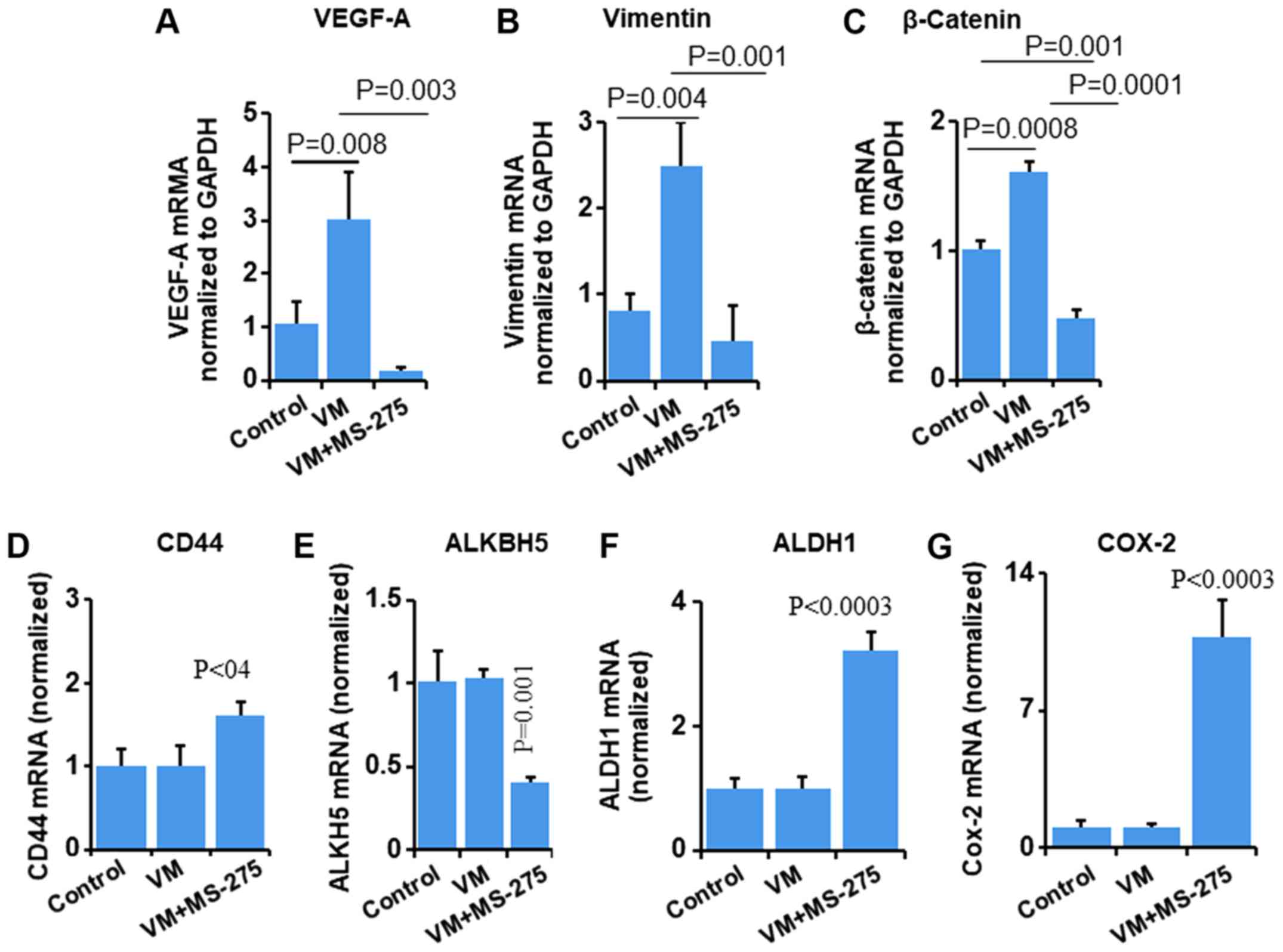
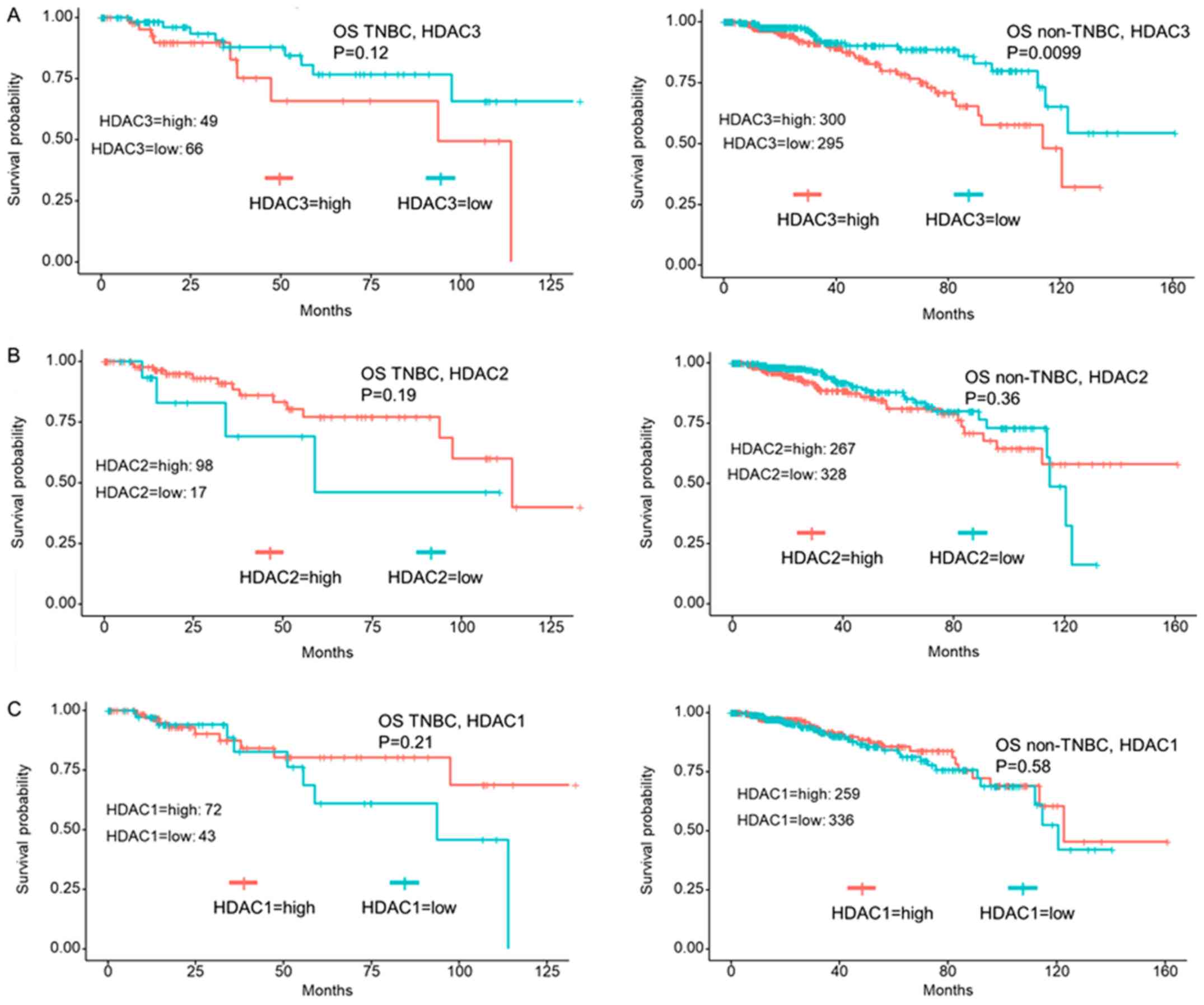
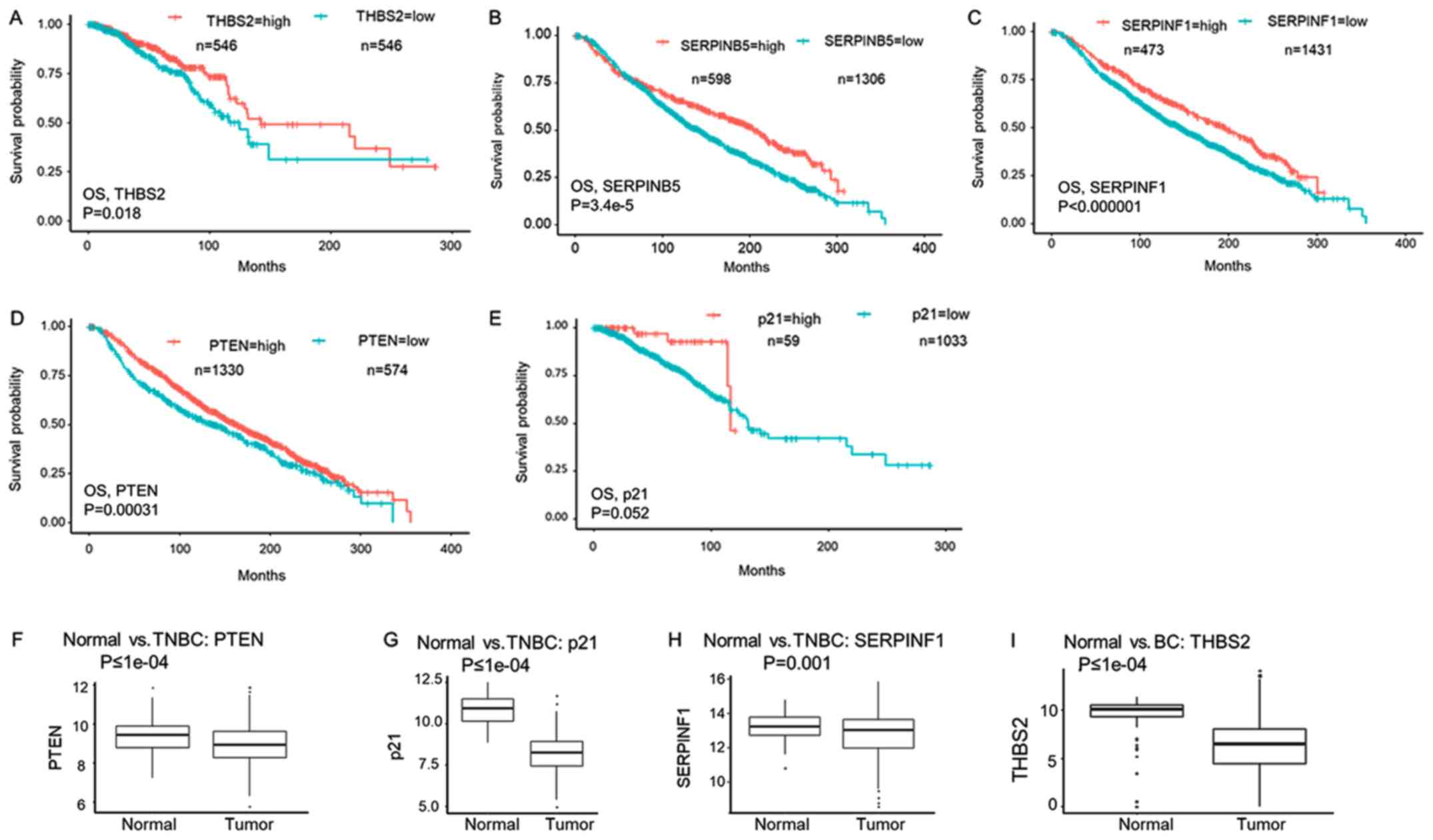
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gacche RN: Compensatory angiogenesis and
tumor refractoriness. Oncogenesis. 4:e1532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pinto MP, Sotomayor P, Carrasco-Avino G,
Corvalan AH and Owen GI: Escaping antiangiogenic therapy:
Strategies employed by cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E14892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA,
Gardner LM, Pe'er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS and Hendrix MJ: Vascular
channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro:
Vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 155:739–752. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Plate KH, Scholz A and Dumont DJ: Tumor
angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy in malignant gliomas
revisited. Acta Neuropathol. 124:763–775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Folberg R and Maniotis AJ: Vasculogenic
mimicry. APMIS. 112:508–525. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Folberg R, Hendrix MJ and Maniotis AJ:
Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
156:361–381. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clemente M, Pérez-Alenza MD, Illera JC and
Peña L: Histological, immunohistological, and ultrastructural
description of vasculogenic mimicry in canine mammary cancer. Vet
Pathol. 47:265–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Seftor RE, Hess AR, Seftor EA, Kirschmann
DA, Hardy KM, Margaryan NV and Hendrix MJ: Tumor cell vasculogenic
mimicry: From controversy to therapeutic promise. Am J Pathol.
181:1115–1125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Hardy KM, Seftor
RE and Hendrix MJ: Molecular pathways: vasculogenic mimicry in
tumor cells: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2726–2732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shirakawa K, Tsuda H, Heike Y, Kato K,
Asada R, Inomata M, Sasaki H, Kasumi F, Yoshimoto M, Iwanaga T, et
al: Absence of endothelial cells, central necrosis, and fibrosis
are associated with aggressive inflammatory breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 61:445–451. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sood AK, Seftor EA, Fletcher MS, Gardner
LM, Heidger PM, Buller RE, Seftor RE and Hendrix MJ: Molecular
determinants of ovarian cancer plasticity. Am J Pathol.
158:1279–1288. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sood AK, Fletcher MS, Zahn CM, Gruman LM,
Coffin JE, Seftor EA and Hendrix MJ: The clinical significance of
tumor cell-lined vasculature in ovarian carcinoma: Implications for
anti-vasculogenic therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:661–664. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sharma N, Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Gruman LM,
Heidger PM Jr, Cohen MB, Lubaroff DM and Hendrix MJ: Prostatic
tumor cell plasticity involves cooperative interactions of distinct
phenotypic subpopulations: Role in vasculogenic mimicry. Prostate.
50:189–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Passalidou E, Trivella M, Singh N,
Ferguson M, Hu J, Cesario A, Granone P, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P,
Ratcliffe C, et al: Vascular phenotype in angiogenic and
non-angiogenic lung non-small cell carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
86:244–249. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yue WY and Chen ZP: Does vasculogenic
mimicry exist in astrocytoma? J Histochem Cytochem. 53:997–1002.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhang S, Zhang W, Guo H
and Zhao X: Hypoxia influences vasculogenic mimicry channel
formation and tumor invasion-related protein expression in
melanoma. Cancer Lett. 249:188–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bayraktar S and Glück S: Molecularly
targeted therapies for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 138:21–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ribatti D, Nico B, Ruggieri S, Tamma R,
Simone G and Mangia A: Angiogenesis and antiangiogenesis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Transl Oncol. 9:453–457. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun H, Zhang D, Yao Z, Lin X, Liu J, Gu Q,
Dong X, Liu F, Wang Y, Yao N, et al: Anti-angiogenic treatment
promotes triple-negative breast cancer invasion via vasculogenic
mimicry. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:205–213. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen Y, Quan J, Wang M, Li S and Yang J,
Lv M, Chen Z, Zhang L, Zhao X and Yang J: Tumor vasculogenic
mimicry formation as an unfavorable prognostic indicator in
patients with breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:56408–56416.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shao F, Sun H and Deng CX: Potential
therapeutic targets of triple-negative breast cancer based on its
intrinsic subtype. Oncotarget. 8:73329–73344. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi L, Song W, Liu Z, Zhao X, Cao W and Sun
B: Wnt3a promotes the vasculogenic mimicry formation of colon
cancer via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
16:18564–18579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Z, Sun B, Qi L, Li H, Gao J and Leng
X: Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 promotes vasculogenic
mimicry in colorectal cancer through induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Sci. 103:813–820.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Demou ZN and Hendrix MJ: Microgenomics
profile the endogenous angiogenic phenotype in subpopulations of
aggressive melanoma. J Cell Biochem. 105:562–573. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Su M, Feng YJ, Yao LQ, Cheng MJ, Xu CJ,
Huang Y, Zhao YQ and Jiang H: Plasticity of ovarian cancer cell
SKOV3ip and vasculogenic mimicry in vivo. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
18:476–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu B, Li J, Liu X, Li C and Chang X:
TXNDC5 is a cervical tumor susceptibility gene that stimulates cell
migration, vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis by down-regulating
SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression. Oncotarget. 8:91009–91024.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y,
Seftor E, Hendrix M, Radmacher M, Simon R, Yakhini Z, Ben-Dor A, et
al: Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by
gene expression profiling. Nature. 406:536–540. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S
and Kataoka T: Phospholipase Cepsilon promotes intestinal
tumorigenesis of Apc(Min/+) mice through augmentation of
inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 30:1424–1432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu S, Yu L, Cheng Z, Song W, Zhou L and
Tao Y: Expression of maspin in non-small cell lung cancer and its
relationship to vasculogenic mimicry. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog
Med Sci. 32:346–352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Marini A, Nambiar S,
Hassan M, Tannapfel A, Ruzicka T and Hengge UR: Epigenetic
silencing of the PTEN gene in melanoma. Cancer Res. 66:6546–6552.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Chen H, Hardy TM and Tollefsbol TO:
Epigenetic regulation of multiple tumor-related genes leads to
suppression of breast tumorigenesis by dietary genistein. PLoS One.
8:e543692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu E, Dul E, Sung CM, Chen Z, Kirkpatrick
R, Zhang GF, Johanson K, Liu R, Lago A, Hofmann G, et al:
Identification of novel isoform-selective inhibitors within class I
histone deacetylases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 307:720–728. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vannini A, Volpari C, Filocamo G, Casavola
EC, Brunetti M, Renzoni D, Chakravarty P, Paolini C, De Francesco
R, Gallinari P, et al: Crystal structure of a eukaryotic
zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a
hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15064–15069.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Inoue S, Mai A, Dyer MJ and Cohen GM:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase class I but not class II is
critical for the sensitization of leukemic cells to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer
Res. 66:6785–6792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bracker TU, Sommer A, Fichtner I, Faus H,
Haendler B and Hess-Stumpp H: Efficacy of MS-275, a selective
inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases, in human colon cancer
models. Int J Oncol. 35:909–920. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ryan QC, Headlee D, Acharya M, Sparreboom
A, Trepel JB, Ye J, Figg WD, Hwang K, Chung EJ, Murgo A, et al:
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of MS-275, a histone deacetylase
inhibitor, in patients with advanced and refractory solid tumors or
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 23:3912–3922. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shah P, Gau Y and Sabnis G: Histone
deacetylase inhibitor entinostat reverses epithelial to mesenchymal
transition of breast cancer cells by reversing the repression of
E-cadherin. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 143:99–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Schech A, Kazi A, Yu S, Shah P and Sabnis
G: Histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat inhibits
tumor-initiating cells in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 14:1848–1857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gangavarapu KJ, Azabdaftari G, Morrison
CD, Miller A, Foster BA and Huss WJ: Aldehyde dehydrogenase and ATP
binding cassette transporter G2 (ABCG2) functional assays isolate
different populations of prostate stem cells where ABCG2 function
selects for cells with increased stem cell activity. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 4:1322013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Maiti A, Takabe K and Hait NC: Metastatic
triple-negative breast cancer is dependent on SphKs/S1P signaling
for growth and survival. Cell Signal. 32:85–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tavallai M, Hamed HA, Roberts JL,
Cruickshanks N, Chuckalovcak J, Poklepovic A, Booth L and Dent P:
Nexavar/Stivarga and viagra interact to kill tumor cells. J Cell
Physiol. 230:2281–2298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
LeBlanc M, Jacobson J and Crowley J:
Partitioning and peeling for constructing prognostic groups. Stat
Methods Med Res. 11:247–274. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Benton G, Arnaoutova I, George J, Kleinman
HK and Koblinski J: Matrigel: From discovery and ECM mimicry to
assays and models for cancer research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
79-80:3–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Izawa Y, Kashii-Magaribuchi K, Yoshida K,
Nosaka M, Tsuji N, Yamamoto A, Kuroyanagi K, Tono K, Tanihata M,
Imanishi M, et al: Stem-like human breast cancer cells initiate
vasculogenic mimicry on matrigel. Acta Histochem Cytochem.
51:173–183. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Williamson SC, Metcalf RL, Trapani F,
Mohan S, Antonello J, Abbott B, Leong HS, Chester CP, Simms N,
Polanski R, et al: Vasculogenic mimicry in small cell lung cancer.
Nat Commun. 7:133222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR and Seftor
RE: Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: Lessons from
melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:411–421. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Paulis YW, Huijbers EJ, van der Schaft DW,
Soetekouw PM, Pauwels P, Tjan-Heijnen VC and Griffioen AW: CD44
enhances tumor aggressiveness by promoting tumor cell plasticity.
Oncotarget. 6:19634–19646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Meyer MJ, Fleming JM, Ali MA, Pesesky MW,
Ginsburg E and Vonderhaar BK: Dynamic regulation of CD24 and the
invasive, CD44posCD24neg phenotype in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer Res. 11:R822009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fillmore CM and Kuperwasser C: Human
breast cancer cell lines contain stem-like cells that self-renew,
give rise to phenotypically diverse progeny and survive
chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R252008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M,
Todaro M, Invernici G, Cenci T, Maira G, Parati EA, Stassi G,
Larocca LM, et al: Tumour vascularization via endothelial
differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature.
468:824–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Aikins AR, Kim M, Raymundo B and Kim CW:
Downregulation of transgelin blocks interleukin-8 utilization and
suppresses vasculogenic mimicry in breast cancer cells. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 242:573–583. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shirakawa K, Kobayashi H, Sobajima J,
Hashimoto D, Shimizu A and Wakasugi H: Inflammatory breast cancer:
Vasculogenic mimicry and its hemodynamics of an inflammatory breast
cancer xenograft model. Breast Cancer Res. 5:136–139. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Basu GD, Liang WS, Stephan DA, Wegener LT,
Conley CR, Pockaj BA and Mukherjee P: A novel role for
cyclooxygenase-2 in regulating vascular channel formation by human
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 8:R692006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver
JL and Wang J: TGF-Beta suppresses VEGFA-mediated angiogenesis in
colon cancer metastasis. PLoS One. 8:e599182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ferrari G, Cook BD, Terushkin V, Pintucci
G and Mignatti P: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1)
induces angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF)-mediated apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 219:449–458. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Krusche CA, Wülfing P, Kersting C, Vloet
A, Böcker W, Kiesel L, Beier HM and Alfer J: Histone deacetylase-1
and -3 protein expression in human breast cancer: A tissue
microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 90:15–23. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Müller BM, Jana L, Kasajima A, Lehmann A,
Prinzler J, Budczies J, Winzer KJ, Dietel M, Weichert W and Denkert
C: Differential expression of histone deacetylases HDAC1, 2 and 3
in human breast cancer - overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 is
associated with clinicopathological indicators of disease
progression. BMC Cancer. 13:2152013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Minamiya Y, Ono T, Saito H, Takahashi N,
Ito M, Mitsui M, Motoyama S and Ogawa J: Expression of histone
deacetylase 1 correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with
adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 74:300–304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H,
Ando Y, Mita K, Hamaguchi M, Hara Y, Kobayashi S and Iwase H:
Quantitation of HDAC1 mRNA expression in invasive carcinoma of the
breast*. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 94:11–16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kim MS, Kwon HJ, Lee YM, Baek JH, Jang JE,
Lee SW, Moon EJ, Kim HS, Lee SK, Chung HY, et al: Histone
deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor
suppressor genes. Nat Med. 7:437–443. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu X, Wang JH, Li S, Li LL, Huang M,
Zhang YH, Liu Y, Yang YT, Ding R and Ke YQ: Histone deacetylase 3
expression correlates with vasculogenic mimicry through the
phos-phoinositide3-kinase/ERK-MMP-laminin5γ2 signaling pathway.
Cancer Sci. 106:857–866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Knipstein J and Gore L: Entinostat for
treatment of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 20:1455–1467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Merino VF, Nguyen N, Jin K, Sadik H, Cho
S, Korangath P, Han L, Foster YM, Zhou XC, Zhang Z, et al: Combined
treatment with epigenetic, differentiating, and chemotherapeutic
agents cooperatively targets tumor-initiating cells in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:2013–2024. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Min A, Im SA, Kim DK, Song SH, Kim HJ, Lee
KH, Kim TY, Han SW, Oh DY, Kim TY, et al: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), enhances
anti-tumor effects of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)
inhibitor olaparib in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast
Cancer Res. 17:332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu XD, Yang L, Zheng LY, Pan YY, Cao ZF,
Zhang ZQ, Zhou QS, Yang B and Cao C: Suberoylanilide hydroxamic
acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, suppresses vasculogenic
mimicry and proliferation of highly aggressive pancreatic cancer
PaTu8988 cells. BMC Cancer. 14:3732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Trapani D, Esposito A, Criscitiello C,
Mazzarella L, Locatelli M, Minchella I, Minucci S and Curigliano G:
Entinostat for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 26:965–971. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shi HY, Liang R, Templeton NS and Zhang M:
Inhibition of breast tumor progression by systemic delivery of the
maspin gene in a syngeneic tumor model. Mol Ther. 5:755–761. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ikenaka Y, Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii
J, Noguchi R, Tsujinoue H, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Imazu H, Masaki T,
et al: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) inhibits
tumor growth and angiogenesis in the TIMP-1 transgenic mouse model.
Int J Cancer. 105:340–346. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka
Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T, Tsujinoue H, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Imazu
H, et al: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 attenuates
spontaneous liver fibrosis resolution in the transgenic mouse.
Hepatology. 36:850–860. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lawler J: Thrombospondin-1 as an
endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. J Cell Mol
Med. 6:1–12. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou XP, Gimm O, Hampel H, Niemann T,
Walker MJ and Eng C: Epigenetic PTEN silencing in malignant
melanomas without PTEN mutation. Am J Pathol. 157:1123–1128. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chueh AC, Tse JW, Tögel L and Mariadason
JM: Mechanisms of histone deacetylase inhibitor-regulated gene
expression in cancer cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 23:66–84. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Aoki K and Taketo MM: Adenomatous
polyposis coli (APC): A multi-functional tumor suppressor gene. J
Cell Sci. 120:3327–3335. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rozic JG, Chakraborty C and Lala PK:
Cyclooxygenase inhibitors retard murine mammary tumor progression
by reducing tumor cell migration, invasiveness and angiogenesis.
Int J Cancer. 93:497–506. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gallo O, Franchi A, Magnelli L, Sardi I,
Vannacci A, Boddi V, Chiarugi V and Masini E: Cyclooxygenase-2
pathway correlates with VEGF expression in head and neck cancer.
Implications for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Neoplasia.
3:53–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kuwano T, Nakao S, Yamamoto H, Tsuneyoshi
M, Yamamoto T, Kuwano M and Ono M: Cyclooxygenase 2 is a key enzyme
for inflammatory cytokine-induced angiogenesis. FASEB J.
18:300–310. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tian J, Hachim MY, Hachim IY, Dai M, Lo C,
Raffa FA, Ali S and Lebrun JJ: Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates
TGFβ-induced cancer stemness in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci
Rep. 7:402582017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Liu S, Zhang C, Zhang K, Gao Y, Wang Z, Li
X, Cheng G, Wang S, Xue X, Li W, et al: FOXP3 inhibits cancer stem
cell self-renewal via transcriptional repression of COX2 in
colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:44694–44704. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhao H, Yu Z, Zhao L, He M, Ren J, Wu H,
Chen Q, Yao W and Wei M: HDAC2 overexpression is a poor prognostic
factor of breast cancer patients with increased multidrug
resistance-associated protein expression who received
anthracyclines therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:893–902. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sa-Nguanraksa D, Chuangsuwanich T,
Pongpruttipan T and O-Charoenrat P: High vascular endothelial
growth factor gene expression predicts poor outcome in patients
with non-luminal A breast cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 3:1103–1108.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ramanathan R, Olex AL, Dozmorov M, Bear
HD, Fernandez LJ and Takabe K: Angiopoietin pathway gene expression
associated with poor breast cancer survival. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 162:191–198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Liu F, Gu LN, Shan BE, Geng CZ and Sang
MX: Biomarkers for EMT and MET in breast cancer: An update. Oncol
Lett. 12:4869–4876. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Patel NA, Patel PS and Vora HH: Role of
PRL-3, Snail, Cytokeratin and Vimentin expression in epithelial
mesenchymal transition in breast carcinoma. Breast Dis. 35:113–127.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, Chen X, Xu J, Sun Y,
Zhao L, Qu H, Fan Y and Wu C: Antagonism of miR-21 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype
through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS One.
7:e395202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pellikainen MJ, Pekola TT, Ropponen KM,
Kataja VV, Kellokoski JK, Eskelinen MJ and Kosma VM: p21WAF1
expression in invasive breast cancer and its association with p53,
AP-2, cell proliferation, and prognosis. J Clin Pathol. 56:214–220.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li X, Yang J, Peng L, Sahin AA, Huo L,
Ward KC, O'Regan R, Torres MA and Meisel JL: Triple-negative breast
cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than
non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
161:279–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Mojic M, Takeda K and Hayakawa Y: The dark
side of IFN-gamma: Its role in promoting cancer immunoevasion. Int
J Mol Sci. 19:E892017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Dutta P, Sarkissyan M, Paico K, Wu Y and
Vadgama JV: MCP-1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast
cancers and drives cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 170:477–486. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gryder BE, Sodji QH and Oyelere AK:
Targeted cancer therapy: Giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all
they need to succeed. Future Med Chem. 4:505–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kim HJ and Bae SC: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action and clinical trials as
anti-cancer drugs. Am J Transl Res. 3:166–179. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Connolly RM, Li H, Jankowitz RC, Zhang Z,
Rudek MA, Jeter SC, Slater SA, Powers P, Wolff AC, Fetting JH, et
al: Combination epigenetic therapy in advanced breast cancer with
5-azacitidine and entinostat: A phase II national cancer
Institute/Stand up to cancer study. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2691–2701.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Connolly RM, Rudek MA and Piekarz R:
Entinostat: A promising treatment option for patients with advanced
breast cancer. Future Oncol. 13:1137–1148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yardley DA, Ismail-Khan RR, Melichar B,
Lichinitser M, Munster PN, Klein PM, Cruickshank S, Miller KD, Lee
MJ and Trepel JB: Randomized phase II, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study of exemestane with or without entinostat
in postmenopausal women with locally recurrent or metastatic
estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer progressing on treatment
with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. J Clin Oncol.
31:2128–2135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang S, Zhu L, Zuo W, Zeng Z, Huang L, Lin
F, Lin R, Wang J, Lu J, Wang Q, et al: MicroRNA-mediated epigenetic
targeting of Survivin significantly enhances the antitumor activity
of paclitaxel against non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
7:37693–37713. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ni L, Wang L, Yao C, Ni Z, Liu F, Gong C,
Zhu X, Yan X, Watowich SS, Lee DA, et al: The histone deacetylase
inhibitor valproic acid inhibits NKG2D expression in natural killer
cells through suppression of STAT3 and HDAC3. Sci Rep. 7:452662017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kazanets A, Shorstova T, Hilmi K, Marques
M and Witcher M: Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes:
Paradigms, puzzles, and potential. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1865:275–288. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Pan L, Lu J, Wang X, Han L, Zhang Y, Han S
and Huang B: Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin a
potentiates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by up-regulating PTEN
expression. Cancer. 109:1676–1688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jiang H, Chen C, Sun Q, Wu J, Qiu L, Gao
C, Liu W, Yang J, Jun N and Dong J: The role of semaphorin 4D in
tumor development and angiogenesis in human breast cancer.
OncoTargets Ther. 9:5737–5750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Paesante S and Bakin
AV: Integrin β5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast
cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways.
Oncogene. 32:3049–3058. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Wang X, Li G, Wang A, Zhang Z, Merchan JR
and Halmos B: Combined histone deacetylase and cyclooxygenase
inhibition achieves enhanced antiangiogenic effects in lung cancer
cells. Mol Carcinog. 52:218–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Peulen O, Gonzalez A, Peixoto P, Turtoi A,
Mottet D, Delvenne P and Castronovo V: The anti-tumor effect of
HDAC inhibition in a human pancreas cancer model is significantly
improved by the simultaneous inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2. PLoS
One. 8:e751022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
New M, Olzscha H and La Thangue NB: HDAC
inhibitor-based therapies: Can we interpret the code? Mol Oncol.
6:637–656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|