|
1
|
Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL,
Patch AM, Gingras MC, Miller DK, Christ AN, Bruxner TJ, Quinn MC,
et al Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome Initiative: Genomic
analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature.
531:47–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De La Cruz MS, Young AP and Ruffin MT:
Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer. Am Fam Physician.
89:626–632. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Souchek JJ, Baine MJ, Lin C, Rachagani S,
Gupta S, Kaur S, Lester K, Zheng D, Chen S, Smith L, et al:
Unbiased analysis of pancreatic cancer radiation resistance reveals
cholesterol biosynthesis as a novel target for radiosensitisation.
Br J Cancer. 111:1139–1149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rossi ML, Rehman AA and Gondi CS:
Therapeutic options for the management of pancreatic cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 20:11142–11159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gianfaldoni S, Gianfaldoni R, Wollina U,
Lotti J, Tchernev G and Lotti T: An overview on radiotherapy: From
its history to its current applications in dermatology. Open Access
Maced J Med Sci. 5:521–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rycaj K and Tang DG: Cancer stem cells and
radioresistance. Int J Radiat Biol. 90:615–621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stone HB, Coleman CN, Anscher MS and
McBride WH: Effects of radiation on normal tissue: Consequences and
mechanisms. Lancet Oncol. 4:529–536. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suit H and Urie M: Proton beams in
radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:155–164. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Habrand JL, Schlienger P, Schwartz L,
Pontvert D, Lenir-Cohen-Solal C, Helfre S, Mammar H, Haie-Meder C,
Ferrand R and Mazal A: Clinical applications of proton therapy.
Bull Cancer Radiother. 83(Suppl): 207s–211s. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yeung RH, Chapman TR, Bowen SR and
Apisarnthanarax S: Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:911–924. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ross GM: Induction of cell death by
radiotherapy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 6:41–44. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Maeda J, Froning CE, Brents CA, Rose BJ,
Thamm DH and Kato TA: Intrinsic Radiosensitivity and Cellular
Characterization of 27 Canine Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS One.
11:e01566892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peltenburg LT: Radiosensitivity of tumor
cells Oncogenes and apoptosis. Q J Nucl Med. 44:355–364. 2000.
|
|
14
|
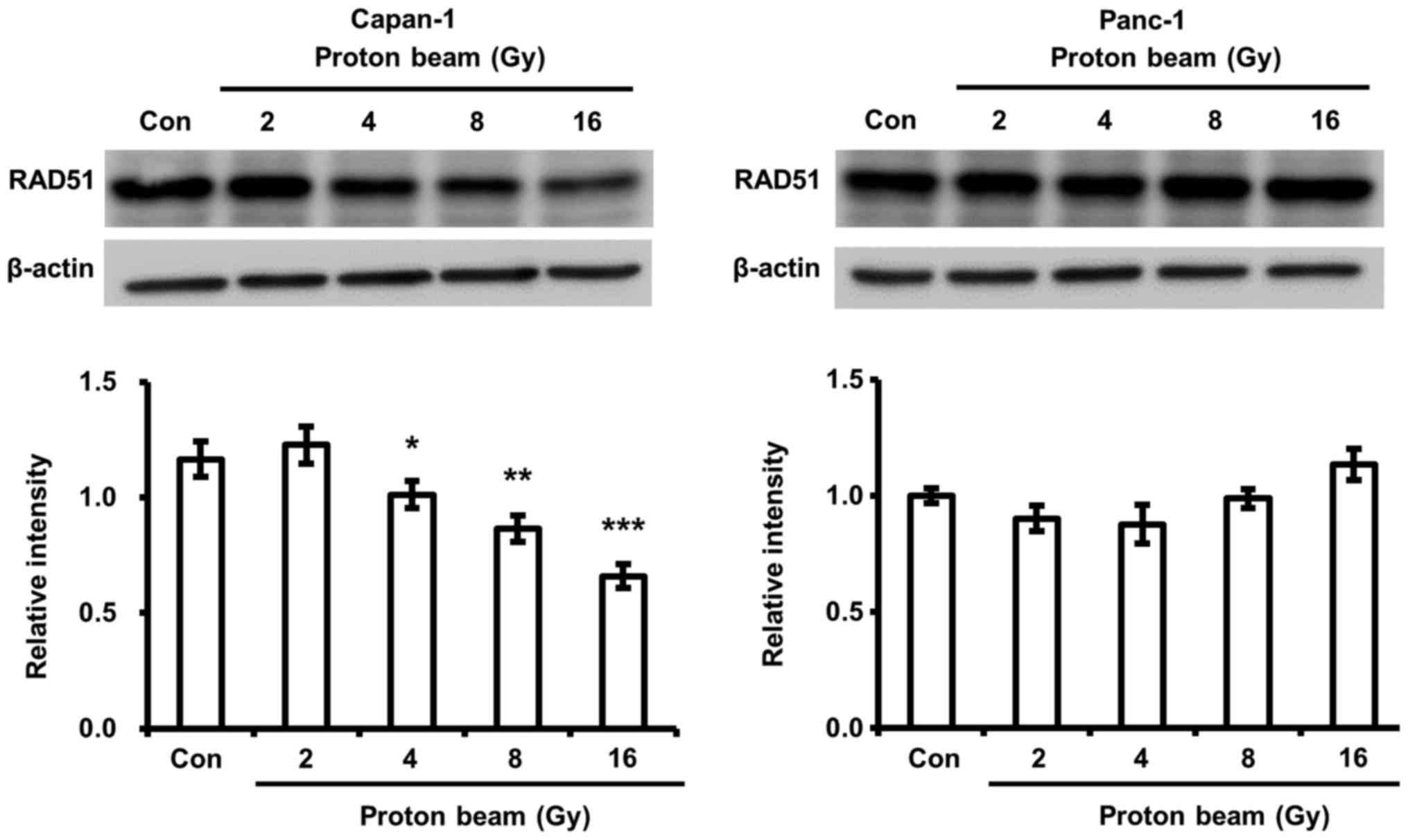
Gildemeister OS, Sage JM and Knight KL:
Cellular redistribution of Rad51 in response to DNA damage: Novel
role for Rad51C. J Biol Chem. 284:31945–31952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
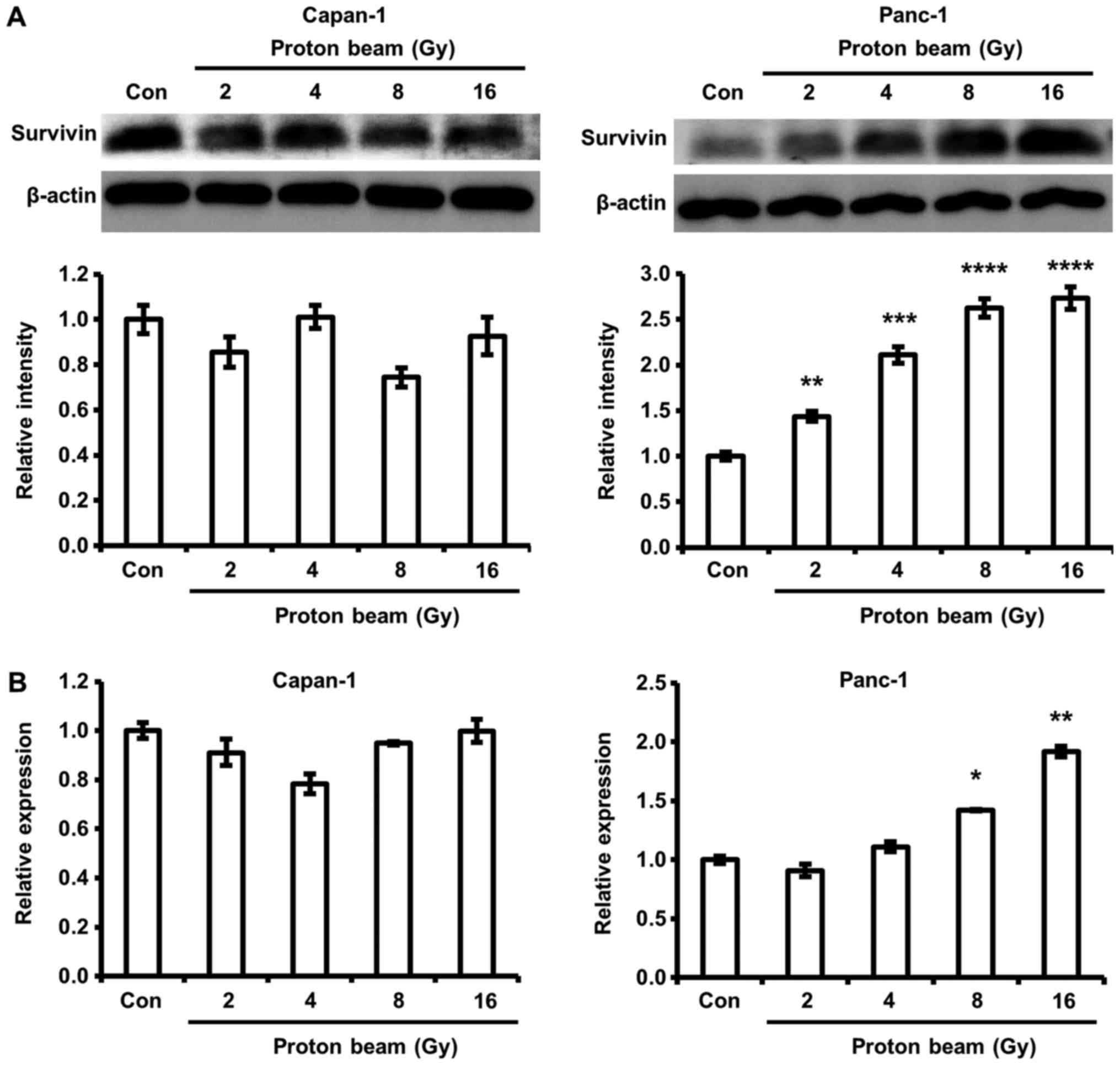
Greve B, Sheikh-Mounessi F, Kemper B,
Ernst I, Götte M and Eich HT: Survivin, a target to modulate the
radiosensitivity of Ewing's sarcoma. Strahlenther Onkol.
188:1038–1047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sak A, Stueben G, Groneberg M, Böcker W
and Stuschke M: Targeting of Rad51-dependent homologous
recombination: Implications for the radiation sensitivity of human
lung cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 92:1089–1097. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du LQ, Wang Y, Wang H, Cao J, Liu Q and
Fan FY: Knockdown of Rad51 expression induces radiation- and
chemo-sensitivity in osteosarcoma cells. Med Oncol. 28:1481–1487.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Graeser M, McCarthy A, Lord CJ, Savage K,
Hills M, Salter J, Orr N, Parton M, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS, et al:
A marker of homologous recombination predicts pathologic complete
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in primary breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:6159–6168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nagathihalli NS and Nagaraju G: RAD51 as a
potential biomarker and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1816:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taki T, Ohnishi T, Yamamoto A, Hiraga S,
Arita N, Izumoto S, Hayakawa T and Morita T: Antisense inhibition
of the RAD51 enhances radiosensitivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
223:434–438. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tennstedt P, Fresow R, Simon R, Marx A,
Terracciano L, Petersen C, Sauter G, Dikomey E and Borgmann K:
RAD51 overexpression is a negative prognostic marker for colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 132:2118–2126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Capalbo G, Dittmann K, Weiss C, Reichert
S, Hausmann E, Rödel C and Rödel F: Radiation-induced survivin
nuclear accumulation is linked to DNA damage repair. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 77:226–234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA,
Vigna N, Oltersdorf T and Reed JC: IAP-family protein survivin
inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax,
caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 58:5315–5320.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asanuma K, Moriai R, Yajima T, Yagihashi
A, Yamada M, Kobayashi D and Watanabe N: Survivin as a
radioresistance factor in pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res.
91:1204–1209. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yip-Schneider MT, Barnard DS, Billings SD,
Cheng L, Heilman DK, Lin A, Marshall SJ, Crowell PL, Marshall MS
and Sweeney CJ: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pancreatic
adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 21:139–146. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garg H, Suri P, Gupta JC, Talwar GP and
Dubey S: Survivin: A unique target for tumor therapy. Cancer Cell
Int. 16:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pennati M, Folini M and Zaffaroni N:
Targeting survivin in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
12:463–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jalalabdi Y, Shirazi A, Ghavam-Nasiri MR,
Davood AA and Sardari D: The role of celecoxib as a Cox-2 inhibitor
increasing the radioswensitivity of tumor tissue. Br J Med Med Res.
8:123–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shin YK, Park JS, Kim HS, Jun HJ, Kim GE,
Suh CO, Yun YS and Pyo H: Radiosensitivity enhancement by
celecoxib, a cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2 selective inhibitor, via
COX-2-dependent cell cycle regulation on human cancer cells
expressing differential COX-2 levels. Cancer Res. 65:9501–9509.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kwon YS, Lee KS, Chun SY, Jang TJ and Nam
KS: Suppressive effects of a proton beam on tumor growth and lung
metastasis through the inhibition of metastatic gene expression in
4T1 orthotopic breast cancer model. Int J Oncol. 49:336–342. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chun SY, Kwon YS, Nam KS and Kim S:
Lapatinib enhances the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin in MCF-7
tumorspheres by inhibiting the drug efflux function of ABC
transporters. Biomed Pharmacother. 72:37–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Degner SC, Kemp MQ, Bowden GT and
Romagnolo DF: Conjugated linoleic acid attenuates cyclooxygenase-2
transcriptional activity via an anti-AP-1 mechanism in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. J Nutr. 136:421–427. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zaffaroni N, Pennati M, Colella G, Perego
P, Supino R, Gatti L, Pilotti S, Zunino F and Daidone MG:
Expression of the anti-apoptotic gene survivin correlates with
taxol resistance in human ovarian cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
59:1406–1412. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guttilla IK, Phoenix KN, Hong X, Tirnauer
JS, Claffey KP and White BA: Prolonged mammosphere culture of MCF-7
cells induces an EMT and repression of the estrogen receptor by
microRNAs. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 132:75–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu XF, Xie CG, Wang XP, Liu J, Yu YC, Hu
HL and Guo CY: Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses
the growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Tohoku
J Exp Med. 215:149–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alan Mitteer R, Wang Y, Shah J, Gordon S,
Fager M, Butter PP, Jun Kim H, Guardiola-Salmeron C,
Carabe-Fernandez A and Fan Y: Proton beam radiation induces DNA
damage and cell apoptosis in glioma stem cells through reactive
oxygen species. Sci Rep. 5:139612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Herceg Z and Wang ZQ: Functions of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in DNA repair, genomic integrity
and cell death. Mutat Res. 477:97–110. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Casao A, Mata-Campuzano M, Ordás L,
Cebrián-Pérez JA, Muiño-Blanco T and Martínez-Pastor F: Cleaved
PARP-1, an Apoptotic Marker, can be Detected in Ram Spermatozoa.
Reprod Domest Anim. 50:688–691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V,
Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S and Smulson M: Role of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis Caspase 3-resistant PARP
mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol
Chem. 274:22932–22940. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Poli V and Camporeale A: STAT3-Mediated
Metabolic Reprograming in Cellular Transformation and Implications
for Drug Resistance. Front Oncol. 5:1212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang
QC, Zhang YJ, Lu R, Chen YX and Fang JY: Inhibition of JAK1,
2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces
tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia.
10:287–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li X, Wang H, Lu X and Di B: Silencing
STAT3 with short hairpin RNA enhances radiosensitivity of human
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in vivo. Exp Ther Med.
1:947–953. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang Q, Pan Q, Li C, Xu Y, Wen C and Sun
F: NRAGE is involved in homologous recombination repair to resist
the DNA-damaging chemotherapy and composes a ternary complex with
RNF8-BARD1 to promote cell survival in squamous esophageal
tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 23:1406–1416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Borràs-Fresneda M, Barquinero JF, Gomolka
M, Hornhardt S, Rössler U, Armengol G and Barrios L: Differences in
DNA Repair Capacity, Cell Death and Transcriptional Response after
Irradiation between a Radiosensitive and a Radioresistant Cell
Line. Sci Rep. 6:270432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhong X, Luo G, Zhou X, Luo W, Wu X, Zhong
R, Wang Y, Xu F and Wang J: Rad51 in regulating the
radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different
epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status. Thorac Cancer.
7:50–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim YB, Kim GE, Cho NH, Pyo HR, Shim SJ,
Chang SK, Park HC, Suh CO, Park TK and Kim BS: Overexpression of
cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with a poor prognosis in patients
with squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated with
radiation and concurrent chemotherapy. Cancer. 95:531–539. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin F, Luo J, Gao W, Wu J, Shao Z, Wang Z,
Meng J, Ou Z and Yang G: COX-2 promotes breast cancer cell
radioresistance via p38/MAPK-mediated cellular anti-apoptosis and
invasiveness. Tumour Biol. 34:2817–2826. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Terakado N, Shintani S, Yano J, Chunnan L,
Mihara M, Nakashiro K and Hamakawa H: Overexpression of
cyclooxy-genase-2 is associated with radioresistance in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 40:383–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen L, Fu L, Kong X, Xu J, Wang Z, Ma X,
Akiyama Y, Chen Y and Fang J: Jumonji domain-containing protein 2B
silencing induces DNA damage response via STAT3 pathway in
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:1014–1026. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wen W, Zhu F, Zhang J, Keum YS, Zykova T,
Yao K, Peng C, Zheng D, Cho YY, Ma WY, et al: MST1 promotes
apoptosis through phosphorylation of histone H2AX. J Biol Chem.
285:39108–39116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Borges HL, Linden R and Wang JY: DNA
damage-induced cell death: Lessons from the central nervous system.
Cell Res. 18:17–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Powell C, Mikropoulos C, Kaye SB, Nutting
CM, Bhide SA, Newbold K and Harrington KJ: Pre-clinical and
clinical evaluation of PARP inhibitors as tumour-specific
radiosensitisers. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:566–575. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Godon C, Cordelières FP, Biard D, Giocanti
N, Mégnin-Chanet F, Hall J and Favaudon V: PARP inhibition versus
PARP-1 silencing: Different outcomes in terms of single-strand
break repair and radiation susceptibility. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:4454–4464. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu ZY, Huang R, Xiao H, Sun WF, Shan YJ,
Wang B, Zhao TT, Dong B, Zhao ZH, Liu XL, et al: Fluacrypyrim, a
novel STAT3 activation inhibitor, induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in cancer cells harboring constitutively-active STAT3.
Int J Cancer. 127:1259–1270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|