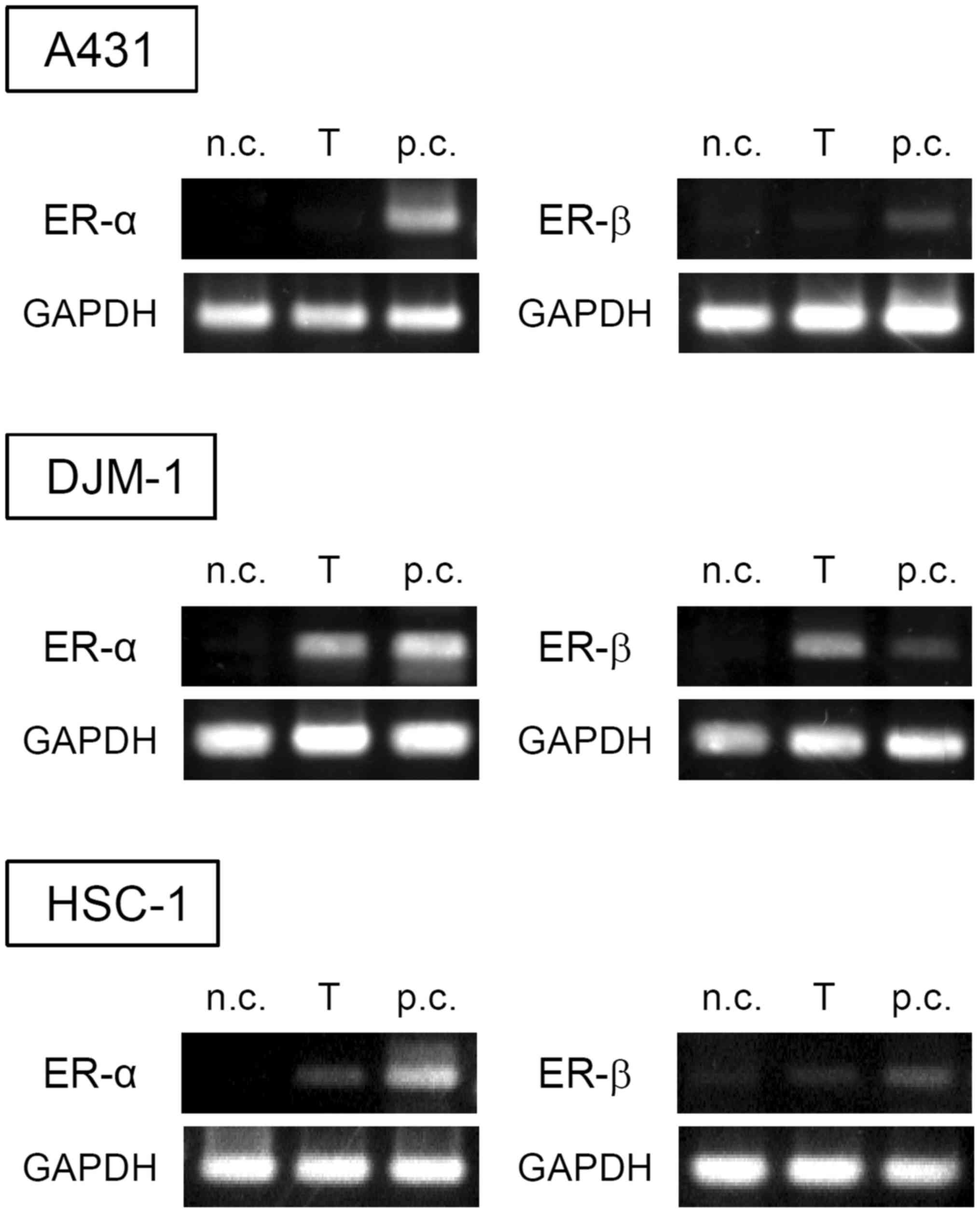
|
1
|
Osborne CK: Tamoxifen in the treatment of
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 339:1609–1618. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnston SR and Dowsett M: Aromatase
inhibitors for breast cancer: Lessons from the laboratory. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:821–831. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crewe HK, Notley LM, Wunsch RM, Lennard MS
and Gillam EM: Metabolism of tamoxifen by recombinant human
cytochrome P450 enzymes: Formation of the 4-hydroxy, 4′-hydroxy and
N-desmethyl metabolites and isomerization of
trans-4-hydroxytamoxifen. Drug Metab Dispos. 30:869–874. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo WZ, Wang Y, Umeda E, Shiina I, Dan S
and Yamori T: Search for novel anti-tumor agents from ridaifens
using JFCR39, a panel of human cancer cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:1008–1016. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer NCCf: 41 Endocrine therapy.
Advanced Breast Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment. National
Collaborating Centre for Cancer (UK); Cardiff: pp. 17–21. 2009
|
|
6
|
Bonneterre J, Buzdar A, Nabholtz JM,
Robertson JF, Thürlimann B, von Euler M, Sahmoud T, Webster A,
Steinberg M, Committee AW, et al Investigators Committee Members:
Anastrozole is superior to tamoxifen as first-line therapy in
hormone receptor positive advanced breast carcinoma. Cancer.
92:2247–2258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patterson J, Furr B, Wakeling A and
Battersby L: The biology and physiology of ‘Nolvadex’ (tamoxifen)
in the treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
2:363–374. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bakkevold KE, Pettersen A, Arnesjø B and
Espehaug B: Tamoxifen therapy in unresectable adenocarcinoma of the
pancreas and the papilla of Vater. Br J Surg. 77:725–730. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosenberg L: Treatment of pancreatic
cancer. Promises and problems of tamoxifen, somatostatin analogs,
and gemcitabine. Int J Pancreatol. 22:81–93. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Couldwell WT, Hinton DR, Surnock AA,
DeGiorgio CM, Weiner LP, Apuzzo ML, Masri L, Law RE and Weiss MH:
Treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas with chronic oral
high-dose tamoxifen. Clin Cancer Res. 2:619–622. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pawar P, Ma L, Byon CH, Liu H, Ahn EY,
Jhala N, Arnoletti JP, McDonald JM and Chen Y: Molecular mechanisms
of tamoxifen therapy for cholangiocarcinoma: Role of calmodulin.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:1288–1296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoelting T, Duh Q-Y, Clark OH and Herfarth
C: Tamoxifen antagonizes proliferation and invasion of estrogen
receptor-negative metastatic follicular thyroid cancer cells via
protein kinase C. Cancer Lett. 100:89–93. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Scandlyn MJ, Stuart EC, Somers-Edgar TJ,
Menzies AR and Rosengren RJ: A new role for tamoxifen in oestrogen
receptor-negative breast cancer when it is combined with
epigallocatechin gallate. Br J Cancer. 99:1056–1063. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen HY, Yang YM, Stevens BM and Noble M:
Inhibition of redox/Fyn/c-Cbl pathway function by Cdc42 controls
tumour initiation capacity and tamoxifen sensitivity in basal-like
breast cancer cells. EMBO Mol Med. 5:723–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moodbidri MS and Shirsat NV: Activated JNK
brings about accelerated apoptosis of Bcl-2-overexpressing C6
glioma cells on treatment with tamoxifen. J Neurochem. 92:1–9.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Maccarrone M, Fantini C, Ranalli M, Melino
G and Agrò AF: Activation of nitric oxide synthase is involved in
tamoxifen-induced apoptosis of human erythroleukemia K562 cells.
FEBS Lett. 434:421–424. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JA, Kang YS, Jung MW, Lee SH and Lee
YS: Involvement of Ca2+ influx in the mechanism of
tamoxifen-induced apoptosis in HepG2 human hepatoblastoma cells.
Cancer Lett. 147:115–123. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shim J-H, Choi C-S, Lee E-C, Kim M-Y and
Chun Y-J: Tamoxifen suppresses clusterin level through Akt
inactivation and proteasome degradation in human prostate cancer
cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 17:25–31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M and Tsien RY: A
new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved
fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 260:3440–3450.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lippman M, Bolan G and Huff K: The effects
of estrogens and antiestrogens on hormone-responsive human breast
cancer in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 36:4595–4601.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Wang N, Fang J, Huang J, Tian F, Li
C and Xie F: Role of PKC-ERK signaling in tamoxifen-induced
apoptosis and tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 27:1879–1886. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD and Roderick HL:
Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 4:517–529. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thastrup O, Cullen PJ, Drøbak BK, Hanley
MR and Dawson AP: Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges
intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the
endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
87:2466–2470. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Racay P and Lehotský J: Intracellular and
molecular aspects of Ca(2+)-mediated signal transduction in
neuronal cells. Gen Physiol Biophys. 15:273–289. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
White CD and Sacks DB: Regulation of MAP
kinase signaling by calcium. MAP Kinase Signaling Protocols. 2nd.
Seger R: Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: pp. 151–165. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Radin DP and Patel P: Delineating the
molecular mechanisms of tamoxifen’s oncolytic actions in estrogen
receptor-negative cancers. Eur J Pharmacol. 781:173–180. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Johnson N, Bentley J, Wang LZ, Newell DR,
Robson CN, Shapiro GI and Curtin NJ: Pre-clinical evaluation of
cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and 1 inhibition in
anti-estrogen-sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 102:342–350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Couldwell WT, Song H, Takano T,
Lin JH and Nedergaard M: Tamoxifen-induced enhancement of calcium
signaling in glioma and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
60:5395–5400. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu YC, Jiann BP, Chang HT, Huang JK, Chen
WC, Su W and Jan CR: Effect of the anti-breast cancer drug
tamoxifen on Ca(2+) movement in human osteosarcoma cells. Pharmacol
Toxicol. 91:34–39. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jones PS, Parrott E and White IN:
Activation of transcription by estrogen receptor alpha and beta is
cell type- and promoter-dependent. J Biol Chem. 274:32008–32014.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jan CR, Cheng JS, Chou KJ, Wang SP, Lee
KC, Tang KY, Tseng LL and Chiang HT: Dual effect of tamoxifen, an
anti-breast-cancer drug, on intracellular Ca(2+) and cytotoxicity
in intact cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 168:58–63. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sandmann S and Unger T: L- and T-type
calcium channel blockade - the efficacy of the calcium channel
antagonist mibefradil. J Clin Basic Cardiol. 2:187–201. 1999.
|
|
33
|
Agabiti-Rosei E, Muiesan ML, Romanelli G,
Castellano M, Beschi M, Corea L and Muiesan G: Similarities and
differences in the antihypertensive effect of two calcium
antagonist drugs, verapamil and nifedipine. J Am Coll Cardiol.
7:916–924. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cullen PJ and Lockyer PJ: Integration of
calcium and Ras signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:339–348. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goldkorn T and Mendelsohn J: Transforming
growth factor beta modulates phosphorylation of the epidermal
growth factor receptor and proliferation of A431 cells. Cell Growth
Differ. 3:101–109. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang F, Dong W, Zeng W, Zhang L, Zhang C,
Qiu Y, Wang L, Yin X, Zhang C and Liang W: Naringenin prevents
TGF-β1 secretion from breast cancer and suppresses pulmonary
metastasis by inhibiting PKC activation. Breast Cancer Res.
18:382016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xiao YQ, Freire-de-Lima CG, Schiemann WP,
Bratton DL, Vandivier RW and Henson PM: Transcriptional and
translational regulation of TGF-beta production in response to
apoptotic cells. J Immunol. 181:3575–3585. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Perry RR, Kang Y and Greaves BR:
Relationship between tamoxifen-induced transforming growth factor
beta 1 expression, cytostasis and apoptosis in human breast cancer
cells. Br J Cancer. 72:1441–1446. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|