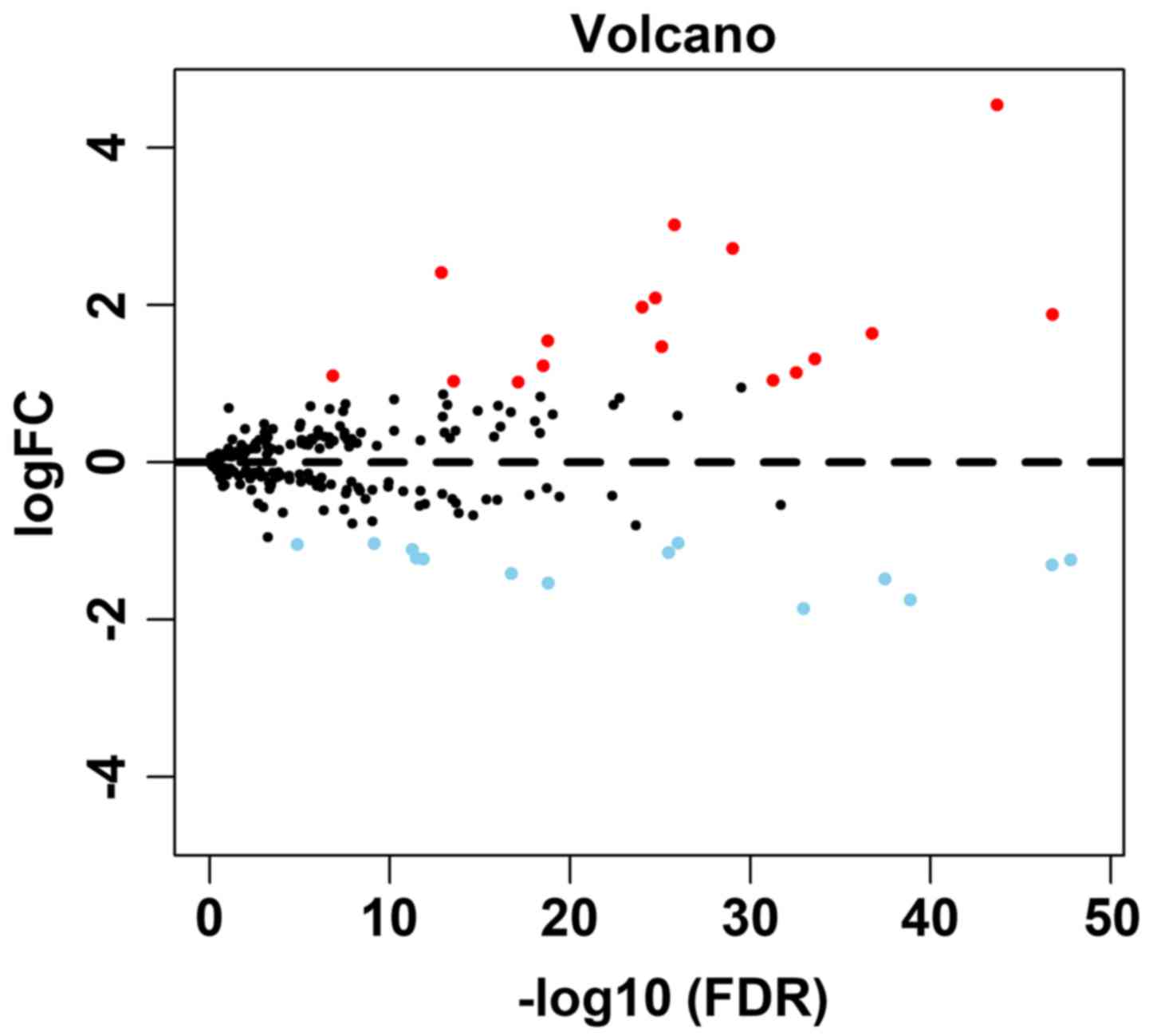
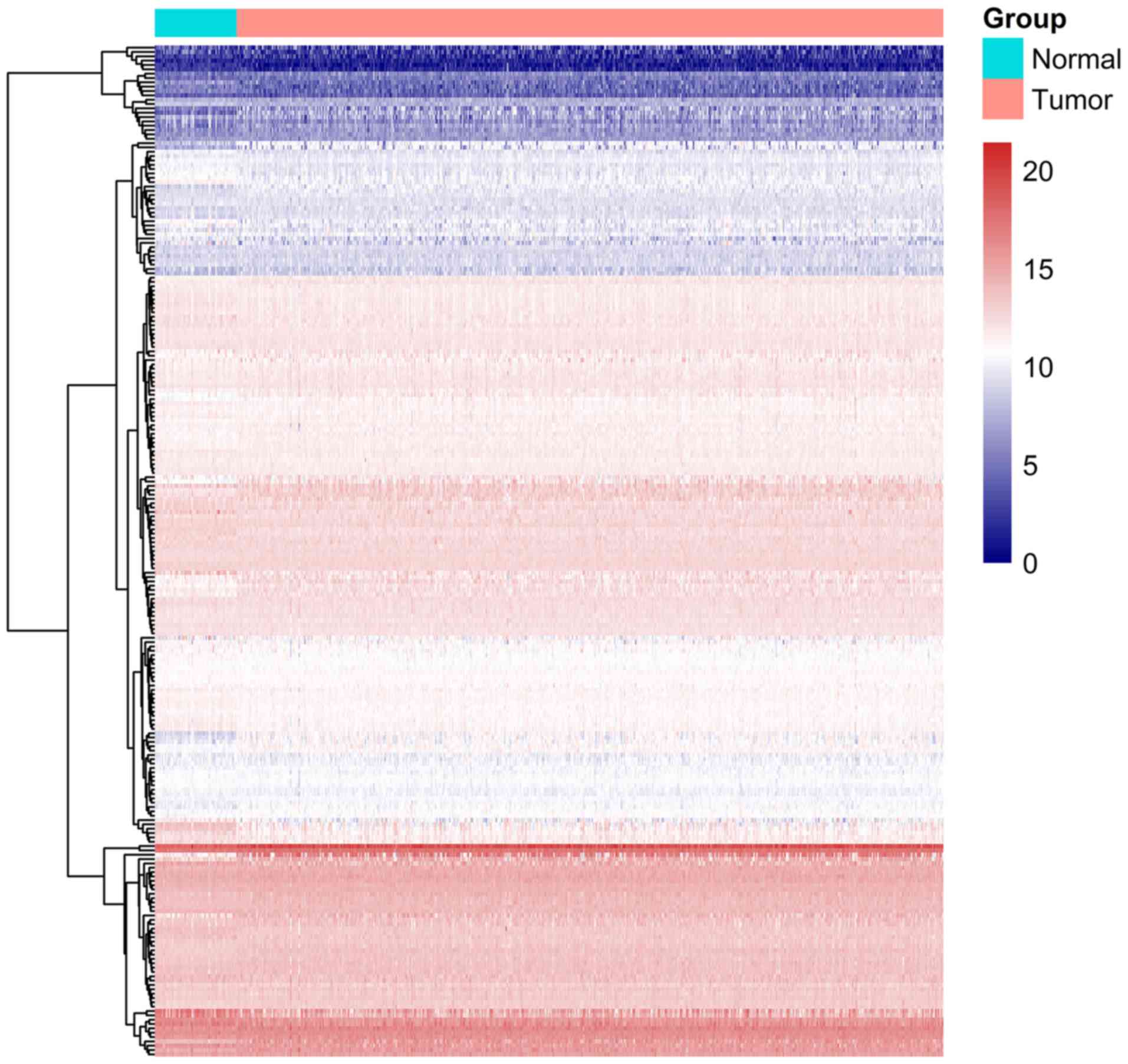
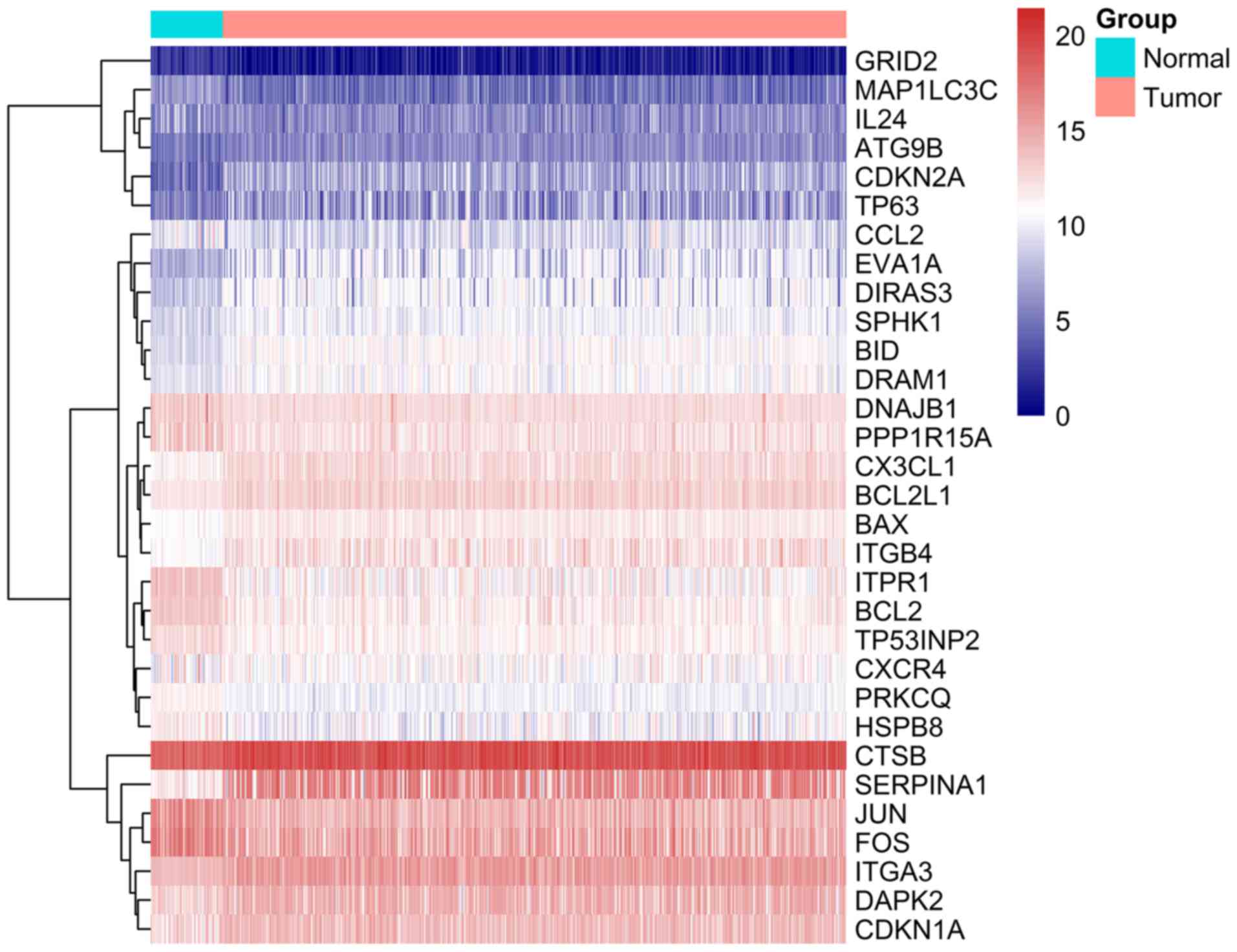
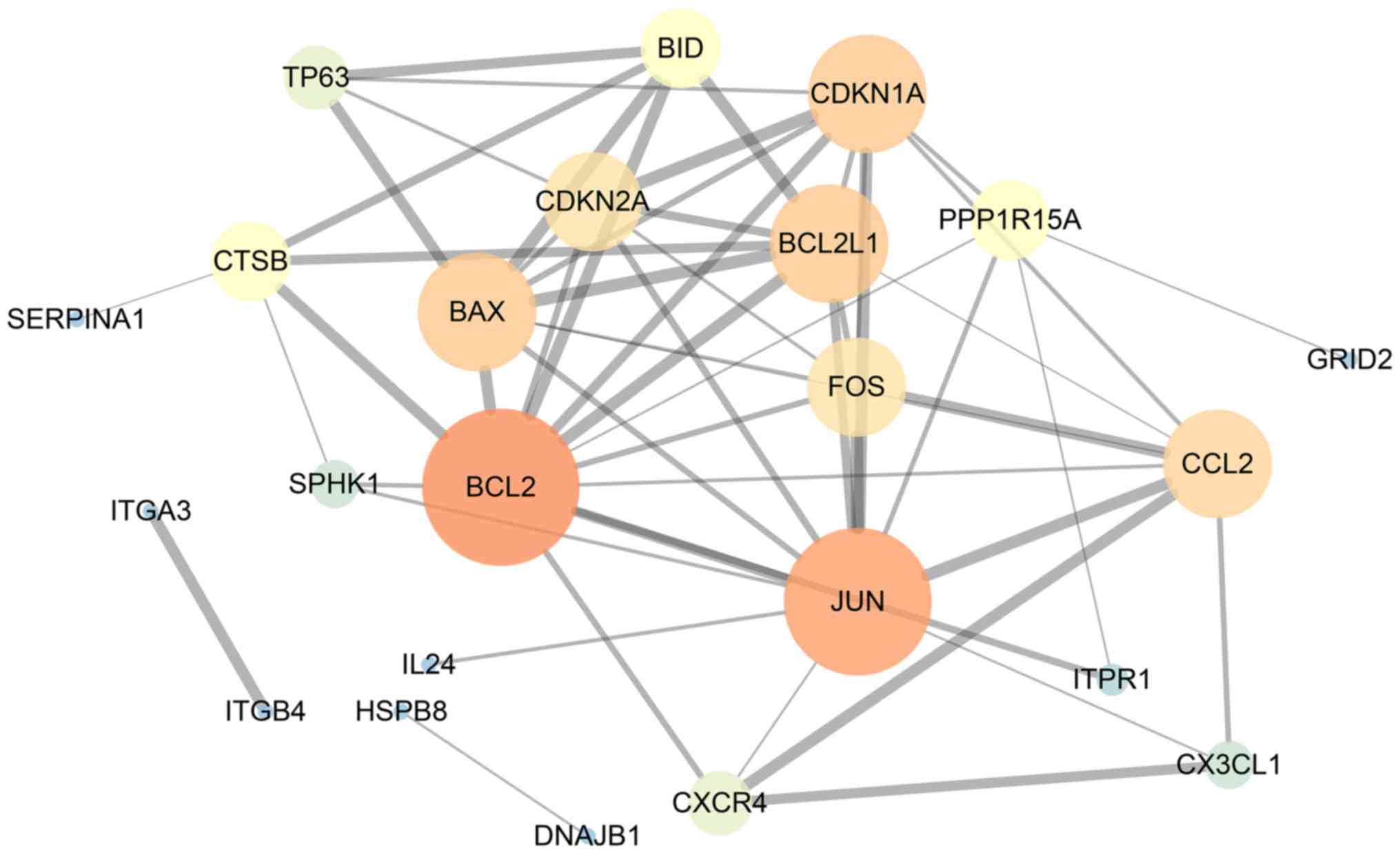
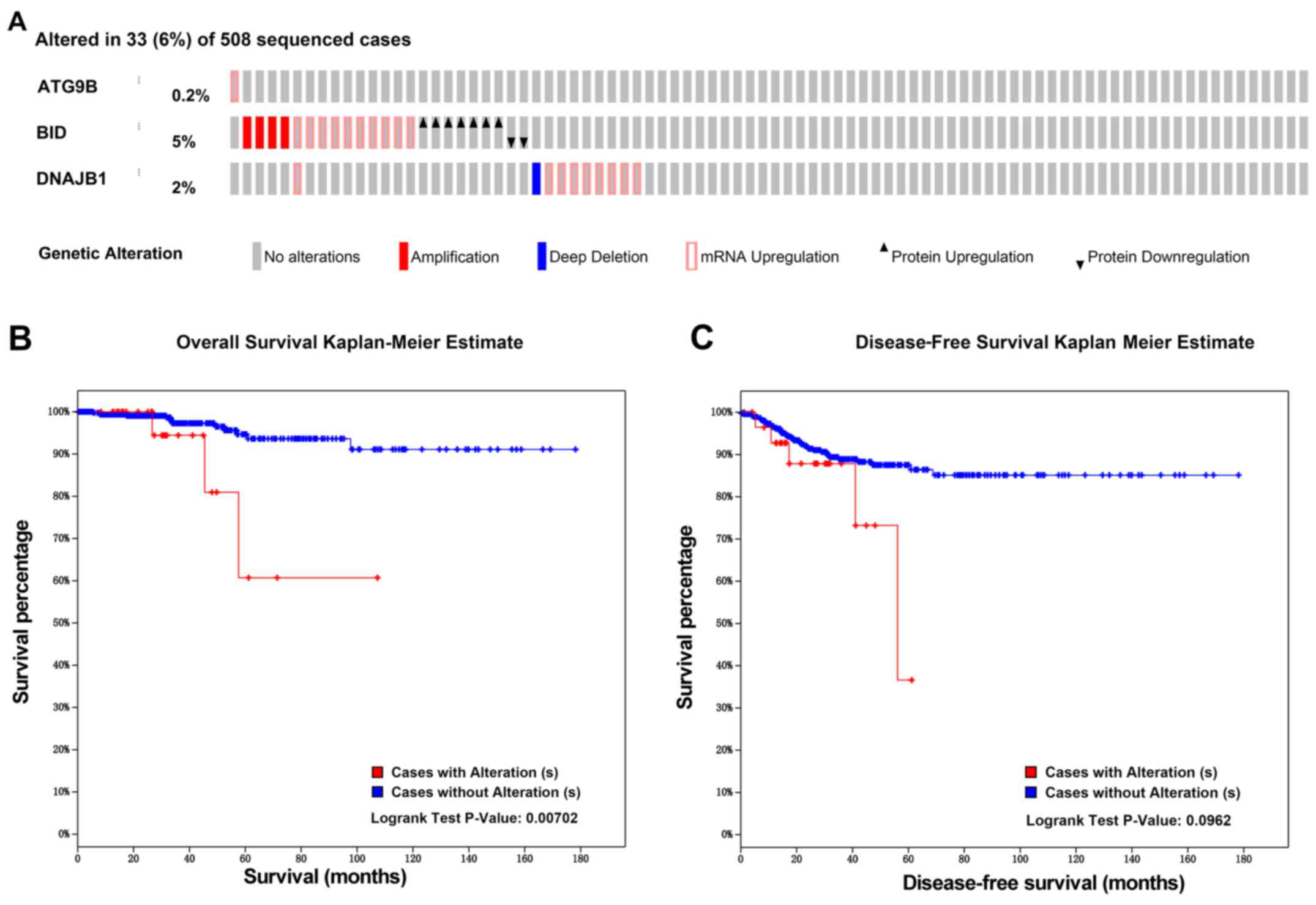
|
1
|
van der Zwan JM, Mallone S, van Dijk B,
Bielska-Lasota M, Otter R, Foschi R and Baudin E: Links TP RARECARE
WG Carcinoma of endocrine organs: Results of the RARECARE project.
Eur J Cancer. 48:1923–1931. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Smith-Bindman R, Lebda P, Feldstein VA,
Sellami D, Goldstein RB, Brasic N, Jin C and Kornak J: Risk of
thyroid cancer based on thyroid ultrasound imaging characteristics:
Results of a population-based study. JAMA Intern Med.
173:1788–1796. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ,
Barry MJ, Davidson KW, Doubeni CA, Epling JW Jr, Kemper AR, Krist
AH, Kurth AE, et al: US Preventive Services Task Force: Screening
for thyroid cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force
Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 317:1882–1887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mazeh H and Chen H: Advances in surgical
therapy for thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 7:581–588. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM and
Schlumberger M: 2015 American Thyroid Association Management
Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and
Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association
Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid
Cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Carling T and Udelsman R: Thyroid cancer.
Annu Rev Med. 65:125–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Thyroid Cancer Treatment (Adult) (PDQ@):
Health Professional Version. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
Bethesda, MD: 2002
|
|
9
|
Li LC, Liu GD, Zhang XJ and Li YB:
Autophagy, a novel target for chemotherapeutic intervention of
thyroid cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 73:439–449. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Acquaviva G, Visani M, Repaci A, Rhoden
KJ, de Biase D, Pession A and Giovanni T: Molecular pathology of
thyroid tumours of follicular cells: A review of genetic
alterations and their clinicopathological relevance.
Histopathology. 72:6–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rockel JS and Kapoor M: Autophagy:
Controlling cell fate in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
12:517–531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G and Galluzzi
L: Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res.
120:1812–1824. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mowers EE, Sharifi MN and Macleod KF:
Functions of autophagy in the tumor microenvironment and cancer
metastasis. FEBS J. Jan 21–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zelenka J, Koncošová M and Ruml T:
Targeting of stress response pathways in the prevention and
treatment of cancer. Biotechnol Adv. Jan 12–2018.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vlodavsky I, Singh P, Boyango I,
Gutter-Kapon L, Elkin M, Sanderson RD and Ilan N: Heparanase: From
basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and
inflammation. Drug Resist Updat. 29:54–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Levine B, Packer M and Codogno P:
Development of autophagy inducers in clinical medicine. J Clin
Invest. 125:14–24. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wei H and Guan JL: Pro-tumorigenic
function of autophagy in mammary oncogenesis. Autophagy. 8:129–131.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang W, Kang H, Zhao Y, Min I, Wyrwas B,
Moore M, Teng L, Zarnegar R, Jiang X and Fahey TJ III: Targeting
autophagy sensitizes BRAF-mutant thyroid cancer to vemurafenib. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 102:634–643. 2017.
|
|
21
|
Feng W and Jia S: Rapamycin inhibits the
invasive ability of thyroid cancer cells by down-regulating the
expression of VEGF-C in vitro. Cell Biochem Funct. 30:487–491.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang M, Bai L, Yu W, Sun X, Xu G, Guan R,
Yang Y, Qiu M, Zhang Y and Tian J: Expression of
autophagy-associated proteins in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 14:411–415. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim HM, Kim ES and Koo JS: Expression of
autophagy-related proteins in different types of thyroid cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017.
|
|
24
|
Moussay E, Kaoma T, Baginska J, Muller A,
Van Moer K, Nicot N, Nazarov PV, Vallar L, Chouaib S and Berchem G:
The acquisition of resistance to TNFα in breast cancer cells is
associated with constitutive activation of autophagy as revealed by
a transcriptome analysis using a custom microarray. Autophagy.
7:760–770. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang H, Lu X, Wang N, Wang J, Cao Y, Wang
T, Zhou X, Jiao Y, Yang L and Wang X: Autophagy-related gene
expression is an independent prognostic indicator of glioma.
Oncotarget. 8:60987–61000. 2017.
|
|
26
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A
and Tsafou KP: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks,
integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D447–D452.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Walter W, Sánchez-Cabo F and Ricote M:
GOplot: An R package for visually combining expression data with
functional analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:2912–2914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBio-Portal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yi H, Ye T, Ge M, Yang M, Zhang L, Jin S,
Ye X, Long B and Li L: Inhibition of autophagy enhances the
targeted therapeutic effect of sorafenib in thyroid cancer. Oncol
Rep. 39:711–720. 2018.
|
|
32
|
Lin CI, Whang EE, Donner DB, Du J, Lorch
J, He F, Jiang X, Price BD, Moore FD Jr and Ruan DT: Autophagy
induction with RAD001 enhances chemosensitivity and
radiosensitivity through Met inhibition in papillary thyroid
cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1217–1226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Paquette M, El-Houjeiri L and Pause A:
mTOR pathways in cancer and autophagy. Cancers (Basel). 10:E182018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xie W and Zhou J: Aberrant regulation of
autophagy in mammalian diseases. Biol Lett. 14:142018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yu C, Li WB, Liu JB, Lu JW and Feng JF:
Autophagy: Novel applications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs for primary cancer. Cancer Med. 7:471–484. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC
and Croce CM: Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B
cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science.
226:1097–1099. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cleary ML, Smith SD and Sklar J: Cloning
and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid
bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18)
translocation. Cell. 47:19–28. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Leverson JD, Sampath D, Souers AJ,
Rosenberg SH, Fairbrother WJ, Amiot M, Konopleva M and Letai A:
Found in translation: How preclinical research is guiding the
clinical development of the BCL2-selective inhibitor venetoclax.
Cancer Discov. 7:1376–1393. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liang ST, Li Y, Li XW, Wang JJ, Tan FX,
Han QR, Li L, Yao XQ and Sun XG: Mechanism of colon cancer cell
apoptosis induced by telocinobufagin: Role of oxidative stress and
apoptosis pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 36. pp. 921–926.
2016, In Chinese.
|
|
40
|
S Soderquist R and Eastman A: BCL2
inhibitors as anticancer drugs: A plethora of misleading BH3
mimetics. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2011–2017. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jeon MJ, Yoon JH, Han JM, Yim JH, Hong SJ,
Song DE, Ryu JS, Kim TY, Shong YK and Kim WB: The prognostic value
of the metastatic lymph node ratio and maximal metastatic tumor
size in pathological N1a papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur J
Endocrinol. 168:219–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sung TY, Yoon JH, Song DE, Lee YM, Kim TY,
Chung KW, Kim WB, Shong YK and Hong SJ: Prognostic value of the
number of retrieved lymph nodes in pathological Nx or N0 classical
papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J Surg. 40:2043–2050. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jeon MJ, Kim TY, Kim WG, Han JM, Jang EK,
Choi YM, Song DE, Yoon JH, Chung KW and Hong SJ: Differentiating
the location of cervical lymph node metastasis is very useful for
estimating the risk of distant metastases in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 81:593–599. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang N, Li L, Wang J, Cao M, Liu G, Xie
G, Yang Z and Li Y: Study of autophagy-related protein light chain
3 (LC3)-II expression levels in thyroid diseases. Biomed
Pharmacother. 69:306–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li X, Xu H and Ma H: Beclin 1 is highly
expressed in papillary thyroid carcinoma and correlates with lymph
node metastasis. Acta Chir Belg. 113:175–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lin H, Yan J, Wang Z, Hua F, Yu J, Sun W,
Li K, Liu H, Yang H and Lv Q: Loss of immunity-supported senescence
enhances susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinogenesis and
progression in Toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice. Hepatology.
57:171–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Amaravadi R, Kimmelman AC and White E:
Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes
Dev. 30:1913–1930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Guo JY, Chen HY, Mathew R, Fan J,
Strohecker AM, Karsli-Uzunbas G, Kamphorst JJ, Chen G, Lemons JM
and Karantza V: Activated Ras requires autophagy to maintain
oxidative metabolism and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 25:460–470.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yang S, Wang X, Contino G, Liesa M, Sahin
E, Ying H, Bause A, Li Y, Stommel JM, Dell’antonio G, et al:
Pancreatic cancers require autophagy for tumor growth. Genes Dev.
25:717–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang N, Tan HY, Li S and Feng Y: Atg9b
deficiency suppresses autophagy and potentiates endoplasmic
reticulum stress-associated hepatocyte apoptosis in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Theranostics. 7:2325–2338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP and Harper
JW: Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature.
466:68–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lamparska-Przybysz M, Gajkowska B and
Motyl T: Cathepsins and BID are involved in the molecular switch
between apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer MCF-7 cells
exposed to camptothecin. J Physiol Pharmacol. 56(Suppl 3): 159–179.
2005.
|