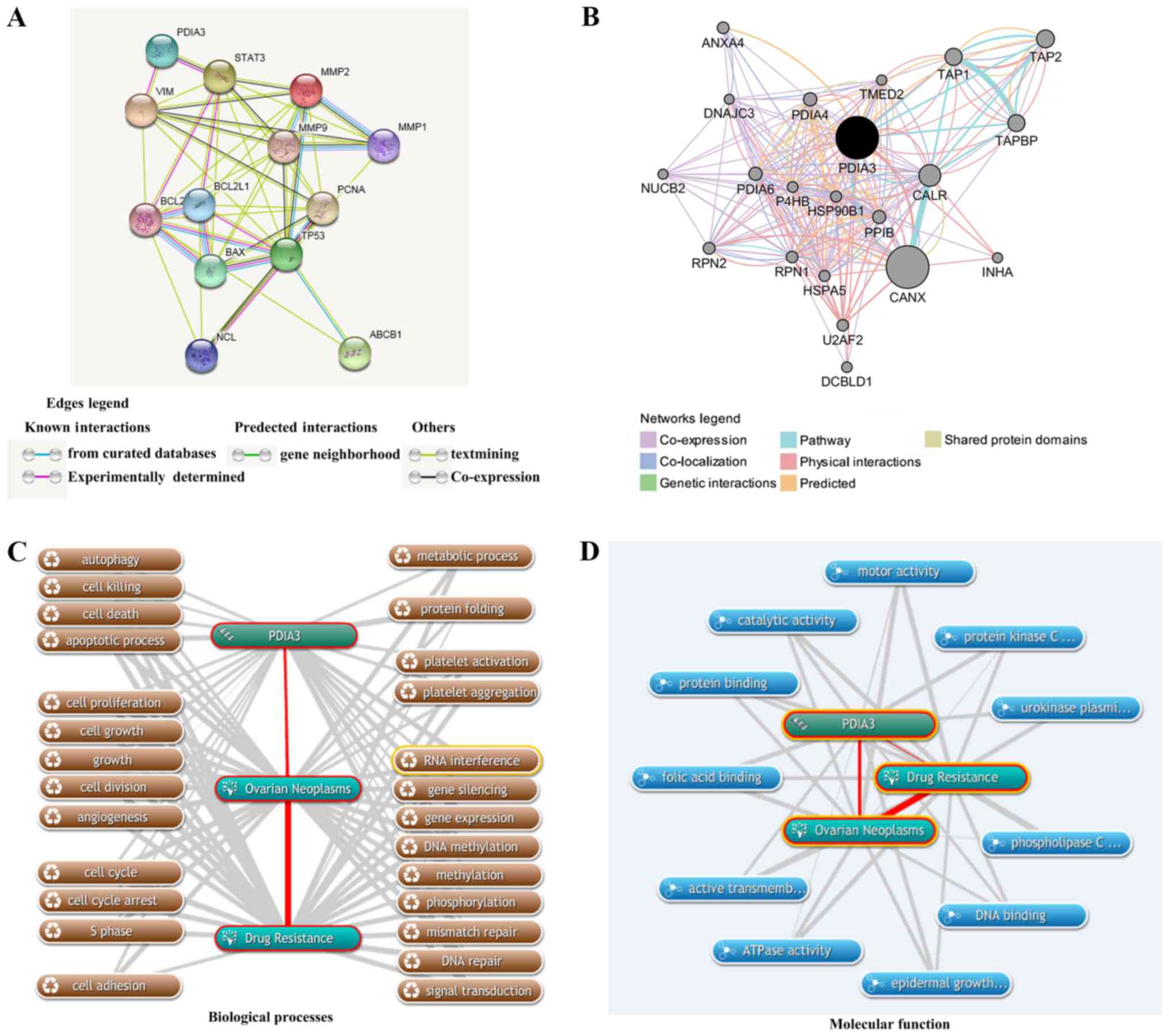
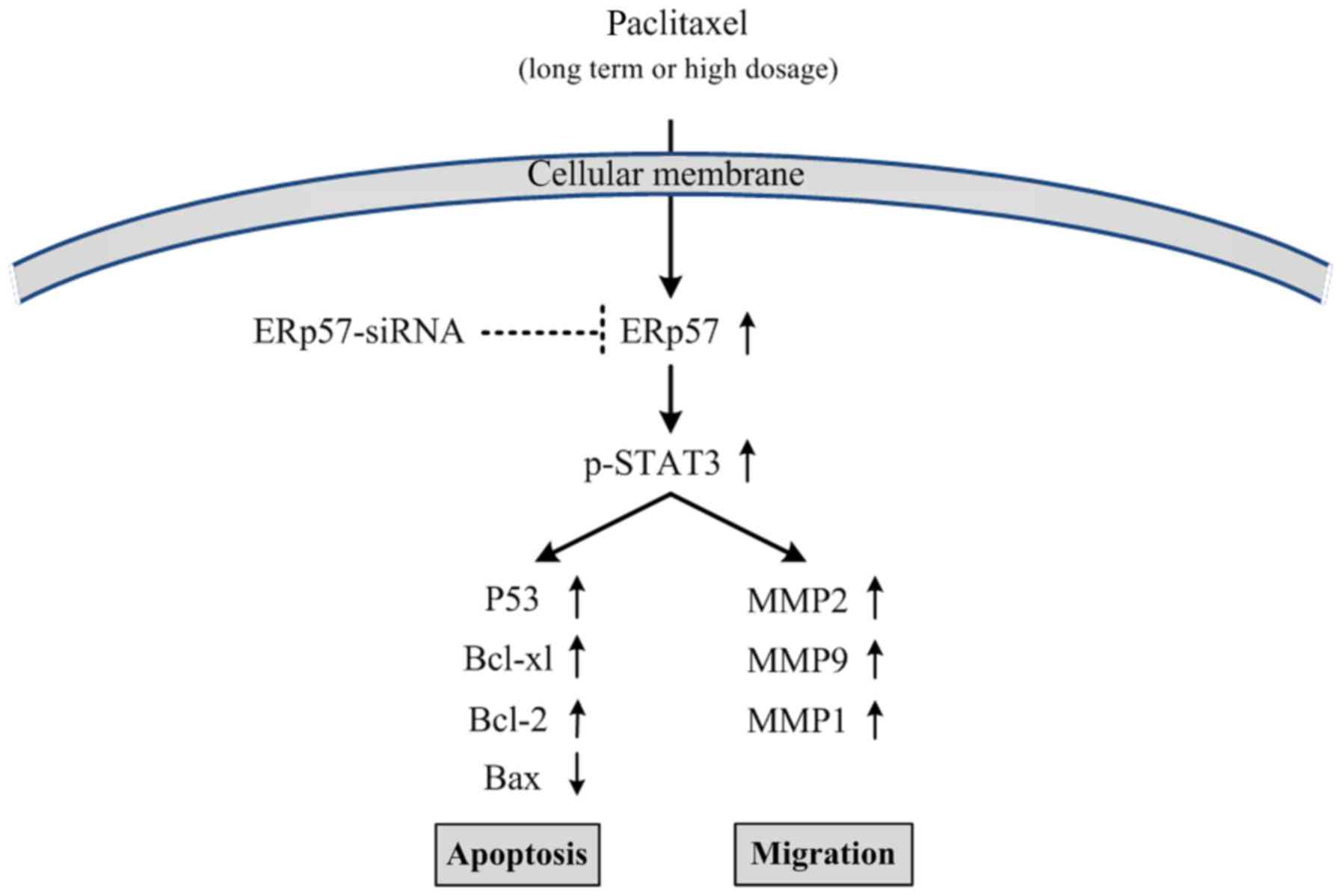
|
1
|
Gloss BS and Samimi G: Epigenetic
biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 342:257–263.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sundar S, Wu J, Hillaby K, Yap J and
Lilford R: A systematic review evaluating the relationship between
progression free survival and post progression survival in advanced
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 125:493–499. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ziebarth AJ, Landen CN Jr and Alvarez RD:
Molecular/genetic therapies in ovarian cancer: Future opportunities
and challenges. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 55:156–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kipps E, Tan DS and Kaye SB: Meeting the
challenge of ascites in ovarian cancer: New avenues for therapy and
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:273–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ford JM, Bruggemann EP, Pastan I,
Gottesman MM and Hait WN: Cellular and biochemical characterization
of thioxanthenes for reversal of multidrug resistance in human and
murine cell lines. Cancer Res. 50:1748–1756. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ranganathan S, Benetatos CA, Colarusso PJ,
Dexter DW and Hudes GR: Altered beta-tubulin isotype expression in
paclitaxel-resistant human prostate carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer.
77:562–566. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hari M, Loganzo F, Annable T, Tan X, Musto
S, Morilla DB, Nettles JH, Snyder JP and Greenberger LM:
Paclitaxel-resistant cells have a mutation in the
paclitaxel-binding region of beta-tubulin (Asp26Glu) and less
stable microtubules. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:270–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haass NK, Beaumont KA, Hill DS, Anfosso A,
Mrass P, Munoz MA, Kinjyo I and Weninger W: Real-time cell cycle
imaging during melanoma growth, invasion, and drug response.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27:764–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kapse-Mistry S, Govender T, Srivastava R
and Yergeri M: Nanodrug delivery in reversing multidrug resistance
in cancer cells. Front Pharmacol. 5:1592014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bordelon JR and Grichnik JM: TGF-β may
control the switch between tumorigenic growth and ‘stem
cell/mesenchymal’ potentially drug-resistant states. Dermatol Ther
(Heidelb). 28:177–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bernardini M, Lee CH, Beheshti B, Prasad
M, Albert M, Marrano P, Begley H, Shaw P, Covens A, Murphy J, et
al: High-resolution mapping of genomic imbalance and identification
of gene expression profiles associated with differential
chemotherapy response in serous epithelial ovarian cancer.
Neoplasia. 7:603–613. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cicchillitti L, Di Michele M, Urbani A,
Ferlini C, Donat MB, Scambia G and Rotilio D: Comparative proteomic
analysis of paclitaxel sensitive A2780 epithelial ovarian cancer
cell line and its resistant counterpart A2780TC1 by 2D-DIGE: The
role of ERp57. J Proteome Res. 8:1902–1912. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan Z, Feller AJ, Penson RT, Chabner BA
and Seiden MV: Discovery of differentially expressed genes
associated with paclitaxel resistance using cDNA array technology:
Analysis of interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8, and monocyte chemotactic
protein 1 in the paclitaxel-resistant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res.
5:3445–3453. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45D:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zuberi K, Franz M, Rodriguez H, Montojo J,
Lopes CT, Bader GD and Morris Q: GeneMANIA prediction server 2013
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41W:W115–W22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
de Leeuw N, Dijkhuizen T, Hehir-Kwa JY,
Carter NP, Feuk L, Firth HV, Kuhn RM, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL, van
Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, et al: Diagnostic interpretation of array data
using public databases and internet sources. Hum Mutat. 33:930–940.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vikhanskaya F, Erba E, D’Incalci M and
Broggini M: Introduction of wild-type p53 in a human ovarian cancer
cell line not expressing endogenous p53. Nucleic Acids Res.
22:1012–1017. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alaseem A, Alhazzani K, Dondapati P,
Alobid S, Bishayee A and Rathinavelu A: Matrix Metalloproteinases:
A challenging paradigm of cancer management. Semin Cancer Biol. Nov
16–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cicchillitti L, Della Corte A, Di Michele
M, Donati MB, Rotilio D and Scambia G: Characterisation of a
multimeric protein complex associated with ERp57 within the nucleus
in paclitaxel-sensitive and -resistant epithelial ovarian cancer
cells: The involvement of specific conformational states of
beta-actin. Int J Oncol. 37:445–454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haufroid V: Genetic polymorphisms of
ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCB1 and ABCC2 and their impact
on drug disposition. Curr Drug Targets. 12:631–646. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kwak JO, Lee SH, Lee GS, Kim MS, Ahn YG,
Lee JH, Kim SW, Kim KH and Lee MG: Selective inhibition of MDR1
(ABCB1) by HM30181 increases oral bioavailability and therapeutic
efficacy of paclitaxel. Eur J Pharmacol. 627:92–98. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Calastretti A, Gatti G, Quaresmini C and
Bevilacqua A: Down-modulation of Bcl-2 sensitizes PTEN-mutated
prostate cancer cells to starvation and taxanes. Prostate.
74:1411–1422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo Y, Tong L, Meng H, Zhu W, Guo L, Wei T
and Zhang J: MiR-335 regulates the chemo-radioresistance of small
cell lung cancer cells by targeting PARP-1. Gene. 600:9–15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Friedrich K, Wieder T, Von Haefen C,
Radetzki S, Jänicke R, Schulze-Osthoff K, Dörken B and Daniel PT:
Overexpression of caspase-3 restores sensitivity for drug-induced
apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with acquired drug
resistance. Oncogene. 20:2749–2760. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turano C, Gaucci E, Grillo C and
Chichiarelli S: ERp57/GRP58: A protein with multiple functions.
Cell Mol Biol Lett. 16:539–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khanal RC and Nemere I: The
ERp57/GRp58/1,25D3-MARRS receptor: Multiple functional roles in
diverse cell systems. Curr Med Chem. 14:1087–1093. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vigneron N, Peaper DR, Leonhardt RM and
Cresswell P: Functional significance of tapasin membrane
association and disulfide linkage to ERp57 in MHC class I
presentation. Eur J Immunol. 39:2371–2376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chapman DC and Williams DB: ER quality
control in the biogenesis of MHC class I molecules. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 21:512–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frenkel Z, Shenkman M, Kondratyev M and
Lederkremer GZ: Separate roles and different routing of calnexin
and ERp57 in endoplasmic reticulum quality control revealed by
interactions with asialoglycoprotein receptor chains. Mol Biol
Cell. 15:2133–2142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Celli CM and Jaiswal AK: Role of GRP58 in
mitomycin C-induced DNA cross-linking. Cancer Res. 63:6016–6025.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He Y, Shao F, Pi W, Shi C, Chen Y, Gong D,
Wang B, Cao Z and Tang K: Largescale transcriptomics analysis
suggests over-expression of BGH3, MMP9 and PDIA3 in oral squamous
vell carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01465302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lovat PE, Corazzari M, Armstrong JL,
Martin S, Pagliarini V, Hill D, Brown AM, Piacentini M,
Birch-Machin MA and Redfern CP: Increasing melanoma cell death
using inhibitors of protein disulfide isomerases to abrogate
survival responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Res.
68:5363–5369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Corazzari M, Lovat PE, Armstrong JL, Fimia
GM, Hill DS, Birch-Machin M, Redfern CP and Piacentini M: Targeting
homeostatic mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress to increase
susceptibility of cancer cells to fenretinide-induced apoptosis:
The role of stress proteins ERdj5 and ERp57. Br J Cancer.
96:1062–1071. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choe MH, Min JW, Jeon HB, Cho DH, Oh JS,
Lee HG, Hwang SG, An S, Han YH and Kim JS: ERp57 modulates STAT3
activity in radioresistant laryngeal cancer cells and serves as a
prognostic marker for laryngeal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:2654–2666.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bourougaa K, Naski N, Boularan C,
Mlynarczyk C, Candeias MM, Marullo S and Fåhraeus R: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress induces G2 cell-cycle arrest via mRNA translation
of the p53 isoform p53/47. Mol Cell. 38:78–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Candeias MM, Powell DJ, Roubalova E,
Apcher S, Bourougaa K, Vojtesek B, Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H and
Fåhraeus R: Expression of p53 and p53/47 are controlled by
alternative mechanisms of messenger RNA translation initiation.
Oncogene. 25:6936–6947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carpenter RL and Lo HW: STAT3 target genes
relevant to human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 6:897–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Guo GG, Patel K, Kumar V, Shah M, Fried
VA, Etlinger JD and Sehgal PB: Association of the chaperone
glucose-regulated protein 58 (GRP58/ER-60/ERp57) with Stat3 in
cytosol and plasma membrane complexes. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
22:555–563. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chichiarelli S, Gaucci E, Ferraro A,
Grillo C, Altieri F, Cocchiola R, Arcangeli V, Turano C and Eufemi
M: Role of ERp57 in the signaling and transcriptional activity of
STAT3 in a melanoma cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys. 494:178–183.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Eufemi M, Coppari S, Altieri F, Grillo C,
Ferraro A and Turano C: ERp57 is present in STAT3-DNA complexes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 323:1306–1312. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gu F, Ma Y, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Kobayashi H,
Zhang L and Fu L: Expression of Stat3 and Notch1 is associated with
cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 23:671–676. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu H, Chen X, Chen B, Chen B, Fan J, Song
W, Xie Z, Jiang D, Li Q, Zhou M, et al: Activating transcription
factor 4 mediates a multidrug resistance phenotype of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cells through transactivation of STAT3
expression. Cancer Lett. 354:142–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ryu K, Susa M, Choy E, Yang C, Hornicek
FJ, Mankin HJ and Duan Z: Oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me induces
apoptosis in multidrug resistant osteosarcoma cells through
inhibition of Stat3 pathway. BMC Cancer. 10:1872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gariboldi MB, Ravizza R, Molteni R, Osella
D, Gabano E and Monti E: Inhibition of Stat3 increases doxorubicin
sensitivity in a human metastatic breast cancer cell line. Cancer
Lett. 258:181–188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Selvendiran K, Bratasz A, Kuppusamy ML,
Tazi MF, Rivera BK and Kuppusamy P: Hypoxia induces chemoresistance
in ovarian cancer cells by activation of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3. Int J Cancer. 125:2198–2204. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang F, Wang Z, Fan Y, Xu Q, Ji W, Tian R
and Niu R: Elevated STAT3 signaling-mediated upregulation of
MMP-2/9 confers enhanced invasion ability in multidrug-resistant
breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:24772–24790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang JM, Xu Z, Wu H, Zhu H, Wu X and Hait
WN: Overexpression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase
inducer in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
1:420–427. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Colone M, Calcabrini A, Toccacieli L,
Bozzuto G, Stringaro A, Gentile M, Cianfriglia M, Ciervo A,
Caraglia M, Budillon A, et al: The multidrug transporter
P-glycoprotein: A mediator of melanoma invasion? J Invest Dermatol.
128:957–971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hikawa T, Mori T, Abe T and Hori S: The
ability in adhesion and invasion of drug-resistant human glioma
cells. Journal of experimental and clinical cancer research CR
(East Lansing Mich). 19:357–362. 2000.
|
|
52
|
Işeri OD, Kars MD, Arpaci F and Gündüz U:
Gene expression analysis of drug-resistant MCF-7 cells:
Implications for relation to extracellular matrix proteins. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 65:447–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Santana-Codina N, Carretero R,
Sanz-Pamplona R, Cabrera T, Guney E, Oliva B, Clezardin P, Olarte
OE, Loza-Alvarez P, Méndez-Lucas A, et al: A transcriptome-proteome
integrated network identifies endoplasmic reticulum thiol
oxidoreductase (ERp57) as a hub that mediates bone metastasis. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 12:2111–2125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu D, Perez RE, Rezaiekhaligh MH, Bourdi M
and Truog WE: Knockdown of ERp57 increases BiP/GRP78 induction and
protects against hyperoxia and tunicamycin-induced apoptosis. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L44–L51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao G, Lu H and Li C: Proapoptotic
activities of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and PDIA3 protein,
a role of the Bcl-2 protein Bak. J Biol Chem. 290:8949–8963. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|