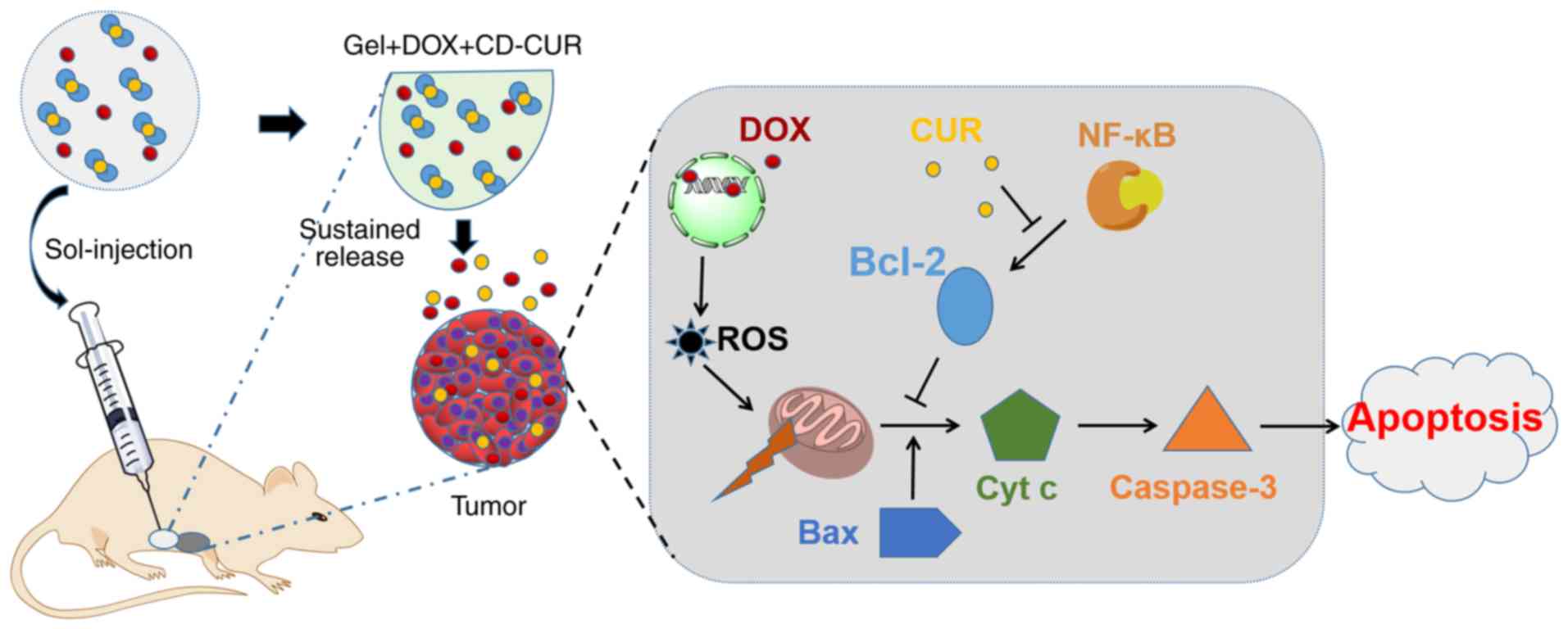
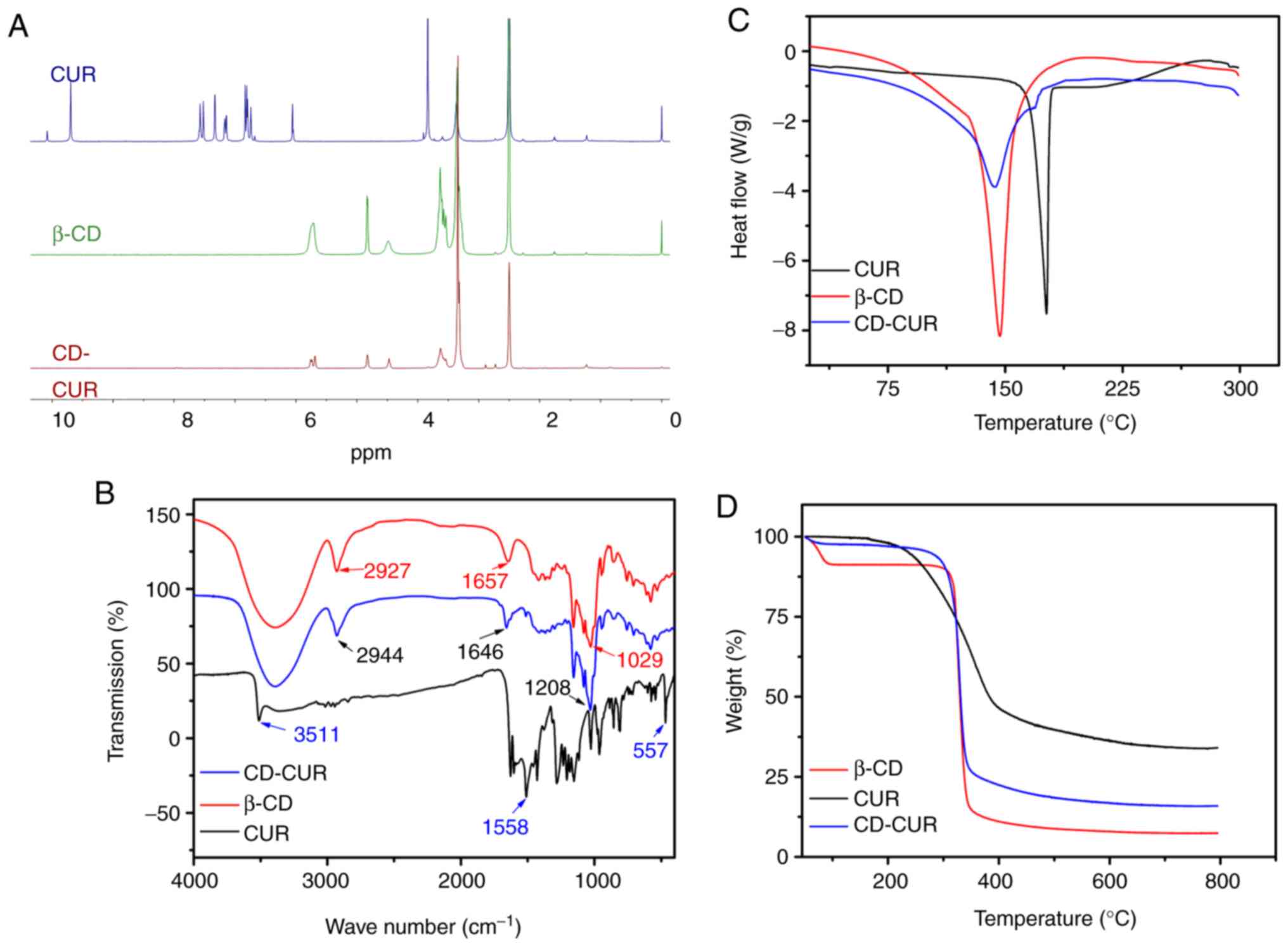
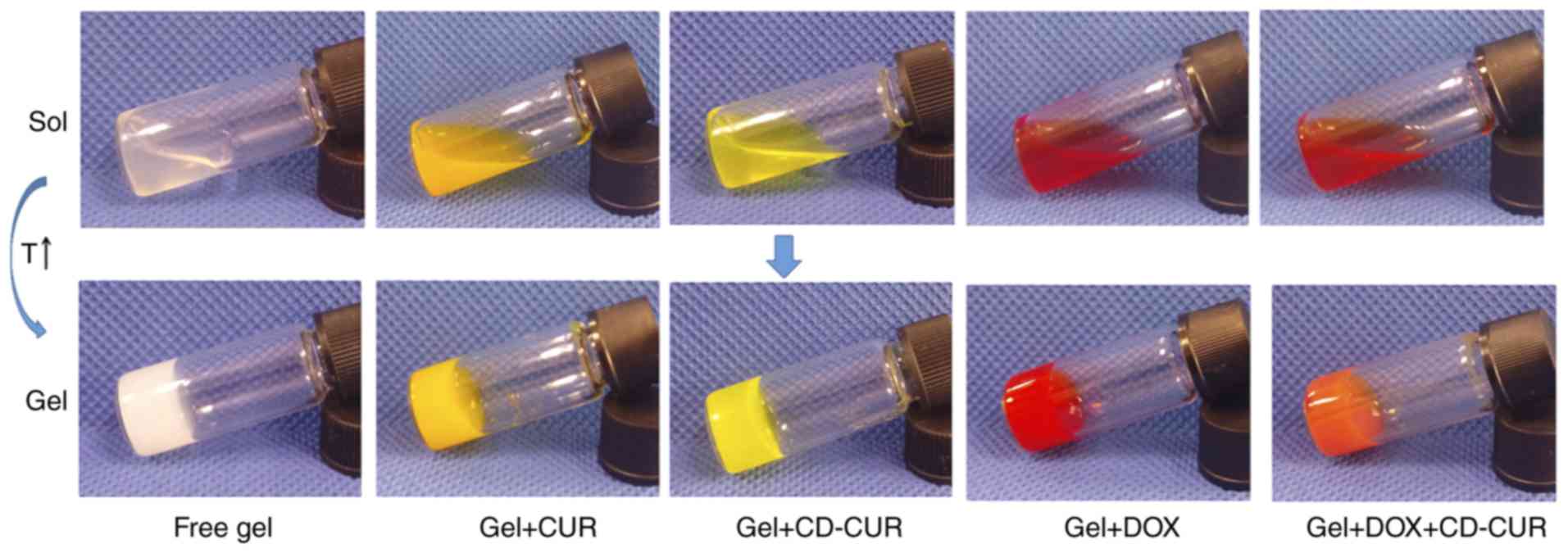
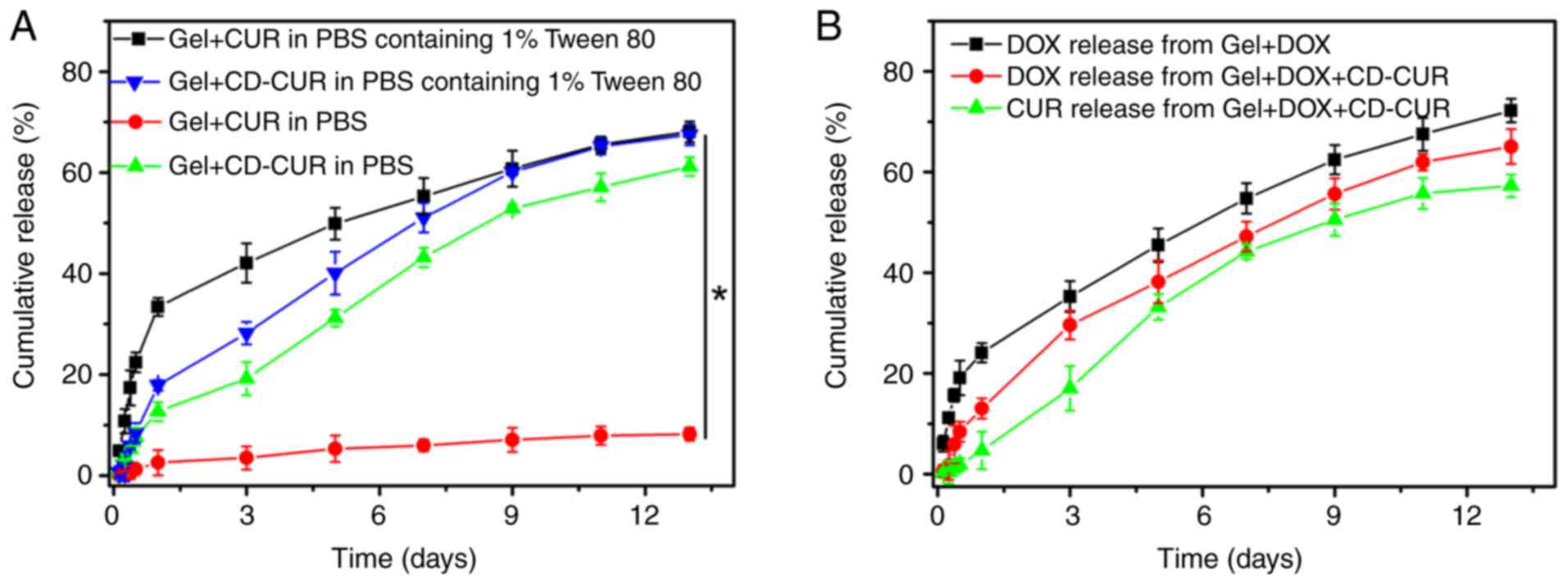
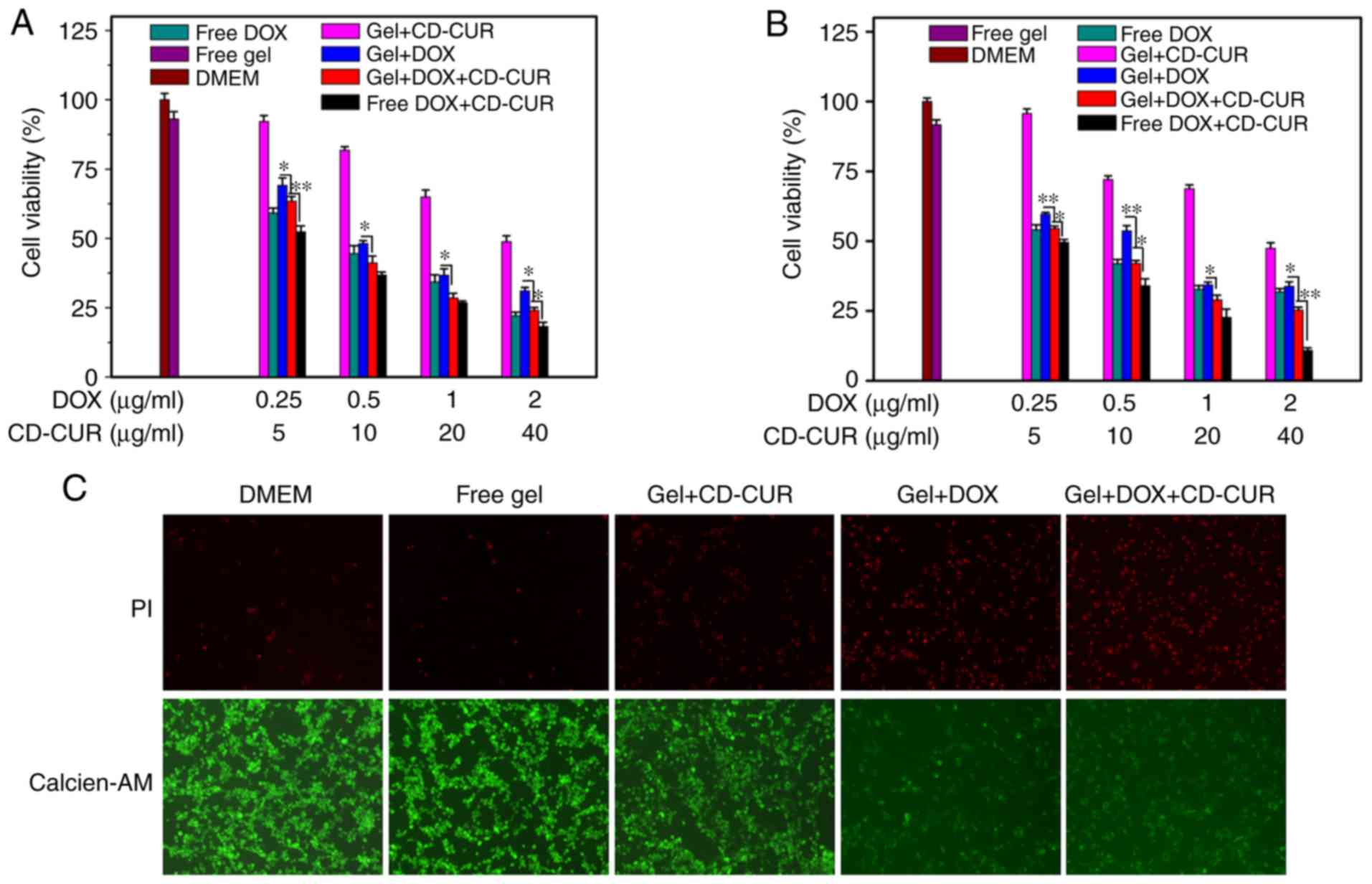
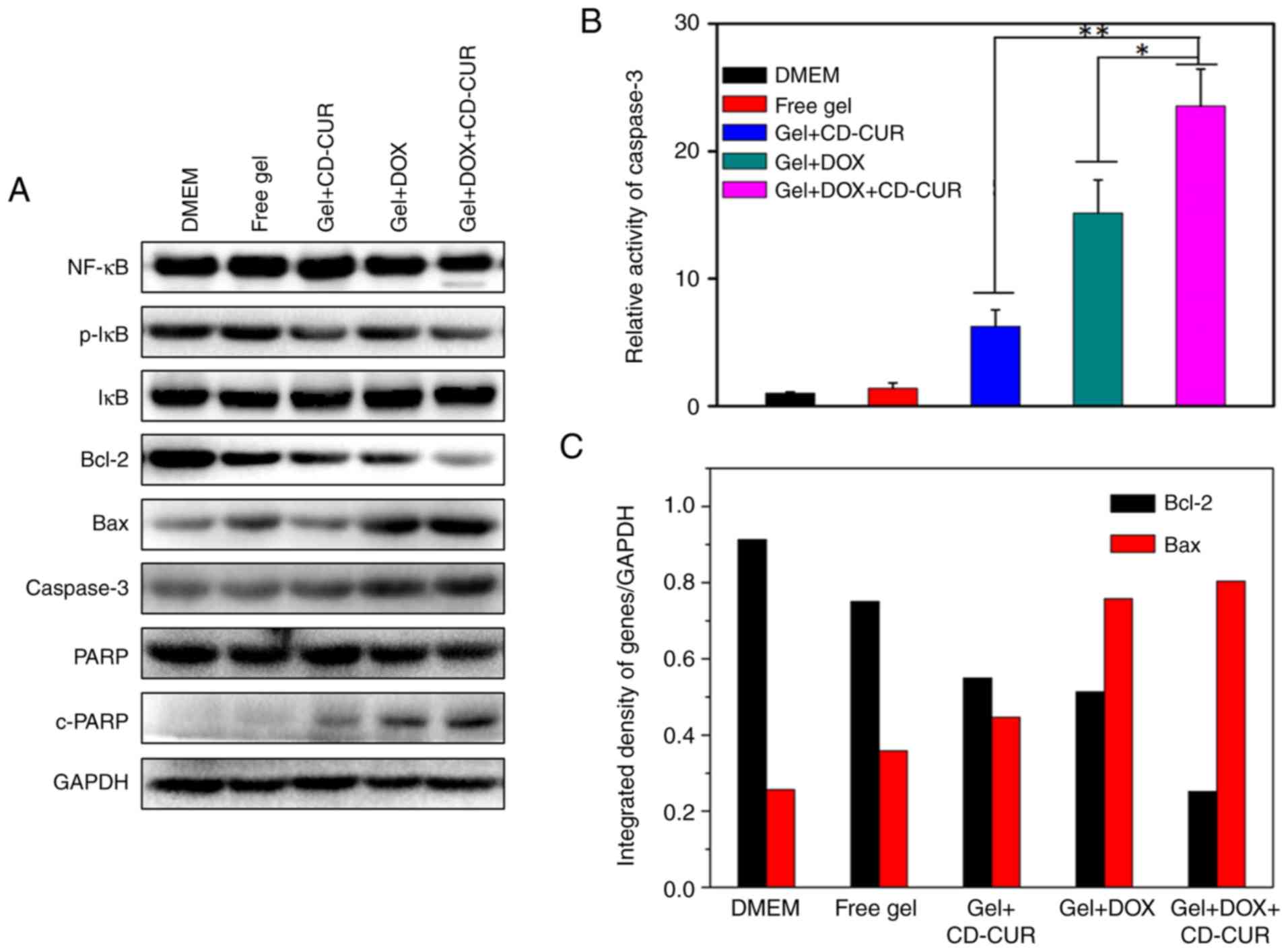
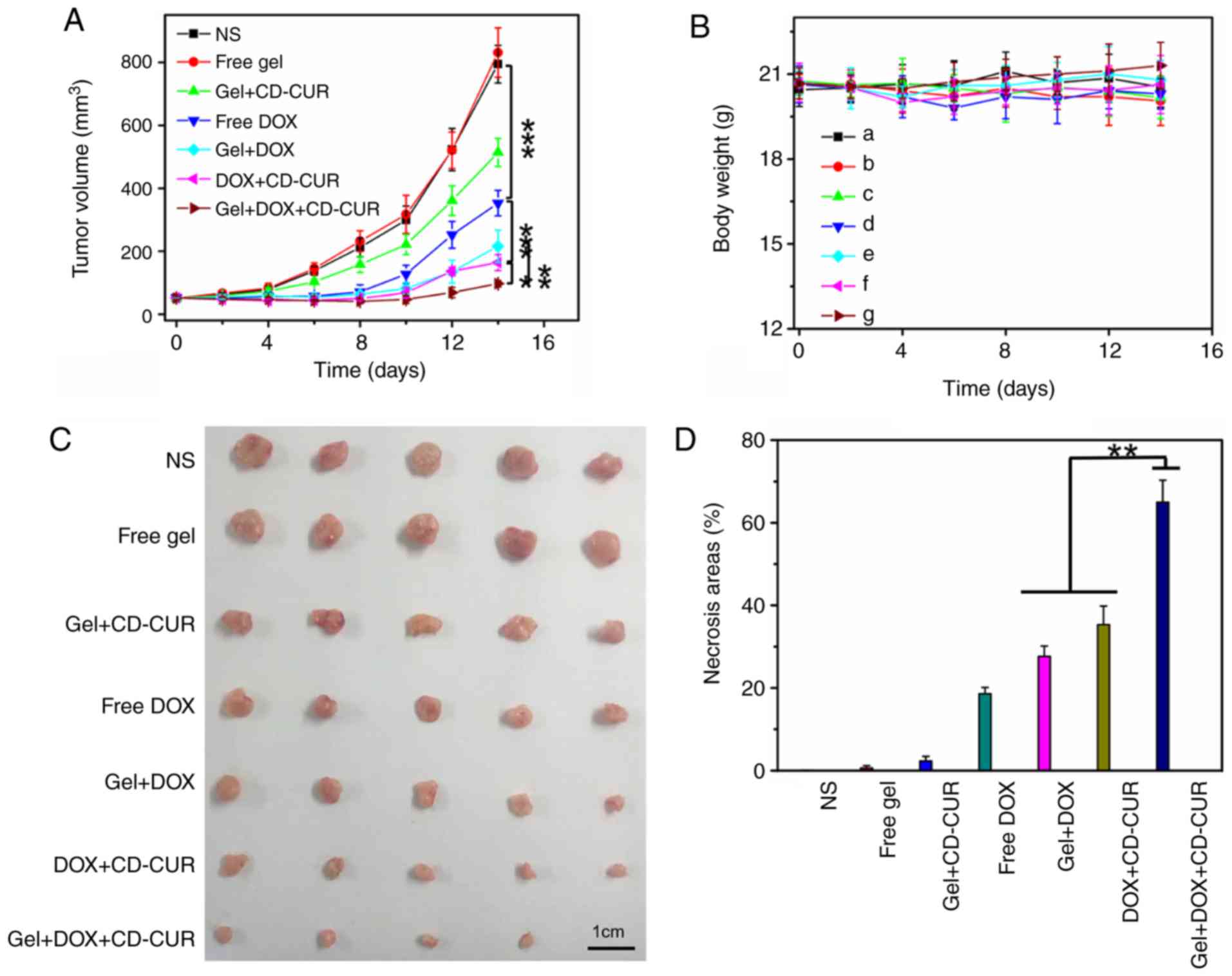
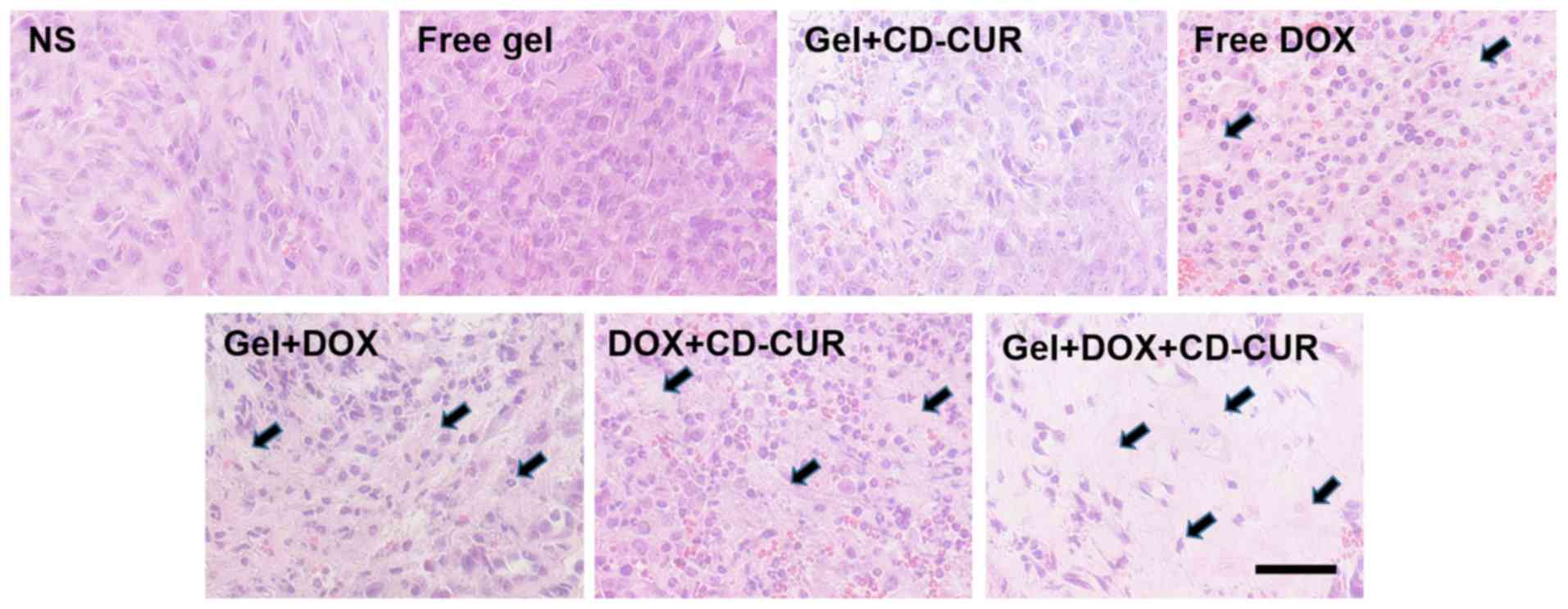
|
1
|
Schwartz CL, Gorlick R, Teot L, Krailo M,
Chen Z, Goorin A, Grier HE, Bernstein ML and Meyers P: Multiple
drug resistance in osteogenic sarcoma: INT0133 from the Children's
Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 25:2057–2062. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nedelcu T, Kubista B, Koller A, Sulzbacher
I, Mosberger I, Arrich F, Trieb K, Kotz R and Toma CD: Livin and
Bcl-2 expression in high-grade osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 134:237–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li S, Sun W, Wang H, Zuo D, Hua Y and Cai
Z: Research progress on the multidrug resistance mechanisms of
osteosarcoma chemotherapy and reversal. Tumour Biol. 36:1329–133.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sen GS, Mohanty S, Hossain DM,
Bhattacharyya S, Banerjee S, Chakraborty J, Saha S, Ray P,
Bhattacharjee P, Mandal D, et al: Curcumin enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy by tailoring p65NFκB-p300 cross-talk in favor of
p53-p300 in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 286:42232–42247. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yardley DA: Drug resistance and the role
of combination chemotherapy in improving patient outcomes. Int J
Breast Cancer. 2013:1374142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwon Y: Curcumin as a cancer chemotherapy
sensitizing agent. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 57:273–280. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Ma W and Tu P: Synergistically
Improved anti-tumor efficacy by co-delivery doxorubicin and
curcumin polymeric micelles. Macromo Biosci. 15:1252–1261. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tsai YM, Jan WC, Chien CF, Lee WC, Lin LC
and Tsai TH: Optimised nano-formulation on the bioavailability of
hydrophobic polyphenol, curcumin, in freely-moving rats. Food chem.
127:918–925. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strimpakos AS: Preventive and therapeutic
properties in laboratory studies and clinical trials. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 10:511–545. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, Hsu MM, Ho YF,
Shen TS, Ko JY, Lin JT, Lin BR, Ming-Shiang W, et al: Phase I
clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients
with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res.
21:2895–2900. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meiyanto E, Putri DD, Susidarti RA,
Murwanti R, Sardjiman, Fitriasari A, Husnaa U, Purnomo H and
Kawaichi M: Curcumin and its analogues (PGV-0 and PGV-1) enhance
sensitivity of resistant MCF-7 cells to doxorubicin through
inhibition of HER2 and NF-kB activation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:179–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chuah AM, Jacob B, Jie Z, Ramesh S, Mandal
S, Puthan JK, Deshpande P, Vaidyanathan VV, Gelling RW, Patel G, et
al: Enhanced bioavailability and bioefficacy of an amorphous solid
dispersion of curcumin. Food Chem. 156:227–233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Misra R and Sahoo SK: Coformulation of
doxorubicin and curcumin in poly(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide)
nanoparticles suppress the development of multi drug resistance in
K562 cells. Mol Pharm. 8:52–866. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nabekura T, Kamiyama S and Kitagawa S:
Effects of dietary chemopreventive phytochemicals on P-glycoprotein
function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 327:866–870. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lv L, Qiu K, Yu X, Chen C, Qin F, Shi Y,
Ou J, Zhang T, Zhu H, Wu J, et al: Amphiphilic copolymeric micelles
for doxorubicin and curcumin co-delivery to reverse multidrug
resistance in breast cancer. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 12:973–985.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aggarwal BB, Kumar A and Bharti AC:
Anticancer potential of curcumin: Preclinical and clinical studies.
Anticancer Res. 23:363–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J, Chen S, Lv L, Song L, Guo S and
Huang S: Recent progress in studying curcumin and its
nano-preparations for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 19:1974–1993.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Cui T, Liu L, Wu Q, Sun L, Li L,
Wang N and Gong C: Improving anti-tumor activity of curcumin by
polymeric micelles in thermosensitive hydrogel system in colorectal
peritoneal carcinomatosis model. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
11:1173–1182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pillarisetti S, Maya S, Sathianarayanan S
and Jayakumar R: Tunable pH and redox-responsive drug release from
curcumin conjugated γ-polyglutamic acid nanoparticles in cancer
microenvironment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 159:809–819. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yallapu MM, Jaggi M and Chauhan SC:
Beta-cyclodextrin-curcumin self-assembly enhances curcumin delivery
in prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
79:113–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Horvath G, Premkumar T, Boztas A, Lee E,
Jon S and Geckeler KE: Supramolecular nanoencapsulation as a tool:
Solubilization of the anticancer drug trans-dichloro(dipyridine)
platinum(II) by complexation with beta-cyclodextrin. Mol Pharm.
5:358–363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rahman S, Cao S, Steadman KJ, Wei M and
Parekh HS: Natural and β-cyclodextrin-enclosed curcumin: Entrapment
within liposomes and their in vitro cytotoxicity in lung and colon
cancer. Drug Deliv. 19:346–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rachmawati H, Edityaningrum CA and
Mauludin R: Molecular inclusion complex of curcumin-β-cyclodextrin
nanoparticle to enhance curcumin skin permeability from hydrophilic
matrix gel. AAPS PharmSciTech. 14:1303–1312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alexander A, Ajazuddin, Khan J and Saraf S
and Saraf S: Poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical
applications. J Control Release. 172:715–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu L and Ding J: Injectable hydrogels as
unique biomedical materials. Chem Soc Rev. 37:1473–1481. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He C, Tang Z, Tian H and Chen X:
Co-delivery of chemotherapeutics and proteins for synergistic
therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 98:64–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang B, Ma L, Wang HY and Zhang GY: Study
on the supramolecular interaction of curcumin and beta-cyclodextrin
by spectrophotometry and its analytical application. J Agric Food
Chem. 50:1355–1361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gerola AP, Silva DC, Jesus S, Carvalha RA,
Rubria AF, Muniz EC, Borges O and Valente AJM: Synthesis and
controlled curcumin supramolecular complex release from
pH-sensitive modified gumarabic-based hydrogels. RSC Adv.
5:94519–94533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG; National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement
and Reduction of Amimals in Research: Animal research: Reporting in
vivo experiments-the ARRIVE guidelines. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
31:991–993. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mohanty C and Sahoo SK: The in vitro
stability and in vivo pharmacokinetics of curcumin prepared as an
aqueous nanoparticulate formulation. Biomaterials. 31:6597–6611.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marcolino VA, Zanin GM, Durrant LR,
Benassi Mde T and Matioli G: Interaction of curcumin and bixin with
β-cyclodextrin: Complexation methods, stability, and applications
in food. J Agric Food Chem. 59:3348–3357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiong X, Luo S, Wu B and Wang J:
Comparative developmental toxicity and stress protein responses of
dimethyl sulfoxide to rare minnow and zebrafish embryos/larvae.
ZEBRAFISH. 14:60–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yu L, Ci T, Zhou S, Zeng W and Ding J: The
thermogelling PLGA-PEG-PLGA block copolymer as a sustained release
matrix of doxorubicin. Biomater Sci. 1:411–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cesteros LC, Gonzalez-Teresa R and Katime
I: Hydrogels of β-cyclodextrin crosslinked by acylated
poly(ethylene glycol): Synthesis and properties. Eur Polym J.
45:674–679. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yoon SJ, Hyun H, Lee DW and Yang DH:
Visible light-cured glycol chitosan hydrogel containing a
beta-cyclodextrin-curcumin inclusion complex improves wound healing
in vivo. Molecules. 22:pp. E15132017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu J, Li X and Sun F:
Cyclodextrin-containing hydrogels for contact lenses as a platform
for drug incorporation and release. Acta Biomater. 6:486–493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Quaglia F, Varricchio G, Miro A, La
Rotonda MI, Larobina D and Mensitieri G: Modulation of drug release
from hydrogels by using cyclodextrins: The case of
nicardipine/beta-cyclodextrin system in crosslinked
polyethylenglycol. J Control Release. 71:329–337. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fryer RA, Galustian C and Dalgleish AG:
Recent advances and developments in treatment strategies against
pancreatic cancer. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 4:102–112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao M, Fan S, Goldberg ID, Laterra J,
Kitsis RN and Rosen EM: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
blocks the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis signaling in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 276:47257–47265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sa G and Das T: Anti cancer effects of
curcumin: Cycle of life and death. Cell Div. 3:142008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|