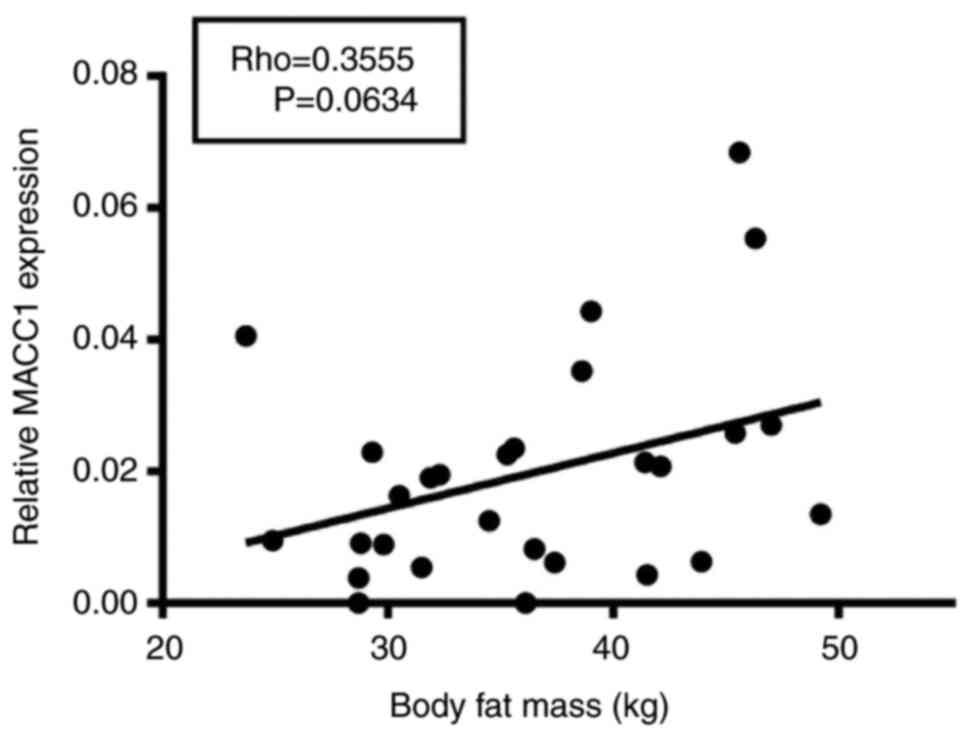
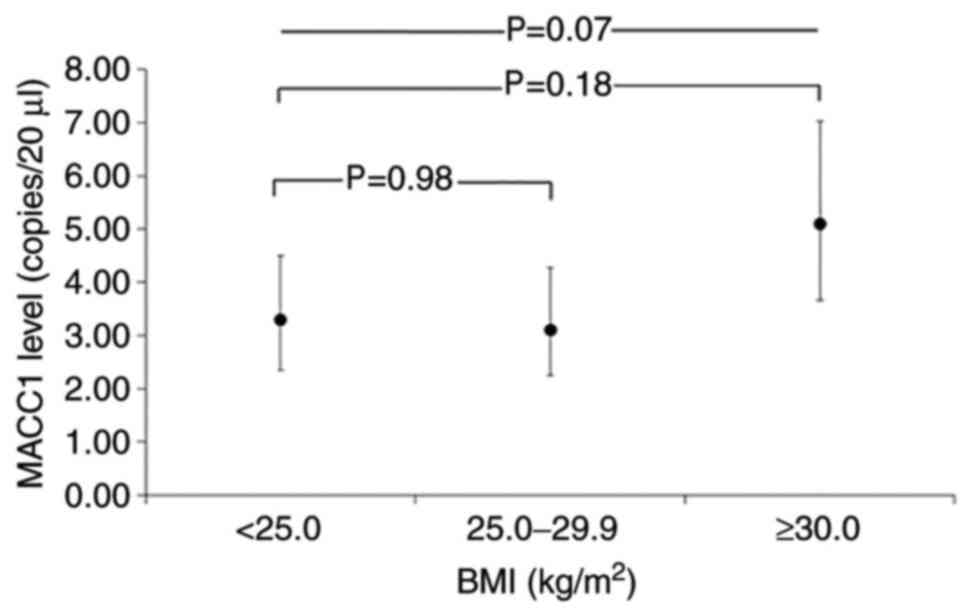
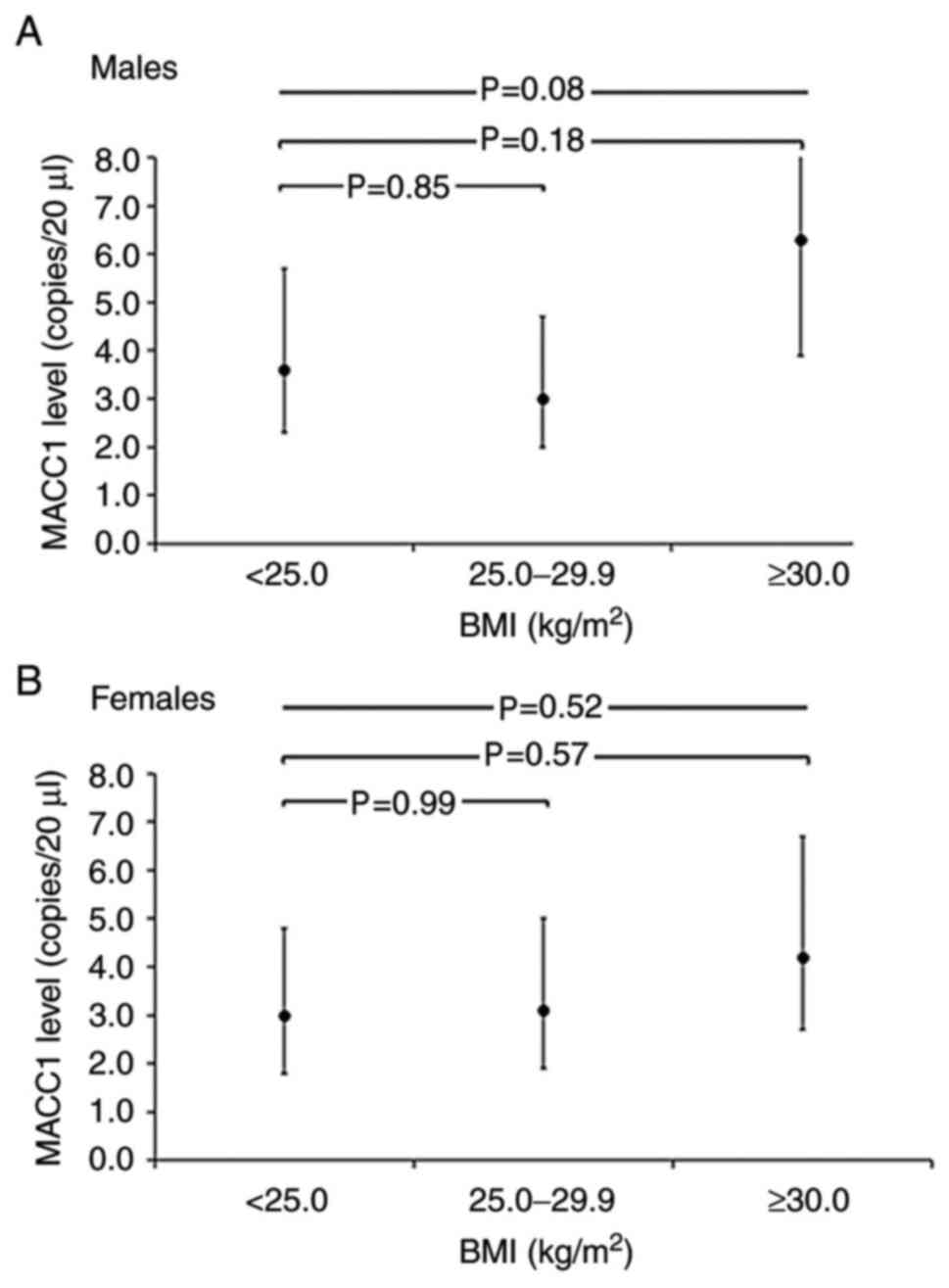
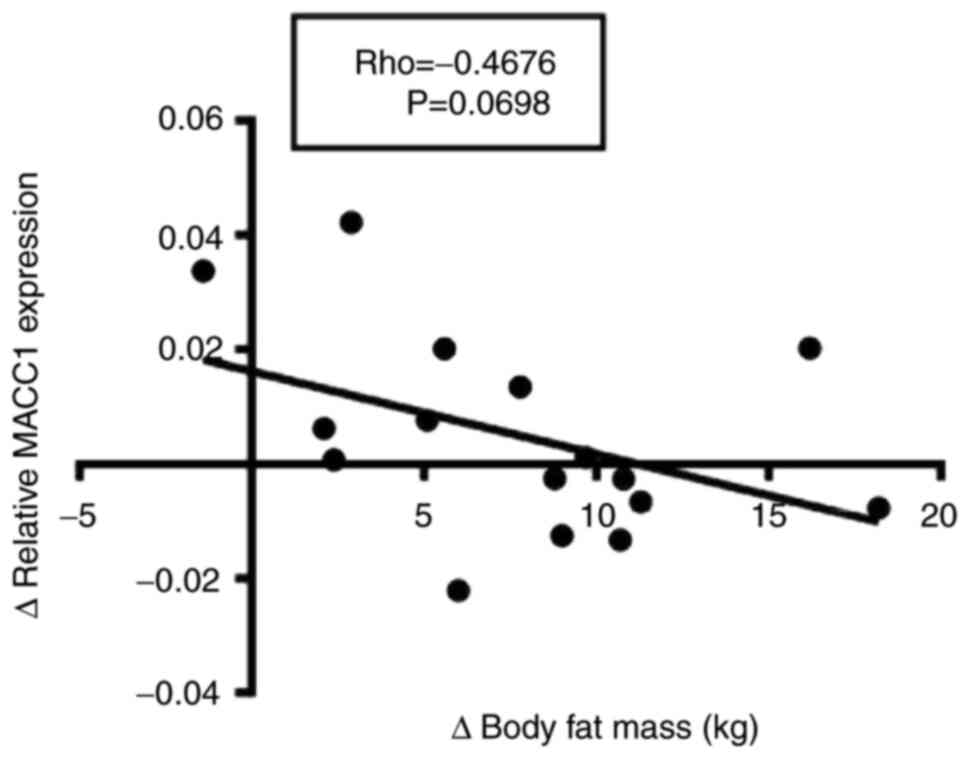
|
1
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC):
Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014:
A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with
192 million participants. Lancet. 387:1377–1396. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
World Health Organisation: Obesity and
Overweight (WHO fact sheet). WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021,
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
Accessed December 22, 2021.
|
|
3
|
Robert Koch Institute: Overweight and
Obesity. Robert Koch Institute; Berlin, Germany: 2021, https://www.rki.de/EN/Content/Health_Monitoring/Main_Topics/Overweight_Obesity/obesity_node.html;jsessionid=B0011790B0977853D808900F073E7775.internet111.
Accessed December 22, 2021.
|
|
4
|
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF
and Zwahlen M: Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational
studies. Lancet. 371:569–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ma Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Zhang P, Shi C, Zou
Y and Qin H: Obesity and risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic
review of prospective studies. PLoS One. 8:e539162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong Y, Zhou J, Zhu Y, Luo L, He T, Hu H,
Liu H, Zhang Y, Luo D, Xu S, et al: Abdominal obesity and
colorectal cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of
prospective studies. Biosci Rep. Dec 12–2017.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Renehan AG and Soerjomataram I: Obesity as
an avoidable cause of cancer (Attributable Risks). Recent Results
Cancer Res. 208:243–256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Larsson SC and Wolk A: Obesity and colon
and rectal cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am
J Clin Nutr. 86:556–565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calle EF, Rodriguez C, Walker-Turmond K
and Tun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a
prospectively studied cohort of U.S. Adults New Engl J Med.
348:1625–1638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Campbell PT, Newton CC, Dehal AN, Jacobs
EJ, Patel AV and Gapstur SM: Impact of body mass index on survival
after colorectal cancer diagnosis: The cancer prevention StudyII
nutrition cohort. J Clin Oncol. 30:42–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Arnold M, Leitzmann M, Freisling H, Bray
F, Romieu I, Renehan A and Soerjomataram I: Obesity and cancer: An
update of the global impact. Cancer Epidemiol. 41:8–15. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stein U, Walther W, Arlt F, Schwabe H,
Smith J, Fichtner I, Birchmeier W and Schlag PM: MACC1, a newly
identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon
cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 15:59–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Radhakrishnan H, Walther W, Zincke F,
Kobelt D, Imbastari F, Erdem M, Kortüm B, Dahlmann M and Stein U:
MACC1-the first decade of a key metastasis molecule from gene
discovery to clinical translation. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
37:805–820. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pichorner A, Sack U, Kobelt D, Kelch I,
Arlt F, Smith J, Walther W, Schlag PM and Stein U: In vivo imaging
of colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting MACC1 with
shRNA in xenografted mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:573–583. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lemos C, Hardt MS, Juneja M, Voss C,
Förster S, Jerchow B, Haider W, Bläker H and Stein U: MACC1 induces
tumor progression in transgenic mice and colorectal cancer patients
via increased pluripotency markers Nanog and Oct4. Clin Cancer Res.
22:2812–2824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang G, Fu Z and Li D: MACC1
overexpression and survival in solid tumors: A meta-analysis.
Tumour Biol. 36:1055–1065. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu Z, Zhou R, Su Y, Sun L, Liao Y and Liao
W: Prognostic value of macc1 in digestive system neoplasms: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int.
2015:2520432015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun DW, Zhang YY, Qi Y, Liu GQ, Chen YG,
Ma J and Lv GY: Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of
MACC1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: A
meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:4769–4777. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Dai C, Wang M, Kang H, Lin S, Yang
P, Liu X, Liu K, Xu P, Zheng Y, et al: Clinicopathological and
prognostic significance of metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1
(MACC1) overexpression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 7:62966–62975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jin Y, Zhou K, Zhao W, Han R, Huo X, Yang
F and Chen J: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 in gastric cancer: A
meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers. 34:27–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Fan L, Xu H and Jiang H:
Prognostic significance of the expression of metastasis-associated
in colon cancer-1 in gynecologic cancers and breast cancer: A
protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100:e242552021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Lu Z, Liang Z, Ji D, Zhang P, Liu Q,
Zheng X and Yao Y: Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 is
associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, partly
by promoting proliferation through enhanced glucose metabolism. Mol
Med Rep. 12:426–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang M, Yang J, Jiang H, Jiang H and Wang
Z: Correlation between glucose metabolism parameters derived from
FDG and tumor TNM stages and metastasis-associated proteins in
colorectal carcinoma patients. BMC Cancer. 21:2582021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Lisec J, Kobelt D, Walther W, Mokrizkij M,
Grötzinger C, Jaeger C, Baum K, Simon M, Wolf J, Beindorff N, et
al: Systematic identification of MACC1-driven metabolic networks in
colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:9782021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jahn J, Spielau M, Brandsch C, Stangl GI,
Delank KS, Bähr I, Berreis T, Wrann CD and Kielstein H: Decreased
NK cell functions in obesity can be reactivated by fat mass
reduction. Obesity (Silver Spring). 23:2233–2241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jaeschke L, Steinbrecher A, Hansen G,
Sommer S, Adler C, Janke J and Pischon T: Association of body
surface scanner-based abdominal volume with parameters of the
Metabolic Syndrome and comparison with manually measured waist
circumference. Sci Rep. 10:93242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bähr I, Goritz V, Doberstein H, Hiller
GGR, Rosenstock P, Jahn J, Pörtner O, Berreis T, Mueller T,
Spielmann J and Kielstein H: Diet-induced obesity is associated
with an impaired NK cell function and an increased colon cancer
incidence. J Nutr Metab. 2017:42970252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bähr I, Pörtner OJ, Glass M, Doberstein H,
Goritz V, Hiller GGR, Spielmann J and Kielstein H: Characterization
of natural killer cells in colorectal tumor tissue of rats fed a
control diet or a high-fat diet. Ann Anat. 233:1515862021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Adler C, Steinbrecher A, Jaeschke L,
Mähler A, Boschmann M, Jeran S and Pischon T: Validity and
reliability of total body volume and relative body fat mass from a
3-dimensional photonic body surface scanner. PLoS One.
12:e01802012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
World Health Organization: Waist
Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Report of a WHO Expert
Consultation; Geneva, 8-11 December 2008; World Health
Organization; Geneva: 2011, Available from: http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/obesity/WHO_report_waistcircumference_and_waisthip_ratio/en/.
|
|
32
|
Schulze MB, Kroke A, Bergmann MM and
Boeing H: Differences of blood pressure estimates between
consecutive measurements on one occasion: Implications for
inter-study comparability of epidemiologic studies. Eur J
Epidemiol. 16:891–898. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet
PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith
SC Jr, et al: Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim
statement of the international diabetes federation Task Force on
epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood
institute; American Heart Association World Heart Federation;
International atherosclerosis society; and International
association for the study of obesity. Circulation. 120:1640–1645.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hagemann C, Neuhaus N, Dahlmann M, Kessler
AF, Kobelt D, Herrmann P, Eyrich M, Freitag B, Linsenmann T,
Monoranu CM, et al: Circulating MACC1 transcripts in glioblastoma
patients predict prognosis and treatment response. Cancers (Basel).
11:8252019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Link T, Kuhlmann JD, Kobelt D, Herrmann P,
Vassileva YD, Kramer M, Frank K, Göckenjan M, Wimberger P and Stein
U: Clinical relevance of circulating MACC1 and S100A4 transcripts
for ovarian cancer. Mol Oncol. 13:1268–1279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ashktorab H, Hermann P, Nouraie M,
Shokrani B, Lee E, Haidary T, Brim H and Stein U: Increased MACC1
levels in tissues and blood identify colon adenoma patients at high
risk. J Transl Med. 14:2152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burock S, Herrmann P, Wendler I,
Niederstrasser M, Wernecke KD and Stein U: Circulating Metastasis
Associated in Colon Cancer 1 transcripts in gastric cancer patient
plasma as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:333–341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stein U, Burock S, Herrmann P, Wendler I,
Niederstrasser M, Wernecke KD and Schlag PM: Circulating MACC1
transcripts in colorectal cancer patient plasma predict metastasis
and prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e492492012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Ackerman SE, Blackburn OA, Marchildon F
and Cohen P: Insights into the link between obesity and cancer.
Curr Obes Rep. 6:195–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berger NA: Obesity and cancer
pathogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1311:57–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Himbert C, Delphan M, Scherer D, Bowers
LW, Hursting S and Ulrich CM: Signals from the adipose
microenvironment and the obesity-cancer link-A systematic review.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 10:494–506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Crawley DJ, Holmberg L, Melvin JC, Loda M,
Chowdhury S, Rudman SM and Van Hemelrijck M: Serum glucose and risk
of cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 14:9852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hope C, Robertshaw A, Cheung KL, Idris I
and English E: Relationship betweenHbA1c and cancer in people with
or without diabetes: A systematic review. Diabet Med. 33:1013–1025.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Luo J, Hendryx M, Manson JE, Figueiredo
JC, LeBlanc ES, Barrington W, Rohan TE, Howard BV, Reding K, Ho GY,
et al: Intentional weight loss and obesity-related cancer risk.
JNCI Cancer Spectr. 3:pkz0542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tee MC, Cao Y, Warnock GL, Hu FB and
Chavarro JE: Effect of bariatric surgery on oncologic out-comes: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 27:4449–4456.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|