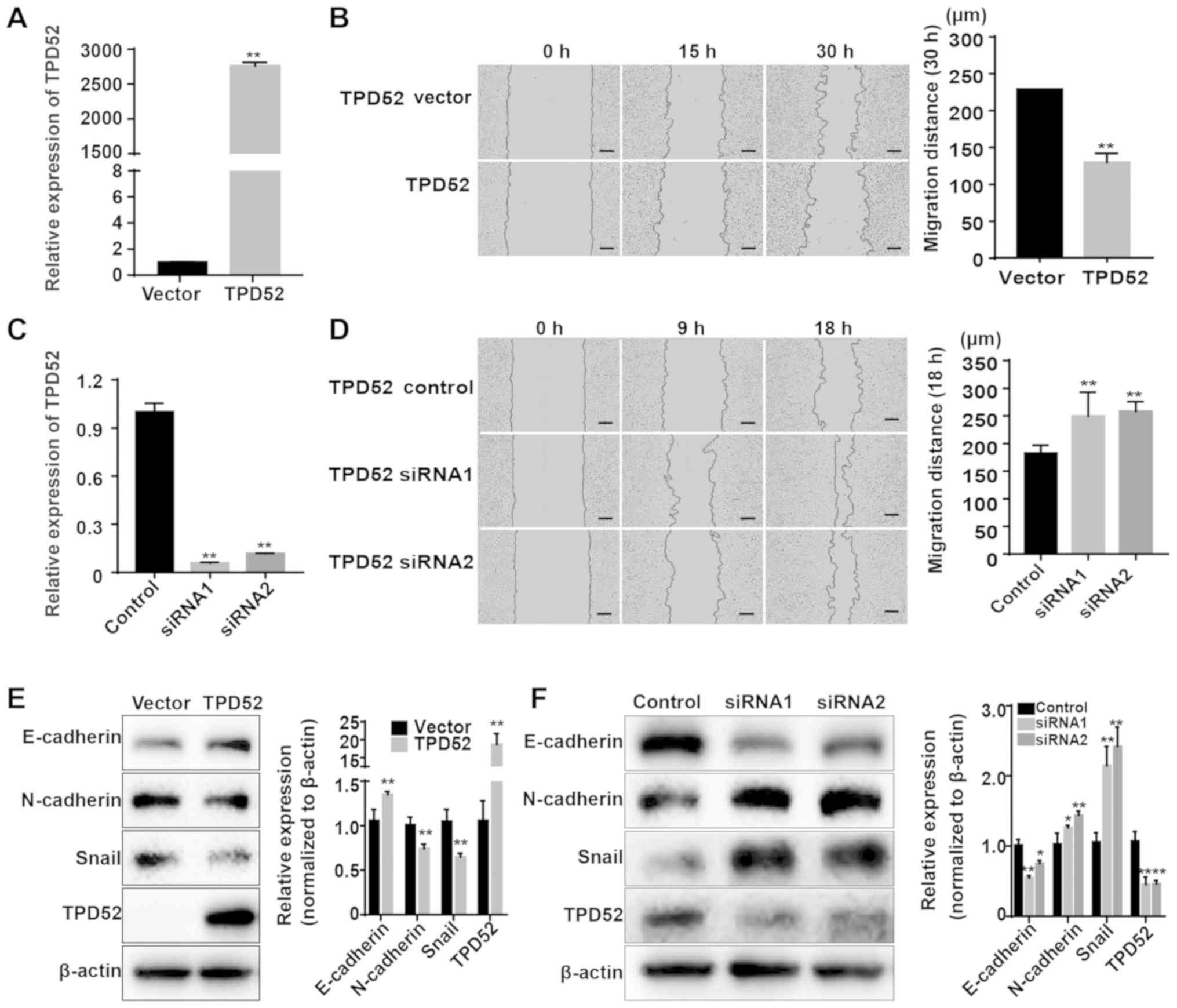
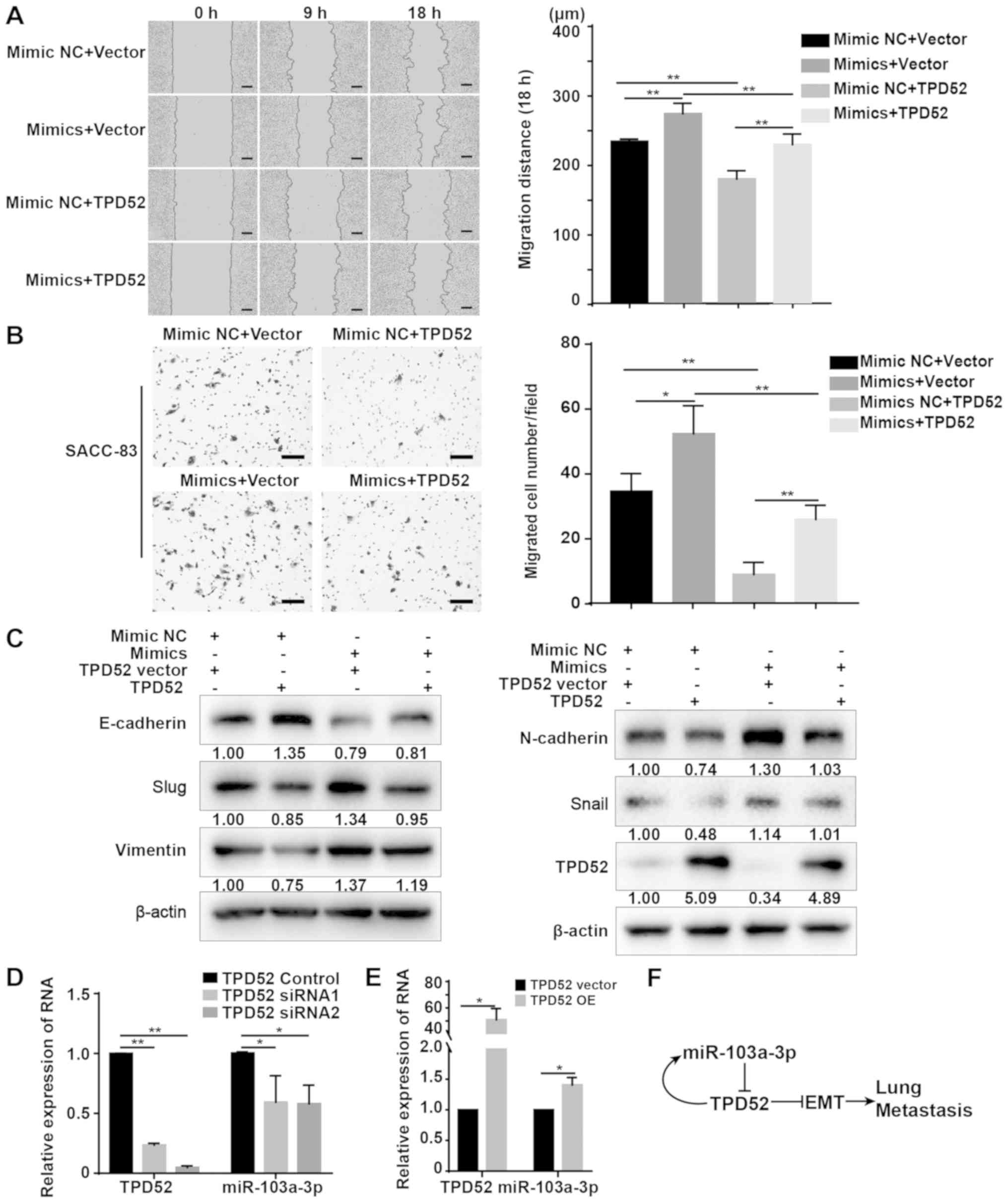
|
1
|
Adelstein DJ, Koyfman SA, El-Naggar AK and
Hanna EY: Biology and management of salivary gland cancers. Semin
Radiat Oncol. 22:245–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rapidis AD, Givalos N, Gakiopoulou H,
Faratzis G, Stavrianos SD, Vilos GA, Douzinas EE and Patsouris E:
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Clinicopathological
analysis of 23 patients and review of the literature. Oral Oncol.
41:328–335. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kokemueller H, Eckardt A, Brachvogel P and
Hausamen JE: Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck - a 20
years experience. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 33:25–31. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gao M, Hao Y, Huang MX, Ma DQ, Luo HY, Gao
Y, Peng X and Yu GY: Clinicopathological study of distant
metastases of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 42:923–928. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ,
Vander Poorten V, Triantafyllou A, Hunt JL, Strojan P, Rinaldo A,
Haigentz M Jr, Takes RP, et al: Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the
head and neck - An update. Oral Oncol. 51:652–661. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Benakanakere MR, Zhao J, Finoti L,
Schattner R, Odabas-Yigit M and Kinane DF: MicroRNA-663 antagonizes
apoptosis antago-nizing transcription factor to induce apoptosis in
epithelial cells. Apoptosis. 24:108–118. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fang JH, Zhang ZJ, Shang LR, Luo YW, Lin
YF, Yuan Y and Zhuang SM: Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal
microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes
metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology.
68:1459–1475. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Jiang L, Wang A, Yu J, Shi F and
Zhou X: MicroRNA-138 suppresses invasion and promotes apoptosis in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett.
286:217–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barbollat-Boutrand L, Joly-Tonetti N, Dos
Santos M, Metral E, Boher A, Masse I, Berthier-Vergnes O, Bertolino
P, Damour O and Lamartine J: MicroRNA-23b-3p regulates human
keratinocyte differentiation through repression of TGIF1 and
activation of the TGF-β-SMAD2 signalling pathway. Exp Dermatol.
26:51–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan F, Wang C, Li T, Cai W and Sun J: Role
of miR-21 in the growth and metastasis of human salivary adenoid
cystic carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 17:4237–4244. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang C, Li T, Yan F, Cai W, Zheng J, Jiang
X and Sun J: Effect of simvastatin and microRNA-21 inhibitor on
metastasis and progression of human salivary adenoid cystic
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:1054–1061. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brown AL, Al-Samadi A, Sperandio M, Soares
AB, Teixeira LN, Martinez EF, Demasi APD, Araújo VC, Leivo I, Salo
T, et al: miR-455-3p, miR-150 and miR-375 are aberrantly expressed
in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous
adenocarcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 48:840–845. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun L, Liu B, Lin Z, Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y,
Chen J, Yu D, Tang Z, Wang B, et al: miR-320a acts as a prognostic
factor and Inhibits metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma
by targeting ITGB3. Mol Cancer. 14:962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang Y, Ye J, Jiao J, Zhang J, Lu Y,
Zhang L, Wan D, Duan L, Wu Y and Zhang B: Down-regulation of
miR-125a-5p is associated with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma
progression via targeting p38/JNK/ERK signal pathway. Am J Transl
Res. 9:1101–1113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, Lang YD, Lin
CJ, Huang J, Wang WC, Lin FM, Chen Z, Huang HD, et al: miR-103/107
promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis
suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 72:3631–3641. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng J, Liu Y, Qiao Y, Zhang L and Lu S:
miR-103 Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting KLF4 in
Gastric Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Liu Y and Song J: MicroRNA-103
suppresses glioma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting the
brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Med Rep. 17:4083–4089.
2018.
|
|
20
|
Yang D, Wang JJ, Li JS and Xu QY: miR-103
Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Directly Targeting Programmed
Cell Death 10 in NSCLC. Oncol Res. 26:519–528. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Kamili A, Hardy JR, Groblewski GE,
Khanna KK and Byrne JA: Tumor protein D52 represents a negative
regulator of ATM protein levels. Cell Cycle. 12:3083–3097. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilson SH, Bailey AM, Nourse CR, Mattei MG
and Byrne JA: Identification of MAL2, a novel member of the mal
proteolipid family, though interactions with TPD52-like proteins in
the yeast two-hybrid system. Genomics. 76:81–88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R,
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Paris PL, Hofer MD, Storz-Schweizer M,
Kuefer R, Fletcher JA, et al: Overexpression, amplification, and
androgen regulation of TPD52 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
64:3814–3822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balleine RL, Fejzo MS, Sathasivam P,
Basset P, Clarke CL and Byrne JA: The hD52 (TPD52) gene is a
candidate target gene for events resulting in increased 8q21 copy
number in human breast carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
29:48–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tennstedt P, Bölch C, Strobel G, Minner S,
Burkhardt L, Grob T, Masser S, Sauter G, Schlomm T and Simon R:
Patterns of TPD52 overexpression in multiple human solid tumor
types analyzed by quantitative PCR. Int J Oncol. 44:609–615. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kumamoto T, Seki N, Mataki H, Mizuno K,
Kamikawaji K, Samukawa T, Koshizuka K, Goto Y and Inoue H:
Regulation of TPD52 by antitumor microRNA-218 suppresses cancer
cell migration and invasion in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 49:1870–1880. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Byrne JA, Frost S, Chen Y and Bright RK:
Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) and cancer-oncogene understudy or
understudied oncogene? Tumour Biol. 35:7369–7382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Chen CL, Pan QZ, Wu YY, Zhao JJ,
Jiang SS, Chao J, Zhang XF, Zhang HX, Zhou ZQ, et al: Decreased
TPD52 expression is associated with poor prognosis in primary
hepato-cellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:6323–6334. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao Z, Liu H, Hou J, Li T, Du X, Zhao X,
Xu W, Xu W and Chang J: Tumor Protein D52 (TPD52) Inhibits Growth
and Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells Through the PI3K/Akt
Signaling Pathway. Oncol Res. 25:773–779. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen H, Xu H, Meng YG, Zhang Y, Chen JY
and Wei XN: miR-139-5p regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and cell
cycle of uterine leiomyoma cells by targeting TPD52. OncoTargets
Ther. 9:6151–6160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu Y, Huang J, Xu H and Gong Z:
Over-expression of miR-15a-3p enhances the radiosensitivity of
cervical cancer by targeting tumor protein D52. Biomed
Pharmacother. 105:1325–1334. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li SL: Establishment of a human cancer
cell line from adenoid cystic carcinoma of the minor salivary
gland. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1990.In Chinese.
|
|
33
|
Dong L, Wang YX, Li SL, Yu GY, Gan YH, Li
D and Wang CY: TGF-beta1 promotes migration and invasion of
salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Dent Res. 90:804–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang W-W, Yang L-Q, Zhao F, Chen CW, Xu
LH, Fu J, Li SL and Ge XY: Epiregulin Promotes Lung Metastasis of
Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Theranostics. 7:3700–3714. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu LH, Zhao F, Yang WW, Chen CW, Du ZH, Fu
M, Ge XY and Li SL: MYB promotes the growth and metastasis of
salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 54:1579–1590.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu Y, Gu J, Li Y, Peng C, Shi M, Wang X,
Wei G, Ge O, Wang D, Zhang B, et al: miR-17-5p enhances pancreatic
cancer proliferation by altering cell cycle profiles via disruption
of RBL2/E2F4-repressing complexes. Cancer Lett. 412:59–68. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang X, Wang S, Wang H, et al: Circular
RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric
cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway. Mol Cancer.
18:202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Andreasen S, Tan Q, Agander TK, Hansen
TVO, Steiner P, Bjørndal K, Høgdall E, Larsen SR, Erentaite D,
Olsen CH, et al: MicroRNA dysregulation in adenoid cystic carcinoma
of the salivary gland in relation to prognosis and gene fusion
status: A cohort study. Virchows Arch. 473:329–340. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He Q, Zhou X, Li S, Jin Y, Chen Z, Chen D,
Cai Y, Liu Z, Zhao T and Wang A: MicroRNA-181a suppresses salivary
adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasis by targeting MAPK-Snai2
pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:5258–5266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Natarelli L, Geissler C, Csaba G, Wei Y,
Zhu M, di Francesco A, Hartmann P, Zimmer R and Schober A: miR-103
promotes endo-thelial maladaptation by targeting lncWDR59. Nat
Commun. 9:26452018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wu L, Fan J and Belasco JG: MicroRNAs
direct rapid dead-enylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4034–4039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, Zimmermann
U, Venz S, Scharf C, Giebel J and Walther R: Altered expression of
tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and migration of prostate
cancer cells. FEBS J. 275:5703–5713. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Croset M, Pantano F, Kan CWS, Bonnelye E,
Descotes F, Alix-Panabières C, Lecellier CH, Bachelier R, Allioli
N, Hong SS, et al: miRNA-30 Family Members Inhibit Breast Cancer
Invasion, Osteomimicry, and Bone Destruction by Directly Targeting
Multiple Bone Metastasis-Associated Genes. Cancer Res.
78:5259–5273. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu Z, Li Z, Wang W, Xia Y, He Z, Li B,
Wang S, Huang X, Sun G, Xu J, et al: MIR-1265 regulates cellular
proliferation and apoptosis by targeting calcium binding protein 39
in gastric cancer and, thereby, impairing oncogenic autophagy.
Cancer Lett. 449:226–236. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dai J, Wang J, Yang L, Xiao Y and Ruan Q:
miR-125a regulates angiogenesis of gastric cancer by targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor A. Int J Oncol. 47:1801–1810.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|