|
1
|
Blechacz B: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current
Knowledge and New Developments. Gut Liver. 11:13–26. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK
and Gores GJ: Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:95–111. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lv Y and Huang S: Role of non-coding RNA
in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett. 18:3963–3973. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Yang B, Zhang M, Guo W, Wu Z, Wang
Y, Jia L, Li S, Xie W, Yang D, et al: Cancer Genome Atlas Research
Network: LncRNA epigenetic landscape analysis identifies EPIC1 as
an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with MYC and promotes cell cycle
progression in cancer. Cancer Cell. 33:706–720.e9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Han D, Gao X, Wang M, Qiao Y, Xu Y, Yang
J, Dong N, He J, Sun Q, Lv G, et al: Long noncoding RNA H19
indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor
growth by recruiting and binding to eIF4A3. Oncotarget.
7:22159–22173. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
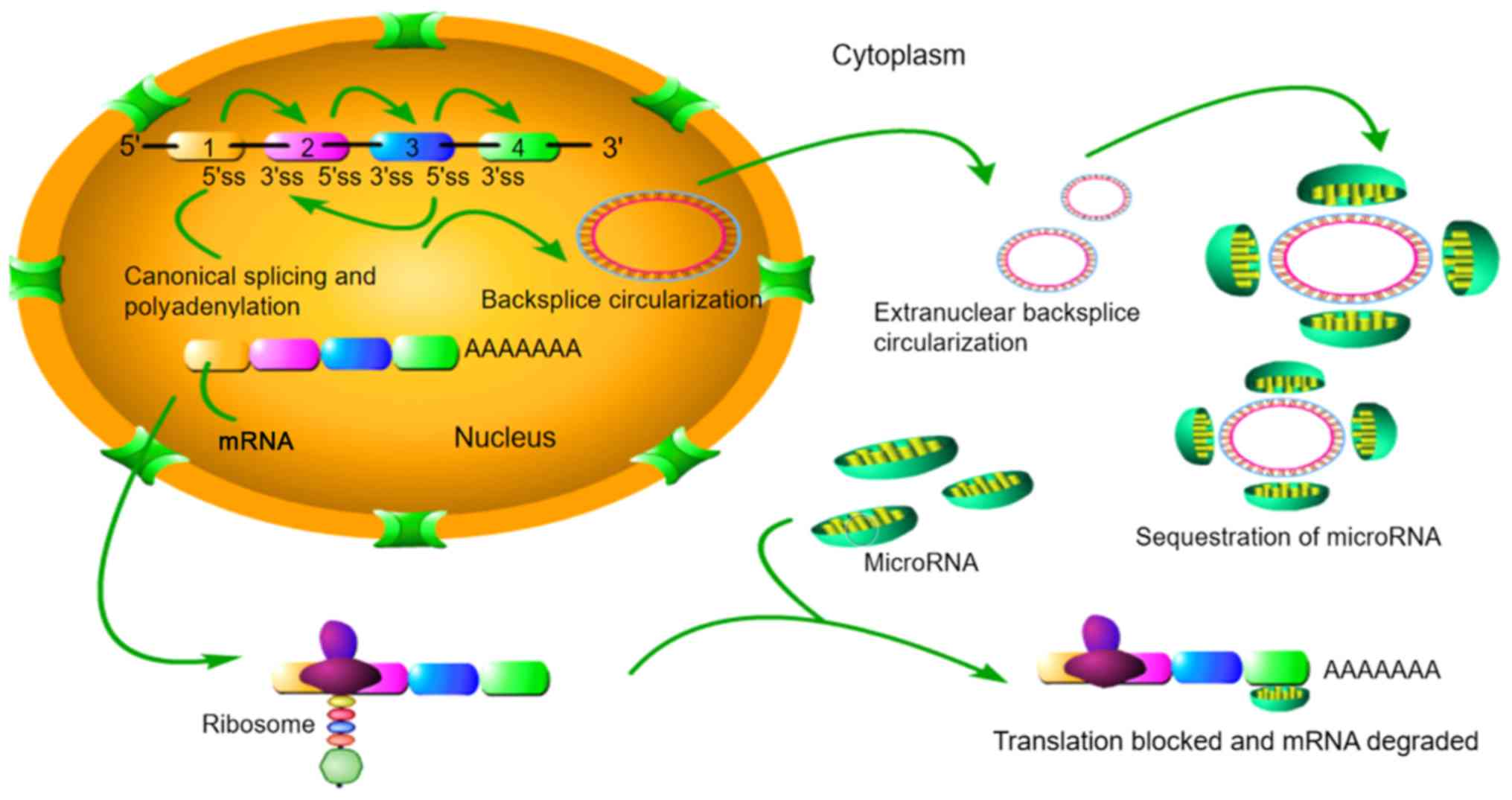
|
8
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heter-ochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
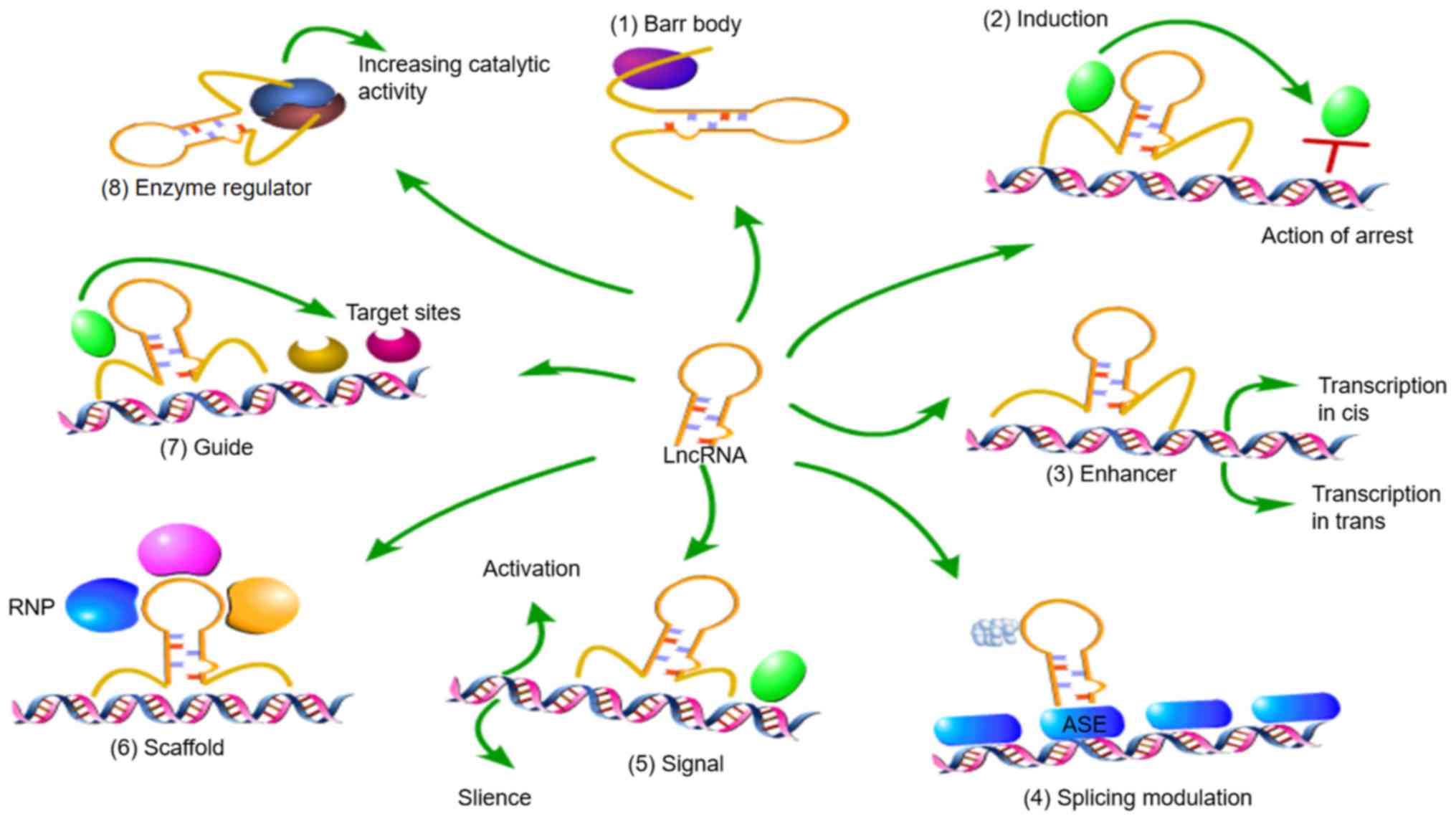
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pandey P, Srivastava PK and Pandey SP:
Prediction of Plant miRNA Targets. Methods Mol Biol. 1932:99–107.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borges F and Martienssen RA: The expanding
world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:727–741.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ushijima K, Yamada Y, Yano T and Tashiro
M: An electrosurgical burn possibly caused by radio-frequency
leakage current through a stainless forceps. Masui. 49:909–912.
2000.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Piontek K and Selaru FM: MicroRNAs in the
biology and diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
35:55–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakaoka T, Saito Y and Saito H: Aberrant
DNA Methylation as a Biomarker and a Therapeutic Target of
Cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017.
|
|
16
|
Plieskatt J, Rinaldi G, Feng Y, Peng J,
Easley S, Jia X, Potriquet J, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Sripa
B, et al: A microRNA profile associated with Opisthorchis
viverrini-induced cholangiocarcinoma in tissue and plasma. BMC
Cancer. 15:3092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Petrache Voicu SN, Dinu D, Sima C,
Hermenean A, Ardelean A, Codrici E, Stan MS, Zărnescu O and
Dinischiotu A: Silica Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative Stress and
Autophagy but Not Apoptosis in the MRC-5 Cell Line. Int J Mol Sci.
16:29398–29416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu H, Han C, Lu D and Wu T: miR-17-92
cluster promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth: Evidence for PTEN as
downstream target and IL-6/Stat3 as upstream activator. Am J
Pathol. 184:2828–2839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu C, Huang F, Deng G, Nie W, Huang W and
Zeng X: miR-31 promotes oncogenesis in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma cells via the direct suppression of RASA1. Exp
Ther Med. 6:1265–1270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Tian F, Li D, Chen J, Jiang P, Zheng
S, Li X and Wang S: miR-605 represses PSMD10/Gankyrin and inhibits
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell progression. FEBS Lett.
588:3491–3500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng Q, Feng F, Zhu L, Zheng Y, Luo X,
Liu C, Yi B and Jiang X: Circulating miR-106a is a Novel Prognostic
and Lymph Node Metastasis Indicator for Cholangiocarcinoma. Sci
Rep. 5:161032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patel T: Extracellular vesicle noncoding
RNA: New players in the diagnosis and pathogenesis of
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 60:782–784. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Canu V, Sacconi A, Lorenzon L, Biagioni F,
Lo Sardo F, Diodoro MG, Muti P, Garofalo A, Strano S, D'Errico A,
et al: miR-204 down-regulation elicited perturbation of a gene
target signature common to human cholangiocarcinoma and gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:29540–29557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H,
Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD and Patel T:
Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to
chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
Gastroenterology. 130:2113–2129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen L, Yan HX, Yang W, Hu L, Yu LX, Liu
Q, Li L, Huang DD, Ding J, Shen F, et al: The role of microRNA
expression pattern in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Hepatol. 50:358–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang G, Zhang R, Chen X, Mu Y, Ai J, Shi
C, Liu Y, Shi C, Sun L, Rainov NG, et al: miR-106a inhibits glioma
cell growth by targeting E2F1 independent of p53 status. J Mol Med
(Berl). 89:1037–1050. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okamoto K, Miyoshi K and Murawaki Y:
miR-29b, miR-205 and miR-221 enhance chemosensitivity to
gemcitabine in HuH28 human cholangiocarcinoma cells. PLoS One.
8:e776232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Gao W, Luo J, Tian R, Sun H and
Zou S: Methyl-CpG binding protein MBD2 is implicated in
methylation-mediated suppression of miR-373 in hilar
cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:443–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
An F, Yamanaka S, Allen S, Roberts LR,
Gores GJ, Pawlik TM, Xie Q, Ishida M, Mezey E, Ferguson-Smith AC,
et al: Silencing of miR-370 in human cholangiocarcinoma by allelic
loss and interleukin-6 induced maternal to paternal epigenotype
switch. PLoS One. 7:e456062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ngankeu A, Ranganathan P, Havelange V,
Nicolet D, Volinia S, Powell BL, Kolitz JE, Uy GL, Stone RM,
Kornblau SM, et al: Discovery and functional implications of a
miR-29b-1/miR-29a cluster polymorphism in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget. 9:4354–4365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mott JL, Kurita S, Cazanave SC, Bronk SF,
Werneburg NW and Fernandez-Zapico ME: Transcriptional suppression
of mir-29b1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J
Cell Biochem. 110:1155–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kwon H, Song K, Han C, Zhang J, Lu L, Chen
W and Wu T: Epigenetic Silencing of miRNA-34a in Human
Cholangiocarcinoma via EZH2 and DNA Methylation: Impact on
Regulation of Notch Pathway. Am J Pathol. 187:2288–2299. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li B, Han Q, Zhu Y, Yu Y, Wang J and Jiang
X: Down-regulation of miR-214 contributes to intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma metastasis by targeting Twist. FEBS J.
279:2393–2398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwaki J, Kikuchi K, Mizuguchi Y,
Kawahigashi Y, Yoshida H, Uchida E and Takizawa T: miR-376c
down-regulation accelerates EGF-dependent migration by targeting
GRB2 in the HuCCT1 human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line.
PLoS One. 8:e694962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peng F, Jiang J, Yu Y, Tian R, Guo X, Li
X, Shen M, Xu M, Zhu F, Shi C, et al: Direct targeting of
SUZ12/ROCK2 by miR-200b/c inhibits cholangiocarcinoma
tumourigenesis and metastasis. Br J Cancer. 109:3092–3104. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang R, Chen Y, Tang C, Li H, Wang B, Yan
Q, Hu J and Zou S: MicroRNA-144 suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell
proliferation and invasion through targeting platelet activating
factor acetylhydrolase isoform 1b. BMC Cancer. 14:9172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Han C, Zhu H, Song K and Wu T:
miR-101 inhibits cholangiocarcinoma angiogenesis through targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Am J Pathol.
182:1629–1639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qiu YH, Wei YP, Shen NJ, Wang ZC, Kan T,
Yu WL, Yi B and Zhang YJ: miR-204 inhibits epithelial to
mesenchymal transition by targeting slug in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:1331–1341. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kobayashi S, Werneburg NW, Bronk SF,
Kaufmann SH and Gores GJ: Interleukin-6 contributes to Mcl-1
up-regulation and TRAIL resistance via an Akt-signaling pathway in
cholangiocar-cinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 128:2054–2065. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiong B, Cheng Y, Ma L and Zhang C: miR-21
regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3 K/Akt signaling
pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:219–228.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, David S, Cheng
Y, Mori Y, Yang J, Paun B, Jin Z, Agarwal R, et al: MicroRNA-21 is
overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed
cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3.
Hepatology. 49:1595–1601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jiang Y, Goldberg ID and Shi YE: Complex
roles of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in cancer.
Oncogene. 21:2245–2252. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He Q, Cai L, Shuai L, Li D, Wang C, Liu Y,
Li X, Li Z and Wang S: Ars2 is overexpressed in human
cholangiocarcinomas and its depletion increases PTEN and PDCD4 by
decreasing microRNA-21. Mol Carcinog. 52:286–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
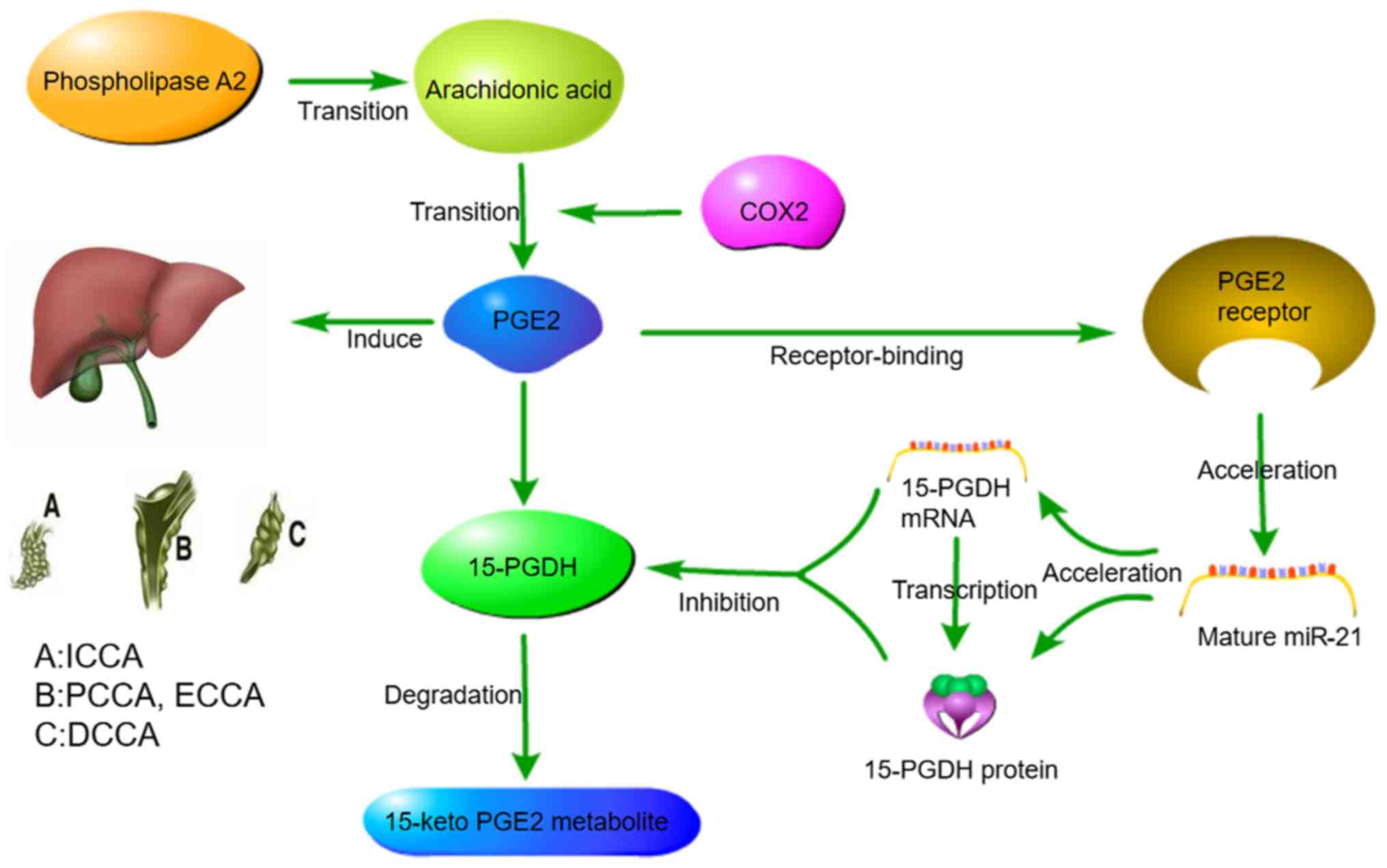
Lu L, Byrnes K, Han C, Wang Y and Wu T:
miR-21 targets 15-PGDH and promotes cholangiocarcinoma growth. Mol
Cancer Res. 12:890–900. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Triboulet R, Pirouz M and Gregory RI: A
Single Let-7 MicroRNA Bypasses LIN28-Mediated Repression. Cell Rep.
13:260–266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xie Y, Zhang H, Guo XJ, Feng YC, He RZ, Li
X, Yu S, Zhao Y, Shen M, Zhu F, et al: Let-7c inhibits
cholangiocarcinoma growth but promotes tumor cell invasion and
growth at extrahepatic sites. Cell Death Dis. 9:2492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin KY, Ye H, Han BW, Wang WT, Wei PP, He
B, Li XJ and Chen YQ: Genome-wide screen identified
let-7c/miR-99a/miR-125b regulating tumor progression and stem-like
properties in cholan-giocarcinoma. Oncogene. 35:3376–3386. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Smith H,
Ueno Y and Patel T: The MicroRNA let-7a modulates
interleukin-6-dependent STAT-3 survival signaling in malignant
human cholangiocytes. J Biol Chem. 282:8256–8264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function
and Role in Human Diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Z, Xie Q, He D, Ling Y, Li Y, Li J
and Zhang H: Circular RNA: new star, new hope in cancer. BMC
Cancer. 18:8342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Werfel S, Nothjunge S, Schwarzmayr T,
Strom TM, Meitinger T and Engelhardt S: Characterization of
circular RNAs in human, mouse and rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
98:103–107. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiong Y, Zhang J and Song C: CircRNA
ZNF609 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate FOXP4
expression by sponging miR-138-5p in renal carcinoma. J Cell
Physiol. 234:10646–10654. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Leng K, Ji D, Qu L, Liu Y and
Cui Y: Increased Expression of Circular RNA circ_0005230 Indicates
Dismal Prognosis in Breast Cancer and Regulates Cell Proliferation
and Invasion via miR-618/CBX8 Signal Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
51:1710–1722. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Hu Z, Su Z, Li
C, Wang H, Jiang X, Kang P, et al: Elevation of circular RNA
circ_0005230 facilitates cell growth and metastasis via sponging
miR-1238 and miR-1299 in cholangiocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY).
11:1907–1917. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Shi X, Zhan L, Xiao C, Lei Z, Yang H, Wang
L, Zhao J and Zhang HT: miR-1238 inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting LHX2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
6:19043–19054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jiang XM, Li ZL, Li JL, Xu Y, Leng KM, Cui
YF and Sun DJ: A novel prognostic biomarker for cholangiocarcinoma:
circRNA Cdr1as. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:365–371.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Zhong X, Leng K, Qin W, Qu L,
Cui Y and Jiang X: Downregulated circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649
regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:455–461.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang S, Hu Y, Lv X, Li B, Gu D, Li Y, Sun
Y and Su Y: Circ-0000284 arouses malignant phenotype of
cholangiocarcinoma cells and regulates the biological functions of
peripheral cells through cellular communication. Clin Sci (Lond).
133:1935–1953. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Sun M and Kraus WL: From discovery to
function: The expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology
and disease. Endocr Rev. 36:25–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Chen J, Miao Z, Xue B, Shan Y, Weng G and
Shen B: Long Non-coding RNAs in Urologic Malignancies: Functional
Roles and Clinical Translation. J Cancer. 7:1842–1855. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang J, Xie H, Ling Q, Lu D, Lv Z, Zhuang
R, Liu Z, Wei X, Zhou L, Xu X, et al: Coding-noncoding gene
expression in intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Transl Res.
168:107–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Hao S, Yao L, Huang J, He H, Yang F, Di Y,
Jin C and Fu D: Genome‑Wide Analysis Identified a Number of
Dysregulated Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) in Human Pancreatic Ductal
Adenocarcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 17:15330346177484292018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Yao Y, Sun Y, Jiang Y, Qu L and Xu Y:
Enhanced expression of lncRNA TP73-AS1 predicts adverse phenotypes
for cholangio-carcinoma and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro
and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:260–266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Y, Cai Q, Li W, Feng F and Yang L: Long
non-coding RNA EPIC1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell growth.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 504:654–659. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu Y, Wang Z, Jiang X and Cui Y:
Overexpression of long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis
for cholangio-carcinoma and promotes cell migration and invasion by
affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biomed Pharmacother.
92:17–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang WT, Ye H, Wei PP, Han BW, He B, Chen
ZH and Chen YQ: LncRNAs H19 and HULC, activated by oxidative
stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma
through a ceRNA manner. J Hematol Oncol. 9:1172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang S, Xiao J, Chai Y, Du YY, Liu Z,
Huang K, Zhou X and Zhou W: LncRNA-CCAT1 Promotes Migration,
Invasion, and EMT in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Through
Suppressing miR-152. Dig Dis Sci. 62:3050–3058. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ma F, Wang SH, Cai Q, Zhang MD, Yang Y and
Ding J: Overexpression of LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 predicts poor prognosis
and promotes cells proliferation and invasion in gallbladder
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1249–1255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang C, Li JY, Tian FZ, Zhao G, Hu H, Ma
YF and Yang YL: Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Promotes Growth and
Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Oncol Res. 26:879–888.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Parasramka M, Yan IK, Wang X, Nguyen P,
Matsuda A, Maji S, Foye C, Asmann Y and Patel T: BAP1 dependent
expression of long non-coding RNA NEAT-1 contributes to sensitivity
to gemcitabine in cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 16:222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ma SL, Li AJ, Hu ZY, Shang FS and Wu MC:
Co expression of the carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 gene and its
long non coding RNA correlates with poor prognosis of patients with
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:7915–7926. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang C, Mao ZP, Wang L, Wu GH, Zhang FH,
Wang DY and Shi JL: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes
cholangio-carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Neoplasma. 64:725–731. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tan X, Huang Z and Li X: Long Non-Coding
RNA MALAT1 Interacts With miR-204 to Modulate Human Hilar
Cholangiocarcinoma Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by
Targeting CXCR4. J Cell Biochem. 118:3643–3653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Qin X, Lu M, Zhou Y, Li G and Liu Z:
LncRNA FENDRR represses proliferation, migration and invasion
through suppression of survivin in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell
Cycle. 18:889–897. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Mehta KR, Danila DC,
Scolavino S, Johnson SR and Klibanski A: A pituitary-derived MEG3
isoform functions as a growth suppressor in tumor cells. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:5119–5126. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xia Y, He Z, Liu B, Wang P and Chen Y:
Downregulation of Meg3 enhances cisplatin resistance of lung cancer
cells through activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 12:4530–4537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sribenja S, Natthasirikul N,
Vaeteewoottacharn K, Sawanyawisuth K, Wongkham C, Jearanaikoon P
and Wongkham S: Thymosin β10 as a predictive biomarker of response
to 5‑fluorouracil chemotherapy in cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Hepatol.
15:577–585. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liang Z, Zhu B, Meng D, Shen X, Li X, Wang
Z and Li L: Down-regulation of lncRNA-NEF indicates poor prognosis
in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Biosci Rep. 39:392019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Hu X, Tan Z, Yang Y and Yang P: Long
non-coding RNA MIR22HG inhibits cell proliferation and migration in
cholangio-carcinoma by negatively regulating the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. J Gene Med. 21:e30852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Luo M, Li Z, Wang W, Zeng Y, Liu Z and Qiu
J: Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by
associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer
Lett. 333:213–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Monnier P, Martinet C, Pontis J, Stancheva
I, Ait-Si-Ali S and Dandolo L: H19 lncRNA controls gene expression
of the Imprinted Gene Network by recruiting MBD1. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:20693–20698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Du Y, Kong G, You X, Zhang S, Zhang T, Gao
Y, Ye L and Zhang X: Elevation of highly up-regulated in liver
cancer (HULC) by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell
proliferation via down-regulating p18. J Biol Chem.
287:26302–26311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A,
Sepulveda AR, Lee JS and Rustgi AK: LIN28B promotes colon cancer
progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:4260–4268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Viswanathan SR and Daley GQ: Lin28: A
microRNA regulator with a macro role. Cell. 140:445–449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Cao MX, Jiang YP, Tang YL and Liang XH:
The crosstalk between lncRNA and microRNA in cancer metastasis:
Orchestrating the epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity. Oncotarget.
8:12472–12483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Jia P, Cai H, Liu X, Chen J, Ma J, Wang P,
Liu Y, Zheng J and Xue Y: Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma
angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated
endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett.
381:359–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gu Y, Li C, Xiao L, Li J, Pei H, Xu D,
Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zhang L, Li K, et al: High expression of long
non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 facilitates progression of
cholangiocarcinoma through promoting epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Transl Res. 11:5438–5456. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang X, Ren M, Li Y, Hu J, Lu G, Ma W, Guo
D, Lu X and He S: Long noncoding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes gastric
cancer proliferation and invasion by regulating microRNA-363
expression. J Cell Biochem. 120:5704–5712. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Hua F, Liu S, Zhu L, Ma N, Jiang S and
Yang J: Highly expressed long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
in cervical cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:1128–1134. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Huang Y, Shi J and Xu Y: Long non-coding
RNA NNT-AS1 contributes to cell proliferation, metastasis and
apoptosis in human ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:9264–9270.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Merry CR, Forrest ME, Sabers JN, Beard L,
Gao XH, Hatzoglou M, Jackson MW, Wang Z, Markowitz SD and Khalil
AM: DNMT1-associated long non-coding RNAs regulate global gene
expression and DNA methylation in colon cancer. Hum Mol Genet.
24:6240–6253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Yu Y, Zhang M, Wang N, Li Q, Yang J, Yan
S, He X, Ji G and Miao L: Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor
gene CDKN1A by oncogenic long non-coding RNA SNHG1 in
cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 9:7462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Jalili A, Wagner C, Pashenkov M, Pathria
G, Mertz KD, Widlund HR, Lupien M, Brunet JP, Golub TR, Stingl G,
et al: Dual suppression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
CDKN2C and CDKN1A in human melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
104:1673–1679. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Guo H, Xu Y and Fu Q: Curcumin inhibits
growth of prostate carcinoma via miR-208-mediated CDKN1A
activation. Tumour Biol. 36:8511–8517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Askari M, Sobti RC, Nikbakht M and Sharma
SC: Aberrant promoter hypermethylation of p21 (WAF1/CIP1) gene and
its impact on expression and role of polymorphism in the risk of
breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 382:19–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yu Y, Zhang M, Liu J, Xu B, Yang J, Wang
N, Yan S, Wang F, He X, Ji G, et al: Long Non-coding RNA PVT1
Promotes Cell Proliferation and Migration by Silencing ANGPTL4
Expression in Cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
13:503–513. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Kong R, Zhang EB, Yin DD, You LH, Xu TP,
Chen WM, Xia R, Wan L, Sun M, Wang ZX, et al: Long noncoding RNA
PVT1 indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell
proliferation through epigenetically regulating p15 and p16. Mol
Cancer. 14:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N,
Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNA as
modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science.
329:689–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Okochi-Takada E, Hattori N, Tsukamoto T,
Miyamoto K, Ando T, Ito S, Yamamura Y, Wakabayashi M, Nobeyama Y
and Ushijima T: ANGPTL4 is a secreted tumor suppressor that
inhibits angiogenesis. Oncogene. 33:2273–2278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Taskoparan B, Seza EG, Demirkol S, Tuncer
S, Stefek M, Gure AO and Banerjee S: Opposing roles of the
aldo‑keto reductases AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 in colorectal cancer. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 40:563–578. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Sinreih M, Štupar S, Čemažar L, Verdenik
I, Frković Grazio S, Smrkolj Š and Rižner TL: STAR and AKR1B10 are
down-regulated in high-grade endometrial cancer. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 171:43–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Qin W, Zhong X, Jiang X and
Cui Y: Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 promotes cholangiocarcinoma cells
migration and invasion by induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Biomed Pharmacother. 99:121–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Bai JG, Tang RF, Shang JF, Qi S, Yu GD and
Sun C: Upregulation of long non coding RNA CCAT2 indicates a poor
prognosis and promotes proliferation and metastasis in intrahepatic
cholangio-carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 17:5328–5335. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Le Gallo M, Lozy F and Bell DW:
Next-Generation Sequencing. Adv Exp Med Biol. 943:119–148. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Levy SE and Myers RM: Advancements in
Next-Generation Sequencing. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 17:95–115.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Slatko BE, Gardner AF and Ausubel FM:
Overview of Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Curr Protoc
Mol Biol. 122:e592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zhang J, Han C and Wu T: MicroRNA-26a
promotes cholangio-carcinoma growth by activating β-catenin.
Gastroenterology. 143:246–56.e8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Namwat N, Chusorn P, Loilome W, Techasen
A, Puetkasichonpasutha J, Pairojkul C, Khuntikeo N and Yongvanit P:
Expression profiles of oncomir miR‑21 and tumor suppressor let-7a
in the progression of opisthorchiasis-associated
cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13(Suppl): 65–69.
2012.
|
|
113
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Razumilava N, Bronk SF, Smoot RL, Fingas
CD, Werneburg NW, Roberts LR and Mott JL: miR-25 targets
TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor-4 and
promotes apoptosis resistance in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology.
55:465–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Khapre RV, Samsa WE and Kondratov RV:
Circadian regulation of cell cycle: Molecular connections between
aging and the circadian clock. Ann Med. 42:404–415. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yang H, Li TW, Peng J, Tang X, Ko KS, Xia
M and Aller MA: A mouse model of cholestasis-associated
cholangiocar-cinoma and transcription factors involved in
progression. Gastroenterology. 141:378–388.e3884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Li Q, Xia X, Ji J, Ma J, Tao L, Mo L and
Chen W: miR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of
cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway and
expression of MDR1. Oncotarget. 8:33621–33630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zhong XY, Yu JH, Zhang WG, Wang ZD, Dong
Q, Tai S, Cui YF and Li H: MicroRNA-421 functions as an oncogenic
miRNA in biliary tract cancer through down-regulating farnesoid X
receptor expression. Gene. 493:44–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Olaru AV, Ghiaur G, Yamanaka S, Luvsanjav
D, An F, Popescu I, Alexandrescu S, Allen S, Pawlik TM, Torbenson
M, et al: MicroRNA down-regulated in human cholangiocarcinoma
control cell cycle through multiple targets involved in the G1/S
checkpoint. Hepatology. 54:2089–2098. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Cermakian N and Sassone-Corsi P:
Multilevel regulation of the circadian clock. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 1:59–67. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Han Y, Meng F, Venter J, Wu N, Wan Y,
Standeford H, Francis H, Meininger C, Greene J Jr, Trzeciakowski
JP, et al: miR-34a-dependent overexpression of Per1 decreases
cholangiocarcinoma growth. J Hepatol. 64:1295–1304. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L and Wu
D: microRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human
cholangio-carcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer. 15:4692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Palumbo T, Poultsides GA, Kouraklis G,
Liakakos T, Drakaki A, Peros G, Hatziapostolou M and Iliopoulos D:
A functional microRNA library screen reveals miR-410 as a novel
anti-apoptotic regulator of cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer.
16:3532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Braconi C, Huang N and Patel T:
MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor
suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant
cholangiocytes. Hepatology. 51:881–890. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Chen Y, Luo J, Tian R, Sun H and Zou S:
miR-373 negatively regulates methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2
(MBD2) in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 56:1693–1701.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Zeng B, Ye H, Chen J, Cheng D, Cai C, Chen
G, Chen X, Xin H, Tang C and Zeng J: LncRNA TUG1 sponges miR-145 to
promote cancer progression and regulate glutamine metabolism via
Sirt3/GDH axis. Oncotarget. 8:113650–113661. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Zhang F, Wan M, Xu Y, Li Z, Leng K, Kang
P, Cui Y and Jiang X: Long noncoding RNA PCAT1 regulates
extrahepatic chol-angiocarcinoma progression via the
Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 94:55–62.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Kong L, Wu Q, Zhao L, Ye J, Li N and Yang
H: Upregulated lncRNA-UCA1 contributes to metastasis of bile duct
carcinoma through regulation of miR-122/CLIC1 and activation of the
ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 18:1212–1228. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Jiang X, Zhong X, Wang Z, Li
C, Kang P, Leng K, Ji D, Li Z, et al: SP1-induced upregulation of
lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 exerts oncogenic properties by scaffolding
EZH2/LSD1/DNMT1 and sponging miR-101-3p in cholangio-carcinoma. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:812018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Carotenuto P, Fassan M, Pandolfo R, Lampis
A, Vicentini C, Cascione L, Paulus-Hock V, Boulter L, Guest R,
Quagliata L, et al: Wnt signalling modulates
transcribed-ultra-conserved regions in hepatobiliary cancers. Gut.
66:1268–1277. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Zhang D, Li H, Xie J, Jiang D, Cao L, Yang
X, Xue P and Jiang X: Long noncoding RNA LINC01296 promotes tumor
growth and progression by sponging miR-5095 in human
chol-angiocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 52:1777–1786. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|