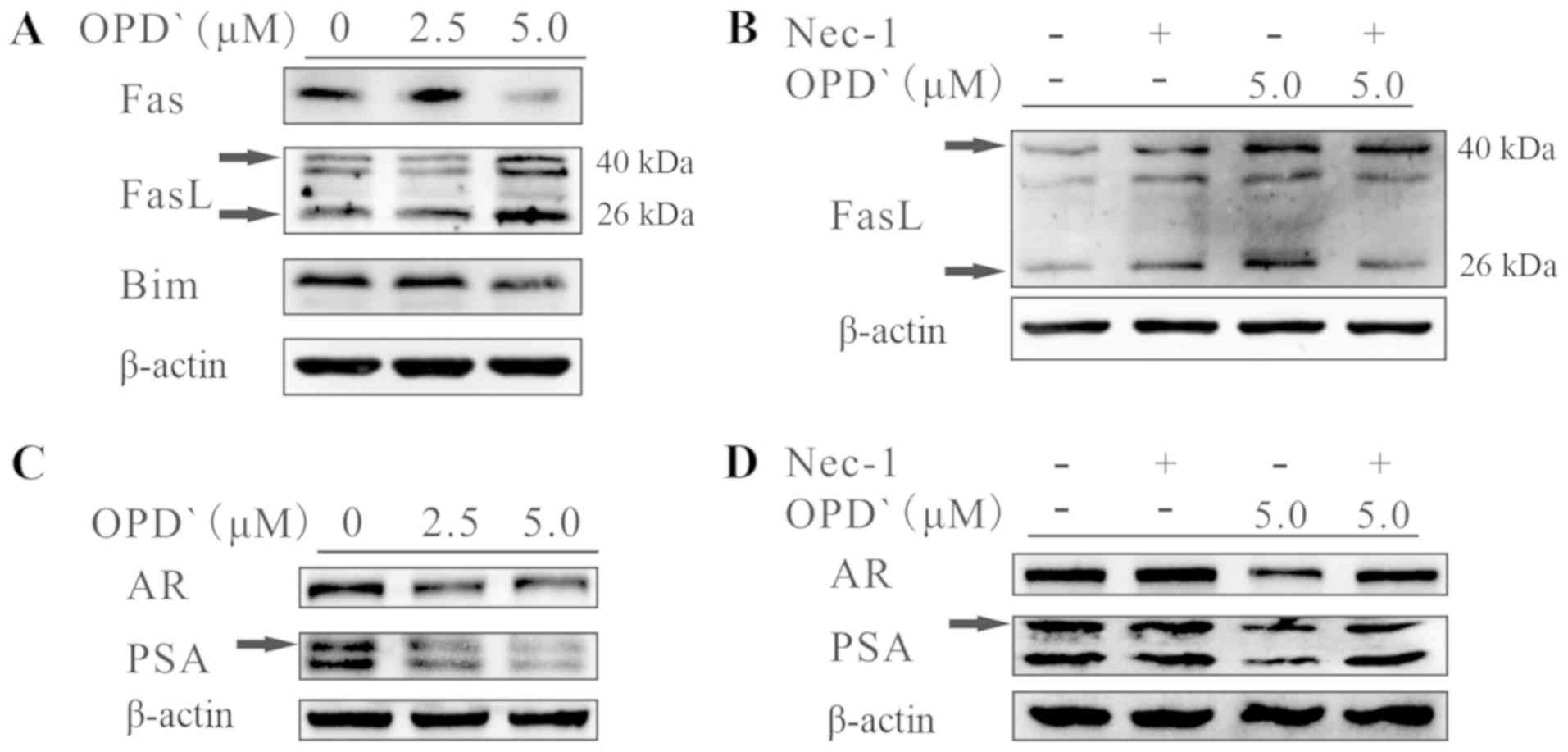
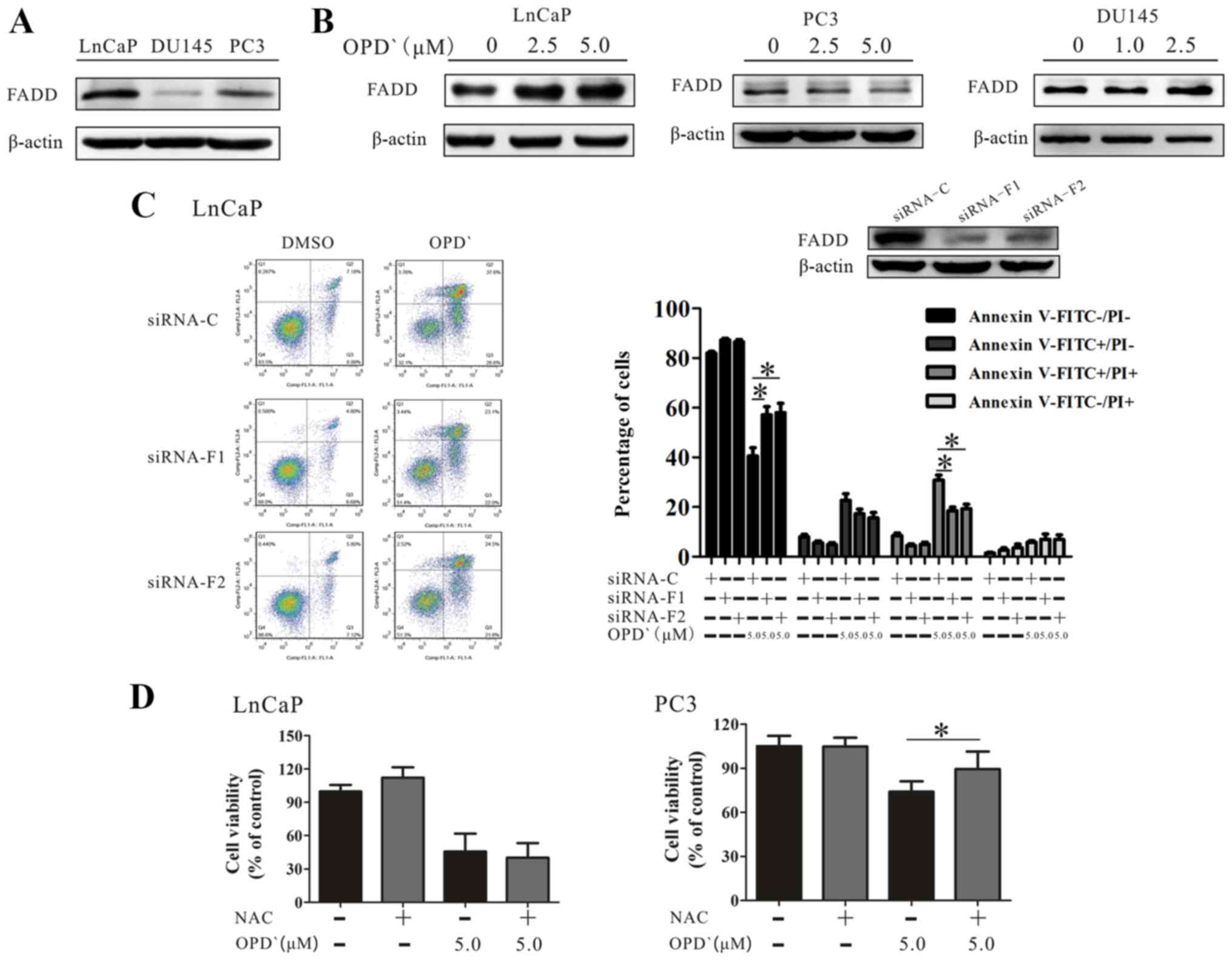
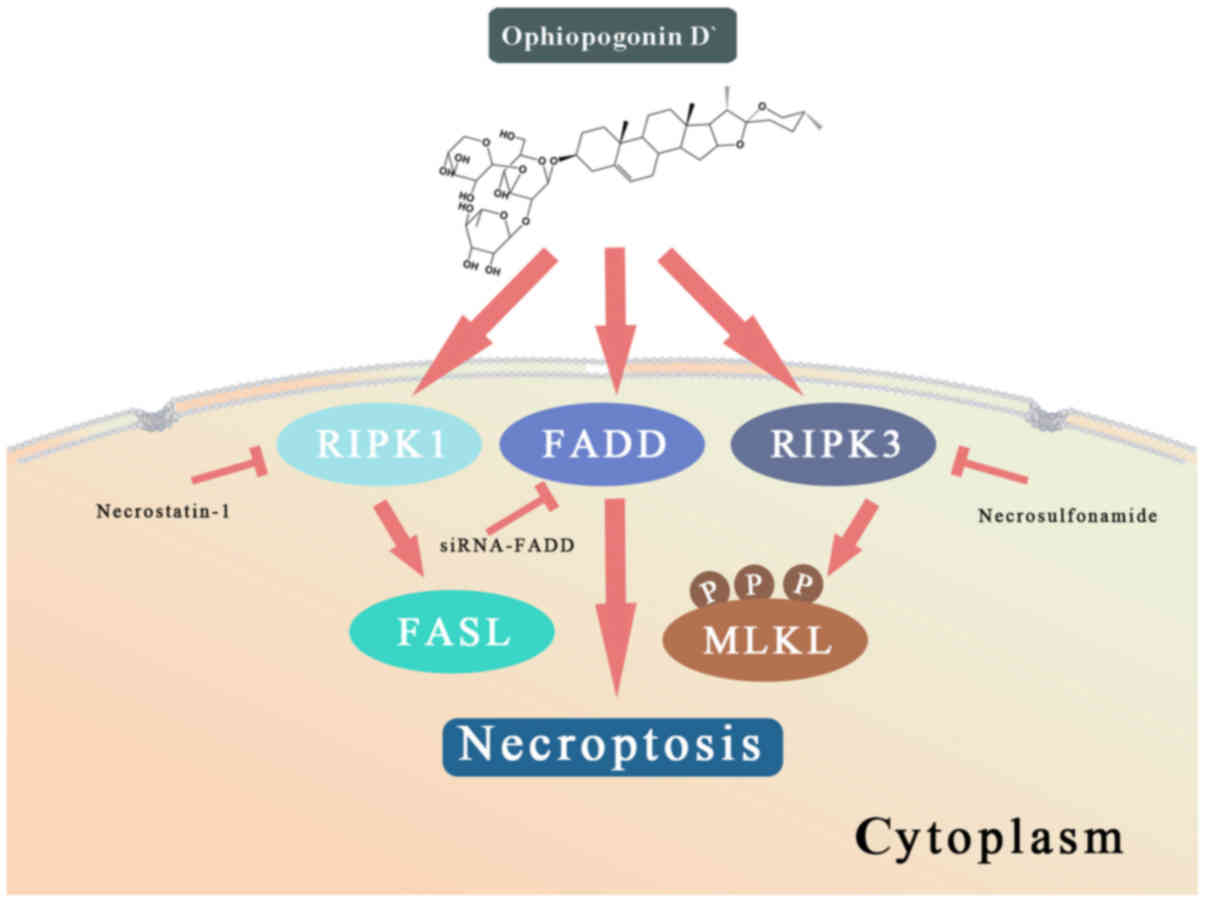
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Keating NL, O'Malley AJ and Smith MR:
Diabetes and cardiovascular disease during androgen deprivation
therapy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:4448–4456. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ross RW and Small EJ: Osteoporosis in men
treated with androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J
Urol. 167:1952–1956. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mohler JL, Wu W and Fiandalo MV: The role
of intracrine androgen metabolism, androgen receptor and apoptosis
in the survival and recurrence of prostate cancer during androgen
deprivation therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 14:420–440. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siler U, Barella L, Spitzer V, Schnorr J,
Lein M, Goralczyk R and Wertz K: Lycopene and vitamin E interfere
with autocrine/paracrine loops in the Dunning prostate cancer
model. FASEB J. 18:1019–1021. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dorff TB, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei DD, Xiong S,
Gross ME, Vogelzang N, Quinn DI and Pinski JK: A Phase II trial of
a combination herbal supplement for men with biochemically
recurrent prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
17:359–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McLarty J, Bigelow RLH, Smith M, Elmajian
D, Ankem M and Cardelli JA: Tea polyphenols decrease serum levels
of prostate-specific antigen, hepatocyte growth factor, and
vascular endothelial growth factor in prostate cancer patients and
inhibit production of hepatocyte growth factor and vascular
endothelial growth factor in vitro. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
2:673–682. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee JH, Kim C, Lee SG, Sethi G and Ahn KS:
Ophiopogonin D, a Steroidal Glycoside Abrogates STAT3 Signaling
Cascade and Exhibits Anti-Cancer Activity by Causing GSH/GSSG
Imbalance in Lung Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 10:E4272018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee JH, Kim C, Lee SG, Yang WM, Um JY,
Sethi G and Ahn KS: Ophiopogonin D modulates multiple oncogenic
signaling pathways, leading to suppression of proliferation and
chemosensitization of human lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine.
40:165–175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu Z, Wang H, Zhu M, Song W, Wang J, Wu C,
Kong Y, Guo J, Li N, Liu J, et al: Ophiopogonin D', a Natural
Product From Radix Ophiopogonis, Induces in Vitro and in Vivo
RIPK1-Dependent and Caspase-Independent Apoptotic Death in
Androgen-Independent Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Front Pharmacol.
9:4322018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Perez-Añorve IX, Gonzalez-De la Rosa CH,
Soto-Reyes E, Beltran-Anaya FO, Del Moral-Hernandez O,
Salgado-Albarran M, Angeles-Zaragoza O, Gonzalez-Barrios JA,
Landero-Huerta DA, Chavez-Saldaña M, et al: New insights into
radioresistance in breast cancer identify a dual function of
miR-122 as a tumor suppressor and oncomiR. Mol Oncol. 13:1249–1267.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Newell M, Goruk S, Mazurak V, Postovit L
and Field CJ: Role of docosahexaenoic acid in enhancement of
docetaxel action in patient-derived breast cancer xenografts.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 177:357–367. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Degterev A, Ofengeim D and Yuan J:
Targeting RIPK1 for the treatment of human diseases. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 116:9714–9722. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hsu CL, Liu JS, Lin TW, Chang YH, Kuo YC,
Lin AC, Ting HJ, Pang ST, Lee LY, Ma WL, et al: Characterization of
a novel androgen receptor (AR) coregulator RIPK1 and related
chemicals that suppress AR-mediated prostate cancer growth via
peptide and chemical screening. Oncotarget. 8:69508–69519. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martens S, Jeong M, Tonnus W, Feldmann F,
Hofmans S, Goossens V, Takahashi N, Bräsen JH, Lee EW, Van der
Veken P, et al: Sorafenib tosylate inhibits directly necrosome
complex formation and protects in mouse models of inflammation and
tissue injury. Cell Death Dis. 8:pp. e29042017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kharaziha P, Chioureas D, Baltatzis G,
Fonseca P, Rodriguez P, Gogvadze V, Lennartsson L, Björklund AC,
Zhivotovsky B, Grandér D, et al: Sorafenib-induced defective
autophagy promotes cell death by necroptosis. Oncotarget.
6:37066–37082. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McCann C, Crawford N, Majkut J, Holohan C,
Armstrong CWD, Maxwell PJ, Ong CW, LaBonte MJ, McDade SS, Waugh DJ
and Longley DB: Cytoplasmic FLIP(S) and nuclear FLIP(L) mediate
resistance of castrate-resistant prostate cancer to apoptosis
induced by IAP antagonists. Cell Death Dis. 9:10812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohammad RM, Muqbil I, Lowe L, Yedjou C,
Hsu HY, Lin LT, Siegelin MD, Fimognari C, Kumar NB, Dou QP, et al:
Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35(Suppl): S78–S103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bock FJ and Tait SWG: Mitochondria as
multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
October 21–2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou W and Yuan J: SnapShot: Necroptosis.
Cell. 158:464–464.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Polykratis A, Martens A, Eren RO,
Shirasaki Y, Yamagishi M, Yamaguchi Y, Uemura S, Miura M, Holzmann
B, Kollias G, et al: A20 prevents inflammasome-dependent arthritis
by inhibiting macrophage necroptosis through its ZnF7
ubiquitin-binding domain. Nat Cell Biol. 21:731–742. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu Z, Zhou R, Kong Y, Wang J, Xia W, Guo
J, Liu J, Sun H, Liu K, Yang J, et al: S-equol, a Secondary
Metabolite of Natural Anticancer Isoflavone Daidzein, Inhibits
Prostate Cancer Growth In Vitro and In Vivo, Though Activating the
Akt/FOXO3a Pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 16:455–465. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sebaugh JL: Guidelines for accurate
EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm Stat. 10:128–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mohler JL, Kantoff PW, Armstrong AJ,
Bahnson RR, Cohen M, D'Amico AV, Eastham JA, Enke CA, Farrington
TA, Higano CS, et al: National comprehensive cancer network:
Prostate cancer, version 1.2014. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
11:1471–1479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Cheng AC, Wang MS and Peng X:
Detection of apoptosis induced by new type gosling viral enteritis
virus in vitro through fluorescein annexin V-FITC/PI double
labeling. World J Gastroenterol. 14:2174–2178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X, et al: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luan Q, Jin L, Jiang CC, Tay KH, Lai F,
Liu XY, Liu YL, Guo ST, Li CY, Yan XG, et al: RIPK1 regulates
survival of human melanoma cells upon endoplasmic reticulum stress
through autophagy. Autophagy. 11:975–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moriwaki K, Bertin J, Gough PJ, Orlowski
GM and Chan FK: Differential roles of RIPK1 and RIPK3 in
TNF-induced necroptosis and chemotherapeutic agent-induced cell
death. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, Cornelis S
and Vandenabeele P: RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's
decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 14:400–410. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cohen M, Pierredon S, Wuillemin C, Delie F
and Petignat P: Acellular fraction of ovarian cancer ascites induce
apoptosis by activating JNK and inducing BRCA1, Fas and FasL
expression in ovarian cancer cells. Oncoscience. 1:262–271. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M,
Attinger A, Valitutti S, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Seed B and Tschopp
J: Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death
pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat Immunol.
1:489–495. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schwabe RF and Luedde T: Apoptosis and
necroptosis in the liver: A matter of life and death. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:738–752. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Antunovic M, Matic I, Nagy B, Caput
Mihalic K, Skelin J, Stambuk J, Josipovic P, Dzinic T, Paradzik M
and Marijanovic I: FADD-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts
undergo RIPK1-dependent apoptosis and autophagy after NB-UVB
irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol B. 194:32–45. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang KX, Firus J, Prieur B, Jia W and
Rennie PS: To die or to survive, a fatal question for the destiny
of prostate cancer cells after androgen deprivation therapy.
Cancers (Basel). 3:1498–1512. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang HY, Ma YD, Zhang Y, Cui J and Wang
ZM: Elevated levels of autophagy-related marker ULK1 and
mitochondrion-associated autophagy inhibitor LRPPRC are associated
with biochemical progression and overall survival after androgen
deprivation therapy in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J
Clin Pathol. 70:383–389. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ziparo E, Petrungaro S, Marini ES, Starace
D, Conti S, Facchiano A, Filippini A and Giampietri C: Autophagy in
prostate cancer and androgen suppression therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
14:12090–12106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Berchem GJ, Bosseler M, Sugars LY, Voeller
HJ, Zeitlin S and Gelmann EP: Androgens induce resistance to
bcl-2-mediated apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 55:735–738. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bonkhoff H, Fixemer T and Remberger K:
Relation between Bcl-2, cell proliferation, and the androgen
receptor status in prostate tissue and precursors of prostate
cancer. Prostate. 34:251–258. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goodall ML, Fitzwalter BE, Zahedi S, Wu M,
Rodriguez D, Mulcahy-Levy JM, Green DR, Morgan M, Cramer SD and
Thorburn A: The Autophagy Machinery Controls Cell Death Switching
between Apoptosis and Necroptosis. Dev Cell. 37:337–349. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma X, Zou L, Li X, Chen Z, Lin Z and Wu X:
Inhibition of Autophagy Improves the Efficacy of Abiraterone for
the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
34:181–188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Newton K, Wickliffe KE, Dugger DL,
Maltzman A, Roose-Girma M, Dohse M, Kőműves L, Webster JD and Dixit
VM: Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting
apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature. 574:428–431. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou H, Zhu P, Guo J, Hu N, Wang S, Li D,
Hu S, Ren J, Cao F and Chen Y: Ripk3 induces mitochondrial
apoptosis via inhibition of FUNDC1 mitophagy in cardiac IR injury.
Redox Biol. 13:498–507. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
LaRocca TJ, Stivison EA, Mal-Sarkar T,
Hooven TA, Hod EA, Spitalnik SL and Ratner AJ: CD59 signaling and
membrane pores drive Syk-dependent erythrocyte necroptosis. Cell
Death Dis. 6:e17732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dehm SM and Tindall DJ: Molecular
regulation of androgen action in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem.
99:333–344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tosoian JJ, Trock BJ, Landis P, Feng Z,
Epstein JI, Partin AW, Walsh PC and Carter HB: Active surveillance
program for prostate cancer: An update of the Johns Hopkins
experience. J Clin Oncol. 29:2185–2190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lev A, Lulla AR, Ross BC, Ralff MD, Makhov
PB, Dicker DT and Eldeiry WS: ONC201 Targets AR and AR-V7
Signaling, Reduces PSA, and Synergizes with Everolimus in Prostate
Cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 16:754–766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bae JS, Park HS, Park JW, Li SH and Chun
YS: Red ginseng and 20(S)-Rg3 control testosterone-induced prostate
hyperplasia by deregulating androgen receptor signaling. J Nat Med.
66:476–485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zabaiou N, Fouache A, Trousson A,
Buñay-Noboa J, Marceau G, Sapin V, Zellagui A, Baron S, Lahouel M
and Lobaccaro JA: Ethanolic extract of Algerian propolis decreases
androgen receptor transcriptional activity in cultured LNCaP cells.
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 189:108–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Paschalis A, Sheehan B, Riisnaes R,
Rodrigues DN, Gurel B, Bertan C, Ferreira A, Lambros MBK, Seed G,
Yuan W, et al: Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Heterogeneity and
DNA Repair Defects in Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol. 76:469–478. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Deng Q and Tang DG: Androgen receptor and
prostate cancer stem cells: Biological mechanisms and clinical
implications. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:T209–T220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yadav N and Heemers HV: Androgen action in
the prostate gland. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 64:35–49. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tourneur L and Chiocchia G: FADD: A
regulator of life and death. Trends Immunol. 31:260–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ang RL and Ting AT: Detection of RIPK1 in
the FADD-Containing Death Inducing Signaling Complex (DISC) During
Necroptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1857:101–107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wiese AK, Prior S, Chambers TC and Higuchi
M: Intracellular Oxygen Concentration Determined By Mitochondrial
Respiration Regulates Production of Reactive Oxygen Species. Integr
Cancer Biol Res. 1:0062017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rasul A, Di J, Millimouno FM, Malhi M,
Tsuji I, Ali M, Li J and Li X: Reactive oxygen species mediate
isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells.
Molecules. 18:9382–9396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Anderton H, Bandala-Sanchez E, Simpson DS,
Rickard JA, Ng AP, Di Rago L, Hall C, Vince JE, Silke J, Liccardi
G, et al: RIPK1 prevents TRADD-driven, but TNFR1 independent,
apoptosis during development. Cell Death Differ. 26:877–889. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|