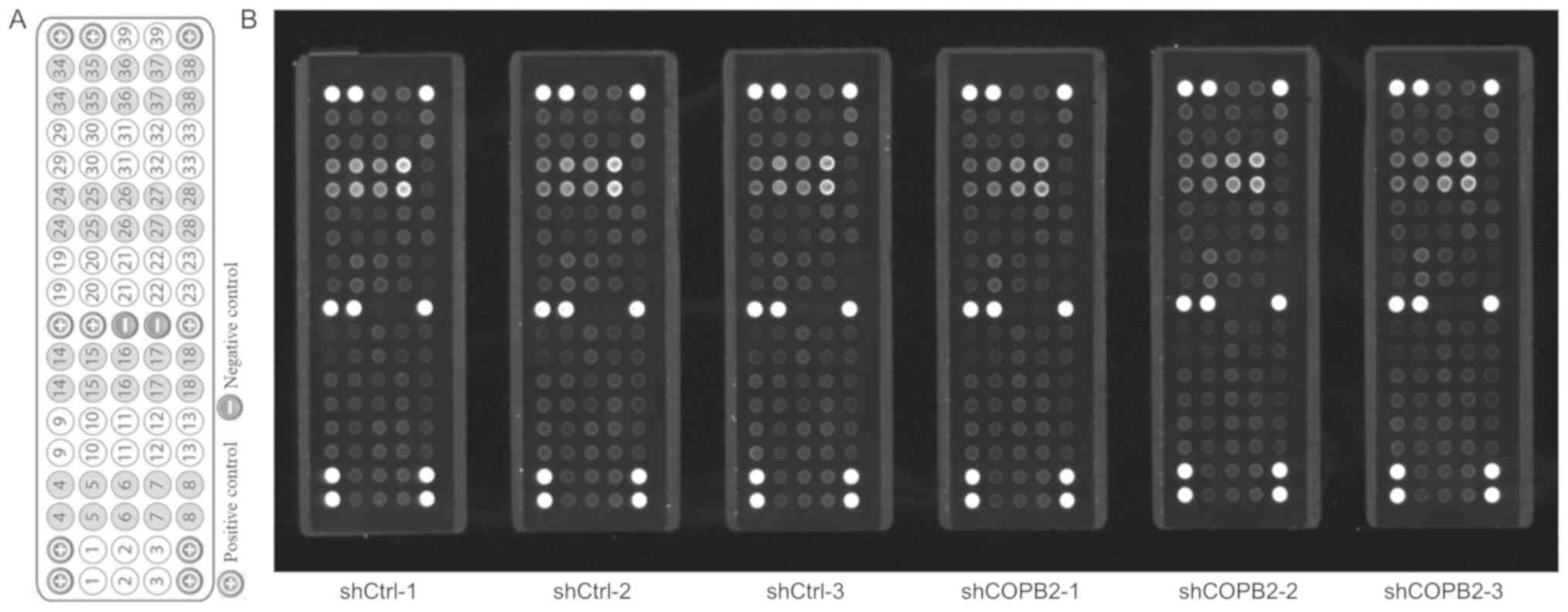
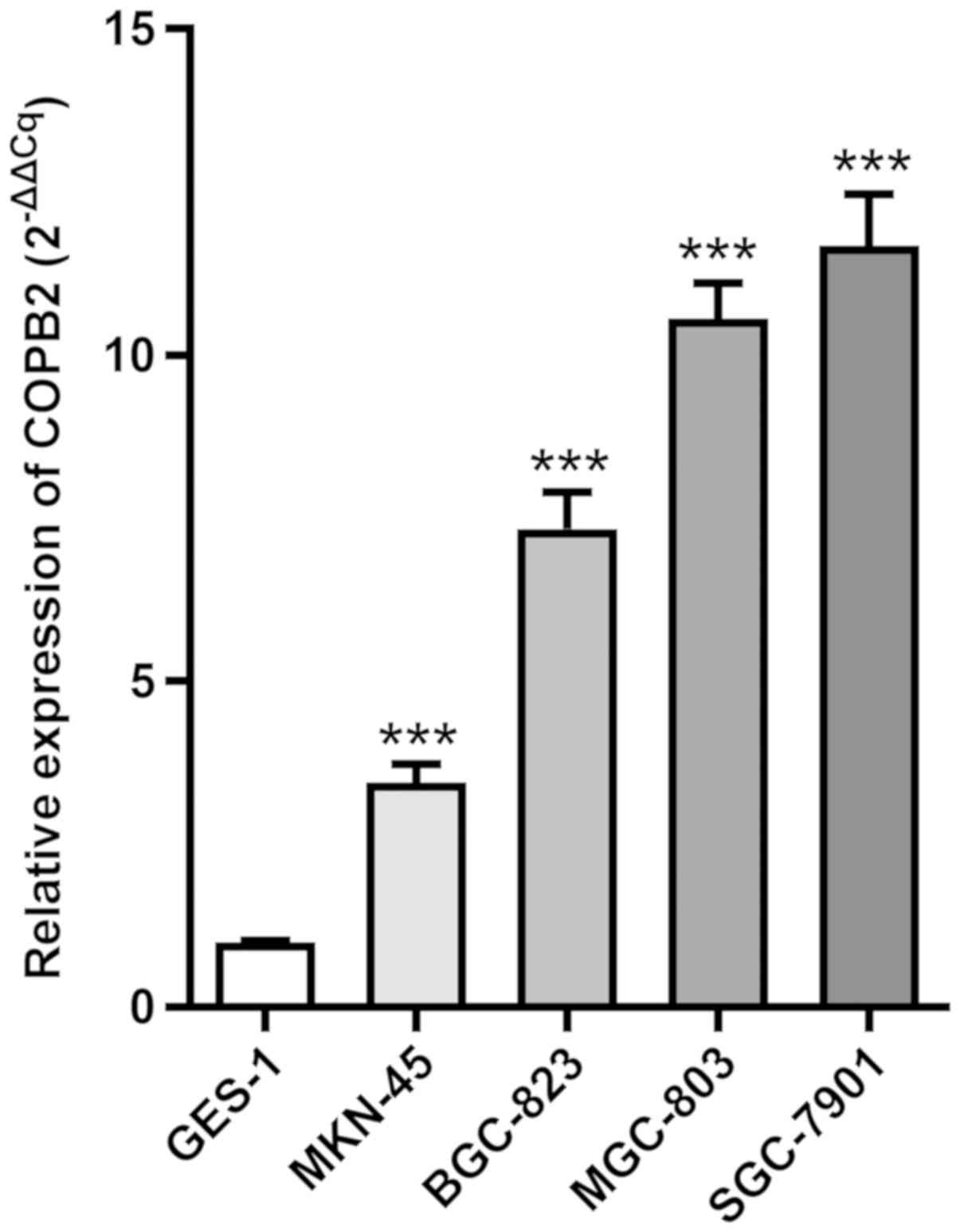
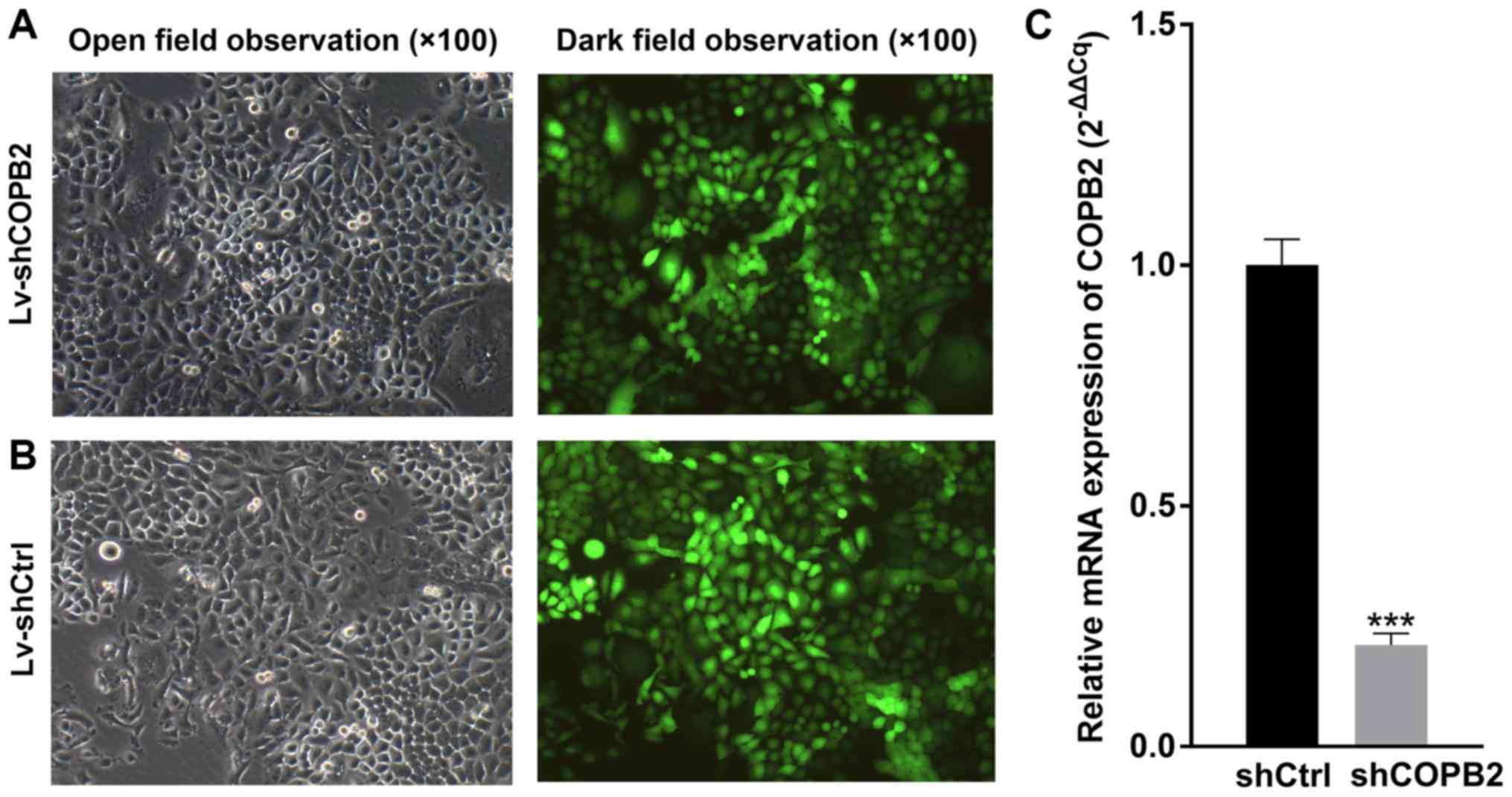
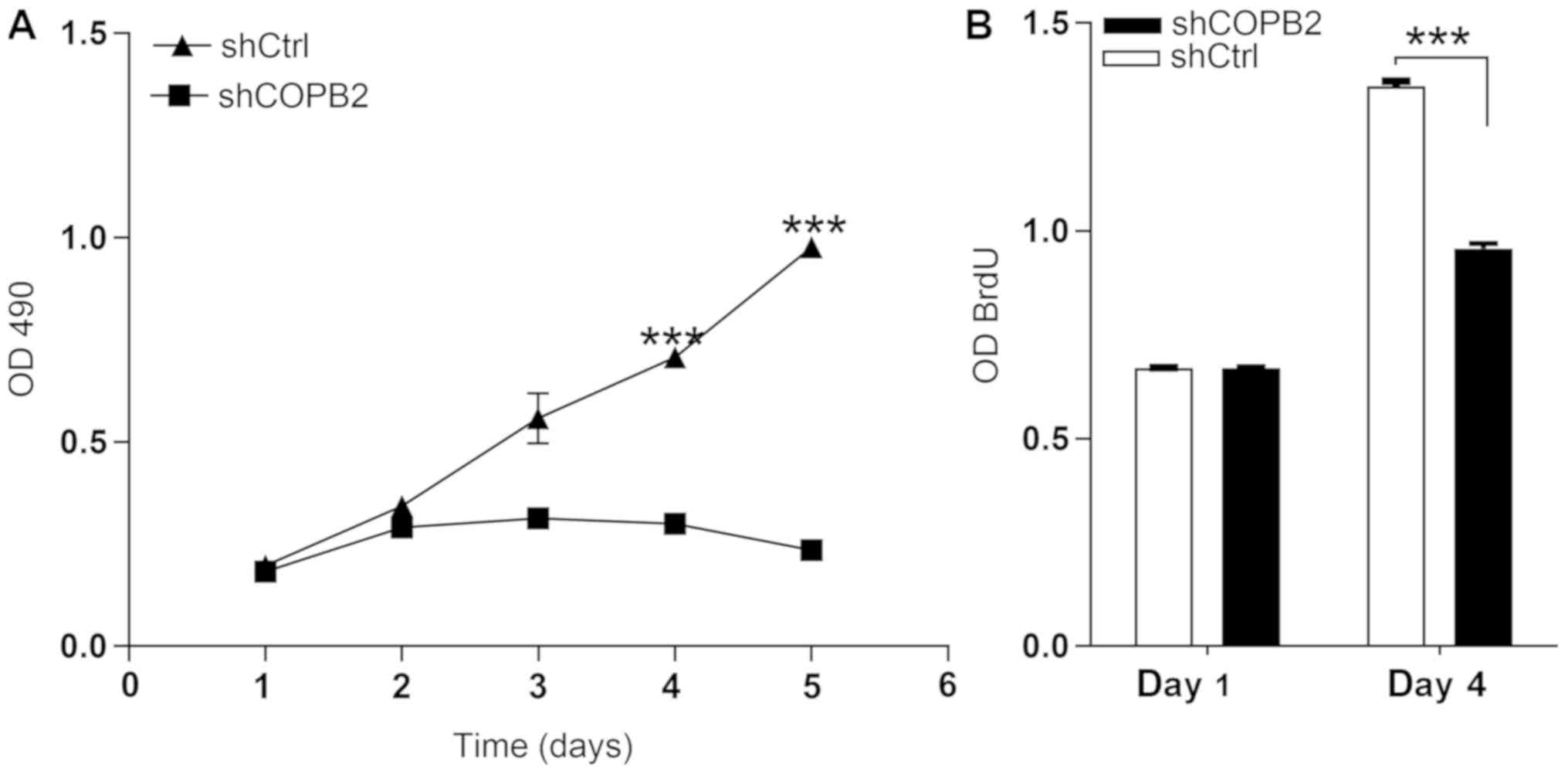
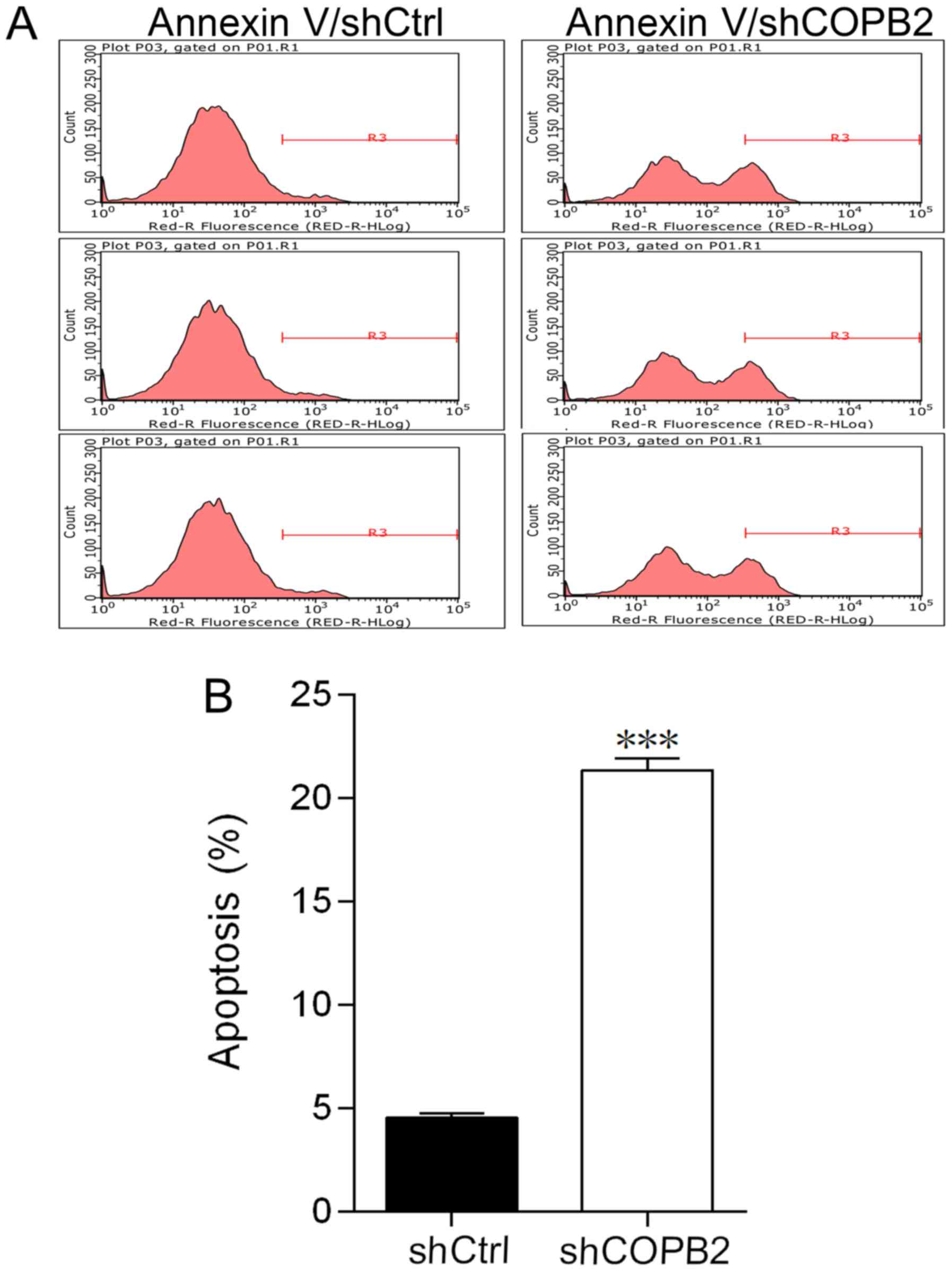
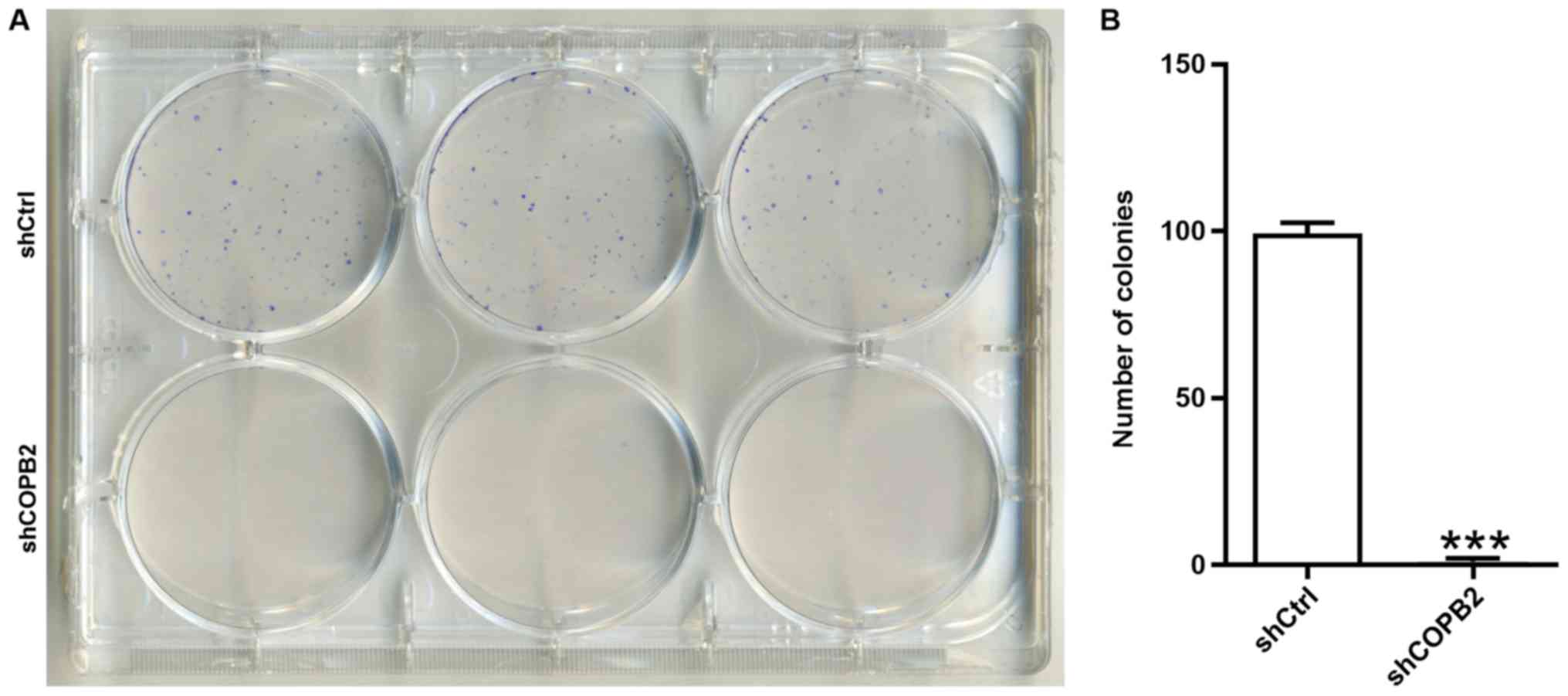
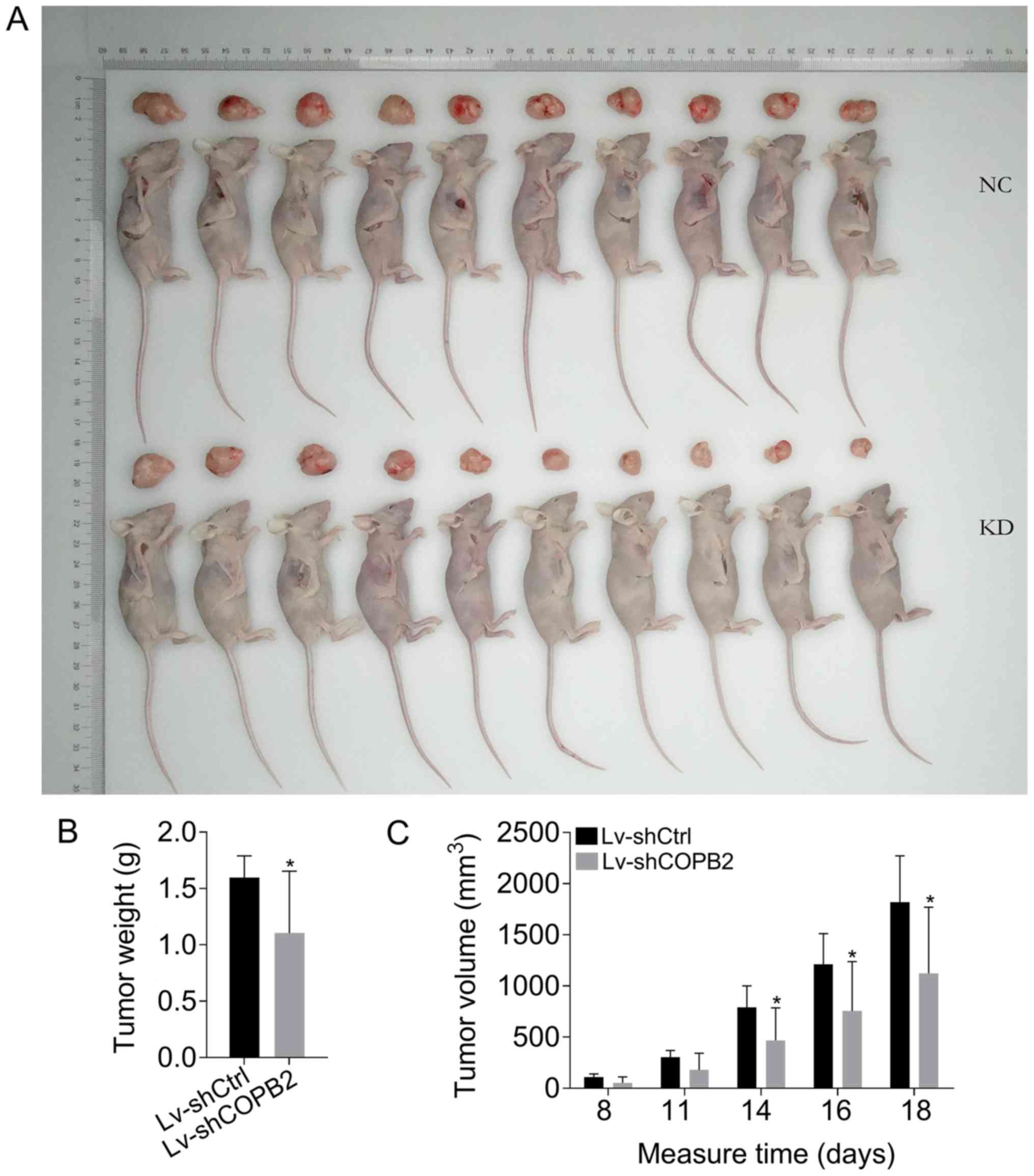
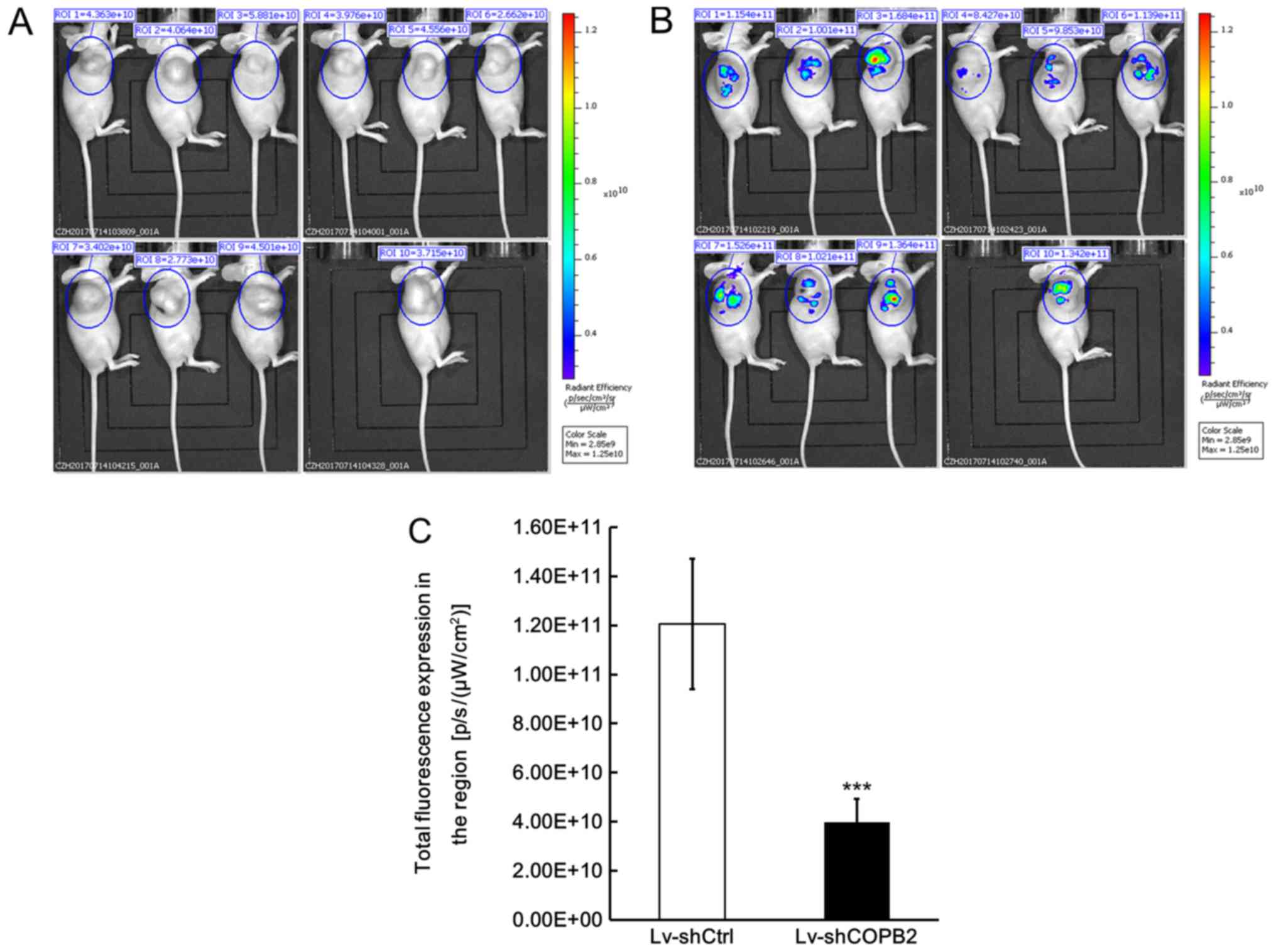
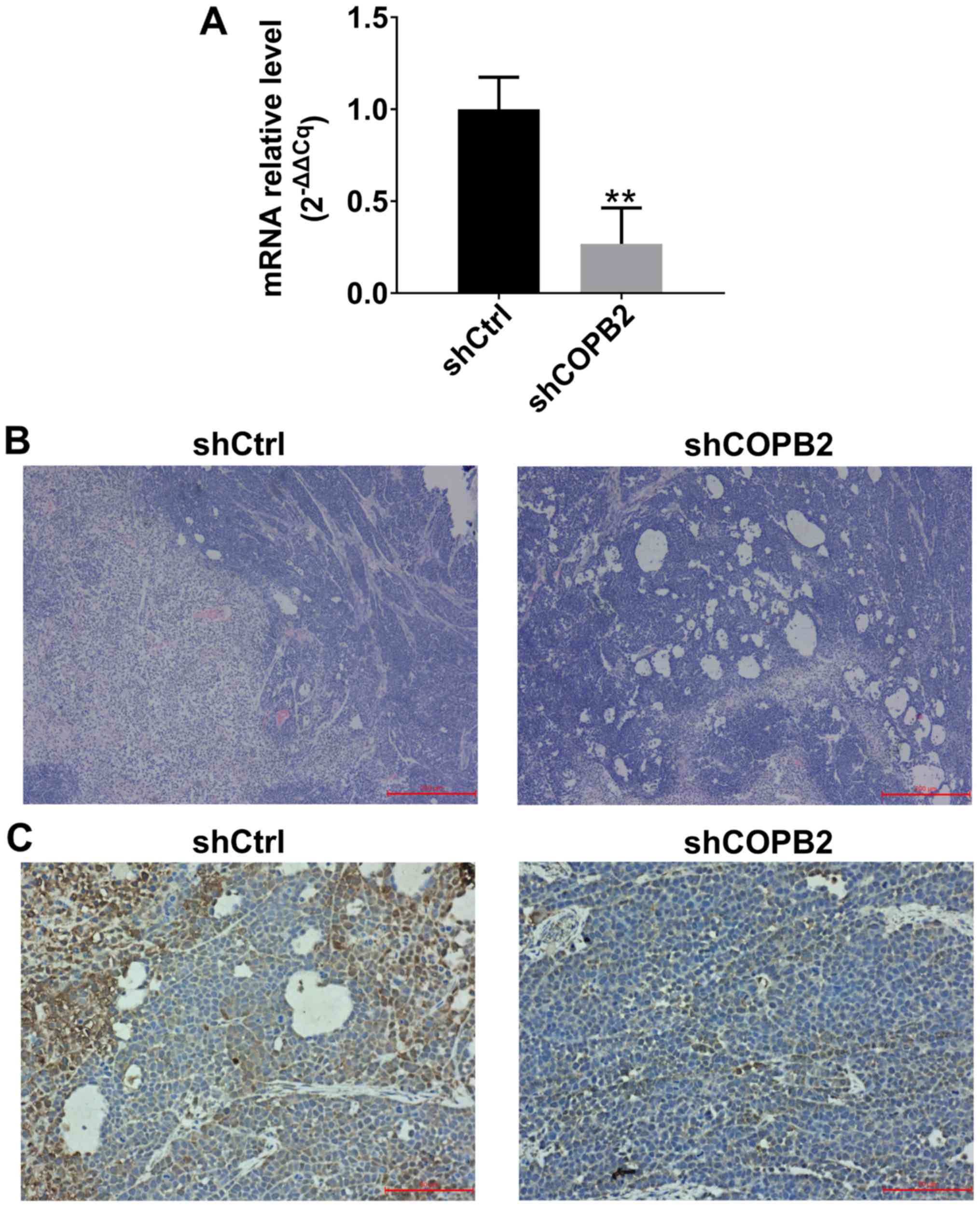
|
1
|
Yang BH, Parkin DM, Cai L and Zhang ZF:
Cancer burden and trends in the Asian Pacific Rim region. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 5:96–117. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and Chen W:
Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin J
Cancer. 36:662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jim MA, Pinheiro PS, Carreira H, Espey DK,
Wiggins CL and Weir HK: Stomach cancer survival in the United
States by race and stage (2001–2009): Findings from the CONCORD-2
study. Cancer. 123(Suppl 24): 4994–5013. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Beck R, Rawet M, Wieland FT and Cassel D:
The COPI system: Molecular mechanisms and function. FEBS Lett.
583:2701–2709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mi Y, Yu M, Zhang L, Sun C, Wei B, Ding W,
Zhu Y, Tang J, Xia G and Zhu L: COPB2 is upregulated in prostate
cancer and regulates PC-3 cell proliferation, cell cycle, and
apoptosis. Arch Med Res. 47:411–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Erdogan E, Klee EW, Thompson EA and Fields
AP: Meta-analysis of oncogenic protein kinase Ciota signaling in
lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1527–1533. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Chai Z, Wang M, Jin Y, Yang A and
Li M: COPB2 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle
arrest in human colon cancer by regulating cell cycle-related
proteins. Exp Ther Med. 15:777–784. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Committee for the Update of the Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, Institute for Laboratory
Animal Research, Division on Earth and Life Studies, National
Research Council of The National Academies: Guide For The Care And
Use Of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. The National Academies
Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
10
|
Schuster C, Malinowsky K, Liebmann S, Berg
D, Wolff C, Tran K, Schott C, Reu S, Neumann J, Faber C, et al:
Antibody validation by combining immunohistochemistry and protein
extraction from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues.
Histopathology. 60(6B): E37–E50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Yu S, Cui L, Wang W, Li J, Wang K
and Lao X: Role of SMC1A overexpression as a predictor of poor
prognosis in late stage colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:902015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song S, Rosen KM and Corfas G: Biological
function of nuclear receptor tyrosine kinase action. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 5:52013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bennasroune A, Gardin A, Aunis D, Crémel G
and Hubert P: Tyrosine kinase receptors as attractive targets of
cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 50:23–38. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choura M and Rebaï A: Receptor tyrosine
kinases: From biology to pathology. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
31:387–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pytel D, Sliwinski T, Poplawski T,
Ferriola D and Majsterek I: Tyrosine kinase blockers: New hope for
successful cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 9:66–76.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cripps C, Winquist E, Devries MC,
Stys-Norman D and Gilbert R; Head and Neck Cancer Disease Site
Group: Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy in stages
III and IV head and neck cancer. Curr Oncol. 17:37–48. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qing L and Qing W: Development of
epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy in pancreatic
cancer. Minerva Chir. 73:488–496. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tiseo M, Loprevite M and Ardizzoni A:
Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: A new prospective in
the treatment of lung cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
4:139–148. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bellmunt J, Hussain M and Dinney CP: Novel
approaches with targeted therapies in bladder cancer. Therapy of
bladder cancer by blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor
family. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 46(Suppl): S85–S104. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye Y, Jiang D, Li J, Wang M, Han C, Zhang
X, Zhao C, Wen J and Kan Q: Silencing of FGFR4 could influence the
biological features of gastric cancer cells and its therapeutic
value in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:3185–3195. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ireton RC and Chen J: EphA2 receptor
tyrosine kinase as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 5:149–157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Durrant DE and Morrison DK: Targeting the
Raf kinases in human cancer: The Raf dimer dilemma. Br J Cancer.
118:3–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Nikitakis NG, Siavash H and Sauk JJ:
Targeting the STAT pathway in head and neck cancer: Recent advances
and future prospects. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:637–651. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Turkson J and Jove R: STAT proteins: Novel
molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene.
19:6613–6626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Heidegger I, Kern J, Ofer P, Klocker H and
Massoner P: Oncogenic functions of IGF1R and INSR in prostate
cancer include enhanced tumor growth, cell migration and
angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 5:2723–2735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ofer P, Heidegger I, Eder IE, Schöpf B,
Neuwirt H, Geley S, Klocker H and Massoner P: Both IGF1R and INSR
knockdown exert antitumorigenic effects in prostate cancer in vitro
and in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 29:1694–1707. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Ji D, Wang C, Liu R, Wu
Z, Liu L, Zhu D, Chang J, Geng R, et al: Functional genetic
approach identifies MET, HER3, IGF1R, INSR pathways as determinants
of lapatinib unresponsiveness in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:4559–4573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kamiya A, Inokuchi M, Otsuki S, Sugita H,
Kato K, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Takagi Y and Kojima K: Prognostic
value of tropomyosin-related kinases A, B, and C in gastric cancer.
Clin Transl Oncol. 18:599–607. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim MS, Suh KW, Hong S and Jin W: TrkC
promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget.
8:41319–41333. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meldolesi J: Neurotrophin Trk receptors:
New targets for cancer therapy. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol.
174:67–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang SY, Nguyen TT, Ung TT and Jung YD:
Role of recepteur d'origine nantais on gastric cancer development
and progression. Chonnam Med J. 53:178–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Song YA, Park YL, Kim KY, Myung E, Chung
CY, Cho SB, Lee WS, Jung YD, Kweon SS and Joo YE: RON is associated
with tumor progression via the inhibition of apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest in human gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 62:127–136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Richardson DS, Lai AZ and Mulligan LM: RET
ligand-induced internalization and its consequences for downstream
signaling. Oncogene. 25:3206–3211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Plaza-Menacho I, Mologni L and McDonald
NQ: Mechanisms of RET signaling in cancer: Current and future
implications for targeted therapy. Cell Signal. 26:1743–1752. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ali S and Ali S: Role of c-kit/SCF in
cause and treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST).
Gene. 401:38–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fletcher JA: KIT oncogenic mutations:
Biologic insights, therapeutic advances, and future directions.
Cancer Res. 76:6140–6142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kiyoi H and Naoe T: Biology, clinical
relevance, and molecularly targeted therapy in acute leukemia with
FLT3 mutation. Int J Hematol. 83:301–308. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schmidt-Arras D, Schwäble J, Böhmer FD and
Serve H: Flt3 receptor tyrosine kinase as a drug target in
leukemia. Curr Pharm Des. 10:1867–1883. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He Y, Sun L, Xu Y, Fu L, Li Y, Bao X, Fu
H, Xie C and Lou L: Combined inhibition of PI3Kδ and FLT3 signaling
exerts synergistic antitumor activity and overcomes acquired drug
resistance in FLT3-activated acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Lett.
420:49–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Charmsaz S and Boyd AW: Eph receptors as
oncotargets. Oncotarget. 8:81727–81728. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bhatia S, Baig NA, Timofeeva O, Pasquale
EB, Hirsch K, MacDonald TJ, Dritschilo A, Lee YC, Henkemeyer M,
Rood B, et al: Knockdown of EphB1 receptor decreases
medul-loblastoma cell growth and migration and increases cellular
radiosensitization. Oncotarget. 6:8929–8946. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nasreen N, Mohammed KA and Antony VB:
Silencing the receptor EphA2 suppresses the growth and haptotaxis
of malignant mesothelioma cells. Cancer. 107:2425–2435. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yuan W, Chen Z, Chen Z, Wu S, Guo J, Ge J,
Yang P and Huang J: Silencing of EphA2 inhibits invasion of human
gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells in vitro and in vivo. Neoplasma.
59:105–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Becerikli M, Merwart B, Lam MC, Suppelna
P, Rittig A, Mirmohammedsadegh A, Stricker I, Theiss C, Singer BB,
Jacobsen F, et al: EPHB4 tyrosine-kinase receptor expression and
biological significance in soft tissue sarcoma. Int J Cancer.
136:1781–1791. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Katoh M: Therapeutics targeting FGF
signaling network in human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
37:1081–1096. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chien CW, Hou PC, Wu HC, Chang YL, Lin SC,
Lin SC, Lin BW, Lee JC, Chang YJ, Sun HS, et al: Targeting TYRO3
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases drug
sensitivity in colon cancer. Oncogene. 35:5872–5881. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schmitz R, Valls AF, Yerbes R, von Richter
S, Kahlert C, Loges S, Weitz J, Schneider M, Ruiz de Almodovar C,
Ulrich A, et al: TAM receptors Tyro3 and Mer as novel targets in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:56355–56370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Duan Y, Wong W, Chua SC, Wee HL, Lim SG,
Chua BT and Ho HK: Overexpression of Tyro3 and its implications on
hepato-cellular carcinoma progression. Int J Oncol. 48:358–366.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ekyalongo RC, Mukohara T, Funakoshi Y,
Tomioka H, Kataoka Y, Shimono Y, Chayahara N, Toyoda M, Kiyota N
and Minami H: TYRO3 as a potential therapeutic target in breast
cancer. Anticancer Res. 34:3337–3345. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling and redox metabolism in
cancer. Front Oncol. 8:1602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Faes S and Dormond O: PI3K and AKT:
Unfaithful partners in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21138–21152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sasaki T, Kuniyasu H, Luo Y, Kitayoshi M,
Tanabe E, Kato D, Shinya S, Fujii K, Ohmori H and Yamashita Y: AKT
activation and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression are
concurrently associated with prognosis of gastric cancer.
Pathobiology. 81:36–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhou Y, Yamada N, Tanaka T, Hori T,
Yokoyama S, Hayakawa Y, Yano S, Fukuoka J, Koizumi K, Saiki I, et
al: Crucial roles of RSK in cell motility by catalysing serine
phosphorylation of EphA2. Nat Commun. 6:76792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hamaoka Y, Negishi M and Katoh H: EphA2 is
a key effector of the MEK/ERK/RSK pathway regulating glioblastoma
cell proliferation. Cell Signal. 28:937–945. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ma Q, Guin S, Padhye SS, Zhou YQ, Zhang RW
and Wang MH: Ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RSK)-2 as a central
effector molecule in RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediated
epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by
macrophage-stimulating protein. Mol Cancer. 10:662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Srinivasan D, Kaetzel DM and Plattner R:
Reciprocal regulation of Abl and receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell
Signal. 21:1143–1150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yezhelyev MV, Koehl G, Guba M, Brabletz T,
Jauch KW, Ryan A, Barge A, Green T, Fennell M and Bruns CJ:
Inhibition of SRC tyrosine kinase as treatment for human pancreatic
cancer growing orthotopically in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res.
10:8028–8036. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bieerkehazhi S, Chen Z, Zhao Y, Yu Y,
Zhang H, Vasudevan SA, Woodfield SE, Tao L, Yi JS, Muscal JA, et
al: Novel Src/Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor bosutinib suppresses
neuroblastoma growth via inhibiting Src/Abl signaling. Oncotarget.
8:1469–1480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Kong L, Deng Z, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Sarkar FH
and Zhang Y: Down-regulation of phospho-non-receptor Src tyrosine
kinases contributes to growth inhibition of cervical cancer cells.
Med Oncol. 28:1495–1506. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Harr MW, Caimi PF, McColl KS, Zhong F,
Patel SN, Barr PM and Distelhorst CW: Inhibition of Lck enhances
glucocorticoid sensitivity and apoptosis in lymphoid cell lines and
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell Death Differ. 17:1381–1391.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim MJ, Park MT, Yoon CH, Byun JY and Lee
SJ: Activation of Lck is critically required for
sphingosine-induced conformational activation of Bak and
mitochondrial cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 370:353–358.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, Marusawa H,
Kanai M, Nakajima T, Kawashima T, Nanakin A, Sawabu T, Uenoyama Y,
et al: STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival
in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells.
Oncogene. 23:4921–4929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Murone M, Vaslin Chessex A, Attinger A,
Ramachandra R, Shetty SJ, Daginakatte G, Sengupta S, Marappan S,
Dhodheri S, Rigotti S, et al: Debio 0617B inhibits growth of
STAT3-driven solid tumors through combined inhibition of JAK, SRC,
and class III/V receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:2334–2343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Leong PL, Andrews GA, Johnson DE, Dyer KF,
Xi S, Mai JC, Robbins PD, Gadiparthi S, Burke NA, Watkins SF, et
al: Targeted inhibition of Stat3 with a decoy oligonucleotide
abrogates head and neck cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:4138–4143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gu J, Li G, Sun T, Su Y, Zhang X, Shen J,
Tian Z and Zhang J: Blockage of the STAT3 signaling pathway with a
decoy oligo-nucleotide suppresses growth of human malignant glioma
cells. J Neurooncol. 89:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J,
Ahmad N, Garcia R, Bowman T, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Cantor A, et
al: Constitutive activation of Stat3 in human prostate tumors and
cell lines: Direct inhibition of Stat3 signaling induces apoptosis
of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:6659–6666. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kim C, Kim JH, Oh EY, Nam D, Lee SG, Lee
J, Kim SH, Shim BS and Ahn KS: Blockage of STAT3 signaling pathway
by morusin induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion in human
pancreatic tumor cells. Pancreas. 45:409–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sun Y, Guo BF, Xu LB, Zhong JT, Liu ZW,
Liang H, Wen NY, Yun WJ, Zhang L and Zhao XJ: Stat3-siRNA inhibits
the growth of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cell Biochem
Funct. 33:495–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|