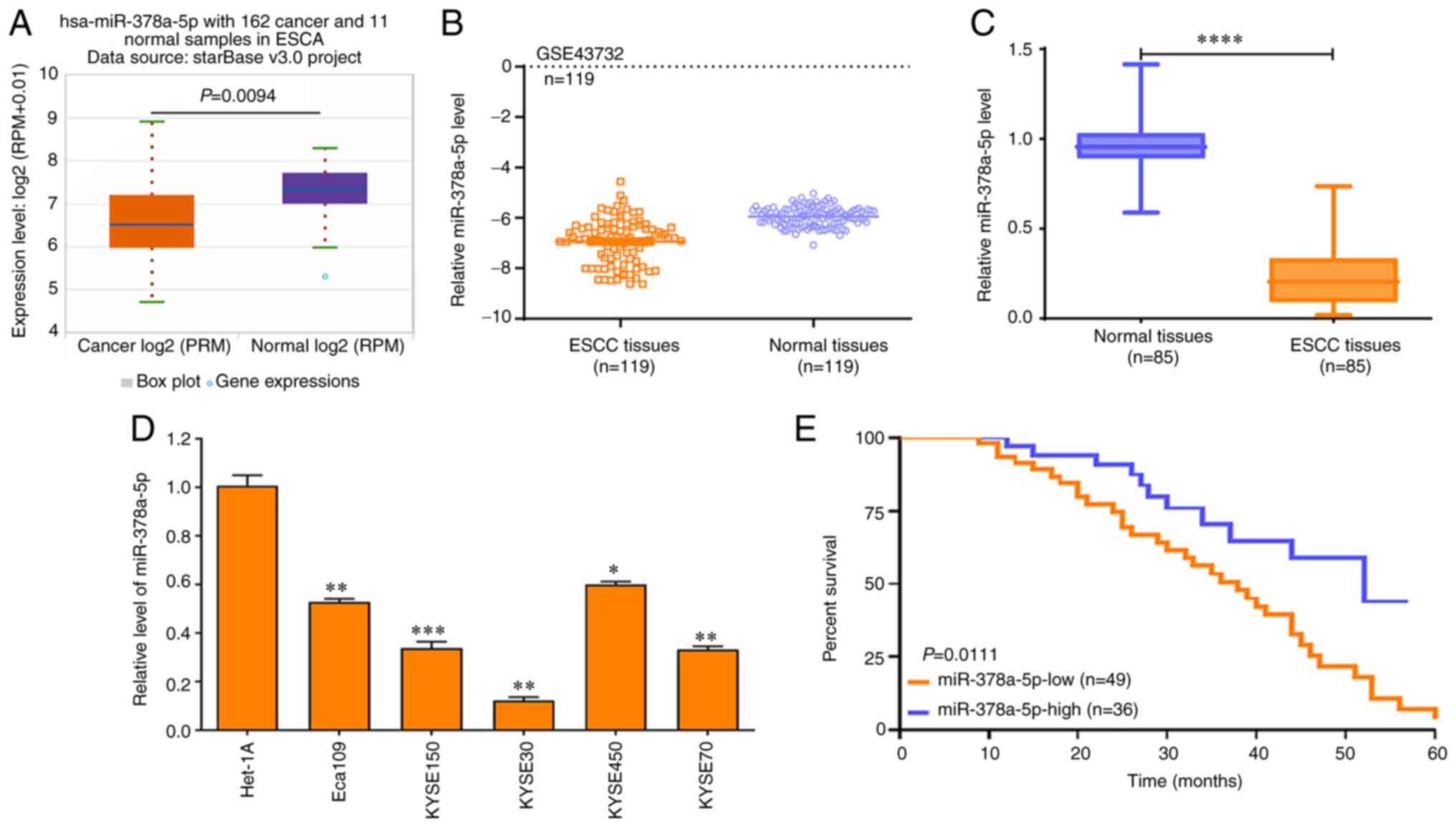
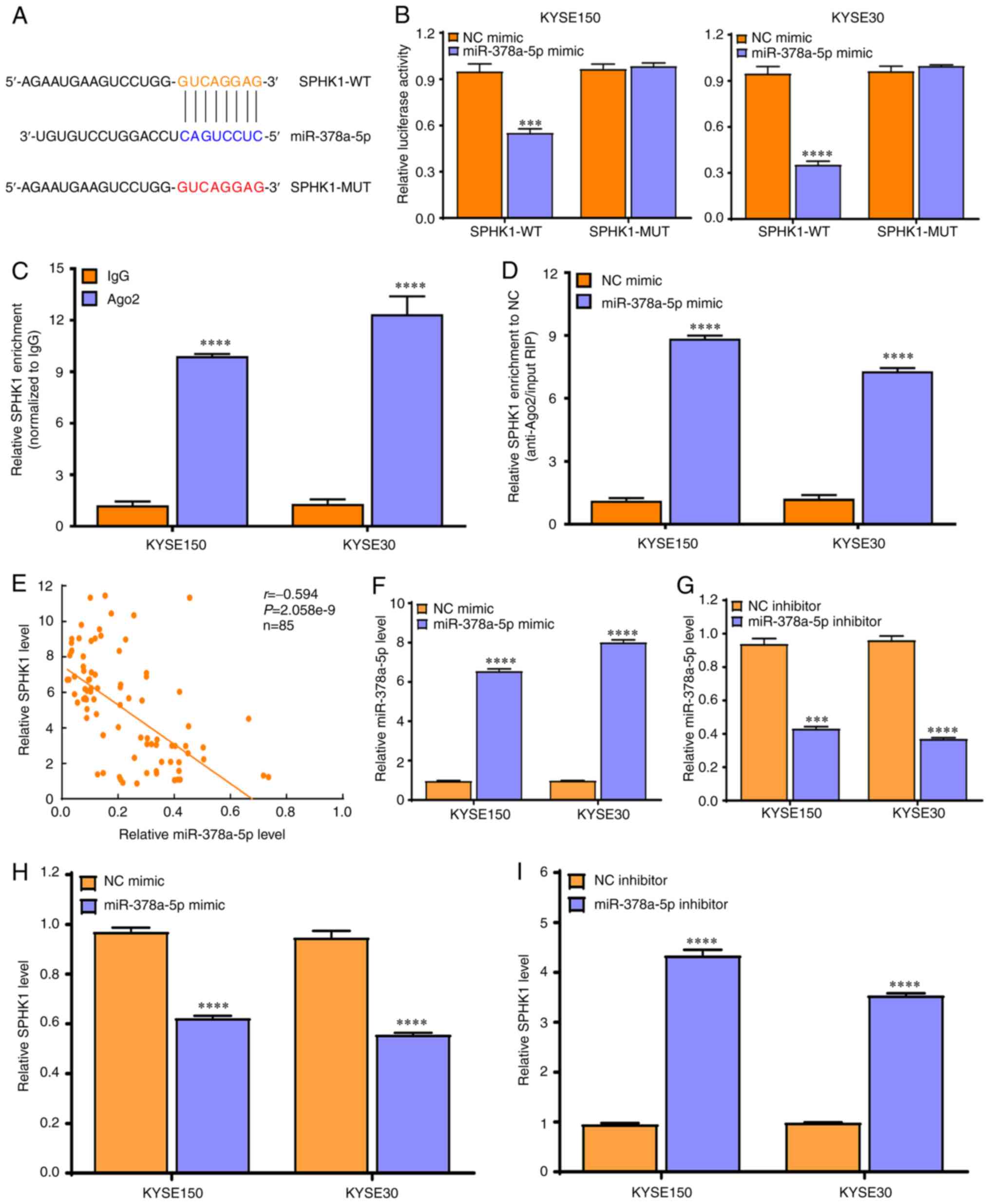
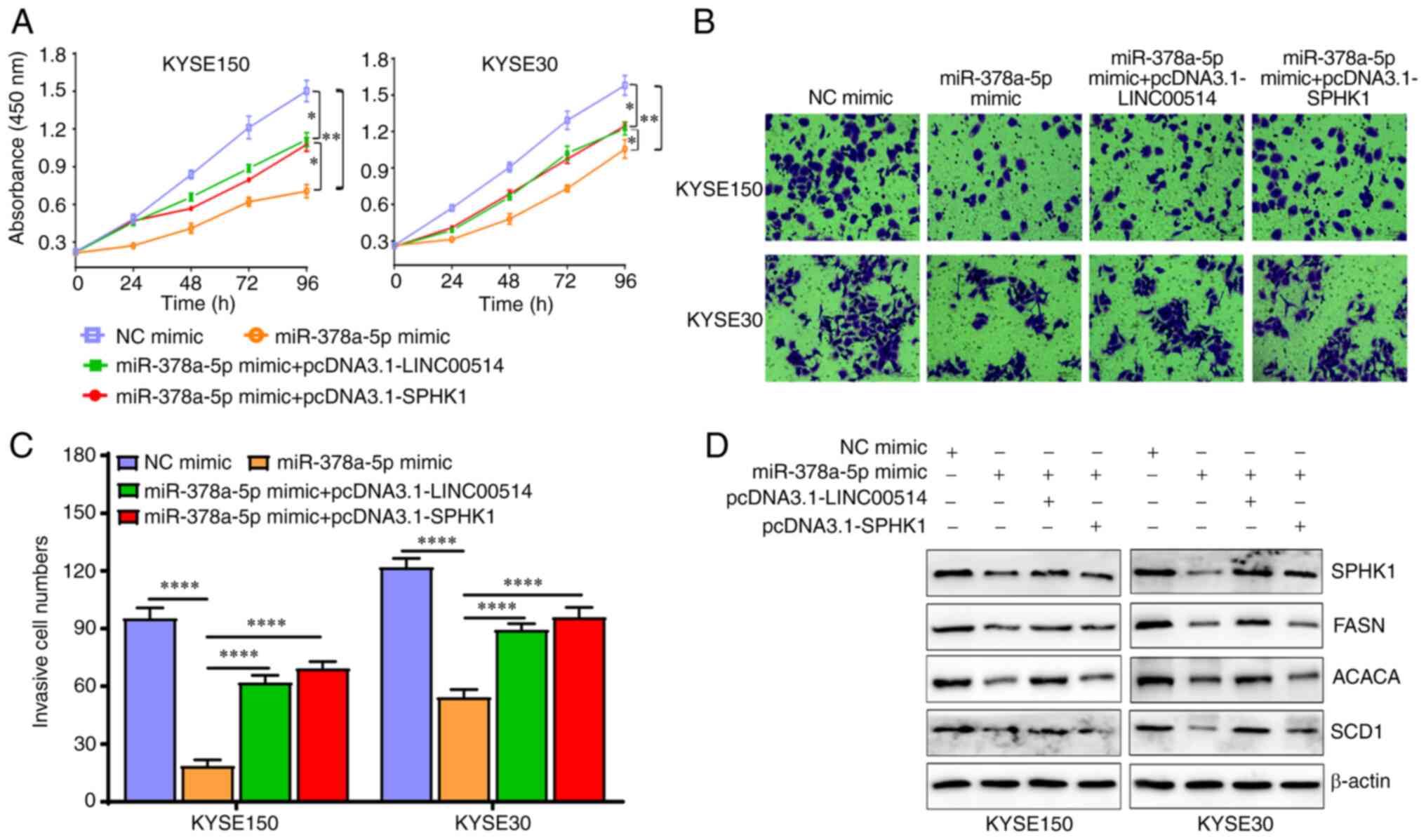
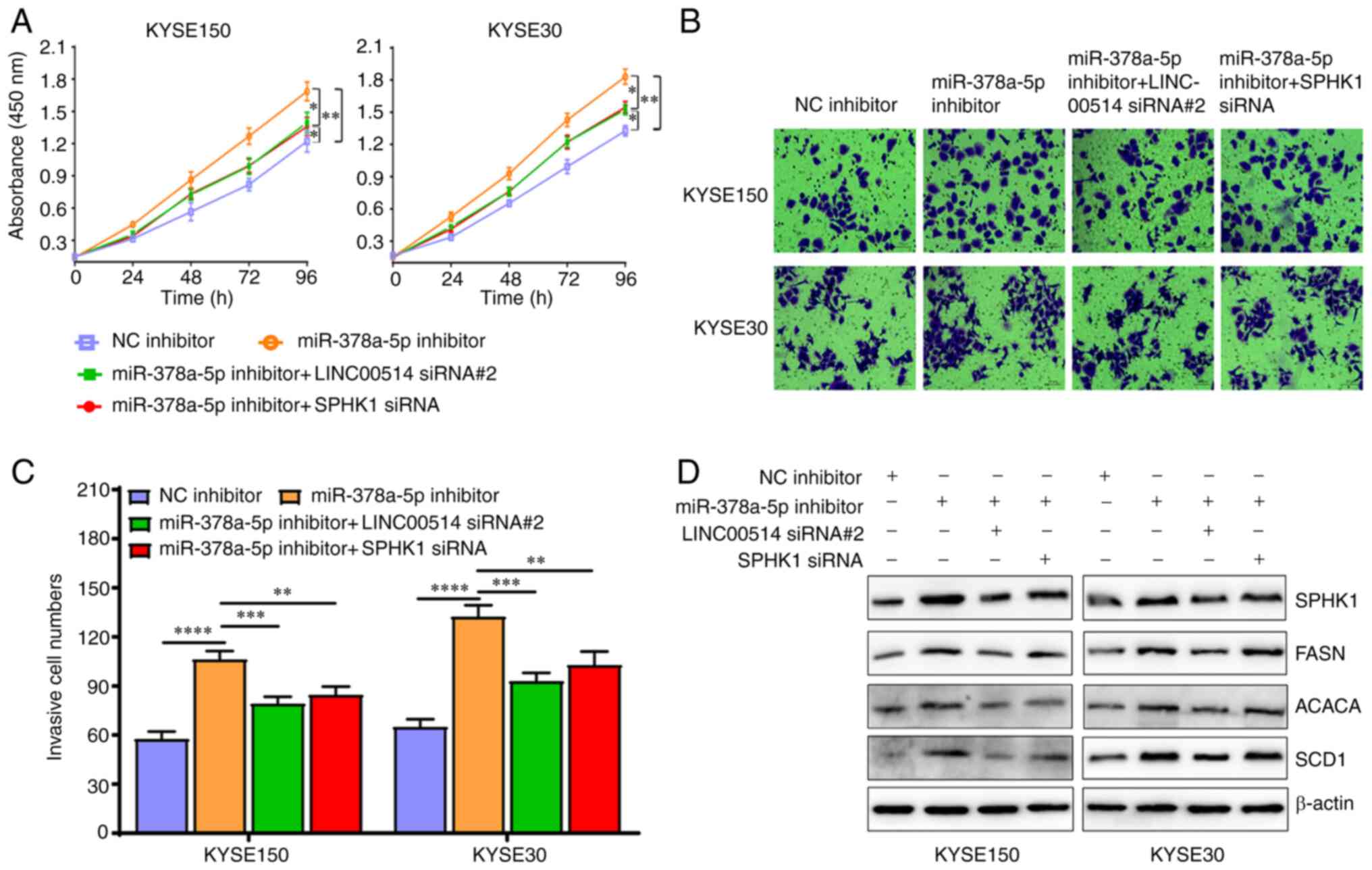
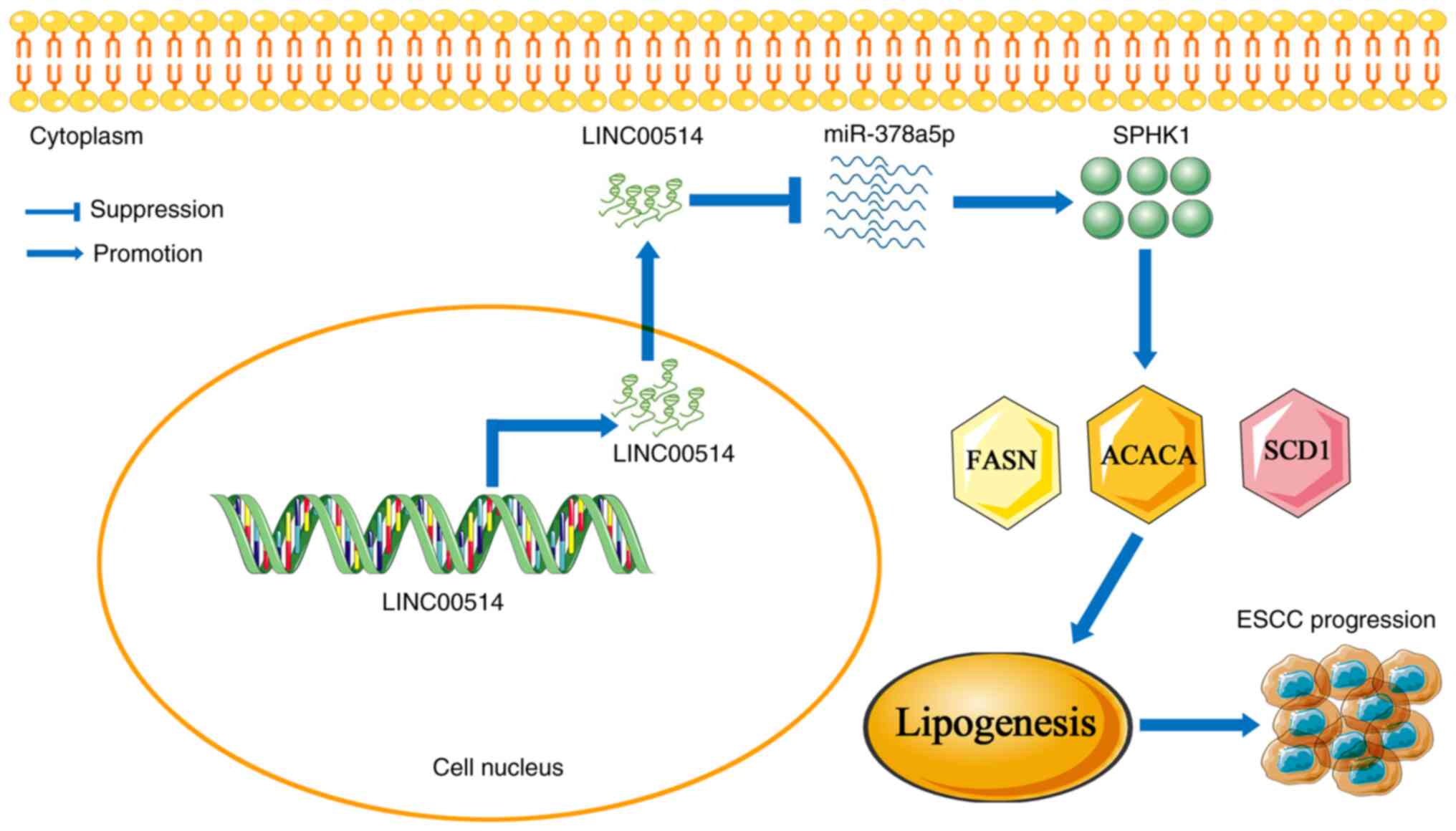
|
1
|
Zhang Y: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5598–5606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stoecklein NH, Hosch SB, Bezler M, Stern
F, Hartmann CH, Vay C, Siegmund A, Scheunemann P, Schurr P, Knoefel
WT, et al: Direct genetic analysis of single disseminated cancer
cells for prediction of outcome and therapy selection in esophageal
cancer. Cancer Cell. 13:441–453. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological
subtype in 2012. Gut. 64:381–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang H, Liu H, Chen Y, Zhu C, Fang W, Yu
Z, Mao W, Xiang J, Han Y, Chen Z, et al: Neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery versus surgery alone for
locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
(NEOCRTEC5010): A phase III multicenter, randomized, open-label
clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 36:2796–2803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pickens A and Orringer MB: Geographical
distribution and racial disparity in esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac
Surg. 76(Suppl): S1367–S1369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ohashi S, Miyamoto S, Kikuchi O, Goto T,
Amanuma Y and Muto M: Recent advances from basic and clinical
studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
149:1700–1715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Morris KV and Mattick JS: The rise of
regulatory RNA. Nat Rev Genet. 15:423–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen MJ, Deng J, Chen C, Hu W, Yuan YC and
Xia ZK: lncRNA H19 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and
metastasis of esophageal cancer via STAT3/EZH2 axis. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 113:27–36. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liang Y, Chen X, Wu Y, Li J, Zhang S, Wang
K, Guan X, Yang K and Bai Y: lncRNA CASC9 promotes esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through upregulating LAMC2
expression by interacting with the CREB-binding protein. Cell Death
Differ. 25:1980–1995. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu Y, Hu L, Liang Y, Li J, Wang K, Chen X,
Meng H, Guan X, Yang K and Bai Y: Up-regulation of lncRNA CASC9
promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth by negatively
regulating PDCD4 expression through EZH2. Mol Cancer. 16:1502017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li W, Zhang L, Guo B, Deng J, Wu S, Li F,
Wang Y, Lu J and Zhou Y: Exosomal FMR1-AS1 facilitates maintaining
cancer stem-like cell dynamic equilibrium via TLR7/NFκB/c-Myc
signaling in female esophageal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 18:222019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tao S, Chen Q, Lin C and Dong H: Linc00514
promotes breast cancer metastasis and M2 polarization of
tumor-associated macrophages via Jagged1-mediated notch signaling
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1912020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu D, Xu X, Li S and Zhang K: LINC00514
drives osteosarcoma progression through sponging microRNA-708 and
consequently increases URGCP expression. Aging. 12:6793–6807. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li X, Zhong W, Xu Y, Yu B and Liu H:
Silencing of lncRNA LINC00514 inhibits the malignant behaviors of
papillary thyroid cancer through miR-204-3p/CDC23 axis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 508:1145–1148. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ramnarine VR, Alshalalfa M, Mo F, Nabavi
N, Erho N, Takhar M, Shukin R, Brahmbhatt S, Gawronski A, Kobelev
M, et al: The long noncoding RNA landscape of neuroendocrine
prostate cancer and its clinical implications. Gigascience.
7:giy0502018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jafari N, Drury J, Morris AJ, Onono FO,
Stevens PD, Gao T, Liu J, Wang C, Lee EY, Weiss HL, et al: De novo
fatty acid synthesis-driven sphingolipid metabolism promotes
metastatic potential of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
17:140–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jairajpuri DS, Mohammad T, Adhikari K,
Gupta P, Hasan GM, Alajmi MF, Rehman MT, Hussain A and Hassan MI:
Identification of sphingosine kinase-1 inhibitors from bioactive
natural products targeting cancer therapy. ACS Omega.
5:14720–14729. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Imbert C, Montfort A, Fraisse M,
Marcheteau E, Gilhodes J, Martin E, Bertrand F, Marcellin M,
Burlet-Schiltz O, Peredo AG, et al: Resistance of melanoma to
immune checkpoint inhibitors is overcome by targeting the
sphingosine kinase-1. Nat Commun. 11:4372020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Arends MJ, Fukayama M, Klimstra DS, Lam
AKY, Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Paradis V, Park YN, Rugge M,
Salto-Tellez M, et al: TNM staging of tumours of the oesophagus.
WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. The WHO
Classification of Tumours Editorial Board IARC Press; Lyon: pp.
252019
|
|
25
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Vlachos IS, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Kanellos I, Vergoulis T, Zagganas K, Tsanakas P,
Floros E, Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-LncBase v2:
Indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:D231–D238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Deng SJ, Chen HY, Ye Z, Deng SC, Zhu S,
Zeng Z, He C, Liu ML, Huang K, Zhong JX, et al: Hypoxia-induced
lncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic
cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene.
37:5811–5828. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim J, Piao HL, Kim BJ, Yao F, Han Z, Wang
Y, Xiao Z, Siverly AN, Lawhon SE, Ton BN, et al: Long noncoding RNA
MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat Genet.
50:1705–1715. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Renganathan A and Felley-Bosco E: Long
noncoding RNAs in cancer and therapeutic potential. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:199–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Arun G, Diermeier SD and Spector DL:
Therapeutic targeting of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Trends Mol
Med. 24:257–277. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li ZX, Zhu QN, Zhang HB, Hu Y, Wang G and
Zhu YS: MALAT1: A potential biomarker in cancer. Cancer Manag Res.
10:6757–6768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Qiu L, Tang Q, Li G and Chen K: Long
non-coding RNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets: Recent
insights into hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 191:273–282.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cossu AM, Mosca L, Zappavigna S, Misso G,
Bocchetti M, De Micco F, Quagliuolo L, Porcelli M, Caraglia M and
Boccellino M: Long non-coding RNAs as important biomarkers in
laryngeal cancer and other head and neck tumours. Int J Mol Sci.
20:34442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Peng Z, Liu C and Wu M: New insights into
long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol Cancer.
17:612018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Bi F, An Y and Yang Q:
Identification of pathological grade and prognosis-associated
lncRNA for ovarian cancer. J Cell Biochem. 120:14444–14454. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chao Y and Zhou D: lncRNA-D16366 is a
potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 25:6581–6586. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yang J, Li C, Mudd A and Gu X: lncRNA PVT1
predicts prognosis and regulates tumor growth in prostate cancer.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 81:2301–2306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mi LD, Sun CX, He SW and Du GY:
SP1-Induced upregulation of lncRNA LINC00514 promotes tumor
proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma by regulating miR-708.
Cancer Manag Res. 12:3311–3322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chaumeil J, Le Baccon P, Wutz A and Heard
E: A novel role for Xist RNA in the formation of a repressive
nuclear compartment into which genes are recruited when silenced.
Genes Dev. 20:2223–2237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E and
Chang HY: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin
domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Krist B, Florczyk U,
Pietraszek-Gremplewicz K, Jozkowicz A and Dulak J: The role of
miR-378a in metabolism, angiogenesis, and muscle biology. Int J
Endocrinol. 2015:2817562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Carrer M, Liu N, Grueter CE, Williams AH,
Frisard MI, Hulver MW, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: Control of
mitochondrial metabolism and systemic energy homeostasis by
microRNAs 378 and 378*. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:15330–15335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Eichner LJ, Perry MC, Dufour CR, Bertos N,
Park M, St-Pierre J and Giguère V: miR-378(*) mediates metabolic
shift in breast cancer cells via the PGC-1beta/ERRgamma
transcriptional pathway. Cell Metab. 12:352–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pan X, Zhao L, Quan J, Liu K, Lai Y, Li Z,
Zhang Z, Xu J, Xu W, Guan X, et al: miR-378a-5p acts as a tumor
suppressor in renal cell carcinoma and is associated with the good
prognosis of patients. Am J Transl Res. 11:2207–2218. 2019.
|
|
47
|
Cui Z, Liu QL, Sun SQ, Jiao K, Liu DR,
Zhou XC and Huang L: miR-378a-5p inhibits angiogenesis of oral
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting KLK4. Neoplasma. 67:85–92.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zadra G, Photopoulos C and Loda M: The fat
side of prostate cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1518–1532.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X and Guo D: Lipid
metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:272018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ishay-Ronen D, Diepenbruck M, Kalathur
RKR, Sugiyama N, Tiede S, Ivanek R, Bantug G, Morini MF, Wang J,
Hess C and Christofori G: Gain Fat-lose metastasis: Converting
invasive breast cancer cells into adipocytes inhibits cancer
metastasis. Cancer Cell. 35:17–32.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Porporato PE, Payen VL, Baselet B and
Sonveaux P: Metabolic changes associated with tumor metastasis,
part 2: Mitochondria, lipid and amino acid metabolism. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 73:1349–1363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tousignant KD, Rockstroh A, Taherian Fard
A, Lehman ML, Wang C, McPherson SJ, Philp LK, Bartonicek N, Dinger
ME, Nelson CC and Sadowski MC: Lipid uptake is an androgen-enhanced
lipid supply pathway associated with prostate cancer disease
progression and bone metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. 17:1166–1179.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li W, Yu CP, Xia JT, Zhang L, Weng GX,
Zheng HQ, Kong QL, Hu LJ, Zeng MS, Zeng YX, et al: Sphingosine
kinase 1 is associated with gastric cancer progression and poor
survival of patients. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1393–1399. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Facchinetti MM, Gandini NA, Fermento ME,
Sterin-Speziale NB, Ji Y, Patel V, Gutkind JS, Rivadulla MG and
Curino AC: The expression of sphingosine kinase-1 in head and neck
carcinoma. Cells Tissues Organs. 192:314–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wang Z, Qu H, Gong W and Liu A:
Up-regulation and tumor-promoting role of SPHK1 were attenuated by
miR-330-3p in gastric cancer. IUBMB Life. 70:1164–1176. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Bae GE, Do SI, Kim K, Park JH, Cho S and
Kim HS: Increased sphingosine kinase 1 expression predicts distant
metastasis and poor outcome in patients with colorectal cancer.
Anticancer Res. 39:663–670. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Liu SQ, Su YJ, Qin MB, Mao YB, Huang JA
and Tang GD: Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes tumor progression and
confers malignancy phenotypes of colon cancer by regulating the
focal adhesion kinase pathway and adhesion molecules. Int J Oncol.
42:617–626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Nemoto M, Ichikawa H, Nagahashi M, Hanyu
T, Ishikawa T, Kano Y, Muneoka Y and Wakai T: Phospho-Sphingosine
Kinase 1 expression in lymphatic spread of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Surg Res. 234:123–131. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|