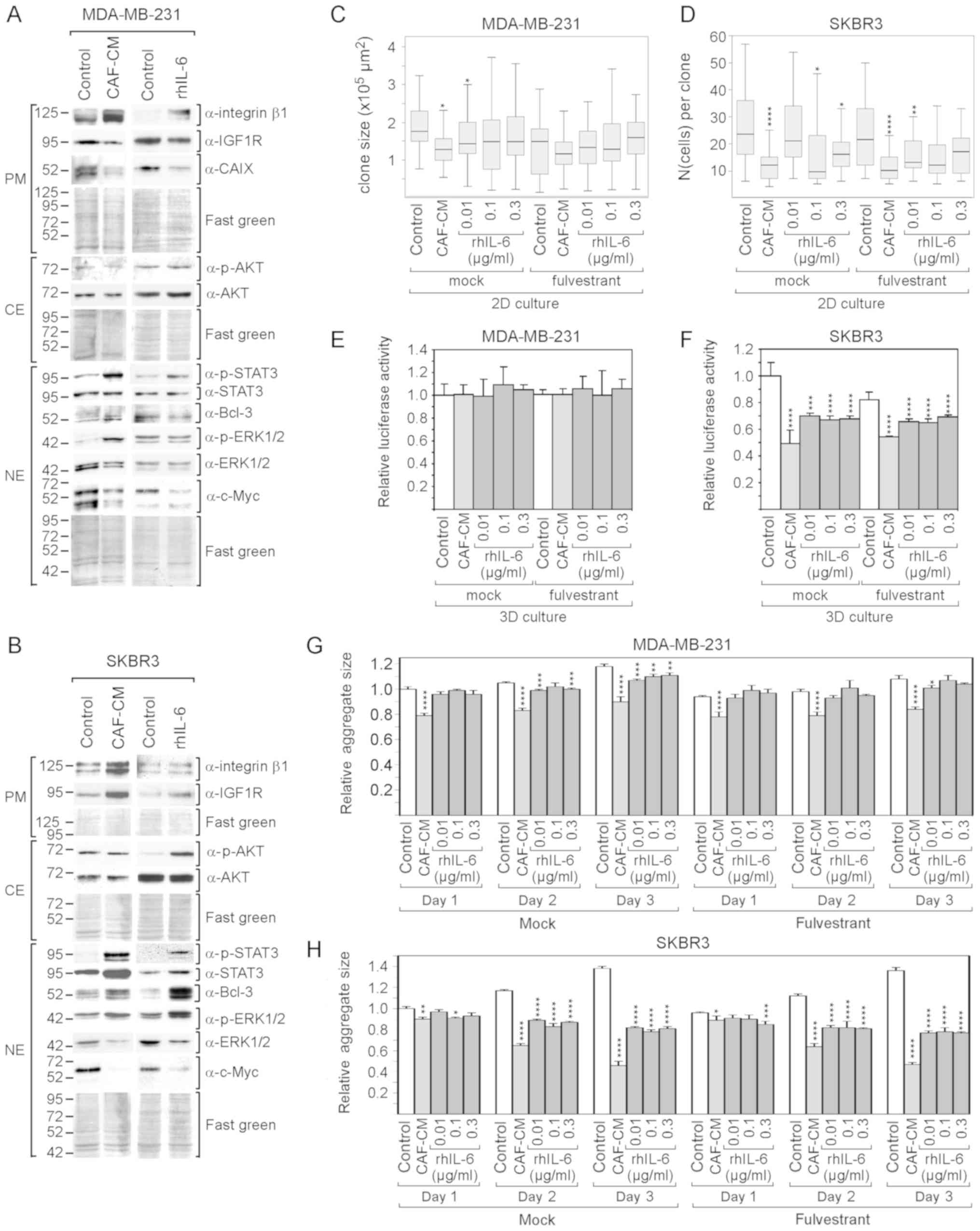
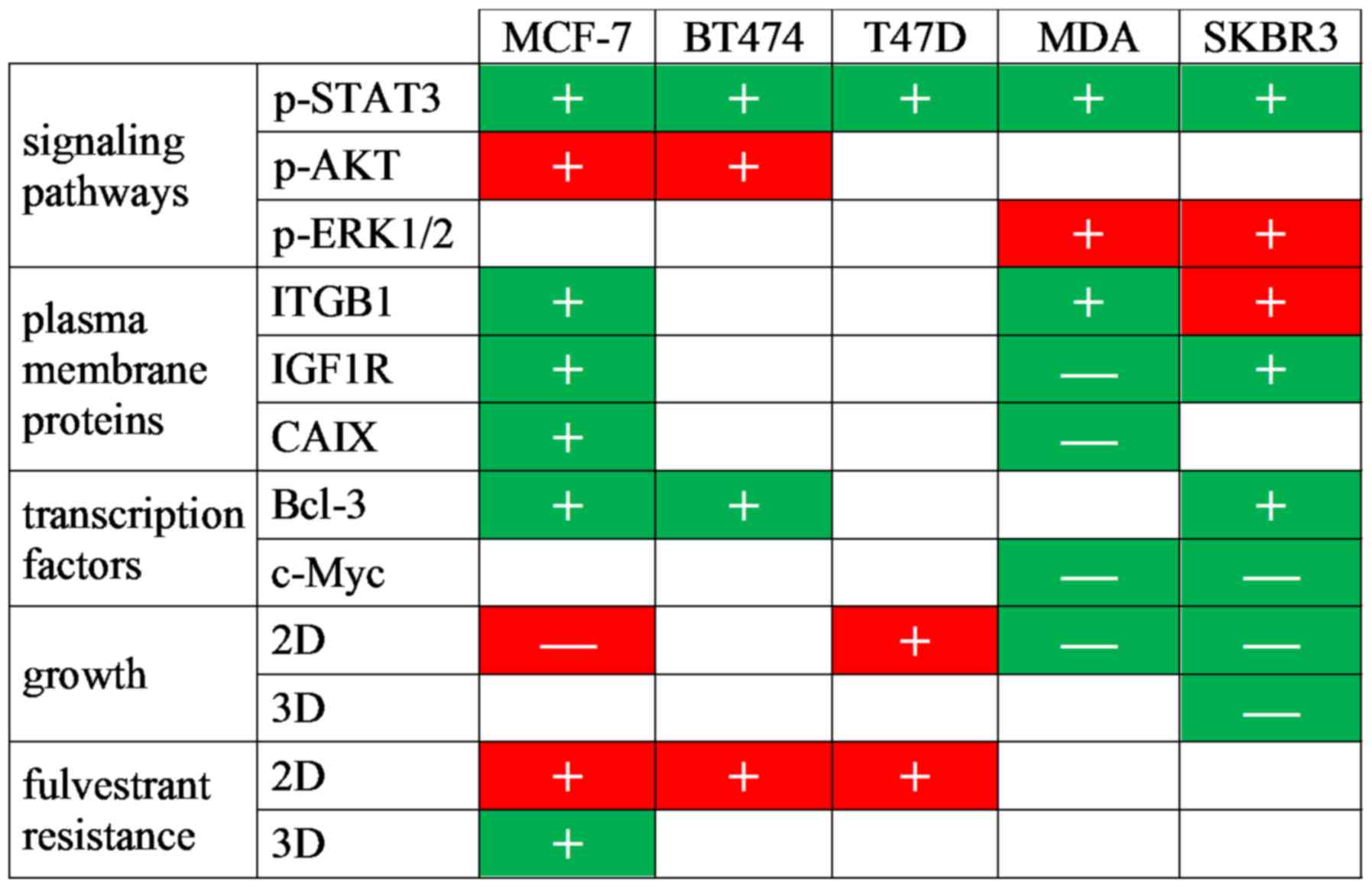
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M,
Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Pan HC, Taylor C, Wang YC, et al Early
Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG): Relevance of
breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy
of adjuvant tamoxifen: Patient-level meta-analysis of randomised
trials. Lancet. 378:771–784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prat A and Perou CM: Deconstructing the
molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 5:5–23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hudis CA: Trastuzumab - mechanism of
action and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 357:39–51. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Omarini C, Guaitoli G, Pipitone S,
Moscetti L, Cortesi L, Cascinu S and Piacentini F: Neoadjuvant
treatments in triple-negative breast cancer patients: Where we are
now and where we are going. Cancer Manag Res. 10:91–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wagner J, Rapsomaniki MA, Chevrier S,
Anzeneder T, Langwieder C, Dykgers A, Rees M, Ramaswamy A, Muenst
S, Soysal SD, et al: A Single-Cell Atlas of the Tumor and Immune
Ecosystem of Human Breast Cancer. Cell. 177:1330–1345.e18. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hong D, Fritz AJ, Zaidi SK, van Wijnen AJ,
Nickerson JA, Imbalzano AN, Lian JB, Stein JL and Stein GS:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells
contribute to breast cancer heterogeneity. J Cell Physiol.
233:9136–9144. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dittmer J: Breast cancer stem cells:
Features, key drivers and treatment options. Semin. Cancer Biol.
53:59–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bailey TA, Luan H, Clubb RJ, Naramura M,
Band V, Raja SM and Band H: Mechanisms of Trastuzumab resistance in
ErbB2-driven breast cancer and newer opportunities to overcome
therapy resistance. J Carcinog. 10:282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Musgrove EA and Sutherland RL: Biological
determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:631–643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Osborne CK and Schiff R: Mechanisms of
endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med. 62:233–247.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dittmer J and Leyh B: The impact of tumor
stroma on drug response in breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
31:3–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Leyh B, Dittmer A, Lange T, Martens JW and
Dittmer J: Stromal cells promote anti-estrogen resistance of breast
cancer cells through an insulin-like growth factor binding protein
5 (IGFBP5)/B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 3 (Bcl-3) axis. Oncotarget.
6:39307–39328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pratt MA, Bishop TE, White D, Yasvinski G,
Ménard M, Niu MY and Clarke R: Estrogen withdrawal-induced
NF-kappaB activity and bcl-3 expression in breast cancer cells:
Roles in growth and hormone independence. Mol Cell Biol.
23:6887–6900. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Cao X, Sun X, Lei R, Chen P, Zhao
Y, Jiang Y, Yin J, Chen R, Ye D, et al: Bcl-3 regulates TGFβ
signaling by stabi-lizing Smad3 during breast cancer pulmonary
metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 7:e25082016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Schuster M, Annemann M, Plaza-Sirvent C
and Schmitz I: Atypical IκB proteins - nuclear modulators of NF-κB
signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 11:232013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sas L, Lardon F, Vermeulen PB, Hauspy J,
Van Dam P, Pauwels P, Dirix LY and Van Laere SJ: The interaction
between ER and NFκB in resistance to endocrine therapy. Breast
Cancer Res. 14:2122012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang VY, Li Y, Kim D, Zhong X, Du Q,
Ghassemian M and Ghosh G: Bcl3 Phosphorylation by Akt, Erk2, and
IKK is required for its transcriptional activity. Mol Cell.
67:484–497.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baxter RC: IGF binding proteins in cancer:
Mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:329–341.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mita K, Zhang Z, Ando Y, Toyama T,
Hamaguchi M, Kobayashi S, Hayashi S, Fujii Y, Iwase H and Yamashita
H: Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor binding
protein (IGFBP)-4 and IGFBP-5 expression in breast cancer. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 37:575–582. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Becker MA, Hou X, Harrington SC, Weroha
SJ, Gonzalez SE, Jacob KA, Carboni JM, Gottardis MM and Haluska P:
IGFBP ratio confers resistance to IGF targeting and correlates with
increased invasion and poor outcome in breast tumors. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:1808–1817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
West NR: Coordination of Immune-Stroma
Crosstalk by IL-6 Family Cytokines. Front Immunol. 10:10932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boulanger MJ, Chow DC, Brevnova EE and
Garcia KC: Hexameric structure and assembly of the
interleukin-6/IL-6 alpha-receptor/gp130 complex. Science.
300:2101–2104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schaper F and Rose-John S: Interleukin-6:
Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 26:475–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Avalle L, Pensa S, Regis G, Novelli F and
Poli V: STAT1 and STAT3 in tumorigenesis: A matter of balance.
JAK-STAT. 1:65–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L, et al: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lacina L, Brábek J, Král V, Kodet O and
Smetana K Jr: Interleukin-6: A molecule with complex biological
impact in cancer. Histol Histopathol. 34:125–136. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Hodge DR, Hurt EM and Farrar WL: The role
of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2502–2512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morrow RJ, Etemadi N, Yeo B and Ernst M:
Challenging a Misnomer? The Role of Inflammatory Pathways in
Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Mediators Inflamm. 2017:47548272017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghandadi M and Sahebkar A: Interleukin-6:
A Critical Cytokine in Cancer Multidrug Resistance. Curr Pharm Des.
22:518–526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim SY, Kang JW, Song X, Kim BK, Yoo YD,
Kwon YT and Lee YJ: Role of the IL-6-JAK1-STAT3-Oct-4 pathway in
the conversion of non-stem cancer cells into cancer stem-like
cells. Cell Signal. 25:961–969. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F,
Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 induces
an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:2940–2947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brooks MD, Burness ML and Wicha MS:
Therapeutic Implications of Cellular Heterogeneity and Plasticity
in Breast Cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 17:260–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Korkaya H, Kim GI, Davis A, Malik F, Henry
NL, Ithimakin S, Quraishi AA, Tawakkol N, D'Angelo R, Paulson AK,
et al: Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab
resistance in HER2+ breast cancer by expanding the cancer stem cell
population. Mol Cell. 47:570–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saha S, Mukherjee S, Khan P, Kajal K,
Mazumdar M, Manna A, Mukherjee S, De S, Jana D, Sarkar DK, et al:
Aspirin Suppresses the Acquisition of Chemoresistance in Breast
Cancer by Disrupting an NFκB-IL6 Signaling Axis Responsible for the
Generation of Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 76:2000–2012. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu S, Ginestier C, Ou SJ, Clouthier SG,
Patel SH, Monville F, Korkaya H, Heath A, Dutcher J, Kleer CG, et
al: Breast cancer stem cells are regulated by mesenchymal stem
cells through cytokine networks. Cancer Res. 71:614–624. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dittmer J: Mechanisms governing metastatic
dormancy in breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 44:72–82. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang GJ and Adachi I: Serum interleukin-6
levels correlate to tumor progression and prognosis in metastatic
breast carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 19(2B): 1427–1432.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Casneuf T, Axel AE, King P, Alvarez JD,
Werbeck JL, Verhulst T, Verstraeten K, Hall BM and Sasser AK:
Interleukin-6 is a potential therapeutic target in interleukin-6
dependent, estrogen receptor-a-positive breast cancer. Breast
Cancer (Dove Med Press). 8:13–27. 2016.
|
|
41
|
Zhang W, Guo J, Li S, Ma T, Xu D, Han C,
Liu F, Yu W and Kong L: Discovery of monocarbonyl curcumin-BTP
hybrids as STAT3 inhibitors for drug-sensitive and drug-resistant
breast cancer therapy. Sci Rep. 7:463522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dittmer A and Dittmer J: Long-term
exposure to carcinoma-associated fibroblasts makes breast cancer
cells addictive to integrin β1. Oncotarget. 9:22079–22094. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dittmer A and Dittmer J: Beta-actin is not
a reliable loading control in Western blot analysis.
Electrophoresis. 27:2844–2845. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moritz CP: Tubulin or Not Tubulin: Heading
Toward Total Protein Staining as Loading Control in Western Blots.
Proteomics. 17:172017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dittmer A, Schunke D and Dittmer J: PTHrP
promotes homotypic aggregation of breast cancer cells in
three-dimensional cultures. Cancer Lett. 260:56–61. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Oerlecke I, Bauer E, Dittmer A, Leyh B and
Dittmer J: Cyclic AMP enhances TGFβ responses of breast cancer
cells by upregulating TGFβ receptor I expression. PLoS One.
8:e542612013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Brocke-Heidrich K, Ge B, Cvijic H, Pfeifer
G, Löffler D, Henze C, McKeithan TW and Horn F: BCL3 is induced by
IL-6 via Stat3 binding to intronic enhancer HS4 and represses its
own transcription. Oncogene. 25:7297–7304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu Z, Jiang Y, Hou Y, Hu Y, Cao X, Tao Y,
Xu C, Liu S, Wang S, Wang L, et al: The IκB family member Bcl-3
stabilizes c-Myc in colorectal cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:280–282.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bretones G, Delgado MD and León J: Myc and
cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:506–516. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Massoumi R, Chmielarska K, Hennecke K,
Pfeifer A and Fässler R: Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by
blocking Bcl-3-dependent NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 125:665–677.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pontiggia O, Sampayo R, Raffo D, Motter A,
Xu R, Bissell MJ, Joffé EB and Simian M: The tumor microenvironment
modulates tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer: A role for soluble
stromal factors and fibronectin through β1 integrin. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 133:459–471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sánchez-Pérez Y, Chirino YI,
Osornio-Vargas AR, Herrera LA, Morales-Bárcenas R, López-Saavedra
A, González-Ramírez I, Miranda J and García-Cuellar CM: Cytoplasmic
p21(CIP1/WAF1), ERK1/2 activation, and cytoskeletal remodeling are
associated with the senescence-like phenotype after airborne
particulate matter (PM(10)) exposure in lung cells. Toxicol Lett.
225:12–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yousefi B, Rahmati M and Ahmadi Y: The
roles of p53R2 in cancer progression based on the new function of
mutant p53 and cytoplasmic p21. Life Sci. 99:14–17. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chiu JJ, Sgagias MK and Cowan KH:
Interleukin 6 acts as a paracrine growth factor in human mammary
carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2:215–221. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kathawala RJ, Gupta P, Ashby CRJ Jr and
Chen ZS: The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug
resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist
Updat. 18:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson
KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ and Wicha MS: In vitro propagation and
transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Genes Dev. 17:1253–1270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
DuFort CC, Paszek MJ and Weaver VM:
Balancing forces: Architectural control of mechanotransduction. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:308–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dittmer A, Fuchs A, Oerlecke I, Leyh B,
Kaiser S, Martens JW, Lützkendorf J, Müller L and Dittmer J:
Mesenchymal stem cells and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
sensitize breast cancer cells in 3D cultures to kinase inhibitors.
Int J Oncol. 39:689–696. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dittmer A, Hohlfeld K, Lützkendorf J,
Müller LP and Dittmer J: Human mesenchymal stem cells induce
E-cadherin degradation in breast carcinoma spheroids by activating
ADAM10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:3053–3065. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sasser AK, Sullivan NJ, Studebaker AW,
Hendey LF, Axel AE and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 is a potent growth
factor for ER-alpha-positive human breast cancer. FASEB J.
21:3763–3770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bharti R, Dey G, Ojha PK, Rajput S,
Jaganathan SK, Sen R and Mandal M: Diacerein-mediated inhibition of
IL-6/IL-6R signaling induces apoptotic effects on breast cancer.
Oncogene. 35:3965–3975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Klinakis A, Szabolcs M, Chen G, Xuan S,
Hibshoosh H and Efstratiadis A: Igf1r as a therapeutic target in a
mouse model of basal-like breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:2359–2364. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ward C, Meehan J, Mullen P, Supuran C,
Dixon JM, Thomas JS, Winum JY, Lambin P, Dubois L, Pavathaneni NK,
et al: Evaluation of carbonic anhydrase IX as a therapeutic target
for inhibition of breast cancer invasion and metastasis using a
series of in vitro breast cancer models. Oncotarget. 6:24856–24870.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen CR, Kang Y and Massagué J: Defective
repression of c-myc in breast cancer cells: A loss at the core of
the transforming growth factor beta growth arrest program. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:992–999. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Friedrich K, Dolznig H, Han X and Moriggl
R: Steering of carcinoma progression by the YIN/YANG interaction of
STAT1/STAT3. Biosci Trends. 11:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Marconett CN, Singhal AK, Sundar SN and
Firestone GL: Indole-3-carbinol disrupts estrogen receptor-alpha
dependent expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and
insulin receptor substrate-1 and proliferation of human breast
cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 363:74–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gaben AM, Sabbah M, Redeuilh G, Bedin M
and Mester J: Ligand-free estrogen receptor activity complements
IGF1R to induce the proliferation of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 12:2912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sun J, Lu Z, Deng Y, Wang W, He Q, Yan W
and Wang A: Up-regulation of INSR/IGF1R by C-myc promotes TSCC
tumorigenesis and metastasis through the NF-κB pathway. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864(5 Pt A): 1873–1882. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ansari MF, Idrees D, Hassan MI, Ahmad K,
Avecilla F and Azam A: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation
of novel pyridine-thiazolidinone derivatives as anticancer agents:
Targeting human carbonic anhydrase IX. Eur J Med Chem. 144:544–556.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sedlakova O, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX, a
hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery
in tumors. Front Physiol. 4:4002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jung YJ, Isaacs JS, Lee S, Trepel J and
Neckers L: IL-1beta-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1alpha via an
NFkappaB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between
inflammation and oncogenesis. FASEB J. 17:2115–2117. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang K, Zhu X, Zhang K, Yin Y, Chen Y and
Zhang T: Interleukin-6 contributes to chemoresistance in MDA-MB-231
cells via targeting HIF-1a. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 32:e220392018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Nass N, Dittmer A, Hellwig V, Lange T,
Beyer JM, Leyh B, Ignatov A, Weiβenborn C, Kirkegaard T,
Lykkesfeldt AE, et al: Expression of transmembrane protein 26
(TMEM26) in breast cancer and its association with drug response.
Oncotarget. 7:38408–38426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hamurcu Z, Kahraman N, Ashour A and
Ozpolat B: FOXM1 transcriptionally regulates expression of integrin
β1 in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
163:485–493. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Gache C, Berthois Y, Martin PM and Saez S:
Positive regulation of normal and tumoral mammary epithelial cell
proliferation by fibroblasts in coculture. In. Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 34:347–351. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Chen L, Shulman LM and Revel M: IL-6
receptors and sensitivity to growth inhibition by IL-6 in clones of
human breast carcinoma cells. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
5:125–136. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Badache A and Hynes NE: Interleukin 6
inhibits proliferation and, in cooperation with an epidermal growth
factor receptor autocrine loop, increases migration of T47D breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:383–391. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ikeda O, Sekine Y, Mizushima A, Nakasuji
M, Miyasaka Y, Yamamoto C, Muromoto R, Nanbo A, Oritani K,
Yoshimura A, Matsuda T, et al: Interactions of STAP-2 with Brk and
STAT3 participate in cell growth of human breast cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 285:38093–38103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Proietti C, Salatino M, Rosemblit C,
Carnevale R, Pecci A, Kornblihtt AR, Molinolo AA, Frahm I, Charreau
EH, Schillaci R, et al: Progestins induce transcriptional
activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
(Stat3) via a Jak- and Src-dependent mechanism in breast cancer
cells. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4826–4840. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Segev DL, Ha TU, Tran TT, Kenneally M,
Harkin P, Jung M, MacLaughlin DT, Donahoe PK and Maheswaran S:
Mullerian inhibiting substance inhibits breast cancer cell growth
through an NFkappa B-mediated pathway. J Biol Chem.
275:28371–28379. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ping B, He X, Xia W, Lee DF, Wei Y, Yu D,
Mills G, Shi D and Hung MC: Cytoplasmic expression of p21CIP1/WAF1
is correlated with IKKβ overexpression in human breast cancers. Int
J Oncol. 29:1103–1110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Neve RM, Sutterlüty H, Pullen N, Lane HA,
Daly JM, Krek W and Hynes NE: Effects of oncogenic ErbB2 on G1 cell
cycle regulators in breast tumour cells. Oncogene. 19:1647–1656.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Weigelt B, Lo AT, Park CC, Gray JW and
Bissell MJ: HER2 signaling pathway activation and response of
breast cancer cells to HER2-targeting agents is dependent strongly
on the 3D micro-environment. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 122:35–43.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Hugo HJ, Lebret S, Tomaskovic-Crook E,
Ahmed N, Blick T, Newgreen DF, Thompson EW and Ackland ML:
Contribution of Fibroblast and Mast Cell (Afferent) and Tumor
(Efferent) IL-6 Effects within the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer
Microenviron. 5:83–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Mao Y, Zhang Y, Qu Q, Zhao M, Lou Y, Liu
J, Huang O, Chen X, Wu J and Shen K: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
induce trastuzumab resistance in HER2 positive breast cancer cells.
Mol Biosyst. 11:1029–1040. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gallo M, Frezzetti D, Roma C, Chicchinelli
N, Barbieri A, Arra C, Scognamiglio G, Botti G, De Luca A and
Normanno N: RANTES and IL-6 cooperate in inducing a more aggressive
phenotype in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 9:17543–17553. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Singh S, Murillo G, Chen D, Parihar AS and
Mehta RG: Suppression of Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation by
Selective Single-Domain Antibody for Intracellular STAT3. Breast
Cancer (Auckl). 12:11782234177508582018.
|
|
90
|
Mosteiro L, Pantoja C, de Martino A and
Serrano M: Senescence promotes in vivo reprogramming through
p16INK4a and IL-6. Aging Cell. 17:172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Correia AL and Bissell MJ: The tumor
microenvironment is a dominant force in multidrug resistance. Drug
Resist Updat. 15:39–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|