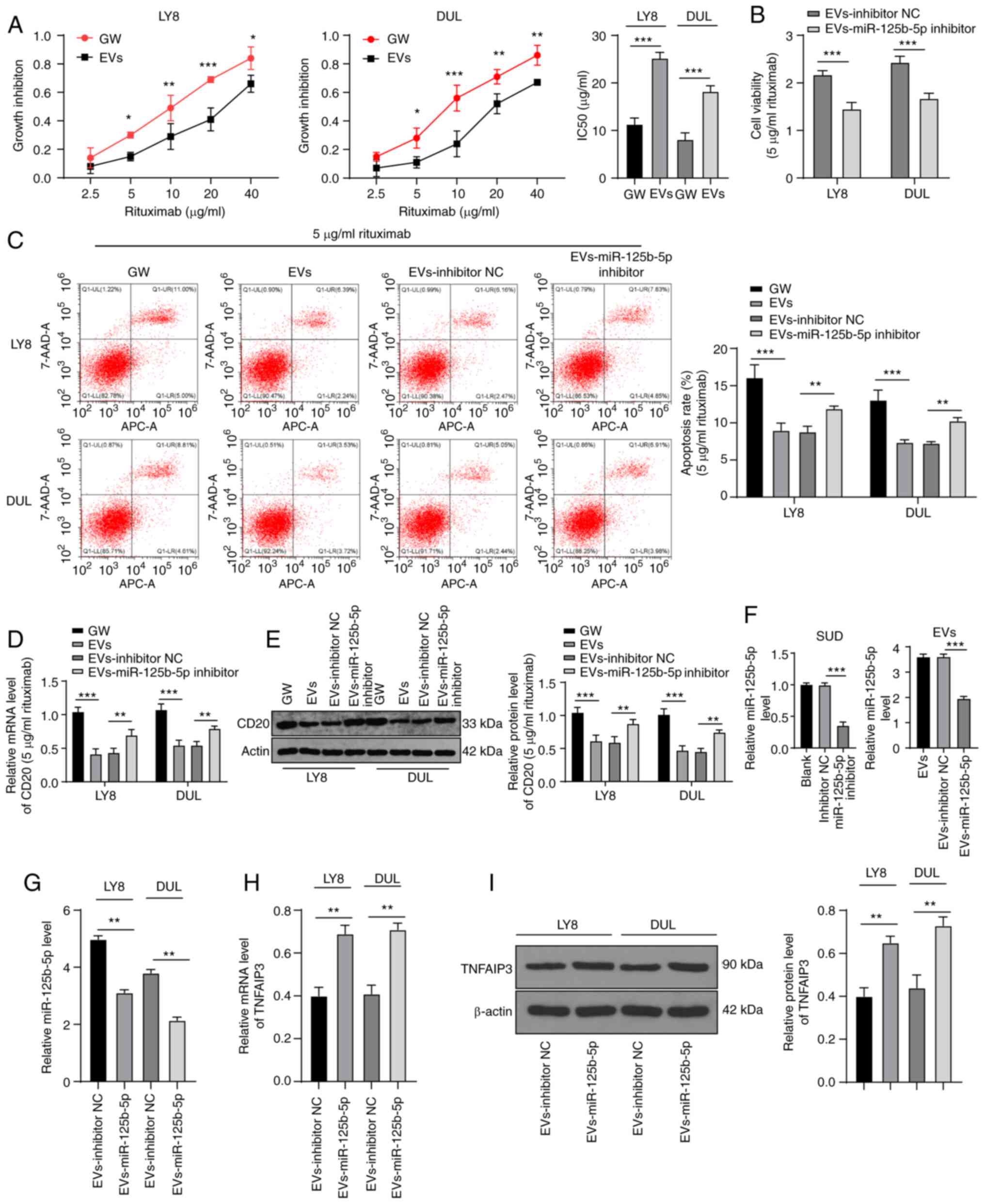
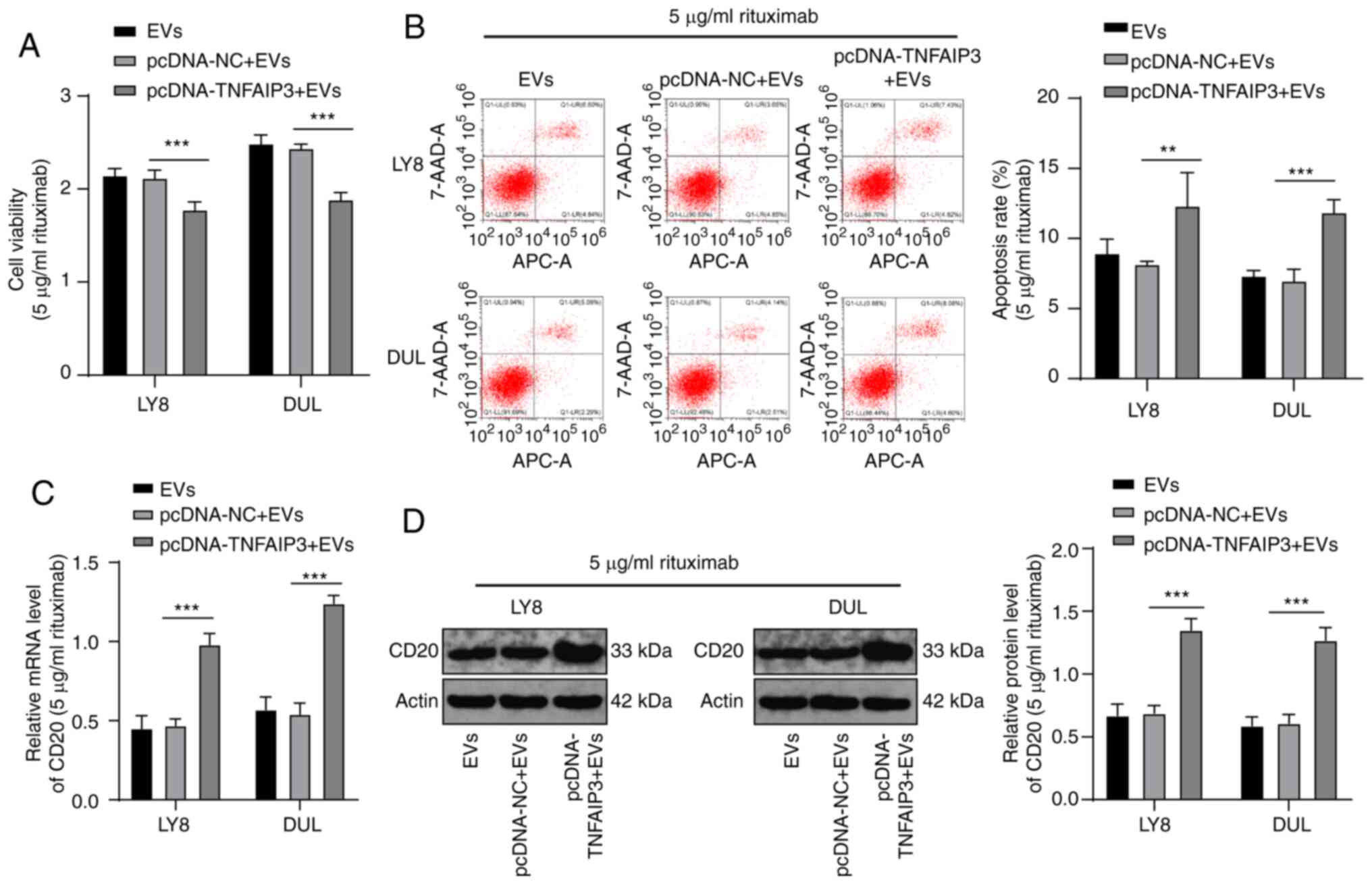
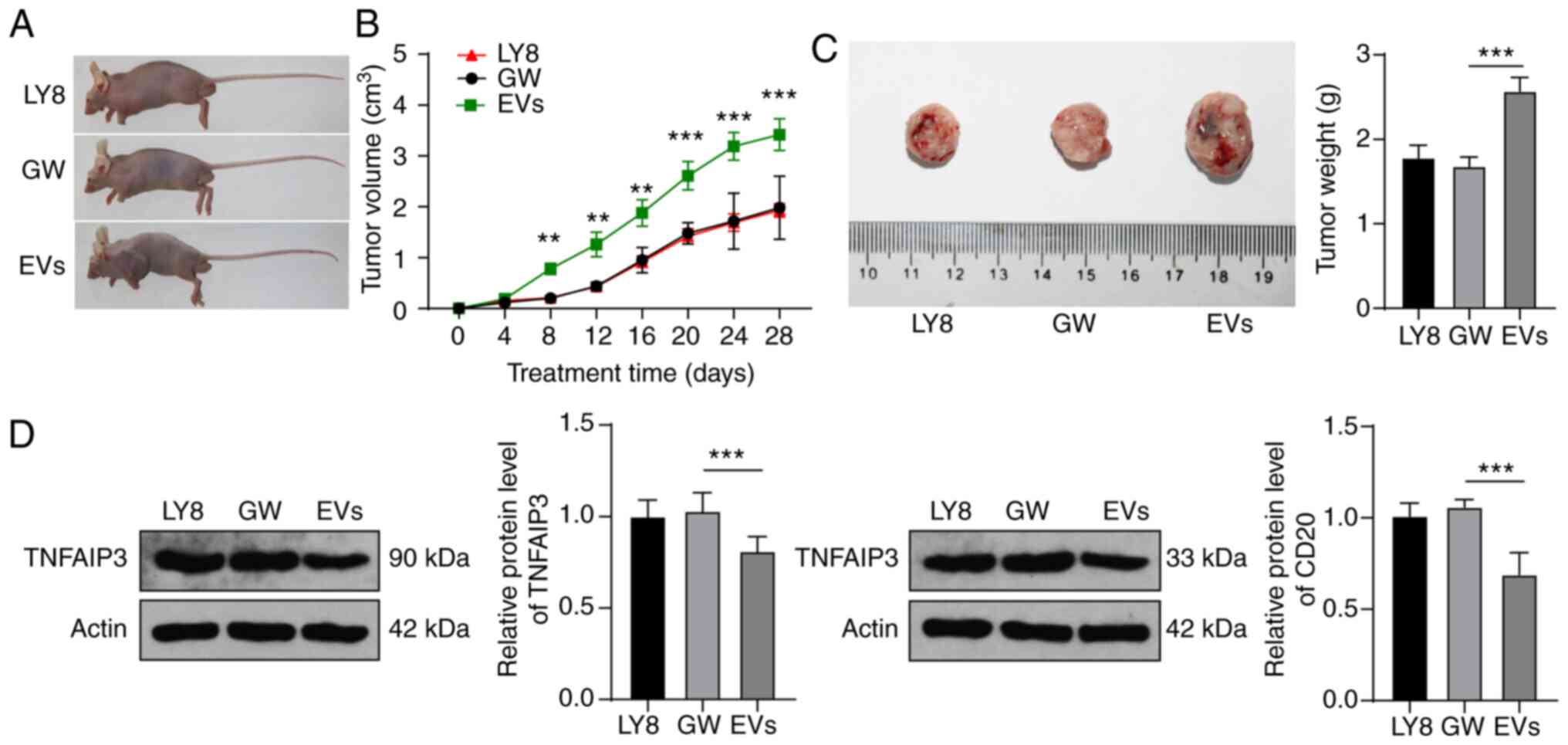
|
1
|
Harker-Murray PD, Pommert L and Barth MJ:
Novel therapies potentially available for pediatric B-cell
non-hodgkin lymphoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 18:1125–1134. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allen P: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in
the elderly: Current approaches. Curr Oncol Rep. 22:1142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Y and Barta SK: Diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and
treatment. Am J Hematol. 94:604–616. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maurer MJ, Jais JP, Ghesquieres H, Witzig
TE, Hong F, Haioun C, Thompson CA, Thieblemont C, Micallef IN,
Porrata LF, et al: Personalized risk prediction for event-free
survival at 24 months in patients with diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 91:179–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Giulino L, Mathew S, Ballon G, Chadburn A,
Barouk S, Antonicelli G, Leoncini L, Liu YF, Gogineni S, Tam W and
Cesarman E: A20 (TNFAIP3) genetic alterations in EBV-associated
AIDS-related lymphoma. Blood. 117:4852–4854. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hovelmeyer N, Reissig S, Xuan NT,
Adams-Quack P, Lukas D, Nikolaev A, Schluter D and Waisman A: A20
deficiency in B cells enhances B-cell proliferation and results in
the development of autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol. 41:595–601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujii M, Takata K, Chuang SS,
Miyata-Takata T, Ando M, Sato Y and Yoshino T: A20 (TNFAIP3)
alterations in primary intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Acta Med Okayama. 72:23–30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dong G, Chanudet E, Zeng N, Appert A, Chen
YW, Au WY, Hamoudi RA, Watkins AJ, Ye H, Liu H, et al: A20,
ABIN-1/2, and CARD11 mutations and their prognostic value in
gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1440–1451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paik JH, Go H, Nam SJ, Kim TM, Heo DS, Kim
CW and Jeon YK: Clinicopathologic implication of A20/TNFAIP3
deletion in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: An analysis according to
immunohistochemical subgroups and rituximab treatment. Leuk
Lymphoma. 54:1934–1941. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cappariello A and Rucci N: Tumour-derived
extracellular vesicles (EVs): A dangerous 'message in a bottle' for
bone. Int J Mol Sci. 20:48052019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Urabe F, Kosaka N, Ito K, Kimura T, Egawa
S and Ochiya T: Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and
therapeutic targets for cancer. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
318:C29–C39. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu W, Zhu M, Wang H, Wang W and Lu Y:
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma-derived extracellular vesicles
educate macrophages to promote tumours progression by increasing
PGC-1β. Scand J Immunol. 91:e128412020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rutherford SC, Fachel AA, Li S, Sawh S,
Muley A, Ishii J, Saxena A, Dominguez PM, Caldas Lopes E, Agirre X,
et al: Extracellular vesicles in DLBCL provide abundant clues to
aberrant transcriptional programming and genomic alterations.
Blood. 132:e13–e23. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ting CY, Liew SM, Price A, Gan GG, Bee-Lan
Ong D, Tan SY and Bee PC: Clinical significance of aberrant
microRNAs expression in predicting disease relapse/refractoriness
to treatment in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 144:1028182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu ZZ, Wang WF, Fu WB, Wang AH, Liu ZY,
Chen LY, Guo P and Li JM: Combination of rituximab and mammalian
target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus (RAD001) in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 55:1151–1157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li S, Young KH and Medeiros LJ: Diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology. 50:74–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sarkozy C and Sehn LH: Management of
relapsed/refractory DLBCL. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
31:209–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamma R, Ranieri G, Ingravallo G, Annese
T, Oranger A, Gaudio F, Musto P, Specchia G and Ribatti D:
Inflammatory cells in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Clin Med.
9:24182020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA,
Gascoyne RD, Cassileth PA, Cohn JB, Dakhil SR, Woda B, Fisher RI,
Peterson BA and Horning SJ: Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or
with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:3121–3127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mounier N, Briere J, Gisselbrecht C, Emile
JF, Lederlin P, Sebban C, Berger F, Bosly A, Morel P, Tilly H, et
al: Rituximab plus CHOP (R-CHOP) overcomes bcl-2-associated
resistance to chemotherapy in elderly patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood. 101:4279–4284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Honma K, Tsuzuki S, Nakagawa M, Tagawa H,
Nakamura S, Morishima Y and Seto M: TNFAIP3/A20 functions as a
novel tumor suppressor gene in several subtypes of non-Hodgkin
lymphomas. Blood. 114:2467–2475. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmitz R, Hansmann ML, Bohle V,
Martin-Subero JI, Hartmann S, Mechtersheimer G, Klapper W, Vater I,
Giefing M, Gesk S, et al: TNFAIP3 (A20) is a tumor suppressor gene
in Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. J Exp
Med. 206:981–989. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vereecke L, Beyaert R and van Loo G: The
ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of
immunopathology. Trends Immunol. 30:383–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Xing H, Li S, Yu J, Li H, Liu S,
Tian Z, Tang K, Rao Q, Wang M and Wang J: Up-regulated A20 promotes
proliferation, regulates cell cycle progression and induces
chemotherapy resistance of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leuk
Res. 39:976–983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
da Silva CG, Minussi DC, Ferran C and
Bredel M: A20 expressing tumors and anticancer drug resistance. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 809:65–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Palanichamy A, Jahn S, Nickles D, Derstine
M, Abounasr A, Hauser SL, Baranzini SE, Leppert D and von Budingen
HC: Rituximab efficiently depletes increased CD20-expressing T
cells in multiple sclerosis patients. J Immunol. 193:580–586. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu S, Chen Q and Wang Y: MiR-125b-5p
suppresses the bladder cancer progression via targeting HK2 and
suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway. Hum Cell. 33:185–194. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yao J, Li Z, Wang X, Xu P, Zhao L and Qian
J: MiR-125a regulates chemo-sensitivity to gemcitabine in human
pancreatic cancer cells through targeting A20. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 48:202–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kara-Terki L, Treps L, Blanquart C and
Fradin D: Critical roles of tumor extracellular vesicles in the
microenvironment of thoracic cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 21:60242020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Maisano D, Mimmi S, Russo R, Fioravanti A,
Fiume G, Vecchio E, Nistico N, Quinto I and Iaccino E: Uncovering
the exosomes diversity: A window of opportunity for tumor
progression monitoring. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 13:1802020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gerloff D, Lutzkendorf J, Moritz RKC,
Wersig T, Mader K, Muller LP and Sunderkotter C: Melanoma-derived
exosomal miR-125b-5p educates tumor associated macrophages (TAMs)
by targeting lysosomal acid lipase A (LIPA). Cancers (Basel).
12:4642020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu M, Tan X, Liu P, Yang Y, Huang Y, Liu
X, Meng X, Yu B, Wu Y and Jin H: Role of exosomal microRNA-125b-5p
in conferring the metastatic phenotype among pancreatic cancer
cells with different potential of metastasis. Life Sci.
255:1178572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Drees EEE and Pegtel DM: Circulating
miRNAs as biomarkers in aggressive B cell lymphomas. Trends Cancer.
6:910–923. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang W, Li Y, Li P and Wang L: PMA/IONO
affects diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell growth through
upregulation of A20 expression. Oncol Rep. 36:1069–1075. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aung T, Chapuy B, Vogel D, Wenzel D,
Oppermann M, Lahmann M, Weinhage T, Menck K, Hupfeld T, Koch R, et
al: Exosomal evasion of humoral immunotherapy in aggressive B-cell
lymphoma modulated by ATP-binding cassette transporter A3. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:15336–15341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I, Sato Y, Takita
J, Takeuchi K, Niwa A, Chen Y, Nakazaki K, Nomoto J, et al:
Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature.
459:712–716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng Y, Zhong M, Zeng S, Wang L, Liu P,
Xiao X and Liu Y: Exosome-derived miRNAs as predictive biomarkers
for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma chemotherapy resistance.
Epigenomics. 11:35–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yuan WX, Gui YX, Na WN, Chao J and Yang X:
Circulating microRNA-125b and microRNA-130a expression profiles
predict chemoresistance to R-CHOP in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
patients. Oncol Lett. 11:423–432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim SW, Ramasamy K, Bouamar H, Lin AP,
Jiang D and Aguiar RC: MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b
constitutively activate the NF-kB pathway by targeting the tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20). Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:7865–7870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li G, So AY, Sookram R, Wong S, Wang JK,
Ouyang Y, He P, Su Y, Casellas R and Baltimore D: Epigenetic
silencing of miR-125b is required for normal B-cell development.
Blood. 131:1920–1930. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Iida K, Fukushi J, Matsumoto Y, Oda Y,
Takahashi Y, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara-Okada Y, Hatano M, Nabashima A,
Kamura S and Iwamoto Y: miR-125b develops chemoresistance in Ewing
sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Cancer Cell Int.
13:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao L, Liu W, Xiao J and Cao B: The role
of exosomes and 'exosomal shuttle microRNA' in tumorigenesis and
drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 356:339–346. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Oksvold MP, Kullmann A, Forfang L, Kierulf
B, Li M, Brech A, Vlassov AV, Smeland EB, Neurauter A and Pedersen
KW: Expression of B-cell surface antigens in subpopulations of
exosomes released from B-cell lymphoma cells. Clin Ther. 36:847–862
e841. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|