|
1
|
Rascon-Cruz Q, Espinoza-Sanchez EA,
Siqueiros-Cendon TS, Nakamura-Bencomo SI, Arévalo-Gallegos S and
Iglesias-Figueroa BF: Lactoferrin: A glycoprotein involved in
immunomodulation, anticancer, and antimicrobial processes.
Molecules. 26:2052021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Baker EN, Baker HM and Kidd RD:
Lactoferrin and transferrin: Functional variations on a common
structural framework. Biochem Cell Biol. 80:27–34. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lambert LA, Perri H and Meehan TJ:
Evolution of duplications in the transferrin family of proteins.
Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 140:11–25. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pierce A, Legrand D and Mazurier J:
Lactoferrin: A multifunctional protein. Med Sci (Paris).
25:361–369. 2009.In French. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hao L, Shan Q, Wei J, Ma F and Sun P:
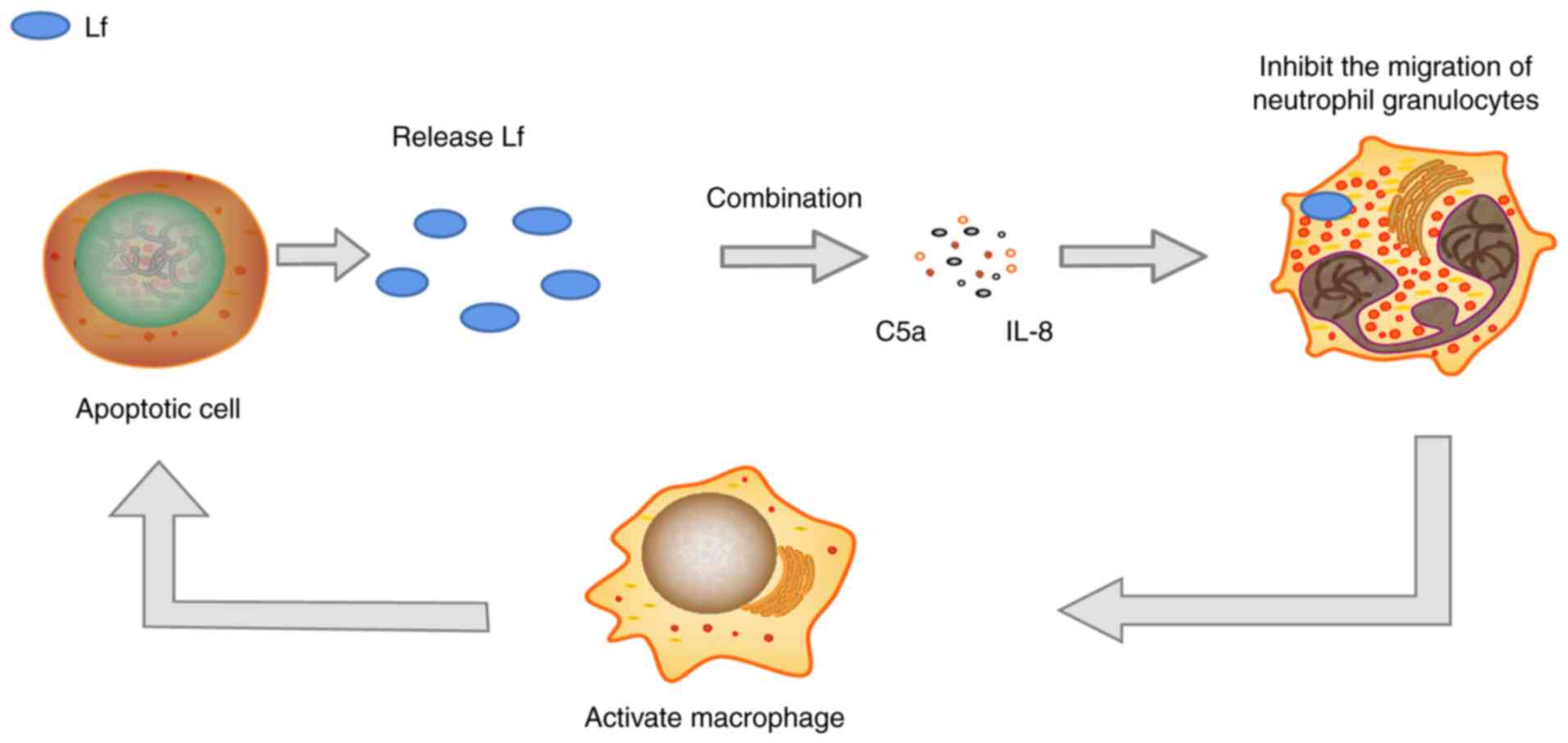
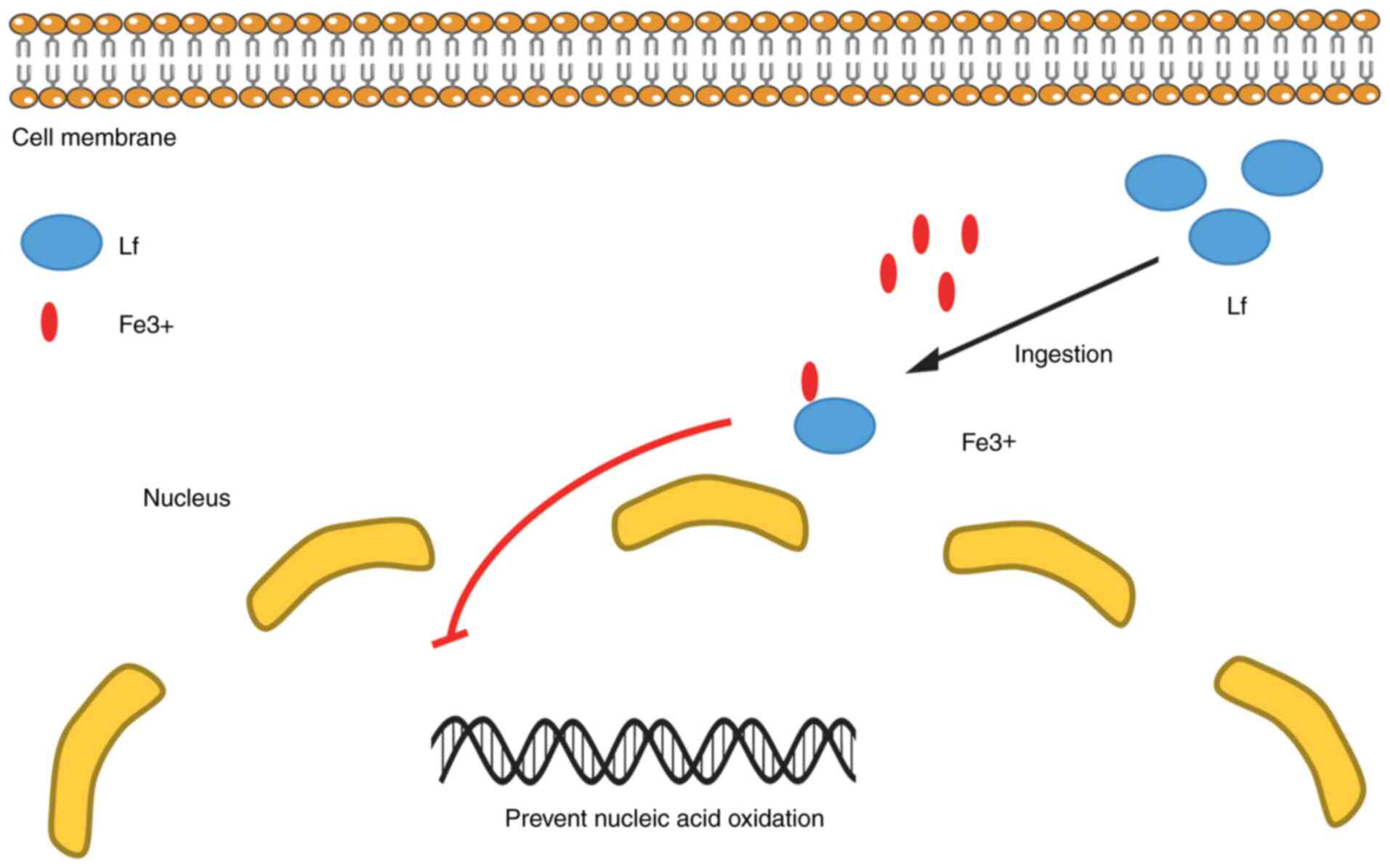
Lactoferrin: Major physiological functions and applications. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 20:139–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Garcia-Montoya IA, Cendon TS,
Arevalo-Gallegos S and Rascon-Cruz Q: Lactoferrin a multiple
bioactive protein: An overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:226–236.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Legrand D, Pierce A, Elass E, Carpentier
M, Mariller C and Mazurier J: Lactoferrin structure and functions.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 606:163–194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yanaihara A, Toma Y, Saito H and Yanaihara
T: Cell proliferation effect of lactoferrin in human endometrial
stroma cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 6:469–473. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang N, Bethell D, Card C, Cornish J,
Marchbank T, Wyatt D, Mabery K and Playford R: Bioactive
recombinant human lactoferrin, derived from rice, stimulates
mammalian cell growth. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 44:464–471.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Siebert PD and Huang BC: Identification of
an alternative form of human lactoferrin mRNA that is expressed
differentially in normal tissues and tumor-derived cell lines. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:2198–2203. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
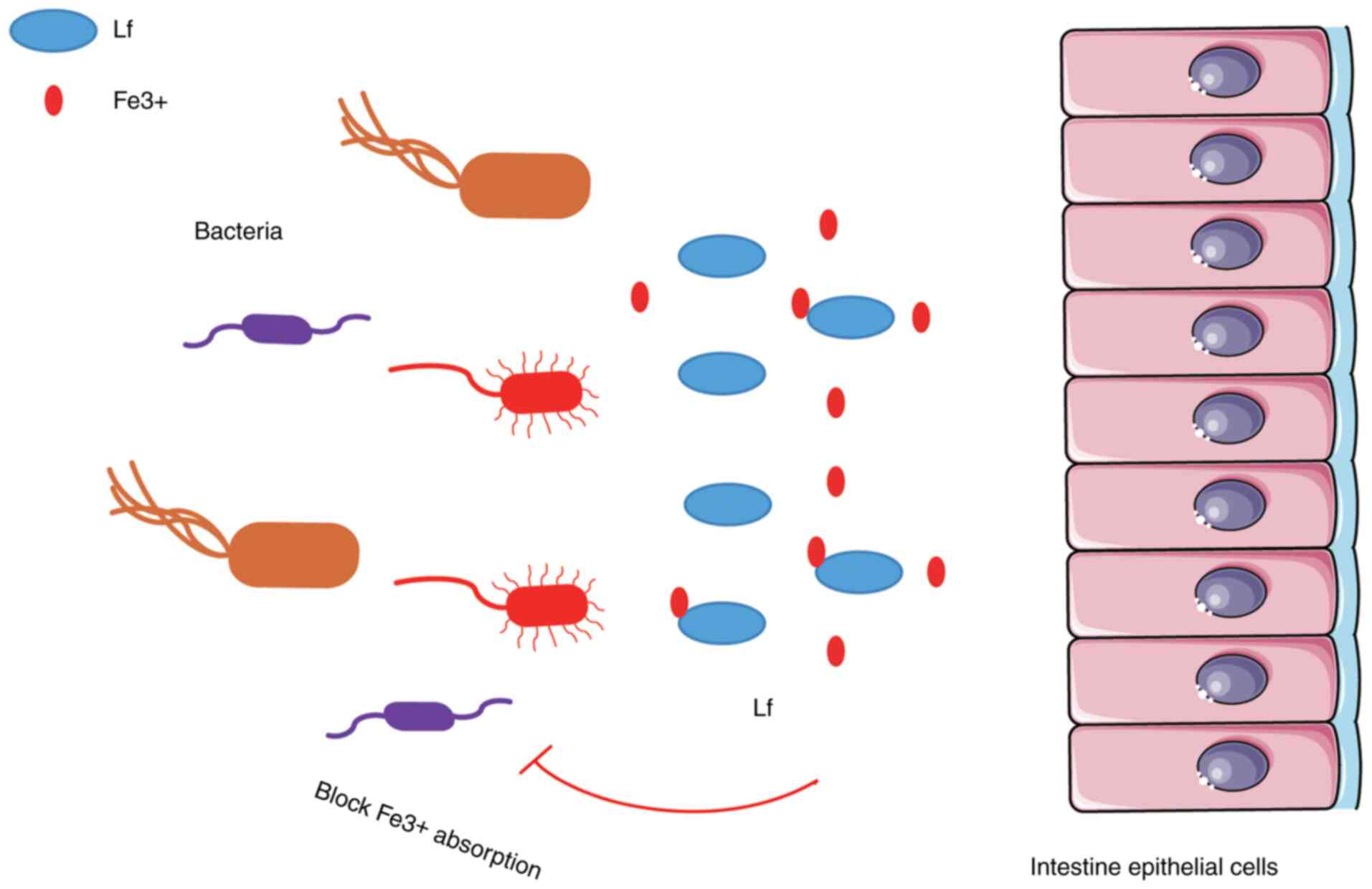
|
Klein G, Imreh S and Zabarovsky ER: Why do
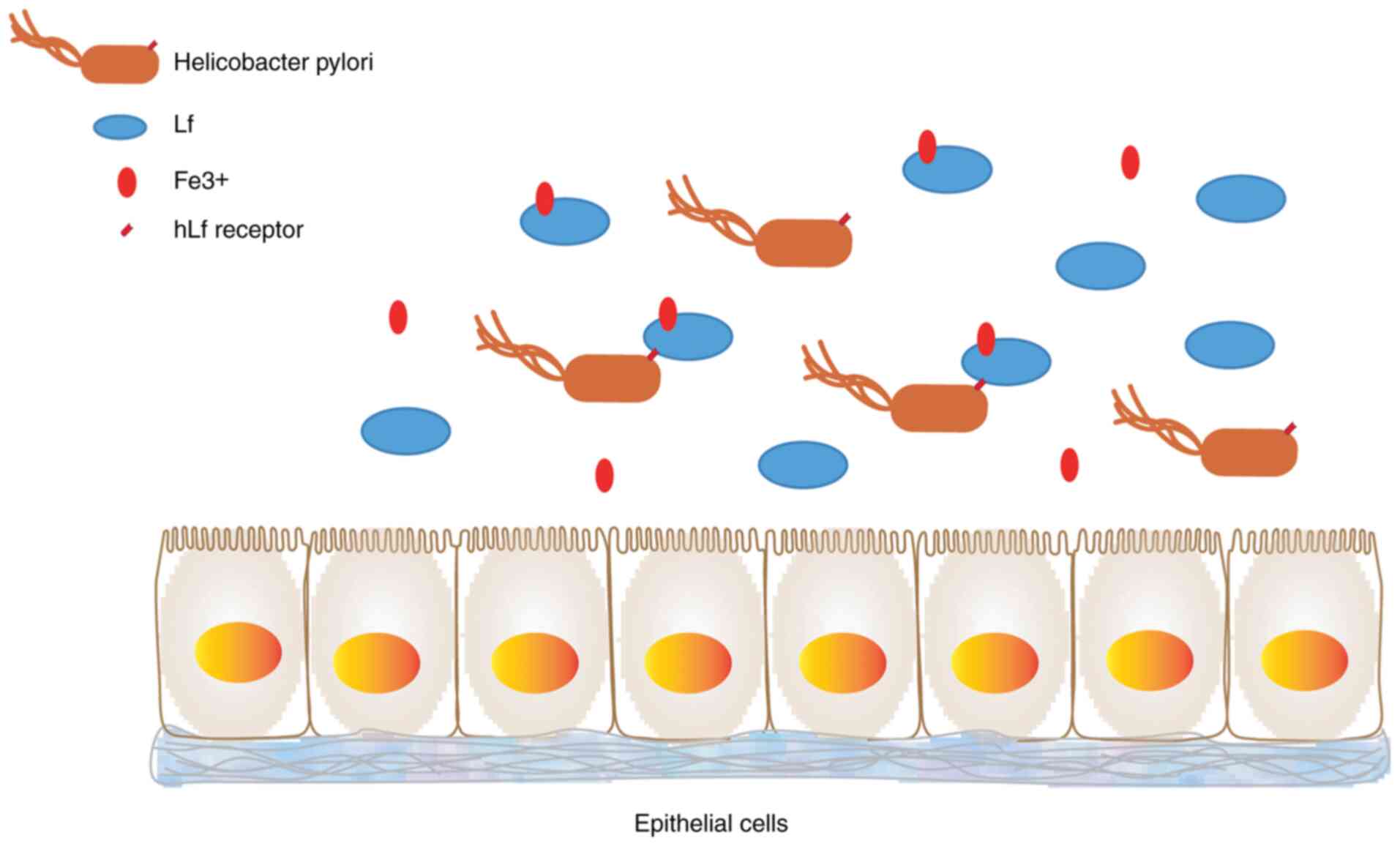
we not all die of cancer at an early age? Adv Cancer Res. 98:1–16.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mariller C, Hardiville S, Hoedt E, Huvent
I, Pina-Canseco S and Pierce A: Delta-lactoferrin, an intracellular
lactoferrin isoform that acts as a transcription factor. Biochem
Cell Biol. 90:307–319. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tsuda H, Ohshima Y, Nomoto H, Fujita K,
Matsuda E, Iigo M, Takasuka N and Moore MA: Cancer prevention by
natural compounds. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 19:245–263. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guedes JP, Pereira CS, Rodrigues LR and
Corte-Real M: Bovine milk lactoferrin selectively kills highly
metastatic prostate cancer PC-3 and osteosarcoma MG-63 cells in
vitro. Front Oncol. 8:2002018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gonzalez-Chavez SA, Arevalo-Gallegos S and
Rascon-Cruz Q: Lactoferrin: Structure, function and applications.
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 33:301.e1–e8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Actor JK, Hwang SA and Kruzel ML:
Lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. Curr Pharm Des.
15:1956–1973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Appelmelk BJ, An YQ, Geerts M, Thijs BG,
de Boer HA, MacLaren DM, de Graaff J and Nuijens JH: Lactoferrin is
a lipid A-binding protein. Infect Immun. 62:2628–2632. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Elass-Rochard E, Roseanu A, Legrand D,
Trif M, Salmon V, Motas C, Montreuil J and Spik G:
Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide interaction: Involvement of the
28-34 loop region of human lactoferrin in the high-affinity binding
to Escherichia coli 055B5 lipopolysaccharide. Biochem J.
312:839–845. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hu P, Zhao F, Wang J and Zhu W:
Lactoferrin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory
responses and barrier impairment through the modulation of
NF-kappaB/MAPK/Nrf2 pathways in IPEC-J2 cells. Food Funct.
11:8516–8526. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Baker HM and Baker EN: A structural
perspective on lactoferrin function. Biochem Cell Biol. 90:320–328.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cools-Lartigue J, Spicer J, McDonald B,
Gowing S, Chow S, Giannias B, Bourdeau F, Kubes P and Ferri L:
Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells
and promote metastasis. J Clin Invest. 123:3446–3458. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
van der Does AM, Hensbergen PJ, Bogaards
SJ, Cansoy M, Deelder AM, van Leeuwen HC, Drijfhout JW, van Dissel
JT and Nibbering PH: The human lactoferrin-derived peptide hLF1-11
exerts immunomodulatory effects by specific inhibition of
myeloperoxidase activity. J Immunol. 188:5012–5019. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Park HW, Park SH, Jo HJ, Kim TG, Lee JH,
Kang SG, Jang YS and Kim PH: Lactoferrin induces tolerogenic bone
marrow-derived dendritic cells. Immune Netw. 20:e382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eipper S, Steiner R, Lesner A, Sienczyk M,
Palesch D, Halatsch ME, Zaczynska E, Heim C, Hartmann MD, Zimecki
M, et al: Lactoferrin is an allosteric enhancer of the proteolytic
activity of cathepsin G. PLoS One. 11:e1515092016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Penco S, Scarfi S, Giovine M, Damonte G,
Millo E, Villaggio B, Passalacqua M, Pozzolini M, Garrè C and
Benatti U: Identification of an import signal for, and the nuclear
localization of, human lactoferrin. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
34:151–159. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vogel HJ: Lactoferrin, a bird's eye view.
Biochem Cell Biol. 90:233–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Takayama Y and Aoki R: Roles of
lactoferrin on skin wound healing. Biochem Cell Biol. 90:497–503.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kabanov AV and Batrakova EV: New
technologies for drug delivery across the blood brain barrier. Curr
Pharm Des. 10:1355–1363. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Elzoghby AO, Abdelmoneem MA, Hassanin IA,
Abd Elwakil MM, Elnaggar MA, Mokhtar S, Fang JY and Elkhodairy KA:
Lactoferrin, a multi-functional glycoprotein: Active therapeutic,
drug nanocarrier & targeting ligand. Biomaterials.
263:1203552020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Thangavel P, Ramachandran B, Chakraborty
S, Kannan R, Lonchin S and Muthuvijayan V: Accelerated healing of
diabetic wounds treated with L-Glutamic acid loaded hydrogels
through enhanced collagen deposition and angiogenesis: An in vivo
study. Sci Rep. 7:107012017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Iigo M, Alexander DB, Long N, Xu J,
Fukamachi K, Futakuchi M, Takase M and Tsuda H: Anticarcinogenesis
pathways activated by bovine lactoferrin in the murine small
intestine. Biochimie. 91:86–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu XX, Jiang HR, Li HB, Zhang TN, Zhou Q
and Liu N: Apoptosis of stomach cancer cell SGC-7901 and regulation
of Akt signaling way induced by bovine lactoferrin. J Dairy Sci.
93:2344–2350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wong SH, Francis N, Chahal H, Raza K,
Salmon M, Scheel-Toellner D and Lord JM: Lactoferrin is a survival
factor for neutrophils in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 48:39–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kruzel ML, Zimecki M and Actor JK:
Lactoferrin in a context of inflammation-induced pathology. Front
Immunol. 8:14382017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bournazou I, Pound JD, Duffin R, Bournazos
S, Melville LA, Brown SB, Rossi AG and Gregory CD: Apoptotic human
cells inhibit migration of granulocytes via release of lactoferrin.
J Clin Invest. 119:20–32. 2009.
|
|
36
|
Bezault J, Bhimani R, Wiprovnick J and
Furmanski P: Human lactoferrin inhibits growth of solid tumors and
development of experimental metastases in mice. Cancer Res.
54:2310–2312. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Damiens E, Mazurier J, el Yazidi I, Masson
M, Duthille I, Spik G and Boilly-Marer Y: Effects of human
lactoferrin on NK cell cytotoxicity against haematopoietic and
epithelial tumour cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1402:277–287. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shi H and Li W: Inhibitory effects of
human lactoferrin on U14 cervical carcinoma through upregulation of
the immune response. Oncol Lett. 7:820–826. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Iyer S, Yip TT, Hutchens TW and Lonnerdal
B: Lactoferrin-receptor interaction. Effect of surface exposed
histidine residues. Adv Exp Med Biol. 357:245–252. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rastogi N, Singh A, Pandey SN, Sinha M,
Bhushan A, Kaur P, Sharma S and Singh TP: Structure of the
iron-free true C-terminal half of bovine lactoferrin produced by
tryptic digestion and its functional significance in the gut. FEBS
J. 281:2871–2882. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Teng CT: Factors regulating lactoferrin
gene expression. Biochem Cell Biol. 84:263–267. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ieni A, Barresi V, Licata L, Cardia R,
Fazzari C, Nuciforo G, Caruso F, Caruso M, Adamo V and Tuccari G:
Immunoexpression of lactoferrin in triple-negative breast cancer
patients: A proposal to select a less aggressive subgroup. Oncol
Lett. 13:3205–3209. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tsuda H, Kozu T, Iinuma G, Ohashi Y, Saito
Y, Saito D, Akasu T, Alexander DB, Futakuchi M, Fukamachi K, et al:
Cancer prevention by bovine lactoferrin: From animal studies to
human trial. Biometals. 23:399–409. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gibbons JA, Kanwar RK and Kanwar JR:
Lactoferrin and cancer in different cancer models. Front Biosci
(Schol Ed). 3:1080–1088. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Digumarti R, Wang Y, Raman G, Doval DC,
Advani SH, Julka PK, Parikh PM, Patil S, Nag S, Madhavan J, et al:
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study of
oral talactoferrin in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel
in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1098–1103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hoedt E, Hardiville S, Mariller C, Elass
E, Perraudin JP and Pierce A: Discrimination and evaluation of
lactoferrin and delta-lactoferrin gene expression levels in cancer
cells and under inflammatory stimuli using TaqMan real-time PCR.
Biometals. 23:441–452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zadvornyi TV, Lukianova NY, Borikun TV and
Chekhun VF: Effects of exogenous lactoferrin on phenotypic profile
and invasiveness of human prostate cancer cells (DU145 and LNCaP)
in vitro. Exp Oncol. 40:184–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cutone A, Ianiro G, Lepanto MS, Rosa L,
Valenti P, Bonaccorsi di Patti MC and Musci G: Lactoferrin in the
prevention and treatment of intestinal inflammatory pathologies
associated with colorectal cancer development. Cancers (Basel).
12:38062020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Duchardt F, Ruttekolk IR, Verdurmen WP,
Lortat-Jacob H, Bürck J, Hufnagel H, Fischer R, van den Heuvel M,
Löwik DW, Vuister GW, et al: A cell-penetrating peptide derived
from human lactoferrin with conformation-dependent uptake
efficiency. J biol Chem. 284:36099–36108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Riedl S, Leber R, Rinner B, Schaider H,
Lohner K and Zweytick D: Human lactoferricin derived di-peptides
deploying loop structures induce apoptosis specifically in cancer
cells through targeting membranous phosphatidylserine. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1848:2918–2931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kühnle A, Veelken R, Galuska CE,
Saftenberger M, Verleih M, Schuppe HC, Rudloff S, Kunz C and
Galuska SP: Polysialic acid interacts with lactoferrin and supports
its activity to inhibit the release of neutrophil extracellular
traps. Carbohydr Polym. 208:32–41. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
El YI, Legrand D, Nuijens J, Slomianny MC,
van Berkel P and Spik G: The binding of lactoferrin to
glycosaminoglycans on enterocyte-like HT29-18-C1 cells is mediated
through basic residues located in the N-terminus. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1568:197–204. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Jiang R and Lönnerdal B: Bovine
lactoferrin and lactoferricin exert antitumor activities on human
colorectal cancer cells (HT-29) by activating various signaling
pathways. Biochem Cell Biol. 95:99–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sharma A, Shandilya UK, Sodhi M, Mohanty
AK, Jain P and Mukesh M: Evaluation of milk colostrum derived
lactoferrin of sahiwal (Bos indicus) and karan fries (Cross-Bred)
cows for its anti-cancerous potential. Int J Mol Sci. 20:63182019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Arias M, Hilchie AL, Haney EF, Bolscher
JG, Hyndman ME, Hancock RE and Vogel HJ: Anticancer activities of
bovine and human lactoferricin-derived peptides. Biochem Cell Biol.
95:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Wu M,
Tan Y, Yi W, Xiao L, Li X, Huang C, et al: Lactotransferrin: A
candidate tumor suppressor-Deficient expression in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibition of NPC cell proliferation
by modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. INT J
Cancer. 123:2065–2072. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Onishi J, Roy MK, Juneja LR, Watanabe Y
and Tamai Y: A lactoferrin-derived peptide with cationic residues
concentrated in a region of its helical structure induces necrotic
cell death in a leukemic cell line (HL-60). J Pept Sci.
14:1032–1038. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lee SH, Park SW, Pyo CW, Yoo NK, Kim J and
Choi SY: Requirement of the JNK-associated Bcl-2 pathway for human
lactoferrin-induced apoptosis in the Jurkat leukemia T cell line.
Biochimie. 91:102–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fujita K, Matsuda E, Sekine K, Iigo M and
Tsuda H: Lactoferrin enhances Fas expression and apoptosis in the
colon mucosa of Azoxymethane-treated rats. Carcinogenesis.
25:1961–1966. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gopal SH and Das SK: Role of lactoferrin
in the carcinogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. J Cancer
Clin Trials. 1:e1052016.
|
|
61
|
Velliyagounder K, Bahdila D, Pawar S and
Fine DH: Role of lactoferrin and lactoferrin-derived peptides in
oral and maxillofacial diseases. Oral Dis. 25:652–669. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Damiens E, El YI, Mazurier J, Duthille I,
Spik G and Boilly-Marer Y: Lactoferrin inhibits G1 cyclin-dependent
kinases during growth arrest of human breast carcinoma cells. J
Cell Biochem. 74:486–498. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ibrahim HM, Mohamed AH, Salem ML, Osman GY
and Morsi DS: Anti-neoplastic and immunomodulatory potency of
co-treatment based on bovine lactoferrin and/or muramyl dipeptide
in tumor-bearing mice. Toxicol Res (Camb). 9:137–147. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Sangermano R, Pernarella S, Straker M,
Lepanto MS, Rosa L, Cutone A, Valenti P and Ottolenghi L: The
treatment of black stain associated with of iron metabolism
disorders with lactoferrin: A litterature search and two case
studies. Clin Ter. 170:e373–e381. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li HY, Li M, Luo CC, Wang JQ and Zheng N:
Lactoferrin exerts antitumor effects by inhibiting angiogenesis in
a HT29 human colon tumor model. J Agric Food Chem. 65:10464–10472.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tammam SN, Azzazy H and Lamprecht A:
Nuclear and cytoplasmic delivery of lactoferrin in glioma using
chitosan nanoparticles: Cellular location dependent-action of
lactoferrin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 129:74–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Golla K, Bhaskar C, Ahmed F and Kondapi
AK: A target-specific oral formulation of Doxorubicin-protein
nanoparticles: Efficacy and safety in hepatocellular cancer. J
Cancer. 4:644–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sabra S and Agwa MM: Lactoferrin, a unique
molecule with diverse therapeutical and nanotechnological
applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 164:1046–1060. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Song MM, Xu HL, Liang JX, Xiang HH, Liu R
and Shen YX: Lactoferrin modified graphene oxide iron oxide
nanocomposite for glioma-targeted drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C
Mater Biol Appl. 77:904–911. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Tomitaka A, Arami H, Gandhi S and Krishnan
KM: Lactoferrin conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting
brain glioma cells in magnetic particle imaging. Nanoscale.
7:16890–16898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhang M, Asghar S, Tian C, Hu Z, Ping Q,
Chen Z, Shao F and Xiao Y: Lactoferrin/phenylboronic
acid-functionalized hyaluronic acid nanogels loading doxorubicin
hydrochloride for targeting glioma. Carbohydr Polym.
253:1171942021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Yin Y, Fu C, Li M, Li X, Wang M, He L,
Zhang LM and Peng Y: A pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid prodrug
modified with lactoferrin for glioma dual-targeted treatment. Mater
Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 67:159–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Guan Q: A comprehensive review and update
on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol Res.
2019:72472382019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Frioni A, Conte MP, Cutone A, Longhi C,
Musci G, di Patti MC, Natalizi T, Marazzato M, Lepanto MS, Puddu P,
et al: Lactoferrin differently modulates the inflammatory response
in epithelial models mimicking human inflammatory and infectious
diseases. Biometals. 27:843–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Sessa R, Di Pietro M, Filardo S, Bressan
A, Rosa L, Cutone A, Frioni A, Berlutti F, Paesano R and Valenti P:
Effect of bovine lactoferrin on chlamydia trachomatis infection and
inflammation. Biochem Cell Biol. 95:34–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Valenti P, Frioni A, Rossi A, Ranucci S,
De Fino I, Cutone A, Rosa L, Bragonzi A and Berlutti F: Aerosolized
bovine lactoferrin reduces neutrophils and pro-inflammatory
cytokines in mouse models of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung
infections. Biochem Cell Biol. 95:41–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Svendsen J, Grant TM, Rennison D, Brimble
MA and Svenson J: Very short and stable lactoferricin-derived
antimicrobial peptides: Design principles and potential uses. Acc
Chem Res. 52:749–759. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Dial EJ, Romero JJ, Headon DR and
Lichtenberger LM: Recombinant human lactoferrin is effective in the
treatment of Helicobacter Felis-infected mice. J Pharm Pharmacol.
52:1541–1546. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Rodríguez-Franco DA, Vázquez-Moreno L and
Ramos-Clamont MG: Antimicrobial mechanisms and potential clinical
application of lactoferrin. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 47:102–111.
2005.In Spanish.
|
|
80
|
Ellison RR and Giehl TJ: Killing of
gram-negative bacteria by lactoferrin and lysozyme. J Clin Invest.
88:1080–1091. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Dhaenens L, Szczebara F and Husson MO:
Identification, characterization, and immunogenicity of the
lactoferrin-binding protein from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun.
65:514–518. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Kuipers ME, de Vries HG, Eikelboom MC,
Meijer DK and Swart PJ: Synergistic fungistatic effects of
lactoferrin in combination with antifungal drugs against clinical
Candida isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 43:2635–2641. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Hakansson A, Roche H, Mirza S, McDaniel
LS, Brooks-Walter A and Briles DE: Characterization of binding of
human lactoferrin to pneumococcal surface protein A. Infect Immun.
69:3372–3381. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
van der Strate BW, Beljaars L, Molema G,
Harmsen MC and Meijer DK: Antiviral activities of lactoferrin.
Antiviral Res. 52:225–239. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Campione E, Cosio T, Rosa L, Lanna C, Di
Girolamo S, Gaziano R, Valenti P and Bianchi L: Lactoferrin as
protective natural barrier of respiratory and intestinal mucosa
against coronavirus infection and inflammation. Int J Mol Sci.
21:49032020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Kell DB, Heyden EL and Pretorius E: The
biology of lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein that can help
defend against viruses and bacteria. Front Immunol. 11:12212020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Fu Q, Sun J, Zhang W, Sui X, Yan Z and He
Z: Nanoparticle albumin-bound (NAB) technology is a promising
method for anti-cancer drug delivery. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug
Discov. 4:262–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Yi M, Kaneko S, Yu DY and Murakami S:
Hepatitis C virus envelope proteins bind lactoferrin. J Virol.
71:5997–6002. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Bennett RM, Merritt MM and Gabor G:
Lactoferrin binds to neutrophilic membrane DNA. Br J Haematol.
63:105–117. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
He J and Furmanski P: Sequence specificity
and transcriptional activation in the binding of lactoferrin to
DNA. Nature. 373:721–724. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Brandl N, Zemann A, Kaupe I, Marlovits S,
Huettinger P, Goldenberg H and Huettinger M: Signal transduction
and metabolism in chondrocytes is modulated by lactoferrin.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:117–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Kanyshkova TG, Babina SE, Semenov DV,
Isaeva N, Vlassov AV, Neustroev KN, Kul'minskaya AA, Buneva VN and
Nevinsky GA: Multiple enzymic activities of human milk lactoferrin.
Eur J Biochem. 270:3353–3361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Fang JH, Lai YH, Chiu TL, Chen YY, Hu SH
and Chen SY: Magnetic core-shell nanocapsules with dual-targeting
capabilities and co-delivery of multiple drugs to treat brain
gliomas. Adv Healthc Mater. 3:1250–1260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wei M, Guo X, Tu L, Zou Q, Li Q, Tang C,
Chen B, Xu Y and Wu C: Lactoferrin-modified PEGylated liposomes
loaded with doxorubicin for targeting delivery to hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:5123–5137. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Golla K, Cherukuvada B, Ahmed F and
Kondapi AK: Efficacy, safety and anticancer activity of protein
nanoparticle-based delivery of doxorubicin through intravenous
administration in rats. PLoS One. 7:e519602012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Kumar P, Lakshmi YS, C B, Golla K and
Kondapi AK: Improved safety, bioavailability and pharmacokinetics
of zidovudine through lactoferrin nanoparticles during oral
administration in rats. PLoS One. 10:e1403992015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Kumari S and Kondapi AK: Receptor-mediated
targeted delivery of DNA using Lactoferrin nanoparticles. Int J
Biol Macromol. 108:401–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Elfinger M, Maucksch C and Rudolph C:
Characterization of lactoferrin as a targeting ligand for nonviral
gene delivery to airway epithelial cells. Biomaterials.
28:3448–3455. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Yan JK, Qiu WY, Wang YY and Wu JY:
Biocompatible polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles from
lactoferrin and pectin as potential vehicles for antioxidative
curcumin. J Agric Food Chem. 65:5720–5730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Wang J, Li Q, Li K, Ou Y, Han Z, Gao D and
Li J: Effects of adenovirus vectors mediated human lactoferrin cDNA
on mice bearing EMT6 breast carcinoma. Pharmazie. 66:704–709.
2011.
|
|
101
|
Pereira CS, Guedes JP, Goncalves M,
Loureiro L, Castro L, Gerós H, Rodrigues LR and Côrte-Real M:
Lactoferrin selectively triggers apoptosis in highly metastatic
breast cancer cells through inhibition of plasmalemmal V-H+-ATPase.
Oncotarget. 7:62144–62158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Lonnerdal B, Jiang R and Du X: Bovine
lactoferrin can be taken up by the human intestinal lactoferrin
receptor and exert bioactivities. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
53:606–614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Machado S, Alves R, Lima M, Leal I and
Massa A: Cutaneous necrobiotic xanthogranuloma (NXG)-successfully
treated with low dose chlorambucil. Eur J Dermatol. 11:458–462.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Arcella A, Oliva MA, Staffieri S, Aalberti
S, Grillea G, Madonna M, Bartolo M, Pavone L, Giangaspero F,
Cantore G and Frati A: In vitro and in vivo effect of human
lactoferrin on glioblastoma growth. J Neurosurg. 123:1026–1035.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Son HJ, Lee SH and Choi SY: Human
lactoferrin controls the level of retinoblastoma protein and its
activity. Biochem Cell Biol. 84:345–350. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Tung YT, Chen HL, Yen CC, Lee PY, Tsai HC,
Lin MF and Chen CM: Bovine lactoferrin inhibits lung cancer growth
through suppression of both inflammation and expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor. J Dairy Sci. 96:2095–2106. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Deng M, Zhang W, Tang H, Ye Q, Liao Q,
Zhou Y, Wu M, Xiong W, Zheng Y, Guo X, et al: Lactotransferrin acts
as a tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing AKT
through multiple mechanisms. Oncogene. 32:4273–4283. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Chea C, Miyauchi M, Inubushi T, Febriyanti
Ayuningtyas N, Subarnbhesaj A, Nguyen PT, Shrestha M, Haing S, Ohta
K and Takata T: Molecular mechanism of inhibitory effects of bovine
lactoferrin on the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS
One. 13:e1916832018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Sabra SA, Elzoghby AO, Sheweita SA, Haroun
M, Helmy MW, Eldemellawy MA, Xia Y, Goodale D, Allan AL and Rohani
S: Self-assembled amphiphilic zein-lactoferrin micelles for tumor
targeted co-delivery of rapamycin and wogonin to breast cancer. Eur
J Pharm Biopharm. 128:156–169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Sabra SA, Sheweita SA, Haroun M, Ragab D,
Eldemellawy MA, Xia Y, Goodale D, Allan AL, Elzoghby AO and Rohani
S: Magnetically guided self-assembled protein micelles for enhanced
delivery of dasatinib to human triple-negative breast cancer cells.
J Pharm Sci. 108:1713–1725. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Abd Elwakil MM, Mabrouk MT, Helmy MW,
Abdelfattah EA, Khiste SK, Elkhodairy KA and Elzoghby AO: Inhalable
lactoferrin-chondroitin nanocomposites for combined delivery of
doxorubicin and ellagic acid to lung carcinoma. Nanomedicine
(Lond). 13:2015–2035. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Kumari S, Ahsan SM, Kumar JM, Kondapi AK
and Rao NM: Overcoming blood brain barrier with a dual purpose
Temozolomide loaded lactoferrin nanoparticles for combating glioma
(SERP-17-12433). Sci Rep. 7:66022017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Kumari S and Kondapi AK: Lactoferrin
nanoparticle mediated targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil for
enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Int J Biol Macromol. 95:232–237.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wang H, Tang Y, Fang Y, Zhang M, Wang H,
He Z, Wang B, Xu Q and Huang Y: Reprogramming Tumor Immune
Microenvironment (TIME) and metabolism via biomimetic targeting
Codelivery of Shikonin/JQ1. Nano Lett. 19:2935–2944. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Kumar P, Lakshmi YS and Kondapi AK: An
oral formulation of efavirenz-loaded lactoferrin nanoparticles with
improved biodistribution and pharmacokinetic profile. HIV Med.
18:452–462. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Zhang ZH, Wang XP, Ayman WY, Munyendo WL,
Lv HX and Zhou JP: Studies on lactoferrin nanoparticles of gambogic
acid for oral delivery. Drug Deliv. 20:86–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Shankaranarayanan JS, Kanwar JR,
Al-Juhaishi AJ and Kanwar RK: Doxorubicin conjugated to
immunomodulatory anticancer lactoferrin displays improved
cytotoxicity overcoming prostate cancer chemo resistance and
inhibits tumour development in TRAMP mice. Sci Rep. 6:320622016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|