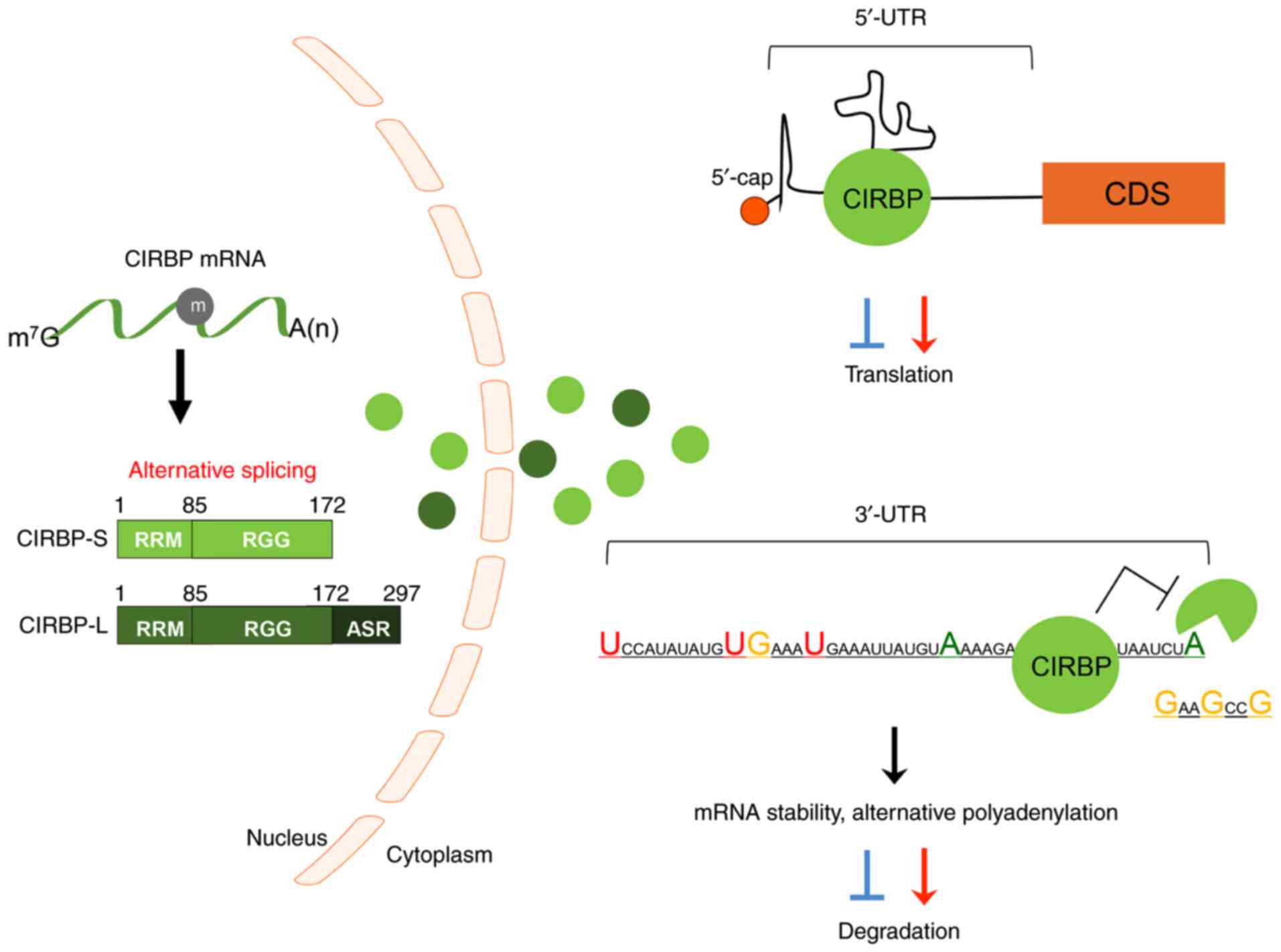
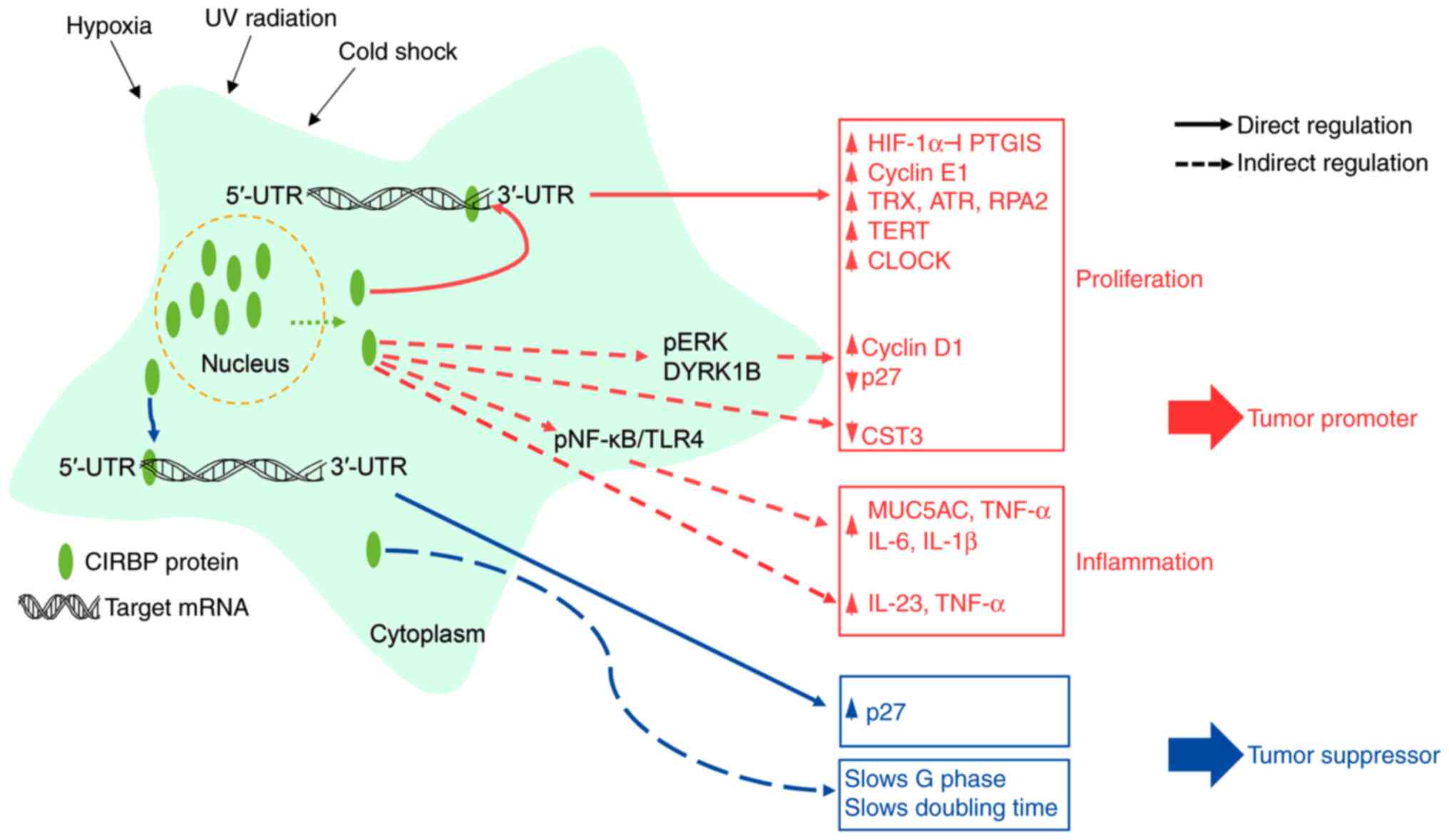
|
1
|
De Leeuw F, Zhang T, Wauquier C, Huez G,
Kruys V and Gueydan C: The cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
migrates from the nucleus to cytoplasmic stress granules by a
methylation-dependent mechanism and acts as a translational
repressor. Exp Cell Res. 313:4130–4144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Fageeh MB and Smales CM: Cold-inducible
RNA binding protein (CIRP) expression is modulated by alternative
mRNAs. RNA. 15:1164–1176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Kaneko T and Kibayashi K: Mild hypothermia
facilitates the expression of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
and heat shock protein 70.1 in mouse brain. Brain Res.
1466:128–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Horii Y, Shimaoka H, Horii K, Shiina T and
Shimizu Y: Mild hypothermia causes a shift in the alternative
splicing of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein transcripts in
Syrian hamsters. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
317:R240–R247. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gokhale NS, McIntyre AB, Mattocks MD,
Holley CL, Lazear HM, Mason CE and Horner SM: Altered
m6A modification of specific cellular transcripts
affects flaviviridae infection. Mol Cell. 77:542–555.e8. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liao Y, Tong L, Tang L and Wu S: The role
of cold-inducible RNA binding protein in cell stress response. Int
J Cancer. 141:2164–2173. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang C and Carrier F: The UV-inducible
RNA-binding protein A18 (A18 hnRNP) plays a protective role in the
genotoxic stress response. J Biol Chem. 276:47277–47284. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sheikh MS, Carrier F, Papathanasiou MA,
Hollander MC, Zhan Q, Yu K and Fornace AJ Jr: Identification of
several human homologs of hamster DNA damage-inducible transcripts.
Cloning and characterization of a novel UV-inducible cDNA that
codes for a putative RNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem.
272:26720–26726. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fujita J: Cold shock response in mammalian
cells. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 1:243–255. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Yang R, Weber DJ and Carrier F:
Post-transcriptional regulation of thioredoxin by the stress
inducible heterogenous ribonucleoprotein A18. Nucleic Acids Res.
34:1224–1236. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Shen Y, Qian HY, Liu LJ, Zhou BC,
Xiao Y, Mao JN, An GY, Rui MZ, Wang T and Zhu CL: Effects of mild
hypothermia on the ROS and expression of caspase-3 mRNA and LC3 of
hippocampus nerve cells in rats after cardiopulmonary
resuscitation. World J Emerg Med. 5:298–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Haley B, Paunesku T, Protić M and
Woloschak GE: Response of heterogeneous ribonuclear proteins
(hnRNP) to ionising radiation and their involvement in DNA damage
repair. Int J Radiat Biol. 85:643–655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Morf J, Rey G, Schneider K, Stratmann M,
Fujita J, Naef F and Schibler U: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
modulates circadian gene expression posttranscriptionally. Science.
338:379–383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Denning NL, Aziz M, Murao A, Gurien SD,
Ochani M, Prince JM and Wang P: Extracellular CIRP as an endogenous
TREM-1 ligand to fuel inflammation in sepsis. JCI Insight.
5:e1341722020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Qiang X, Yang WL, Wu R, Zhou M, Jacob A,
Dong W, Kuncewitch M, Ji Y, Yang H, Wang H, et al: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein (CIRP) triggers inflammatory responses in
hemorrhagic shock and sepsis. Nat Med. 19:1489–1495. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhong P, Peng J, Yuan M, Kong B and Huang
H: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) in inflammatory
diseases: Molecular insights of its associated signalling pathways.
Scand J Immunol. 93:e129492021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xie D, Geng L, Wang S, Xiong K, Zhao T,
Wang G, Feng Z, Lv F, Wang C, Liang D, et al: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein modulates atrial fibrillation onset by
targeting multiple ion channels. Heart Rhythm. 17:998–1008. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xie D, Geng L, Xiong K, Zhao T, Wang S,
Xue J, Wang C, Wang G, Feng Z, Zhou H, et al: Cold-Inducible
RNA-binding protein prevents an excessive heart rate response to
stress by targeting phosphodiesterase. Circ Res. 126:1706–1720.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Aziz M, Brenner M and Wang P:
Extracellular CIRP (eCIRP) and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol.
106:133–146. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Dong H, Zhong Y, Huang J, Lv J and
Li J: The cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) level in
peripheral blood predicts sepsis outcome. PLoS One.
10:e01377212015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Gong JD, Qi XF, Zhang Y and Li HL:
Increased admission serum cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
concentration is associated with prognosis of severe acute
pancreatitis. Clin Chim Acta. 471:135–142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sharma A, Brenner M and Wang P: Potential
role of extracellular CIRP in alcohol-induced Alzheimer's disease.
Mol Neurobiol. 57:5000–5010. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoo IS, Lee SY, Park CK, Lee JC, Kim Y,
Yoo SJ, Shim SC, Choi YS, Lee Y and Kang SW: Serum and synovial
fluid concentrations of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 21:148–154.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lujan DA, Ochoa JL and Hartley RS:
Cold-inducible RNA binding protein in cancer and inflammation.
Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. Jan 11–2018.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kanemura Y, Mori K, Sakakibara S, Fujikawa
H, Hayashi H, Nakano A, Matsumoto T, Tamura K, Imai T, Ohnishi T,
et al: Musashi1, an evolutionarily conserved neural RNA-binding
protein, is a versatile marker of human glioma cells in determining
their cellular origin, malignancy, and proliferative activity.
Differentiation. 68:141–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang Q, Wang F, Zhong W, Ling H, Wang J,
Cui J, Xie T, Wen S and Chen J: RNA-binding protein RBM6 as a tumor
suppressor gene represses the growth and progression in
laryngocarcinoma. Gene. 697:26–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kong N, Zhang H, Feng C, Liu C, Xiao Y,
Zhang X, Mei L, Kim JS, Tao W and Ji X: Arsenene-mediated multiple
independently targeted reactive oxygen species burst for cancer
therapy. Nat Commun. 12:47772021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Lu M, Ge Q, Wang G, Luo Y and Wang X,
Jiang W, Liu X, Wu CL, Xiao Y and Wang X: CIRBP is a novel oncogene
in human bladder cancer inducing expression of HIF-1α. Cell Death
Dis. 9:10462018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chang ET, Parekh PR, Yang Q, Nguyen DM and
Carrier F: Heterogenous ribonucleoprotein A18 (hnRNP A18) promotes
tumor growth by increasing protein translation of selected
transcripts in cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:10578–10593. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Indacochea A, Guerrero S, Ureña M, Araujo
F, Coll O, LLeonart ME and Gebauer F: Cold-inducible RNA binding
protein promotes breast cancer cell malignancy by regulating
Cystatin C levels. RNA. 27:190–201. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Masuda T, Itoh K, Higashitsuji H,
Higashitsuji H, Nakazawa N, Sakurai T, Liu Y, Tokuchi H, Fujita T,
Zhao Y, et al: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (Cirp) interacts
with Dyrk1b/Mirk and promotes proliferation of immature male germ
cells in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:10885–10890. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jian F, Chen Y, Ning G, Fu W, Tang H, Chen
X, Zhao Y, Zheng L, Pan S, Wang W, et al: Cold inducible RNA
binding protein upregulation in pituitary corticotroph adenoma
induces corticotroph cell proliferation via Erk signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:9175–9187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peri S, de Cicco RL, Santucci-Pereira J,
Slifker M, Ross EA, Russo IH, Russo PA, Arslan AA, Belitskaya-Lévy
I, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, et al: Defining the genomic signature of
the parous breast. BMC Med Genomics. 5:462012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lujan DA, Garcia S, Vanderhoof J,
Sifuentes J, Brandt Y, Wu Y, Guo X, Mitchell T, Howard T, Hathaway
HJ and Hartley RS: Cold-inducible RNA binding protein in mouse
mammary gland development. Tissue Cell. 48:577–587. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hamid AA, Mandai M, Fujita J, Nanbu K,
Kariya M, Kusakari T, Fukuhara K and Fujii S: Expression of
cold-inducible RNA-binding protein in the normal endometrium,
endometrial hyperplasia, and endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol
Pathol. 22:240–247. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Roilo M, Kullmann MK and Hengst L:
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) induces translation of
the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:3198–3210.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Roake CM and Artandi SE: Regulation of
human telomerase in homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:384–397. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yuan X, Larsson C and Xu D: Mechanisms
underlying the activation of TERT transcription and telomerase
activity in human cancer: Old actors and new players. Oncogene.
38:6172–6183. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Mao P, Li F, Han X, Zhang
Y, Jiang S, Chen Y, Huang J, Liu D, et al: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein CIRP/hnRNP A18 regulates telomerase activity in
a temperature-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:761–775.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lee HN, Ahn SM and Jang HH: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein, CIRP, inhibits DNA damage-induced apoptosis by
regulating p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 464:916–921. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sun W, Bergmeier AP, Liao Y, Wu S and Tong
L: CIRP sensitizes cancer cell responses to ionizing radiation.
Radiat Res. 195:93–100. 2021.
|
|
44
|
Su F, Yang S, Wang H, Qiao Z, Zhao H and
Qu Z: CIRBP ameliorates neuronal amyloid toxicity via antioxidative
and antiapoptotic pathways in primary cortical neurons. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2020:27861392020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang WL, Sharma A, Wang Z, Li Z, Fan J and
Wang P: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein causes endothelial
dysfunction via activation of Nlrp3 inflammasome. Sci Rep.
6:265712016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li H, Han X, Yang S, Wang Y, Dong Y and
Tang T: FOXP1 drives osteosarcoma development by repressing P21 and
RB transcription downstream of P53. Oncogene. 40:2785–2802. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhou KW, Zheng XM, Yang ZW, Zhang L and
Chen HD: Overexpression of CIRP may reduce testicular damage
induced by cryptorchidism. Clin Invest Med. 32:E103–E111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cho SY, Oh Y, Jeong EM, Park S, Lee D,
Wang X, Zeng Q, Qin H, Hu F, Gong H, et al: Amplification of
transglutaminase 2 enhances tumor-promoting inflammation in gastric
cancers. Exp Mol Med. 52:854–864. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Means AL, Freeman TJ, Zhu J, Woodbury LG,
Marincola-Smith P, Wu C, Meyer AR, Weaver CJ, Padmanabhan C, An H,
et al: Epithelial Smad4 Deletion Up-regulates inflammation and
promotes inflammation-associated cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 6:257–276. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Kortylewski M, Xin H, Kujawski M, Lee H,
Liu Y, Harris T, Drake C, Pardoll D and Yu H: Regulation of the
IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 15:114–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wu D, Wu P, Huang Q, Liu Y, Ye J and Huang
J: Interleukin-17: A promoter in colorectal cancer progression.
Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:4363072013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sakurai T, Kashida H, Watanabe T, Hagiwara
S, Mizushima T, Iijima H, Nishida N, Higashitsuji H, Fujita J and
Kudo M: Stress response protein cirp links inflammation and
tumorigenesis in colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Res.
74:6119–6128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sakurai T, Yada N, Watanabe T, Arizumi T,
Hagiwara S, Ueshima K, Nishida N, Fujita J and Kudo M:
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein promotes the development of
liver cancer. Cancer Sci. 106:352–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Feller L, Altini M and Lemmer J:
Inflammation in the context of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 49:887–892.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ren WH, Zhang LM, Liu HQ, Gao L, Chen C,
Qiang C, Wang XL, Liu CY, Li SM, Huang C, et al: Protein
overexpression of CIRP and TLR4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An
immunohistochemical and clinical correlation analysis. Med Oncol.
31:1202014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lin TY, Chen Y, Jia JS, Zhou C, Lian M,
Wen YT, Li XY, Chen HW, Lin XL, Zhang XL, et al: Loss of Cirbp
expression is correlated with the malignant progression and poor
prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res.
11:6959–6969. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Chen Z, Xiong S, Li J, Ou L, Li C, Tao J,
Jiang Z, Fan J, He J and Liang W: DNA methylation markers that
correlate with occult lymph node metastases of non-small cell lung
cancer and a preliminary prediction model. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
9:280–287. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Fahad Ullah M: Breast cancer: Current
perspectives on the disease status. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1152:51–64.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Huang R, Guo J, Yan P, Zhai S, Hu P, Zhu
X, Zhang J, Qiao Y, Zhang Y, Liu H, et al: The construction of bone
metastasis-specific prognostic model and co-expressed network of
alternative splicing in breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:7902020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Dankner M, Caron M, Al-Saadi T, Yu W,
Ouellet V, Ezzeddine R, Maritan SM, Annis MG, Le PU, Nadaf J, et
al: Invasive growth associated with Cold-Inducible RNA-Binding
Protein expression drives recurrence of surgically resected brain
metastases. Neuro Oncol. 23:1470–1480. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Lee HN, Ahn SM and Jang HH: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
activating ERK and p38 pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
477:1038–1044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Joe S and Nam H: Prognostic factor
analysis for breast cancer using gene expression profiles. BMC Med
Inform Decis Mak. 16(Suppl 1): 562016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69(Suppl 3): S4–S10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Hashemi Goradel N, Ghiyami-Hour F,
Jahangiri S, Negahdari B, Sahebkar A, Masoudifar A and Mirzaei H:
Nanoparticles as new tools for inhibition of cancer angiogenesis. J
Cell Physiol. 233:2902–2910. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Idrovo JP, Jacob A, Yang WL, Wang Z, Yen
HT, Nicastro J, Coppa GF and Wang P: A deficiency in cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein accelerates the inflammation phase and improves
wound healing. Int J Mol Med. 37:423–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kübler M, Beck S, Fischer S, Götz P,
Kumaraswami K, Ishikawa-Ankerhold H, Lasch M and Deindl E: Absence
of cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) promotes angiogenesis
and regeneration of ischemic tissue by inducing M2-Like macrophage
polarization. Biomedicines. 9:3952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu Y, Hu W, Murakawa Y, Yin J, Wang G,
Landthaler M and Yan J: Cold-induced RNA-binding proteins regulate
circadian gene expression by controlling alternative
polyadenylation. Sci Rep. 3:20542013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Guo X, Wu Y and Hartley RS: Cold-inducible
RNA-binding protein contributes to human antigen R and cyclin E1
deregulation in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 49:130–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Yang R, Zhan M, Nalabothula NR, Yang Q,
Indig FE and Carrier F: Functional significance for a heterogenous
ribonucleo-protein A18 signature RNA motif in the 3′-untranslated
region of ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3-related (ATR)
transcript. J Biol Chem. 285:8887–8893. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Ouellette MM, Liao M, Herbert BS, Johnson
M, Holt SE, Liss HS, Shay JW and Wright WE: Subsenescent telomere
lengths in fibroblasts immortalized by limiting amounts of
telomerase. J Biol Chem. 275:10072–10076. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Nakayama J, Tahara H, Tahara E, Saito M,
Ito K, Nakamura H, Nakanishi T, Tahara E, Ide T and Ishikawa F:
Telomerase activation by hTRT in human normal fibroblasts and
hepatocellular carcinomas. Nat Genet. 18:65–68. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Artero-Castro A, Callejas FB, Castellvi J,
Kondoh H, Carnero A, Fernández-Marcos PJ, Serrano M, Ramón y Cajal
S and Lleonart ME: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein bypasses
replicative senescence in primary cells through extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 activation. Mol Cell Biol.
29:1855–1868. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
García-Gómez R, Bustelo XR and Crespo P:
Protein-protein interactions: Emerging oncotargets in the RAS-ERK
pathway. Trends Cancer. 4:616–633. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Kim JY, Lee SG, Chung JY, Kim YJ, Park JE,
Koh H, Han MS, Park YC, Yoo YH and Kim JM: Ellipticine induces
apoptosis in human endometrial cancer cells: the potential
involvement of reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated
protein kinases. Toxicology. 289:91–102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chen L, Ran D, Xie W, Xu Q and Zhou X:
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein mediates cold air inducible
airway mucin production through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 39:48–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Li J, Zhou W, Wei J, Xiao X, An T, Wu W
and He Y: Prognostic value and biological functions of RNA binding
proteins in stomach adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther.
14:1689–1705. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Zhang J, Xu A, Miao C, Yang J, Gu M and
Song N: Prognostic value of Lin28A and Lin28B in various human
malignancies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell
Int. 19:792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Koedoot E, Smid M, Foekens JA, Martens
JWM, Le Dévédec SE and van de Water B: Co-regulated gene expression
of splicing factors as drivers of cancer progression. Sci Rep.
9:54842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
He R and Zuo S: A robust 8-gene prognostic
signature for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol.
9:6932019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Biade S, Marinucci M, Schick J, Roberts D,
Workman G, Sage EH, O'Dwyer PJ, Livolsi VA and Johnson SW: Gene
expression profiling of human ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer.
95:1092–1100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Virnig BA, Tuttle TM, Shamliyan T and Kane
RL: Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: A systematic review of
incidence, treatment, and outcomes. J Natl Cancer Inst.
102:170–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Mangé A, Lacombe J, Bascoul-Mollevi C,
Jarlier M, Lamy PJ, Rouanet P, Maudelonde T and Solassol J: Serum
autoantibody signature of ductal carcinoma in situ progression to
invasive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1992–2000. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Sveen A, Kilpinen S, Ruusulehto A, Lothe
RA and Skotheim RI: Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer; expression
changes and driver mutations of splicing factor genes. Oncogene.
35:2413–2427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Anczuków O and Krainer AR: Splicing-factor
alterations in cancers. RNA. 22:1285–1301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Zhao D, Zhang C, Jiang M, Wang Y, Liang Y,
Wang L, Qin K, Rehman FU and Zhang X: Survival-associated
alternative splicing signatures in non-small cell lung cancer.
Aging (Albany NY). 12:5878–5893. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Anczuków O, Akerman M, Cléry A, Wu J, Shen
C, Shirole NH, Raimer A, Sun S, Jensen MA, Hua Y, et al:
SRSF1-regulated alternative splicing in breast cancer. Mol Cell.
60:105–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Martins F, Sofiya L, Sykiotis GP, Lamine
F, Maillard M, Fraga M, Shabafrouz K, Ribi C, Cairoli A,
Guex-Crosier Y, et al: Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint
inhibitors: Epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 16:563–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Rajput S, Volk-Draper LD and Ran S: TLR4
is a novel determinant of the response to paclitaxel in breast
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1676–1687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Perera PY, Mayadas TN, Takeuchi O, Akira
S, Zaks-Zilberman M, Goyert SM and Vogel SN: CD11b/CD18 acts in
concert with CD14 and Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 to elicit full
lipopolysaccharide and taxol-inducible gene expression. J Immunol.
166:574–581. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Bolognese AC, Sharma A, Yang WL, Nicastro
J, Coppa GF and Wang P: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein
activates splenic T cells during sepsis in a TLR4-dependent manner.
Cell Mol Immunol. 15:38–47. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Khan MM, Yang WL, Brenner M, Bolognese AC
and Wang P: Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) causes
sepsis-associated acute lung injury via induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Sci Rep. 7:413632017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Zhang F, Brenner M, Yang WL and Wang P: A
cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP)-derived peptide
attenuates inflammation and organ injury in septic mice. Sci Rep.
8:30522018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Sulli G, Lam MTY and Panda S: Interplay
between circadian clock and cancer: New frontiers for cancer
treatment. Trends Cancer. 5:475–494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Hadadi E, Taylor W, Li XM, Aslan Y,
Villote M, Rivière J, Duvallet G, Auriau C, Dulong S,
Raymond-Letron I, et al: Chronic circadian disruption modulates
breast cancer stemness and immune microenvironment to drive
metastasis in mice. Nat Commun. 11:31932020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Fang L, Yang Z, Zhou J, Tung JY, Hsiao CD,
Wang L, Deng Y, Wang P, Wang J and Lee MH: Circadian clock gene
CRY2 degradation is involved in chemoresistance of colorectal
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1476–1487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Rosenberg LH, Lafitte M, Quereda V, Grant
W, Chen W, Bibian M, Noguchi Y, Fallahi M, Yang C, Chang JC, et al:
Therapeutic targeting of casein kinase 1δ in breast cancer. Sci
Transl Med. 7:318ra2022015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Oshima T, Niwa Y, Kuwata K, Srivastava A,
Hyoda T, Tsuchiya Y, Kumagai M, Tsuyuguchi M, Tamaru T, Sugiyama A,
et al: Cell-based screen identifies a new potent and highly
selective CK2 inhibitor for modulation of circadian rhythms and
cancer cell growth. Sci Adv. 5:eaau90602019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Ricci MS and Zong WX: Chemotherapeutic
approaches for targeting cell death pathways. Oncologist.
11:342–357. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Chen M, Fu H, Zhang J, Huang H and Zhong
P: CIRP downregulation renders cardiac cells prone to apoptosis in
heart failure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 517:545–550. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Li S, Zhang Z, Xue J, Liu A and Zhang H:
Cold-inducible RNA binding protein inhibits
H2O2-induced apoptosis in rat cortical
neurons. Brain Res. 1441:47–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Wang L, Rowe RG, Jaimes A, Yu C, Nam Y,
Pearson DS, Zhang J, Xie X, Marion W, Heffron GJ, et al:
Small-molecule inhibitors disrupt let-7 oligouridylation and
release the selective blockade of let-7 processing by LIN28. Cell
Rep. 23:3091–3101. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Minuesa G, Albanese SK, Xie W, Kazansky Y,
Worroll D, Chow A, Schurer A, Park SM, Rotsides CZ, Taggart J, et
al: Small-molecule targeting of MUSASHI RNA-binding activity in
acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Commun. 10:26912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wu X, Gardashova G, Lan L, Han S, Zhong C,
Marquez RT, Wei L, Wood S, Roy S, Gowthaman R, et al: Targeting the
interaction between RNA-binding protein HuR and FOXQ1 suppresses
breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Commun Biol. 3:1932020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
François-Moutal L, Felemban R, Scott DD,
Sayegh MR, Miranda VG, Perez-Miller S, Khanna R, Gokhale V,
Zarnescu DC and Khanna M: Small molecule targeting TDP-43's RNA
recognition motifs reduces locomotor defects in a drosophila model
of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ACS Chem Biol.
14:2006–2013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Baker JD, Uhrich RL, Strovas TJ, Saxton AD
and Kraemer BC: Targeting pathological tau by small molecule
inhibition of the poly(A):MSUT2 RNA-protein interaction. ACS Chem
Neurosci. 11:2277–2285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Solano-Gonzalez E, Coburn KM, Yu W, Wilson
GM, Nurmemmedov E, Kesari S, Chang ET, MacKerell AD, Weber DJ and
Carrier F: Small molecules inhibitors of the heterogeneous
ribonuclear protein A18 (hnRNP A18): A regulator of protein
translation and an immune checkpoint. Nucleic Acids Res.
49:1235–1246. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|