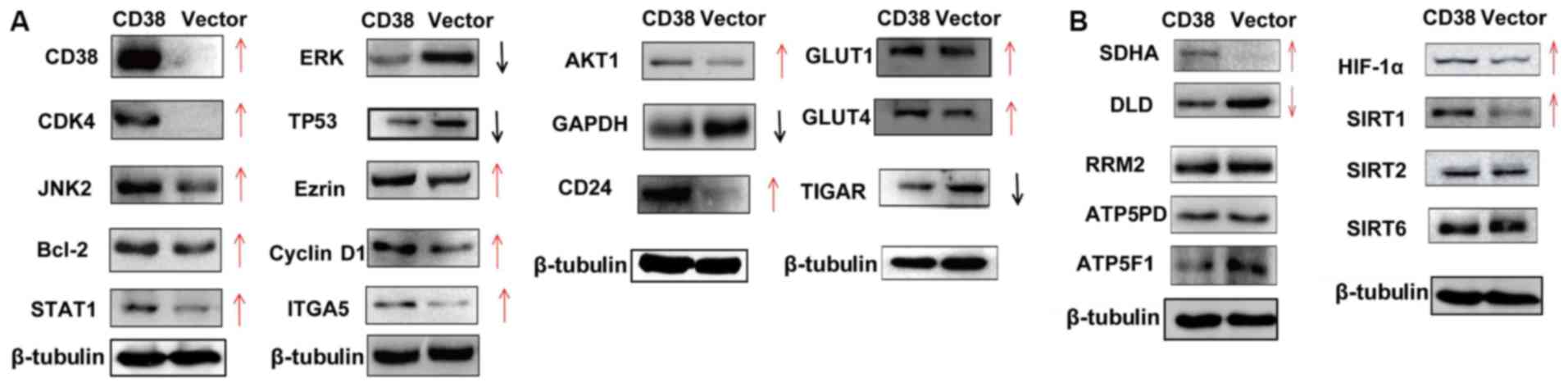
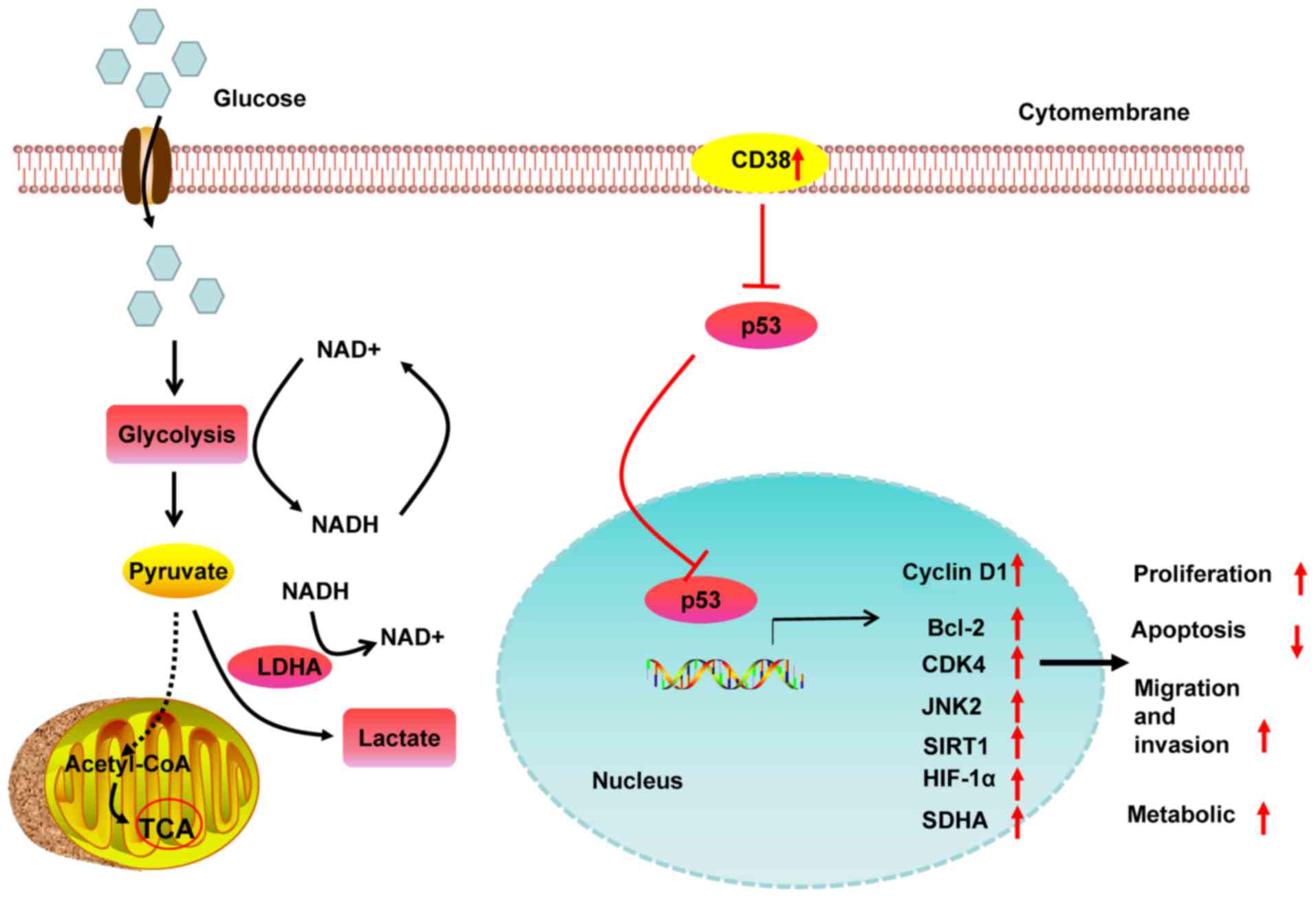
|
1
|
Spano JP, Busson P, Atlan D, Bourhis J,
Pignon JP, Esteban C and Armand JP: Nasopharyngeal carcinomas: An
update. Eur J Cancer. 39:2121–2135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan LL, Hung WM, Chan CC,
Sze HC, Chan OS, Chang AT and Yeung RM: Evolution of treatment for
nasopharyngeal cancer - success and setback in the
intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother Oncol. 110:377–384.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Epidemiology of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:421–429. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fu ZT, Guo XL, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Sun KX,
Chen WQ and He J: Incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma in China, 2014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 40:566–571.
2018.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scott RS: Epstein-Barr virus: A master
epigenetic manipulator. Curr Opin Virol. 26:74–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Li X,
Zhang B, Yi W, Xiao L, Wu M, Shen S, et al: Identification of
candidate molecular markers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
microarray analysis of subtracted cDNA libraries constructed by
suppression subtractive hybridization. Eur J Cancer Prev.
17:561–571. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakanishi Y, Wakisaka N, Kondo S, Endo K,
Sugimoto H, Hatano M, Ueno T, Ishikawa K and Yoshizaki T:
Progression of understanding for the role of Epstein-Barr virus and
management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
36:435–447. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Luo X, Zhang W,
Li X, Fan S, Cao L, Tang K, Wu M, et al: Analysis of gene
expression identifies candidate molecular markers in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma using microdissection and cDNA microarray. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 133:71–81. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Li X, Xiong W,
Liu H, Fan S, Qian J, Wang L, Li Z, et al: Family-based association
analysis validates chromosome 3p21 as a putative nasopharyngeal
carcinoma susceptibility locus. Genet Med. 8:156–160. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie SH, Yu IT, Tse LA, Mang OW and Yue L:
Sex difference in the incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Hong
Kong 1983–2008: Suggestion of a potential protective role of
oestrogen. Eur J Cancer. 49:150–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Q, Chen JO, Huang QH and Li YH: Trends
in the survival of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma between
1976 and 2005 in Sihui, China: A population-based study. Chin J
Cancer. 32:325–333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Brouwer CL, Steenbakkers RJ, van den
Heuvel E, Duppen JC, Navran A, Bijl HP, Chouvalova O, Burlage FR,
Meertens H, Langendijk JA, et al: 3D Variation in delineation of
head and neck organs at risk. Radiat Oncol. 7:322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang LQ, Lu TY, Li Y, Guo SY, Zhong QY,
Zou MS, Chen BL, Tang QN, Chen WH, Guo SS, et al: Patterns of
Failure and Survival Trends Of 720 Patients with Stage I
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosed from 1990–2012: A Large-scale
Retrospective Cohort Study. J Cancer. 9:1308–1317. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Huang CI, Chen LF, Chang SL, Wu HC, Ting
WC and Yang CC: Accuracy of a staging system for prognosis of
5-year survival of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma who
underwent chemoradiotherapy. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
143:1086–1091. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shuang H, Feng J, Caineng C, Qifeng J, Tin
J, Yuanyuan C and Xiaozhong C: The value of radical radiotherapy in
the primary tumor of newly diagnosed oligo-metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Clin Transl Oncol. Jun
25–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kwong DL, Sham JS, Au GK, Chua DT, Kwong
PW, Cheng AC, Wu PM, Law MW, Kwok CC, Yau CC, et al: Concurrent and
adjuvant chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A factorial
study. J Clin Oncol. 22:2643–2653. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan-Shan GE and Yan-Hong ZHOU: SDHA and
tumor cell metabolism. Prog Biochem Biophys. 45:621–628. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Deshpande DA, Guedes AGP, Graeff R, Dogan
S, Subramanian S, Walseth TF and Kannan MS: CD38/cADPR signaling
pathway in airway disease: Regulatory mechanisms. Mediators
Inflamm. 2018.8942042:2018.
|
|
19
|
Itoh M, Ishihara K, Tomizawa H, Tanaka H,
Kobune Y, Ishikawa J, Kaisho T and Hirano T: Molecular cloning of
murine BST-1 having homology with CD38 and Aplysia ADP-ribosyl
cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 203:1309–1317. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Terhorst C, van Agthoven A, LeClair K,
Snow P, Reinherz E and Schlossman S: Biochemical studies of the
human thymocyte cell-surface antigens T6, T9 and T10. Cell.
23:771–780. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakagawara K, Mori M, Takasawa S, Nata K,
Takamura T, Berlova A, Tohgo A, Karasawa T, Yonekura H, Takeuchi T,
et al: Assignment of CD38, the gene encoding human leukocyte
antigen CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase), to
chromosome 4p15. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 69:38–39. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao YJ, Lam CM and Lee HC: The
membrane-bound enzyme CD38 exists in two opposing orientations. Sci
Signal. 5:ra672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao YJ, Zhu WJ, Wang XW, Zhang LH and Lee
HC: Determinants of the membrane orientation of a calcium signaling
enzyme CD38. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853.2095–2103. 2015.
|
|
24
|
Lin P, Owens R, Tricot G and Wilson CS:
Flow cytometric immunophenotypic analysis of 306 cases of multiple
myeloma. Am J Clin Pathol. 121:482–488. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sherbenou DW, Behrens CR, Su Y, Wolf JL,
Martin TG III and Liu B: The development of potential
antibody-based therapies for myeloma. Blood Rev. 29:81–91. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Bataille R, Jégo G, Robillard N,
Barillé-Nion S, Harousseau JL, Moreau P, Amiot M and
Pellat-Deceunynck C: The phenotype of normal, reactive and
malignant plasma cells. Identification of ‘many and multiple
myelomas’ and of new targets for myeloma therapy. Haematologica.
91:1234–1240. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leo R, Boeker M, Peest D, Hein R, Bartl R,
Gessner JE, Selbach J, Wacker G and Deicher H: Multiparameter
analyses of normal and malignant human plasma cells:
CD38++, CD56+, CD54+,
cIg+ is the common phenotype of myeloma cells. Ann
Hematol. 64:132–139. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu Y, Wang H, Wang Q and Deng H:
Overexpression of CD38 decreases cellular NAD levels and alters the
expression of proteins involved in energy metabolism and
antioxidant defense. J Proteome Res. 13:786–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liao S, Xiao S, Chen H, Zhang M, Chen Z,
Long Y, Gao L, He J, Ge Y, Yi W, et al: The receptor for activated
protein kinase C promotes cell growth, invasion and migration in
cervical cancer. Int J Oncol. 51:1497–1507. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hara A and Okayasu I: Cyclooxygenase-2 and
inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in human astrocytic
gliomas: Correlation with angiogenesis and prognostic significance.
Acta Neuropathol. 108:43–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bose S, Yap LF, Fung M, Starzcynski J,
Saleh A, Morgan S, Dawson C, Chukwuma MB, Maina E, Buettner M, et
al: The ATM tumour suppressor gene is down-regulated in
EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol. 217:345–352.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ge Y, Zhang C, Xiao S, Liang L, Liao S,
Xiang Y, Cao K, Chen H and Zhou Y: Identification of differentially
expressed genes in cervical cancer by bioinformatics analysis.
Oncol Lett. 16:2549–2558. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang C, Peng L, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Li W,
Chen S and Li G: The identification of key genes and pathways in
hepatocellular carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis of
high-throughput data. Med Oncol. 34:1012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arndt C, Koristka S, Feldmann A, Bergmann
R and Bachmann M: Coomassie Brilliant blue staining of
polyacrylamide gels. Methods Mol Biol. 1853.27–30. 2018.
|
|
35
|
Zheng D, Liao S, Zhu G, Luo G, Xiao S, He
J, Pei Z, Li G and Zhou Y: CD38 is a putative functional marker for
side population cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines.
Mol Carcinog. 55:300–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lefranc F, Le Rhun E, Kiss R and Weller M:
Glioblastoma quo vadis: Will migration and invasiveness reemerge as
therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat Rev. 68:145–154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu CA, Chang CY, Hsueh KW, Su HL, Chiou
TW, Lin SZ and Harn HJ: Migration/invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for therapeutic treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
19:E11152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bhatia-Dey N, Kanherkar RR, Stair SE,
Makarev EO and Csoka AB: Cellular senescence as the causal nexus of
aging. Front Genet. 7:132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee M and Lee JS: Exploiting tumor cell
senescence in anticancer therapy. BMB Rep. 47:51–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liao S, Xiao S, Chen H, Zhang M, Chen Z,
Long Y, Gao L, Zhu G, He J, Peng S, et al: CD38 enhances the
proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of cervical cancer cells
by affecting the mitochondria functions. Mol Carcinog.
56:2245–2257. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Abudoureyimu A and Muhemaitibake A:
Arsenic trioxide regulates gastric cancer cell apoptosis by
mediating cAMP. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:612–617.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Das D, Khan PP and Maitra S: Endocrine and
paracrine regulation of meiotic cell cycle progression in teleost
oocytes: cAMP at the centre of complex intra-oocyte signalling
events. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 241:33–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Goodman RP, Calvo SE and Mootha VK:
Spatiotemporal compartmentalization of hepatic NADH and NADPH
metabolism. J Biol Chem. 293:7508–7516. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tanabe H, Fujii Y, Okada-Iwabu M, Iwabu M,
Nakamura Y, Hosaka T, Motoyama K, Ikeda M, Wakiyama M, Terada T, et
al: Crystal structures of the human adiponectin receptors. Nature.
520:312–316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karimi-Busheri F, Zadorozhny V, Li T, Lin
H, Shawler DL and Fakhrai H: Pivotal role of CD38 biomarker in
combination with CD24, EpCAM, and ALDH for identification of H460
derived lung cancer stem cells. J Stem Cells. 6:9–20.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Karimi-Busheri F, Rasouli-Nia A,
Zadorozhny V and Fakhrai H: CD24+/CD38− as
new prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer. Multidiscip
Respir Med. 8:652013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chouzouris TM, Dovolou E, Krania F, Pappas
IS, Dafopoulos K, Messinis IE, Anifandis G and Amiridis GS: Effects
of ghrelin on activation of Akt1 and ERK1/2 pathways during in
vitro maturation of bovine oocytes. Zygote. 25:183–189. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheng R, Yong H, Xia Y, Xie Q, Gao G and
Zhou X: Chemotherapy regimen based on sorafenib combined with 5-FU
on HIF-1α and VEGF expression and survival in advanced gastric
cancer patients. Oncol Lett. 13:2703–2707. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ganesan R, Hos NJ, Gutierrez S, Fischer J,
Stepek JM, Daglidu E, Krönke M and Robinson N: Salmonella
Typhimurium disrupts Sirt1/AMPK checkpoint control of mTOR to
impair autophagy. PLoS Pathog. 13:e10062272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Keyhani A, Huh YO, Jendiroba D, Pagliaro
L, Cortez J, Pierce S, Pearlman M, Estey E, Kantarjian H and
Freireich EJ: Increased CD38 expression is associated with
favorable prognosis in adult acute leukemia. Leuk Res. 24:153–159.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Aarhus R, Graeff RM, Dickey DM, Walseth TF
and Lee HC: ADP-ribosyl cyclase and CD38 catalyze the synthesis of
a calcium-mobilizing metabolite from NADP. J Biol Chem.
270:30327–30333. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mallone R, Funaro A, Zubiaur M, Baj G,
Ausiello CM, Tacchetti C, Sancho J, Grossi C and Malavasi F:
Signaling through CD38 induces NK cell activation. Int Immunol.
13:397–409. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liao S, Xiao S, Zhu G, Zheng D, He J, Pei
Z, Li G and Zhou Y: CD38 is highly expressed and affects the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer. Oncol Rep.
32:2703–2709. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Blacher E, Ben Baruch B, Levy A, Geva N,
Green KD, Garneau-Tsodikova S, Fridman M and Stein R: Inhibition of
glioma progression by a newly discovered CD38 inhibitor. Int J
Cancer. 136:1422–1433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Savarino A, Bottarel F, Calosso L, Feito
MJ, Bensi T, Bragardo M, Rojo JM, Pugliese A, Abbate I, Capobianchi
MR, et al: Effects of the human CD38 glycoprotein on the early
stages of the HIV-1 replication cycle. FASEB J. 13:2265–2276. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yamada M, Mizuguchi M, Otsuka N, Ikeda K
and Takahashi H: Ultrastructural localization of CD38
immunoreactivity in rat brain. Brain Res. 756:52–60. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Churchill GC, O'Neill JS, Masgrau R, Patel
S, Thomas JM, Genazzani AA and Galione A: Sperm deliver a new
second messenger: NAADP. Curr Biol. 13:125–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dianzani U, Funaro A, DiFranco D,
Garbarino G, Bragardo M, Redoglia V, Buonfiglio D, De Monte LB,
Pileri A and Malavasi F: Interaction between endothelium and
CD4+CD45RA+ lymphocytes. Role of the human
CD38 molecule. J Immunol. 153:952–959. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guse AH, da Silva CP, Berg I, Skapenko AL,
Weber K, Heyer P, Hohenegger M, Ashamu GA, Schulze-Koops H, Potter
BV, et al: Regulation of calcium signalling in T lymphocytes by the
second messenger cyclic ADP-ribose. Nature. 398:70–73. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kim SY, Cho BH and Kim UH: CD38-mediated
Ca2+ signaling contributes to angiotensin II-induced
activation of hepatic stellate cells: Attenuation of hepatic
fibrosis by CD38 ablation. J Biol Chem. 285:576–582. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Guedes AG, Rude EP and Kannan MS:
Potential role of the CD38/cADPR signaling pathway as an underlying
mechanism of the effects of medetomidine on insulin and glucose
homeostasis. Vet Anaesth Analg. 40:512–516. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Young LS and Rickinson AB: Epstein-Barr
virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:757–768. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schiattarella GG and Hill JA: Therapeutic
targeting of autophagy in cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 95:86–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Yang E, Al-Mugheiry TS, Normando EM and
Cordeiro MF: Real-time imaging of retinal cell apoptosis by
confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy and its role in glaucoma.
Front Neurol. 9:3382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kountouras J, Kouklakis G, Zavos C,
Chatzopoulos D, Moschos J, Molyvas E and Zavos N: Apoptosis,
inflammatory bowel disease and carcinogenesis: Overview of
international and Greek experiences. Can J Gastroenterol.
17:249–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Blacher E, Dadali T, Bespalko A,
Haupenthal VJ, Grimm MO, Hartmann T, Lund FE, Stein R and Levy A:
Alzheimer's disease pathology is attenuated in a CD38-deficient
mouse model. Ann Neurol. 78:88–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Levy A, Blacher E, Vaknine H, Lund FE,
Stein R and Mayo L: CD38 deficiency in the tumor microenvironment
attenuates glioma progression and modulates features of
tumor-associated microglia/macrophages. Neuro Oncol. 14:1037–1049.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Karakasheva TA, Waldron TJ, Eruslanov E,
Kim SB, Lee JS, O'Brien S, Hicks PD, Basu D, Singhal S, Malavasi F,
et al: CD38-expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote
tumor growth in a murine model of esophageal cancer. Cancer Res.
75:4074–4085. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Poret N, Fu Q, Guihard S, Cheok M, Miller
K, Zeng G, Quesnel B, Troussard X, Galiègue-Zouitina S and Shelley
CS: CD38 in hairy cell leukemia is a marker of poor prognosis and a
new target for therapy. Cancer Res. 75:3902–3911. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Deaglio S, Capobianco A, Bergui L, Dürig
J, Morabito F, Dührsen U and Malavasi F: CD38 is a signaling
molecule in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood.
102:2146–2155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chini CC, Guerrico AM, Nin V,
Camacho-Pereira J, Escande C, Barbosa MT and Chini EN: Targeting of
NAD metabolism in pancreatic cancer cells: Potential novel therapy
for pancreatic tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 20:120–130. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: Cycling on
cue. Cell. 79:551–555. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bartek J, Bartkova J and Lukas J: The
retinoblastoma protein pathway and the restriction point. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 8:805–814. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Donjerkovic D and Scott DW: Regulation of
the G1 phase of the mammalian cell cycle. Cell Res. 10:1–16. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou P, Jiang W, Weghorst CM and Weinstein
IB: Overexpression of cyclin D1 enhances gene amplification. Cancer
Res. 56:36–39. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Izzo JG, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Li XQ,
Ibarguen H, Lee JS, Ro JY, El-Naggar A, Hong WK and Hittelman WN:
Dysregulated cyclin D1 expression early in head and neck
tumorigenesis: In vivo evidence for an association with subsequent
gene amplification. Oncogene. 17:2313–2322. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sapio L, Gallo M, Illiano M, Chiosi E,
Naviglio D, Spina A and Naviglio S: The Natural cAMP elevating
compound forskolin in cancer therapy: Is It Time. J Cell Physiol.
232:922–927. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Banerjee J, Papu John AM, Al-Wadei MH and
Schuller HM: Prevention of pancreatic cancer in a hamster model by
cAMP decrease. Oncotarget. 7:44430–44441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xie L, Boyle D, Sanford D, Scherer PE,
Pessin JE and Mora S: Intracellular trafficking and secretion of
adiponectin is dependent on GGA-coated vesicles. J Biol Chem.
281:7253–7259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Miele M, Costantini S and Colonna G:
Structural and functional similarities between osmotin from
Nicotiana tabacum seeds and human adiponectin. PLoS One.
6:e166902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu DG, Liu HL, Song TJ, Huang HY, Li X
and Tang QQ: Functional expression of the globular domain of human
adiponectin in Pichia pastoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
363:769–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Feng L, Tao L, Dawei H, Xuliang L and
Xiaodong L: HIF-1α expression correlates with cellular apoptosis,
angiogenesis and clinical prognosis in rectal carcinoma. Pathol
Oncol Res. 20:603–610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Robb KP, Cotechini T, Allaire C, Sperou A
and Graham CH: Inflammation-induced fetal growth restriction in
rats is associated with increased placental HIF-1α accumulation.
PLoS One. 12:e01758052017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Guo Y, Han B, Luo K, Ren Z, Cai L and Sun
L: NOX2-ROS-HIF-1α signaling is critical for the inhibitory effect
of oleanolic acid on rectal cancer cell proliferation. Biomed
Pharmacother. 85:733–739. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Madu C, Li L and Lu Y: Selection, analysis
and improvement of anti-angiogenesis compounds identified by an
anti-HIF-1α screening and validation system. J Cancer. 7:1926–1938.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Kim MH, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Hoe HS, Park KK,
Park YY, Choi YH, Kim CH, Chang HW, Park YJ, et al: Delphinidin
inhibits angiogenesis through the suppression of HIF-1α and VEGF
expression in A549 lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 37:777–784. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|