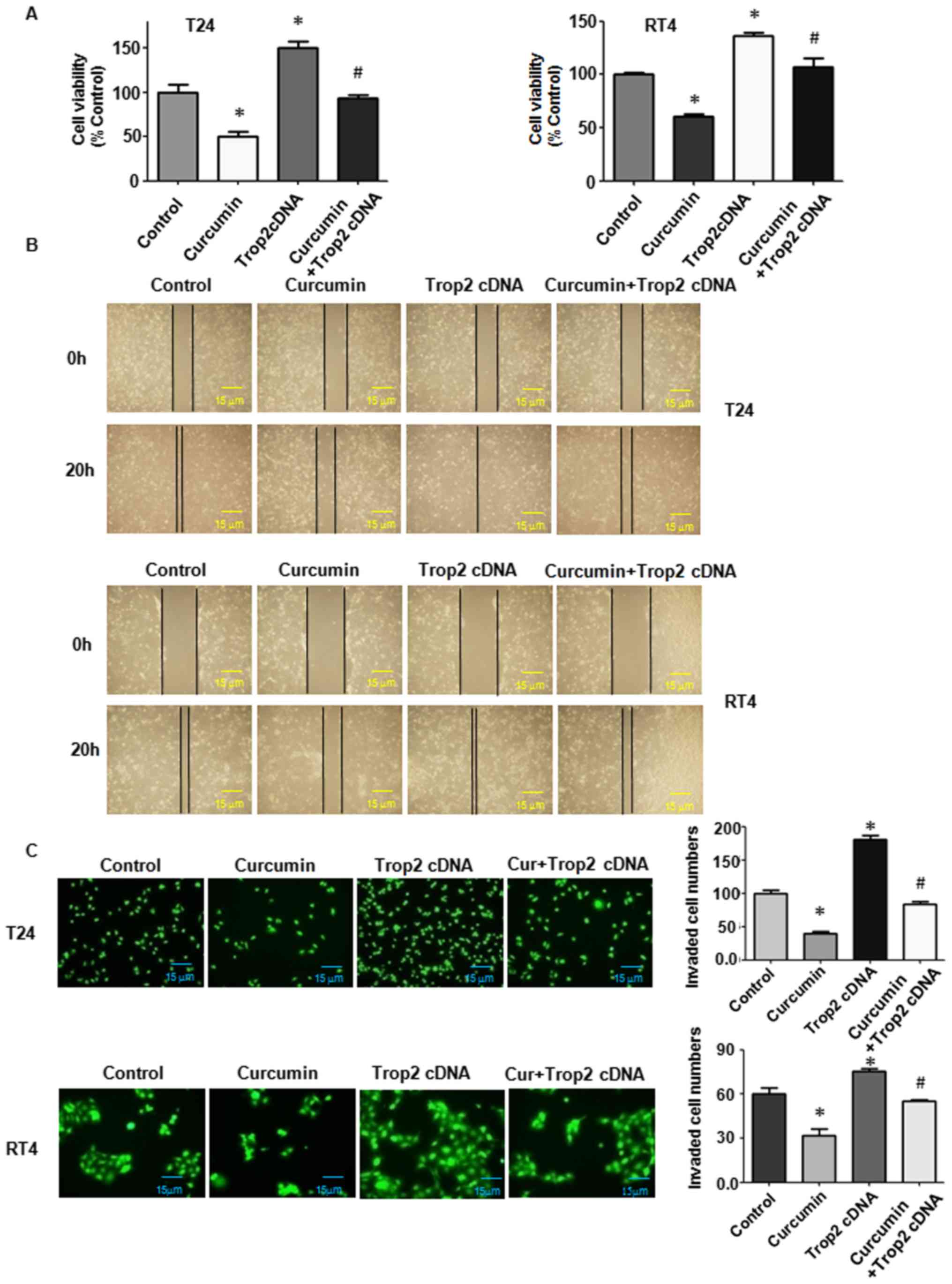
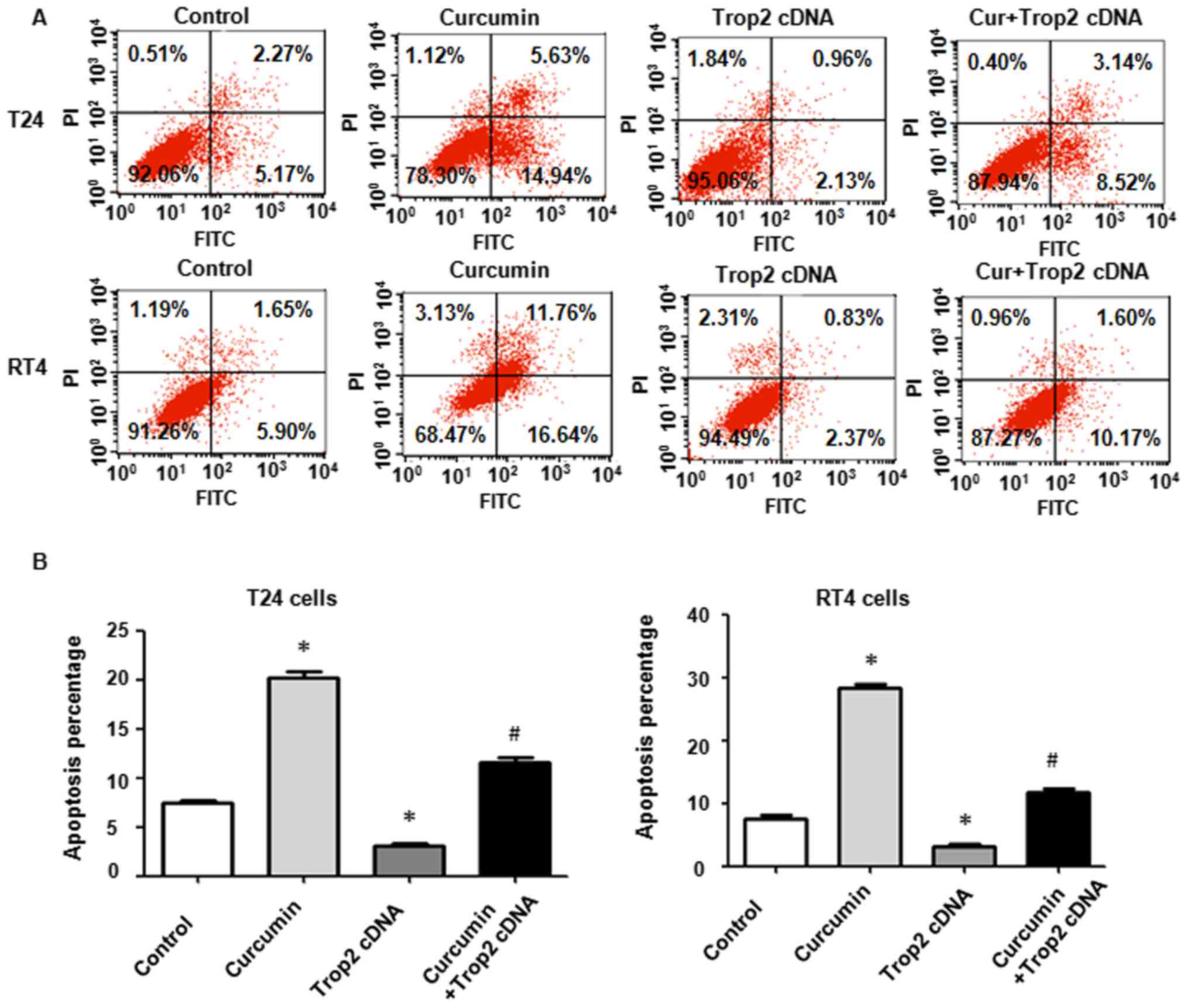
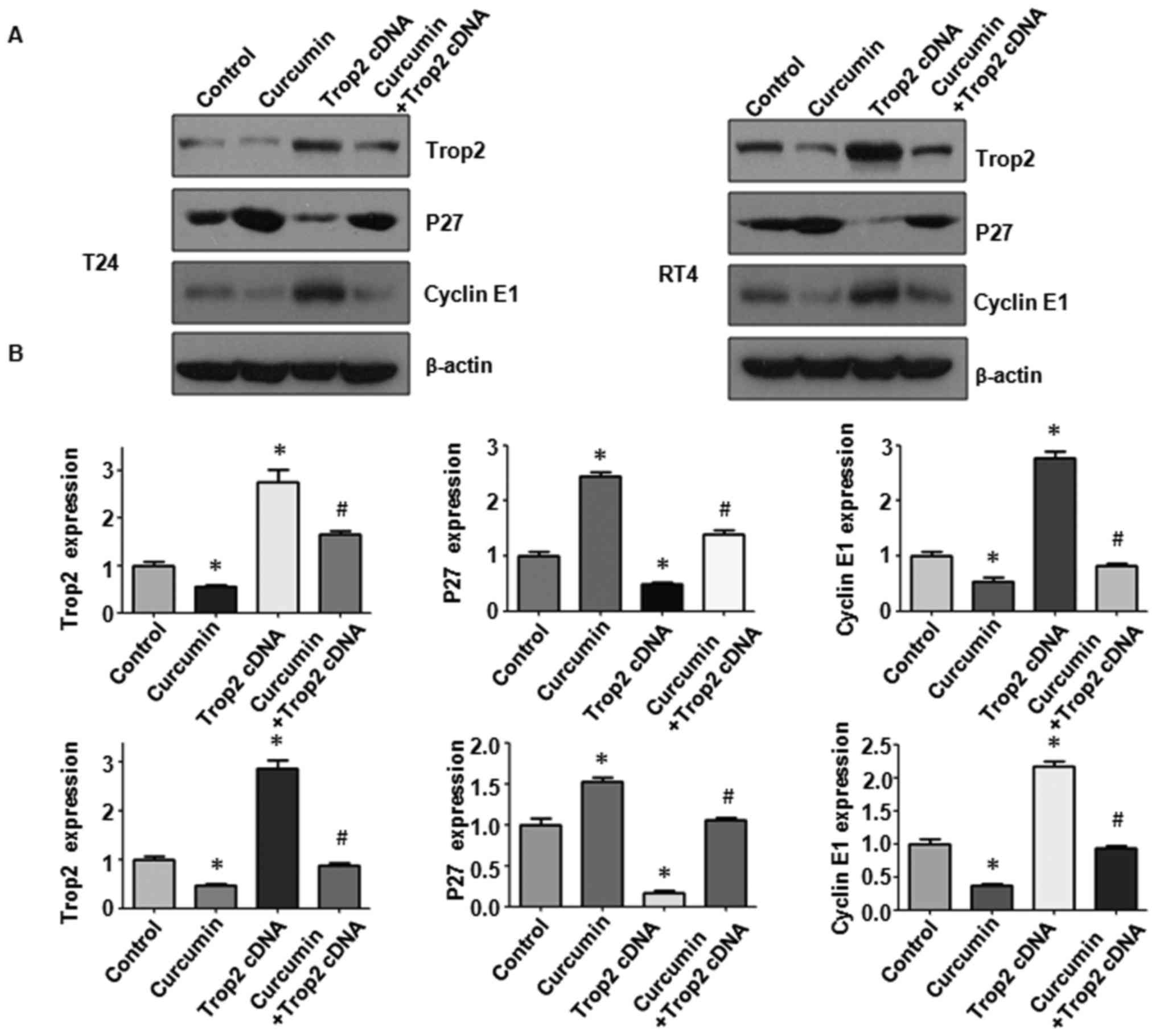
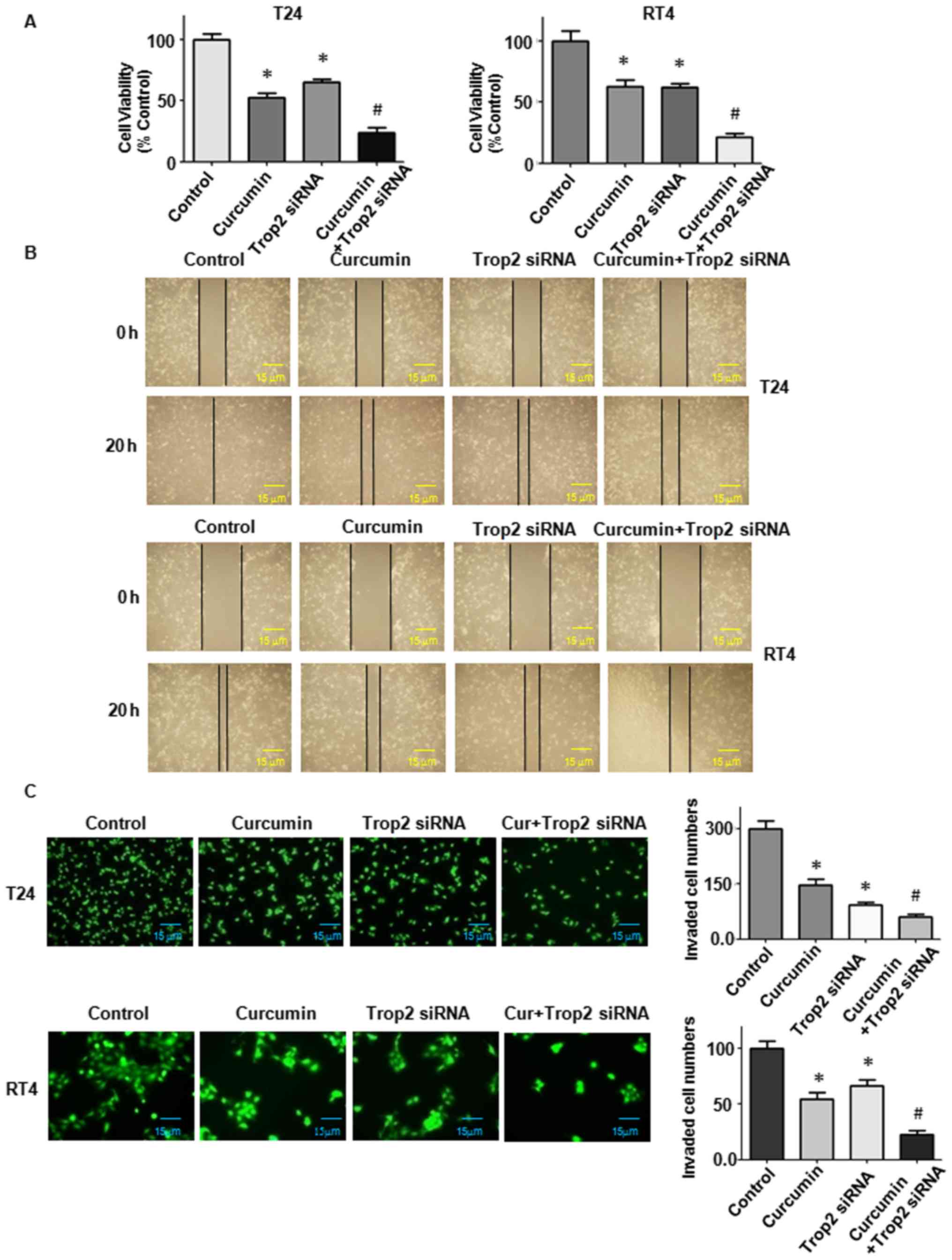
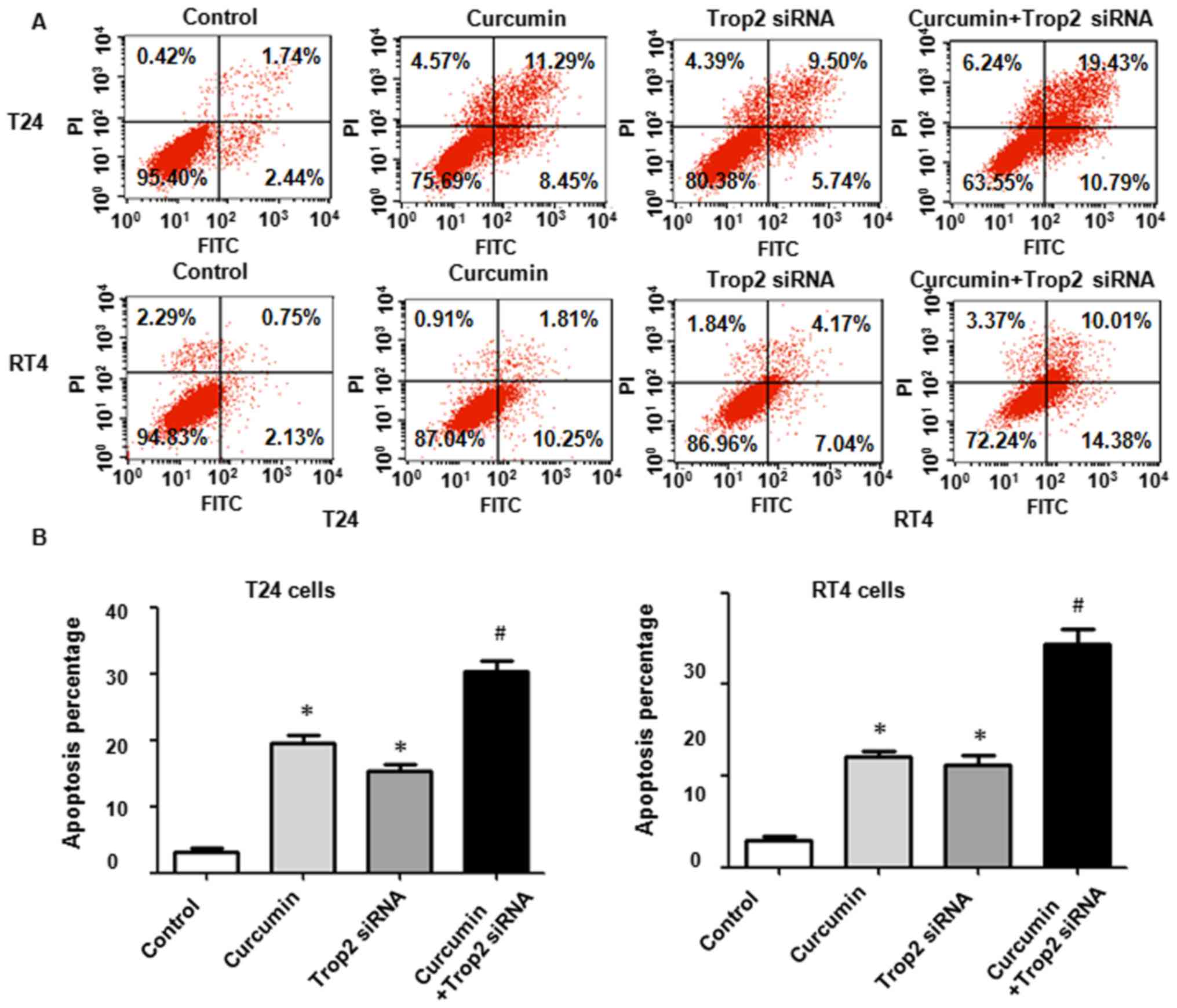
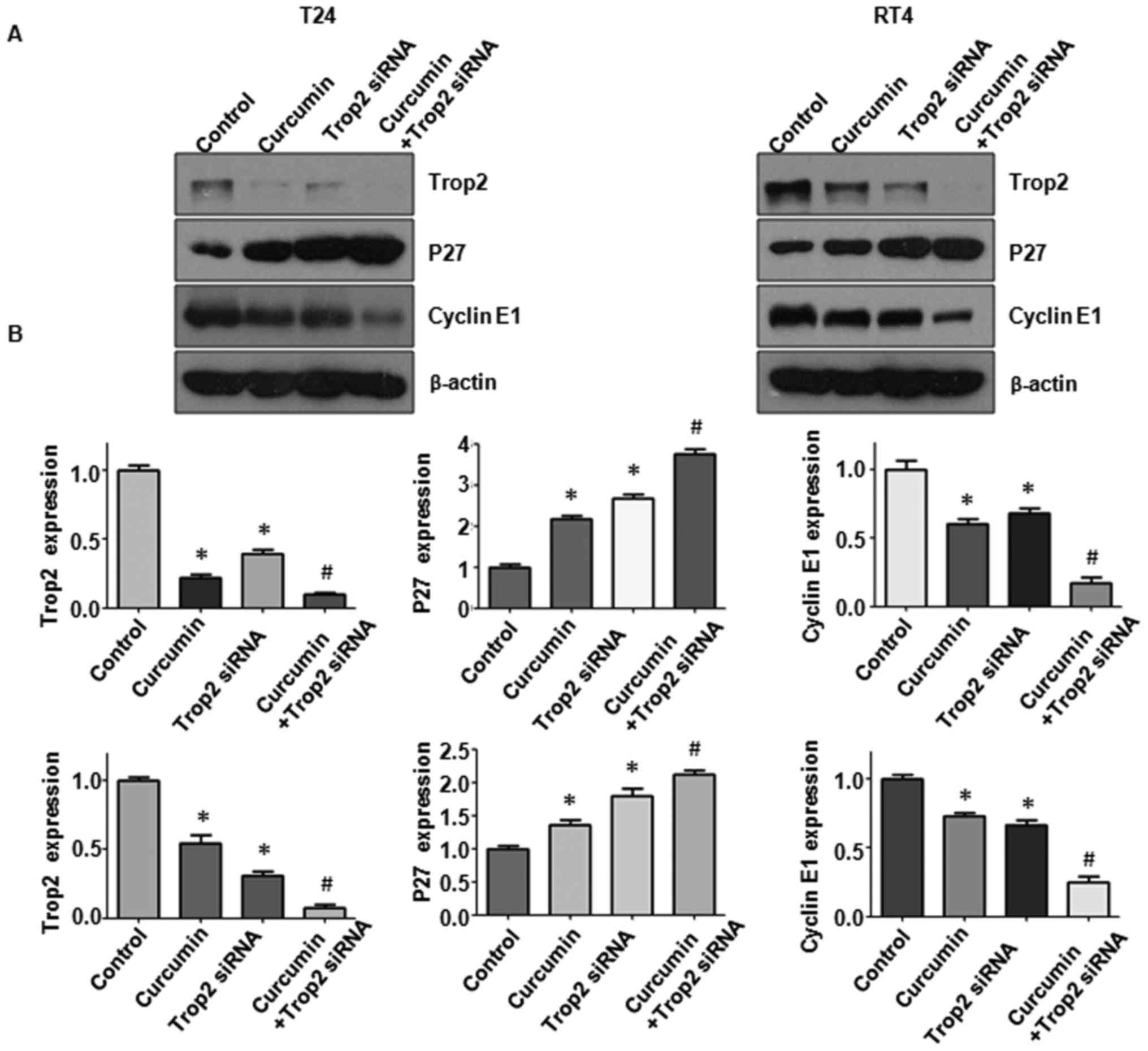
|
1
|
PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board:
Bladder cancer treatment (PDQ®): Patient version. PDQ
Cancer Information Summaries. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda,
MD: 2002
|
|
2
|
Disease GBD, Injury I and Prevalence C;
GBD 2015 disease and injury incidence and prevalence collaborators:
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years
lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.
Lancet. 388:1545–1602. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor
A, Jemal A and Bray F: Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: A
global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 71:96–108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
McDougall AR, Tolcos M, Hooper SB, Cole TJ
and Wallace MJ: Trop2: From development to disease. Dev Dyn.
244:99–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cubas R, Li M, Chen C and Yao Q: Trop2: A
possible therapeutic target for late stage epithelial carcinomas.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:309–314. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Lipinski M, Parks DR, Rouse RV and
Herzenberg LA: Human trophoblast cell-surface antigens defined by
monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:5147–5150. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Linnenbach AJ, Wojcierowski J, Wu SA, Pyrc
JJ, Ross AH, Dietzschold B, Speicher D and Koprowski H: Sequence
investigation of the major gastrointestinal tumor-associated
antigen gene family, GA733. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:27–31. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dean M: Cancer as a complex developmental
disorder–nineteenth Cornelius P. Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture.
Cancer Res. 58:5633–5636. 1998.
|
|
11
|
Trerotola M, Cantanelli P, Guerra E,
Tripaldi R, Aloisi AL, Bonasera V, Lattanzio R, de Lange R, Weidle
UH, Piantelli M, et al: Upregulation of Trop-2 quantitatively
stimulates human cancer growth. Oncogene. 32:222–233. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nakashima K, Shimada H, Ochiai T,
Kuboshima M, Kuroiwa N, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Nomura F, Takiguchi
M and Hiwasa T: Serological identification of TROP2 by recombinant
cDNA expression cloning using sera of patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 112:1029–1035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ohmachi T, Tanaka F, Mimori K, Inoue H,
Yanaga K and Mori M: Clinical significance of TROP2 expression in
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3057–3063. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fong D, Spizzo G, Gostner JM, Gastl G,
Moser P, Krammel C, Gerhard S, Rasse M and Laimer K: TROP2: A novel
prognostic marker in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity.
Mod Pathol. 21:186–191. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fong D, Moser P, Krammel C, Gostner JM,
Margreiter R, Mitterer M, Gastl G and Spizzo G: High expression of
TROP2 correlates with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Br J
Cancer. 99:1290–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pau Ni IB, Zakaria Z, Muhammad R, Abdullah
N, Ibrahim N, Aina Emran N, Hisham Abdullah N and Syed Hussain SN:
Gene expression patterns distinguish breast carcinomas from normal
breast tissues: The Malaysian context. Pathol Res Pract.
206:223–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ning S, Liang N, Liu B, Chen X, Pang Q and
Xin T: TROP2 expression and its correlation with tumor
proliferation and angiogenesis in human gliomas. Neurol Sci.
34:1745–1750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Varughese J, Cocco E, Bellone S, de Leon
M, Bellone M, Todeschini P, Schwartz PE, Rutherford TJ, Pecorelli S
and Santin AD: Uterine serous papillary carcinomas overexpress
human trophoblast-cell-surface marker (Trop-2) and are highly
sensitive to immunotherapy with hRS7, a humanized anti-Trop-2
monoclonal antibody. Cancer. 117:3163–3172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Varughese J, Cocco E, Bellone S, Bellone
M, Todeschini P, Carrara L, Schwartz PE, Rutherford TJ, Pecorelli S
and Santin AD: High-grade, chemotherapy-resistant primary ovarian
carcinoma cell lines overexpress human trophoblast cell-surface
marker (Trop-2) and are highly sensitive to immunotherapy with
hRS7, a humanized monoclonal anti-Trop-2 antibody. Gynecol Oncol.
122:171–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Trerotola M, Jernigan DL, Liu Q, Siddiqui
J, Fatatis A and Languino LR: Trop-2 promotes prostate cancer
metastasis by modulating β(1) integrin functions. Cancer Res.
73:3155–3167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Okudan N, Belviranlı M, Gökbel H, Oz M and
Kumak A: Protective effects of curcumin supplementation on
intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 20:844–848.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kanai M: Therapeutic applications of
curcumin for patients with pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:9384–9391. 2014.
|
|
23
|
Aggarwal BB and Harikumar KB: Potential
therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent,
against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic,
autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:40–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zong H, Wang F, Fan QX and Wang LX:
Curcumin inhibits metastatic progression of breast cancer cell
through suppression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by
NF-kappa B signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 39:4803–4808. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gonçalves VP, Ortega AA, Guimarães MR,
Curylofo FA, Rossa Junior C, Ribeiro DA and Spolidorio LC:
Chemopreventive activity of systemically administered curcumin on
oral cancer in the 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide model. J Cell Biochem.
116:787–796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Beevers CS, Zhou H and Huang S: Hitting
the golden TORget: Curcumin's effects on mTOR signaling. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 13:988–994. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Su J, Zhou X, Wang L, Yin X and Wang Z:
Curcumin inhibits cell growth and invasion and induces apoptosis
through downregulation of Skp2 in pancreatic cancer cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 6:1949–1962. 2016.
|
|
28
|
Shehzad A and Lee YS: Molecular mechanisms
of curcumin action: Signal transduction. Biofactors. 39:27–36.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Momtazi AA, Shahabipour F, Khatibi S,
Johnston TP, Pirro M and Sahebkar A: Curcumin as a microRNA
regulator in cancer: A review. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol.
171:1–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gao Y, Shi Q, Xu S, Du C, Liang L, Wu K,
Wang K, Wang X, Chang LS, He D, et al: Curcumin promotes KLF5
proteasome degradation through downregulating YAP/TAZ in bladder
cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 15:15173–15187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shi J, Zhang X, Shi T and Li H: Antitumor
effects of curcumin in human bladder cance in vitro. Oncol Lett.
14:1157–1161. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Witjes JA, Compérat E, Cowan NC, De Santis
M, Gakis G, Lebret T, Ribal MJ, Van der Heijden AG and Sherif A;
European Association of Urology: EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive
and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2013 guidelines. Eur
Urol. 65:778–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shirodkar SP and Lokeshwar VB: Potential
new urinary markers in the early detection of bladder cancer. Curr
Opin Urol. 19:488–493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kamat AM, Tharakan ST, Sung B and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin potentiates the antitumor effects of Bacillus
Calmette-Guerin against bladder cancer through the downregulation
of NF-kappaB and upregulation of TRAIL receptors. Cancer Res.
69:8958–8966. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang P, Lai ZL, Chen HF, Zhang M, Wang A,
Jia T, Sun WQ, Zhu XM, Chen XF, Zhao Z, et al: Curcumin synergizes
with 5-fluorouracil by impairing AMPK/ULK1-dependent autophagy, AKT
activity and enhancing apoptosis in colon cancer cells with tumor
growth inhibition in xenograft mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:1902017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao Z, Li C, Xi H, Gao Y and Xu D:
Curcumin induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through the
induction of forkhead box O1 and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 12:5415–5422. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou X, Su J, Feng S, Wang L, Yin X, Yan J
and Wang Z: Antitumor activity of curcumin is involved in
downregulation of YAP/TAZ expression in pancreatic cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:79076–79088. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shi J, Wang Y, Jia Z, Gao Y, Zhao C and
Yao Y: Curcumin inhibits bladder cancer progression via regulation
of β-catenin expression. Tumour Biol. 39:1010428317702548. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cubas R, Zhang S, Li M, Chen C and Yao Q:
Trop2 expression contributes to tumor pathogenesis by activating
the ERK MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer. 9:2532010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Day R, Dong Y, Weintraub SJ and
Michel L: Identification of Trop-2 as an oncogene and an attractive
therapeutic target in colon cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:280–285.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Guan H, Guo Z, Liang W, Li H, Wei G, Xu L,
Xiao H and Li Y: Trop2 enhances invasion of thyroid cancer by
inducing MMP2 through ERK and JNK pathways. BMC Cancer. 17:4862017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li X, Teng S, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhang X,
Xu K, Yao H, Yao J, Wang H, Liang X, et al: TROP2 promotes
proliferation, migration and metastasis of gallbladder cancer cells
by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway and inducing EMT. Oncotarget.
8:47052–47063. 2017.
|