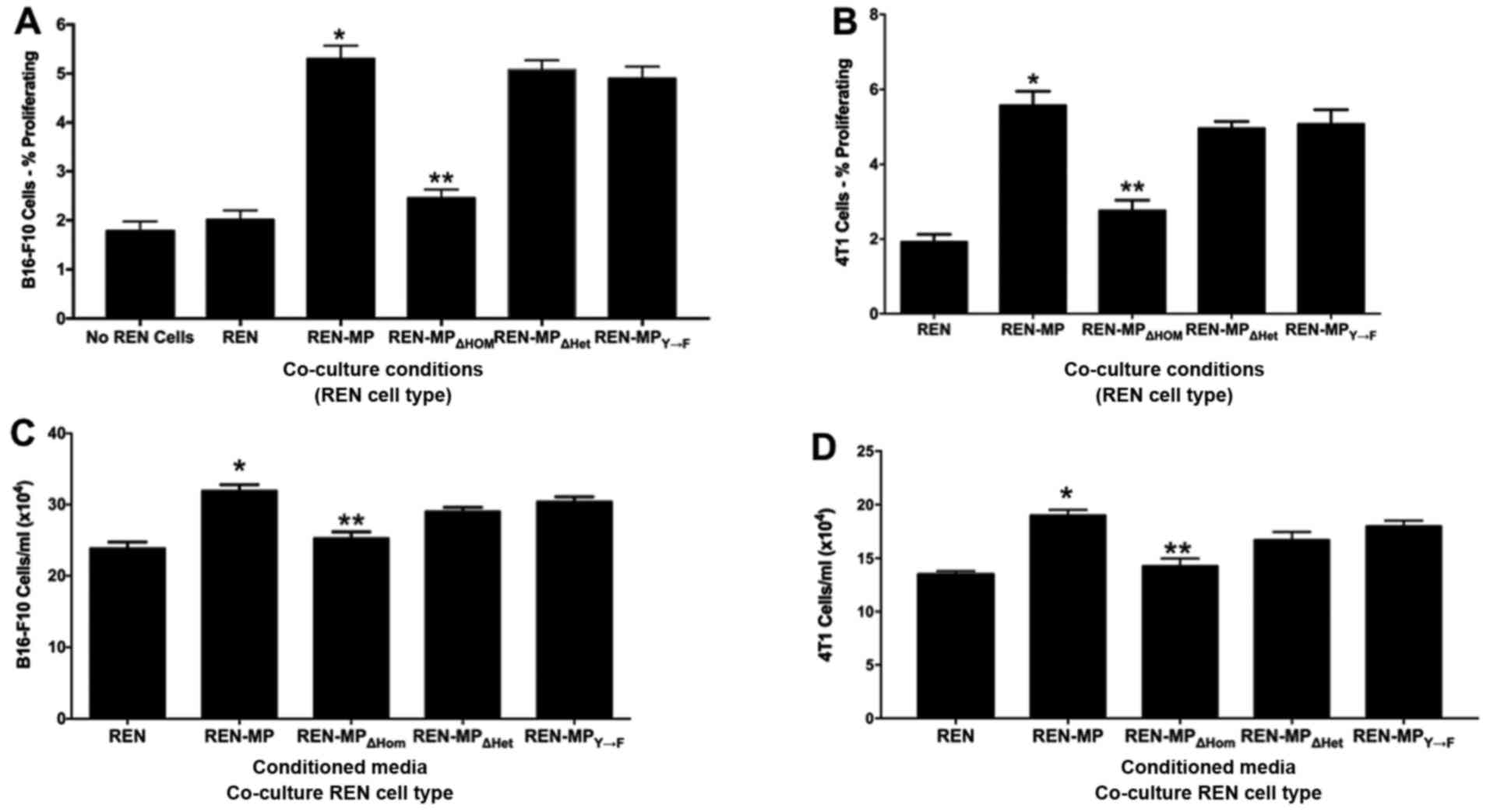
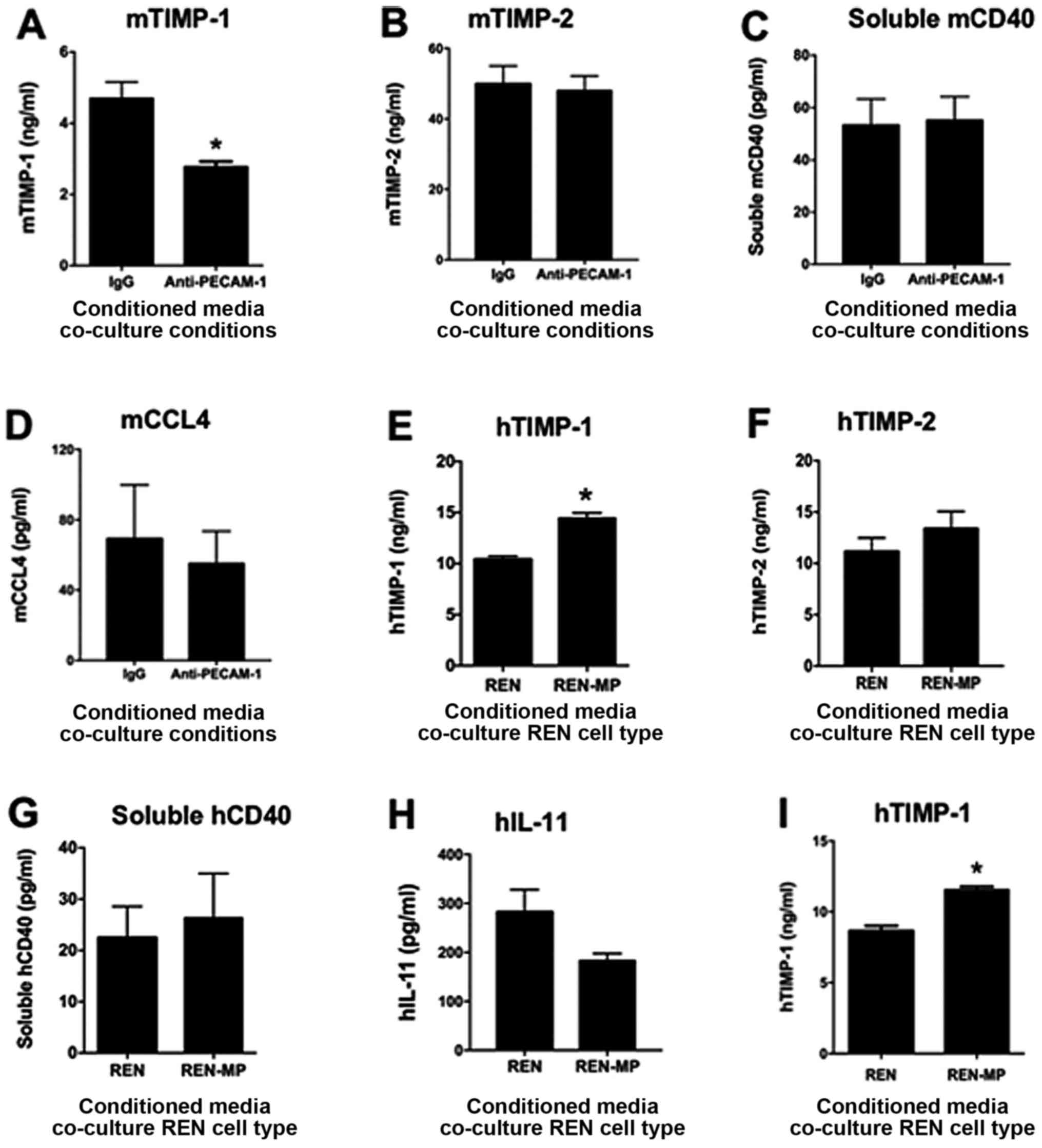
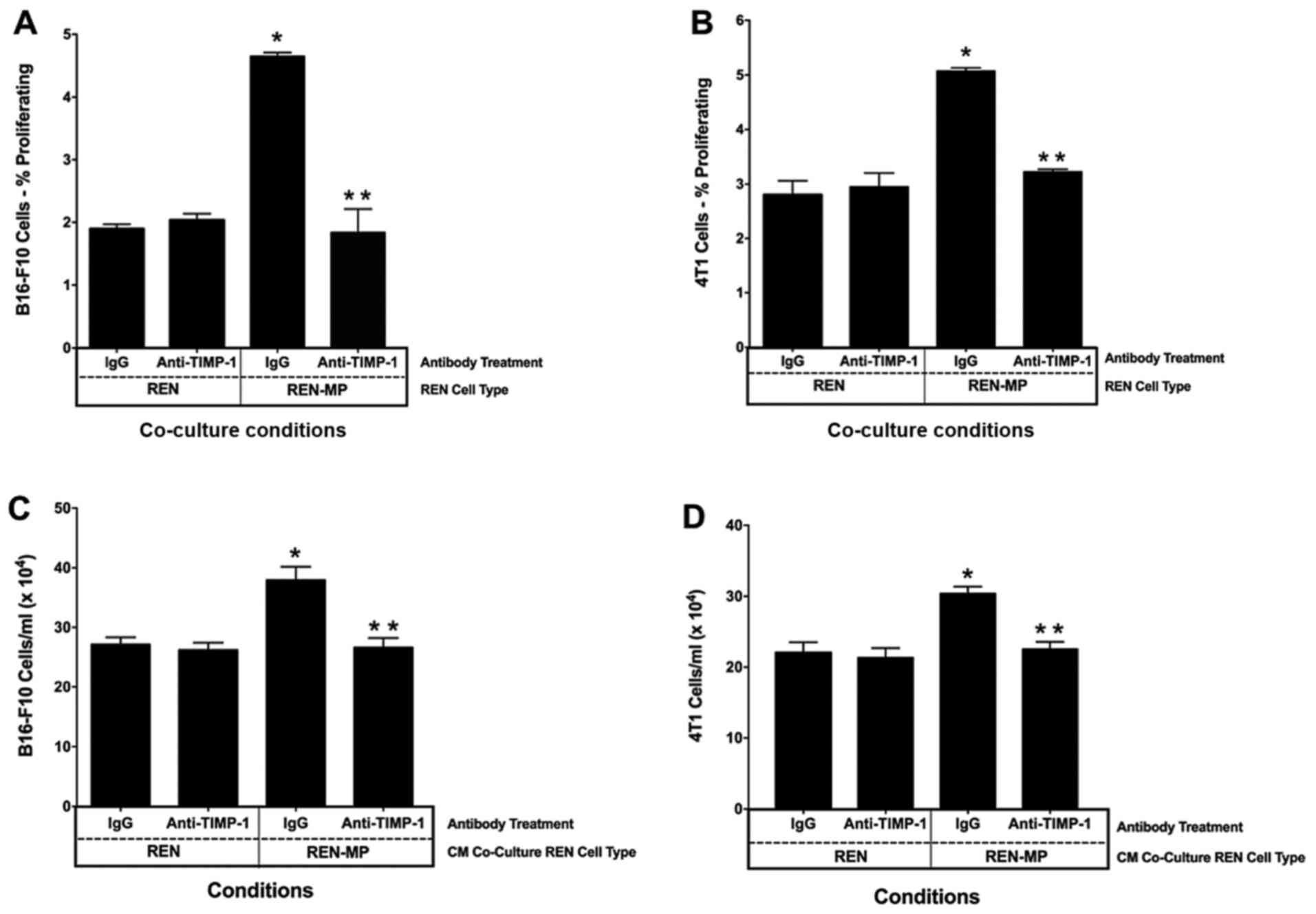
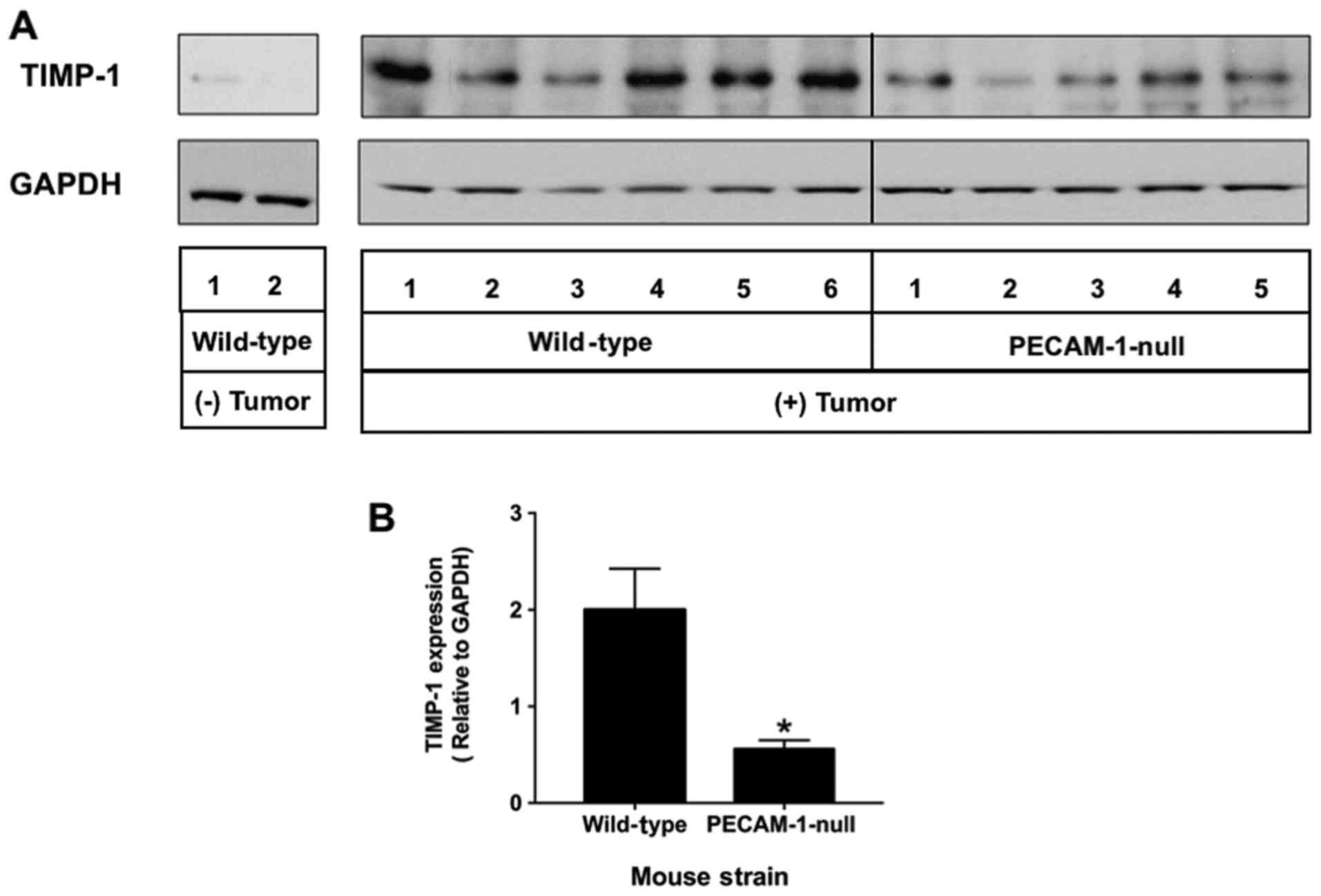
|
1
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massagué J:
Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Butler JM, Kobayashi H and Rafii S:
Instructive role of the vascular niche in promoting tumour growth
and tissue repair by angiocrine factors. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:138–146. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Junttila MR and de Sauvage FJ: Influence
of tumour microenvironment heterogeneity on therapeutic response.
Nature. 501:346–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen F, Zhuang X, Lin L, Yu P, Wang Y, Shi
Y, Hu G and Sun Y: New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology:
Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. 13:452015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Klemm F and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of therapeutic response in cancer. Trends Cell Biol.
25:198–213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Tumor
microvasculature and microenvironment: Targets for
anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res. 74:72–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ilan N and Madri JA: PECAM-1: Old friend,
new partners. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:515–524. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Woodfin A, Voisin MB and Nourshargh S:
PECAM-1: A multi-functional molecule in inflammation and vascular
biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:2514–2523. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lertkiatmongkol P, Liao D, Mei H, Hu Y and
Newman PJ: Endothelial functions of platelet/endothelial cell
adhesion molecule-1 (CD31). Curr Opin Hematol. 23:253–259. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Paddock C, Zhou D, Lertkiatmongkol P,
Newman PJ and Zhu J: Structural basis for PECAM-1 homophilic
binding. Blood. 127:1052–1061. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Newton JP, Buckley CD, Jones EY and
Simmons DL: Residues on both faces of the first immunoglobulin fold
contribute to homophilic binding sites of PECAM-1/CD31. J Biol
Chem. 272:20555–20563. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nakada MT, Amin K, Christofidou-Solomidou
M, O'Brien CD, Sun J, Gurubhagavatula I, Heavner GA, Taylor AH,
Paddock C, Sun QH, et al: Antibodies against the first Ig-like
domain of human platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
(PECAM-1) that inhibit PECAM-1-dependent homophilic adhesion block
in vivo neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol. 164:452–462. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Coombe DR, Stevenson SM, Kinnear BF,
Gandhi NS, Mancera RL, Osmond RI and Kett WC: Platelet endothelial
cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) and its interactions with
glycosaminoglycans: 2. Biochemical analyses. Biochemistry.
47:4863–4875. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sun J, Williams J, Yan HC, Amin KM,
Albelda SM and DeLisser HM: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion
molecule-1 (PECAM-1) homophilic adhesion is mediated by
immunoglobulin-like domains 1 and 2 and depends on the cytoplasmic
domain and the level of surface expression. J Biol Chem.
271:18561–18570. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun QH, DeLisser HM, Zukowski MM, Paddock
C, Albelda SM and Newman PJ: Individually distinct Ig homology
domains in PECAM-1 regulate homophilic binding and modulate
receptor affinity. J Biol Chem. 271:11090–11098. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lee C, Liu A, Miranda-Ribera A, Hyun SW,
Lillehoj EP, Cross AS, Passaniti A, Grimm PR, Kim BY, Welling PA,
et al: NEU1 sialidase regulates the sialylation state of CD31 and
disrupts CD31-driven capillary-like tube formation in human lung
microvascular endothelia. J Biol Chem. 289:9121–9135. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lertkiatmongkol P, Paddock C, Newman DK,
Zhu J, Thomas MJ and Newman PJ: The role of sialylated glycans in
human platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
(PECAM-1)-mediated trans homophilic interactions and endothelial
cell barrier function. J Biol Chem. 291:26216–26225. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jackson DE, Kupcho KR and Newman PJ:
Characterization of phosphotyrosine binding motifs in the
cytoplasmic domain of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
(PECAM-1) that are required for the cellular association and
activation of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-2. J Biol Chem.
272:24868–24875. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jackson DE, Ward CM, Wang R and Newman PJ:
The protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 binds platelet/endothelial
cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) and forms a distinct signaling
complex during platelet aggregation. Evidence for a mechanistic
link between PECAM-1- and integrin-mediated cellular signaling. J
Biol Chem. 272:6986–6993. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cao MY, Huber M, Beauchemin N, Famiglietti
J, Albelda SM and Veillette A: Regulation of mouse PECAM-1 tyrosine
phosphorylation by the Src and Csk families of protein-tyrosine
kinases. J Biol Chem. 273:15765–15772. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sagawa K, Kimura T, Swieter M and
Siraganian RP: The protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 associates
with tyrosine-phosphorylated adhesion molecule PECAM-1 (CD31). J
Biol Chem. 272:31086–31091. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pumphrey NJ, Taylor V, Freeman S, Douglas
MR, Bradfield PF, Young SP, Lord JM, Wakelam MJ, Bird IN, Salmon M,
et al: Differential association of cytoplasmic signalling molecules
SHP-1, SHP-2, SHIP and phospholipase C-gamma1 with PECAM-1/CD31.
FEBS Lett. 450:77–83. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Vaporciyan AA, DeLisser HM, Yan HC,
Mendiguren II, Thom SR, Jones ML, Ward PA and Albelda SM:
Involvement of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in
neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Science. 262:1580–1582. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Thompson RD, Wakelin MW, Larbi KY, Dewar
A, Asimakopoulos G, Horton MA, Nakada MT and Nourshargh S:
Divergent effects of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
and beta 3 integrin blockade on leukocyte transmigration in vivo. J
Immunol. 165:426–434. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Woodfin A, Reichel CA, Khandoga A, Corada
M, Voisin MB, Scheiermann C, Haskard DO, Dejana E, Krombach F and
Nourshargh S: JAM-A mediates neutrophil transmigration in a
stimulus-specific manner in vivo: Evidence for sequential roles for
JAM-A and PECAM-1 in neutrophil transmigration. Blood.
110:1848–1856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Newton-Nash DK and Newman PJ: A new role
for platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31):
Inhibition of TCR-mediated signal transduction. J Immunol.
163:682–688. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Prager E, Staffler G, Majdic O, Säemann M,
Godár S, Zlabinger G and Stockinger H: Induction of
hyporesponsiveness and impaired T lymphocyte activation by the CD31
receptor:ligand pathway in T cells. J Immunol. 166:2364–2371. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rosenblum WI, Murata S, Nelson GH, Werner
PK, Ranken R and Harmon RC: Anti-CD31 delays platelet
adhesion/aggregation at sites of endothelial injury in mouse
cerebral arterioles. Am J Pathol. 145:33–36. 1994.
|
|
31
|
Patil S, Newman DK and Newman PJ: Platelet
endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 serves as an inhibitory
receptor that modulates platelet responses to collagen. Blood.
97:1727–1732. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
DeLisser HM, Christofidou-Solomidou M,
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Robinson CS, Wexler RS, Kerr JS, Garlanda
C, Merwin JR, Madri JA, et al: Involvement of endothelial
PECAM-1/CD31 in angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 151:671–677. 1997.
|
|
33
|
Zhou Z, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Garlanda
C and DeLisser HM: Antibody against murine PECAM-1 inhibits tumor
angiogenesis in mice. Angiogenesis. 3:181–188. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cao G, O'Brien CD, Zhou Z, Sanders SM,
Greenbaum JN, Makrigiannakis A and DeLisser HM: Involvement of
human PECAM-1 in angiogenesis and in vitro endothelial cell
migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 282:C1181–C1190. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cao G, Fehrenbach ML, Williams JT,
Finklestein JM, Zhu JX and Delisser HM: Angiogenesis in platelet
endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1-null mice. Am J Pathol.
175:903–915. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Carrithers M, Tandon S, Canosa S, Michaud
M, Graesser D and Madri JA: Enhanced susceptibility to endotoxic
shock and impaired STAT3 signaling in CD31-deficient mice. Am J
Pathol. 166:185–196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Maas M, Stapleton M, Bergom C, Mattson DL,
Newman DK and Newman PJ: Endothelial cell PECAM-1 confers
protection against endotoxic shock. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 288:H159–H164. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
DeLisser H, Liu Y, Desprez PY, Thor A,
Briasouli P, Handumrongkul C, Wilfong J, Yount G, Nosrati M, Fong
S, et al: Vascular endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1)
regulates advanced metastatic progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:18616–18621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Clark IM, Swingler TE, Sampieri CL and
Edwards DR: The regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1362–1378. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Brew K and Nagase H: The tissue inhibitors
of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): An ancient family with structural
and functional diversity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:55–71. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chesler L, Golde DW, Bersch N and Johnson
MD: Metallo-proteinase inhibition and erythroid potentiation are
independent activities of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1.
Blood. 86:4506–4515. 1995.
|
|
42
|
Liu XW, Taube ME, Jung KK, Dong Z, Lee YJ,
Roshy S, Sloane BF, Fridman R and Kim HR: Tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 protects human breast epithelial cells from
extrinsic cell death: A potential oncogenic activity of tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1. Cancer Res. 65:898–906. 2005.
|
|
43
|
Toricelli M, Melo FH, Peres GB, Silva DC
and Jasiulionis MG: Timp1 interacts with beta-1 integrin and CD63
along melanoma genesis and confers anoikis resistance by activating
PI3-K signaling pathway independently of Akt phosphorylation. Mol
Cancer. 12:222013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chirco R, Liu XW, Jung KK and Kim HR:
Novel functions of TIMPs in cell signaling. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:99–113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in cell signaling: Metalloproteinase-independent
biological activities. Sci Signal. 1:re62008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Aljada IS, Ramnath N, Donohue K, Harvey S,
Brooks JJ, Wiseman SM, Khoury T, Loewen G, Slocum HK, Anderson TM,
et al: Upregulation of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1
protein is associated with progression of human non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:3218–3229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pesta M, Kulda V, Kucera R, Pesek M,
Vrzalova J, Liska V, Pecen L, Treska V, Safranek J, Prazakova M, et
al: Prognostic significance of TIMP-1 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:4031–4038. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Grunnet M, Mau-Sørensen M and Brünner N:
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1) as a biomarker in
gastric cancer: A review. Scand J Gastroenterol. 48:899–905. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Cui H, Seubert B, Stahl E, Dietz H,
Reuning U, Moreno-Leon L, Ilie M, Hofman P, Nagase H, Mari B, et
al: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a
pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells
and their exosomes. Oncogene. 34:3640–3650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Song G, Xu S, Zhang H, Wang Y, Xiao C,
Jiang T, Wu L, Zhang T, Sun X, Zhong L, et al: TIMP1 is a
prognostic marker for the progression and metastasis of colon
cancer through FAK-PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 35:1482016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Smythe WR, Hwang HC, Amin KM, Eck SL,
Davidson BL, Wilson JM, Kaiser LR and Albelda SM: Use of
recombinant adenovirus to transfer the herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase (HSVtk) gene to thoracic neoplasms: An effective
in vitro drug sensitization system. Cancer Res. 54:2055–2059.
1994.
|
|
52
|
Zhu JX, Cao G, Williams JT and Delisser
HM: SHP-2 phosphatase activity is required for PECAM-1-dependent
cell motility. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C854–C865. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Abraham V, Parambath A, Joe DS and
DeLisser HM: Influence of PECAM-1 ligand interactions on
PECAM-1-dependent cell motility and filopodia extension. Physiol
Rep. 4:e130302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Fehrenbach ML, Cao G, Williams JT,
Finklestein JM and Delisser HM: Isolation of murine lung
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L1096–L1103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Duncan GS, Andrew DP, Takimoto H, Kaufman
SA, Yoshida H, Spellberg J, de la Pompa JL, Elia A, Wakeham A,
Karan-Tamir B, et al: Genetic evidence for functional redundancy of
Platelet/Endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1):
CD31-deficient mice reveal PECAM-1-dependent and
PECAM-1-independent functions. J Immunol. 162:3022–3030. 1999.
|
|
56
|
Fowlkes JL, Serra DM, Bunn RC, Thrailkill
KM, Enghild JJ and Nagase H: Regulation of insulin-like growth
factor (IGF)-I action by matrix metalloproteinase-3 involves
selective disruption of IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 complexes.
Endocrinology. 145:620–626. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang P, Henning SM and Heber D:
Limitations of MTT and MTS-based assays for measurement of
antiproliferative activity of green tea polyphenols. PLoS One.
5:e102022010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lovelock JD, Baker AH, Gao F, Dong JF,
Bergeron AL, McPheat W, Sivasubramanian N and Mann DL:
Heterogeneous effects of tissue inhibitors of matrix
metalloproteinases on cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 288:H461–H468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kalra J, Dragowska WH and Bally MB: Using
pharmacokinetic profiles and digital quantification of stained
tissue microarrays as a medium-throughput, quantitative method for
measuring the kinetics of early signaling changes following
integrin-linked kinase inhibition in an in vivo model of cancer. J
Histochem Cytochem. 63:691–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Dunleavey JM, Xiao L, Thompson J, Kim MM,
Shields JM, Shelton SE, Irvin DM, Brings VE, Ollila DW, Brekken RA,
et al: Vascular channels formed by subpopulations of PECAM1+
melanoma cells. Nat Commun. 5:52002014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Chacko AM, Nayak M, Greineder CF, Delisser
HM and Muzykantov VR: Collaborative enhancement of antibody binding
to distinct PECAM-1 epitopes modulates endothelial targeting. PLoS
One. 7:e349582012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Siemianowicz K, Likus W, Francuz T and
Garczorz W: Effect of elastin-derived peptides on the production of
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, -2, and -3 and the ratios
in various endo-thelial cell lines. Exp Ther Med. 9:2245–2250.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kim HI, Lee HS, Kim TH, Lee JS, Lee ST and
Lee SJ: Growth-stimulatory activity of TIMP-2 is mediated through
c-Src activation followed by activation of FAK, PI3-kinase/AKT, and
ERK1/2 independent of MMP inhibition in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Oncotarget. 6:42905–42922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Ernst M and Putoczki TL: Molecular
pathways: IL11 as a tumor-promoting cytokine-translational
implications for cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5579–5588. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Johnstone CN, Chand A, Putoczki TL and
Ernst M: Emerging roles for IL-11 signaling in cancer development
and progression: Focus on breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 26:489–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Karmann K, Hughes CC, Schechner J, Fanslow
WC and Pober JS: CD40 on human endothelial cells: Inducibility by
cytokines and functional regulation of adhesion molecule
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:4342–4346. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Korniluk A, Kemona H and Dymicka-Piekarska
V: Multi-functional CD40L: Pro- and anti-neoplastic activity.
Tumour Biol. 35:9447–9457. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Geng L, Cuneo KC, Cooper MK, Wang H,
Sekhar K, Fu A and Hallahan DE: Hedgehog signaling in the murine
melanoma microenvironment. Angiogenesis. 10:259–267. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M
and Lo HW: Targeting the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway: Review
of smoothened and GLI inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 8. pp. E222016,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Velasco-Velázquez M, Jiao X, De La Fuente
M, Pestell TG, Ertel A, Lisanti MP and Pestell RG: CCR5 antagonist
blocks metastasis of basal breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
72:3839–3850. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Sasaki S, Baba T, Nishimura T, Hayakawa Y,
Hashimoto S, Gotoh N and Mukaida N: Essential roles of the
interaction between cancer cell-derived chemokine, CCL4, and
intra-bone CCR5-expressing fibroblasts in breast cancer bone
metastasis. Cancer Lett. 378:23–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Fantozzi A and Christofori G: Mouse models
of breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 8:2122006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
de Jong GM, Aarts F, Hendriks T, Boerman
OC and Bleichrodt RP: Animal models for liver metastases of
colorectal cancer: Research review of preclinical studies in
rodents. J Surg Res. 154:167–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Novinska MS, Pietz BC, Ellis TM, Newman DK
and Newman PJ: The alleles of PECAM-1. Gene. 376:95–101. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Sun W, Li FS, Zhang YH, Wang XP and Wang
CR: Association of susceptibility to septic shock with platelet
endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 gene Leu125Val polymorphism
and serum sPECAM-1 levels in sepsis patients. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:20490–20498. 2015.
|
|
76
|
Elrayess MA, Webb KE, Flavell DM, Syvänne
M, Taskinen MR, Frick MH, Nieminen MS, Kesäniemi YA, Pasternack A,
Jukema JW, et al: A novel functional polymorphism in the PECAM-1
gene (53G>A) is associated with progression of atherosclerosis
in the LOCAT and REGRESS studies. Atherosclerosis. 168:131–138.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Elrayess MA, Webb KE, Bellingan GJ,
Whittall RA, Kabir J, Hawe E, Syvänne M, Taskinen MR, Frick MH, et
al: R643G polymorphism in PECAM-1 influences transendothelial
migration of monocytes and is associated with progression of CHD
and CHD events. Atherosclerosis. 177:127–135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Wei YS, Lan Y, Liu YG, Meng LQ, Xu QQ and
Xie HY: Platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 gene
polymorphism and its soluble level are associated with ischemic
stroke. DNA Cell Biol. 28:151–158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Sahebkar A, Morris DR, Biros E and
Golledge J: Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the
gene encoding platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 with
the risk of myocardial infarction: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 132:227–233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Song Y, Zhao R, Long L, Zhang N and Liu Y:
Leu125Val polymorphism of platelet endothelial cell adhesion
molecule-1 is associated with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction
in Chinese Han population. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:5808–5813.
2014.
|
|
81
|
Jung KK, Liu XW, Chirco R, Fridman R and
Kim HR: Identification of CD63 as a tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 interacting cell surface protein. EMBO J.
25:3934–3942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Radford KJ, Thorne RF and Hersey P:
Regulation of tumor cell motility and migration by CD63 in a human
melanoma cell line. J Immunol. 158:3353–3358. 1997.
|
|
83
|
Iida J, Skubitz AP, McCarthy JB and
Skubitz KM: Protein kinase activity is associated with CD63 in
melanoma cells. J Transl Med. 3:422005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Seubert B, Cui H, Simonavicius N, Honert
K, Schäfer S, Reuning U, Heikenwalder M, Mari B and Krüger A:
Tetraspanin CD63 acts as a pro-metastatic factor via β-catenin
stabilization. Int J Cancer. 136:2304–2315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Huang Y and Zhu H: Protein array-based
approaches for biomarker discovery in cancer. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 15:73–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Spinella F, Caprara V, Cianfrocca R,
Rosanò L, Di Castro V, Garrafa E, Natali PG and Bagnato A: The
interplay between hypoxia, endothelial and melanoma cells regulates
vascularization and cell motility through endothelin-1 and vascular
endothelial growth factor. Carcinogenesis. 35:840–848. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Tzima E, Irani-Tehrani M, Kiosses WB,
Dejana E, Schultz DA, Engelhardt B, Cao G, DeLisser H and Schwartz
MA: A mecha-nosensory complex that mediates the endothelial cell
response to fluid shear stress. Nature. 437:426–431. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|