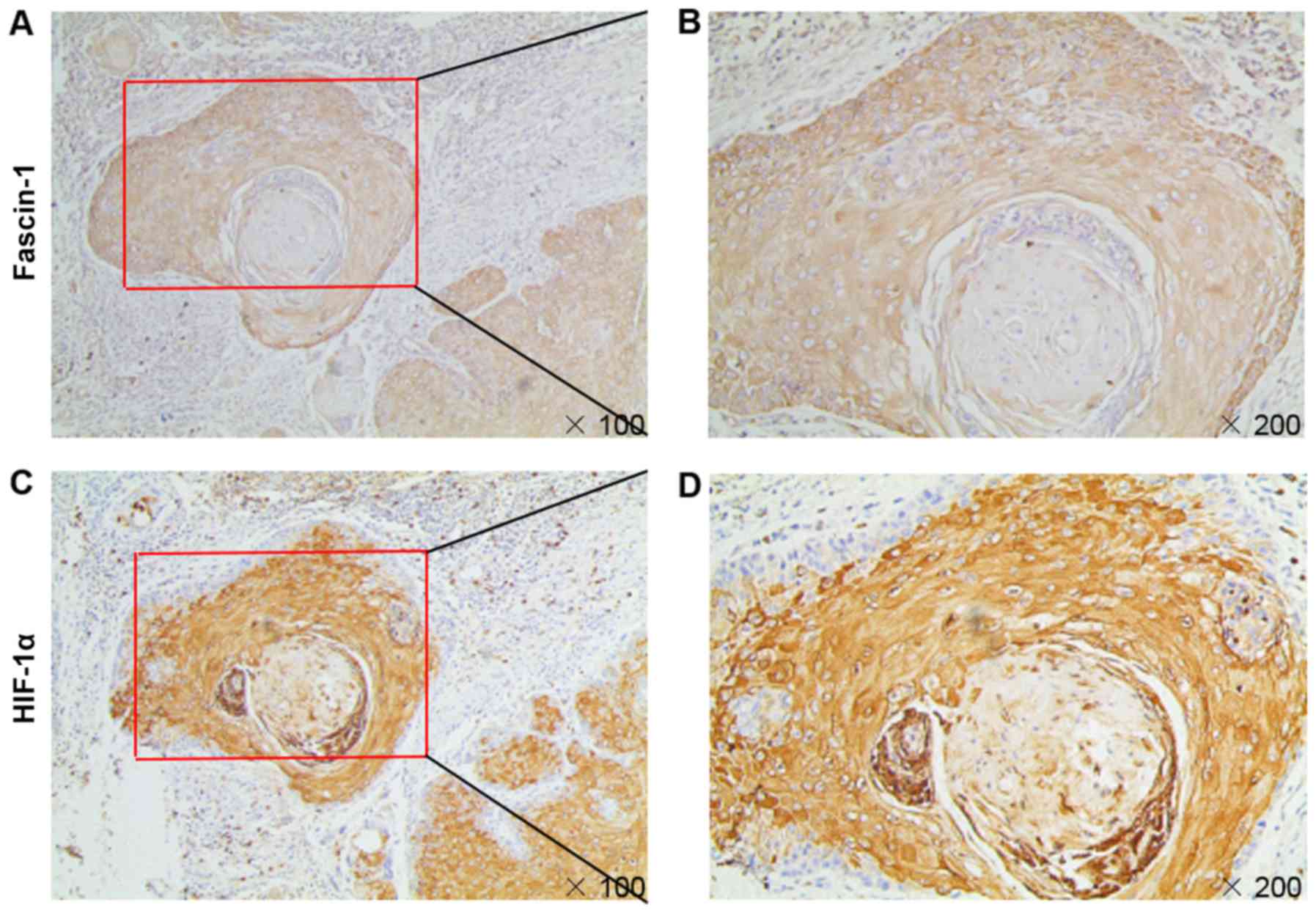
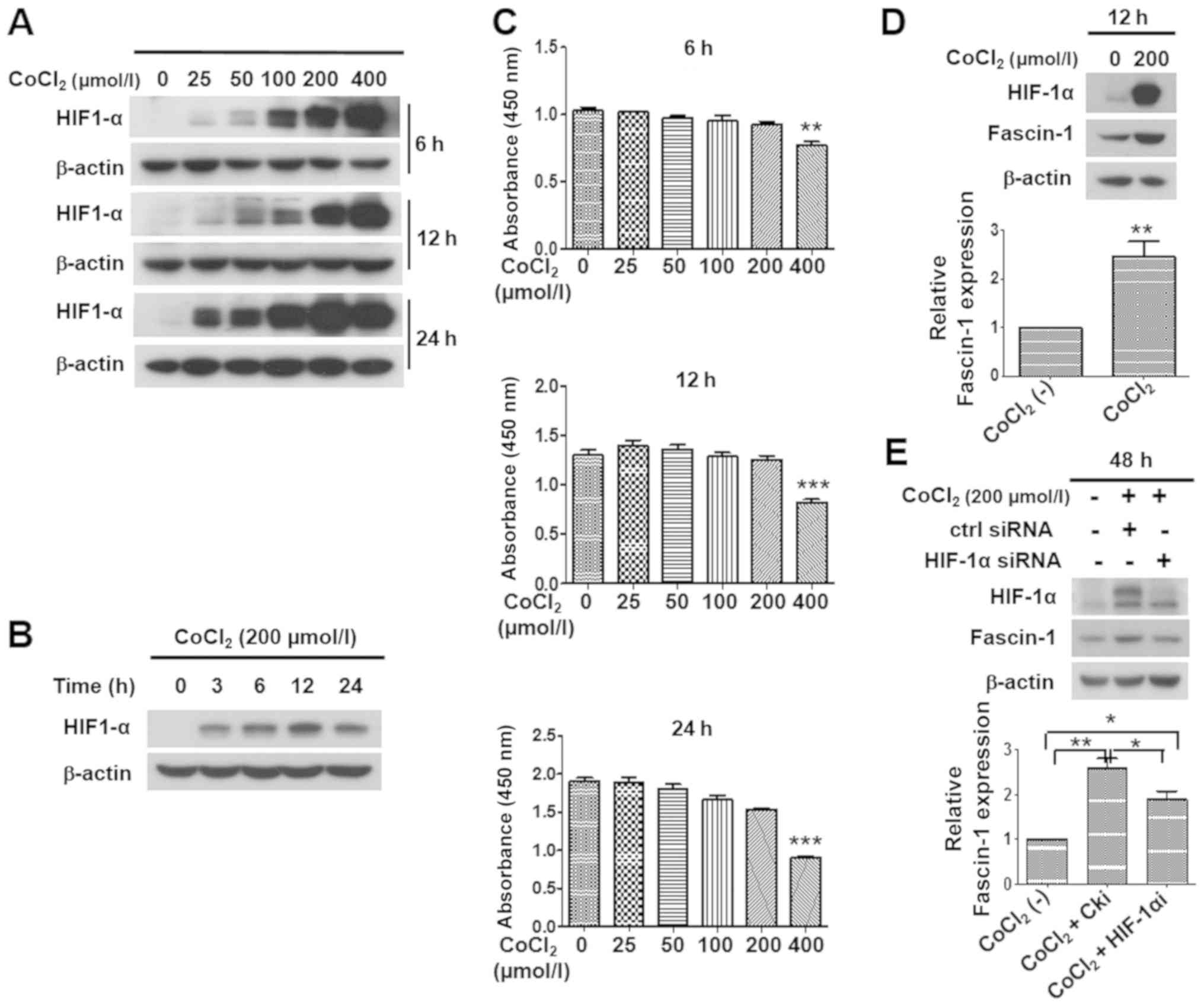
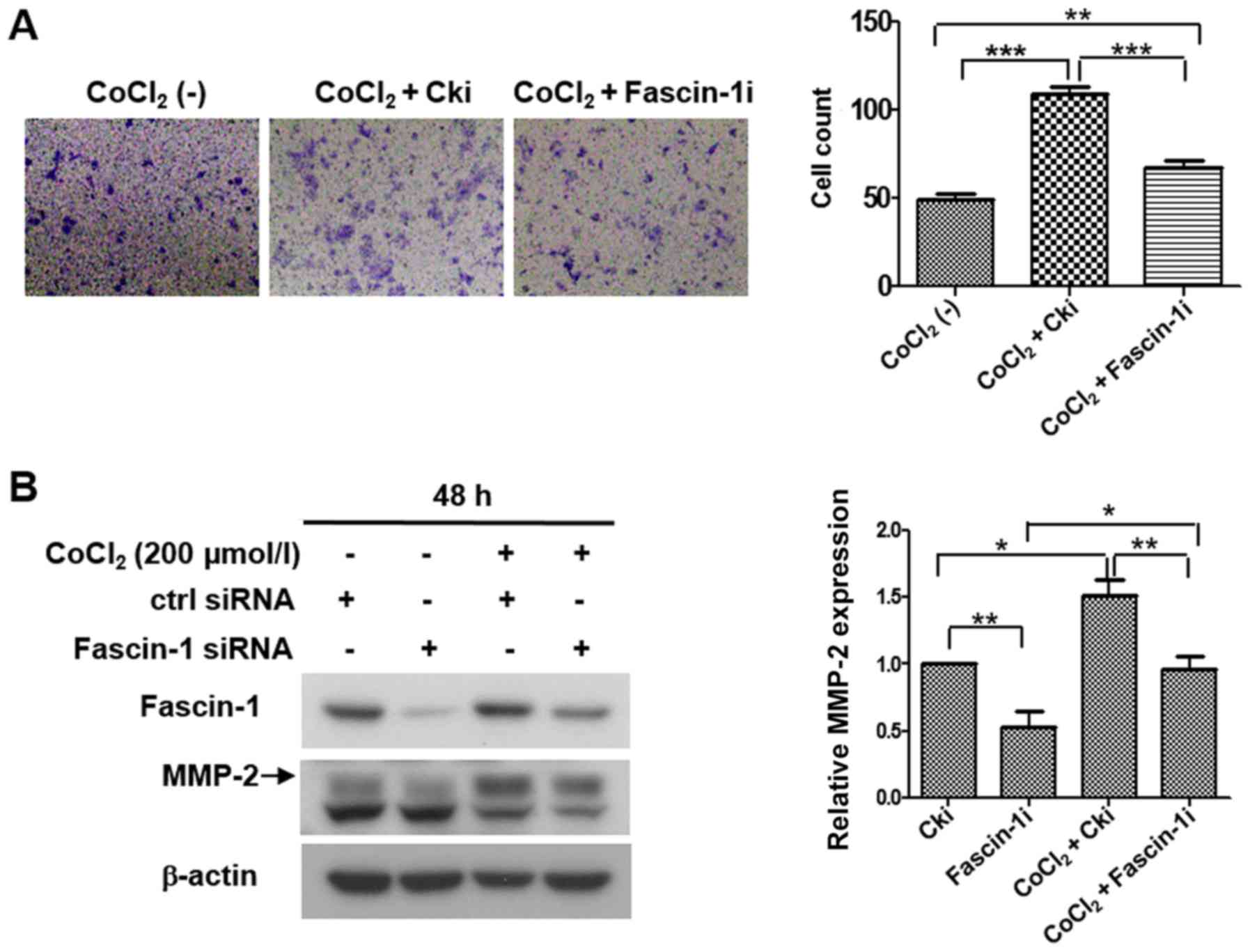
|
1
|
Gooi Z, Fakhry C, Goldenberg D, Richmon J
and Kiess AP; Education Committee of the American Head and Neck
Society (AHNS): AHNS Series: Do you know your guidelines?
Principles of radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: A review
of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines. Head Neck.
38:987–992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lewis CM, Hessel AC, Roberts DB, Guo YZ,
Holsinger FC, Ginsberg LE, El-Naggar AK and Weber RS: Prereferral
head and neck cancer treatment: Compliance with national
comprehensive cancer network treatment guidelines. Arch Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 136:1205–1211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wycliffe ND, Grover RS, Kim PD and
Simental A Jr: Hypopharyngeal cancer. Top Magn Reson Imaging.
18:243–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ge N, Lin HX, Xiao XS, Guo L, Xu HM, Wang
X, Jin T, Cai XY, Liang Y, Hu WH, et al: Prognostic significance of
Oct4 and Sox2 expression in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
J Transl Med. 8:942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kotwall C, Sako K, Razack MS, Rao U,
Bakamjian V and Shedd DP: Metastatic patterns in squamous cell
cancer of the head and neck. Am J Surg. 154:439–442. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hui AB, Bruce JP, Alajez NM, Shi W, Yue S,
Perez-Ordonez B, Xu W, O'Sullivan B, Waldron J, Cummings B, et al:
Significance of dysregulated metadherin and microRNA-375 in head
and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7539–7550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Loberg RD, Bradley DA, Tomlins SA,
Chinnaiyan AM and Pienta KJ: The lethal phenotype of cancer: The
molecular basis of death due to malignancy. CA Cancer J Clin.
57:225–241. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams JC: Formation of stable microspikes
containing actin and the 55 kDa actin bundling protein, fascin, is
a consequence of cell adhesion to thrombospondin-1: Implications
for the anti-adhesive activities of thrombospondin-1. J Cell Sci.
108:1977–1990. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adams JC: Fascin protrusions in cell
interactions. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 14:221–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Duh FM, Latif F, Weng Y, Geil L, Modi W,
Stackhouse T, Matsumura F, Duan DR, Linehan WM, Lerman MI, et al:
cDNA cloning and expression of the human homolog of the sea urchin
fascin and Drosophila singed genes which encodes an actin-bundling
protein. DNA Cell Biol. 13:821–827. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Arcangelis A, Georges-Labouesse E and
Adams JC: Expression of fascin-1, the gene encoding the
actin-bundling protein fascin-1, during mouse embryogenesis. Gene
Expr Patterns. 4:637–643. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang FR, Tao LH, Shen ZY, Lv Z, Xu LY and
Li EM: Fascin expression in human embryonic, fetal, and normal
adult tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 56:193–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zou J, Yang H, Chen F, Zhao H, Lin P,
Zhang J, Ye H, Wang L and Liu S: Prognostic significance of
fascin-1 and E-cadherin expression in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 19:11–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Alam H, Bhate AV, Gangadaran P, Sawant SS,
Salot S, Sehgal L, Dange PP, Chaukar DA, D'cruz AK, Kannanl S, et
al: Fascin overexpression promotes neoplastic progression in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 12:322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papaspyrou K, Brochhausen C, Schmidtmann
I, Fruth K, Gouveris H, Kirckpatrick J, Mann W and Brieger J:
Fascin upregulation in primary head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma is associated with lymphatic metastasis. Oncol Lett.
7:2041–2046. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shay JE and Celeste Simon M:
Hypoxia-inducible factors: Crosstalk between inflammation and
metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:389–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subarsky P and Hill RP: The hypoxic tumour
microenvironment and metastatic progression. Clin Exp Metastasis.
20:237–250. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL and Wirtz D: Hypoxia
and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:430–439. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Semenza GL: Hydroxylation of HIF-1: Oxygen
sensing at the molecular level. Physiology (Bethesda). 19:176–182.
2004.
|
|
20
|
Brahimi-Horn MC, Bellot G and Pouysségur
J: Hypoxia and energetic tumour metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
21:67–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhu G, Peng F, Gong W, She L, Wei M, Tan
H, Chen C, Zhang D, Li G, Huang D, et al: Hypoxia promotes
migration/invasion and glycolysis in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma via an HIF-1α-MTDH loop. Oncol Rep. 38:2893–2900. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun
J, Yang S and Hao J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocar-cinoma invasion and metastasis by activating
transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res.
74:2455–2464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Yue P, Zhou Z, Khuri FR and Sun SY:
Death receptor regulation and celecoxib-induced apoptosis in human
lung cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1769–1780. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition.
Springer; New York, NY: 2010
|
|
25
|
Haynes J, Srivastava J, Madson N, Wittmann
T and Barber DL: Dynamic actin remodeling during
epithelial-mesenchymal transition depends on increased moesin
expression. Mol Biol Cell. 22:4750–4764. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu SC, Jen YM, Jiang SS, Chang JL, Hsiung
CA, Wang CH and Juang JL: G(alpha)12-mediated pathway promotes
invasiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by modulating actin
cytoskeleton reorganization. Cancer Res. 69:6122–6130. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sato H, Kida Y, Mai M, Endo Y, Sasaki T,
Tanaka J and Seiki M: Expression of genes encoding type IV
collagen-degrading metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in various human tumor cells. Oncogene. 7:77–83.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Okazaki I and Inagaki Y: Novel strategies
for hepatocellular carcinoma based on MMPs science. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:753–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Edwards RA and Bryan J: Fascins, a family
of actin bundling proteins. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 32:1–9. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao W, Gao J, Wu J, Liu QH, Wang ZG, Li
HL and Xing LH: Expression of Fascin-1 on human lung cancer and
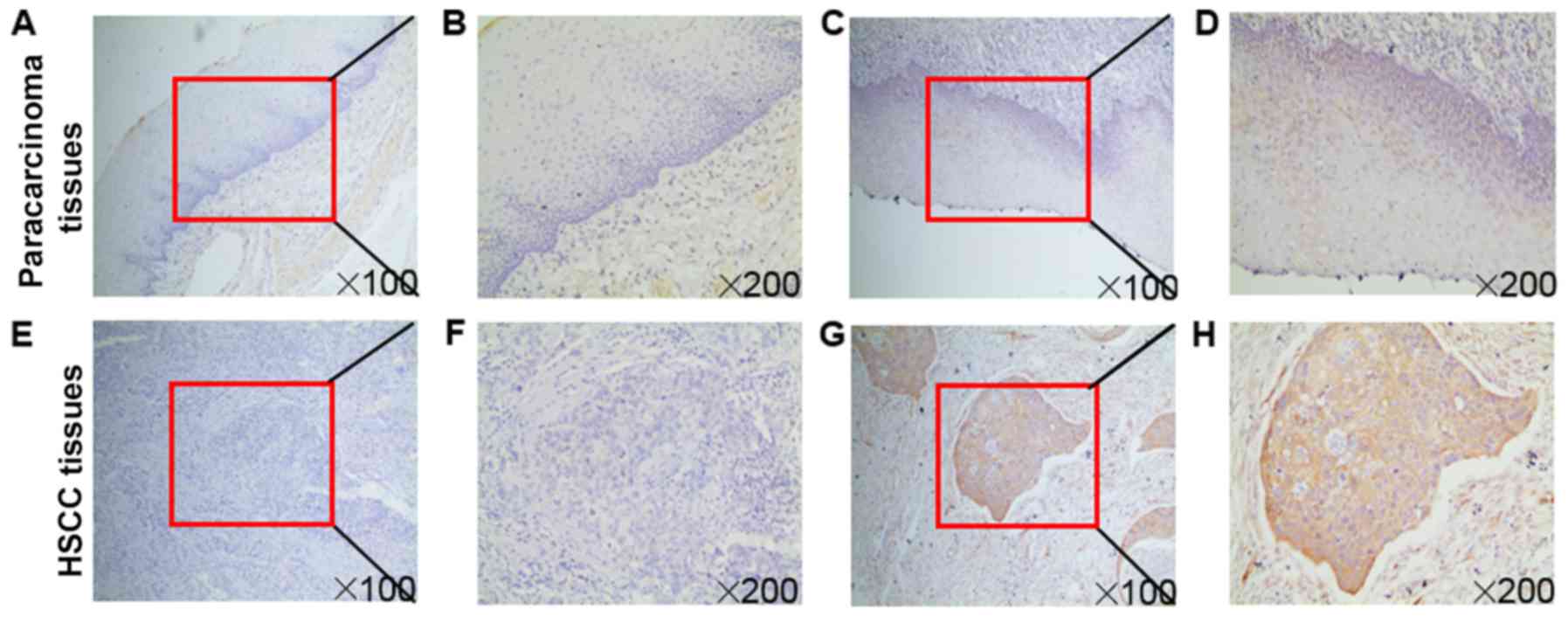
paracarcinoma tissue and its relation to clinicopathological
characteristics in patients with lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
8:2571–2576. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang ZM, Tang PZ, Xu ZG, Li QH, Hu YH, Xu
GZ, Gao L and Tu GY: Long-term results of different treatment
modalities in 464 hypopharyngeal squamous-cell carcinoma patients.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 27:48–51. 2005.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hoffman HT, Karnell LH, Shah JP, Ariyan S,
Brown GS, Fee WE, Glass AG, Goepfert H, Ossoff RH and Fremgen AM:
Hypopharyngeal cancer patient care evaluation. Laryngoscope.
107:1005–1017. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao D, Zhang T, Hou XM and Ling XL:
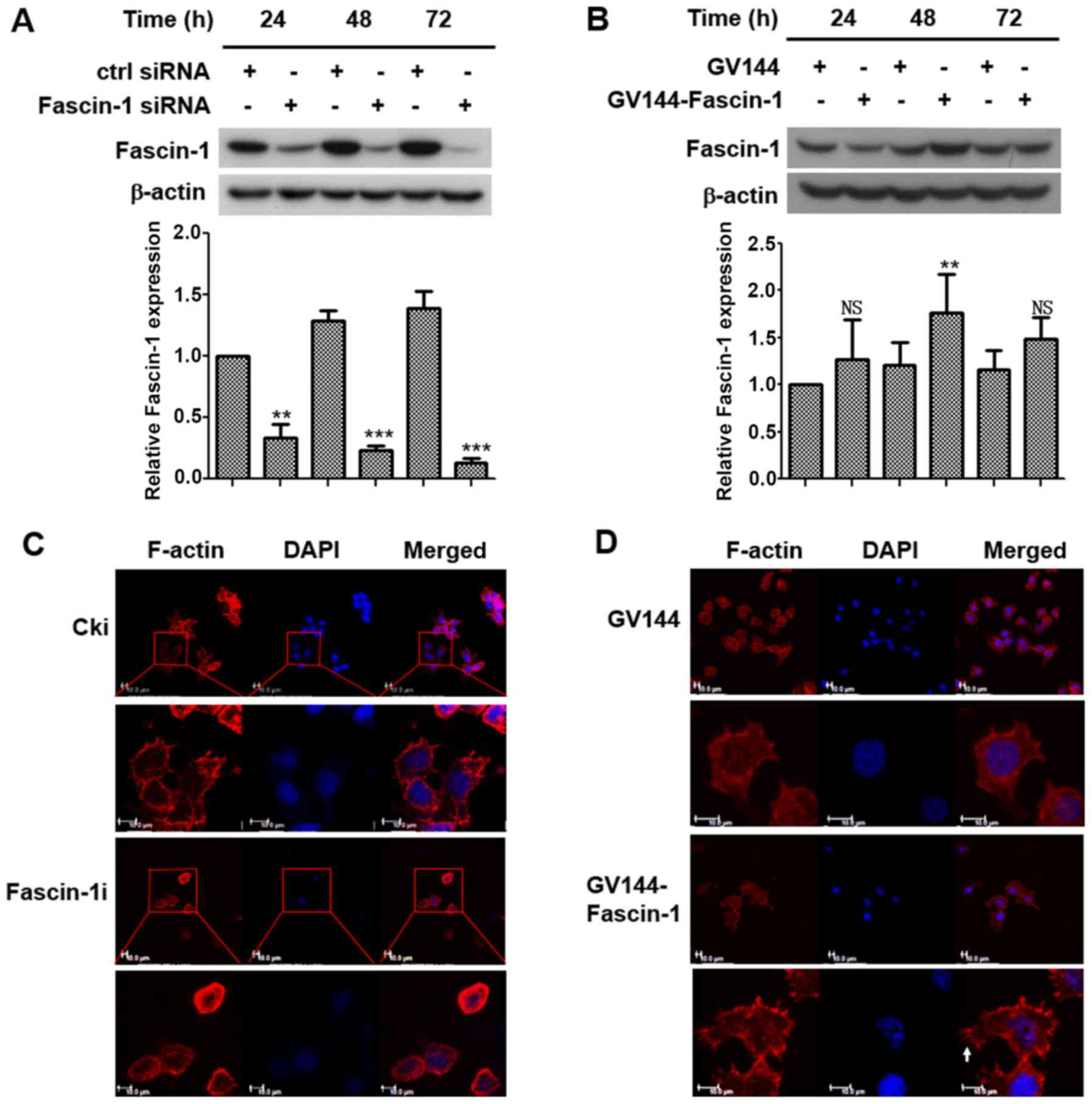
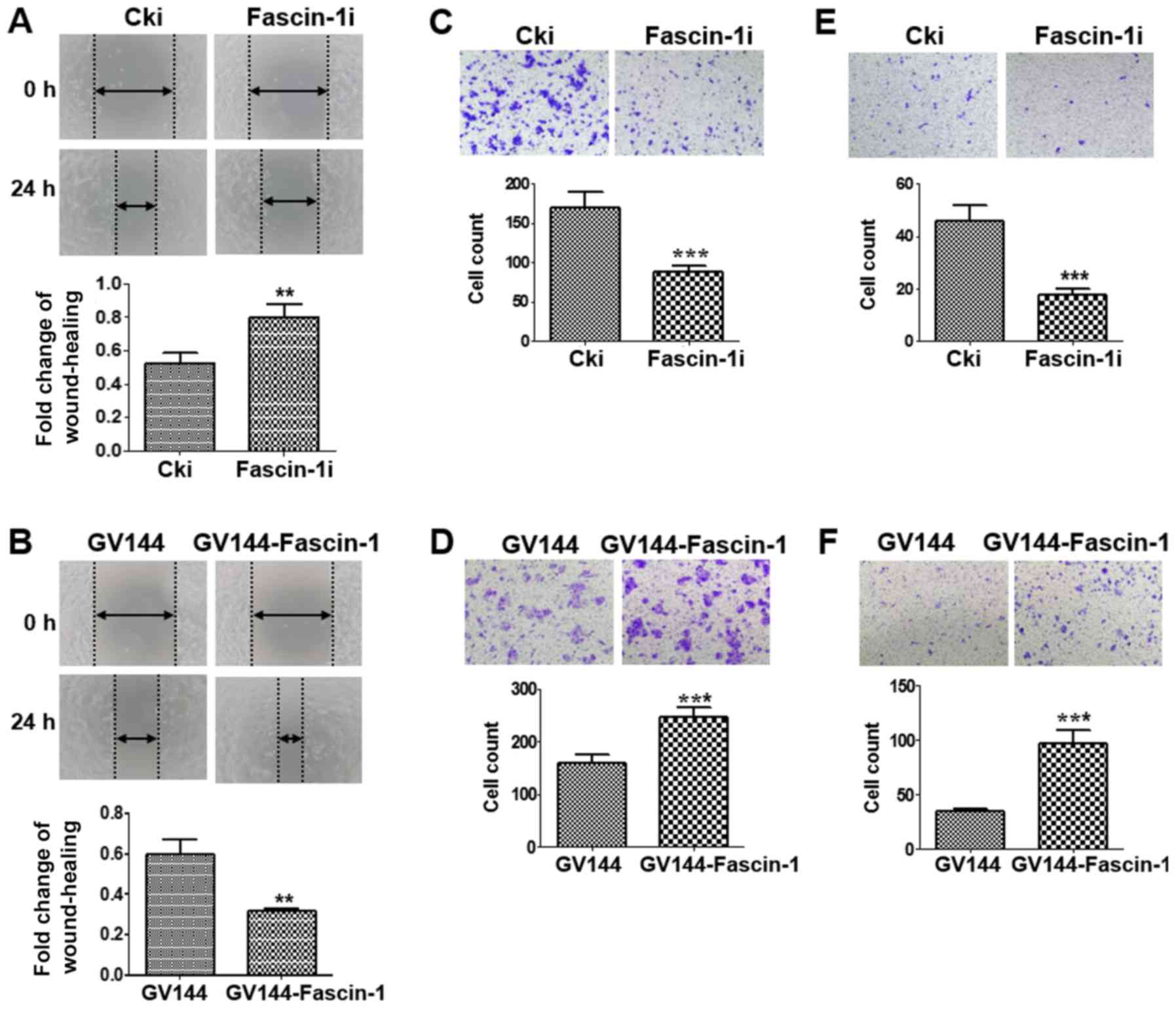
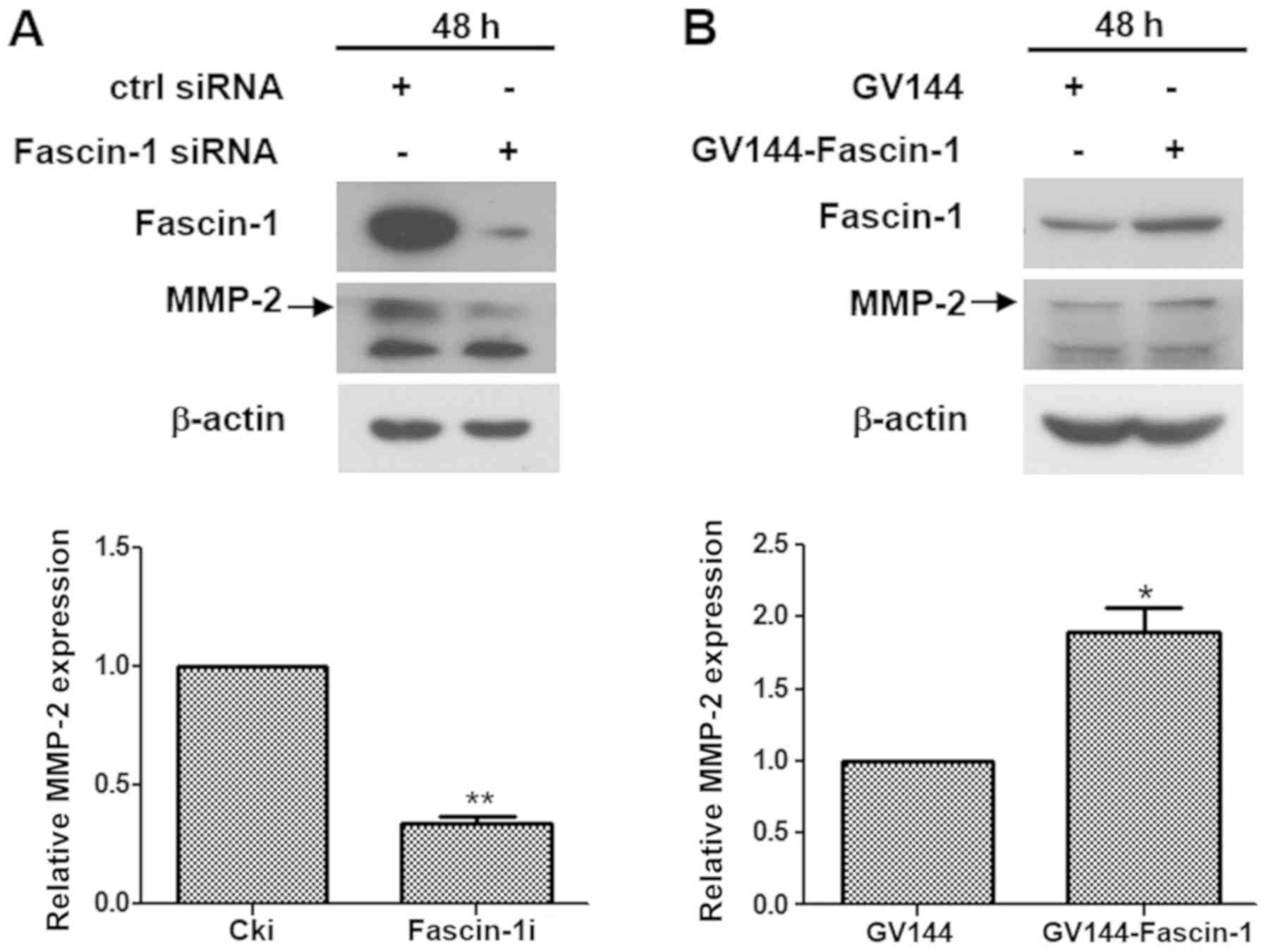
Knockdown of fascin-1 expression suppresses cell migration and
invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the MAPK
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 497:694–699. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang BW, Miyazawa M and Tsuji Y: Distinct
regulatory mechanisms of the human ferritin gene by hypoxia and
hypoxia mimetic cobalt chloride at the transcriptional and
post-transcriptional levels. Cell Signal. 26:2702–2709. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Yang S, Jakoncic J, Zhang JJ and
Huang XY: Migrastatin analogues target fascin to block tumour
metastasis. Nature. 464:1062–1066. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|