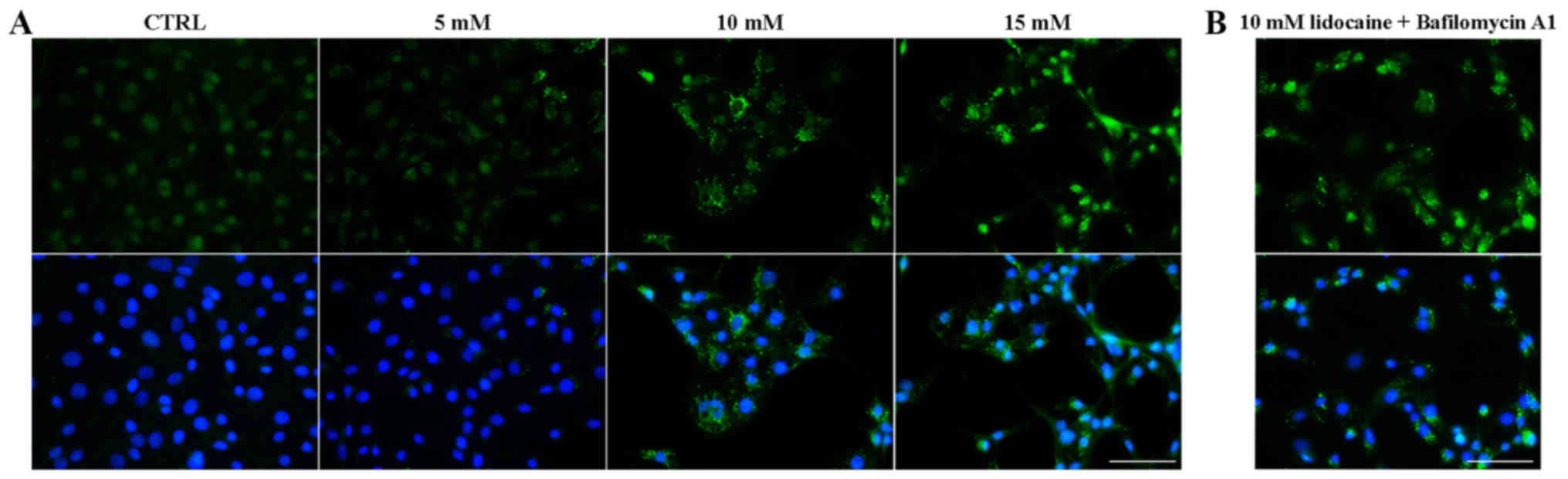
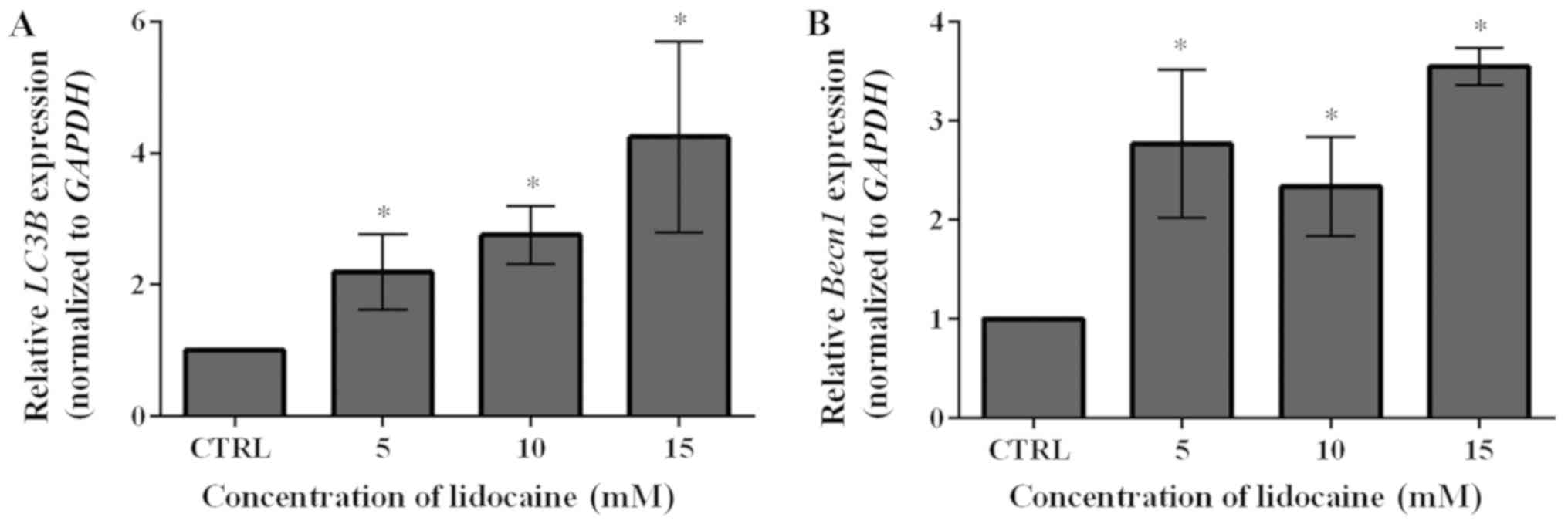
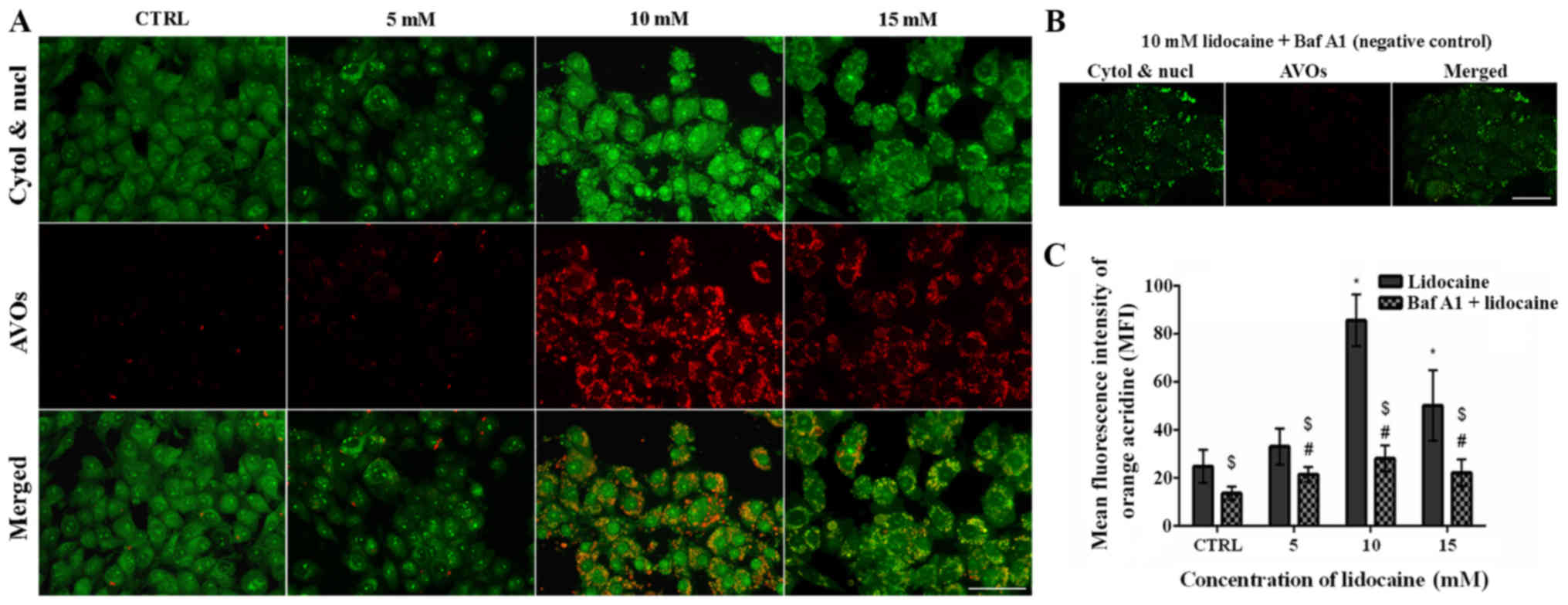
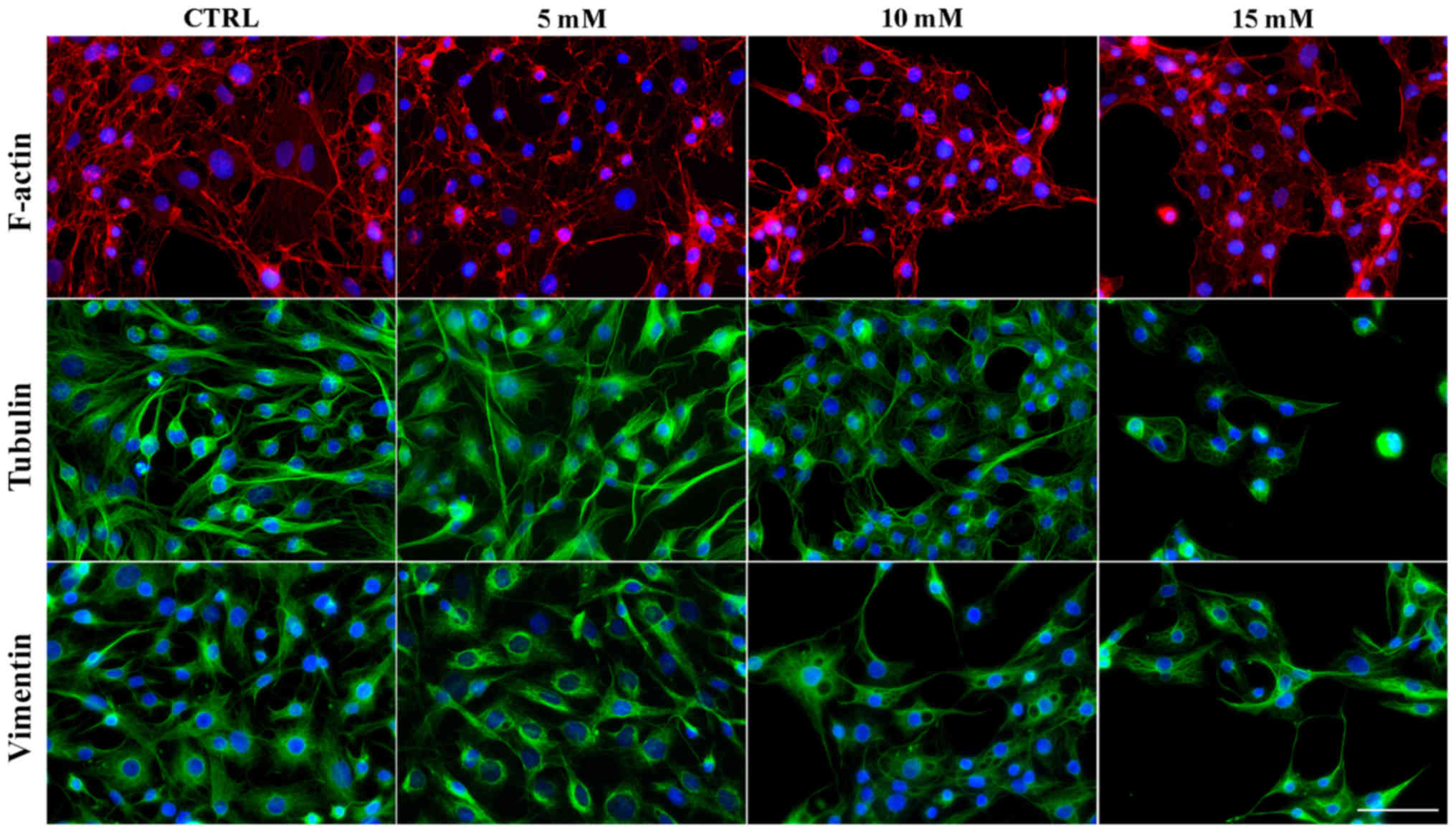
|
1
|
Goodenberger ML and Jenkins RB: Genetics
of adult glioma. Cancer Genet. 205:613–621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Population-based
studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in
astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
64:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bleeker FE, Molenaar RJ and Leenstra S:
Recent advances in the molecular understanding of glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 108:11–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burdett S and Stewart L; Glioma
Meta-Analysis Trialists Group: Chemotherapy for high-grade glioma.
Neuroepidemiology. 22:3662003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Neeman E and Ben-Eliyahu S: Surgery and
stress promote cancer metastasis: New outlooks on perioperative
mediating mechanisms and immune involvement. Brain Behav Immun.
30(Suppl): S32–S40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gottschalk A, Sharma S, Ford J, Durieux ME
and Tiouririne M: Review article: The role of the perioperative
period in recurrence after cancer surgery. Anesth Analg.
110:1636–1643. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roger S, Rollin J, Barascu A, Besson P,
Raynal PI, Iochmann S, Lei M, Bougnoux P, Gruel Y and Le Guennec
JY: Voltage-gated sodium channels potentiate the invasive
capacities of human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 39:774–786. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao R, Shen Y, Cai J, Lei M and Wang Z:
Expression of voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit in human
ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 23:1293–1299. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Diss JK, Archer SN, Hirano J, Fraser SP
and Djamgoz MB: Expression profiles of voltage-gated Na(+) channel
alpha-subunit genes in rat and human prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 48:165–178. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang M, Kozminski DJ, Wold LA, Modak R,
Calhoun JD, Isom LL and Brackenbury WJ: Therapeutic potential for
phenytoin: Targeting Na(v)1.5 sodium channels to reduce migration
and invasion in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
134:603–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grimes JA, Fraser SP, Stephens GJ, Downing
JEG, Laniado ME, Foster CS, Abel PD and Djamgoz MBA: Differential
expression of voltage-activated Na+ currents in two
prostatic tumour cell lines: Contribution to invasiveness in vitro.
FEBS Lett. 369:290–294. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Laniado ME, Lalani EN, Fraser SP, Grimes
JA, Bhangal G, Djamgoz MB and Abel PD: Expression and functional
analysis of voltage-activated Na+ channels in human
prostate cancer cell lines and their contribution to invasion in
vitro. Am J Pathol. 150:1213–1221. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang HW, Wang LY, Jiang L, Tian SM, Zhong
TD and Fang XM: Amide-linked local anesthetics induce apoptosis in
human non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 8:2748–2757. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Piegeler T, Votta-Velis EG, Liu G, Place
AT, Schwartz DE, Beck-Schimmer B, Minshall RD and Borgeat A:
Antimetastatic potential of amide-linked local anesthetics:
Inhibition of lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and inflammatory
Src signaling independent of sodium channel blockade.
Anesthesiology. 117:548–559. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lirk P, Berger R, Hollmann MW and Fiegl H:
Lidocaine time- and dose-dependently demethylates deoxyribonucleic
acid in breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Br J Anaesth.
110:1652013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xing W, Chen DT, Pan JH, Chen YH, Yan Y,
Li Q, Xue RF, Yuan YF and Zeng WA: Lidocaine induces apoptosis and
suppresses tumor growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in
vitro and in a xenograft model in vivo. Anesthesiology.
126:868–881. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leng T, Lin S, Xiong Z and Lin J:
Lidocaine suppresses glioma cell proliferation by inhibiting TRPM7
channels. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 9:8–15.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson ME, Saenz JA, DaSilva AD, Uhl CB
and Gores GJ: Effect of local anesthetic on neuronal cytoplasmic
calcium and plasma membrane lysis (necrosis) in a cell culture
model. Anesthesiology. 97:1466–1476. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson ME, Uhl CB, Spittler KH, Wang H
and Gores GJ: Mitochondrial injury and caspase activation by the
local anesthetic lidocaine. Anesthesiology. 101:1184–1194. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lirk P, Haller I, Hausott B, Ingorokva S,
Deibl M, Gerner P and Klimaschewski L: The neurotoxic effects of
amitriptyline are mediated by apoptosis and are effectively blocked
by inhibition of caspase activity. Anesth Analg. 102:1728–1733.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh
H, Troxel A, Rosen J, Eskelinen EL, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, et al:
Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin
1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. 112:1809–1820. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ and Heintz
N: Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic
development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:15077–15082. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mariño G, Salvador-Montoliu N, Fueyo A,
Knecht E, Mizushima N and López-Otín C: Tissue-specific autophagy
alterations and increased tumorigenesis in mice deficient in Atg4C
autophagin-3. J Biol Chem. 282:18573–18583. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ekiz HA, Can G and Baran Y: Role of
autophagy in the progression and suppression of leukemias. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 81:275–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Izdebska M, Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska A,
Hałas M, Gagat M and Grzanka A: Green tea extract induces
protective autophagy in A549 non-small lung cancer cell line.
Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 69:1478–1484. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jurj A, Tomuleasa C, Tat TT,
Berindan-Neagoe I, Vesa SV and Ionescu DC: Antiproliferative and
apoptotic effects of lidocaine on human hepatocarcinoma cells. A
preliminary study. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 26:45–50.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Klionsky DJ, Elazar Z, Seglen PO and
Rubinsztein DC: Does bafilomycin A1 block the fusion of
autophagosomes with lysosomes? Autophagy. 4:849–850. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3 and
autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. 445:77–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee YK and Lee JA: Role of the mammalian
ATG8/LC3 family in autophagy: Differential and compensatory roles
in the spatiotemporal regulation of autophagy. BMB Rep. 49:424–430.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett
N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D and Yahalom J: A novel response
of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of
acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Izdebska M, Zielińska W, Grzanka D and
Gagat M: The role of actin dynamics and actin-binding proteins
expression in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its
association with cancer progression and evaluation of possible
therapeutic targets. BioMed Res Int. 2018:45783732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grzanka D, Gagat M and Izdebska M:
Involvement of the SATB1/F-actin complex in chromatin
reorganization during active cell death. Int J Mol Med.
33:1441–1450. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sampetrean O and Saya H: Modeling
phenotypes of malignant gliomas. Cancer Sci. 109:6–14. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Nakada M, Nakada S, Demuth T, Tran NL,
Hoelzinger DB and Berens ME: Molecular targets of glioma invasion.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:458–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li G, Qin Z, Chen Z, Xie L, Wang R and
Zhao H: Tumor microenvironment in treatment of glioma. Open Med
(Wars). 12:247–251. 2017.
|
|
38
|
MostovenkoEVégváriÁRezeliMLichtiCFFenyöDWangQLangFFSulmanEPSahlinKBMarko-VargaGet
al: Large scale identification of variant proteins in glioma stem
cells. ACS Chem Neurosci. 9:73–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Sakaguchi M, Kuroda Y and Hirose M: The
antiproliferative effect of lidocaine on human tongue cancer cells
with inhibition of the activity of epidermal growth factor
receptor. Anesth Analg. 102:1103–1107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang X, Zhao L, Li M, Yan L, Zhang S, Mi
Z, Ren L and Xu J: Lidocaine enhances the effects of
chemotherapeutic drugs against bladder cancer. Sci Rep. 8:5982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chamaraux-Tran TN, Mathelin C, Aprahamian
M, Joshi GP, Tomasetto C, Diemunsch P and Akladios C: Antitumor
effects of lidocaine on human breast cancer cells: An in vitro and
in vivo experimental trial. Anticancer Res. 38:95–105. 2018.
|
|
42
|
Le Gac G, Angenard G, Clément B, Laviolle
B, Coulouarn C and Beloeil H: Local anesthetics inhibit the growth
of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anesth Analg.
125:1600–1609. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang L, Hu R, Cheng Y, Wu X, Xi S, Sun Y
and Jiang H: Lidocaine inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer by
regulating the expression of GOLT1A. Cell Prolif. 50:502017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chang YC, Hsu YC, Liu CL, Huang SY, Hu MC
and Cheng SP: Local anesthetics induce apoptosis in human thyroid
cancer cells through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
PLoS One. 9:e895632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu J, Ju YT, Li C, Hua FZ, Xu GH and Hu
YH: Effect of TRPV1 combined with lidocaine on cell state and
apoptosis of U87-MG glioma cell lines. Asian Pac J Trop Med.
9:288–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Martinou JC and Youle RJ: Mitochondria in
apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev
Cell. 21:92–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Werdehausen R, Braun S, Essmann F,
Schulze-Osthoff K, Walczak H, Lipfert P and Stevens MF: Lidocaine
induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway independently of
death receptor signaling. Anesthesiology. 107:136–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li K and Han X: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress is involved in the lidocaine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells. J Mol Neurosci. 56:122–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kawasaki C, Kawasaki T, Ogata M, Sata T
and Chaudry IH: Lidocaine enhances apoptosis and suppresses
mitochondrial functions of human neutrophil in vitro. J Trauma.
68:401–408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kamiya Y, Ohta K and Kaneko Y:
Lidocaine-induced apoptosis and necrosis in U937 cells depending on
its dosage. Biomed Res. 26:231–239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Martinet W, Timmermans JP and De Meyer
GRY: Methods to assess autophagy in situ - transmission electron
microscopy versus immunohistochemistry. Methods Enzymol.
543:89–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Valentin M and Yang E: Autophagy is
activated, but is not required for the G0 function of BCL-2 or
BCL-xL. Cell Cycle. 7:2762–2768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Reyjal J, Cormier K and Turcotte S:
Autophagy and cell death to target cancer cells: Exploiting
synthetic lethality as cancer therapies. Adv Exp Med Biol.
772:167–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Eskelinen EL: The dual role of autophagy
in cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 11:294–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou J, Hu SE, Tan SH, Cao R, Chen Y, Xia
D, Zhu X, Yang XF, Ong CN and Shen HM: Andrographolide sensitizes
cisplatin-induced apoptosis via suppression of
autophagosome-lysosome fusion in human cancer cells. Autophagy.
8:338–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen G, Ke Z, Xu M, Liao M, Wang X, Qi Y,
Zhang T, Frank JA, Bower KA, Shi X, et al: Autophagy is a
protective response to ethanol neurotoxicity. Autophagy.
8:1577–1589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yin Z, Pascual C and Klionsky DJ:
Autophagy: Machinery and regulation. Microb Cell. 3:588–596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Xiong J, Kong Q, Dai L, Ma H, Cao X, Liu L
and Ding Z: Autophagy activated by tuberin/mTOR/p70S6K suppression
is a protective mechanism against local anaesthetics neurotoxicity.
J Cell Mol Med. 21:579–587. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wirawan E, Lippens S, Vanden Berghe T,
Romagnoli A, Fimia GM, Piacentini M and Vandenabeele P: Beclin1: A
role in membrane dynamics and beyond. Autophagy. 8:6–17. 6–17.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Decuypere JP, Parys JB and Bultynck G:
Regulation of the autophagic Bcl-2/Beclin 1 interaction. Cells.
1:284–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Marquez RT and Xu L: Bcl-2:Beclin 1
complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle
switch. Am J Cancer Res. 2:214–221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huang X, Qi Q, Hua X, Li X, Zhang W, Sun
H, Li S, Wang X and Li B: Beclin 1, an autophagy-related gene,
augments apoptosis in U87 glioblastoma cells. Oncol Rep.
31:1761–1767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Du H, Che J, Shi M, Zhu L, Hang JB, Chen Z
and Li H: Beclin 1 expression is associated with the occurrence and
development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
14:6823–6828. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pawlak G and Helfman DM: Cytoskeletal
changes in cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 11:41–47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pegoraro AF, Janmey P and Weitz DA:
Mechanical properties of the cytoskeleton and cells. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 9:a0220382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hall A: The cytoskeleton and cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:5–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pollard TD: The cytoskeleton, cellular
motility and the reductionist agenda. Nature. 422:741–745. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kast DJ and Dominguez R: The
cytoskeleton-autophagy connection. Curr Biol. 27:R318–R326. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kruppa AJ, Kendrick-Jones J and Buss F:
Myosins, actin and autophagy. Traffic. 17:878–890. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Aplin A, Jasionowski T, Tuttle DL, Lenk SE
and Dunn WA Jr: Cytoskeletal elements are required for the
formation and maturation of autophagic vacuoles. J Cell Physiol.
152:458–466. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Aguilera MO, Berón W and Colombo MI: The
actin cytoskeleton participates in the early events of
autophagosome formation upon starvation induced autophagy.
Autophagy. 8:1590–1603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Reggiori F, Monastyrska I, Shintani T and
Klionsky DJ: The actin cytoskeleton is required for selective types
of autophagy, but not nonspecific autophagy, in the yeast
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 16:5843–5856. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Monastyrska I, He C, Geng J, Hoppe AD, Li
Z and Klionsky DJ: Arp2 links autophagic machinery with the actin
cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell. 19:1962–1975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Monastyrska I, Rieter E, Klionsky DJ and
Reggiori F: Multiple roles of the cytoskeleton in autophagy. Biol
Rev Camb Philos Soc. 84:431–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kast DJ, Zajac AL, Holzbaur EL, Ostap EM
and Dominguez R: WHAMM directs the Arp2 3 complex to the ER for
autophagosome biogenesis through an actin comet tail mechanism.
Curr Biol. 25:1791–1797. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mi N, Chen Y, Wang S, Chen M, Zhao M, Yang
G, Ma M, Su Q, Luo S, Shi J, et al: CapZ regulates autophagosomal
membrane shaping by promoting actin assembly inside the isolation
membrane. Nat Cell Biol. 17:1112–1123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Coutts AS and La Thangue NB: Regulation of
actin nucleation and autophagosome formation. Cell Mol Life Sci.
73:3249–3263. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Fehrenbacher K, Huckaba T, Yang HC,
Boldogh I and Pon L: Actin comet tails, endosomes and
endosymbionts. J Exp Biol. 206:1977–1984. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Taunton J, Rowning BA, Coughlin ML, Wu M,
Moon RT, Mitchison TJ and Larabell CA: Actin-dependent propulsion
of endosomes and lysosomes by recruitment of N-WASP. J Cell Biol.
148:519–530. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y, Tang W, Wong
E, Gao YS, Pandey UB, Kaushik S, Tresse E, Lu J, et al: HDAC6
controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective
quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 29:969–980. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mackeh R, Perdiz D, Lorin S, Codogno P and
Poüs C: Autophagy and microtubules - new story, old players. J Cell
Sci. 126:1071–1080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jahreiss L, Menzies FM and Rubinsztein DC:
The itinerary of autophagosomes: From peripheral formation to
kiss-and-run fusion with lysosomes. Traffic. 9:574–587. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kimura S, Noda T and Yoshimori T:
Dynein-dependent movement of autophagosomes mediates efficient
encounters with lysosomes. Cell Struct Funct. 33:109–122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ruangjaroon T, Chokchaichamnankit D,
Srisomsap C, Svasti J and Paricharttanakul NM: Involvement of
vimentin in neurite outgrowth damage induced by fipronil in SH-SY5Y
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:652–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang RC, Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z, Xiao G,
Bhagat G, White M, Reichelt J and Levine B: Akt-mediated regulation
of autophagy and tumorigenesis through Beclin 1 phosphorylation.
Science. 338:956–959. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N,
Zhang M, Han W, Lou F, Yang J, Zhang Q, et al: Autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance: A promising therapeutic target for cancer
treatment. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Redmann M, Benavides GA, Berryhill TF,
Wani WY, Ouyang X, Johnson MS, Ravi S, Barnes S, Darley-Usmar VM
and Zhang J: Inhibition of autophagy with bafilomycin and
chloroquine decreases mitochondrial quality and bioenergetic
function in primary neurons. Redox Biol. 11:73–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yang YP, Hu LF, Zheng HF, Mao CJ, Hu WD,
Xiong KP, Wang F and Liu CF: Application and interpretation of
current autophagy inhibitors and activators. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:625–635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sun WL, Chen J, Wang YP and Zheng H:
Autophagy protects breast cancer cells from epirubicin-induced
apoptosis and facilitates epirubicin-resistance development.
Autophagy. 7:1035–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Liu D, Yang Y, Liu Q and Wang J:
Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA potentiates cisplatin-induced
apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Med Oncol.
28:105–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S and
Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy augments 5-fluorouracil
chemotherapy in human colon cancer in vitro and in vivo model. Eur
J Cancer. 46:1900–1909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|