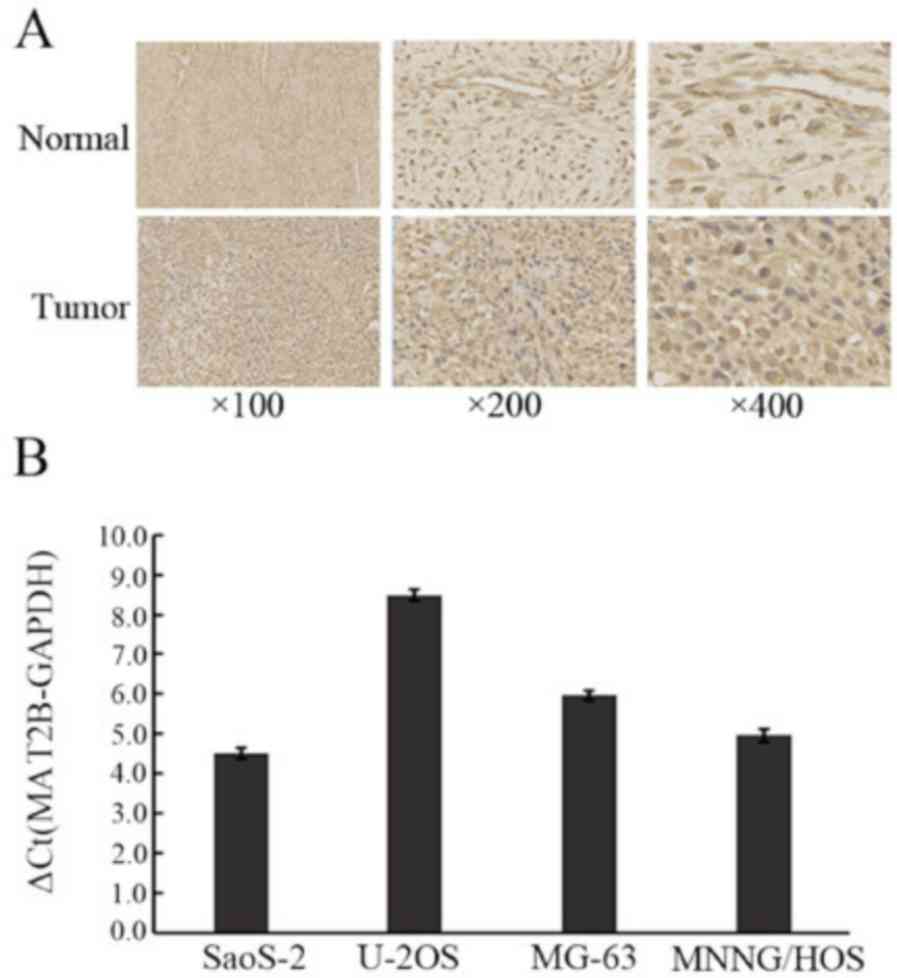
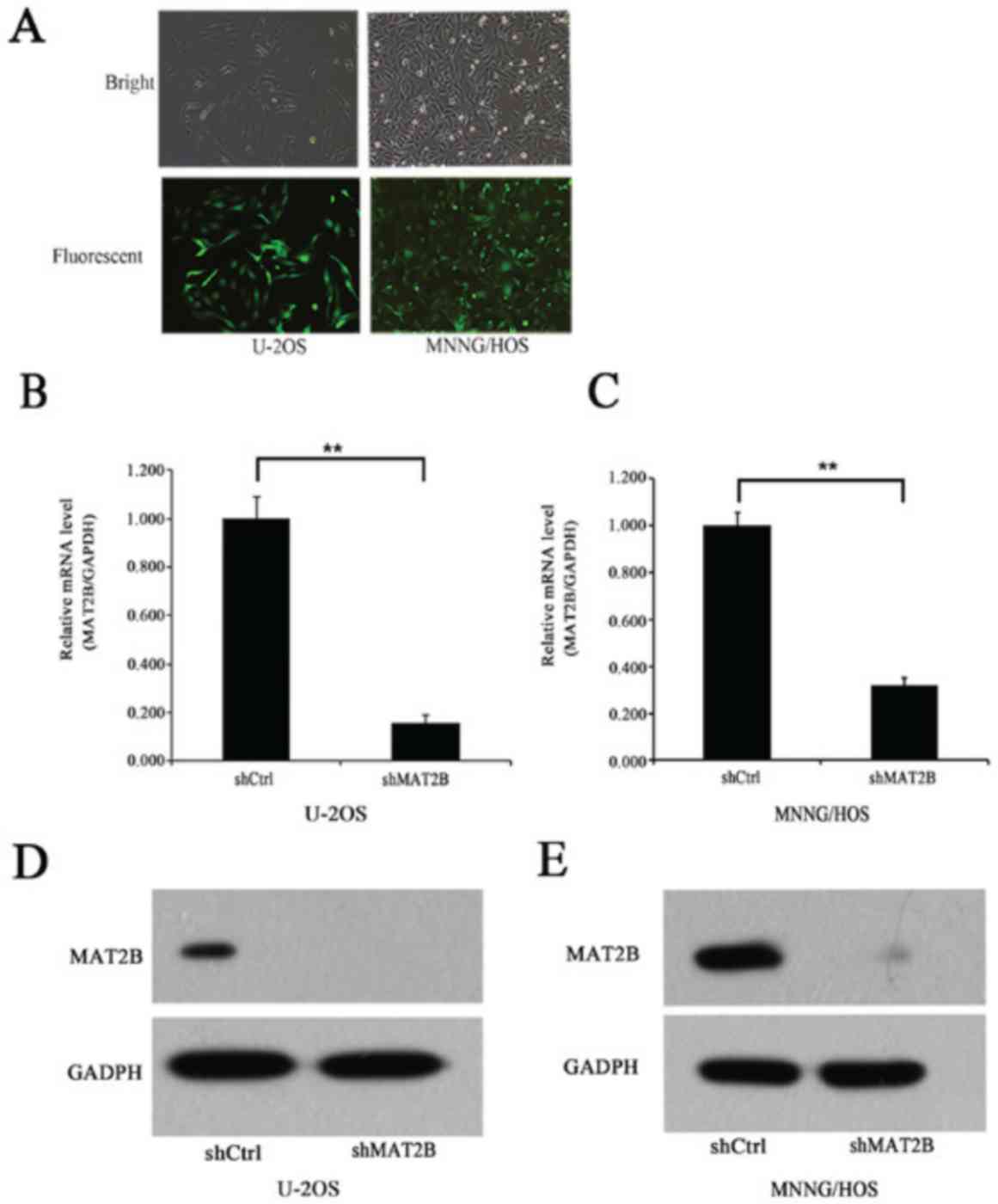
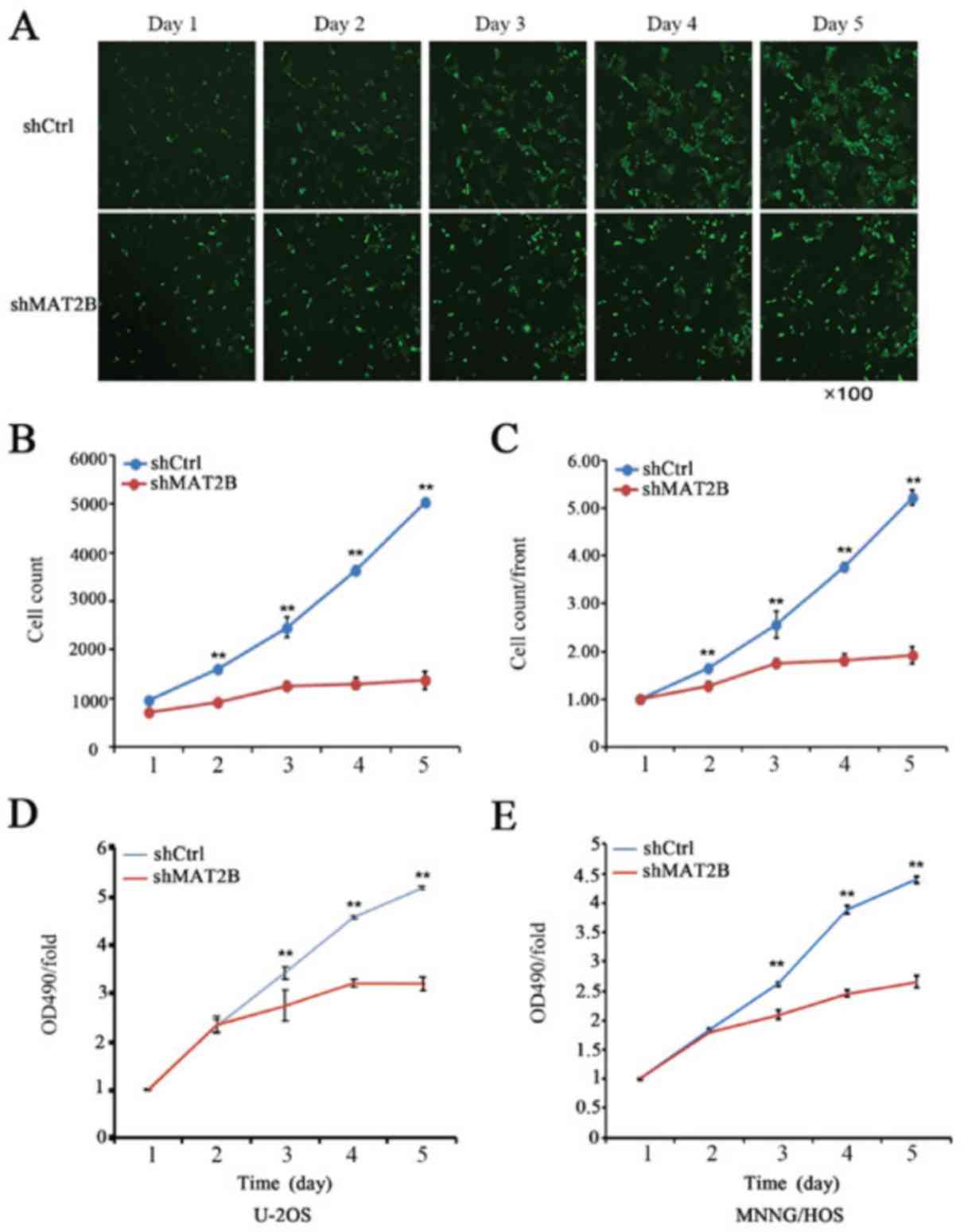
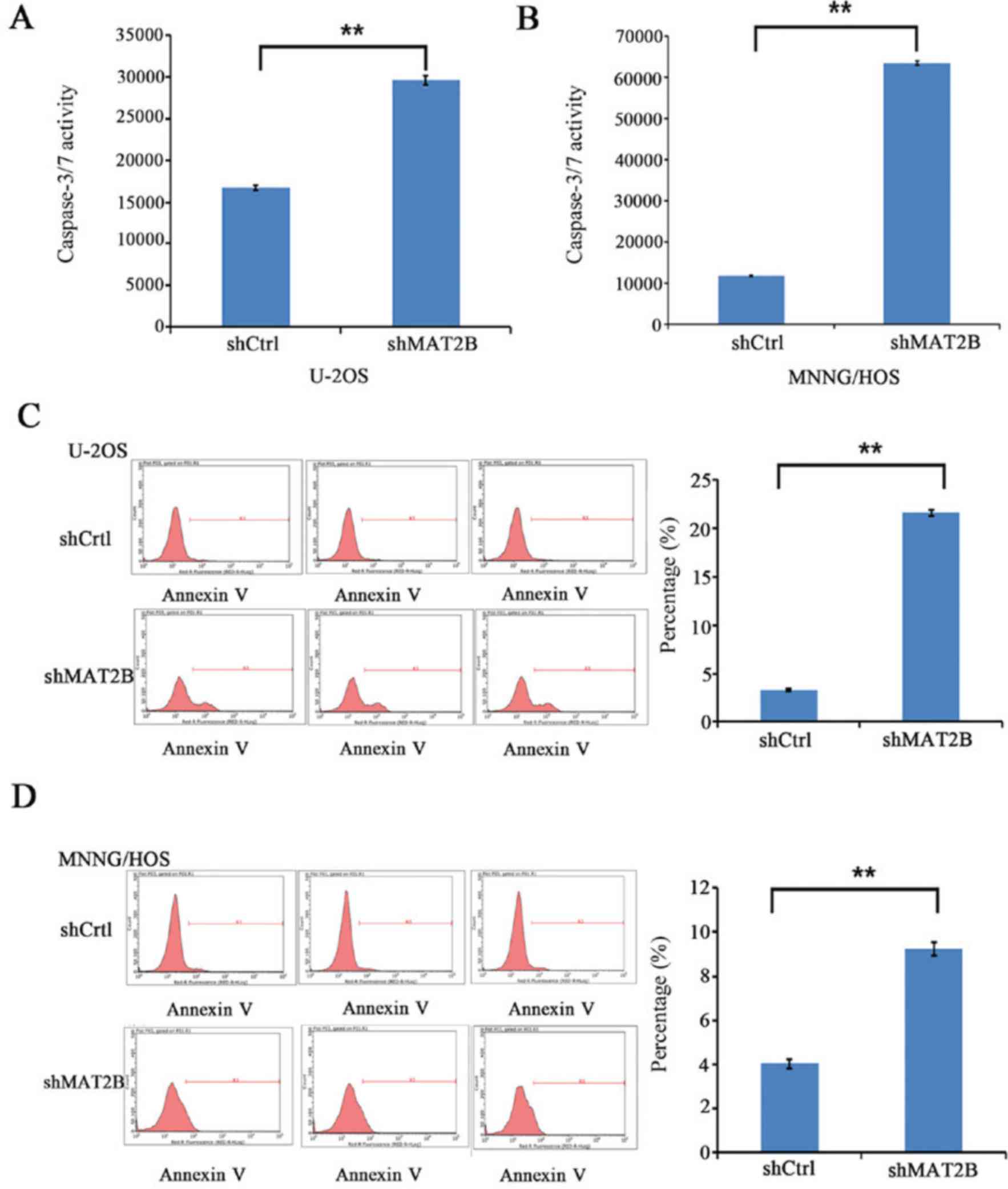
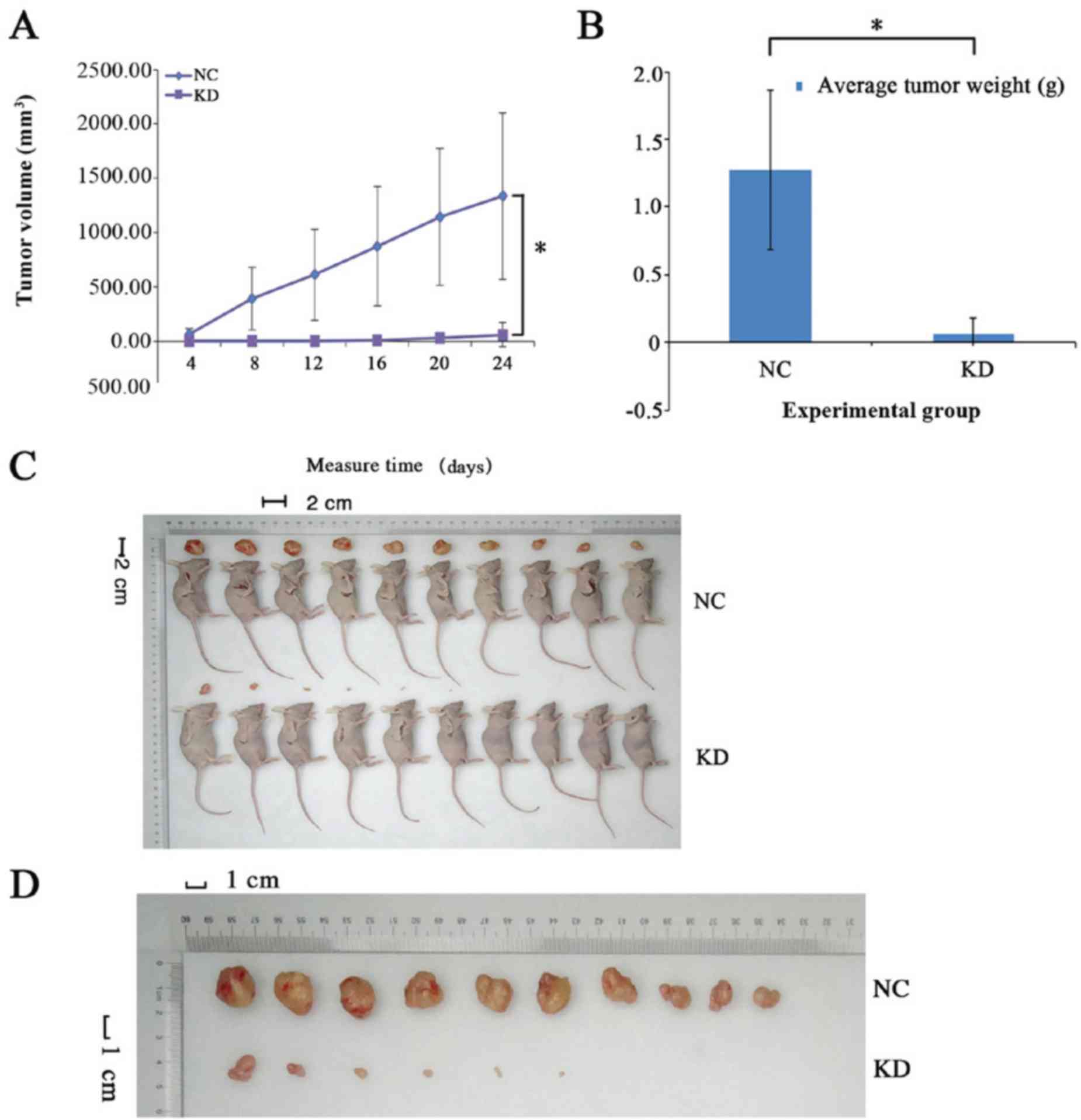
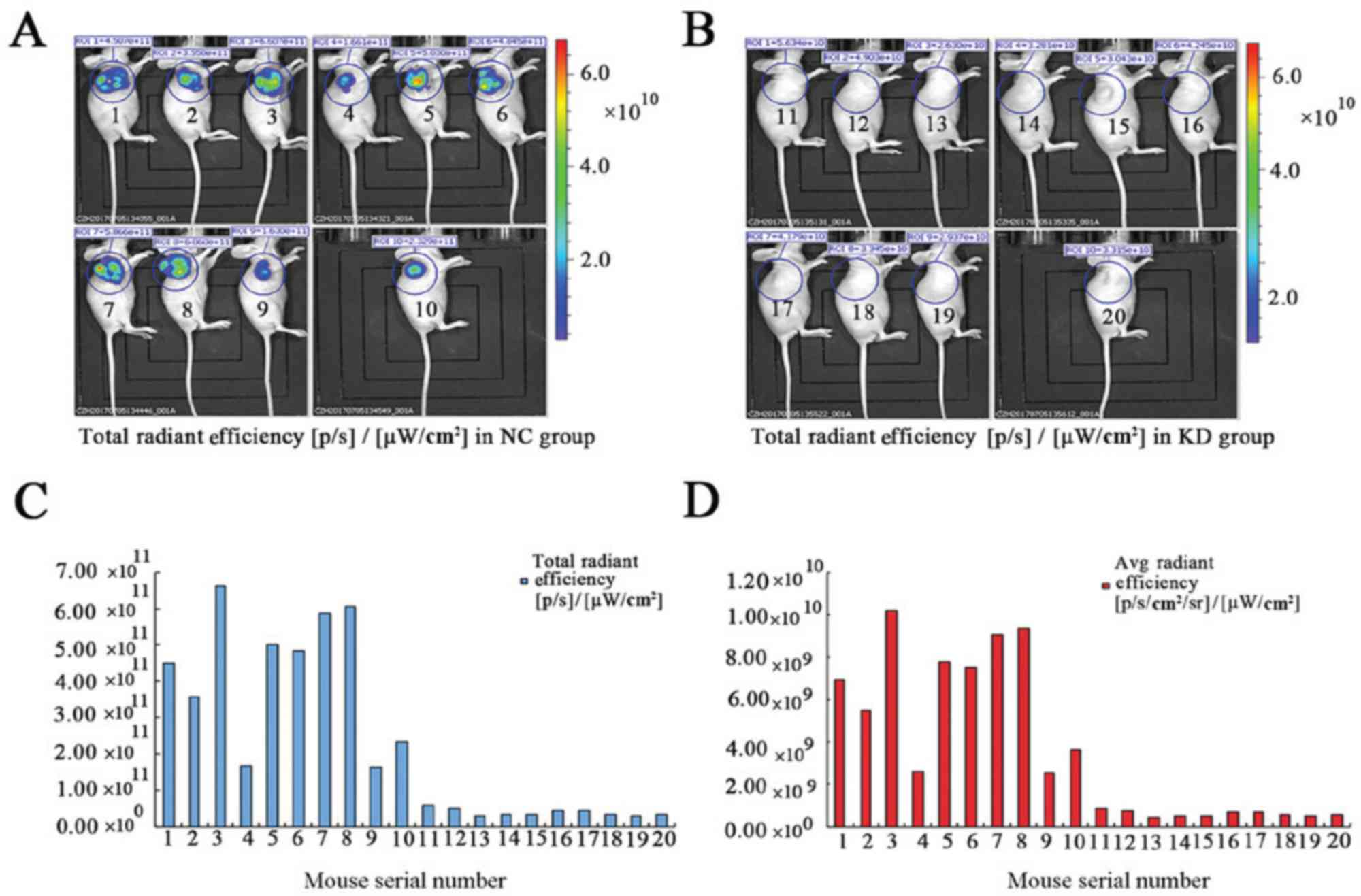
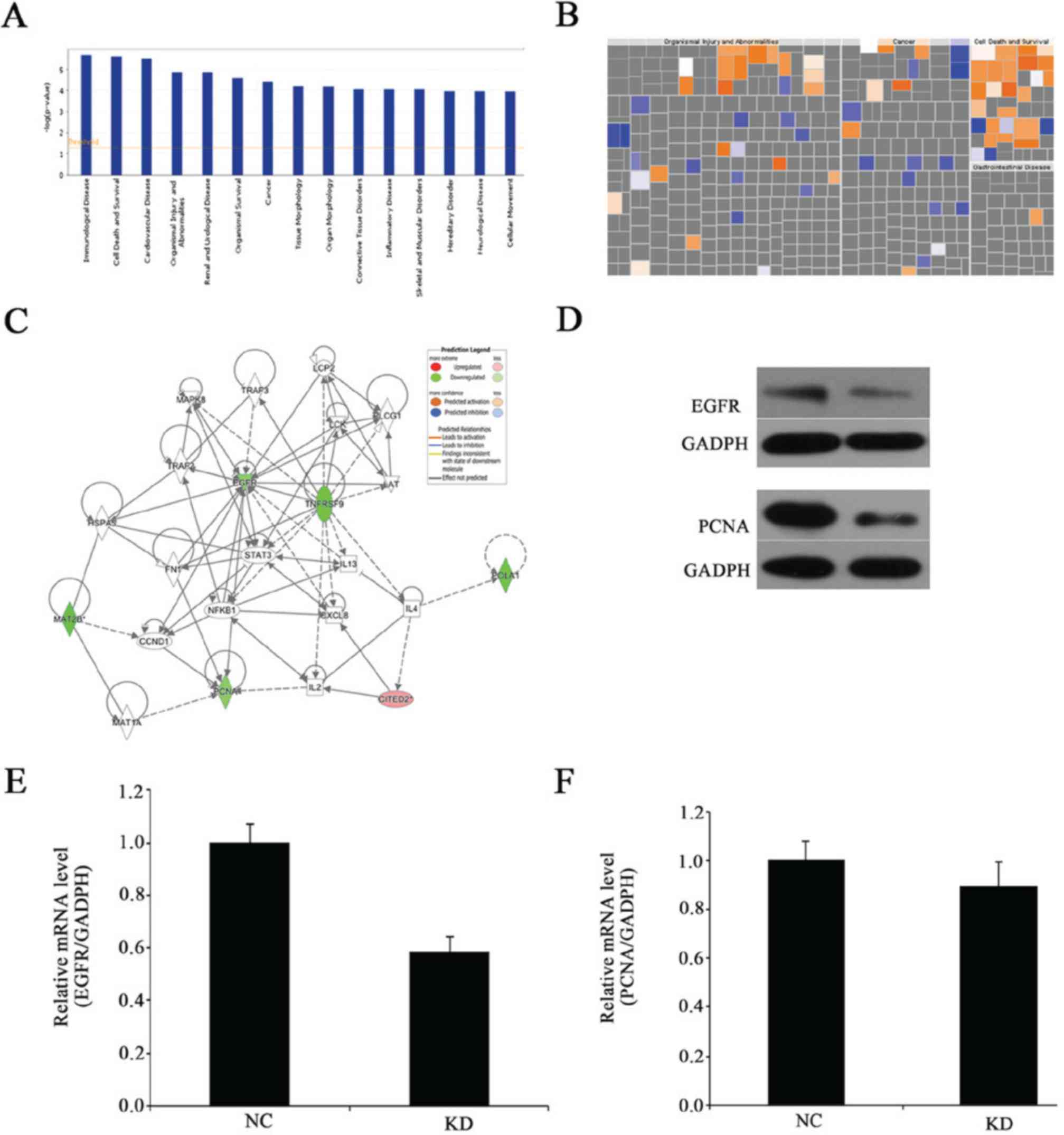
|
1
|
Ferguson JL and Turner SP: Bone cancer:
Diagnosis and treatment principles. Am Fam Physician. 98:205–213.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harrison DJ and Schwartz CL: Osteogenic
sarcoma: Systemic chemotherapy options for localized disease. Curr
Treat Options Oncol. 18:242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferrari S, Mercuri M, Bacci G, Bielack SS
and Jürgens H: Comment on “Prognostic factors in high-grade
osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702
patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study
Group protocols”. J Clin Oncol. 20:2910–2911; author reply
2910–2911. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu SC and Mato JM: S-adenosylmethionine in
liver health, injury, and cancer. Physiol Rev. 92:1515–1542. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun H, Kang J, Su J, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu
X, Zhang J, Wang F, Lu Z, Xing X, et al: Methionine
adenosyltransferase 2A regulates mouse zygotic genome activation
and morula to blastocyst transition. Biol Reprod. Sep 27–2018.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Inoue-Choi M, Nelson HH, Robien K, Arning
E, Bottiglieri T, Koh WP and Yuan JM: One-carbon metabolism
nutrient status and plasma S-adenosylmethionine concentrations in
middle-aged and older Chinese in Singapore. Int J Mol Epidemiol
Genet. 3:160–173. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Ara AI, Magilnick N, Xia M, Ramani
K, Chen H, Lee TD, Mato JM and Lu SC: Expression pattern,
regulation, and functions of methionine adenosyltransferase 2beta
splicing variants in hepatoma cells. Gastroenterology. 134:281–291.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ramani K and Lu SC: Methionine
adenosyltransferases in liver health and diseases. Liver Res.
1:103–111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nordgren KK, Peng Y, Pelleymounter LL,
Moon I, Abo R, Feng Q, Eckloff B, Yee VC, Wieben E and Weinshilboum
RM: Methionine adenosyltransferase 2A/2B and methylation: Gene
sequence variation and functional genomics. Drug Metab Dispos.
39:2135–2147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng H, Dara L, Li TW, Zheng Y, Yang H,
Tomasi ML, Tomasi I, Giordano P, Mato JM and Lu SC: MAT2B-GIT1
interplay activates MEK1/ERK 1 and 2 to induce growth in human
liver and colon cancer. Hepatology. 57:2299–2313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lei Y, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Sun J,
Zhang X and Yang S: Lentivirus-mediated downregulation of MAT2B
inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in melanoma. Int
J Oncol. 49:981–990. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang Z, He G, Xu J and Zhongfu L:
Knockdown of Cbp/P300-interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp-rich
carboxy-terminal domain 2 inhibits cell division and increases
apoptosis in gastric cancer. J Surg Res. 211:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Liu H, Zhao C, Li W, Xu H and Chen
Y: The DEAD-box RNA helicase 51 controls non-small cell lung cancer
proliferation by regulating cell cycle progression via multiple
pathways. Sci Rep. 6:261082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Δ Δ C(T)). Method Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Singh B, Carpenter G and Coffey RJ: EGF
receptor ligands: Recent advances. F1000 Res. 5:52016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Zhao HF, Yao TF and Gong H:
Advanced development of ErbB family-targeted therapies in
osteosarcoma treatment. Invest New Drugs. Oct 24–2018.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Prabhu VV and Devaraj N: Epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase: A potential target in treatment of
non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.
36:151–158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gonzalez-Conchas GA, Rodriguez-Romo L,
Hernandez-Barajas D, Gonzalez-Guerrero JF, Rodriguez-Fernandez IA,
Verdines-Perez A, Templeton AJ, Ocana A, Seruga B, Tannock IF, et
al: Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression and outcomes in
early breast cancer: A systematic review and a meta-analysis.
Cancer Treat Rev. 62:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wen YH, Koeppen H, Garcia R, Chiriboga L,
Tarlow BD, Peters BA, Eigenbrot C, Yee H, Steiner G and Greco MA:
Epidermal growth factor receptor in osteosarcoma: Expression and
mutational analysis. Hum Pathol. 38:1184–1191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kersting C, Gebert C, Agelopoulos K,
Schmidt H, van Diest PJ, Juergens H, Winkelmann W, Kevric M,
Gosheger G, Brandt B, et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor
expression in high-grade osteosarcomas is associated with a good
clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2998–3005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Linder M, Glitzner E, Srivatsa S, Bakiri
L, Matsuoka K, Shahrouzi P, Dumanic M, Novoszel P, Mohr T, Langer
O, et al: EGFR is required for FOS-dependent bone tumor development
via RSK2/CREB signaling. EMBO Mol Med. 10:e94082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou CH, Lin FL, Tong KB, Hou SM and Liu
JF: Transforming growth factor alpha promotes osteosarcoma
metastasis by ICAM-1 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biochem
Pharmacol. 89:453–463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin H, Zhang C, Zhang H, Xia YZ, Zhang CY,
Luo J, Yang L and Kong LY: Physakengose induces apoptosis via
EGFR/mTOR signaling and inhibits autophagic flux in human
osteosarcoma cells. Phytomedicine. 42:190–198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Do SI, Jung WW, Kim HS and Park YK: The
expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream
signaling molecules in osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 34:797–803.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu H, Muscato NE, Gonzalez A and Shyr Y:
An EGFR and AKT signaling pathway was identified with mediation
model in osteosarcomas clinical study. Biomark Insights. 2:469–476.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Agarwal P, Sen AK, Bhardwaj M, Dinand V,
Ahuja A and Sood R: Study of proliferating cell nuclear antigen
expression and angiogenesis in urothelial neoplasms: Correlation
with tumor grade and stage. Urol Ann. 10:209–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan Z, Wortman M, Dillehay KL, Seibel WL,
Evelyn CR, Smith SJ, Malkas LH, Zheng Y, Lu S and Dong Z:
Small-molecule targeting of proliferating cell nuclear antigen
chromatin association inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Pharmacol.
81:811–819. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Unal VS, Ayhan A and Tokgozoglu MA:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen index and nm23 expression in
osteosarcoma in relation to disease- free survival and tumor grade.
Saudi Med J. 26:1475–1477. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Juríková M, Danihel Ľ, Polák Š and Varga
I: Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 118:544–552. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lv Q, Zhang J, Yi Y, Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang
Y and Zhang W: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen has an
association with prognosis and risks factors of cancer patients: A
systematic review. Mol Neurobiol. 53:6209–6217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dong Y, Liang G, Yuan B, Yang C, Gao R and
Zhou X: MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:1477–1486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liang G, Xu E, Yang C, Zhang C, Sheng X
and Zhou X: Nucleosome-binding protein HMGN2 exhibits antitumor
activity in human SaO2 and U2-OS osteosarcoma cell lines. Oncol
Rep. 33:1300–1306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tu B, Du L, Fan QM, Tang Z and Tang TT:
STAT3 activation by IL-6 from mesenchymal stem cells promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett.
325:80–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang W, Luo H and Wang A: Expression of
survivin and correlation with PCNA in osteosarcoma. J Surg Oncol.
93:578–584. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P and Syrjänen K:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolabeling as a
prognostic factor in axillary lymph node negative breast cancer.
Anticancer Res. 13:533–538. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|