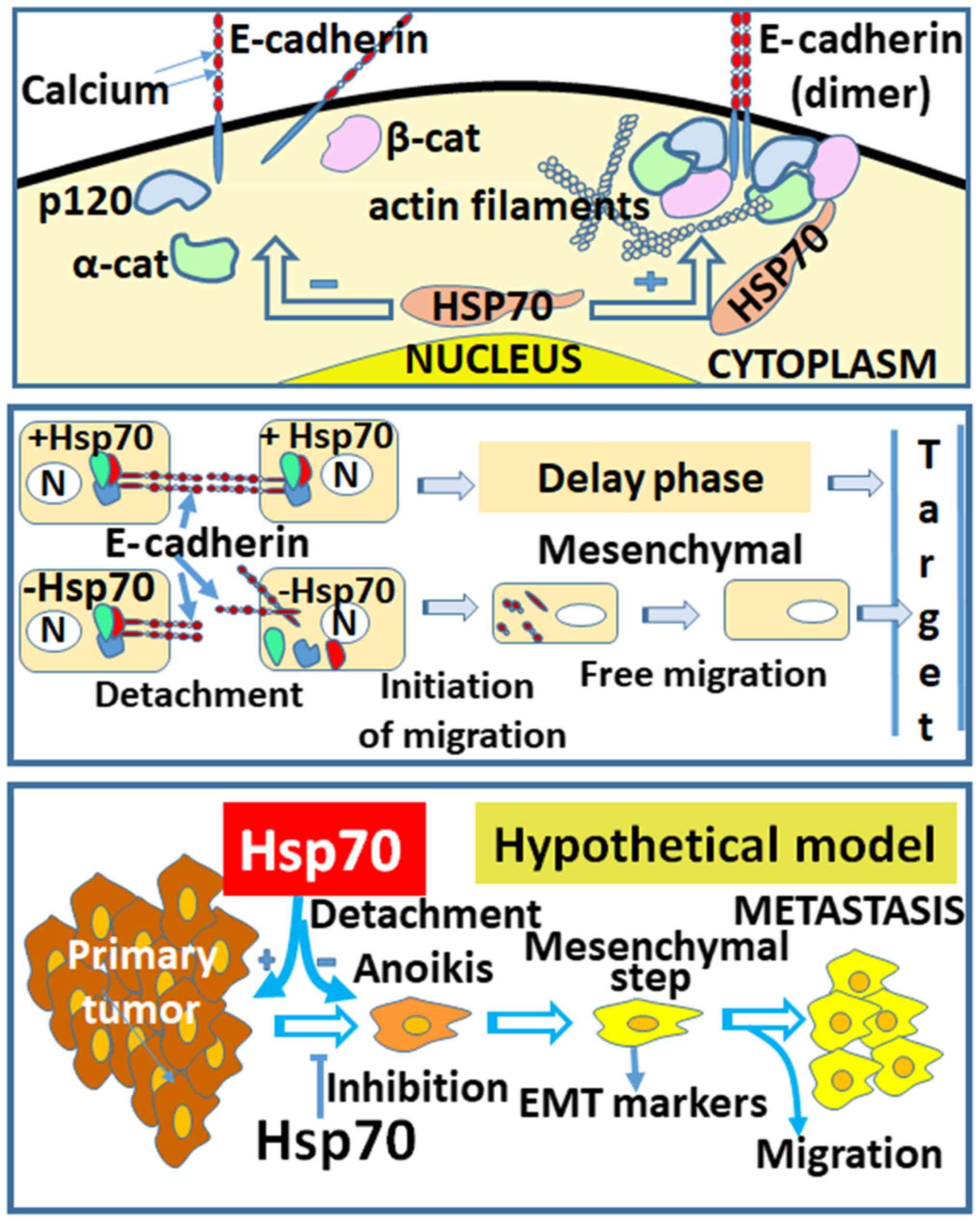
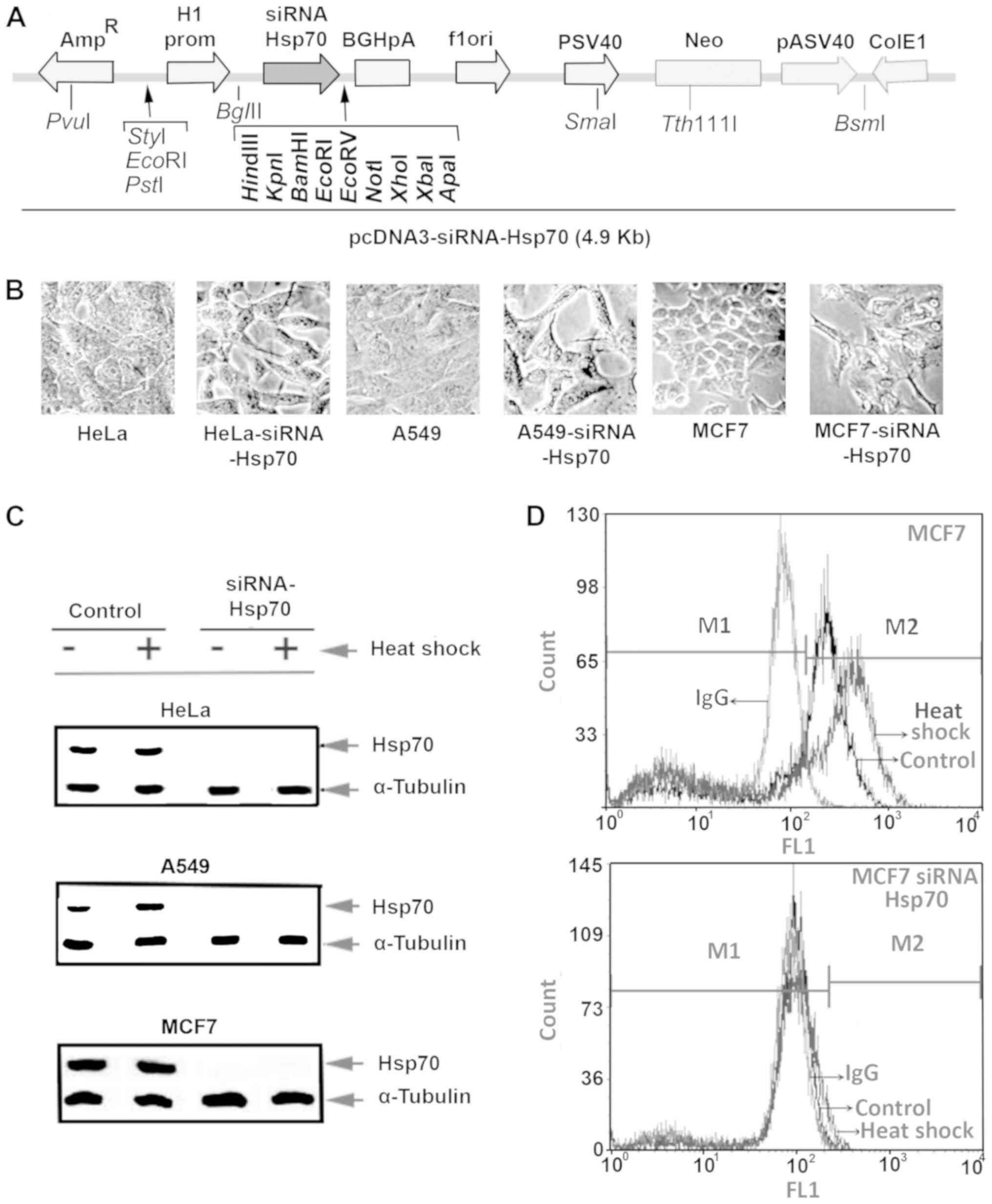
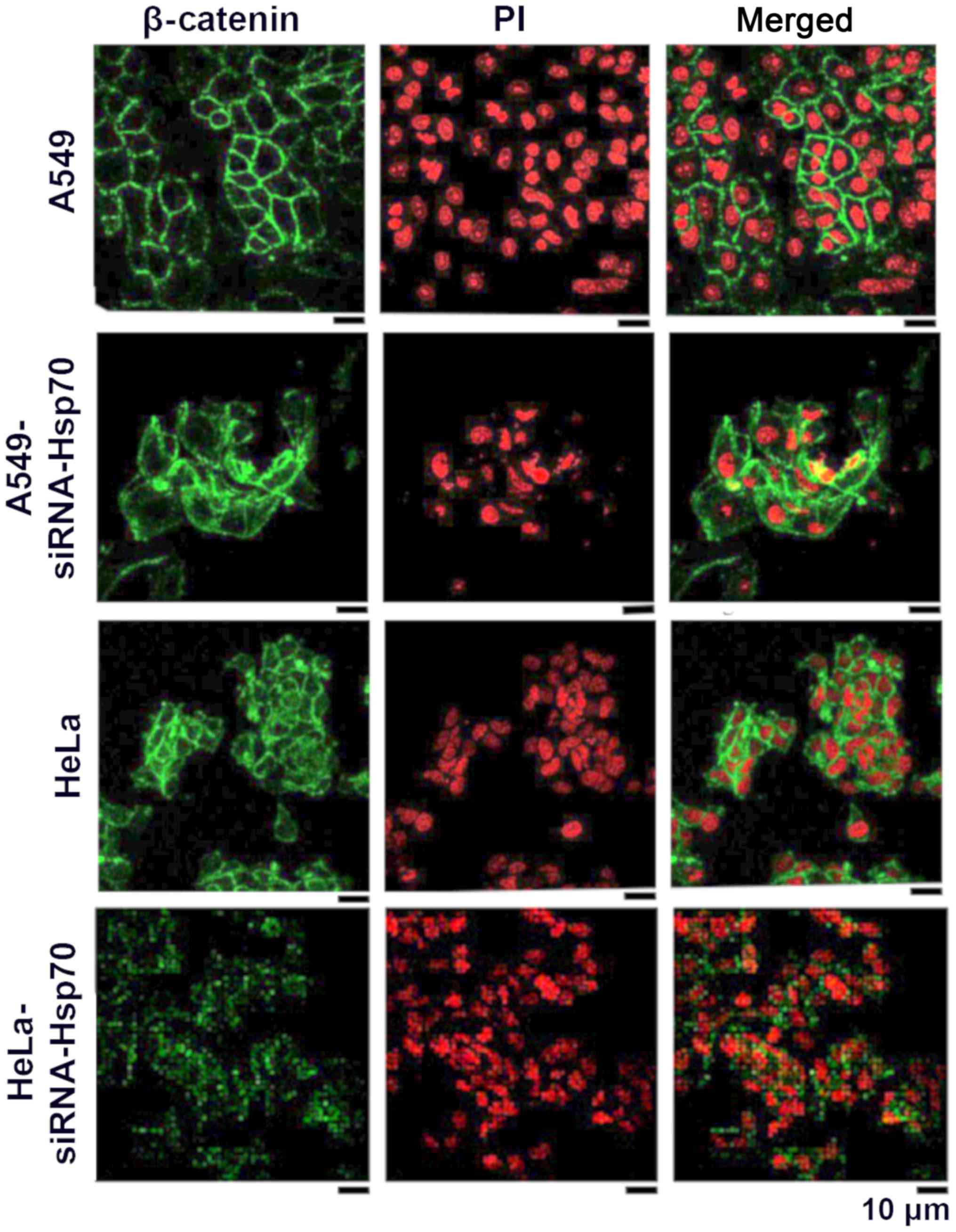
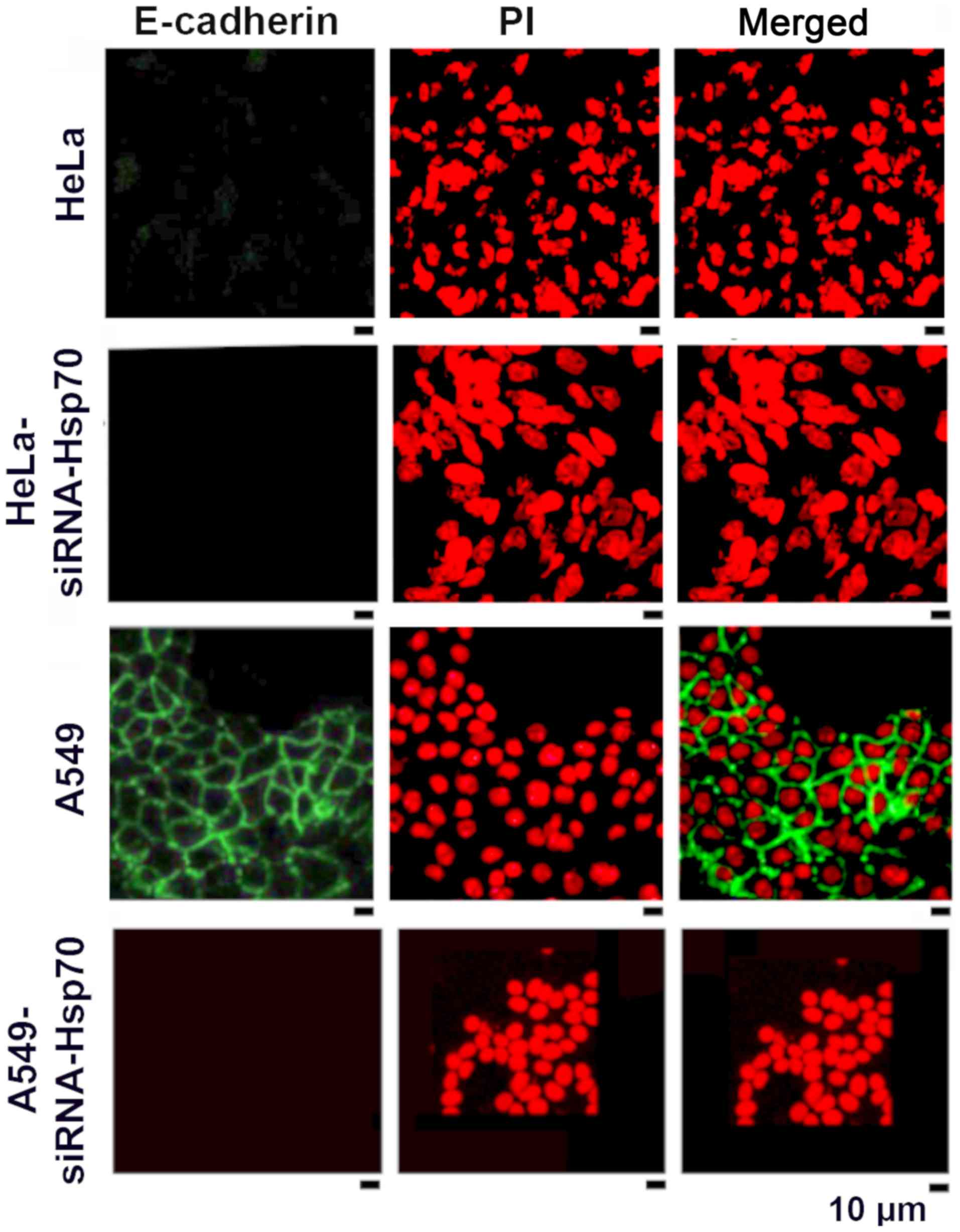
|
1
|
Murphy ME: The HSP70 family and cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1181–1188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lindquist S and Craig EA: The heat-shock
proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 22:631–677. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morimoto RI, Tissières A and Georgopoulos
C: The stress response, function of the proteins, and perspectives.
Stress Proteins in Biology and Medicine. Morimoto RI, Tissières A
and Georgopoulos C: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold
Spring Harbor; New York: pp. 1–36. 1990
|
|
4
|
Hightower LE: Heat shock, stress proteins,
chaperones, and proteotoxicity. Cell. 66:191–197. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Minami Y, Höhfeld J, Ohtsuka K and Hartl
F-U: Regulation of the heat-shock protein 70 reaction cycle by the
mammalian DnaJ homolog, Hsp40. J Biol Chem. 271:19617–19624. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang HC, Sherman MY, Kandror O and
Goldberg AL: The molecular chaperone DnaJ is required for the
degradation of a soluble abnormal protein in Escherichia coli. J
Biol Chem. 276:3920–3928. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bozidis P, Lazaridis I, Pagoulatos GN and
Angelidis CE: Mydj2 as a potent partner of hsc70 in mammalian
cells. Eur J Biochem. 269:1553–1560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Angelidis CE, Lazaridis I and Pagoulatos
GN: Aggregation of hsp70 and hsc70 in vivo is distinct and
temperature-dependent and their chaperone function is directly
related to non-aggregated forms. Eur J Biochem. 259:505–512. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE and Welch WJ:
Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: Implications
for protein folding and assembly. Science. 248:850–854. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saliba RS, Munro PM, Luthert PJ and
Cheetham ME: The cellular fate of mutant rhodopsin: Quality
control, degradation and aggresome formation. J Cell Sci.
115:2907–2918. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chirico WJ, Waters MG and Blobel G: 70K
heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into
microsomes. Nature. 332:805–810. 1988. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kotoglou P, Kalaitzakis A, Vezyraki P,
Tzavaras T, Michalis LK, Dantzer F, Jung JU and Angelidis C: Hsp70
translocates to the nuclei and nucleoli, binds to XRCC1 and PARP-1,
and protects HeLa cells from single-strand DNA breaks. Cell Stress
Chaperones. 14:391–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Angelidis CE, Lazaridis I and Pagoulatos
GN: Constitutive expression of heat-shock protein 70 in mammalian
cells confers thermoresistance. Eur J Biochem. 199:35–39. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Angelidis C, Nova C, Lazaridis I,
Kontoyiannis D, Kollias G and Pagoulatos GN: Overexpression of
HSP70 in transgenic mice results in increased cell thermotolerance.
Transgenics. 2:111–117. 1996.
|
|
15
|
Jäättelä M, Wissing D, Kokholm K, Kallunki
T and Egeblad M: Hsp70 exerts its anti-apoptotic function
downstream of caspase-3-like proteases. EMBO J. 17:6124–6134. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Damalas A, Velimezi G, Kalaitzakis A,
Liontos M, Papavassiliou AG, Gorgoulis V and Angelidis C: Loss of
p14(ARF) confers resistance to heat shock- and oxidative
stress-mediated cell death by upregulating β-catenin. Int J Cancer.
128:1989–1995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cummings CJ, Cummings CJ, Sun Y, Opal P,
Antalffy B, Mestril R, Orr HT, Dillmann WH and Zoghbi HY:
Overexpression of inducible HSP70 chaperone suppresses
neuropathology and improves motor function in SCA1 mice. Hum Mol
Genet. 10:1511–1518. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Adachi H, Katsuno M, Minamiyama M, Sang C,
Pagoulatos G, Angelidis C, Kusakabe M, Yoshiki A, Kobayashi Y, Doyu
M, et al: Heat shock protein 70 chaperone overexpression
ameliorates phenotypes of the spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
transgenic mouse model by reducing nuclear-localized mutant
androgen receptor protein. J Neurosci. 23:2203–2211. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scott MD and Frydman J: Aberrant protein
folding as the molecular basis of cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
232:67–76. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mosser DD and Morimoto RI: Molecular
chaperones and the stress of oncogenesis. Oncogene. 23:2907–2918.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ammon-Treiber S, Grecksch G, Angelidis C,
Vezyraki P, Höllt V and Becker A: Emotional and learning behaviour
in mice over-expressing heat shock protein 70. Neurobiol Learn Mem.
90:358–364. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Plumier JC, Ross BM, Currie RW, Angelidis
CE, Kazlaris H, Kollias G and Pagoulatos GN: Transgenic mice
expressing the human heat shock protein 70 have improved
post-ischemic myocardial recovery. J Clin Invest. 95:1854–1860.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lysitsas DN, Katsouras CS, Papakostas JC,
Toumpoulis IK, Angelidis C, Bozidis P, Thomas CG, Seferiadis K,
Psychoyios N, Frillingos S, et al: Antirestenotic effects of a
novel polymer-coated d-24851 eluting stent. Experimental data in a
rabbit iliac artery model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.
30:1192–1200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Naka KK, Vezyraki P, Kalaitzakis A,
Zerikiotis S, Michalis L and Angelidis C: Hsp70 regulates the
doxorubicin-mediated heart failure in Hsp70-transgenic mice. Cell
Stress Chaperones. 19:853–864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kyrou IE, Papakostas JC, Ioachim E,
Koulouras V, Arnaoutoglou E, Angelidis C and Matsagkas MI: Early
ischaemic preconditioning of spinal cord enhanced the binding
profile of heat shock protein 70 with neurofilaments and promoted
its nuclear translocation after thoraco-abdominal aortic occlusion
in pigs. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 43:408–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ninomiya H, Ohgami N, Oshino R, Kato M,
Ohgami K, Li X, Shen D, Iida M, Yajima I, Angelidis CE, et al:
Increased expression level of Hsp70 in the inner ears of mice by
exposure to low frequency noise. Hear Res. 363:49–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morano KA: New tricks for an old dog: The
evolving world of Hsp70. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1113:1–14. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dudeja V, Mujumdar N, Phillips P, Chugh R,
Borja-Cacho D, Dawra RK, Vickers SM and Saluja AK: Heat shock
protein 70 inhibits apoptosis in cancer cells through simultaneous
and independent mechanisms. Gastroenterology. 136:1772–1782. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei YQ, Zhao X, Kariya Y, Teshigawara K
and Uchida A: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of
apoptosis by abrogation of heat-shock protein (HSP) 70 expression
in tumor cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 40:73–78. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nylandsted J, Rohde M, Brand K, Bastholm
L, Elling F and Jäättelä M: Selective depletion of heat shock
protein 70 (Hsp70) activates a tumor-specific death program that is
independent of caspases and bypasses Bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:7871–7876. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nylandsted J, Wick W, Hirt UA, Brand K,
Rohde M, Leist M, Weller M and Jäättelä M: Eradication of
glioblastoma, and breast and colon carcinoma xenografts by Hsp70
depletion. Cancer Res. 62:7139–7142. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
124:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guan JL and Shalloway D: Regulation of
focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular
adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 358:690–692. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ruoslahti E and Reed JC: Anchorage
dependence, integrins, and apoptosis. Cell. 77:477–478. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jäättelä M: Escaping cell death: Survival
proteins in cancer. Exp Cell Res. 248:30–43. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM and Green DR:
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment
of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang RY, Guilford P and Thiery JP: Early
events in cell adhesion and polarity during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Sci. 125:4417–4422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: Mechanisms of
motility in metastasizing cells. Mol Cancer Res. 8:629–642. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G, Yilmaz M and
Christofori G: EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Niehrs C: The complex world of WNT
receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:767–779. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kourtidis A, Ngok SP and Anastasiadis PZ:
p120 catenin: An essential regulator of cadherin stability,
adhesion-induced signaling, and cancer progression. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 116:409–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hajra KM and Fearon ER: Cadherin and
catenin alterations in human cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
34:255–268. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wheelock MJ, Shintani Y, Maeda M, Fukumoto
Y and Johnson KR: Cadherin switching. J Cell Sci. 121:727–735.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Theveneau E and Mayor R: Cadherins in
collective cell migration of mesenchymal cells. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 24:677–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Franke WW, Grund C, Kuhn C, Jackson BW and
Illmensee K: Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse
embryogenesis. III. Primary mesenchymal cells and the first
appearance of vimentin filaments. Differentiation. 23:43–59. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
McInroy L and Määttä A: Down-regulation of
vimentin expression inhibits carcinoma cell migration and adhesion.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360:109–114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vuoriluoto K, Haugen H, Kiviluoto S,
Mpindi JP, Nevo J, Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Lorens JB and Ivaska J:
Vimentin regulates EMT induction by Slug and oncogenic H-Ras and
migration by governing Axl expression in breast cancer. Oncogene.
30:1436–1448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sun Y, Song GD, Sun N, Chen JQ and Yang
SS: Slug overexpression induces stemness and promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Oncol Lett.
7:1936–1940. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Angelidis CE, Lazaridis I and Pagoulatos
GN: Specific inhibition of simian virus 40 protein synthesis by
heat and arsenite treatment. Eur J Biochem. 172:27–34. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Doulias P-T, Kotoglou P, Tenopoulou M,
Keramisanou D, Tzavaras T, Brunk U, Galaris D and Angelidis C:
Involvement of heat shock protein-70 in the mechanism of hydrogen
peroxide-induced DNA damage: The role of lysosomes and iron. Free
Radic Biol Med. 42:567–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gabai VL, Yaglom JA, Wang Y, Meng L, Shao
H, Kim G, Colvin T, Gestwicki J and Sherman MY: Anti-cancer effects
of targeting Hsp70 in tumor stromal cells. Cancer Res.
76:5926–5932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Novak A and Dedhar S: Signaling through
beta-catenin and Lef/Tcf. Cell Mol Life Sci. 56:523–537. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chaw SY, Abdul Majeed A, Dalley AJ, Chan
A, Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers - E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin - in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mao J, Hu X, Xiao Y, Yang C, Ding Y, Hou
N, Wang J, Cheng H and Zhang X: Overnutrition stimulates intestinal
epithelium proliferation through β-catenin signaling in obese mice.
Diabetes. 62:3736–3746. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cowin P, Rowlands TM, Hatsell SJ and Cowin
P: Rowlands TM and Hatsell SJ: Cadherins and Catenins in breast
cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:499–508. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wu CY, Tsai YP, Wu MZ, Teng SC and Wu KJ:
Epigenetic reprogramming and post-transcriptional regulation during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Trends Genet. 28:454–463.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rodriguez LG, Wu X and Guan JL:
Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol Biol. 294:23–29. 2005.
|
|
60
|
Ciocca DR and Calderwood SK: Heat shock
proteins in cancer: Diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and
treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones. 10:86–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Garg M, Kanojia D, Seth A, Kumar R, Gupta
A, Surolia A and Suri A: Heat-shock protein 70-2(HSP70-2)
expression in bladder urothelial carcinoma is associated with
tumour progression and promotes migration and invasion. Eur J
Cancer. 46:207–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Teng Y, Ngoka L, Mei Y, Lesoon L and
Cowell JK: HSP90 and HSP70 proteins are essential for stabilization
and activation of WASF3 metastasis-promoting protein. J Biol Chem.
287:10051–10059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Peinado H, Molina P,
Olmeda D, Cubillo E, Santos V, Palacios J, Portillo F and Cano A:
The morphological and molecular features of the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat Protoc. 4:1591–1613.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Buxton RS and Magee AI: Structure and
interactions of desmosomal and other cadherins. Semin Cell Biol.
3:157–167. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Banh A, Deschamps PA, Vijayan MM, Sivak JG
and West-Mays JA: The role of Hsp70 and Hsp90 in TGF-β-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in rat lens epithelial
explants. Mol Vis. 13:2248–2262. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yun CH, Yoon SY, Nguyen TT, Cho HY, Kim
TH, Kim ST, Kim BC, Hong YS, Kim SJ and Lee HJ: Geldanamycin
inhibits TGF-β signaling through induction of Hsp70. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 495:8–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Yang J, Zhu T, Liu X, Zhang L, Yang Y,
Zhang J and Guο M: Heat shock protein 70 protects rat peritoneal
mesothelial cells from advanced glycation end-products-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through mitogen activated
protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases and
transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathways. Mol Med Rep.
11:4473–4481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li Y, Kang X and Wang Q: HSP70 decreases
receptor-dependent phosphorylation of Smad2 and blocks
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Genet Genomics.
38:111–116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu J, Bao J, Hao J, Peng Y and Hong F:
HSP70 inhibits high glucose-induced Smad3 activation and attenuates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial
cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:1089–1095. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Klymkowsky MW and Savagner P:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A cancer researcher's conceptual
friend and foe. Am J Pathol. 174:1588–1593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in cancer onset and progression. Bull Acad Natl Med.
193:1969–1979. 2009.In French.
|
|
75
|
Steeg PS: Targeting metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:201–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Qian CN, Mei Y and Zhang J: Cancer
metastasis: Issues and challenges. Chin J Cancer. 36:382017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|