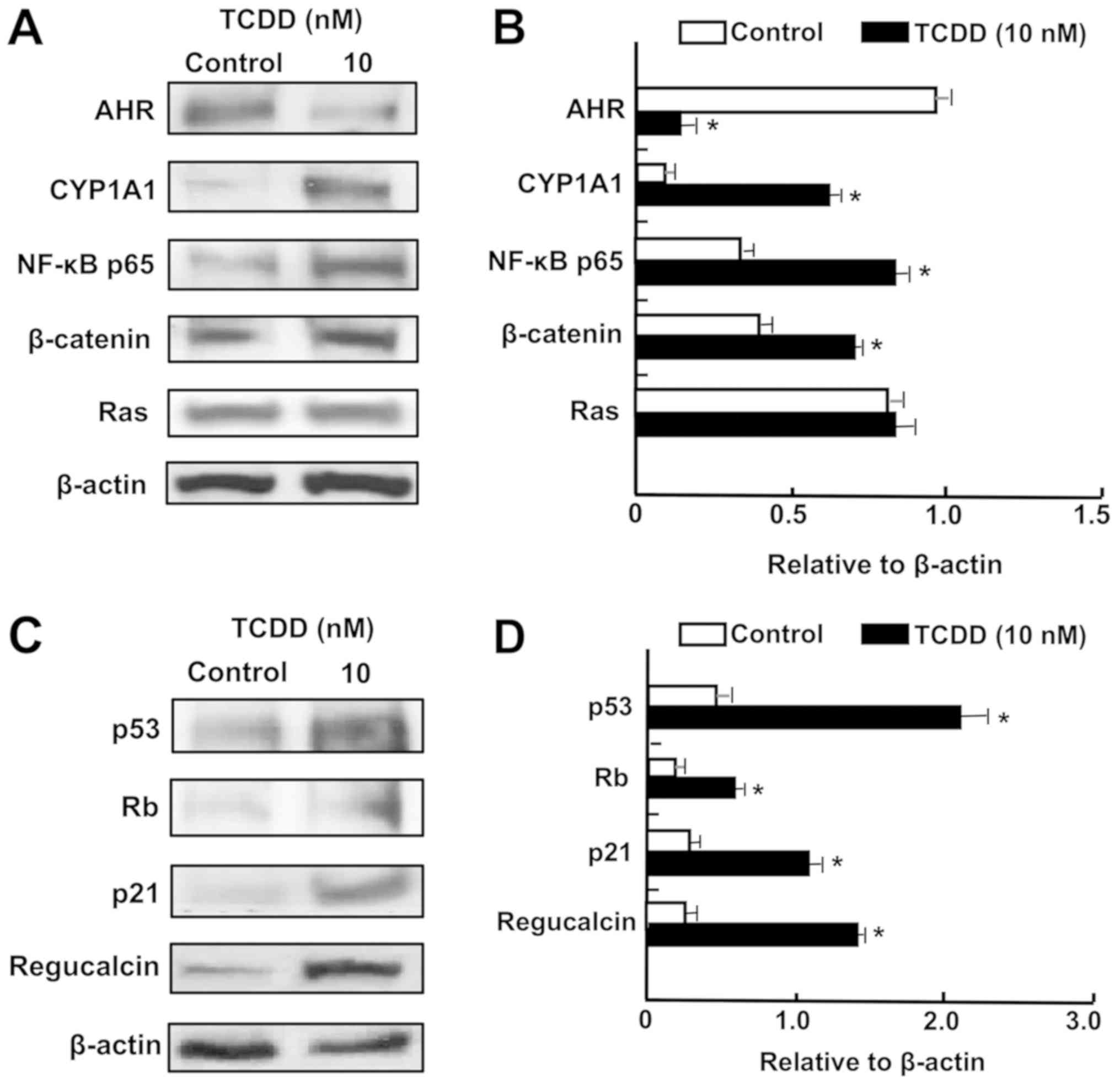
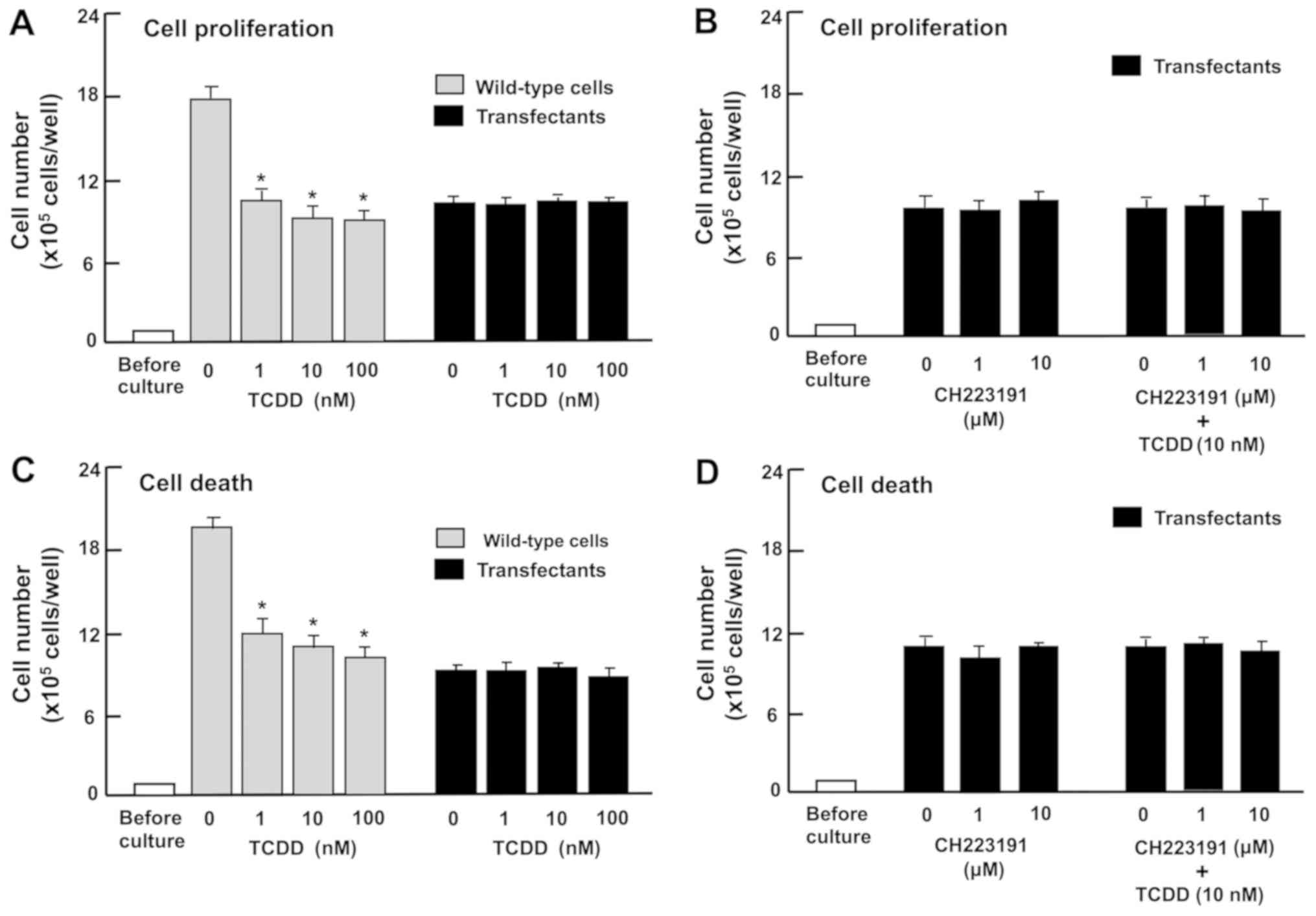
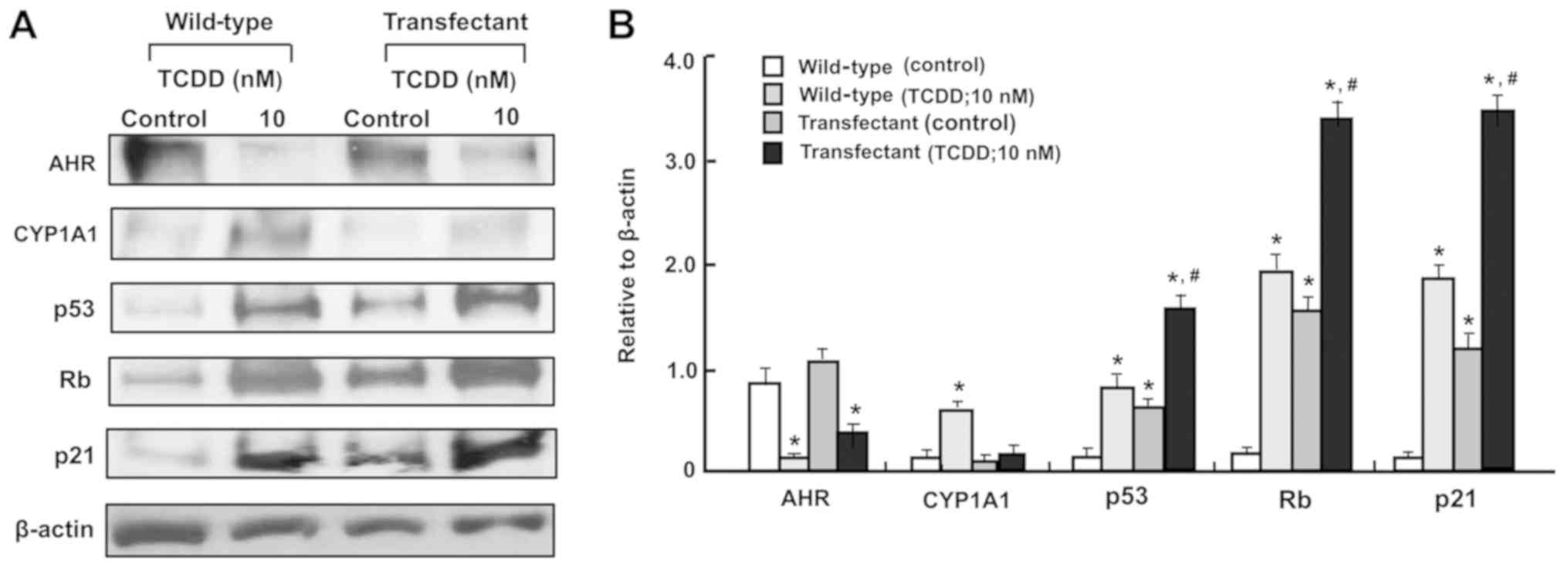
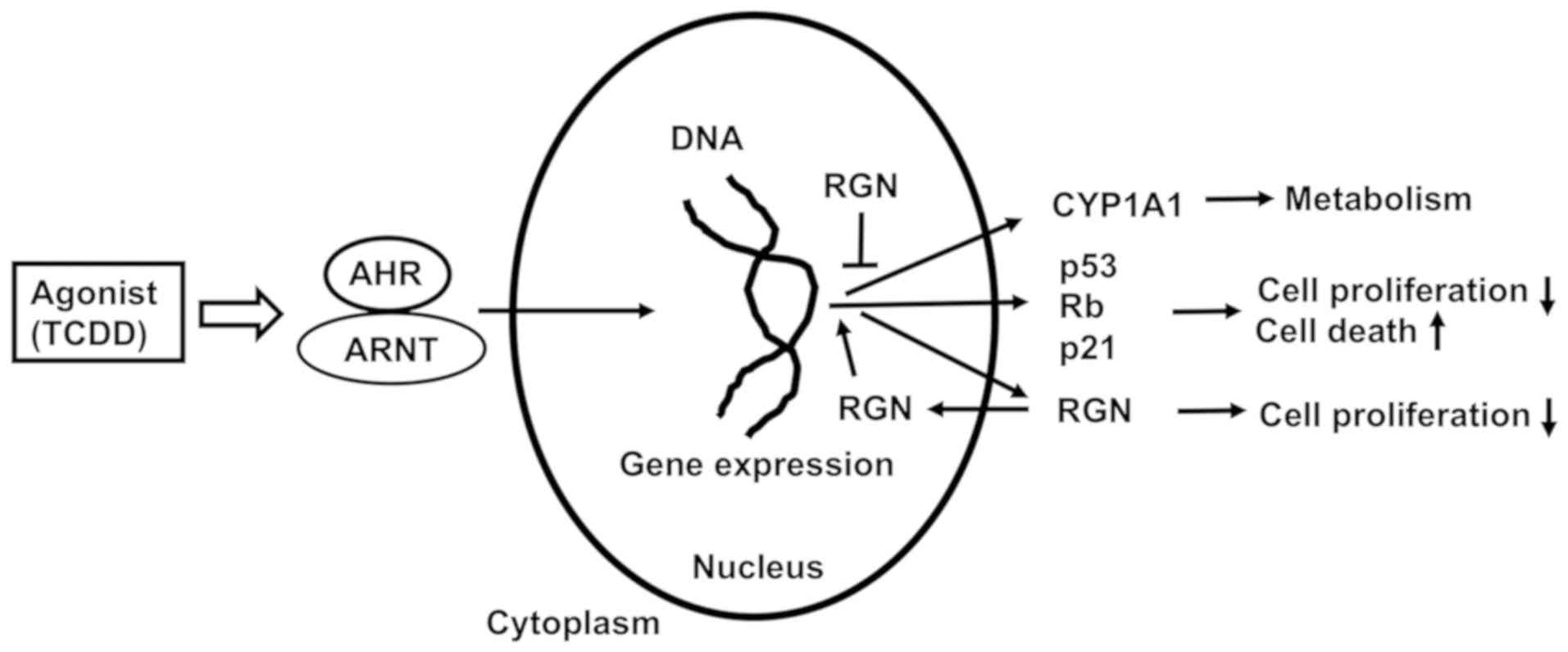
|
1
|
Medema JP and Vermeulen L:
Microenvironmental regulation of stem cells in intestinal
homeostasis and cancer. Nature. 474:318–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Porter MG and Stoeger SM: Atypical
colorectal neoplasms. Surg Clin North Am. 97:641–656. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer facts and
figures 2016. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA: 2016,
https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2016.html.
Accessed January 24, 2017.
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alnabulsi A and Murray GI: Integrative
analysis of the colorectal cancer proteome: Potential clinical
impact. Expert Rev Proteomics. 13:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Alnabulsi A, Swan R, Cash B, Alnabulsi A
and Murray GI: The differential expression of omega-3 and omega-6
fatty acid metabolising enzymes in colorectal cancer and its
prognostic significance. Br J Cancer. 116:1612–1620. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carini F, Mazzola M, Rappa F, Jurjus A,
Geagea AG, Al Kattar S, Bou-Assi T, Jurjus R, Damiani P, Leone A,
et al: Colorectal carcinogenesis: Role of oxidative stress and
antioxidants. Anticancer Res. 37:4759–4766. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Colussi D, Brandi G, Bazzoli F and
Ricciardiello L: Molecular pathways involved in colorectal cancer:
Implications for disease behavior and prevention. Int J Mol Sci.
14:16365–16385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kudryavtseva AV, Lipatova AV, Zaretsky AR,
Moskalev AA, Fedorova MS, Rasskazova AS, Shibukhova GA, Snezhkina
AV, Kaprin AD, Alekseev BY, et al: Important molecular genetic
markers of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:53959–53983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hankinson O: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor
complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 35:307–340. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hankinson O: Role of coactivators in
transcriptional activation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 433:379–386. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Denison MS and Nagy SR: Activation of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and
endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:309–334. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nguyen LP and Bradfield CA: The search for
endogenous activators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Chem Res
Toxicol. 21:102–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Nukaya M, Díaz-Díaz
CJ, Megna BW, Carney PR, Geiger PG and Kennedy GD: Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor-dependent apoptotic cell death induced by the flavonoid
chrysin in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 370:91–99.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Ikuta T, Kurosumi M, Yatsuoka T and
Nishimura Y: Tissue distribution of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
the intestine: Implication of putative roles in tumor suppression.
Exp Cell Res. 343:126–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pastorková B, Vrzalová A, Bachleda P and
Dvořák Z: Hydroxystilbenes and methoxystilbenes activate human aryl
hydrocarbon receptor and induce CYP1A genes in human hepatoma cells
and human hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 103:122–132. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Safe S, Lee SO and Jin UH: Role of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as a drug
target. Toxicol Sci. 135:1–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mulero-Navarro S and Fernandez-Salguero
PM: New trends in aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 4:452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stejskalova L and Pavek P: The function of
cytochrome P450 1A1 enzyme (CYP1A1) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor
(AhR) in the placenta. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:715–730. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nukaya M, Moran S and Bradfield CA: The
role of the dioxin-responsive element cluster between the Cyp1a1
and Cyp1a2 loci in aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:4923–4928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pierre S, Chevallier A, Teixeira-Clerc F,
Ambolet-Camoit A, Bui LC, Bats AS, Fournet JC, Fernandez-Salguero
P, Aggerbeck M, Lotersztajn S, et al: Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor-dependent induction of liver fibrosis by dioxin. Toxicol
Sci. 137:114–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu D, Nishimura N, Kuo V, Fiehn O, Shahbaz
S, Van Winkle L, Matsumura F and Vogel CF: Activation of aryl
hydrocarbon receptor induces vascular inflammation and promotes
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E−/− mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1260–1267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brito JS, Borges NA, Esgalhado M, Magliano
DC, Soulage CO and Mafra D: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in
chronic kidney disease: Role of uremic toxins. Nephron. 137:1–7.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Esser C: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
immunity: Tools and potential. Methods Mol Biol. 1371:239–257.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Murray IA, Patterson AD and Perdew GH:
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat
Rev Cancer. 14:801–814. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Barouki R, Coumoul X and
Fernandez-Salguero PM: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor, more than a
xenobiotic-interacting protein. FEBS Lett. 581:3608–3615. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moennikes O, Loeppen S, Buchmann A,
Andersson P, Ittrich C, Poellinger L and Schwarz M: A
constitutively active dioxin/aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes
hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 64:4707–4710. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan Y, Boivin GP, Knudsen ES, Nebert DW,
Xia Y and Puga A: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor functions as a
tumor suppressor of liver carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 70:212–220.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mathew LK, Simonich MT and Tanguay RL:
AHR-dependent misregulation of Wnt signaling disrupts tissue
regeneration. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:498–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Jackson DP, Li H, Mitchell KA, Joshi AD
and Elferink CJ: Ah receptor-mediated suppression of liver
regeneration through NC-XRE-driven p21Cip1 expression.
Mol Pharmacol. 85:533–541. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamaguchi M and Hankinson O:
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo- p-dioxin suppresses the growth of human
liver cancer HepG2 cells in vitro: Involvement of cell signaling
factors. Int J Oncol. 53:1657–1666. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harper PA, Prokipcak RD, Bush LE, Golas CL
and Okey AB: Detection and characterization of the Ah receptor for
2,3,7,8-tetra-chlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the human colon
adenocarcinoma cell line LS180. Arch Biochem Biophys. 290:27–36.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Megna BW, Carney PR, Nukaya M, Geiger P
and Kennedy GD: Indole-3-carbinol induces tumor cell death:
Function follows form. J Surg Res. 204:47–54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Megna BW, Carney PR, Depke MG, Nukaya M,
McNally J, Larsen L, Rosengren RJ and Kennedy GD: The aryl
hydrocarbon receptor as an antitumor target of synthetic
curcuminoids in colorectal cancer. J Surg Res. 213:16–24. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wohak LE, Krais AM, Kucab JE, Stertmann J,
Øvrebø S, Seidel A, Phillips DH and Arlt VM: Carcinogenic
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce CYP1A1 in human cells via a
p53-dependent mechanism. Arch Toxicol. 90:291–304. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Li W, Harper PA, Tang BK and Okey AB:
Regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes by aryl hydrocarbon receptor
in human cells: CYP1A2 expression in the LS180 colon carcinoma cell
line after treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or
3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 56:599–612. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xie G and Raufman J-P: Role of the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in colon neoplasia. Cancers (Basel). 7. pp.
1436–1446. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kawajiri K, Kobayashi Y, Ohtake F, Ikuta
T, Matsushima Y, Mimura J, Pettersson S, Pollenz RS, Sakaki T,
Hirokawa T, et al: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor suppresses intestinal
carcinogenesis in ApcMin/+ mice with natural ligands.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13481–13486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fang Z, Tang Y, Fang J, Zhou Z, Xing Z,
Guo Z, Guo X, Wang W, Jiao W, Xu Z and Liu Z: Simvastatin inhibits
renal cancer cell growth and metastasis via AKT/mTOR, ERK and
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 8:e628232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang K, Li Y, Jiang YZ, Dai CF, Patankar
MS, Song JS and Zheng J: An endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor
ligand inhibits proliferation and migration of human ovarian cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 340:63–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Misawa H, Inagaki S and Yamaguchi M:
Suppression of cell proliferation and deoxyribonucleic acid
synthesis in the cloned rat hepatoma H4-II-E cells overexpressing
regucalcin. J Cell Biochem. 84:143–149. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S and Murata T:
Prolonged survival of patients with colorectal cancer is associated
with a higher regucalcin gene expression: Overexpression of
regucalcin suppresses the growth of human colorectal carcinoma
cells in vitro. Int J Oncol. 53:1313–1322. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamaguchi M and Daimon Y: Overexpression
of regucalcin suppresses cell proliferation in cloned rat hepatoma
H4-II-E cells: Involvement of intracellular signaling factors and
cell cycle-related genes. J Cell Biochem. 95:1169–1177. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Izumi T and Yamaguchi M: Overexpression of
regucalcin suppresses cell death in cloned rat hepatoma H4-II-E
cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha or thapsigargin. J
Cell Biochem. 92:296–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yamaguchi M and Isogai M: Tissue
concentration of calcium-binding protein regucalcin in rats by
enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem. 122:65–68.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Choi E-Y, Lee H, Dingle RWC, Kim KB and
Swanson HI: Development of novel CH223191-based antagonists of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 81:3–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Tsurusaki Y and Yamaguchi M: Role of
regucalcin in liver nuclear function: Binding of regucalcin to
nuclear protein or DNA and modulation of tumor-related gene
expression. Int J Mol Med. 14:277–281. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamaguchi M: Suppressive role of
regucalcin in liver cell proliferation: Involvement in
carcinogenesis. Cell Prolif. 46:243–253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Weitzmann MN,
El-Rayes BF, Shoji M and Murata T: Prolonged survival in pancreatic
cancer patients with increased regucalcin gene expression:
Overexpression of regucalcin suppresses the proliferation in human
pancreatic cancer MIA PaCa-2 cells in vitro. Int J Oncol.
48:1955–1964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamaguchi M, Osuka S, Weitzmann MN,
El-Rayes BF, Shoji M and Murata T: Prolonged survival in
hepatocarcinoma patients with increased regucalcin gene expression:
HepG2 cell proliferation is suppressed by overexpression of
regucalcin in vitro. Int J Oncol. 49:1686–1694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nejak-Bowen KN, Zeng G, Tan X, Cieply B
and Monga SP: Beta-catenin regulates vitamin C biosynthesis and
cell survival in murine liver. J Biol Chem. 284:28115–28127. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kochhar A, Kopelovich L, Sue E, Guttenplan
JB, Herbert BS, Dannenberg AJ and Subbaramaiah K: p53 modulates
Hsp90 ATPase activity and regulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor
signaling. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 7:596–606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yamaguchi M: Role of regucalcin in cell
nuclear regulation: Involvement as a transcription factor. Cell
Tissue Res. 354:331–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|