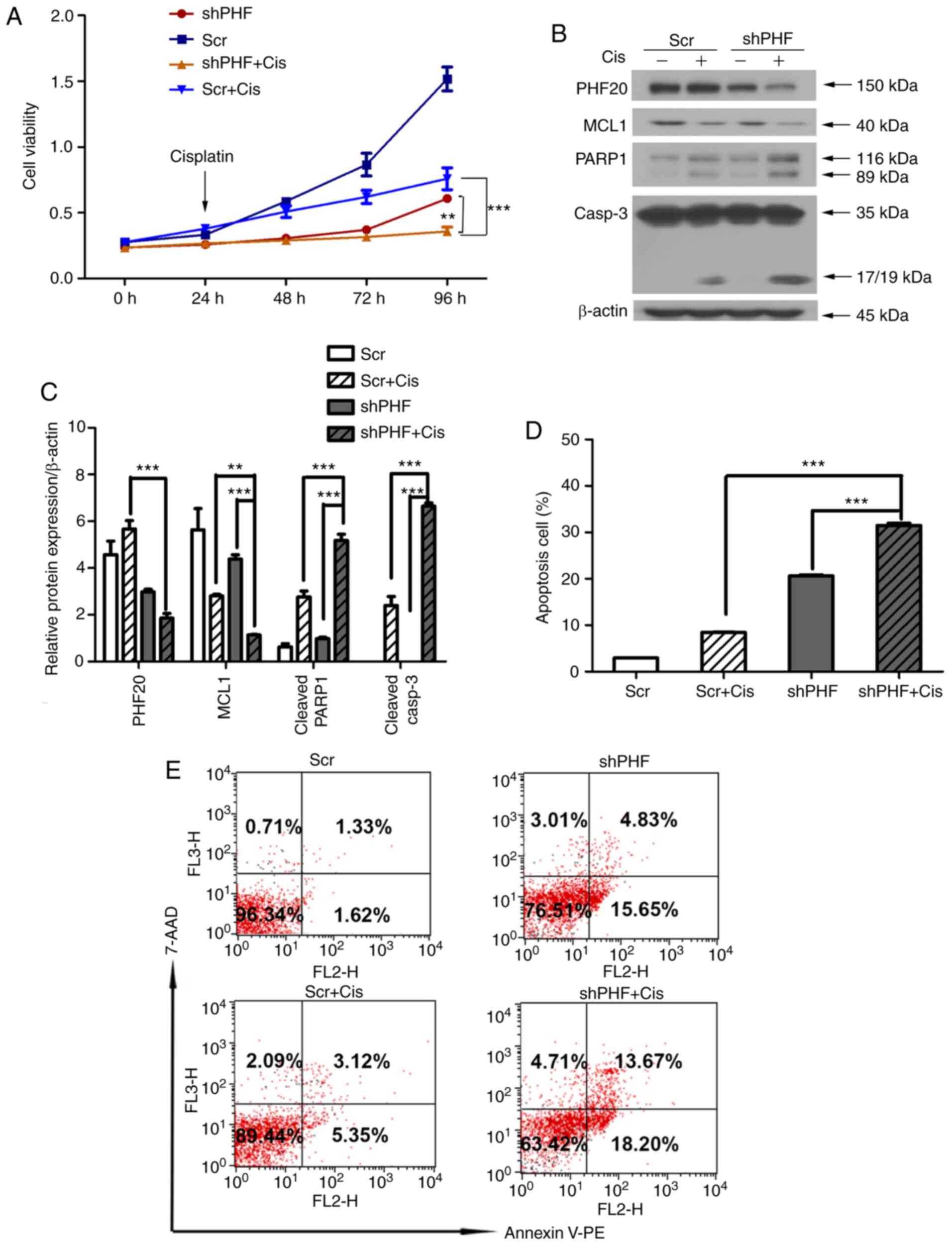
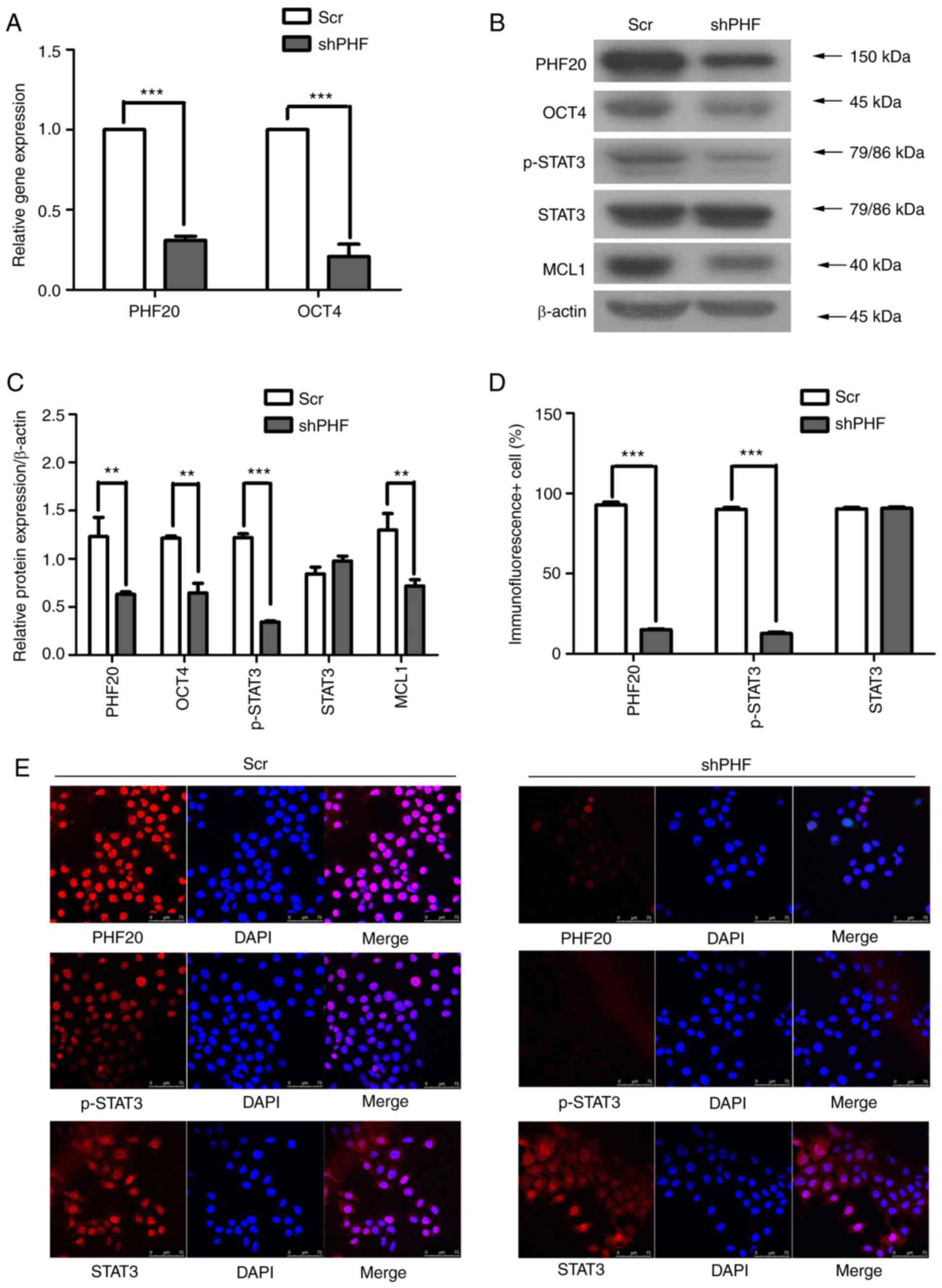
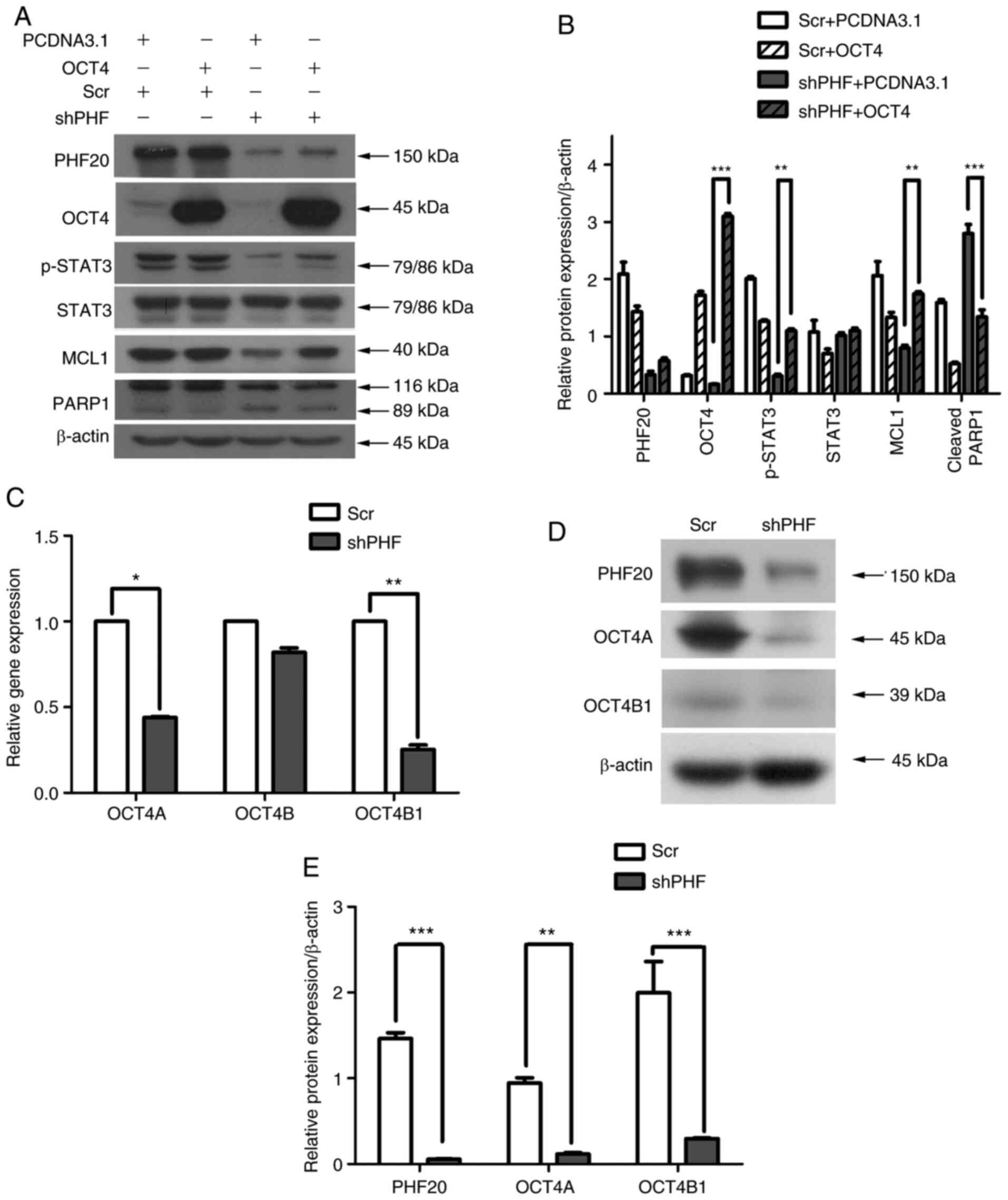
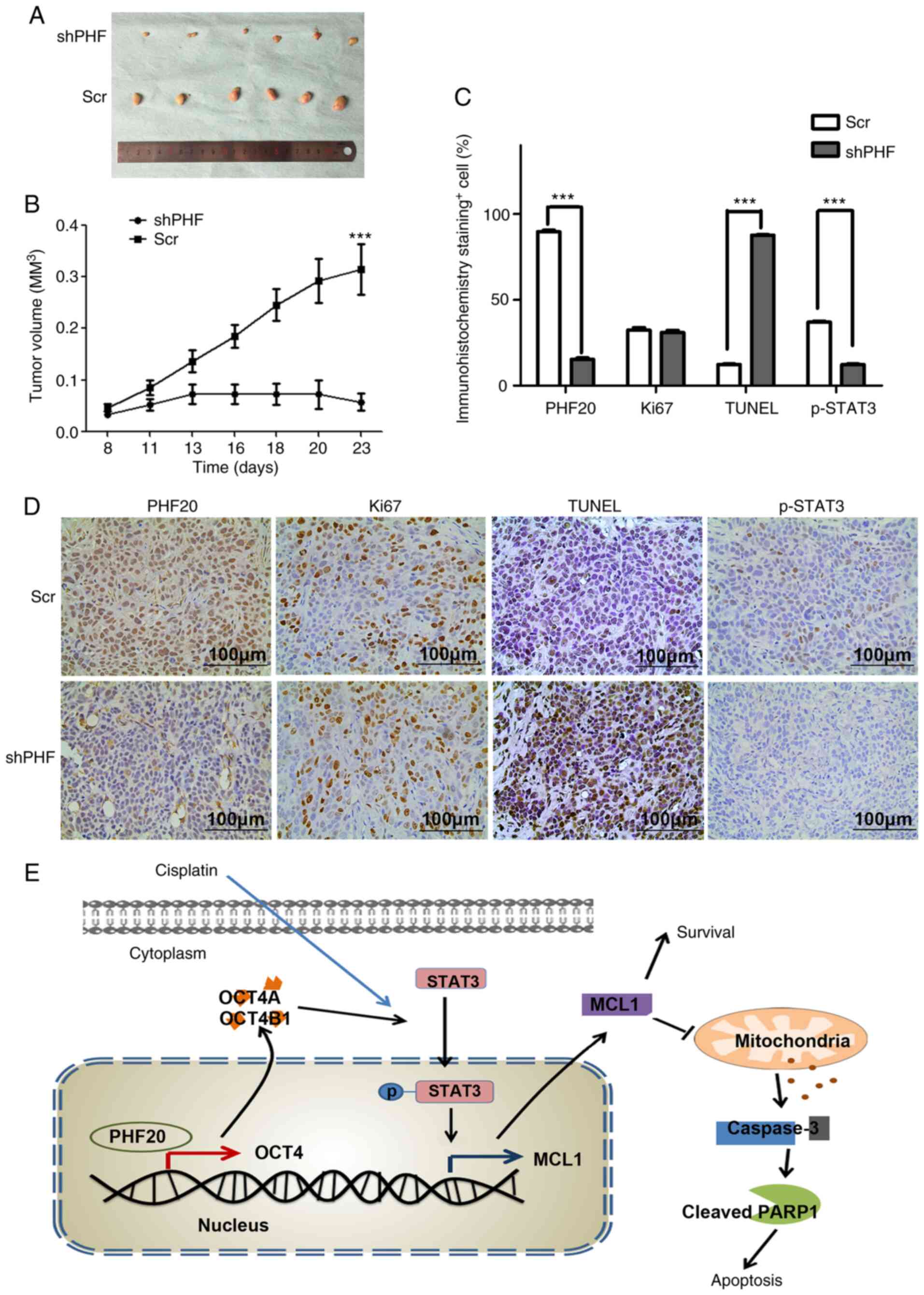
|
1
|
Takes RP, Strojan P, Silver CE, Bradley
PJ, Haigentz M Jr, Wolf GT, Shaha AR, Hartl DM, Olofsson J,
Langendijk JA, et al: Current trends in initial management of
hypopharyngeal cancer: The declining use of open surgery. Head
Neck. 34:270–281. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spector JG, Sessions DG, Haughey BH, Chao
KS, Simpson J, El Mofty S and Perez CA: Delayed regional
metastases, distant metastases, and second primary malignancies in
squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx and hypopharynx.
Laryngoscope. 111:1079–1087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bova R, Goh R, Poulson M and Coman WB:
Total pharyngolaryngectomy for squamous cell carcinoma of the
hypopharynx: A review. Laryngoscope. 115:864–869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bandu R, Ahn HS, Lee JW, Kim YW, Choi SH,
Kim HJ and Kim KP: Liquid chromatography electrospray ionization
tandem mass spectrometric (LC/ESI-MS/MS) Study for the
identification and characterization of in vivo metabolites of
cisplatin in rat kidney cancer tissues: Online Hydrogen/Deuterium
(H/D) exchange study. PLoS One. 10:e01340272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu DW, Lee MC, Hsu NY, Wu TC, Wu JY, Wang
YC, Cheng YW, Chen CY and Lee H: FHIT loss confers cisplatin
resistance in lung cancer via the AKT/NF-κB/Slug-mediated PUMA
reduction. Oncogene. 34:2505–2515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Degterev A, Boyce M and Yuan J: A decade
of caspases. Oncogene. 22:8543–8567. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C,
Garufi A and D'Orazi G: Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function
and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic
strategies. Aging. 8:603–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu X, Li W, Xia Z, Xie L, Ma X, Liang Q,
Liu L, Wang J, Zhou X, Yang Y and Liu H: Targeting MCL-1 sensitizes
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced
apoptosis. BMC Cancer. 17:4492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Badeaux AI, Yang Y, Cardenas K,
Vemulapalli V, Chen K, Kusewitt D, Richie E, Li W and Bedford MT:
Loss of the methyl lysine effector protein PHF20 impacts the
expression of genes regulated by the lysine acetyltransferase MOF.
J Biol Chem. 287:429–437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Bankovic J, Stojsic J, Jovanovic D,
Andjelkovic T, Milinkovic V, Ruzdijic S and Tanic N: Identification
of genes associated with non-small-cell lung cancer promotion and
progression. Lung Cancer. 67:151–159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tang N, Ma L, Lin XY, Zhang Y, Yang DL,
Wang EH and Qiu XS: Expression of PHF20 protein contributes to good
prognosis of NSCLC and is associated with Bax expression. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12198–12206. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Long W, Zhao W, Ning B, Huang J, Chu J, Li
L, Ma Q, Xing C, Wang HY, Liu Q and Wang RF: PHF20 collaborates
with PARP1 to promote stemness and aggressiveness of neuroblastoma
cells through activation of SOX2 and OCT4. J Mol Cell Biol.
10:147–160. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ji J and Zheng PS: Expression of Sox2 in
human cervical carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 41:1438–1447. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen J, Park JY, Park KH, Chung HW, Bang S,
Park SW and Song SY: Oct4 and Nanog expression is associated with
early stages of pancreatic carcinogenesis. Pancreas. 39:622–626.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei D, Kanai M, Jia Z, Le X and Xie K:
Kruppel-like factor 4 induces p27Kip1 expression in and suppresses
the growth and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 68:4631–4639. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YD, Cai N, Wu XL, Cao HZ, Xie LL and
Zheng PS: OCT4 promotes tumorigenesis and inhibits apoptosis of
cervical cancer cells by miR-125b/BAK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis.
4:e7602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang G, Zhou H, Gu Z, Gao Q and Shen G:
Oct4 promotes cancer cell proliferation and migration and leads to
poor prognosis associated with the survivin/STAT3 pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 40:979–987. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng F, Sun G, Zhong M, Yu Y and Brewer
MA: Anticancer efficacy of cisplatin and trichostatin A or
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine on ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 108:579–586.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Wang H, Zheng X,
Lou Y and Han B: Antigen presentation of the Oct4 and Sox2 peptides
by CD154-activated B lymphocytes enhances the killing effect of
cytotoxic T lymphocytes on tumor stem-like cells derived from
cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. J Cancer. 9:367–374. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Ma M, Duan X, Zhang H and Yang M:
Knockdown of OCT4 may sensitize NSCLC cells to cisplatin. Clin
Transl Oncol. 19:587–592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lu CS, Shieh GS, Wang CT, Su BH, Su YC,
Chen YC, Su WC, Wu P, Yang WH, Shiau AL and Wu CL:
Chemotherapeutics-induced Oct4 expression contributes to drug
resistance and tumor recurrence in bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
8:30844–30858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Kato M, Onoyama I, Yoshida S, Cui L,
Kawamura K, Kodama K, Hori E, Matsumura Y, Yagi H, Asanoma K, et
al: Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 plays a critical role in the
maintenance of a cancer stem-like cell phenotype in human
endometrial cancer. Int J Cancer. 147:1987–1999. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X and Zhang X:
DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes
from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics. 26:136–138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Goldie FC, Fulton RL, Dawson J, Bluhmki E
and Lees KR: Exploration of time-course combinations of outcome
scales for use in a global test of stroke recovery. Int J Stroke.
9:755–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao W, Li Q, Ayers S, Gu Y, Shi Z, Zhu Q,
Chen Y, Wang HY and Wang RF: Jmjd3 inhibits reprogramming by
upregulating expression of INK4a/Arf and targeting PHF20 for
ubiquitination. Cell. 152:1037–1050. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu T, Zhang T, Zhou F, Wang J, Zhai X, Mu
N, Park J, Liu M, Liu W, Shang P, et al: Identification of genes
and pathways potentially related to PHF20 by gene expression
profile analysis of glioblastoma U87 cell line. Cancer Cell Int.
17:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramezankhani B, Taha MF and Javeri A:
Vitamin C counteracts miR-302/367-induced reprogramming of human
breast cancer cells and restores their invasive and proliferative
capacity. J Cell Physiol. 234:2672–2682. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Ma Q, Shen S and Hu H: Inhibition
of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by propranolol occurs
through apoptosis induction: The study of beta-adrenoceptor
antagonist's anticancer effect in pancreatic cancer cell. Pancreas.
38:94–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cui G, Park S, Badeaux AI, Kim D, Lee J,
Thompson JR, Yan F, Kaneko S, Yuan Z, Botuyan MV, et al: PHF20 is
an effector protein of p53 double lysine methylation that
stabilizes and activates p53. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:916–924.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qin Z, Ren G, Yuan J, Chen H, Lu Y, Li N,
Zhang Y, Chen X and Zhao D: Systemic evaluation on the
pharmacokinetics of platinum-based anticancer drugs from animal to
cell level: Based on total platinum and intact drugs. Front
Pharmacol. 10:14852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pointreau Y, Garaud P, Chapet S, Sire C,
Tuchais C, Tortochaux J, Faivre S, Guerrif S, Alfonsi M and Calais
G: Randomized trial of induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and
5-fluorouracil with or without docetaxel for larynx preservation. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 101:498–506. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Knox RJ, Friedlos F, Lydall DA and Roberts
JJ: Mechanism of cytotoxicity of anticancer platinum drugs:
Evidence that cis-di amminedichloroplatinum(II) and
cis-diammine-(1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato)platinum(II) differ only
in the kinetics of their interaction with DNA. Cancer Res.
46:1972–1979. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang J, Ju Z and Dong S: Cisplatin and
paclitaxel co-delivered by folate-decorated lipid carriers for the
treatment of head and neck cancer. Drug Deliv. 24:792–799. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Khan Z, Khan AA, Prasad GB, Khan N, Tiwari
RP and Bisen PS: Growth inhibition and chemo-radiosensitization of
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) by survivin-siRNA
lentivirus. Radiother Oncol. 118:359–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bu M, Liu X and Xu W: Upregulation of
fascin-1 is involved in HIF-1α-dependent invasion and migration of
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 55:488–498.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Asadi MH, Mowla SJ, Fathi F, Aleyasin A,
Asadzadeh J and Atlasi Y: OCT4B1, a novel spliced variant of OCT4,
is highly expressed in gastric cancer and acts as an antiapoptotic
factor. Int J Cancer. 128:2645–2652. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cortes-Dericks L, Yazd EF, Mowla SJ,
Schmid RA and Karoubi G: Suppression of OCT4B enhances sensitivity
of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells to cisplatin via increased
apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 33:5365–5373. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li SW, Wu XL, Dong CL, Xie XY, Wu JF and
Zhang X: The differential expression of OCT4 isoforms in cervical
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01180332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang X, Zhao Y, Xiao Z, Chen B, Wei Z,
Wang B, Zhang J, Han J, Gao Y, Li L, et al: Alternative translation
of OCT4 by an internal ribosome entry site and its novel function
in stress response. Stem Cells. 27:1265–1275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsai SC, Chang DF, Hong CM, Xia P,
Senadheera D, Trump L, Mishra S and Lutzko C: Induced
overexpression of OCT4A in human embryonic stem cells increases
cloning efficiency. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 306:C1108–1118.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mirzaei MR, Najafi A, Arababadi MK, Asadi
MH and Mowla SJ: Altered expression of apoptotic genes in response
to OCT4B1 suppression in human tumor cell lines. Tumour Biol.
35:9999–10009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|