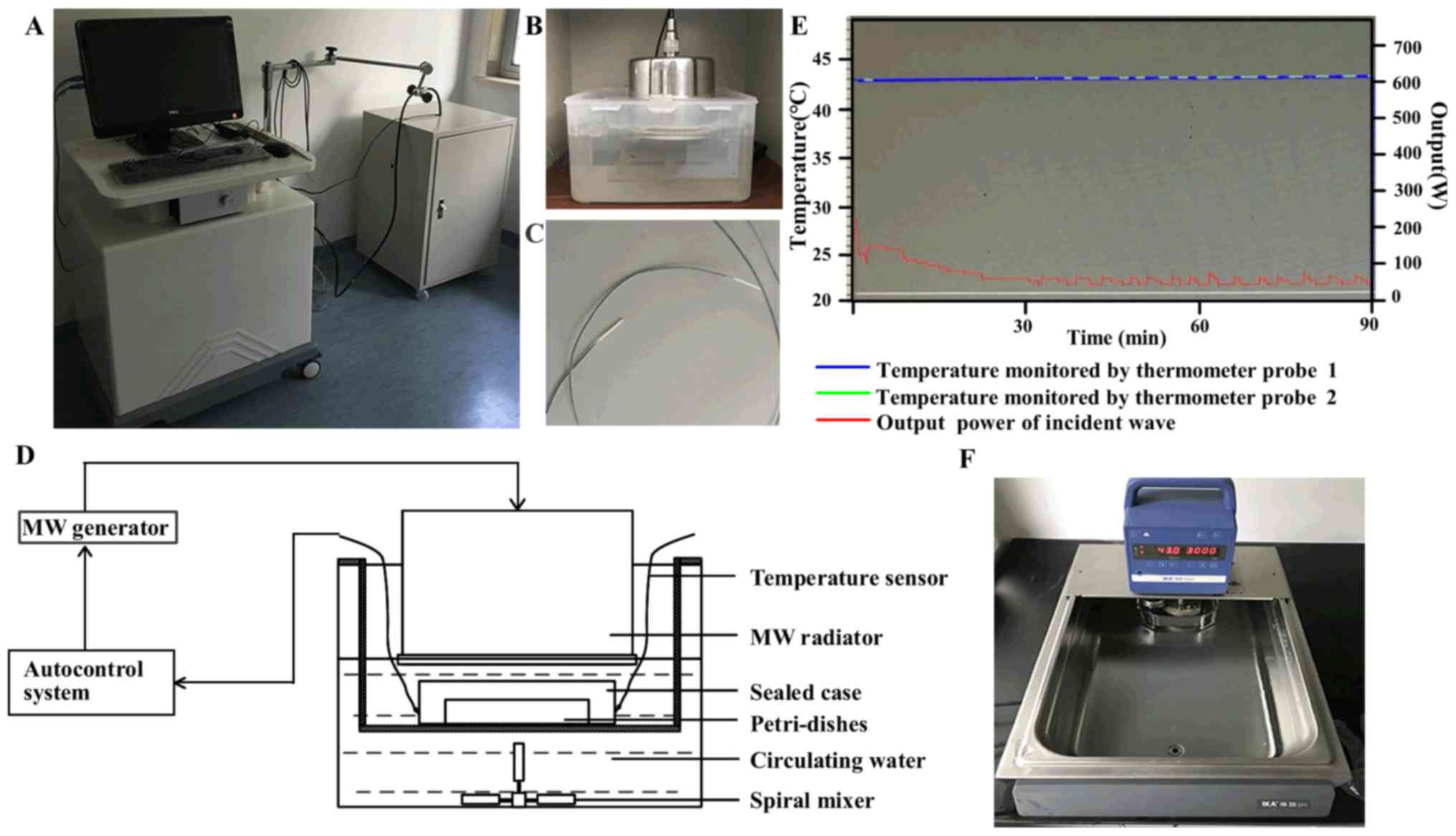
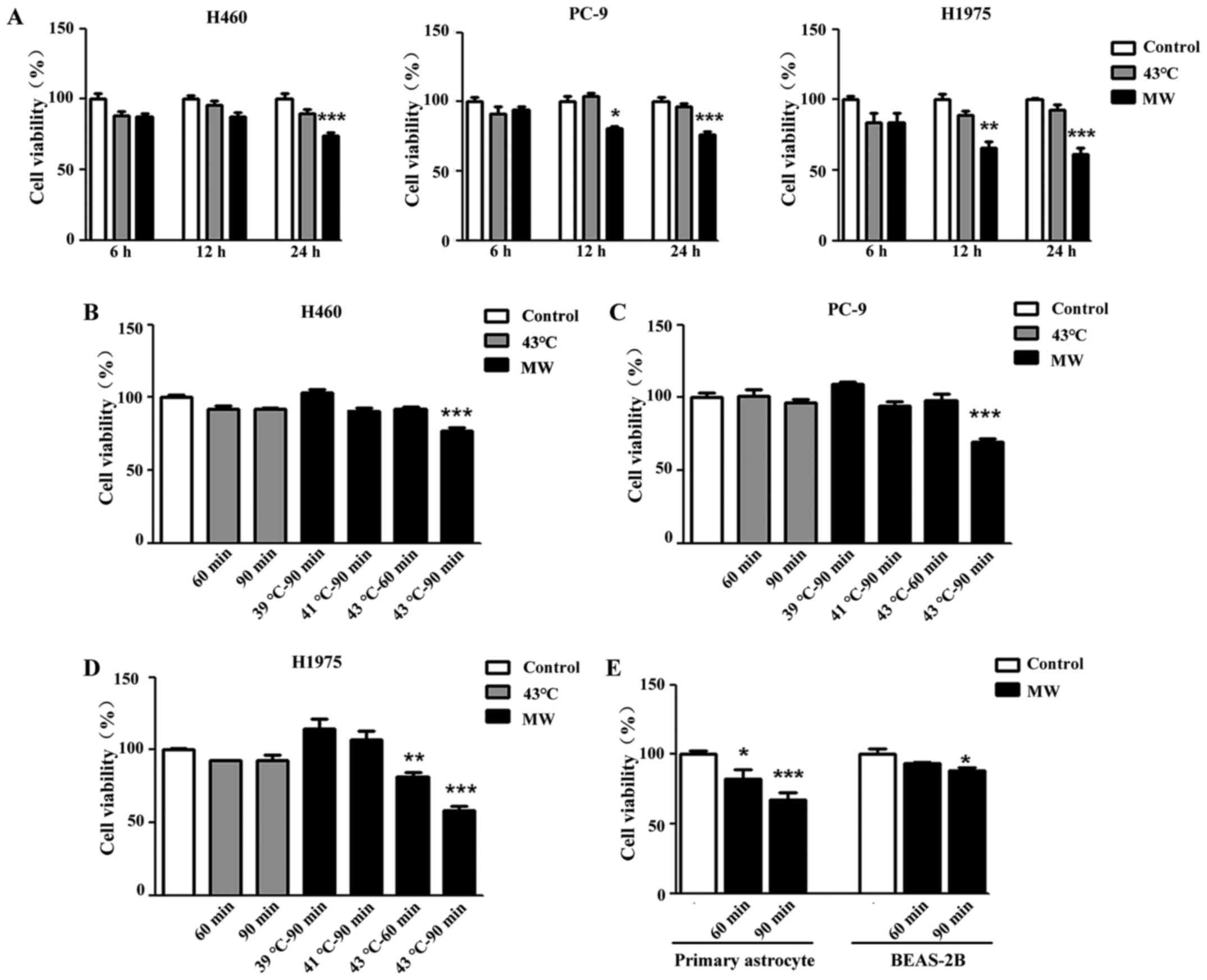
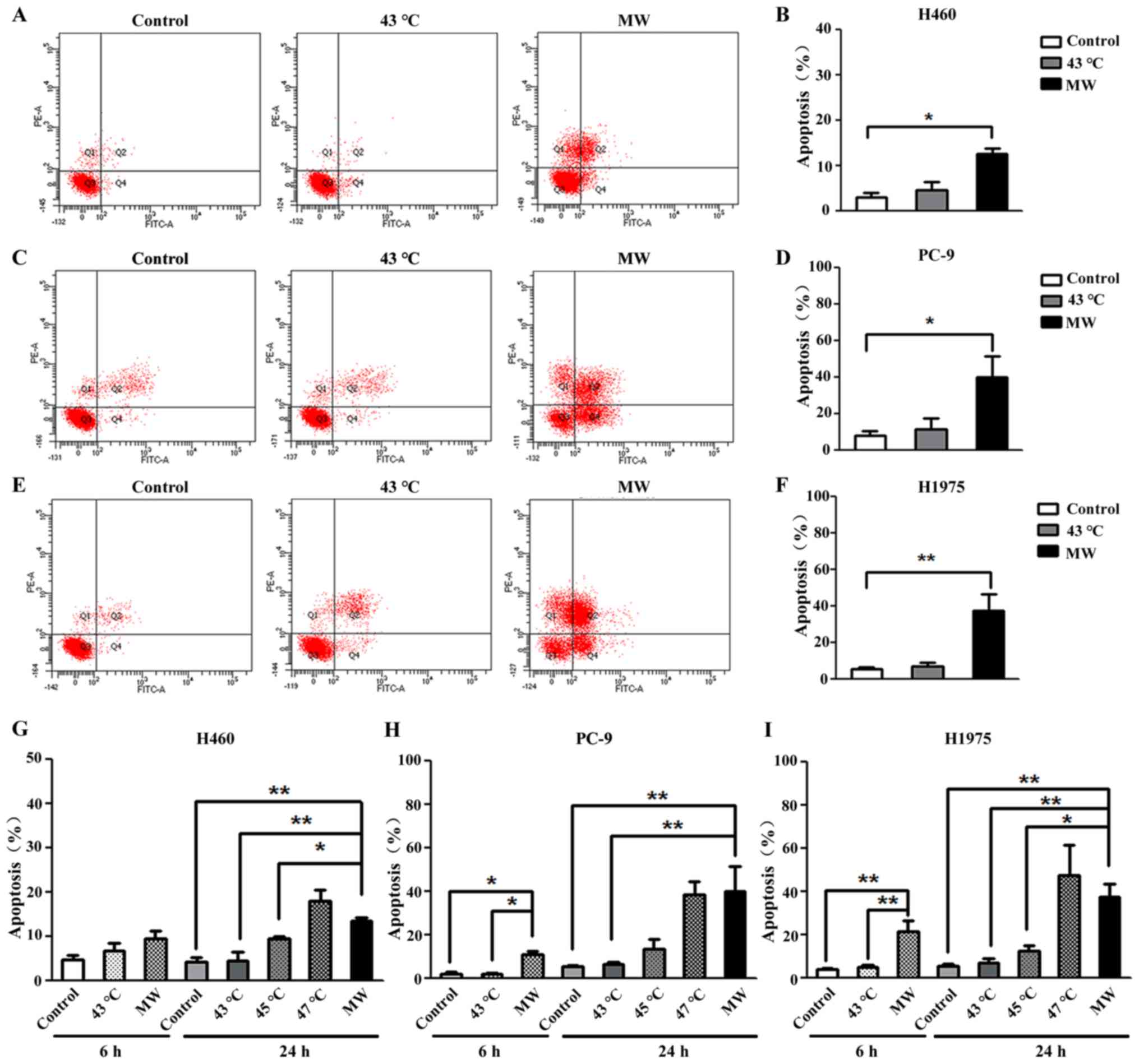
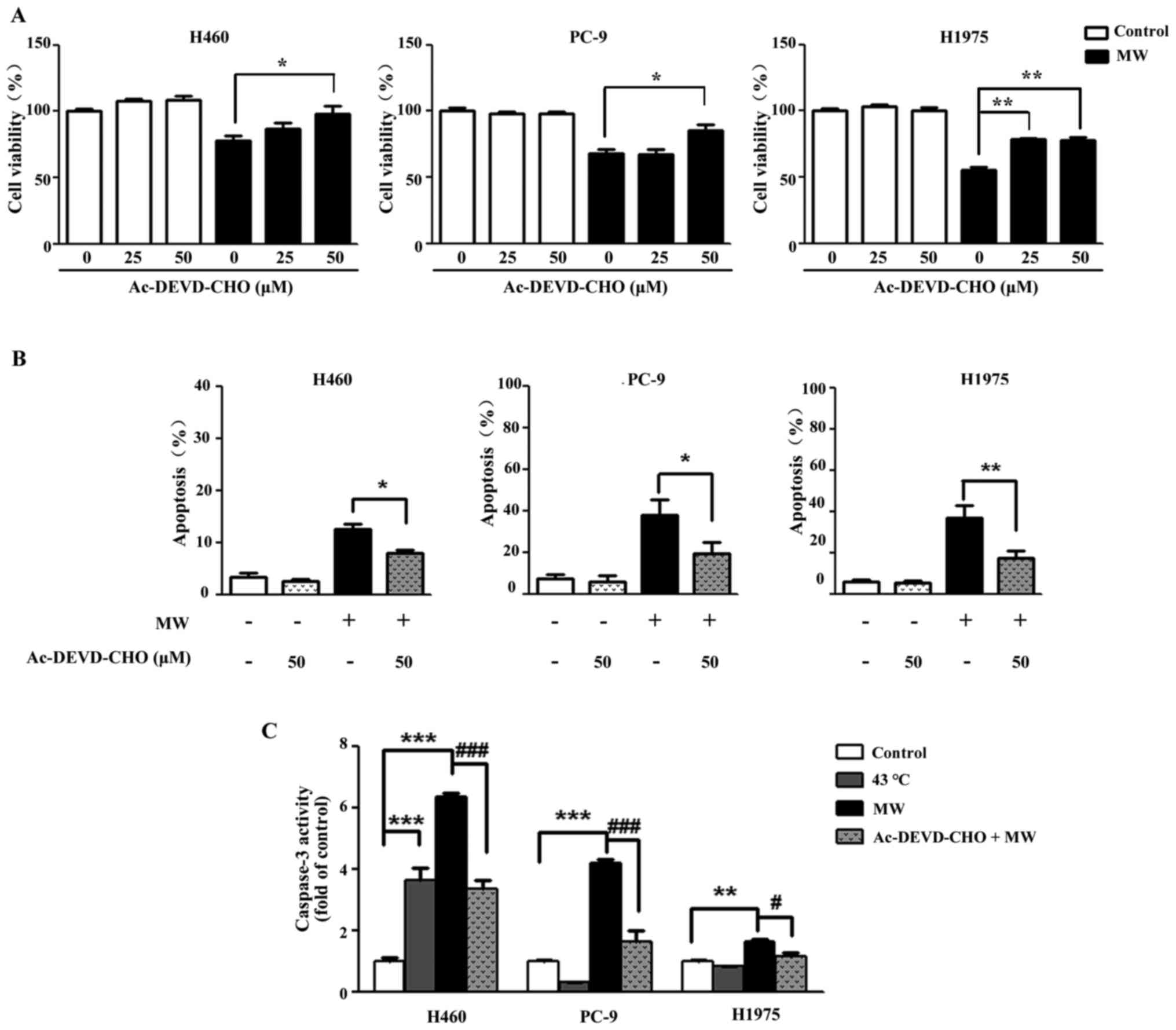
|
1
|
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J,
Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, Nicholson AG, Groome P,
Mitchell A, Bolejack V, et al International Association for the
Study of Lung Cancer Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee,
Advisory Boards, and Participating Institutions; International
Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Staging and Prognostic
Factors Committee Advisory Boards and Participating Institutions:
The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of
the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the
TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 11:39–51. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein
C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, Orme JP, Finlay MR, Ward RA, Mellor MJ,
et al: AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated
resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov.
4:1046–1061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu YL, Sequist LV, Tan EH, Geater SL,
Orlov S, Zhang L, Lee KH, Tsai CM, Kato T, Barrios CH, et al:
Afatinib as first-line treatment of older patients with EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Subgroup analyses of
the LUX-lung 3, LUX-lung 6, and LUX-lung 7 trials. Clin Lung
Cancer. S1525-7304(18): 30051–2. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Issels RD, Lindner LH, Verweij J, Wust P,
Reichardt P, Schem BC, Abdel-Rahman S, Daugaard S, Salat C,
Wendtner CM, et al European Organisation for Research and Treatment
of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (EORTC-STBSG);
European Society for Hyperthermic Oncology (ESHO): Neo-adjuvant
chemotherapy alone or with regional hyperthermia for localised
high-risk soft-tissue sarcoma: A randomised phase 3 multicentre
study. Lancet Oncol. 11:561–570. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Datta NR, Rogers S, Ordóñez SG, Puric E
and Bodis S: Hyperthermia and radiotherapy in the management of
head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J
Hyperthermia. 32:31–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Han JB, Kong FW, Ding H, Zhang YF, Liu JM,
Wei Q, Hu L, Zhao L, Xu CJ and Yi YX: Hepatectomy combined with
microwave ablation of the spleen for treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma complicated with splenomegaly: A retrospective study. Mol
Clin Oncol. 6:204–208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Poulou LS, Thanos L, Ziakas PD, Merikas E,
Achimastos A, Gennatas C and Syrigos KN: Thermal ablation may
improve outcomes in patients with colorectal liver metastasis: A
case-control study. J BUON. 22:673–678. 2017.
|
|
9
|
Bäcklund M and Freedman J: Microwave
ablation and immune activation in the treatment of recurrent
colorectal lung metastases: A case report. Case Rep Oncol.
10:383–387. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sherar MD, Liu FF, Newcombe DJ, Cooper B,
Levin W, Taylor WB and Hunt JW: Beam shaping for microwave
waveguide hyperthermia applicators. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
25:849–857. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vernon CC, Hand JW, Field SB, Machin D,
Whaley JB, van der Zee J, van Putten WL, van Rhoon GC, van Dijk JD,
González González D, et al International Collaborative Hyperthermia
Group: Radiotherapy with or without hyperthermia in the treatment
of superficial localized breast cancer: Results from five
randomized controlled trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
35:731–744. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kouloulias V, Triantopoulou S, Vrouvas J,
Gennatas K, Ouzounoglou N, Kouvaris J, Karaiskos P, Aggelakis P,
Antypas C, Zygogianni A, et al: Combined chemoradiotherapy with
local microwave hyperthermia for treatment of T3N0 laryngeal
carcinoma: A retrospective study with long-term follow-up. Acta
Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 34:167–173. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Kouloulias V, Triantopoulou S,
Efstathopoulos E, Platoni K, Kouvaris J, Uzunoglou N, Antypas C,
Karaiskos P, Aggelakis P, Vrouvas J, et al: Microwave hyperthermia
in conjunction with radiotherapy in superficial tumours:
Correlation of thermal parameters with tumour regression. West
Indian Med J. 62:752–757. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Agostinelli E, Belli F, Dalla Vedova L,
Marra M, Crateri P and Arancia G: Hyperthermia enhances
cytotoxicity of amine oxidase and spermine on drug-resistant LoVo
colon adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 28:1543–1553. 2006.
|
|
15
|
Li L, Wang W, Pan H, Ma G, Shi X, Xie H,
Liu X, Ding Q, Zhou W and Wang S: Microwave ablation combined with
OK-432 induces Th1-type response and specific antitumor immunity in
a murine model of breast cancer. J Transl Med. 15:232017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Asano M, Sakaguchi M, Tanaka S, Kashimura
K, Mitani T, Kawase M, Matsumura H, Yamaguchi T, Fujita Y and
Tabuse K: Effects of normothermic conditioned microwave irradiation
on cultured cells using an irradiation system with semiconductor
oscillator and thermo-regulatory applicator. Sci Rep. 7:412442017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zagar TM, Oleson JR, Vujaskovic Z,
Dewhirst MW, Craciunescu OI, Blackwell KL, Prosnitz LR and Jones
EL: Hyperthermia combined with radiation therapy for superficial
breast cancer and chest wall recurrence: A review of the randomised
data. Int J Hyperthermia. 26:612–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mallory M, Gogineni E, Jones GC, Greer L
and Simone CB II: Therapeutic hyperthermia: The old, the new, and
the upcoming. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 97:56–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee H, Park HJ, Park CS, Oh ET, Choi BH,
Williams B, Lee CK and Song CW: Response of breast cancer cells and
cancer stem cells to metformin and hyperthermia alone or combined.
PLoS One. 9:e879792014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gao F, Ye Y, Zhang Y and Yang J: Water
bath hyperthermia reduces stemness of colon cancer cells. Clin
Biochem. 46:1747–1750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wu ZB, Ma SL, Zhu J, Long JP, Li XD, Yao
XY, Lu HQ, Zhang YM, Chen SM and Jing SS: An experimental device
for heating tumor cell. CN Patent 2015205415415. Filed July 23,
2015; issued December 2, 2015.
|
|
22
|
Wang R, Zhang X, Zhang J, Fan Y, Shen Y,
Hu W and Chen Z: Oxygen-glucose deprivation induced glial scar-like
change in astrocytes. PLoS One. 7:e375742012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Levison SW and McCarthy KD: Astroglia in
culture. Nerve Cell Culture. G Banker and K Goslin: MIT Press;
Cambridge, MA: pp. 309–336. 1991
|
|
24
|
Stauffer PR: Evolving technology for
thermal therapy of cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 21:731–744. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
van Leeuwen CM, Oei AL, Chin KWTK, Crezee
J, Bel A, Westermann AM, Buist MR, Franken NAP, Stalpers LJA and
Kok HP: A short time interval between radiotherapy and hyperthermia
reduces in-field recurrence and mortality in women with advanced
cervical cancer. Radiat Oncol. 12:752017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rietveld PJ, van Putten WL, van der Zee J
and van Rhoon GC: Comparison of the clinical effectiveness of the
433 MHz Lucite cone applicator with that of a conventional
waveguide applicator in applications of superficial hyperthermia.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 43:681–687. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Paulides MM, Bakker JF, Chavannes N and
Van Rhoon GC: A patch antenna design for application in a
phased-array head and neck hyperthermia applicator. IEEE Trans
Biomed Eng. 54:2057–2063. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xing F, Zhan Q, He Y, Cui J, He S and Wang
G: 1800MHz microwave induces p53 and p53-mediated caspase-3
activation leading to cell apoptosis in vitro. PLoS One.
11:e01639352016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang JF, Yan XM, Lan B, Lei YR, Li XH,
Gao S, Guo YF and Guo F: Molecular mechanisms of synergistic
induction of apoptosis by the combination therapy with hyperthermia
and cisplatin in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
479:159–165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pawlik A, Nowak JM, Grzanka D, Gackowska
L, Michalkiewicz J and Grzanka A: Hyperthermia induces cytoskeletal
alterations and mitotic catastrophe in p53-deficient H1299 lung
cancer cells. Acta Histochem. 115:8–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Asano M, Tanaka S, Sakaguchi M, Matsumura
H, Yamaguchi T, Fujita Y and Tabuse K: Normothermic microwave
irradiation induces death of HL-60 cells through heat-independent
apoptosis. Sci Rep. 7:114062017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Cai F, Chen X, Luo M, Hu L and Lu
Y: The role of mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in
hyperthermia-induced platelet apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e750442013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Katschinski DM, Boos K, Schindler SG and
Fandrey J: Pivotal role of reactive oxygen species as intracellular
mediators of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
275:21094–21098. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hou CH, Lin FL, Hou SM and Liu JF:
Hyperthermia induces apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum and
reactive oxygen species in human osteosarcoma cells. Int J Mol Sci.
15:17380–17395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee H, Kim S, Choi BH, Park MT, Lee J,
Jeong SY, Choi EK, Lim BU, Kim C and Park HJ: Hyperthermia improves
therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin carried by mesoporous silica
nanocontainers in human lung cancer cells. Int J Hyperthermia.
27:698–707. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gu Y, Chen T, Fu S, Sun X, Wang L, Wang J,
Lu Y, Ding S, Ruan G, Teng L, et al: Perioperative dynamics and
significance of amino acid profiles in patients with cancer. J
Transl Med. 13:352015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ahmed K, Tabuchi Y and Kondo T:
Hyperthermia: An effective strategy to induce apoptosis in cancer
cells. Apoptosis. 20:1411–1419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Furusawa Y, Iizumi T, Fujiwara Y, Zhao QL,
Tabuchi Y, Nomura T and Kondo T: Inhibition of checkpoint kinase 1
abrogates G2/M checkpoint activation and promotes
apoptosis under heat stress. Apoptosis. 17:102–112. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Roskoski R Jr: Cyclin-dependent protein
kinase inhibitors including palbociclib as anticancer drugs.
Pharmacol Res. 107:249–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kurz EU and Lees-Miller SP: DNA
damage-induced activation of ATM and ATM-dependent signaling
pathways. DNA Repair (Amst). 3:889–900. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shaltiel IA, Krenning L, Bruinsma W and
Medema RH: The same, only different - DNA damage checkpoints and
their reversal throughout the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 128:607–620.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lavin MF and Kozlov S: ATM activation and
DNA damage response. Cell Cycle. 6:931–942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Beecken WD, Ringel EM, Babica J, Oppermann
E, Jonas D and Blaheta RA: Plasmin-clipped beta(2)-glycoprotein-I
inhibits endothelial cell growth by down-regulating cyclin A, B and
D1 and up-regulating p21 and p27. Cancer Lett. 296:160–167. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yin H, Jiang M, Peng X, Cui H, Zhou Y, He
M, Zuo Z, Ouyang P, Fan J and Fang J: The molecular mechanism of
G2M cell cycle arrest induced by AFB1 in the jejunum.
Oncotarget. 7:35592–35606. 2016.
|
|
46
|
Wang Z, Fan M, Candas D, Zhang TQ, Qin L,
Eldridge A, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Ahmed KM, Chromy BA, Nantajit D, et
al: Cyclin B1/Cdk1 coordinates mitochondrial respiration for
cell-cycle G2/M progression. Dev Cell. 29:217–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cheng YM, Tsai CC and Hsu YC:
Sulforaphane, a dietary isothiocyanate, induces G(2)/M arrest in
cervical cancer cells through cyclin B1 downregulation and
GADD45beta/CDC2 association. Int J Mol Sci. 17:15302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang H, Zhan C, Ke J, Xue Z, Zhang A, Xu
K, Shen Z, Yu L and Chen L: EGFR kinase domain mutation positive
lung cancers are sensitive to intrapleural perfusion with
hyperthermic chemotherapy (IPHC) complete treatment. Oncotarget.
7:3367–3378. 2016.
|