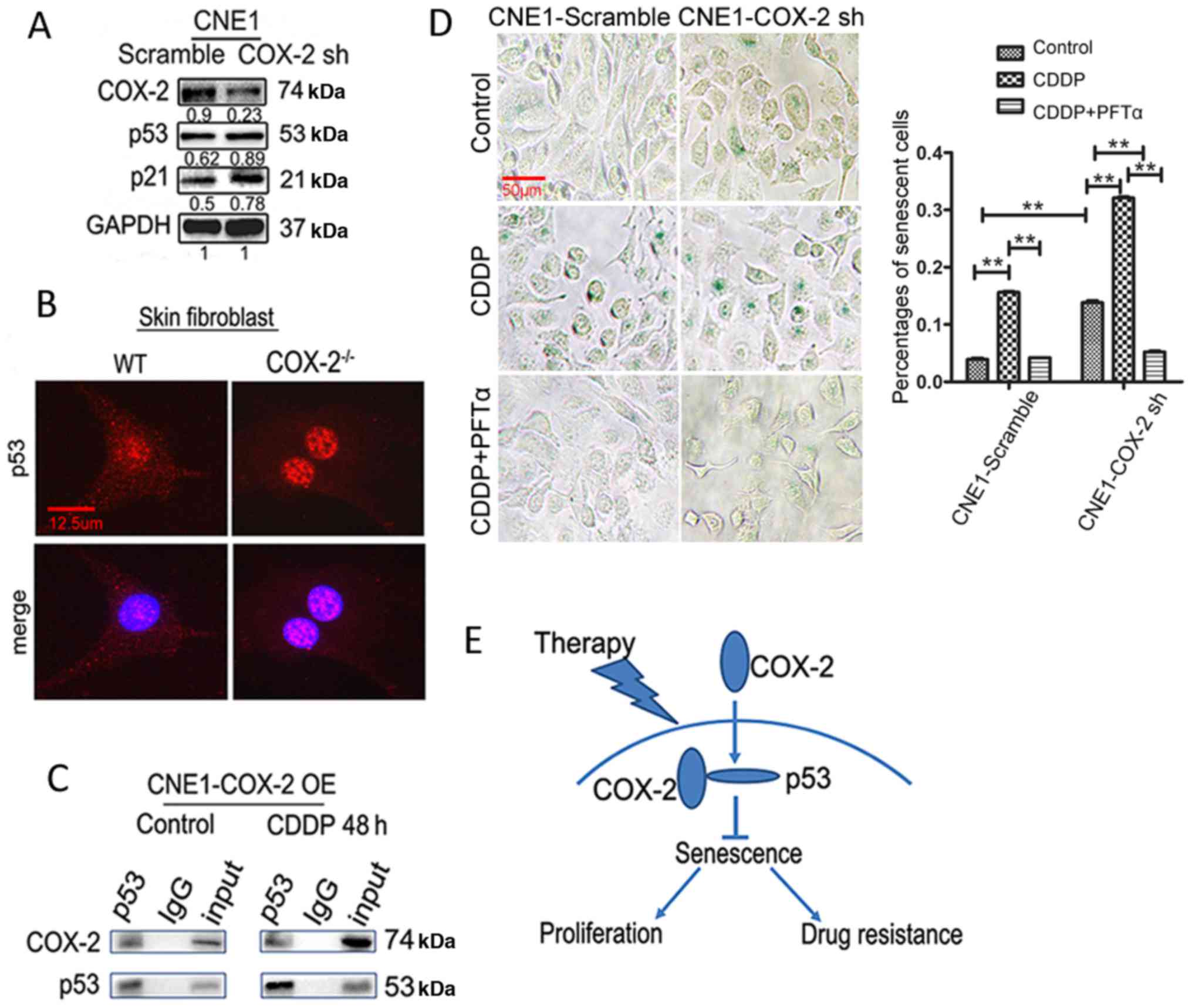
|
1
|
Ma BB, Hui EP and Chan AT: Investigational
drugs for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
26:677–685. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP and Chan AT:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shao JY, Wang HY, Huang XM, Feng QS, Huang
P, Feng BJ, Huang LX, Yu XJ, Li JT, Hu LF, et al: Genome-wide
allelotype analysis of sporadic primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma
from southern China. Int J Oncol. 17:1267–1275. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan AT: Current treatment of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 47(Suppl 3): S302–S303.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan AT, Grégoire V, Lefebvre JL, Licitra
L, Hui EP, Leung SF and Felip E; EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Guidelines Working
Group: Nasopharyngeal cancer: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice
Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol.
23(Suppl 7): vii83–vii85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen C, Chen T, Huang C, Wang J and Fei Z:
Experience of weekly cisplatin concurrent with intensity-modulated
radiotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients
with resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Medicine (Baltimore).
96. pp. e84342017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soto-Gamez A and Demaria M: Therapeutic
interventions for aging: The case of cellular senescence. Drug
Discov Today. 22:786–795. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loaiza N and Demaria M: Cellular
senescence and tumor promotion: Is aging the key. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1865.155–167. 2016.
|
|
11
|
Lee M and Lee JS: Exploiting tumor cell
senescence in anticancer therapy. BMB Rep. 47:51–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gordon RR and Nelson PS: Cellular
senescence and cancer chemotherapy resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
15:123–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Petrova NV, Velichko AK, Razin SV and
Kantidze OL: Small molecule compounds that induce cellular
senescence. Aging Cell. 15:999–1017. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Wong SC, Pan J, Tsao SW, Fung KH,
Kwong DL, Sham JS and Nicholls JM: Evidence of cisplatin-induced
senescent-like growth arrest in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 58:5019–5022. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Z, Pan X, Zou Z, Ding Q, Wu G and Peng
G: Increased SHP-1 expression results in radioresistance,
inhibition of cellular senescence, and cell cycle redistribution in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Radiat Oncol. 10:1522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Zou F, Tang J, Zhang Q, Gong Y,
Wang Q, Shen Y, Xiong L, Breyer RM, Lazarus M, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E2 promotes
injury-induced vascular neointimal hyperplasia through the
E-prostanoid 3 receptor. Circ Res. 113:104–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schumacher Y, Aparicio T, Ourabah S,
Baraille F, Martin A, Wind P, Dentin R, Postic C and Guilmeau S:
Dysregulated CRTC1 activity is a novel component of PGE2
signaling that contributes to colon cancer growth. Oncogene.
35:2602–2614. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu K, Fukuda K, Xing F, Zhang Y, Sharma S,
Liu Y, Chan MD, Zhou X, Qasem SA, Pochampally R, et al: Roles of
the cyclooxygenase 2 matrix metalloproteinase 1 pathway in brain
metastasis of breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 290:9842–9854. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu X, Cheng JC, Chang HM and Leung PC:
COX2 and PGE2 mediate EGF-induced E-cadherin-independent
human ovarian cancer cell invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer.
21:533–543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan J, Tang T, Xu L, Lu JJ, Lin S, Qiu S,
Chen G and K Tham IW: Prognostic significance of expression of
cyclooxygenase-2, vascular endothelial growth factor, and epidermal
growth factor receptor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck.
35:1238–1247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Majumder M, Dunn L, Liu L, Hasan A,
Vincent K, Brackstone M, Hess D and Lala PK: COX-2 induces
oncogenic micro RNA miR655 in human breast cancer. Sci Rep.
8:3272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le CP, Nowell CJ, Kim-Fuchs C, Botteri E,
Hiller JG, Ismail H, Pimentel MA, Chai MG, Karnezis T, Rotmensz N,
et al: Chronic stress in mice remodels lymph vasculature to promote
tumour cell dissemination. Nat Commun. 7:106342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao CX, Luo CL and Wu XH: Hypoxia
promotes 786-O cells invasiveness and resistance to sorafenib via
HIF-2α/COX-2. Med Oncol. 32:4192015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kurtova AV, Xiao J, Mo Q, Pazhanisamy S,
Krasnow R, Lerner SP, Chen F, Roh TT, Lay E, Ho PL, et al: Blocking
PGE2-induced tumour repopulation abrogates bladder
cancer chemoresistance. Nature. 517:209–213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhou W, Feng X, Ren C, Jiang X, Liu W,
Huang W, Liu Z, Li Z, Zeng L, Wang L, et al: Over-expression of
BCAT1, a c-Myc target gene, induces cell proliferation, migration
and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 12:532013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Khamaisi M, Katagiri S, Keenan H, Park K,
Maeda Y, Li Q, Qi W, Thomou T, Eschuk D, Tellechea A, et al: PKCδ
inhibition normalizes the wound-healing capacity of diabetic human
fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 126:837–853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu T, Ding Y, Xie W, Li Z, Bai X, Li X,
Fang W, Ren C, Wang S, Hoffman RM, et al: An imageable metastatic
treatment model of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3960–3967. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Campisi J: Aging, cellular senescence, and
cancer. Annu Rev Physiol. 75:685–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dirac AM and Bernards R: Reversal of
senescence in mouse fibroblasts through lentiviral suppression of
p53. J Biol Chem. 278:11731–11734. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu Y, Fan J, Chen XS, Wang D, Klein-Szanto
AJ, Campbell RL, FitzGerald GA and Funk CD: Genetic model of
selective COX2 inhibition reveals novel heterodimer signaling. Nat
Med. 12:699–704. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu H, Kauffman ME, Trush MA, Jia Z and Li
YR: A simple bioluminescence imaging method for studying cancer
cell growth and metastasis after subcutaneous injection of Lewis
lung carcinoma cells in syngeneic C57BL/6 mice. React Oxyg Species
(Apex). 5. pp. 118–125. 2018
|
|
32
|
Choi EM, Kim SR, Lee EJ and Han JA:
Cyclooxygenase-2 functionally inactivates p53 through a physical
interaction with p53. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1354–1365. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liao Q, Zeng Z, Guo X, Li X, Wei F, Zhang
W, Li X, Chen P, Liang F, Xiang B, et al: LPLUNC1 suppresses
IL-6-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via
inhibiting the Stat3 activation. Oncogene. 33:2098–2109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bourouba M, Zergoun AA, Maffei JS, Chila
D, Djennaoui D, Asselah F, Amir-Tidadini ZC, Touil-Boukoffa C and
Zaman MH: TNFα antagonization alters NOS2 dependent nasopharyngeal
carcinoma tumor growth. Cytokine. 74:157–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou TJ, Zhang SL, He CY, Zhuang QY, Han
PY, Jiang SW, Yao H, Huang YJ, Ling WH, Lin YC, et al:
Downregulation of mitochondrial cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits the
stemness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by decreasing the activity of
dynamin-related protein 1. Theranostics. 7:1389–1406. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Braumüller H, Wieder T, Brenner E, Aßmann
S, Hahn M, Alkhaled M, Schilbach K, Essmann F, Kneilling M,
Griessinger C, et al: T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into
senescence. Nature. 494:361–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Goel S, Wang Q, Watt AC, Tolaney SM,
Dillon DA, Li W, Ramm S, Palmer AC, Yuzugullu H, Varadan V, et al:
Overcoming therapeutic resistance in HER2-positive breast cancers
with CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 29:255–269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Lei D, Swindell WR, Xia W, Weng S,
Fu J, Worthen CA, Okubo T, Johnston A, Gudjonsson JE, et al:
Age-associated increase in skin fibroblast-derived prostaglandin E2
contributes to reduced collagen levels in elderly human skin. J
Invest Dermatol. 135:2181–2188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim J, Vaish V, Feng M, Field K,
Chatzistamou I and Shim M: Transgenic expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) causes premature aging phenotypes in mice.
Aging (Albany NY). 8:2392–2406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, Hwang DH,
Ballou LR, Mahale A, Aaronson SA and Lee SW: P53-mediated induction
of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO J. 21:5635–5644. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chan SY, Choy KW, Tsao SW, Tao Q, Tang T,
Chung GT and Lo KW: Authentication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
tumor lines. Int J Cancer. 122:2169–2171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|