|
1
|
Cardis E, Deltour I, Mann S, Moissonnier
M, Taki M, Varsier N, Wake K and Wiart J: Distribution of RF energy
emitted by mobile phones in anatomical structures of the brain.
Phys Med Biol. 53:2771–2783. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gandhi OP, Morgan LL, de Salles AA, Han
YY, Herberman RB and Davis DL: Exposure limits: The underestimation
of absorbed cell phone radiation, especially in children.
Electromagn Biol Med. 31:34–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hardell L, Näsman A, Påhlson A, Hallquist
A and Hansson Mild K: Use of cellular telephones and the risk for
brain tumours: A case-control study. Int J Oncol. 15:113–116.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardell L, Mild KH and Carlberg M:
Case-control study on the use of cellular and cordless phones and
the risk for malignant brain tumours. Int J Radiat Biol.
78:931–936. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hardell L, Hansson Mild K, Sandström M,
Carlberg M, Hallquist A and Påhlson A: Vestibular schwannoma,
tinnitus and cellular telephones. Neuroepidemiology. 22:124–129.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carlberg M and Hardell L: Evaluation of
mobile phone and cordless phone use and glioma risk using the
Bradford Hill viewpoints from 1965 on association or causation.
BioMed Res Int. 2017.9218486:2017.
|
|
7
|
Baan R, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El
Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Islami F and
Galichet L: Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic
fields. Lancet Oncol. 12:624–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Non-ionizing radiation, part 2:
Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. IARC Monographs on the
Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 102:International
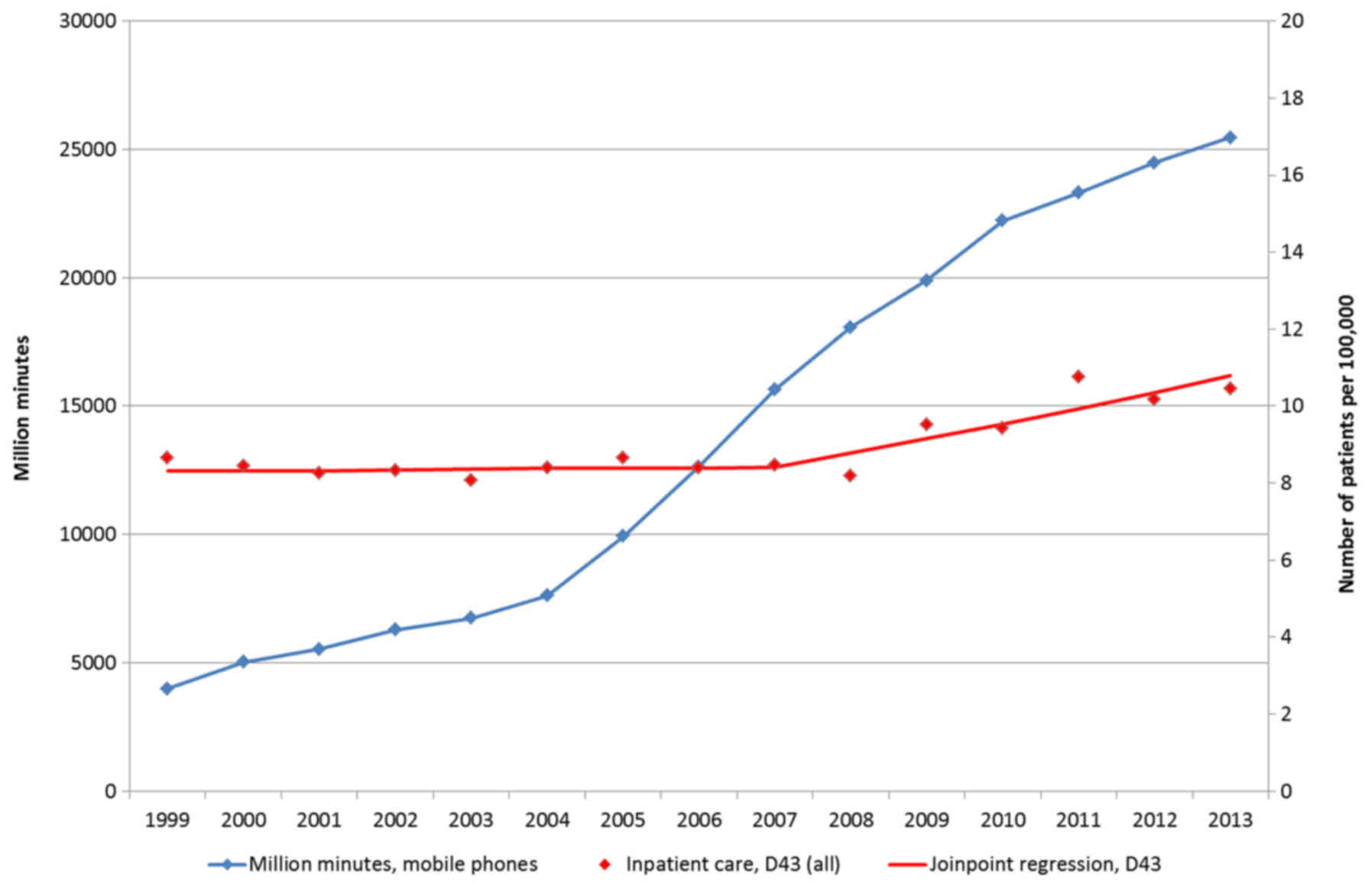
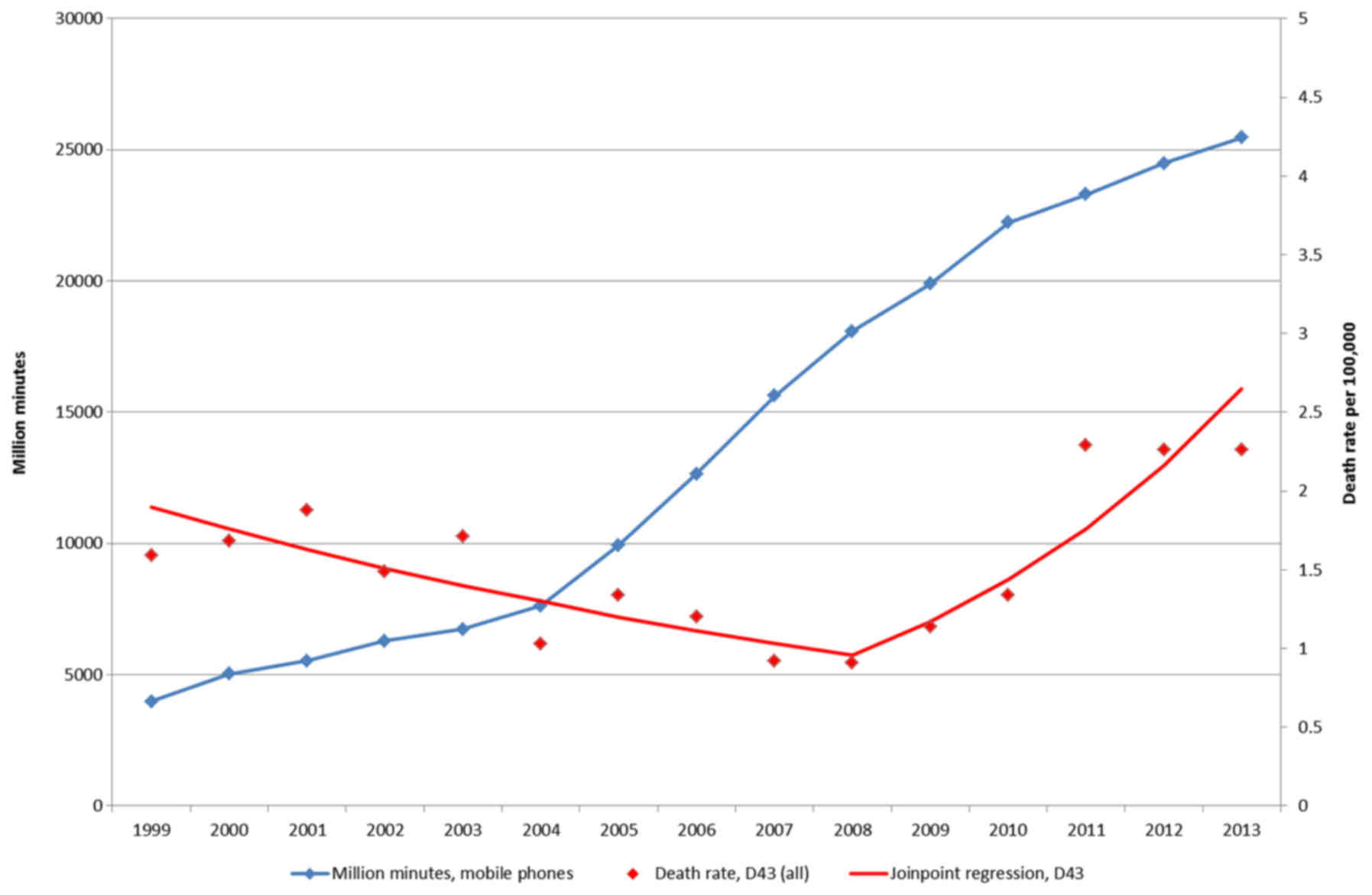
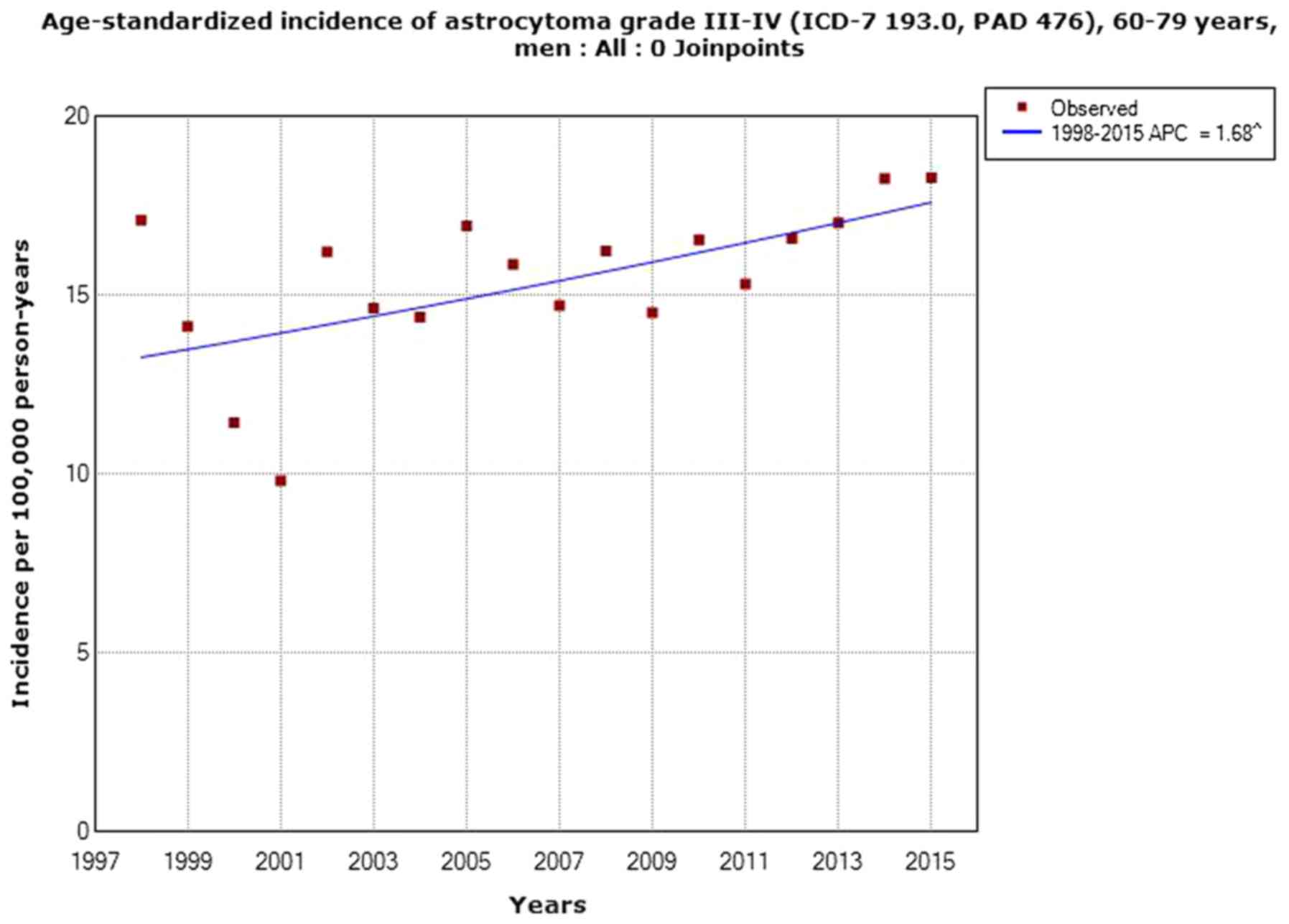
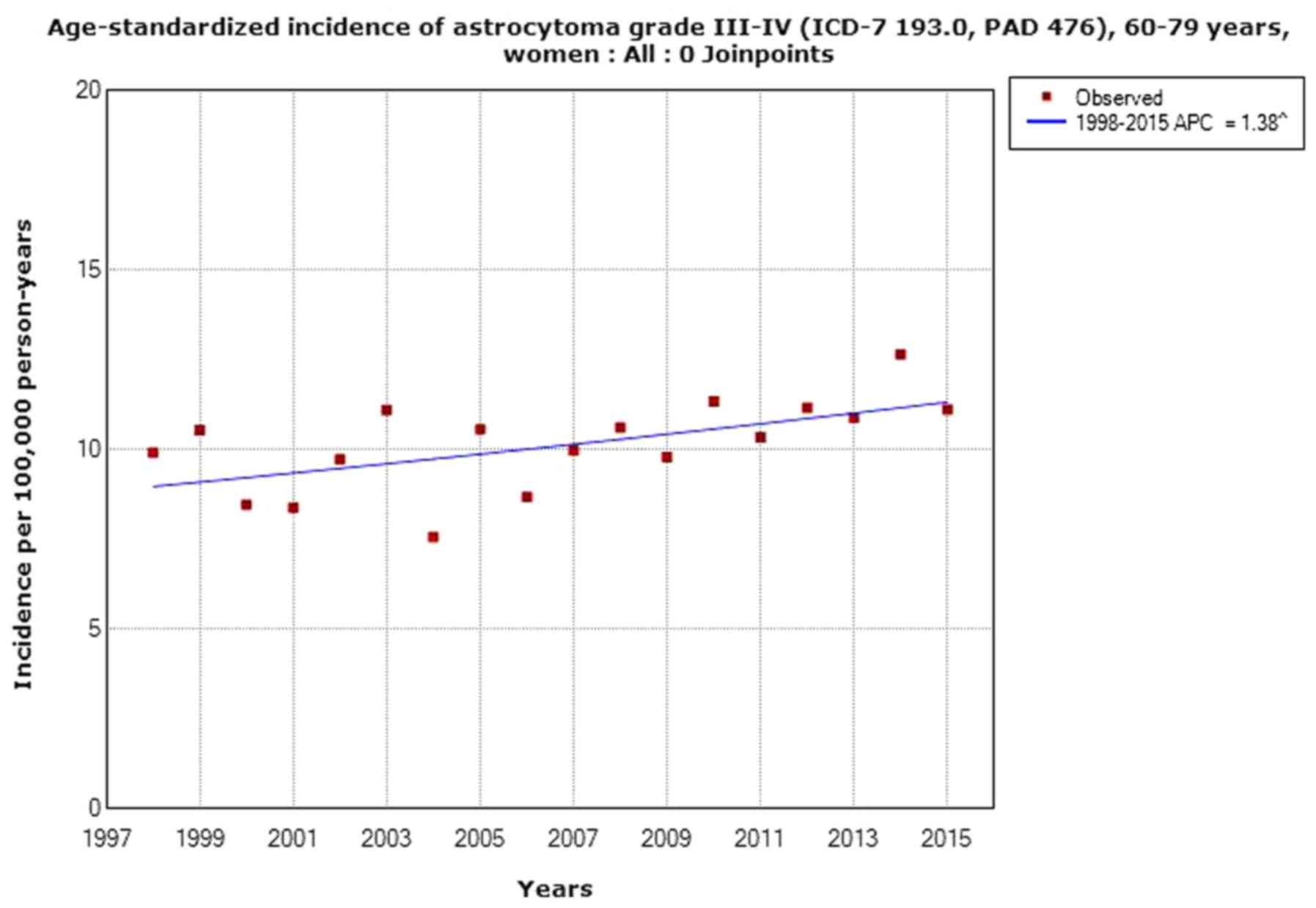
Agency for Research on Cancer Press; Lyon: 2013, http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol102/mono102.pdf.
4–July, 2018
|
|
9
|
Starkey SJ: Inaccurate official assessment
of radiofrequency safety by the advisory group on non-ionising
radiation. Rev Environ Health. 31:493–503. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hardell L: World Health Organization,
radiofrequency radiation and health - a hard nut to crack (Review).
Int J Oncol. 51:405–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maisch D: Conflict of interest and bias in
health advisory committees: A case study of the WHO's
Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Task Group. J Aust Coll Nutr Environ
Med. 25:15–17. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Belpomme D, Hardell L, Belyaev I, Ernesto
Burgio E and Carpenter DO: Thermal and non-thermal health effects
of non-ionizing radiation: an international perspective. Env Poll.
242:643–658. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hedendahl L, Carlberg M and Hardell L:
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity - an increasing challenge to the
medical profession. Rev Environ Health. 30:209–215. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
No authors listed: Guidelines for limiting
exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic
fields (up to 300 GHz). International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection. Health Phys. 74:494–522. 1998.
|
|
15
|
International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection: ICNIRP statement on the ‘Guidelines for
limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and
electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz)’. Health Phys. 97:257–258.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
BioInitiative Working Group: BioInitiative
Report: A Rationale for a Biologically-based Public Exposure
Standard for Electromagnetic Fields (ELF and RF). Sage C and
Carpenter DO: Bioinitiative. 2007, Available from: http://www.bioinitiative.org/table-of-contents/
(Accessed on 4 July, 2018).
|
|
17
|
BioInitiative Working Group: BioInitiative
Report 2012: A Rationale for a Biologically-based Exposure Standard
for Electromagnetic Fields (ELF and RF). Sage C and Carpenter DO:
Bioinitiative. 2012, Available from: http://www.bioinitiative.org/table-of-contents/
(Accessed on 4 July, 2018).
|
|
18
|
Wyde M, Cesta M, Blystone C, Bucher J,
Elmore S, Foster P, Hooth M, Kissling G, Malarkey D, Sills R, et
al: Report of Partial Findings from the National Toxicology Program
Carcinogenesis Studies of Cell Phone Radiofrequency Radiation in
Hsd: Sprague Dawley® SD rats (Whole Body Exposure).
Draft 519-2016. US National Toxicology Program (NTP). http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/055699.
Available from: http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2016/05/26/055699.full.pdf.
4–July. 2018
|
|
19
|
National Toxicology Program: NTP technical
report on the toxicology and carcinogenesis studies in Hsd: Sprague
Dawley sd rats exposed to whole-body radio frequency radiation at a
frequency (900 MHz) and modulations (GSM and CDMA) used by cell
phones. NTP TR. 595:March 26-28–2018.Available from: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/about_ntp/trpanel/2018/march/tr595peerdraft.pdf.
4–July.2018.
|
|
20
|
National Toxicology Program: NTP technical
report on the toxicology and carcinogenesis studies in B6C3F1/N
mice exposed to whole-body radio frequency radiation at a frequency
(1,900 MHz) and modulations (GSM and CDMA) used by cell phones. NTP
TR. 596:March 26-28–2018.Available from: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/about_ntp/trpanel/2018/march/tr596peerdraft.pdf.
4–July.2018.
|
|
21
|
Szmigielski S, Szudzinski A, Pietraszek A,
Bielec M, Janiak M and Wrembel JK: Accelerated development of
spontaneous and benzopyrene-induced skin cancer in mice exposed to
2450-MHz microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 3:179–191. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cleary SF, Liu LM and Merchant RE: Glioma
proliferation modulated in vitro by isothermal radiofrequency
radiation exposure. Radiat Res. 121:38–45. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cleary SF, Liu LM and Merchant RE: In
vitro lymphocyte proliferation induced by radio-frequency
electromagnetic radiation under isothermal conditions.
Bioelectromagnetics. 11:47–56. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chou CK, Guy AW, Kunz LL, Johnson RB,
Crowley JJ and Krupp JH: Long-term, low-level microwave irradiation
of rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 13:469–496. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Repacholi MH, Basten A, Gebski V, Noonan
D, Finnie J and Harris AW: Lymphomas in E mu-Pim1 transgenic mice
exposed to pulsed 900 MHZ electromagnetic fields. Radiat Res.
147:631–640. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Utteridge TD, Gebski V, Finnie JW,
Vernon-Roberts B and Kuchel TR: Long-term exposure of E-mu-Pim1
transgenic mice to 898.4 MHz microwaves does not increase lymphoma
incidence. Radiat Res. 158:357–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hardell L, Eriksson M, Carlberg M,
Sundström C and Mild KH: Use of cellular or cordless telephones and
the risk for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Int Arch Occup Environ Health.
78:625–632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Linet MS, Taggart T, Severson RK, Cerhan
JR, Cozen W, Hartge P and Colt J: Cellular telephones and
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 119:2382–2388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lauer O, Frei P, Gosselin MC, Joseph W,
Röösli M and Fröhlich J: Combining near- and far-field exposure for
an organ-specific and whole-body RF-EMF proxy for epidemiological
research: A reference case. Bioelectromagnetics. 34:366–374. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu M and Wu XY: Study of specific
absorption rate (SAR) induced in human endocrine glands for using
mobile phones. IEEE Asia-Pacific International Symposium on
Electromagnetic Compatibility (APEMC). 1084–1086. 2016.
|
|
31
|
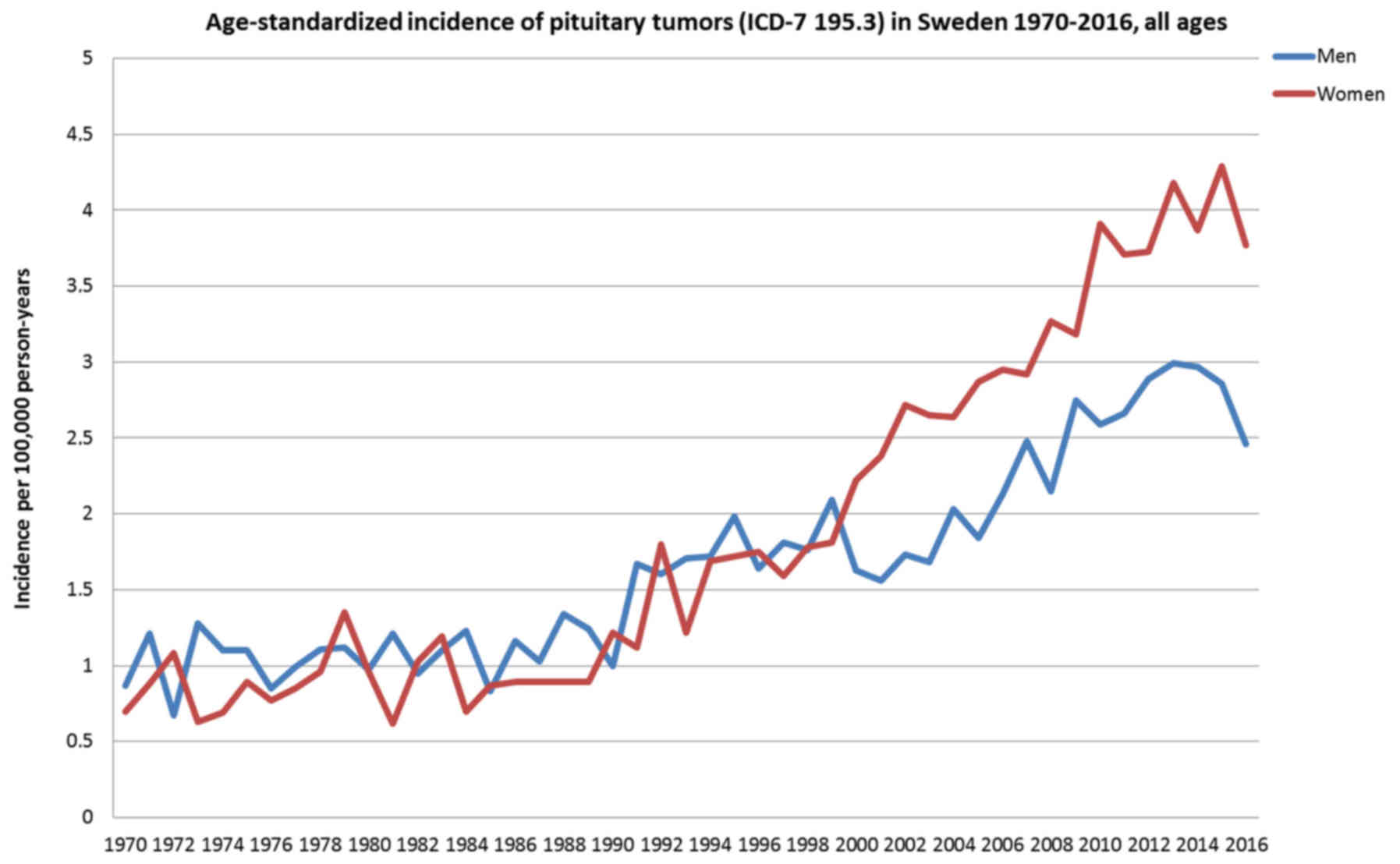
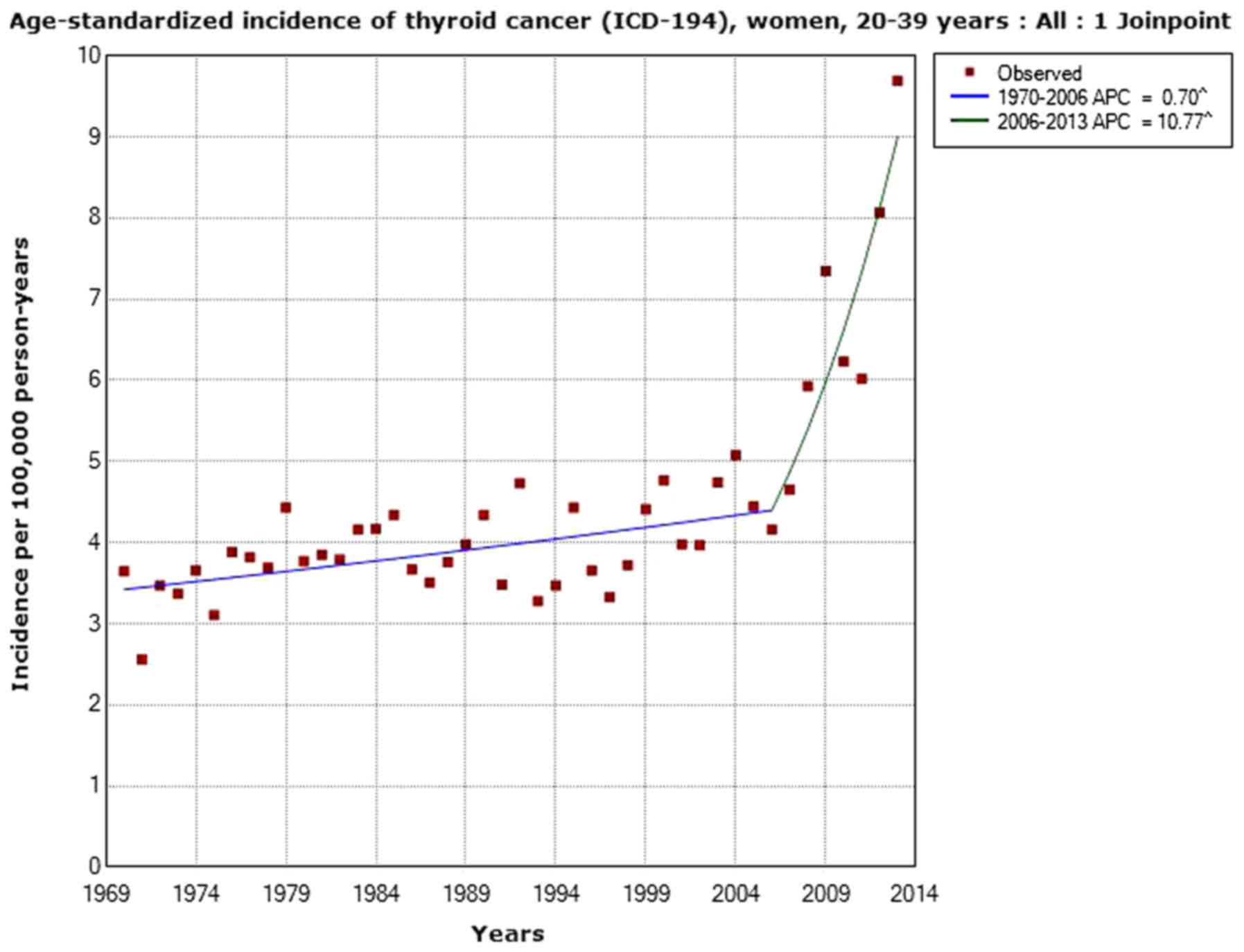
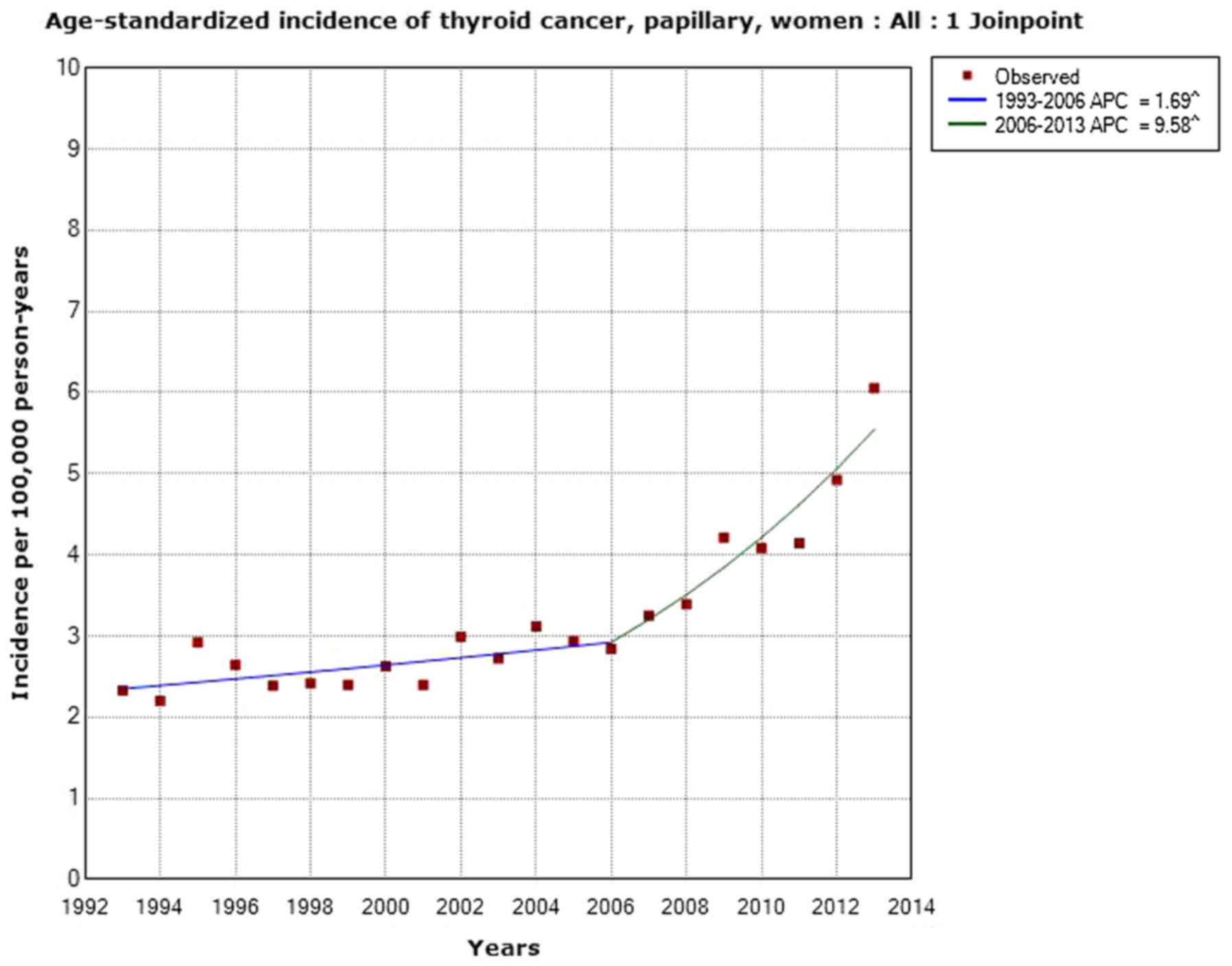
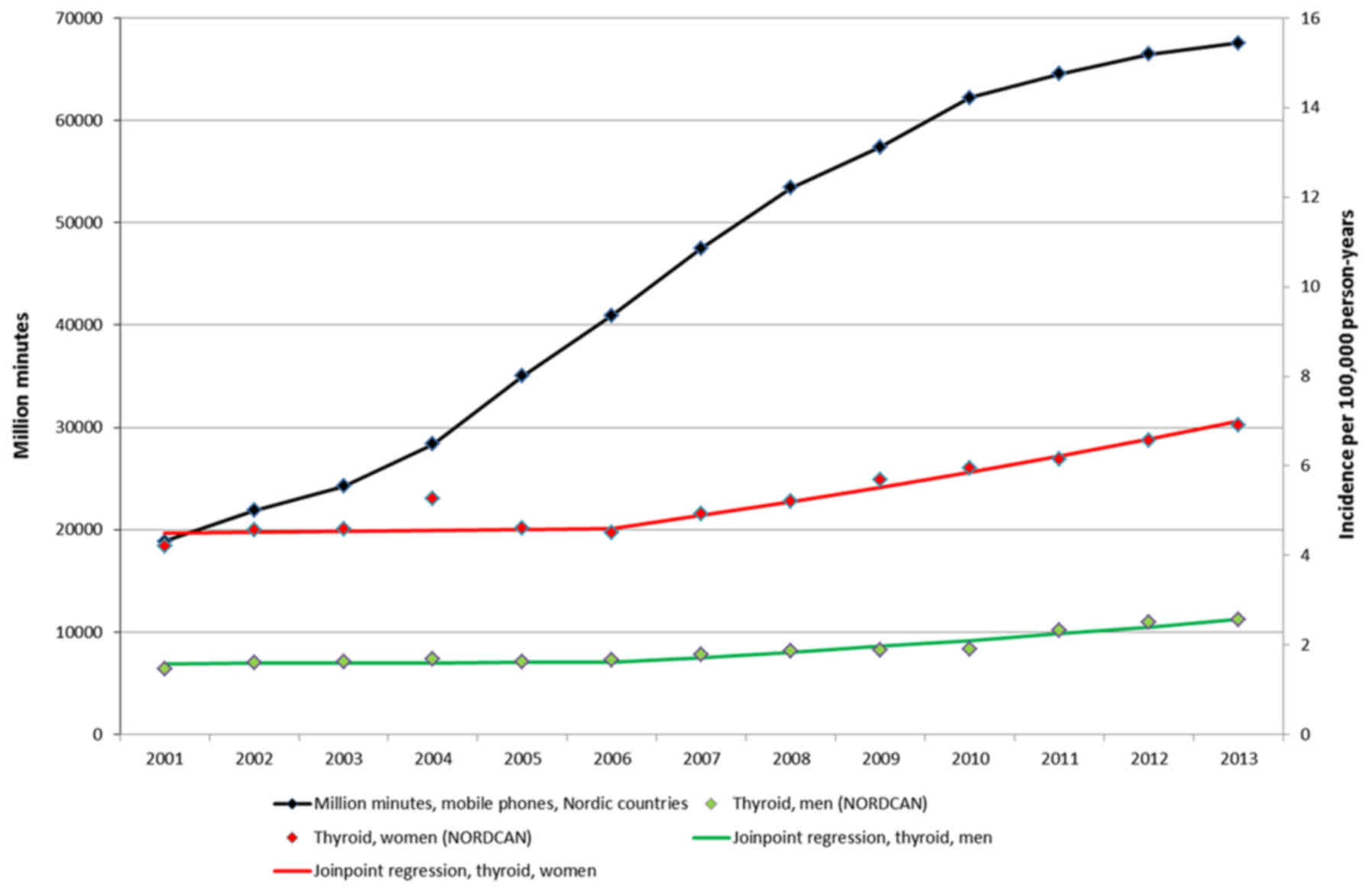
Carlberg M, Hedendahl L, Ahonen M, Koppel
T and Hardell L: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the
Nordic countries with main focus on Swedish data. BMC Cancer.
16:4262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tillmann T, Ernst H, Streckert J, Zhou Y,
Taugner F, Hansen V and Dasenbrock C: Indication of cocarcinogenic
potential of chronic UMTS-modulated radiofrequency exposure in an
ethyl-nitrosourea mouse model. Int J Radiat Biol. 86:529–541. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lerchl A, Klose M, Grote K, Wilhelm AF,
Spathmann O, Fiedler T, Streckert J, Hansen V and Clemens M: Tumor
promotion by exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
below exposure limits for humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
459:585–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Falcioni L, Bua L, Tibaldi E, Lauriola M,
De Angelis L, Gnudi F, Mandrioli D, Manservigi M, Manservisi F,
Manzoli I, et al: Report of final results regarding brain and heart
tumors in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed from prenatal life until
natural death to mobile phone radiofrequency field representative
of a 1.8 GHz GSM base station environmental emission. Environ Res.
165:496–503. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Johansen C, Boice J Jr, McLaughlin J and
Olsen J: Cellular telephones and cancer - a nationwide cohort study
in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:203–207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schüz J, Jacobsen R, Olsen JH, Boice JD
Jr, McLaughlin JK and Johansen C: Cellular telephone use and cancer
risk: Update of a nationwide Danish cohort. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1707–1713. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Söderqvist F, Carlberg M and Hardell L:
Review of four publications on the Danish cohort study on mobile
phone subscribers and risk of brain tumors. Rev Environ Health.
27:51–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Benson VS, Pirie K, Schüz J, Reeves GK,
Beral V and Green J; Million Women Study Collaborators: Mobile
phone use and risk of brain neoplasms and other cancers:
Prospective study. Int J Epidemiol. 42:792–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Population-based
studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in
astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
64:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
INTERPHONE Study Group: Brain tumour risk
in relation to mobile telephone use: Results of the INTERPHONE
international case-control study. Int J Epidemiol. 39:675–694.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Coureau G, Bouvier G, Lebailly P,
Fabbro-Peray P, Gruber A, Leffondre K, Guillamo JS, Loiseau H,
Mathoulin-Pélissier S, Salamon R, et al: Mobile phone use and brain
tumours in the CERENAT case-control study. Occup Environ Med.
71:514–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Mobile phones,
cordless phones and the risk for brain tumours. Int J Oncol.
35:5–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Mobile phone and
cordless phone use and the risk for glioma - Analysis of pooled
case-control studies in Sweden, 1997–2003 and 2007–2009.
Pathophysiology. 22:1–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Pooled analysis of two case-control studies on use of cellular and
cordless telephones and the risk for malignant brain tumours
diagnosed in 1997–2003. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 79:630–639.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Re-analysis of risk for glioma in relation to mobile telephone use:
Comparison with the results of the Interphone international
case-control study. Int J Epidemiol. 40:1126–1128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Hansson Mild K:
Pooled analysis of case-control studies on malignant brain tumours
and the use of mobile and cordless phones including living and
deceased subjects. Int J Oncol. 38:1465–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cardis E, Armstrong BK, Bowman JD, Giles
GG, Hours M, Krewski D, McBride M, Parent ME, Sadetzki S, Woodward
A, et al: Risk of brain tumours in relation to estimated RF dose
from mobile phones: Results from five Interphone countries. Occup
Environ Med. 68:631–640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grell K, Frederiksen K, Schüz J, Cardis E,
Armstrong B, Siemiatycki J, Krewski DR, McBride ML, Johansen C,
Auvinen A, et al: The intracranial distribution of gliomas in
relation to exposure from mobile phones: Analyses from the
INTERPHONE study. Am J Epidemiol. 184:818–828. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Momoli F, Siemiatycki J, McBride ML,
Parent ME, Richardson L, Bedard D, Platt R, Vrijheid M, Cardis E
and Krewski D: Probabilistic multiple-bias modeling applied to the
Canadian data from the INTERPHONE study of mobile phone use and
risk of glioma, meningioma, acoustic neuroma, and parotid gland
tumors. Am J Epidemiol. 186:885–893. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Carlberg M and Hardell L: Decreased
survival of glioma patients with astrocytoma grade IV (glioblastoma
multiforme) associated with long-term use of mobile and cordless
phones. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 11:10790–10805. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Akhavan-Sigari R, Mazloum Farsi Baf M,
Ariabod V, Rohde V and Rahighi S: Connection between cell phone
use, p53 gene expression in different zones of glioblastoma
multiforme and survival prognoses. Rare Tumors. 6:53502014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Turner MC, Benke G, Bowman JD, Figuerola
J, Fleming S, Hours M, Kincl L, Krewski D, McLean D, Parent ME, et
al: Occupational exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic
fields and brain tumor risks in the INTEROCC study. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:1863–1872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Carlberg M, Koppel T, Ahonen M and Hardell
L: Case-control study on occupational exposure to extremely
low-frequency electromagnetic fields and glioma risk. Am J Ind Med.
60:494–503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Peleg M, Nativ O and Richter ED: Radio
frequency radiation-related cancer: Assessing causation in the
occupational/military setting. Environ Res. 163:123–133. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cea-Soriano L, Wallander MA and García
Rodríguez LA: Epidemiology of meningioma in the United Kingdom.
Neuroepidemiology. 39:27–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Carlberg M and Hardell L: Pooled analysis
of Swedish case-control studies during 1997–2003 and 2007–2009 on
meningioma risk associated with the use of mobile and cordless
phones. Oncol Rep. 33:3093–3098. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shrestha B, Khalid M, Gayam V, Mukhtar O,
Thapa S, Mandal AK, Kaler J, Khalid M, Garlapati P, Iqbal S, et al:
Metachronous granular cell tumor of the descending colon.
Gastroenterol Res. 11:317–320. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim HJ and Lee MG: Granular cell tumors on
unusual anatomic locations. Yonsei Med J. 56:1731–1734. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rejas RA, Campos MS, Cortes AR, Pinto DD
and de Sousa SC: The neural histogenetic origin of the oral
granular cell tumor: An immunohistochemical evidence. Med Oral
Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 16:e6–e10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kamal SA and Othman EO: Granular cell
tumour of the larynx. J Laryngol Otol. 112:83–85. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Deltour I, Johansen C, Auvinen A,
Feychting M, Klaeboe L and Schüz J: Time trends in brain tumor
incidence rates in Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden, 1974–2003.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:1721–1724. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Increasing rates
of brain tumours in the Swedish national inpatient register and the
causes of death register. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
12:3793–3813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Mobile phones,
cordless phones and rates of brain tumors in different age groups
in the Swedish National Inpatient Register and the Swedish Cancer
Register during 1998–2015. PLoS One. 12:e01854612017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Philips A, Henshaw DL, Lamburn G and
O'Carroll MJ: Brain tumours: Rise in glioblastoma multiforme
incidence in England 1995–2015 suggests an adverse environmental or
lifestyle factor. J Environ Public Health. 7910754:20182018.
|
|
65
|
INTERPHONE Study Group: Acoustic neuroma
risk in relation to mobile telephone use: Results of the INTERPHONE
international case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol. 35:453–464.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Mild KH: Pooled analysis of case-control studies on acoustic
neuroma diagnosed 1997–2003 and 2007–2009 and use of mobile and
cordless phones. Int J Oncol. 43:1036–1044. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Moon IS, Kim BG, Kim J, Lee JD and Lee WS:
Association between vestibular schwannomas and mobile phone use.
Tumour Biol. 35:581–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Sato Y, Akiba S, Kubo O and Yamaguchi N: A
case-case study of mobile phone use and acoustic neuroma risk in
Japan. Bioelectromagnetics. 32:85–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pettersson D, Mathiesen T, Prochazka M,
Bergenheim T, Florentzson R, Harder H, Nyberg G, Siesjö P and
Feychting M: Long-term mobile phone use and acoustic neuroma risk.
Epidemiology. 25:233–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Long-term mobile
phone use and acoustic neuroma. Epidemiology. 25:7782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Christensen HC, Schüz J, Kosteljanetz M,
Poulsen HS, Thomsen J and Johansen C: Cellular telephone use and
risk of acoustic neuroma. Am J Epidemiol. 159:277–283. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Takebayashi T, Varsier N, Kikuchi Y, Wake
K, Taki M, Watanabe S, Akiba S and Yamaguchi N: Mobile phone use,
exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic field, and brain tumour:
A case-control study. Br J Cancer. 98:652–659. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Schoemaker MJ and Swerdlow AJ: Risk of
pituitary tumors in cellular phone users: A case-control study.
Epidemiology. 20:348–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Leng L and Zhang Y: Etiology of pituitary
tumors: A case control study. Turk Neurosurg. 26:195–199.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Gittleman H, Ostrom QT, Farah PD, Ondracek
A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Singer J, Kshettry VR, Laws ER,
et al: Descriptive epidemiology of pituitary tumors in the United
States, 2004–2009. J Neurosurg. 121:527–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Garg R, Bhartia P, Bahl I and Ittipiboon
A: Microstrip Antenna Design Handbook. Artech House; Norwood:
2001
|
|
77
|
Misa-Agustiño MJ, Jorge-Mora T,
Jorge-Barreiro FJ, Suarez-Quintanilla J, Moreno-Piquero E,
Ares-Pena FJ and López-Martín E: Exposure to non-ionizing radiation
provokes changes in rat thyroid morphology and expression of
HSP-90. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:1123–1135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Eşmekaya MA, Seyhan N and Ömeroğlu S:
Pulse modulated 900 MHz radiation induces hypothyroidism and
apoptosis in thyroid cells: A light, electron microscopy and
immunohisto-chemical study. Int J Radiat Biol. 86:1106–1116. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, Besson C, Clarke
CA, Morton LM, Nogueira L, Pawlish K, Yanik EL, Suneja G and Engels
EA: Trends in primary central nervous system lymphoma incidence and
survival in the U.S. Br J Haematol. 174:417–424. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Eloranta S, Brånvall E, Celsing F,
Papworth K, Ljungqvist M, Enblad G and Ekström-Smedby K: Increasing
incidence of primary central nervous system lymphoma but no
improvement in survival in Sweden 2000–2013. Eur J Haematol.
100:61–68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Poulsen AH, Friis S, Johansen C, Jensen A,
Frei P, Kjaear SK, Dalton SO and Schüz J: Mobile phone use and the
risk of skin cancer: A nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Am J
Epidemiol. 178:190–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Hansson Mild K and
Eriksson M: Case-control study on the use of mobile and cordless
phones and the risk for malignant melanoma in the head and neck
region. Pathophysiology. 18:325–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Smith-Roe SL, Wyde ME, Stout MD, Winters
JW, Hobbs CA, Shepard KG, Green AS, Kissling GE, Tice RR, Bucher
JR, et al: Evaluation of the genotoxicity of cell phone
radiofrequency radiation in male and female rats and mice following
subchronic exposure. In: Environmental Mutagenesis and Genomics
Society, Annual Meeting; Raleigh, North Carolina, USA. September
9-13, 2017;
|
|
84
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Melatonin and a
spin-trap compound block radiofrequency electromagnetic
radiation-induced DNA strand breaks in rat brain cells.
Bioelectromagnetics. 18:446–454. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yakymenko I, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E,
Henshel D, Kyrylenko O and Kyrylenko S: Oxidative mechanisms of
biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation.
Electromagn Biol Med. 35:186–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD,
Tripathi AK, Ahmed R and Abegaonkar MP: Low intensity microwave
radiation induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and DNA
damage in rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 51:158–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Using the Hill
viewpoints from 1965 for evaluating strengths of evidence of the
risk for brain tumors associated with use of mobile and cordless
phones. Rev Environ Health. 28:97–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
The 5G Appeal: Scientists and doctors warn
of potential serious health effects of 5G. Available from:
http://www.5gappeal.eu/scientists-and-doctors-warn-of-potential-serious-health-effects-of-5g/
(Accessed on 4 July, 2018).
|
|
89
|
Russell CL: 5 G wireless
telecommunications expansion: Public health and environmental
implications. Environ Res. 165:484–495. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Betzalel N, Ben Ishai P and Feldman Y: The
human skin as a sub-THz receiver - Does 5G pose a danger to it or
not? Environ Res. 163:208–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Melnick RL: Commentary on the utility of
the National Toxicology Program Study on cell phone radiofrequency
radiation data for assessing human health risks despite unfounded
criticisms aimed at minimizing the findings of adverse health
effects. Environ Res. 168:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|