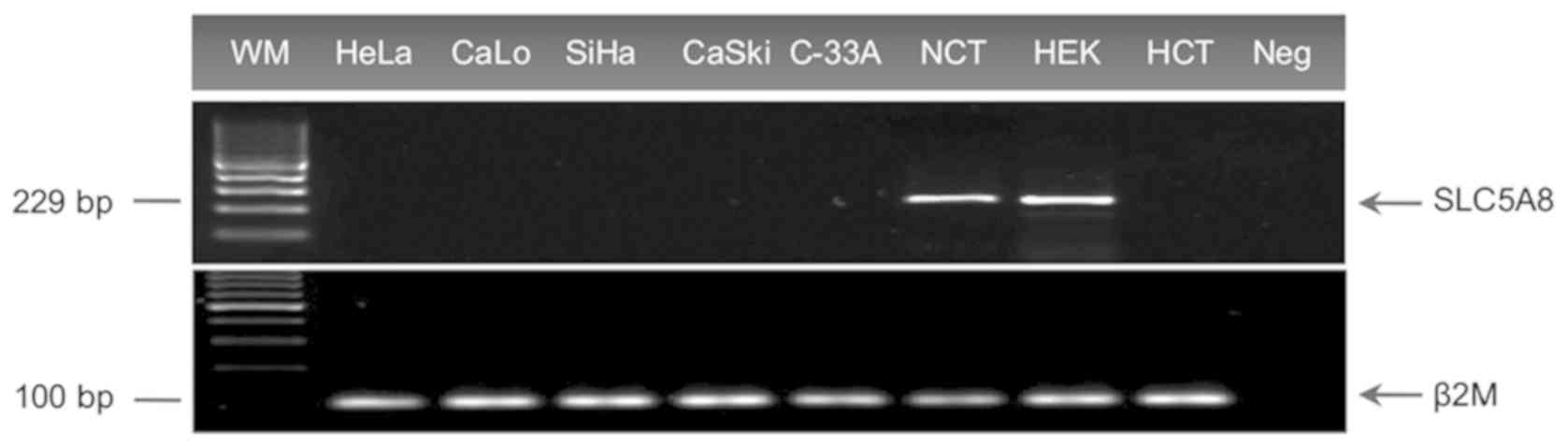
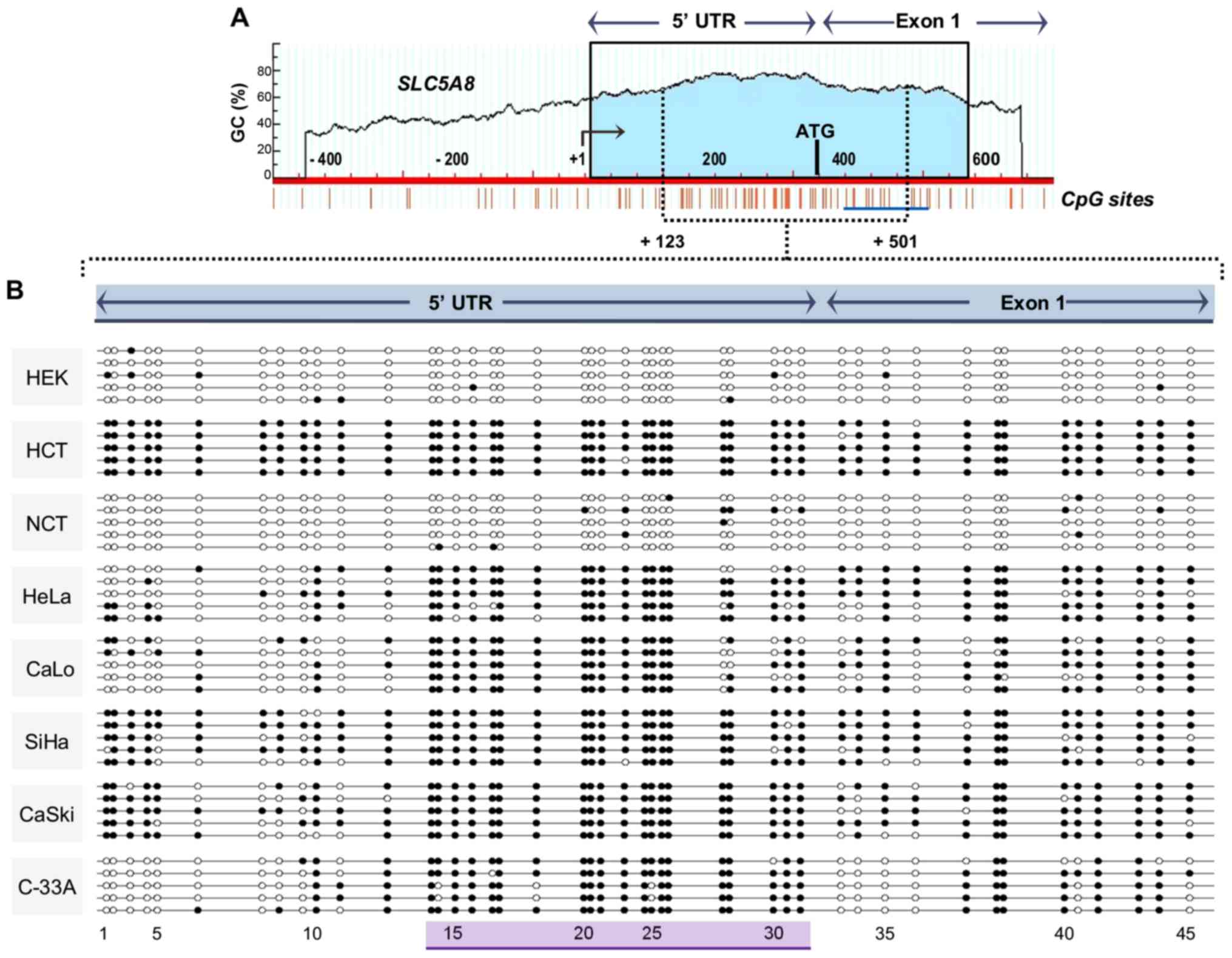
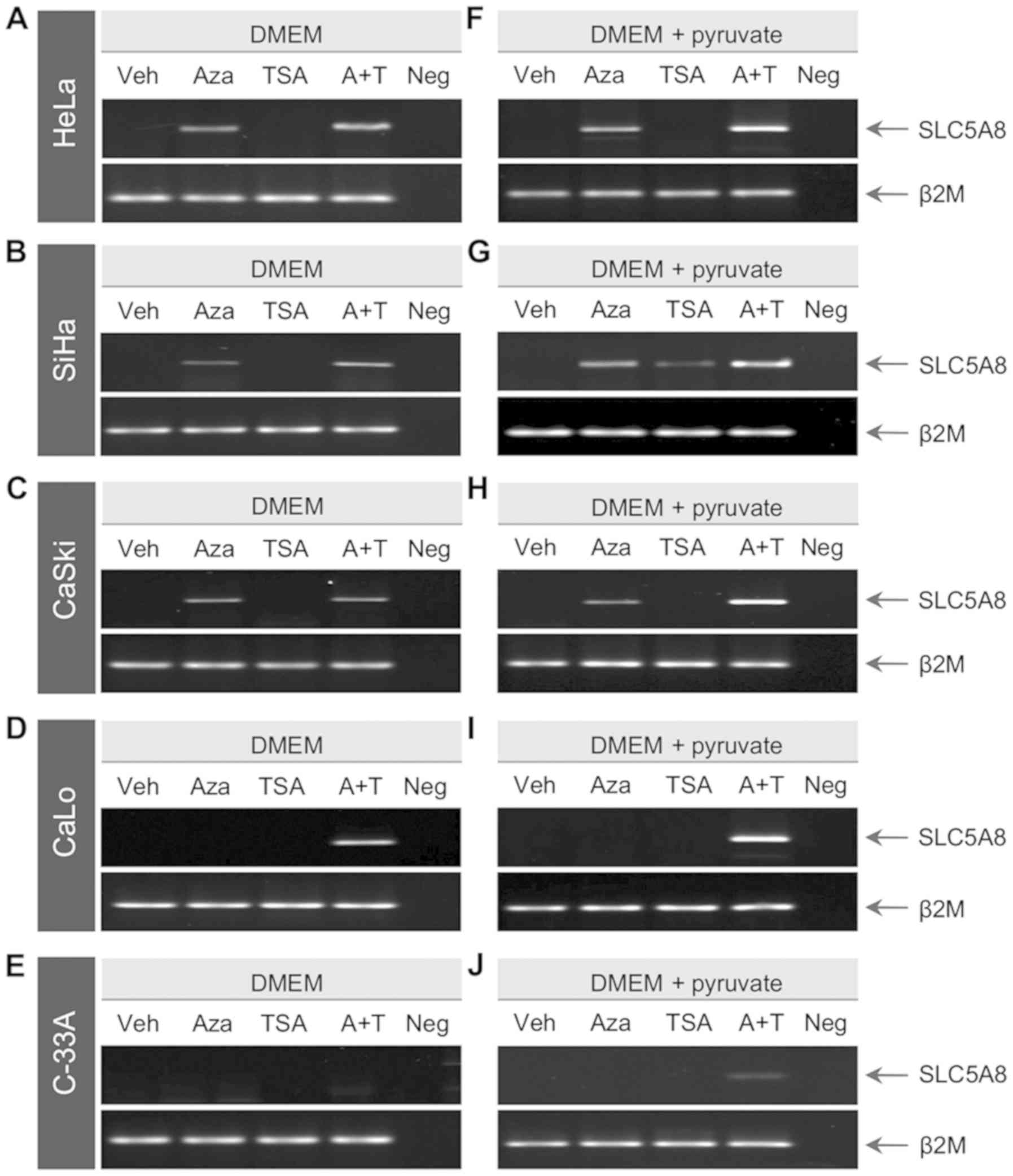
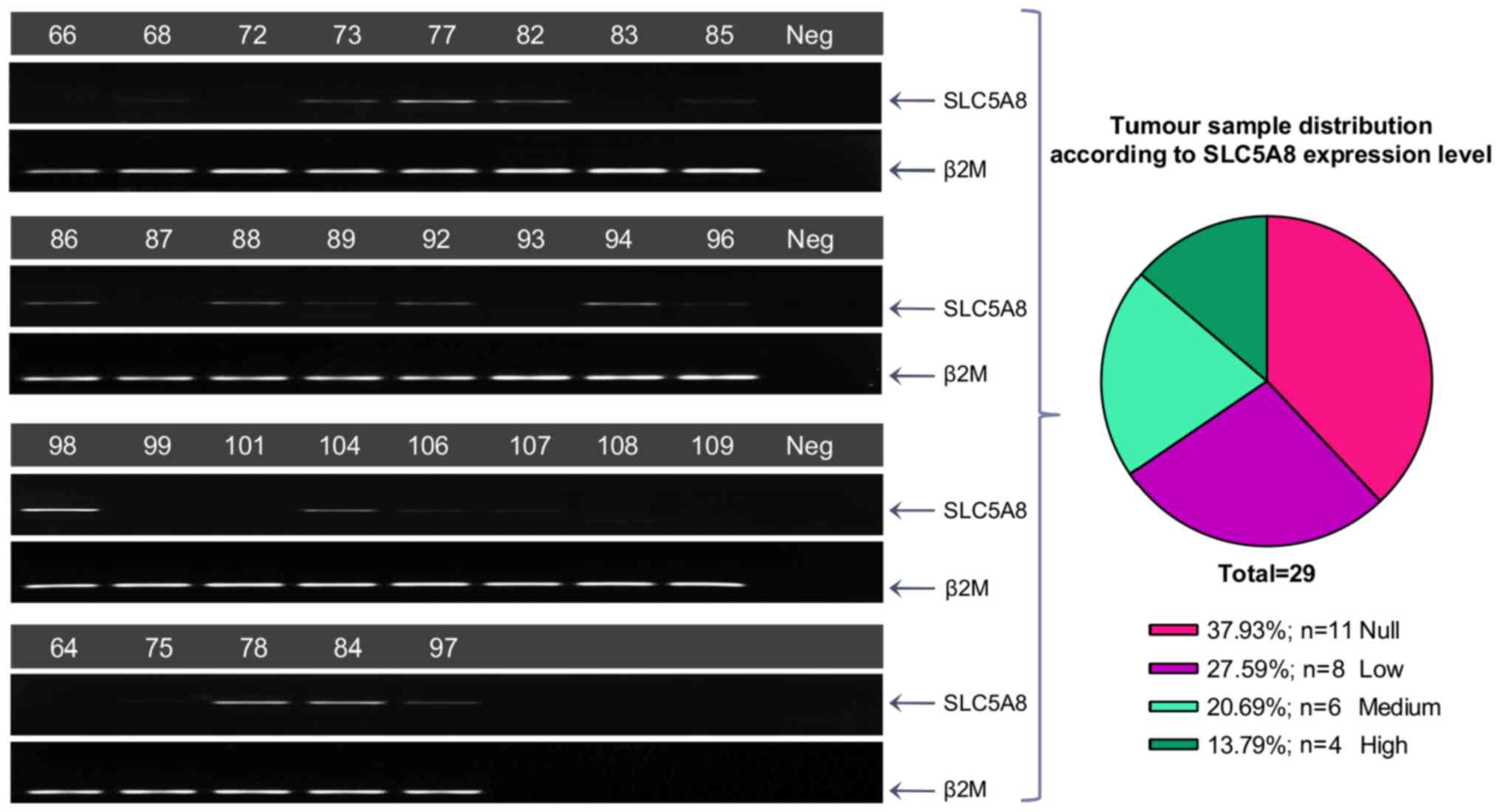
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Subramanya D and Grivas PD: HPV and
cervical cancer: Updates on an established relationship. Postgrad
Med. 120:7–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fang J, Zhang H and Jin S: Epigenetics and
cervical cancer: From pathogenesis to therapy. Tumour Biol.
35:5083–5093. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li E and Zhang Y: DNA methylation in
mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:a0191332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Portela A and Esteller M: Epigenetic
modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 28:1057–1068.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kazanets A, Shorstova T, Hilmi K, Marques
M and Witcher M: Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes:
Paradigms, puzzles, and potential. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1865:275–288. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhutia YD, Babu E, Ramachandran S, Yang S,
Thangaraju M and Ganapathy V: SLC transporters as a novel class of
tumour suppressors: Identity, function and molecular mechanisms.
Biochem J. 473:1113–1124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li H, Myeroff L, Smiraglia D, Romero MF,
Pretlow TP, Kasturi L, Lutterbaugh J, Rerko RM, Casey G, Issa JP,
et al: SLC5A8, a sodium transporter, is a tumor suppressor gene
silenced by meth-ylation in human colon aberrant crypt foci and
cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8412–8417. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Whitman SP, Hackanson B, Liyanarachchi S,
Liu S, Rush LJ, Maharry K, Margeson D, Davuluri R, Wen J, Witte T,
et al: DNA hypermethylation and epigenetic silencing of the tumor
suppressor gene, SLC5A8, in acute myeloid leukemia with the MLL
partial tandem duplication. Blood. 112:2013–2016. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M, Gopal E, Martin
PM, Itagaki S, Miyauchi S and Prasad PD: Sodium-coupled
monocarboxylate transporters in normal tissues and in cancer. AAPS
J. 10:193–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elangovan S, Pathania R, Ramachandran S,
Ananth S, Padia RN, Srinivas SR, Babu E, Hawthorn L, Schoenlein PV,
Boettger T, et al: Molecular mechanism of SLC5A8 inactivation in
breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 33:3920–3935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thangaraju M, Cresci G, Itagaki S,
Mellinger J, Browning DD, Berger FG, Prasad PD and Ganapathy V:
Sodium-coupled transport of the short chain fatty acid butyrate by
SLC5A8 and its relevance to colon cancer. J Gastrointest Surg.
12:1773–1782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thangaraju M, Gopal E, Martin PM, Ananth
S, Smith SB, Prasad PD, Sterneck E and Ganapathy V: SLC5A8 triggers
tumor cell apoptosis through pyruvate-dependent inhibition of
histone deacetylases. Cancer Res. 66:11560–11564. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thangaraju M, Carswell KN, Prasad PD and
Ganapathy V: Colon cancer cells maintain low levels of pyruvate to
avoid cell death caused by inhibition of HDAC1/HDAC3. Biochem J.
417:379–389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M and Prasad PD:
Nutrient transporters in cancer: Relevance to Warburg hypothesis
and beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 121:29–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Durzynska J, Lesniewicz K and Poreba E:
Human papilloma-viruses in epigenetic regulations. Mutat Res Rev
Mutat Res. 772:36–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sen P, Ganguly P and Ganguly N: Modulation
of DNA methylation by human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins
in cervical cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:11–22. 2018.
|
|
18
|
Hirschowitz L, Nucci M and Zaino RJ:
Problematic issues in the staging of endometrial, cervical and
vulval carcinomas. Histopathology. 62:176–202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN and
Sankaranarayanan R: Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 143(Suppl 2): 22–36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sotlar K, Diemer D, Dethleffs A, Hack Y,
Stubner A, Vollmer N, Menton S, Menton M, Dietz K, Wallwiener D, et
al: Detection and typing of human papillomavirus by e6 nested
multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 42:3176–3184. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bock C, Reither S, Mikeska T, Paulsen M,
Walter J and Lengauer T: BiQ Analyzer: Visualization and quality
control for DNA methylation data from bisulfite sequencing.
Bioinformatics. 21:4067–4068. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Skinner MK: Epigenetics: A reference
manual edited by Jeffrey M. Craig and Nicholas C. Wong. Q Rev Biol.
88:351–352. 2013.
|
|
23
|
César-Razquin A, Snijder B,
Frappier-Brinton T, Isserlin R, Gyimesi G, Bai X, Reithmeier RA,
Hepworth D, Hediger MA, Edwards AM, et al: A call for systematic
research on solute carriers. Cell. 162:478–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park JY, Kim D, Yang M, Park HY, Lee SH,
Rincon M, Kreahling J, Plass C, Smiraglia DJ, Tockman MS, et al:
Gene silencing of SLC5A8 identified by genome-wide methylation
profiling in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 79:198–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin HY, Park HY, Radlein S, Mahajan NP,
Sellers TA, Zachariah B, Pow-Sang J, Coppola D, Ganapathy V and
Park JY: Protein expressions and genetic variations of SLC5A8 in
prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness. Urology. 78:971.e1–971.e9.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang HJ: Aberrant DNA methylation in
cervical carcinogenesis. Chin J Cancer. 32:42–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Huang Z, Bassil CF and Murphy SK:
Methylation-specific PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 1049:75–82. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD
and Baylin SB: Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for
methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9821–9826. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada N and Yonezawa S: Understanding
epigenetic status: DNA methylation and cancer. J Cancer Biol Res.
1:10082013.
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Bao YL, Wu Y, Yu CL, Sun Y and Li
YX: Identification and characterization of the human SLC5A8 gene
promoter. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 196:124–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sengupta PK and Smith BD: Methylation in
the initiation region of the first exon suppresses collagen
pro-α2(I) gene transcription. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1443:75–89.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brenet F, Moh M, Funk P, Feierstein E,
Viale AJ, Socci ND and Scandura JM: DNA methylation of the first
exon is tightly linked to transcriptional silencing. PLoS One.
6:e145242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deaton AM and Bird A: CpG islands and the
regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25:1010–1022. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baron B: Breaking the silence: The
interplay between transcription factors and DNA methylation.
Methylation-From DNA, RNA and Histones to Diseases and Treatment.
IntechOpen Limited; London: 2012, View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen YJ, Chen YL, Chang Y, Wu CC, Ko YC,
Tsao SW, Chen JY and Lin SF: Epstein-Barr Virus Rta-Mediated
Accumulation of DNA Methylation Interferes with CTCF Binding in
both Host and Viral Genomes. J Virol. 91:e00736–e17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wong DJ, Foster SA, Galloway DA and Reid
BJ: Progressive region-specific de novo methylation of the p16 CpG
island in primary human mammary epithelial cell strains during
escape from M(0) growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 19:5642–5651. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Turker MS: Gene silencing in mammalian
cells and the spread of DNA methylation. Oncogene. 21:5388–5393.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Delcuve GP, Khan DH and Davie JR:
Targeting class I histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 17:29–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen GD, Qian DY, Li ZG, Fan GY, You KL
and Wu YL: Down-regulation of p16 and MGMT promotes the
anti-prolif-erative and pro-apoptotic effects of 5-Aza-dC and
radiation on cervical cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 35:488–496.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wilting SM, Verlaat W, Jaspers A, Makazaji
NA, Agami R, Meijer CJ, Snijders PJ and Steenbergen RD:
Methylation-mediated transcriptional repression of microRNAs during
cervical carcinogenesis. Epigenetics. 8:220–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Stich M, Ganss L, Puschhof J, Prigge ES,
Reuschenbach M, Guiterrez A, Vinokurova S and von Knebel Doeberitz
M: 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (DAC) treatment downregulates the HPV E6
and E7 oncogene expression and blocks neoplastic growth of
HPV-associated cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:52104–52117. 2016.
|
|
42
|
Lin RK, Wu CY, Chang JW, Juan LJ, Hsu HS,
Chen CY, Lu YY, Tang YA, Yang YC, Yang PC, et al: Dysregulation of
p53/Sp1 control leads to DNA methyltransferase-1 overexpression in
lung cancer. Cancer Res. 70:5807–5817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang Z, Li XG, Hu J, Lu DR, Zhou W, Jiang
YQ and Li CY: The methylation and mRNA expression of SLC5A8 and
TMS1/ASC genes in human glioma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 87:292–297.
2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Michelakis ED, Webster L and Mackey JR:
Dichloroacetate (DCA) as a potential metabolic-targeting therapy
for cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:989–994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|