|
1
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bengtsson A, Andersson R and Ansari D: The
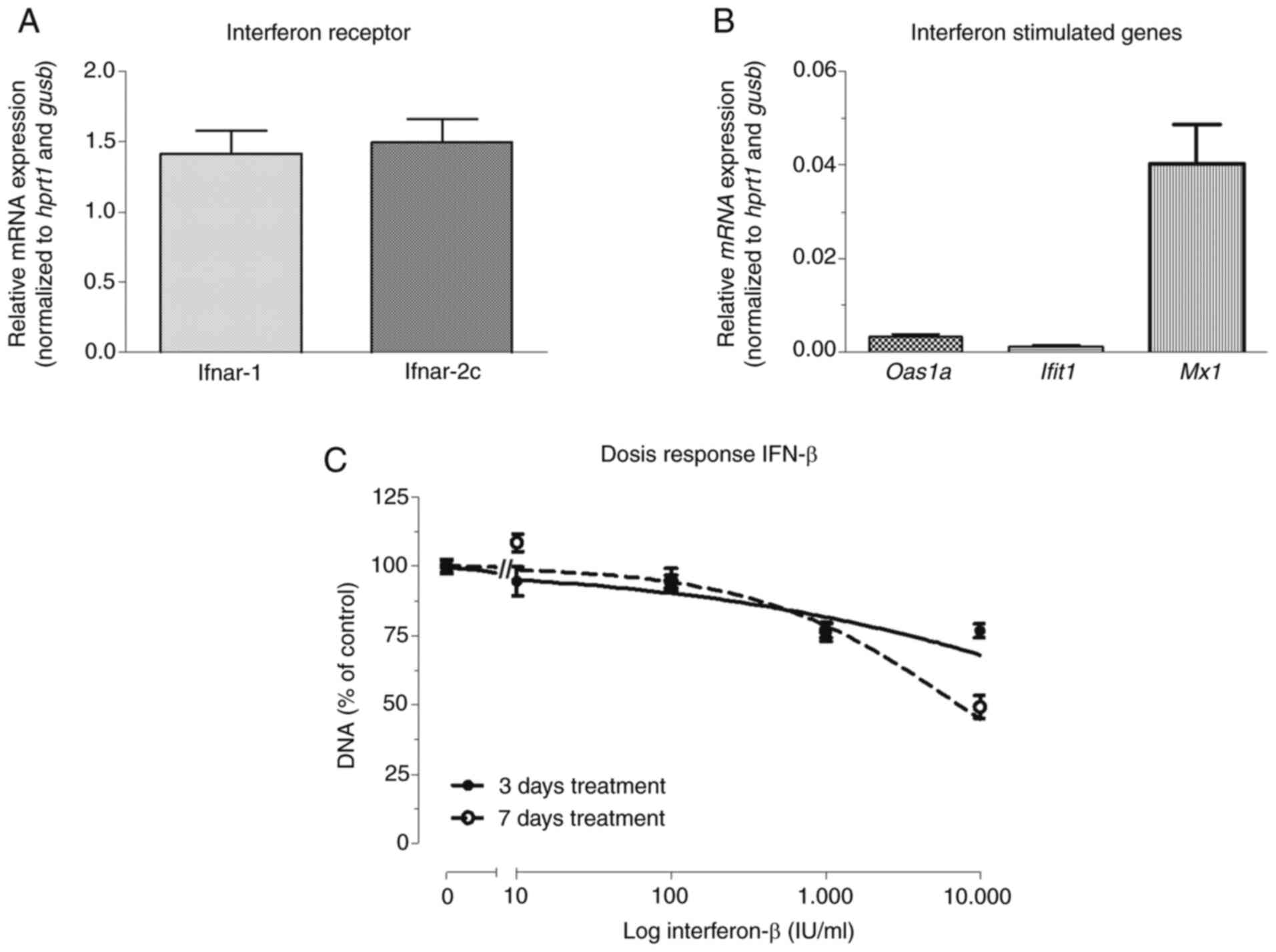
actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based
on real-world data. Sci Rep. 10:164252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, Ben
Abdelghani M, Wei AC, Raoul JL, Choné L, Francois E, Artru P, Biagi
JJ, et al: FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for
pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 379:2395–2406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amrutkar M and Gladhaug IP: Pancreatic
cancer chemoresistance to gemcitabine. Cancers (Basel). 9:1572017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Linehan DC, Tan MC, Strasberg SM, Drebin
JA, Hawkins WG, Picus J, Myerson RJ, Malyapa RS, Hull M, Trinkaus K
and Tan BR Jr: Adjuvant interferon-based chemoradiation followed by
gemcitabine for resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A
single-institution phase II study. Ann Surg. 248:145–151. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ohman KA, Liu J, Linehan DC, Tan MC, Tan
BR, Fields RC, Strasberg SM and Hawkins WG: Interferon-based
chemoradiation followed by gemcitabine for resected pancreatic
adenocarcinoma: Long-term follow-up. HPB (Oxford). 19:449–457.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Maeyer E and De Maeyer-Guignard J: Type
I interferons. Int Rev Immunol. 17:53–73. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blaauboer A, Sideras K, van Eijck CHJ and
Hofland LJ: Type I interferons in pancreatic cancer and development
of new therapeutic approaches. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
159:1032042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Blaauboer A, Booy S, van Koetsveld PM,
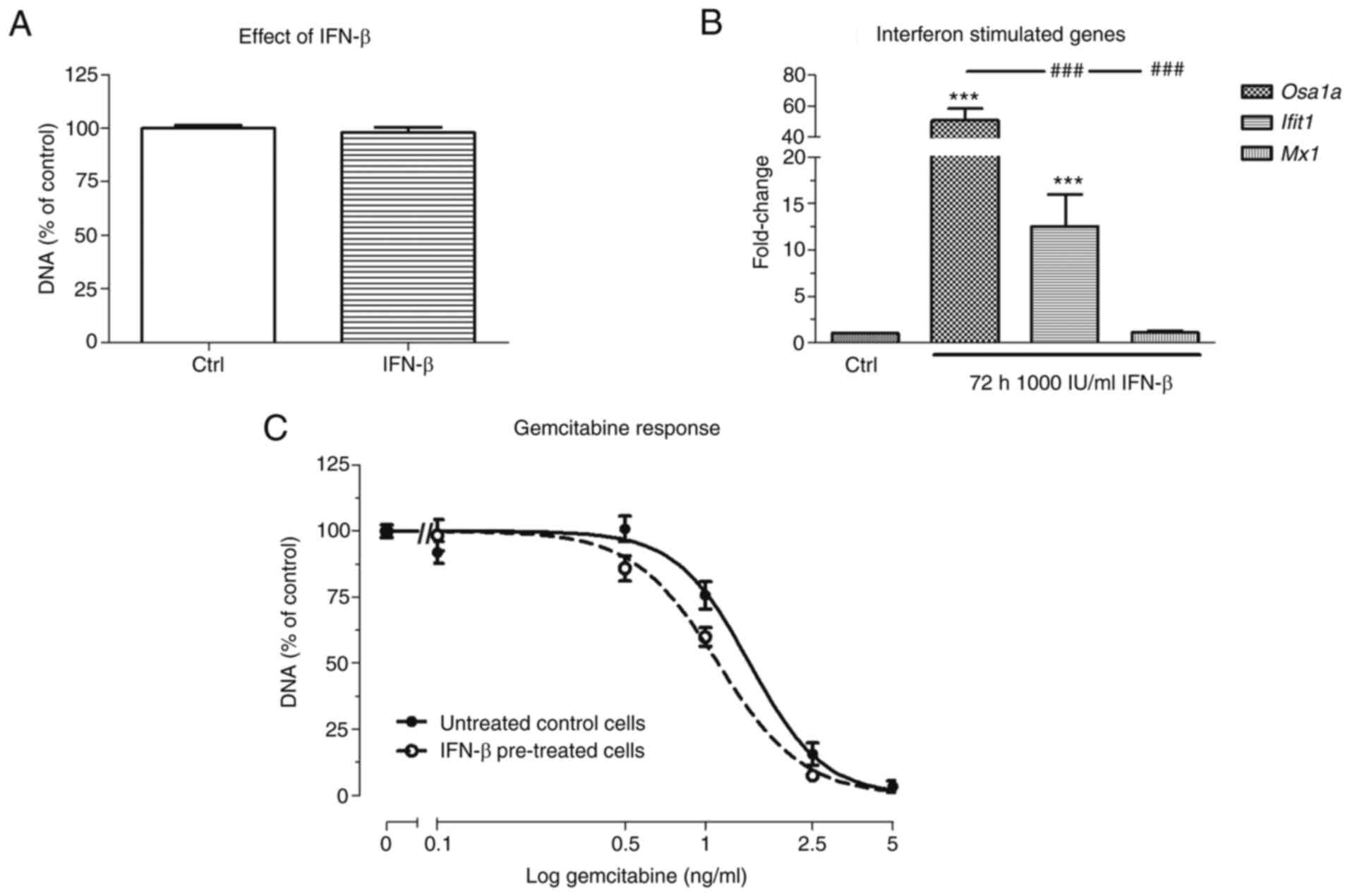
Karels B, Dogan F, van Zwienen S, van Eijck CHJ and Hofland LJ:
Interferon-beta enhances sensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic
cancer. BMC Cancer. 20:9132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Wada H, Tomokuni A,
Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Takeda Y, Tanemura M, Umeshita K, Mori M,
et al: Synergistic antitumor effect of interferon-β with
gemcitabine in interferon-α-non-responsive pancreatic cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 38:1237–1243. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Domanski P and Colamonici OR: The type-I
interferon receptor. The long and short of it. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 7:143–151. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wagner TC, Velichko S, Chesney SK, Biroc
S, Harde D, Vogel D and Croze E: Interferon receptor expression
regulates the antiproliferative effects of interferons on cancer
cells and solid tumors. Int J Cancer. 111:32–42. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Booy S, Hofland LJ, Waaijers AM, Croze E,
van Koetsveld PM, de Vogel L, Biermann K and van Eijck CH: Type I
interferon receptor expression in human pancreatic and
periampullary cancer tissue. Pancreas. 44:99–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Booy S, van Eijck CH, Dogan F, van
Koetsveld PM and Hofland LJ: Influence of type-I Interferon
receptor expression level on the response to type-I Interferons in
human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:492–502. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
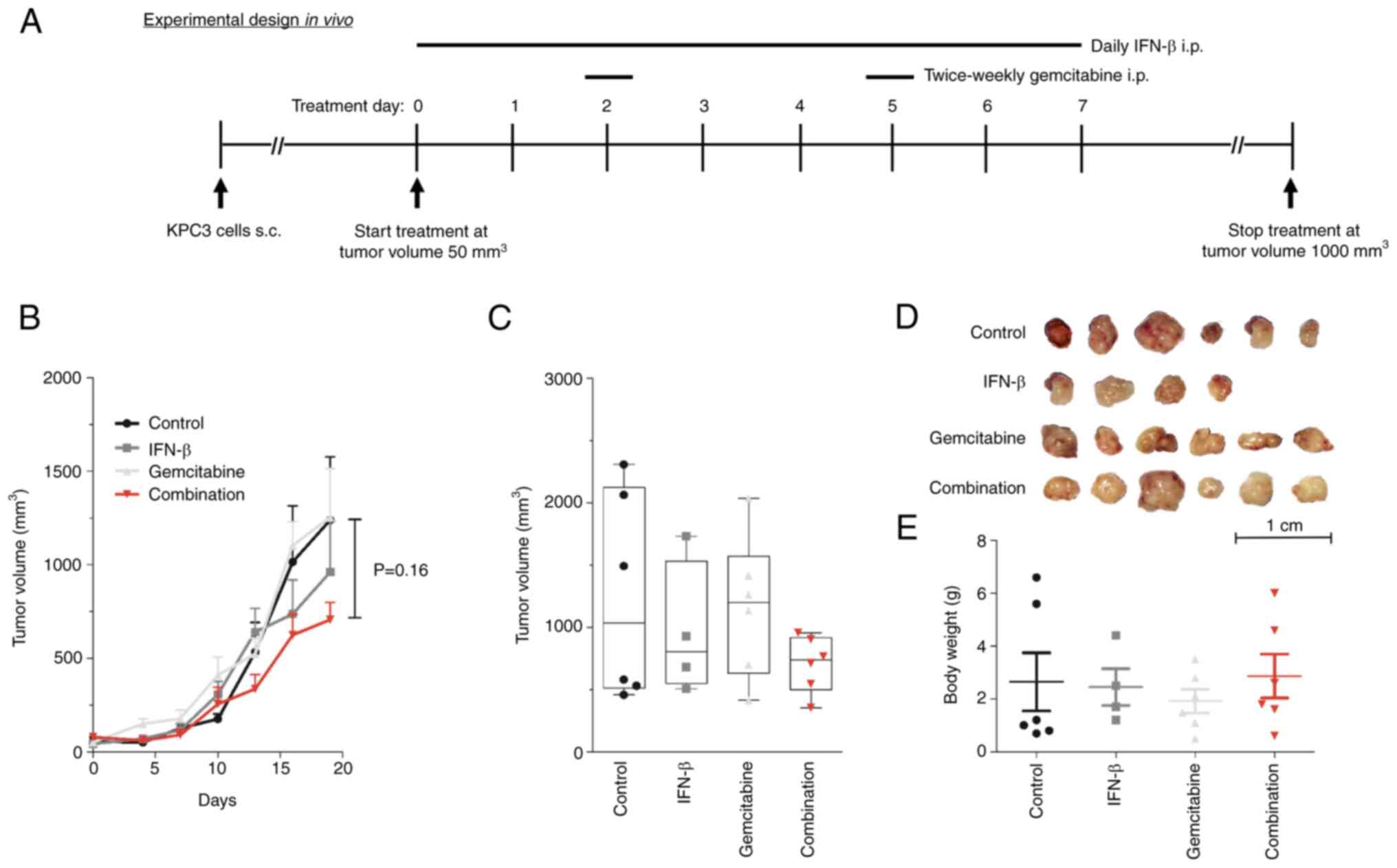
Lee JW, Komar CA, Bengsch F, Graham K and
Beatty GL: Genetically engineered mouse models of pancreatic
cancer: The KPC model
[LSL-Kras(G12D/+);LSL-Trp53(R172H/+);Pdx-1-Cre], its variants, and
their application in immuno-oncology drug discovery. Curr Protoc
Pharmacol. 73:14.39.1–14.39.20. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Herrera-Martínez AD, Feelders RA, de
Herder WW, Castaño JP, Gálvez Moreno M, Dogan F, van Dungen R, van
Koetsveld P and Hofland LJ: Effects of Ketoconazole on
ACTH-producing and Non-ACTH-producing neuroendocrine tumor cells.
Horm Cancer. 10:107–119. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Blaauboer A, van Koetsveld PM, Mustafa
DAM, Dumas J, Dogan F, van Zwienen S, van Eijck CHJ and Hofland LJ:
The Class I HDAC inhibitor valproic acid strongly potentiates
gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic cancer by immune system
activation. Biomedicines. 10:5172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
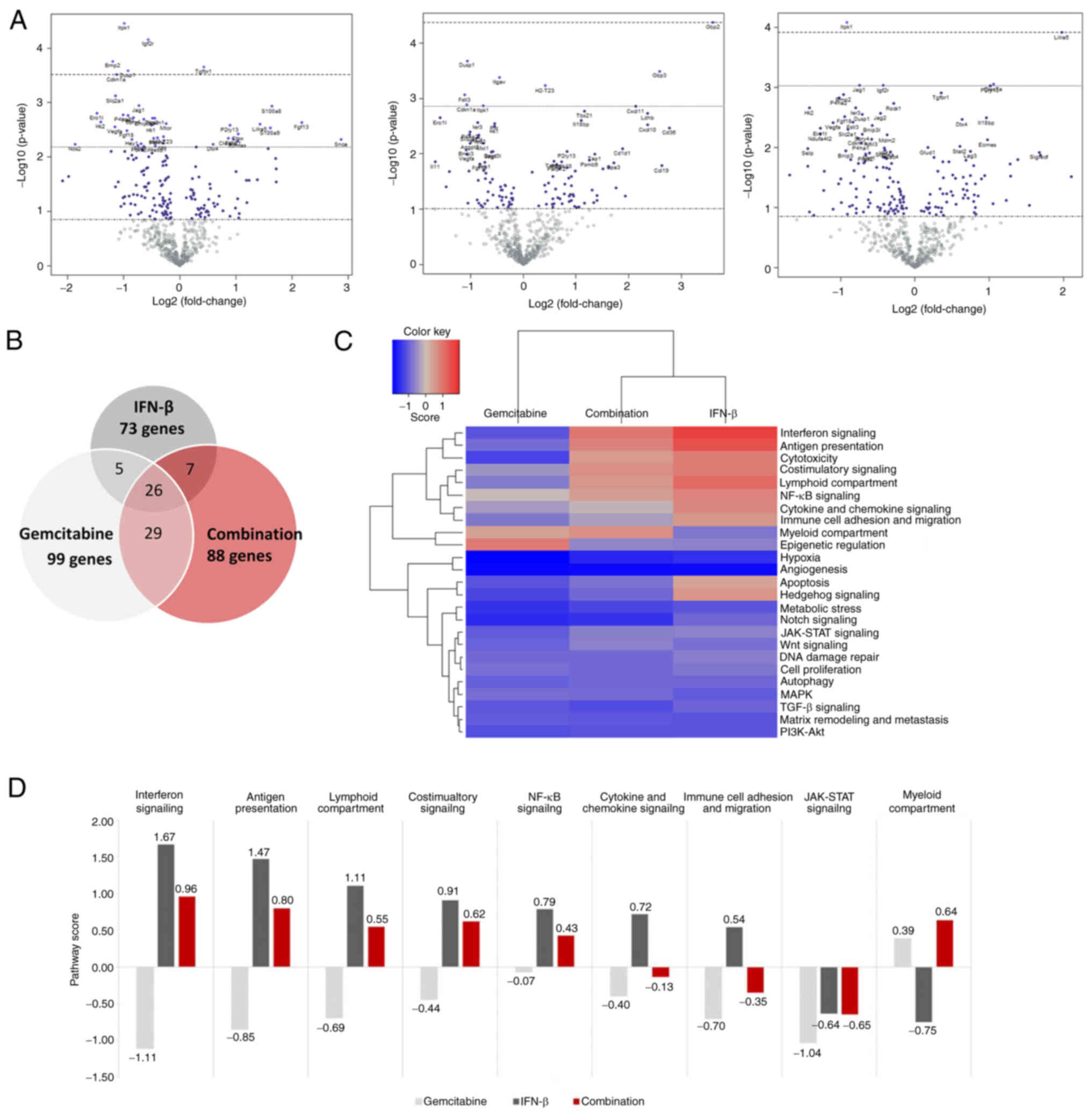
Iwanaszko M and Kimmel M: NF-κB and IRF
pathways: Cross-regulation on target genes promoter level. BMC
Genomics. 16:3072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Solis M, Goubau D, Romieu-Mourez R, Genin
P, Civas A and Hiscott J: Distinct functions of IRF-3 and IRF-7 in
IFN-alpha gene regulation and control of anti-tumor activity in
primary macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1469–1476. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Platanitis E and Decker T: Regulatory
Networks involving STATs, IRFs, and NFκB in inflammation. Front
Immunol. 9:25422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marié I, Durbin JE and Levy DE:
Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-alpha genes by
positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. EMBO J.
17:6660–6669. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sato M, Hata N, Asagiri M, Nakaya T,
Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Positive feedback regulation of type I
IFN genes by the IFN-inducible transcription factor IRF-7. FEBS
Lett. 441:106–110. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deshmukh SK, Tyagi N, Khan MA, Srivastava
SK, Al-Ghadhban A, Dugger K, Carter JE, Singh S and Singh AP:
Gemcitabine treatment promotes immunosuppressive microenvironment
in pancreatic tumors by supporting the infiltration, growth, and
polarization of macrophages. Sci Rep. 8:120002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Smyth MJ
and Kroemer G: Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 15:405–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tempero M, Plunkett W, Ruiz Van Haperen V,
Hainsworth J, Hochster H, Lenzi R and Abbruzzese J: Randomized
phase II comparison of dose-intense gemcitabine: Thirty-minute
infusion and fixed dose rate infusion in patients with pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 21:3402–3408. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller BW, Morton JP, Pinese M, Saturno G,
Jamieson NB, McGhee E, Timpson P, Leach J, McGarry L, Shanks E, et
al: Targeting the LOX/hypoxia axis reverses many of the features
that make pancreatic cancer deadly: Inhibition of LOX abrogates
metastasis and enhances drug efficacy. EMBO Mol Med. 7:1063–1076.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cook N, Frese KK, Bapiro TE, Jacobetz MA,
Gopinathan A, Miller JL, Rao SS, Demuth T, Howat WJ, Jodrell DI and
Tuveson DA: Gamma secretase inhibition promotes hypoxic necrosis in
mouse pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Exp Med. 209:437–444.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Belardelli F and Gresser I: The neglected
role of type I interferon in the T-cell response: Implications for
its clinical use. Immunol Today. 17:369–372. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Belardelli F and Ferrantini M: Cytokines
as a link between innate and adaptive antitumor immunity. Trends
Immunol. 23:201–208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rizza P, Capone I, Moretti F, Proietti E
and Belardelli F: IFN-α as a vaccine adjuvant: Recent insights into
the mechanisms and perspectives for its clinical use. Expert Rev
Vaccines. 10:487–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spaapen RM, Leung MY, Fuertes MB, Kline
JP, Zhang L, Zheng Y, Fu YX, Luo X, Cohen KS and Gajewski TF:
Therapeutic activity of high-dose intratumoral IFN-β requires
direct effect on the tumor vasculature. J Immunol. 193:4254–4260.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schiavoni G, Sistigu A, Valentini M,
Mattei F, Sestili P, Spadaro F, Sanchez M, Lorenzi S, D'Urso MT,
Belardelli F, et al: Cyclophosphamide synergizes with type I
interferons through systemic dendritic cell reactivation and
induction of immunogenic tumor apoptosis. Cancer Res. 71:768–778.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang X, Zhang X, Fu ML, Weichselbaum RR,
Gajewski TF, Guo Y and Fu YX: Targeting the tumor microenvironment
with interferon-β bridges innate and adaptive immune responses.
Cancer Cell. 25:37–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Borden EC: Interferons α and β in cancer:
Therapeutic opportunities from new insights. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
18:219–234. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pepinsky RB, LePage DJ, Gill A,
Chakraborty A, Vaidyanathan S, Green M, Baker DP, Whalley E,
Hochman PS and Martin P: Improved pharmacokinetic properties of a
polyethylene glycol-modified form of interferon-beta-1a with
preserved in vitro bioactivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
297:1059–1066. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ravet E, Lulka H, Gross F, Casteilla L,
Buscail L and Cordelier P: Using lentiviral vectors for efficient
pancreatic cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:315–324. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Endou M, Mizuno M, Nagata T, Tsukada K,
Nakahara N, Tsuno T, Osawa H, Kuno T, Fujita M, Hatano M and
Yoshida J: Growth inhibition of human pancreatic cancer cells by
human interferon-beta gene combined with gemcitabine. Int J Mol
Med. 15:277–283. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ohashi M, Yoshida K, Kushida M, Miura Y,
Ohnami S, Ikarashi Y, Kitade Y, Yoshida T and Aoki K:
Adenovirus-mediated interferon alpha gene transfer induces regional
direct cytotoxicity and possible systemic immunity against
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 93:441–449. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deonarain R, Chan DC, Platanias LC and
Fish EN: Interferon-alpha/beta-receptor interactions: A complex
story unfolding. Curr Pharm Des. 8:2131–2137. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Budhwani M, Mazzieri R and Dolcetti R:
Plasticity of Type I Interferon-mediated responses in cancer
therapy: From Anti-tumor immunity to resistance. Front Oncol.
8:3222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Patel SJ, Sanjana NE, Kishton RJ,
Eidizadeh A, Vodnala SK, Cam M, Gartner JJ, Jia L, Steinberg SM,
Yamamoto TN, et al: Identification of essential genes for cancer
immunotherapy. Nature. 548:537–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weichselbaum RR, Ishwaran H, Yoon T,
Nuyten DS, Baker SW, Khodarev N, Su AW, Shaikh AY, Roach P, Kreike
B, et al: An interferon-related gene signature for DNA damage
resistance is a predictive marker for chemotherapy and radiation
for breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18490–18495. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Erdal E, Haider S, Rehwinkel J, Harris AL
and McHugh PJ: A prosurvival DNA damage-induced cytoplasmic
interferon response is mediated by end resection factors and is
limited by Trex1. Genes Dev. 31:353–369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Post AEM, Smid M, Nagelkerke A, Martens
JWM, Bussink J, Sweep F and Span PN: Interferon-stimulated genes
are involved in Cross-resistance to radiotherapy in
tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:3397–3408.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Benci JL, Xu B, Qiu Y, Wu TJ, Dada H,
Twyman-Saint Victor C, Cucolo L, Lee DSM, Pauken KE, Huang AC, et
al: Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance
program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell. 167:1540–1554.e12.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Terawaki S, Chikuma S, Shibayama S,
Hayashi T, Yoshida T, Okazaki T and Honjo T: IFN-α directly
promotes programmed cell death-1 transcription and limits the
duration of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 186:2772–2779.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pitroda SP, Stack ME, Liu GF, Song SS,
Chen L, Liang H, Parekh AD, Huang X, Roach P, Posner MC, et al:
JAK2 inhibitor SAR302503 abrogates PD-L1 expression and targets
therapy-resistant non-small cell lung cancers. Mol Cancer Ther.
17:732–739. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Doherty MR, Cheon H, Junk DJ, Vinayak S,
Varadan V, Telli ML, Ford JM, Stark GR and Jackson MW:
Interferon-beta represses cancer stem cell properties in
triple-negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:13792–13797. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|