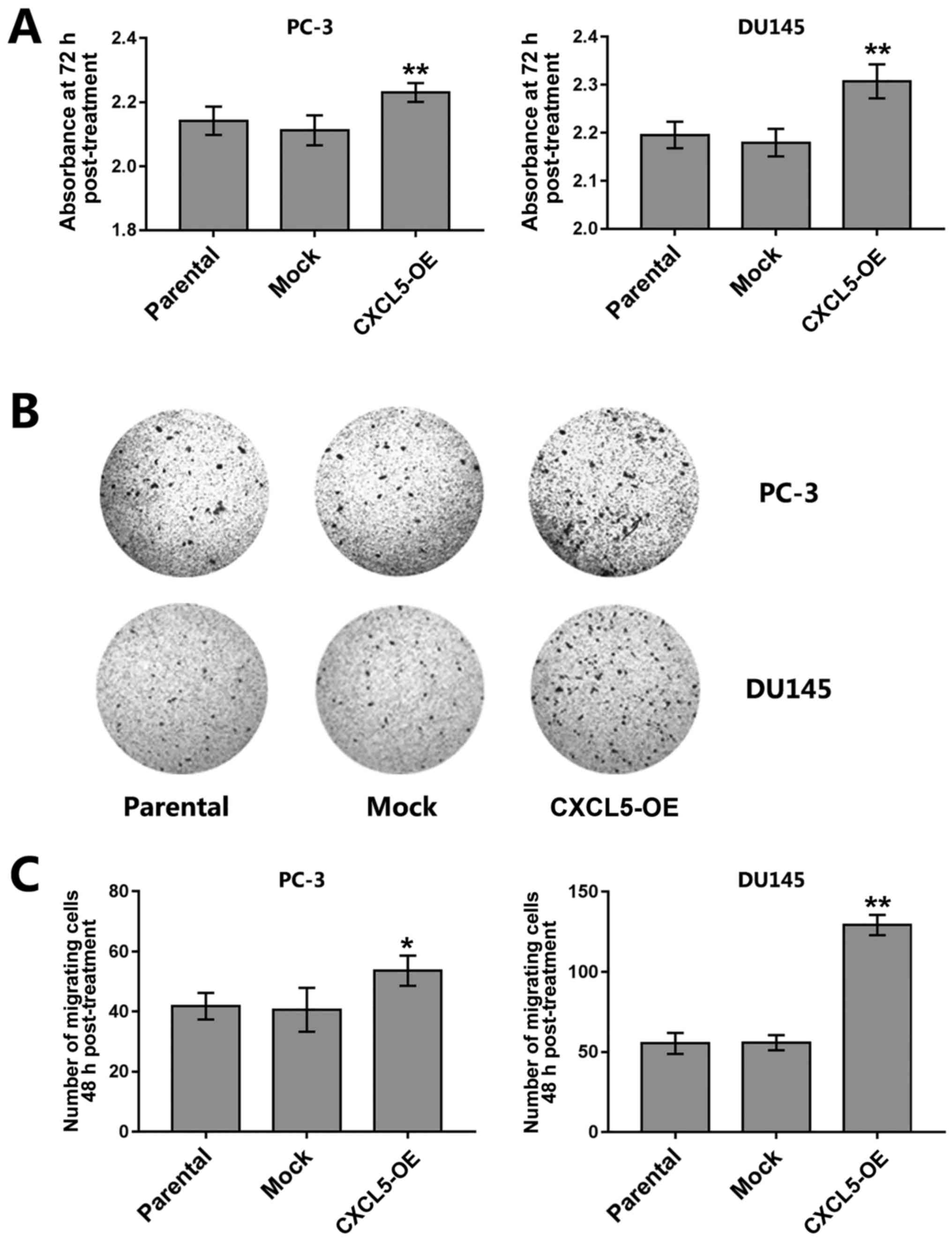
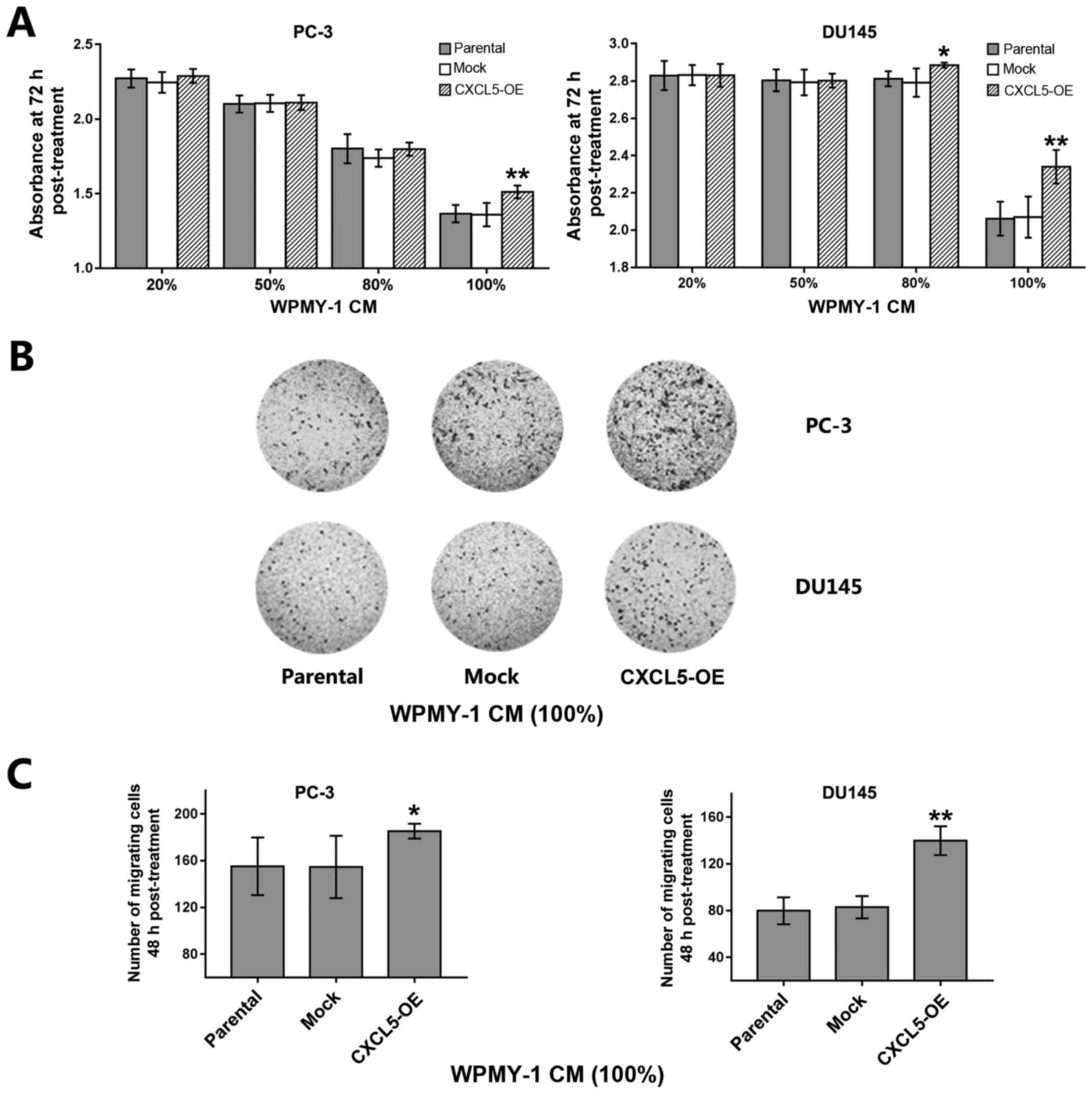
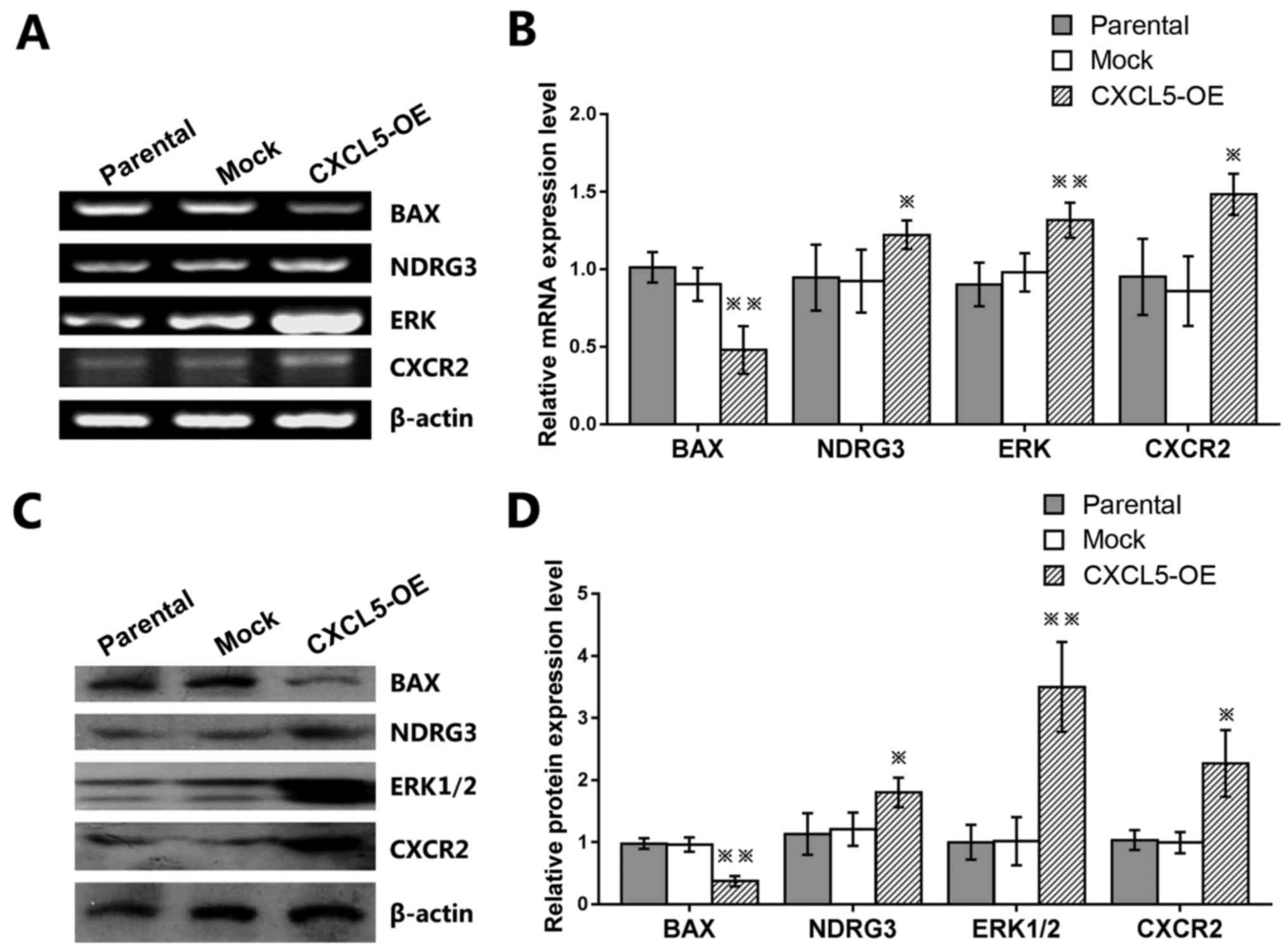
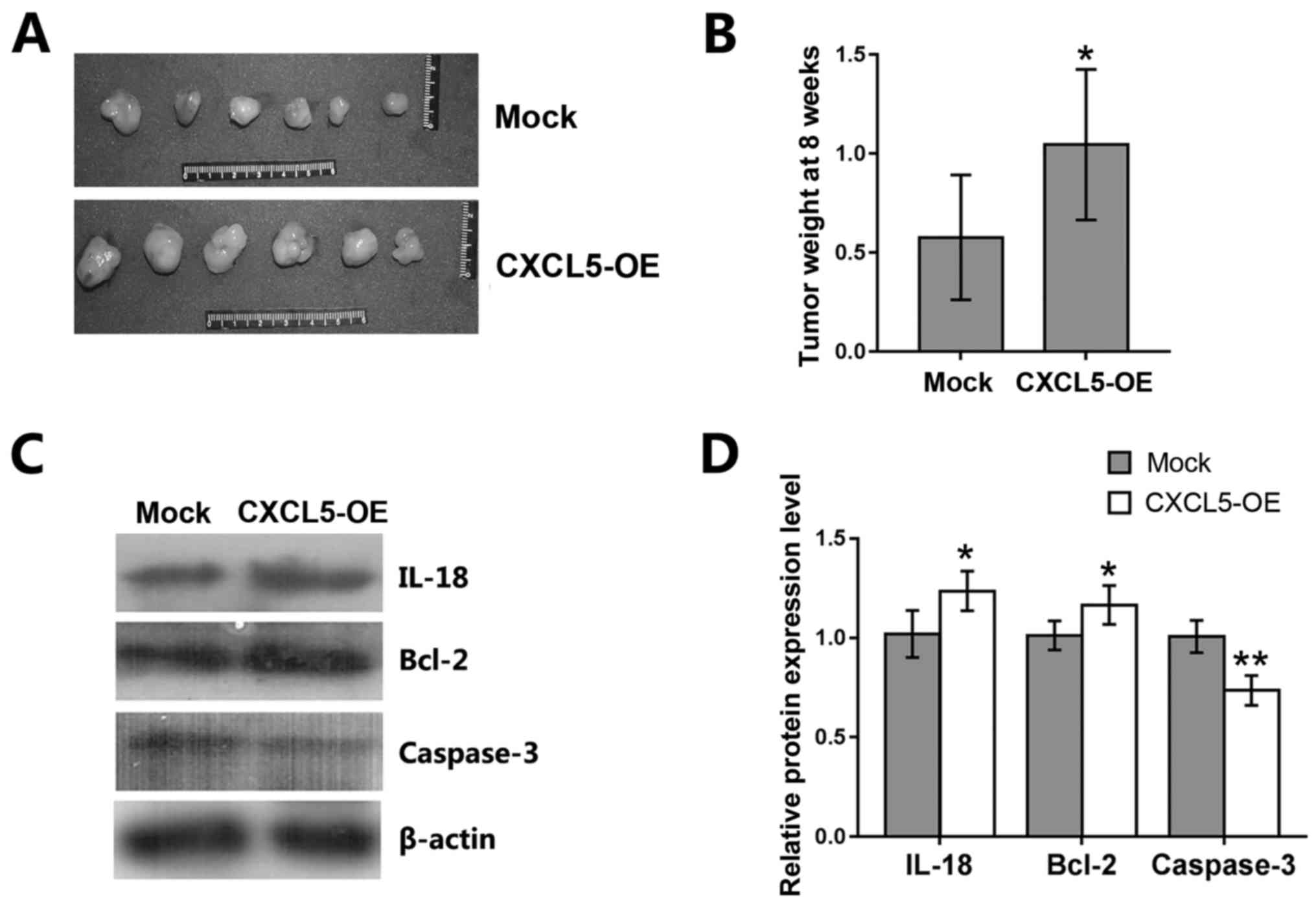
|
1
|
Catalona WJ: Prostate Cancer Screening.
Med Clin North Am. 102:199–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer: World Cancer Report. 2014, http://www.who.int/cancer/publications/WRC_2014/en/.
Accessed April 17, 2017.
|
|
3
|
Wang W, Li Y, Li Y, Hong A, Wang J, Lin B
and Li R: NDRG3 is an androgen regulated and prostate enriched gene
that promotes in vitro and in vivo prostate cancer cell growth. Int
J Cancer. 124:521–530. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Begley LA, Kasina S, Mehra R, Adsule S,
Admon AJ, Lonigro RJ, Chinnaiyan AM and Macoska JA: CXCL5 promotes
prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia. 10:244–254. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kawamura M, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Saigusa
S, Okugawa Y, Hiro J, Uchida K, Mohri Y, Inoue Y and Kusunoki M:
CXCL5, a promoter of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, is
a novel serum prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer.
Eur J Cancer. 48:2244–2251. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chang MS, McNinch J, Basu R and Simonet S:
Cloning and characterization of the human neutrophil-activating
peptide (ENA-78) gene. J Biol Chem. 269:25277–25282.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Persson T, Monsef N, Andersson P, Bjartell
A, Malm J, Calafat J and Egesten A: Expression of the
neutrophil-activating CXC chemokine ENA-78/CXCL5 by human
eosinophils. Clin Exp Allergy. 33:531–537. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Long X, Ye Y, Zhang L, Liu P, Yu W, Wei F,
Ren X and Yu J: IL-8, a novel messenger to cross-link inflammation
and tumor EMT via autocrine and paracrine pathways (Review). Int J
Oncol. 48:5–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu X, Huang P, Yang B, Wang X and Xia J:
Roles of CXCL5 on migration and invasion of liver cancer cells. J
Transl Med. 12:1932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li A, King J, Moro A, Sugi MD, Dawson DW,
Kaplan J, Li G, Lu X, Strieter RM, Burdick M, et al: Overexpression
of CXCL5 is associated with poor survival in patients with
pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol. 178:1340–1349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park JY, Park KH, Bang S, Kim MH, Lee J-E,
Gang J, Koh SS and Song SY: CXCL5 overexpression is associated with
late stage gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 133:835–840.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou SL, Dai Z, Zhou ZJ, Wang XY, Yang GH,
Wang Z, Huang XW, Fan J and Zhou J: Overexpression of CXCL5
mediates neutrophil infiltration and indicates poor prognosis for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:2242–2254. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuo PL, Huang MS, Hung JY, Chou SH, Chiang
SY, Huang YF, Yang C-J, Tsai M-J, Chang W-A and Hsu Y-L:
Synergistic effect of lung tumor-associated dendritic cell-derived
HB-EGF and CXCL5 on cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 135:96–108.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Speetjens FM, Kuppen PJK, Sandel MH, Menon
AG, Burg D, van de Velde CJH, Tollenaar RAEM, de Bont HJGM and
Nagelkerke JF: Disrupted expression of CXCL5 in colorectal cancer
is associated with rapid tumor formation in rats and poor prognosis
in patients. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2276–2284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu X, Qiao Y, Liu W, Wang W, Shen H, Lu
Y, Hao G, Zheng J and Tian Y: CXCL5 is a potential diagnostic and
prognostic marker for bladder cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
37:4569–4577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gui SL, Teng LC, Wang SQ, Liu S, Lin YL,
Zhao XL, Liu L, Sui H-Y, Yang Y, Liang L-C, et al: Overexpression
of CXCL3 can enhance the oncogenic potential of prostate cancer.
Int Urol Nephrol. 48:701–709. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mantovani A: Cancer: Inflaming metastasis.
Nature. 457:36–37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mantovani A, Savino B, Locati M, Zammataro
L, Allavena P and Bonecchi R: The chemokine system in cancer
biology and therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:27–39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vindrieux D, Escobar P and Lazennec G:
Emerging roles of chemokines in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 16:663–673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verbeke H, Geboes K, Van Damme J and
Struyf S: The role of CXC chemokines in the transition of chronic
inflammation to esophageal and gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825:117–129. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Balkwill F: Cancer and the chemokine
network. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:540–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Douglas MR, Morrison KE, Salmon M and
Buckley CD: Why does inflammation persist: A dominant role for the
stromal microenvironment? Expert Rev Mol Med. 4:1–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hembruff SL and Cheng N: Chemokine
signaling in cancer: Implications on the tumor microenvironment and
therapeutic targeting. Cancer Ther. 7A:254–267. 2009.
|
|
25
|
Amagai Y, Tanaka A, Matsuda A, Jung K,
Ohmori K and Matsuda H: Stem cell factor contributes to
tumorigenesis of mast cells via an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. J
Leukoc Biol. 93:245–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang CK, Yang CY, Jeng YM, Chen CL, Wu
HH, Chang YC, Ma C, Kuo WH, Chang KJ, Shew JY, et al:
Autocrine/paracrine mechanism of interleukin-17B receptor promotes
breast tumorigenesis through NF-κB-mediated antiapoptotic pathway.
Oncogene. 33:2968–2977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee JL, Lin CT, Chueh LL and Chang CJ:
Autocrine/paracrine secreted Frizzled-related protein 2 induces
cellular resistance to apoptosis: A possible mechanism of mammary
tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem. 279:14602–14609. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rollins BJ: Inflammatory chemokines in
cancer growth and progression. Eur J Cancer. 42:760–767. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Strieter RM: Chemokines: Not just
leukocyte chemoattractants in the promotion of cancer. Nat Immunol.
2:285–286. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tough DF, Borrow P and Sprent J: Induction
of bystander T cell proliferation by viruses and type I interferon
in vivo. Science. 272:1947–1950. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsutsui H, Nakanishi K, Matsui K,
Higashino K, Okamura H, Miyazawa Y and Kaneda K: IFN-gamma-inducing
factor up-regulates Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxic activity of
murine natural killer cell clones. J Immunol. 157:3967–3973.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hashimoto W, Osaki T, Okamura H, Robbins
PD, Kurimoto M, Nagata S, Lotze MT and Tahara H: Differential
antitumor effects of administration of recombinant IL-18 or
recombinant IL-12 are mediated primarily by Fas-Fas ligand- and
perforin-induced tumor apoptosis, respectively. J Immunol.
163:583–589. 1999.
|
|
33
|
Micallef MJ, Tanimoto T, Kohno K, Ikeda M
and Kurimoto M: Interleukin 18 induces the sequential activation of
natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes to protect
syngeneic mice from transplantation with Meth A sarcoma. Cancer
Res. 57:4557–4563. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li K, Wei L, Huang Y, Wu Y, Su M, Pang X,
Wang N, Ji F, Zhong C and Chen T: Leptin promotes breast cancer
cell migration and invasion via IL-18 expression and secretion. Int
J Oncol. 48:2479–2487. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bian Y, Yu Y, Wang S and Li L:
Up-regulation of fatty acid synthase induced by EGFR/ERK activation
promotes tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 463:612–617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hamaoka Y, Negishi M and Katoh H: EphA2 is
a key effector of the MEK/ERK/RSK pathway regulating glioblastoma
cell proliferation. Cell Signal. 28:937–945. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Uekita T, Fujii S, Miyazawa Y, Iwakawa R,
Narisawa-Saito M, Nakashima K, Tsuta K, Tsuda H, Kiyono T, Yokota
J, et al: Oncogenic Ras/ERK signaling activates CDCP1 to promote
tumor invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. 12:1449–1459. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Floros KV, Thomadaki H, Florou D, Talieri
M and Scorilas A: Alterations in mRNA expression of
apoptosis-related genes BCL2, BAX, FAS, caspase-3, and the novel
member BCL2L12 after treatment of human leukemic cell line HL60
with the anti-neoplastic agent etoposide. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1090:89–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hajiahmadi S, Panjehpour M, Aghaei M and
Shabani M: Activation of A2b adenosine receptor regulates ovarian
cancer cell growth: Involvement of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3. Biochem
Cell Biol. 93:321–329. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharifi AM, Hoda FE and Noor AM: Studying
the effect of LPS on cytotoxicity and apoptosis in PC12 neuronal
cells: Role of Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 protein expression.
Toxicol Mech Methods. 20:316–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zeng J, Chen S, Li N, Chen L, Su J, Niu G,
Zhu S and Liang Y: Sasanquasaponin from Camellia oleifera Abel.
induces apoptosis via Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 activation in HepG2
cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1997–2002. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|