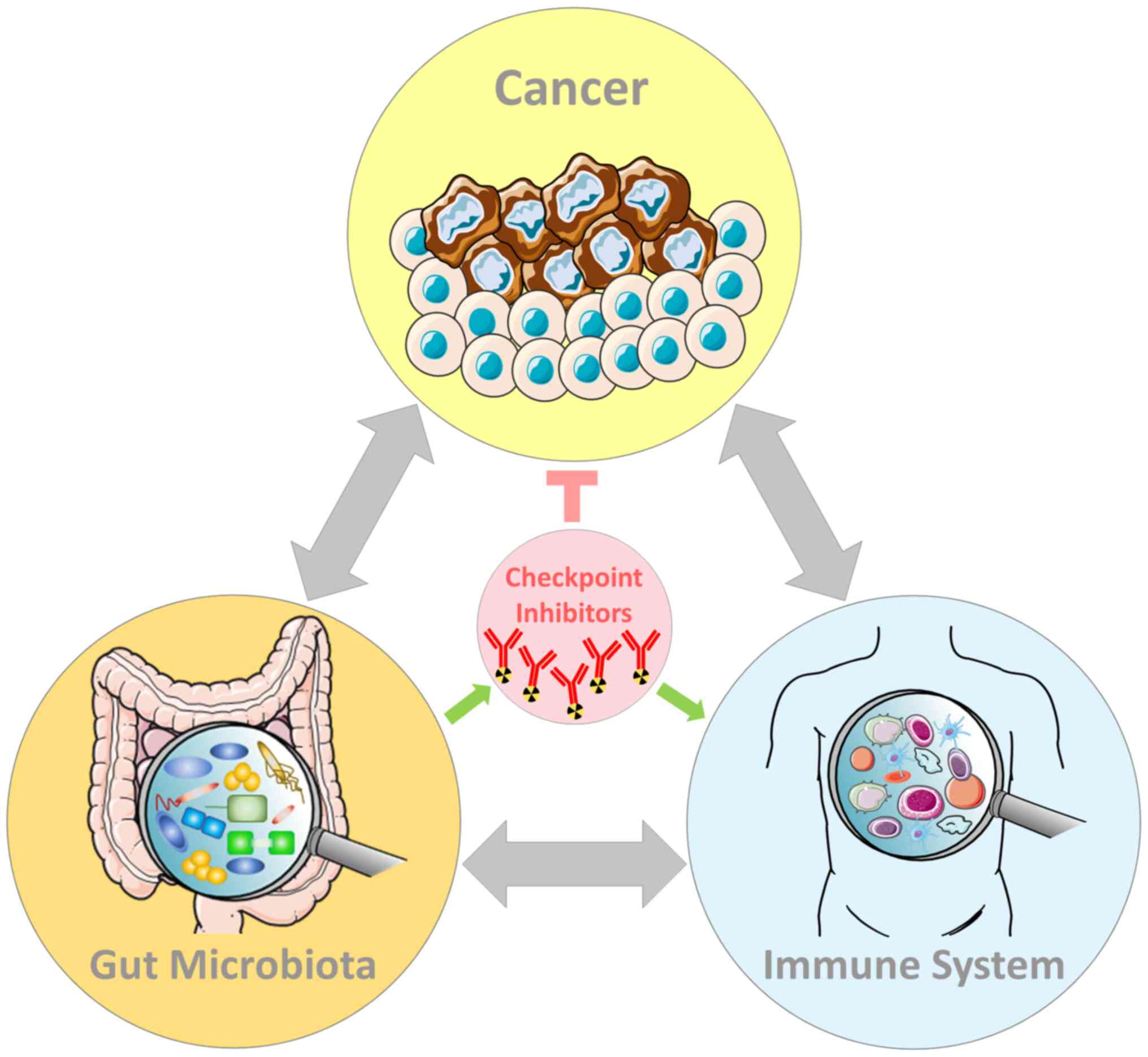
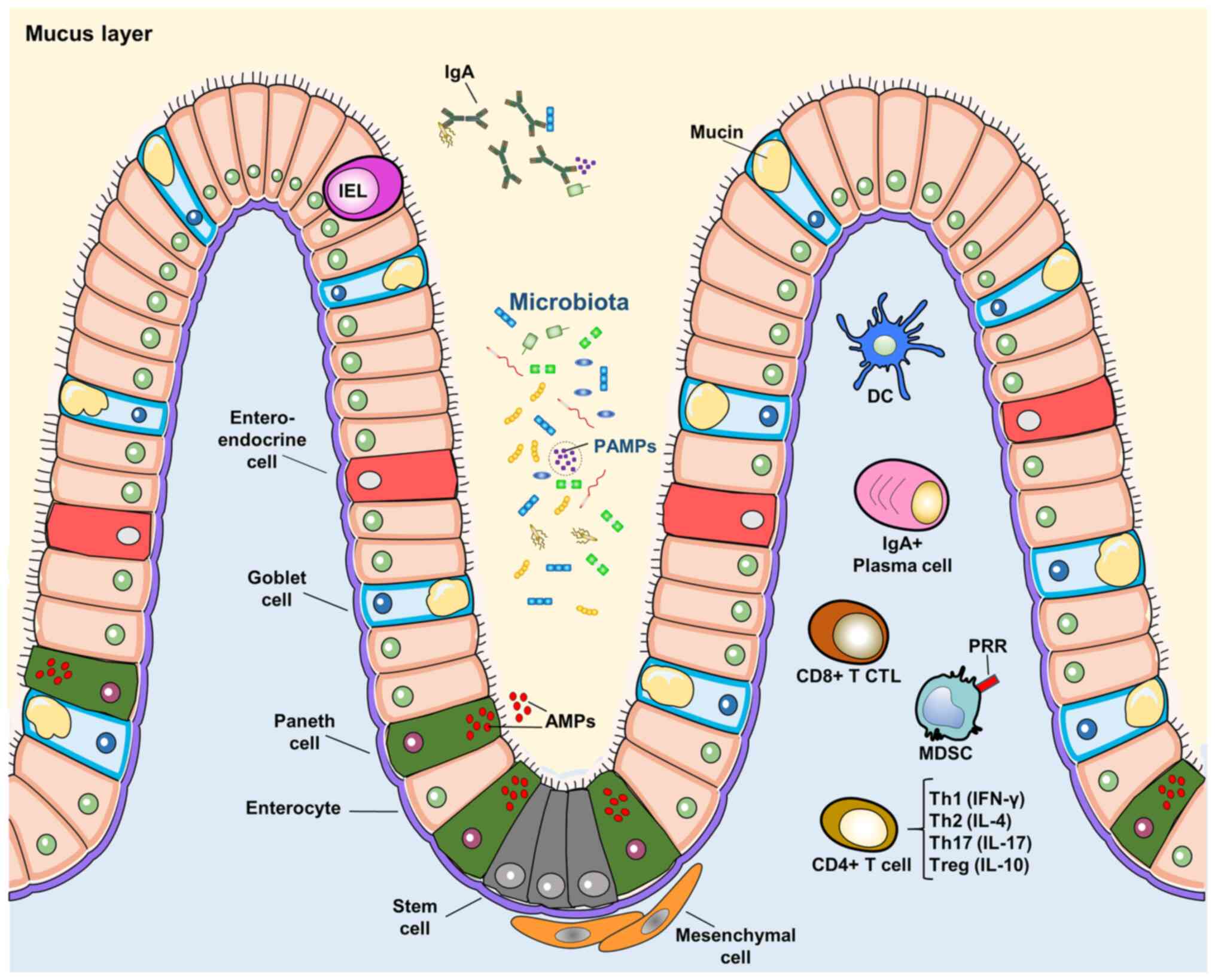
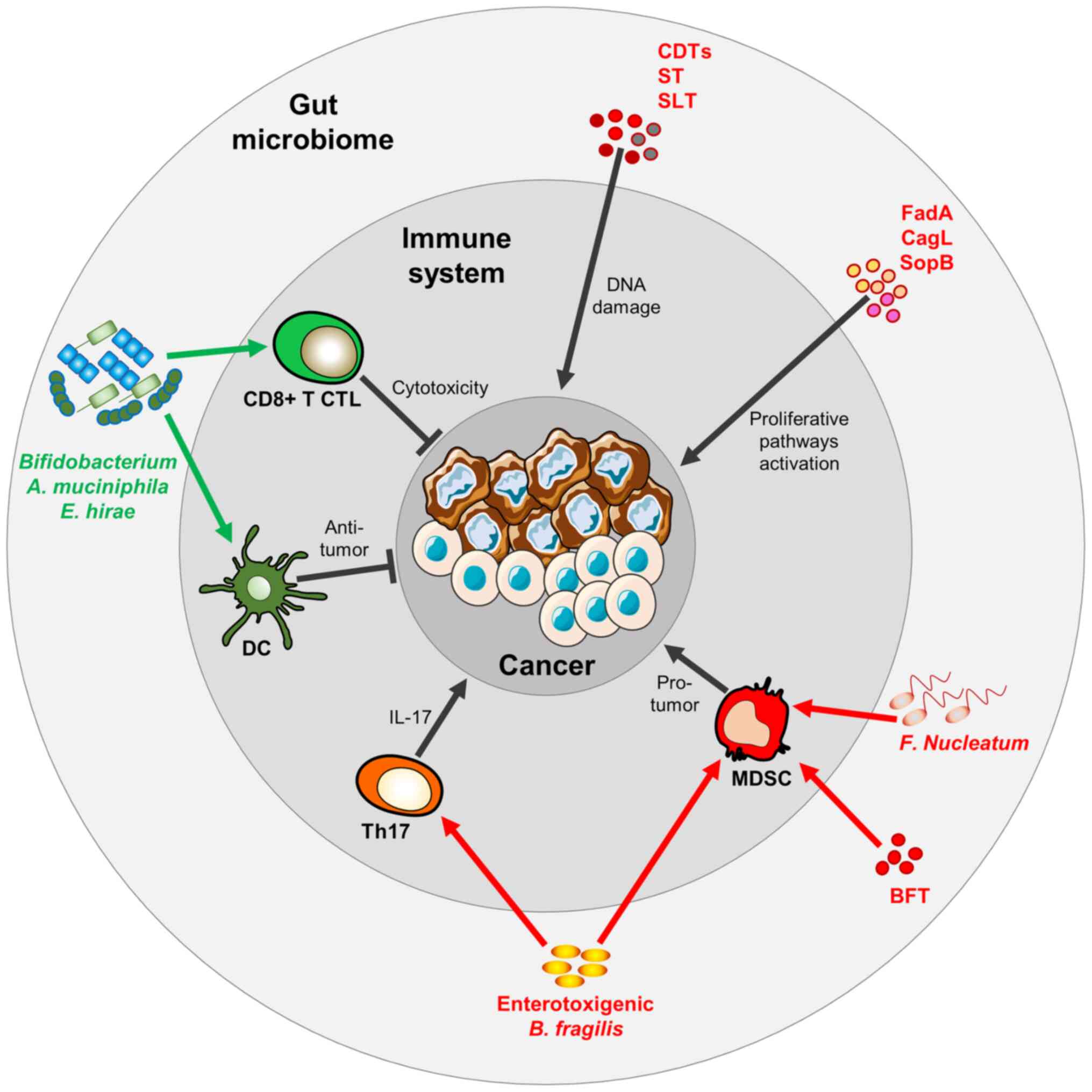
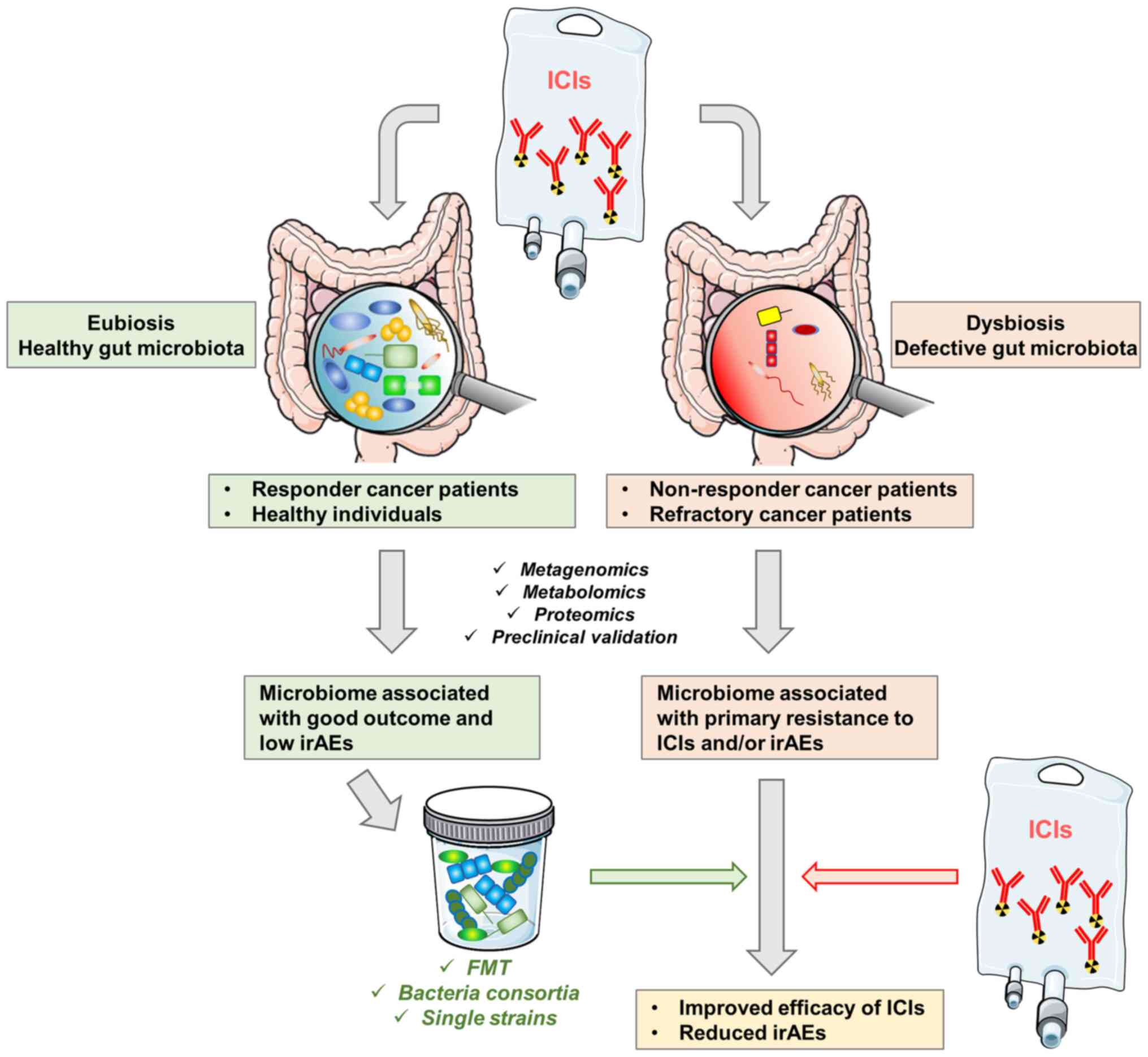
|
1
|
Leviatan S and Segal E: Identifying gut
microbes that affect human health. Nature. 587:373–374. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Greenhalgh K, Meyer KM, Aagaard KM and
Wilmes P: The human gut microbiome in health: Establishment and
resilience of microbiota over a lifetime. Environ Microbiol.
18:2103–2116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Feng Q, Chen WD and Wang YD: Gut
microbiota: An integral moderator in health and disease. Front
Microbiol. 9:1512018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vaishnava S, Behrendt CL, Ismail AS,
Eckmann L and Hooper LV: Paneth cells directly sense gut commensals
and maintain homeostasis at the intestinal host-microbial
interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:20858–20863. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Belkaid Y and Naik S: Compartmentalized
and systemic control of tissue immunity by commensals. Nat Immunol.
14:646–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Magnúsdóttir S, Ravcheev D, de
Crécy-Lagard V and Thiele I: Systematic genome assessment of
B-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes.
Front Genet. 6:1482015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zheng D, Liwinski T and Elinav E:
Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease.
Cell Res. 30:492–506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sharma VR, Singh M, Kumar V, Yadav M,
Sehrawat N, Sharma DK and Sharma AK: Microbiome dysbiosis in
cancer: Exploring therapeutic strategies to counter the disease.
Semin Cancer Biol. 70:61–70. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sepich-Poore GD, Zitvogel L, Straussman R,
Hasty J, Wargo JA and Knight R: The microbiome and human cancer.
Science. 371:eabc45522021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
The integrative human microbiome project.
Nature. 569:641–648. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E,
Kurilshikov A, Korem T, Zeevi D, Costea PI, Godneva A, Kalka IN,
Bar N, et al: Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping
human gut microbiota. Nature. 555:210–215. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Korem T, Zeevi D, Suez J, Weinberger A,
Avnit-Sagi T, Pompan-Lotan M, Matot E, Jona G, Harmelin A, Cohen N,
et al: Growth dynamics of gut microbiota in health and disease
inferred from single metagenomic samples. Science. 349:1101–1106.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Whon TW, Shin NR, Kim JY and Roh SW: Omics
in gut microbiome analysis. J Microbiol. 59:292–297. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Geva-Zatorsky N, Sefik E, Kua L, Pasman L,
Tan TG, Ortiz-Lopez A, Yanortsang TB, Yang L, Jupp R, Mathis D, et
al: Mining the human gut microbiota for immunomodulatory organisms.
Cell. 168:928–943.e11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Haber AL, Biton M, Rogel N, Herbst RH,
Shekhar K, Smillie C, Burgin G, Delorey TM, Howitt MR, Katz Y, et
al: A single-cell survey of the small intestinal epithelium.
Nature. 551:333–339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Almeida A, Nayfach S, Boland M, Strozzi F,
Beracochea M, Shi ZJ, Pollard KS, Sakharova E, Parks DH, Hugenholtz
P, et al: A unified catalog of 204,938 reference genomes from the
human gut microbiome. Nat Biotechnol. 39:105–114. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Sklar J, Jiang L,
Natarajan L, Knight R and Belkaid Y: Host variables confound gut
microbiota studies of human disease. Nature. 587:448–454. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Esfahani K, Roudaia L, Buhlaiga N, Del
Rincon SV, Papneja N and Miller WH Jr: A review of cancer
immunotherapy: From the past, to the present, to the future. Curr
Oncol. 27(Suppl 2): S87–S97. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Baghban R, Roshangar L, Jahanban-Esfahlan
R, Seidi K, Ebrahimi-Kalan A, Jaymand M, Kolahian S, Javaheri T and
Zare P: Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic
implications at a glance. Cell Commun Signal. 18:592020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Robert C: A decade of immune-checkpoint
inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 11:38012020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fridman WH, Zitvogel L, Sautès-Fridman C
and Kroemer G: The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and
treatment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:717–734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hiam-Galvez KJ, Allen BM and Spitzer MH:
Systemic immunity in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:345–359. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ledford H, Else H and Warren M: Cancer
immunologists scoop medicine nobel prize. Nature. 562:20–21. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shin EC: Cancer immunotherapy: Special
issue of BMB Reports in 2021. BMB Rep. 54:12021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Oncology meets
immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. 39:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huang PW and Chang JWC: Immune checkpoint
inhibitors win the 2018 nobel prize. Biomed J. 42:299–306. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Waldman AD, Fritz JM and Lenardo MJ: A
guide to cancer immunotherapy: From T cell basic science to
clinical practice. Nat Rev Immunol. 20:651–668. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shen CR and Chen YS: Immune checkpoint
blockade therapy: The 2014 tang prize in biopharmaceutical science.
Biomed J. 38:5–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Long J, Qi Z and Rongxin Z: PD-1/PD-L1
pathway blockade works as an effective and practical therapy for
cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Biol Med. 15:116–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Seidel JA, Otsuka A and Kabashima K:
Anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 therapies in cancer: Mechanisms of
action, efficacy, and limitations. Front Oncol. 8:862018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wei SC, Duffy CR and Allison JP:
Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Cancer Discov. 8:1069–1086. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Twomey JD and Zhang B: Cancer
immunotherapy update: FDA-approved checkpoint inhibitors and
companion diagnostics. AAPS J. 23:392021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xin Yu J, Hubbard-Lucey VM and Tang J:
Immuno-oncology drug development goes global. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
18:899–900. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, Tatiparti K,
Bhise K, Kashaw SK and Iyer AK: PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling
inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: Mechanism, combinations, and
clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 8:5612017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, Gogas
HJ, Arance AM, Cowey CL, Dalle S, Schenker M, Chiarion-Sileni V,
Marquez-Rodas I, et al: Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in
resected stage III or IV melanoma. N Engl J Med. 377:1824–1835.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Eggermont AMM, Blank CU, Mandala M, Long
GV, Atkinson V, Dalle S, Haydon A, Lichinitser M, Khattak A,
Carlino MS, et al: Adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in
resected stage III melanoma. N Engl J Med. 378:1789–1801. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kennedy LB and Salama AKS: A review of
cancer immunotherapy toxicity. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:86–104. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Barrueto L, Caminero F, Cash L, Makris C,
Lamichhane P and Deshmukh RR: Resistance to checkpoint inhibition
in cancer immunotherapy. Transl Oncol. 13:1007382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen PL, Roh W, Reuben A, Cooper ZA,
Spencer CN, Prieto PA, Miller JP, Bassett RL, Gopalakrishnan V,
Wani K, et al: Analysis of immune signatures in longitudinal tumor
samples yields insight into biomarkers of response and mechanisms
of resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Discov.
6:827–837. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Moslehi JJ, Salem JE, Sosman JA,
Lebrun-Vignes B and Johnson DB: Increased reporting of fatal immune
checkpoint inhibitor-associated myocarditis. Lancet. 391:9332018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Teixidor E and Bosch-Barrera J: The dark
side of immunotherapy: Challenges facing the new hope in cancer
treatment. Ann Transl Med. 7(Suppl 6): S1832019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Havel JJ, Chowell D and Chan TA: The
evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:133–150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pezo RC, Wong M and Martin A: Impact of
the gut microbiota on immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated
toxicities. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 12:17562848198709112019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chang AE, Golob JL, Schmidt TM, Peltier
DC, Lao CD and Tewari M: Targeting the gut microbiome to mitigate
immunotherapy-induced colitis in cancer. Trends Cancer. 7:583–593.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sarshar M, Scribano D, Ambrosi C, Palamara
AT and Masotti A: Fecal microRNAs as innovative biomarkers of
intestinal diseases and effective players in host-microbiome
interactions. Cancers (Basel). 12:21742020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Murciano-Goroff YR, Warner AB and Wolchok
JD: The future of cancer immunotherapy: Microenvironment-targeting
combinations. Cell Res. 30:507–519. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Vivarelli S, Salemi R, Candido S, Falzone
L, Santagati M, Stefani S, Torino F, Banna GL, Tonini G and Libra
M: Gut microbiota and cancer: From pathogenesis to therapy. Cancers
(Basel). 11:382019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Davar D, Dzutsev AK, McCulloch JA,
Rodrigues RR, Chauvin JM, Morrison RM, Deblasio RN, Menna C, Ding
Q, Pagliano O, et al: Fecal microbiota transplant overcomes
resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. Science.
371:595–602. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Baruch EN, Youngster I, Ben-Betzalel G,
Ortenberg R, Lahat A, Katz L, Adler K, Dick-Necula D, Raskin S,
Bloch N, et al: Fecal microbiota transplant promotes response in
immunotherapy-refractory melanoma patients. Science. 371:602–609.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Maynard CL, Elson CO, Hatton RD and Weaver
CT: Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune
system. Nature. 489:231–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Belkaid Y and Hand TW: Role of the
microbiota in immunity and Inflammation. Cell. 157:121–141. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Jain T, Sharma P, Are AC, Vickers SM and
Dudeja V: New insights into the cancer-microbiome-immune axis:
Decrypting a decade of discoveries. Front Immunol. 12:6220642021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Koenig JE, Spor A, Scalfone N, Fricker AD,
Stombaugh J, Knight R, Angenent LT and Ley RE: Succession of
microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108(Suppl 1): S4578–S4585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Gomez de Agüero M, Ganal-Vonarburg SC,
Fuhrer T, Rupp S, Uchimura Y, Li H, Steinert A, Heikenwalder M,
Hapfelmeier S, Sauer U, et al: The maternal microbiota drives early
postnatal innate immune development. Science. 351:1296–1302. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Russell SL, Gold MJ, Hartmann M, Willing
BP, Thorson L, Wlodarska M, Gill N, Blanchet MR, Mohn WW, McNagny
KM and Finlay BB: Early life antibiotic-driven changes in
microbiota enhance susceptibility to allergic asthma. EMBO Rep.
13:440–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cahenzli J, Köller Y, Wyss M, Geuking MB
and McCoy KD: Intestinal microbial diversity during early-life
colonization shapes long-term IgE levels. Cell Host Microbe.
14:559–570. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ge Y, Wang X, Guo Y, Yan J, Abuduwaili A,
Aximujiang K, Yan J and Wu M: Gut microbiota influence tumor
development and alter interactions with the human immune system. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:422021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Shi N, Li N, Duan X and Niu H: Interaction
between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil Med Res.
4:142017.
|
|
61
|
Lazar V, Ditu LM, Pircalabioru GG,
Gheorghe I, Curutiu C, Holban AM, Picu A, Petcu L and Chifiriuc MC:
Aspects of gut microbiota and immune system interactions in
infectious diseases, immunopathology, and cancer. Front Immunol.
9:18302018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Shan M, Gentile M, Yeiser JR, Walland AC,
Bornstein VU, Chen K, He B, Cassis L, Bigas A, Cols M, et al: Mucus
enhances gut homeostasis and oral tolerance by delivering
immunoregulatory signals. Science. 342:447–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Macpherson AJ and Uhr T: Induction of
protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal
bacteria. Science. 303:1662–1665. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Bevins CL and Salzman NH: Paneth cells,
antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 9:356–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chu H and Mazmanian SK: Innate immune
recognition of the microbiota promotes host-microbial symbiosis.
Nat Immunol. 14:668–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Vance RE, Isberg RR and Portnoy DA:
Patterns of pathogenesis: Discrimination of pathogenic and
nonpathogenic microbes by the innate immune system. Cell Host
Microbe. 6:10–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Mogensen TH: Pathogen recognition and
inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 22:240–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Suresh R and Mosser DM: Pattern
recognition receptors in innate immunity, host defense, and
immunopathology. Adv Physiol Educ. 37:284–291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Gaudet RG, Guo CX, Molinaro R, Kottwitz H,
Rohde JR, Dangeard AS, Arrieumerlou C, Girardin SE and Gray-Owen
SD: Innate recognition of intracellular bacterial growth is driven
by the TIFA-dependent cytosolic surveillance pathway. Cell Rep.
19:1418–1430. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Bai L, Li W, Zheng W, Xu D, Chen N and Cui
J: Promising targets based on pattern recognition receptors for
cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol Res. 159:1050172020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Luis Muñoz-Carrillo J, Francisco
Contreras-Cordero J, Gutiérrez-Coronado O, Trinidad
Villalobos-Gutiérrez P, Guillermo Ramos-Gracia L and Elizabeth
Hernández-Reyes V: Cytokine profiling plays a crucial role in
activating immune system to clear infectious pathogens. Immune
Response Activation and Immunomodulation. IntechOpen; 2019,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Kim M and Kim CH: Regulation of humoral
immunity by gut microbial products. Gut Microbes. 8:392–399. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Nagashima K, Sawa S, Nitta T, Tsutsumi M,
Okamura T, Penninger JM, Nakashima T and Takayanagi H:
Identification of subepithelial mesenchymal cells that induce IgA
and diversify gut microbiota. Nat Immunol. 18:675–682. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cong Y, Feng T, Fujihashi K, Schoeb TR and
Elson CO: A dominant, coordinated T regulatory cell-IgA response to
the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:19256–19261.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Tezuka H and Ohteki T: Regulation of IgA
production by intestinal dendritic cells and related cells. Front
Immunol. 10:18912019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wu HJ and Wu E: The role of gut microbiota
in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes. 3:4–14. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lee GR: The Balance of Th17 versus Treg
cells in autoimmunity. Int J Mol Sci. 19:7302018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO and
Kasper DL: An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria
directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell. 122:107–118.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Gaboriau-Routhiau V, Rakotobe S, Lécuyer
E, Mulder I, Lan A, Bridonneau C, Rochet V, Pisi A, De Paepe M,
Brandi G, et al: The key role of segmented filamentous bacteria in
the coordinated maturation of gut helper T cell responses.
Immunity. 31:677–689. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Valeri M and Raffatellu M: Cytokines IL-17
and IL-22 in the host response to infection. Pathog Dis.
74:ftw1112016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Liu R, Lauridsen HM, Amezquita RA, Pierce
RW, Jane-Wit D, Fang C, Pellowe AS, Kirkiles-Smith NC, Gonzalez AL
and Pober JS: IL-17 promotes neutrophil-mediated immunity by
activating microvascular pericytes and not endothelium. J Immunol.
197:2400–2408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Stary G, Olive A, Radovic-Moreno AF,
Gondek D, Alvarez D, Basto PA, Perro M, Vrbanac VD, Tager AM, Shi
J, et al: VACCINES. A mucosal vaccine against chlamydia trachomatis
generates two waves of protective memory T cells. Science.
348:aaa82052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Hirota K, Duarte JH, Veldhoen M, Hornsby
E, Li Y, Cua DJ, Ahlfors H, Wilhelm C, Tolaini M, Menzel U, et al:
Fate mapping of IL-17-producing T cells in inflammatory responses.
Nat Immunol. 12:255–263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Oh JZ, Ravindran R, Chassaing B, Carvalho
FA, Maddur MS, Bower M, Hakimpour P, Gill KP, Nakaya HI, Yarovinsky
F, et al: TLR5-mediated sensing of gut microbiota is necessary for
antibody responses to seasonal influenza vaccination. Immunity.
41:478–492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Sandrini S, Aldriwesh M, Alruways M and
Freestone P: Microbial endocrinology: Host-bacteria communication
within the gut microbiome. J Endocrinol. 225:R21–R34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Gensollen T, Iyer SS, Kasper DL and
Blumberg RS: How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes
the immune system. Science. 352:539–544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Schmidt TSB, Raes J and Bork P: The human
gut microbiome: From association to modulation. Cell.
172:1198–1215. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Bultman SJ: Emerging roles of the
microbiome in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 35:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Cani PD: Human gut microbiome: Hopes,
threats and promises. Gut. 67:1716–1725. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
LeBlanc JG, Chain F, Martín R,
Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Courau S and Langella P: Beneficial effects on
host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins
produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb Cell Fact.
16:792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Nakkarach A, Foo HL, Song AA, Mutalib NEA,
Nitisinprasert S and Withayagiat U: Anti-cancer and
anti-inflammatory effects elicited by short chain fatty acids
produced by Escherichia coli isolated from healthy human gut
microbiota. Microb Cell Fact. 20:362021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Clarke G, Stilling RM, Kennedy PJ, Stanton
C, Cryan JF and Dinan TG: Minireview: Gut microbiota: The neglected
endocrine organ. Mol Endocrinol. 28:1221–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Pabst O: New concepts in the generation
and functions of IgA. Nat Rev Immunol. 12:821–832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Mantis NJ, Rol N and Corthésy B: Secretory
IgA's complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut.
Mucosal Immunol. 4:603–611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Mathias A, Pais B, Favre L, Benyacoub J
and Corthésy B: Role of secretory IgA in the mucosal sensing of
commensal bacteria. Gut Microbes. 5:688–695. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA and
Elinav E: Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol.
17:219–232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Round JL and Mazmanian SK: Inducible
Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal
bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:12204–12209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Cianci R, Franza L, Schinzari G, Rossi E,
Ianiro G, Tortora G, Gasbarrini A, Gambassi G and Cammarota G: The
interplay between immunity and microbiota at intestinal
immunological niche: The case of cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:5012019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Shui L, Yang X, Li J, Yi C, Sun Q and Zhu
H: Gut microbiome as a potential factor for modulating resistance
to cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 10:29892020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Zipkin M: Fecal microbiota potentiate
checkpoint inhibitors, unleash microbiome startups. Nat Biotechnol.
39:529–532. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Niedzwiecki MM, Walker DI, Vermeulen R,
Chadeau-Hyam M, Jones DP and Miller GW: The exposome: Molecules to
populations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 59:107–127. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Arem H and Loftfield E: Cancer
epidemiology: A survey of modifiable risk factors for prevention
and survivorship. Am J Lifestyle Med. 12:200–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Biological agents. Volume 100 B. A
review of human carcinogens. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum.
100:1–441. 2012.
|
|
105
|
Wroblewski LE, Peek RM Jr and Wilson KT:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Factors that modulate
disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev. 23:713–739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Whisner CM and Athena Aktipis C: The role
of the microbiome in cancer initiation and progression: How
microbes and cancer cells utilize excess energy and promote one
another's growth. Curr Nutr Rep. 8:42–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Villéger R, Lopès A, Carrier G, Veziant J,
Billard E, Barnich N, Gagnière J, Vazeille E and Bonnet M:
Intestinal microbiota: A novel target to improve anti-tumor
treatment? Int J Mol Sci. 20:45842019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Li W, Deng X and Chen T: Exploring the
modulatory effects of gut microbiota in anti-cancer therapy. Front
Oncol. 11:6444542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Guerra L, Cortes-Bratti X, Guidi R and
Frisan T: The biology of the cytolethal distending toxins. Toxins
(Basel). 3:172–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Sun J, Hobert ME, Duan Y, Rao AS, He TC,
Chang EB and Madara JL: Crosstalk between NF-kappaB and
beta-catenin pathways in bacterial-colonized intestinal epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 289:G129–G137.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Liu X, Lu R, Wu S and Sun J: Salmonella
regulation of intestinal stem cells through the Wnt/beta-catenin
pathway. FEBS Lett. 584:911–916. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Scanu T, Spaapen RM, Bakker JM, Pratap CB,
Wu LE, Hofland I, Broeks A, Shukla VK, Kumar M, Janssen H, et al:
Salmonella manipulation of host signaling pathways provokes
cellular transformation associated with gallbladder carcinoma. Cell
Host Microbe. 17:763–774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Li Y, Tinoco R, Elmé L, Segota I, Xian Y,
Fujita Y, Sahu A, Zarecki R, Marie K, Feng Y, et al: Gut microbiota
dependent anti-tumor immunity restricts melanoma growth in
Rnf5−/− mice. Nat Commun. 10:14922019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Tanoue T, Morita S, Plichta DR, Skelly AN,
Suda W, Sugiura Y, Narushima S, Vlamakis H, Motoo I, Sugita K, et
al: A defined commensal consortium elicits CD8 T cells and
anti-cancer immunity. Nature. 565:600–605. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Valguarnera E and Wardenburg JB: Good gone
bad: One toxin away from disease for Bacteroides fragilis. J Mol
Biol. 432:765–785. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Thiele Orberg E, Fan H, Tam AJ, Dejea CM,
Destefano Shields CE, Wu S, Chung L, Finard BB, Wu X, Fathi P, et
al: The myeloid immune signature of enterotoxigenic Bacteroides
fragilis-induced murine colon tumorigenesis. Mucosal Immunol.
10:421–433. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Geis AL, Fan H, Wu X, Wu S, Huso DL, Wolfe
JL, Sears CL, Pardoll DM and Housseau F: Regulatory T-cell response
to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis colonization triggers
IL17-dependent colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Discov. 5:1098–1109.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Kostic AD, Chun E, Robertson L, Glickman
JN, Gallini CA, Michaud M, Clancy TE, Chung DC, Lochhead P, Hold
GL, et al: Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal
tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell
Host Microbe. 14:207–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Sivan A, Corrales L, Hubert N, Williams
JB, Aquino-Michaels K, Earley ZM, Benyamin FW, Lei YM, Jabri B,
Alegre ML, et al: Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor
immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science.
350:1084–1089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Routy B, Le Chatelier E, Derosa L, Duong
CPM, Alou MT, Daillère R, Fluckiger A, Messaoudene M, Rauber C,
Roberti MP, et al: Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based
immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science. 359:91–97. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Sharifi-Rad J, Rodrigues CF,
Stojanović-Radić Z, Dimitrijević M, Aleksić A, Neffe-Skocińska K,
Zielińska D, Kołożyn-Krajewska D, Salehi B, Milton Prabu S, et al:
Probiotics: Versatile bioactive components in promoting human
health. Medicina (Kaunas). 56:4332020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Banna GL, Torino F, Marletta F, Santagati
M, Salemi R, Cannarozzo E, Falzone L, Ferraù F and Libra M:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: An overview to explore the rationale of
its use in cancer. Front Pharmacol. 8:6032017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Vétizou M, Pitt JM, Daillère R, Lepage P,
Waldschmitt N, Flament C, Rusakiewicz S, Routy B, Roberti MP, Duong
CP, et al: Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on
the gut microbiota. Science. 350:1079–1084. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Dubin K, Callahan MK, Ren B, Khanin R,
Viale A, Ling L, No D, Gobourne A, Littmann E, Huttenhower C, et
al: Intestinal microbiome analyses identify melanoma patients at
risk for checkpoint-blockade-induced colitis. Nat Commun.
7:103912016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Frankel AE, Coughlin LA, Kim J, Froehlich
TW, Xie Y, Frenkel EP and Koh AY: Metagenomic shotgun sequencing
and unbiased metabolomic profiling identify specific human gut
microbiota and metabolites associated with immune checkpoint
therapy efficacy in melanoma patients. Neoplasia. 19:848–855. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Chaput N, Lepage P, Coutzac C, Soularue E,
Le Roux K, Monot C, Boselli L, Routier E, Cassard L, Collins M, et
al: Baseline gut microbiota predicts clinical response and colitis
in metastatic melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Ann Oncol.
28:1368–1379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Matson V, Fessler J, Bao R, Chongsuwat T,
Zha Y, Alegre ML, Luke JJ and Gajewski TF: The commensal microbiome
is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma
patients. Science. 359:104–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L,
Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, Prieto PA, Vicente D, Hoffman
K, Wei SC, et al: Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 359:97–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Derosa L, Hellmann MD, Spaziano M,
Halpenny D, Fidelle M, Rizvi H, Long N, Plodkowski AJ, Arbour KC,
Chaft JE, et al: Negative association of antibiotics on clinical
activity of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced
renal cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 29:1437–1444.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Jin Y, Dong H, Xia L, Yang Y, Zhu Y, Shen
Y, Zheng H, Yao C, Wang Y and Lu S: The diversity of gut microbiome
is associated with favorable responses to anti-programmed death 1
immunotherapy in chinese patients with NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
14:1378–1389. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Zheng Y, Wang T, Tu X, Huang Y, Zhang H,
Tan D, Jiang W, Cai S, Zhao P, Song R, et al: Gut microbiome
affects the response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 7:1932019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Salgia NJ, Bergerot PG, Maia MC, Dizman N,
Hsu J, Gillece JD, Folkerts M, Reining L, Trent J, Highlander SK
and Pal SK: Stool microbiome profiling of patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma receiving anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint
inhibitors. Eur Urol. 78:498–502. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Xu X, Lv J, Guo F, Li J, Jia Y, Jiang D,
Wang N, Zhang C, Kong L, Liu Y, et al: Gut Microbiome influences
the efficacy of PD-1 antibody immunotherapy on MSS-type colorectal
cancer via metabolic pathway. Front Microbiol. 11:8142020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Mager LF, Burkhard R, Pett N, Cooke NCA,
Brown K, Ramay H, Paik S, Stagg J, Groves RA, Gallo M, et al:
Microbiome-derived inosine modulates response to checkpoint
inhibitor immunotherapy. Science. 369:1481–1489. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Si W, Liang H, Bugno J, Xu Q, Ding X, Yang
K, Fu Y, Weichselbaum RR, Zhao X and Wang L: Lactobacillus
rhamnosus GG induces cGAS/STING-dependent type I interferon and
improves response to immune checkpoint blockade. Gut.
gutjnl-2020-323426. 2021.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Shi Y, Zheng W, Yang K, Harris KG, Ni K,
Xue L, Lin W, Chang EB, Weichselbaum RR and Fu YX: Intratumoral
accumulation of gut microbiota facilitates CD47-based immunotherapy
via STING signaling. J Exp Med. 217:e201922822020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Beer TM, Kwon ED, Drake CG, Fizazi K,
Logothetis C, Gravis G, Ganju V, Polikoff J, Saad F, Humanski P, et
al: Randomized, double-blind, phase III Trial of ipilimumab versus
placebo in asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic patients with
metastatic chemotherapy-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 35:40–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Berger MF, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F,
Drier Y, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko AY, Sboner A, Esgueva R, Pflueger
D, Sougnez C, et al: The genomic complexity of primary human
prostate cancer. Nature. 470:214–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Nicholson LT and Fong L: Immune checkpoint
inhibition in prostate cancer. Trends Cancer. 6:174–177. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Venkatachalam S, McFarland TR, Agarwal N
and Swami U: Immune checkpoint inhibitors in prostate cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 13. pp. 21872021, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Crocetto F, Boccellino M, Barone B, Di
Zazzo E, Sciarra A, Galasso G, Settembre G, Quagliuolo L, Imbimbo
C, Boffo S, et al: The crosstalk between prostate cancer and
microbiota inflammation: Nutraceutical products are useful to
balance this interplay? Nutrients. 12:26482020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Ferro M, Lucarelli G, Crocetto F, Dolce P,
Verde A, La Civita E, Zappavigna S, de Cobelli O, Di Lorenzo G,
Facchini BA, et al: First-line systemic therapy for metastatic
castration-sensitive prostate cancer: An updated systematic review
with novel findings. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 157:1031982021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Barbosa AM, Gomes-Gonçalves A, Castro AG
and Torrado E: Immune system efficiency in cancer and the
microbiota influence. Pathobiology. 88:170–186. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Chen D, Wu J, Jin D, Wang B and Cao H:
Fecal microbiota transplantation in cancer management: Current
status and perspectives. Int J Cancer. 145:2021–2031. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Thompson S, Guetterman H, Taylor A, Bogner
A, Martin D, Farrell JJ, Swanson KS and Holscher H: Dietary
predictors of fecal microbiota transplantation success. J Acad Nutr
Diet. 116(Suppl 9): A762016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Diefenbach CS, Hong F, Ambinder RF, Cohen
JB, Robertson MJ, David KA, Advani RH, Fenske TS, Barta SK,
Palmisiano ND, et al: Ipilimumab, nivolumab, and brentuximab
vedotin combination therapies in patients with relapsed or
refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Phase 1 results of an open-label,
multicentre, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 7:e660–e670. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Bensch F, van der Veen EL, Lub-de Hooge
MN, Jorritsma-Smit A, Boellaard R, Kok IC, Oosting SF, Schröder CP,
Hiltermann TJN, van der Wekken AJ, et al:
89Zr-atezolizumab imaging as a non-invasive approach to
assess clinical response to PD-L1 blockade in cancer. Nat Med.
24:1852–1858. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Kyte JA, Røssevold A, Falk RS and Naume B:
ALICE: A randomized placebo-controlled phase II study evaluating
atezolizumab combined with immunogenic chemotherapy in patients
with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. J Transl Med.
18:2522020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Cohen R, Pudlarz T, Garcia-Larnicol ML,
Vernerey D, Dray X, Clavel L, Jary M, Piessen G, Zaanan A, Aparicio
T, et al: Localized MSI/dMMR gastric cancer patients, perioperative
immunotherapy instead of chemotherapy: The GERCOR NEONIPIGA phase
II study is opened to recruitment. Bull Cancer. 107:438–446.
2020.In French. View Article : Google Scholar
|