|
1
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rynkeviciene R, Simiene J, Strainiene E,
Stankevicius V, Usinskiene J, Miseikyte Kaubriene E, Meskinyte I,
Cicenas J and Suziedelis K: Non-coding RNAs in glioma. Cancers
(Basel). 11:172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
De Sanctis V, Mazzarella G, Osti MF,
Valeriani M, Alfó M, Salvati M, Banelli E, Tombolini V and Enrici
RM: Radiotherapy and sequential temozolomide compared with
radiotherapy with concomitant and sequential temozolomide in the
treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Anticancer
Drugs. 17:969–975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Taillibert S, Kanner A, Read W,
Steinberg D, Lhermitte B, Toms S, Idbaih A, Ahluwalia MS, Fink K,
et al: Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance
temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in
patients with glioblastoma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
318:2306–2316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Strobel H, Baisch T, Fitzel R, Schilberg
K, Siegelin MD, Karpel-Massler G, Debatin KM and Westhoff MA:
Temozolomide and other alkylating agents in glioblastoma therapy.
Biomedicines. 7:692019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Stevens MF and Bradshaw TD:
Temozolomide: Mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 5:102–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stupp R, Brada M, van den Bent MJ and Tonn
JC: High-grade glioma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 25(Suppl 3):
iii93–iii101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee SY: Temozolomide resistance in
glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis. 3:198–210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanzawa T, Bedwell J, Kondo Y, Kondo S and
Germano IM: Inhibition of DNA repair for sensitizing resistant
glioma cells to temozolomide. J Neurosurg. 99:1047–1052. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jiang G, Li LT, Xin Y, Zhang L, Liu YQ and
Zheng JN: Strategies to improve the killing of tumors using
temozolomide: Targeting the DNA repair protein MGMT. Curr Med Chem.
19:3886–3892. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Perazzoli G, Prados J, Ortiz R, Caba O,
Cabeza L, Berdasco M, Gónzalez B and Melguizo C: Temozolomide
resistance in glioblastoma cell lines: Implication of MGMT, MMR,
P-glycoprotein and CD133 expression. PLoS One. 10:e01401312015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang JB, Svilar D, Trivedi RN, Wang XH,
Goellner EM, Moore B, Hamilton RL, Banze LA, Brown AR and Sobol RW:
N-methylpurine DNA glycosylase and DNA polymerase beta modulate BER
inhibitor potentiation of glioma cells to temozolomide. Neuro
Oncol. 13:471–486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
ENCODE Project Consortium: An integrated
encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature.
489:57–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Comings DE: The structure and function of
chromatin. Adv Hum Genet. 3:237–431. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hombach S and Kretz M: Non-coding RNAs:
Classification, biology and functioning. Non-coding RNAs in
Colorectal Cancer. Slaby O and Calin GA: Springer International
Publishing; Cham: pp. 3–17. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ling H, Vincent K, Pichler M, Fodde R,
Berindan-Neagoe I, Slack FJ and Calin GA: Junk DNA and the long
non-coding RNA twist in cancer genetics. Oncogene. 34:5003–5011.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer
A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, Guernec G, Martin D, Merkel A, Knowles DG,
et al: The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs:
Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome
Res. 22:1775–1789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmitz SU, Grote P and Herrmann BG:
Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2491–2509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu B and Wang S: Angio-LncRs: LncRNAs that
regulate angiogenesis and vascular disease. Theranostics.
8:3654–3675. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 34:9–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han L, Zhang K, Shi Z, Zhang J, Zhu J, Zhu
S, Zhang A, Jia Z, Wang G, Yu S, et al: LncRNA profile of
glioblastoma reveals the potential role of lncRNAs in contributing
to glioblastoma pathogenesis. Int J Oncol. 40:2004–2012.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Zhang Z, Chen Z and Deng L:
Integrating multiple heterogeneous networks for novel
LncRNA-disease association inference. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol
Bioinform. 16:396–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M and Glavač D:
Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers.
2017:72439682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mahinfar P, Baradaran B, Davoudian S,
Vahidian F, Cho WC and Mansoori B: Long Non-coding RNAs in
multidrug resistance of glioblastoma. Genes (Basel). 12:4552021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang Y, Guo H, Tong T, Xie F, Qin X, Wang
X, Chen W and Zhang J: lncRNA lnc-POP11 upregulated by VN1R5
promotes cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma through interaction with MCM5. Mol Ther. 30:448–467.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen KY, Zhu SG, He JW and Duan XP: LncRNA
CRNDE is involved in radiation resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma via modulating the SP1/PDK1 axis. Neoplasma.
211230N18532022.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Xu S, Li W, Lu Y, Zhou Y, Xie M, Luo
Y, Cao Y, He Y, Zeng T and Ling H: lncRNAs as hallmarks for
individualized treatment of gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 22:1440–1457. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ye X, Wang LP, Han C, Hu H, Ni CM, Qiao
GL, Ouyang L and Ni JS: Increased m6A modification of
lncRNA DBH-AS1 suppresses pancreatic cancer growth and gemcitabine
resistance via the miR-3163/USP44 axis. Ann Transl Med. 10:3042022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jiang X, Li H, Fang Y and Xu C: LncRNA
PVT1 contributes to invasion and doxorubicin resistance of bladder
cancer cells through promoting MDM2 expression and AURKB-mediated
p53 ubiquitination. Environ Toxicol. 37:1495–1508. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng M, Wang Q, Chen L, Zhao D, Tang J,
Xu J and He Z: LncRNA UCA1/miR-182-5p/MGMT axis modulates glioma
cell sensitivity to temozolomide through MGMT-related DNA damage
pathways. Hum Pathol. 123:59–73. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JK, Tsang AC, Lee D,
Man VO, Lui WM, Wong ST and Leung GK: Long non-coding RNA
expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma.
Neurobiol Dis. 48:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin X, Zhuang S, Chen X, Du J, Zhong L,
Ding J, Wang L, Yi J, Hu G, Tang G, et al: lncRNA ITGB8-AS1
functions as a ceRNA to promote colorectal cancer growth and
migration through integrin-mediated focal adhesion signaling. Mol
Ther. 30:688–702. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li DQ, Ding YR, Che JH, Su Z, Yang WZ, Xu
L, Li YJ, Wang HH and Zhou WY: Tumor suppressive lncRNA MEG3 binds
to EZH2 and enhances CXCL3 methylation in gallbladder cancer.
Neoplasma. 69:538–549. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan D, Guo T, Zhu D, Ge H, Zhao Y, Huang
A, Wang X, Cao X, He C, Qian H and Yu H: Exosomal lncRNA ATB
derived from ovarian cancer cells promotes angiogenesis via
regulating miR-204-3p/TGFβR2 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 14:327–337.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Yan Y, Xu Z, Li Z, Sun L and Gong Z: An
insight into the increasing role of LncRNAs in the pathogenesis of
gliomas. Front Mol Neurosci. 10:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng Z, Liu C and Wu M: New insights into
long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol Cancer.
17:612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li J, Bian EB, He XJ, Ma CC, Zong G, Wang
HL and Zhao B: Epigenetic repression of long non-coding RNA MEG3
mediated by DNMT1 represses the p53 pathway in gliomas. Int J
Oncol. 48:723–733. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zeng H, Xu N, Liu Y, Liu B, Yang Z, Fu Z,
Lian C and Guo H: Genomic profiling of long non-coding RNA and mRNA
expression associated with acquired temozolomide resistance in
glioblastoma cells. Int J Oncol. 51:445–455. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Li XD, Fu Z, Zhou Y, Huang X and
Jiang X: Long non-coding RNA LINC00473/miR-195-5p promotes glioma
progression via YAP1-TEAD1-Hippo signaling. Int J Oncol.
56:508–521. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lei W, Wang ZL, Feng HJ, Lin XD, Li CZ and
Fan D: Long non-coding RNA SNHG12promotes the proliferation and
migration of glioma cells by binding to HuR. Int J Oncol.
53:1374–1384. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fang K, Liu P, Dong S, Guo Y, Cui X, Zhu
X, Li X, Jiang L, Liu T and Wu Y: Magnetofection based on
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-mediated low lncRNA
HOTAIR expression decreases the proliferation and invasion of
glioma stem cells. Int J Oncol. 49:509–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu ZZ, Tian YF, Wu H, Ouyang SY and Kuang
WL: LncRNA H19 promotes glioma angiogenesis through
miR-138/HIF-1α/VEGF axis. Neoplasma. 67:111–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jia P, Cai H, Liu X, Chen J, Ma J, Wang P,
Liu Y, Zheng J and Xue Y: Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma
angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated
endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett.
381:359–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Yin H and
Han B: CRNDE, a long-noncoding RNA, promotes glioma cell growth and
invasion through mTOR signaling. Cancer Lett. 367:122–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zheng J, Liu X, Wang P, Xue Y, Ma J, Qu C
and Liu Y: CRNDE promotes malignant progression of glioma by
attenuating miR-384/PIWIL4/STAT3 axis. Mol Ther. 24:1199–1215.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shree B, Tripathi S and Sharma V:
Transforming growth factor-beta-regulated LncRNA-MUF promotes
invasion by modulating the miR-34a snail1 axis in glioblastoma
multiforme. Front Oncol. 11:7887552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li J, Zhang M, An G and Ma Q: LncRNA TUG1
acts as a tumor suppressor in human glioma by promoting cell
apoptosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 241:644–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Arscott WT, Tandle AT, Zhao S, Shabason
JE, Gordon IK, Schlaff CD, Zhang G, Tofilon PJ and Camphausen KA:
Ionizing radiation and glioblastoma exosomes: Implications in tumor
biology and cell migration. Transl Oncol. 6:638–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Skog J, Würdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer
DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky
AM and Breakefield XO: Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and
proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic
biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 10:1470–1476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bian EB, Chen EF, Xu YD, Yang ZH, Tang F,
Ma CC, Wang HL and Zhao B: Exosomal lncRNA-ATB activates astrocytes
that promote glioma cell invasion. Int J Oncol. 54:713–721.
2019.
|
|
53
|
Lang HL, Hu GW, Chen Y, Liu Y, Tu W, Lu
YM, Wu L and Xu GH: Glioma cells promote angiogenesis through the
release of exosomes containing long non-coding RNA POU3F3. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:959–972. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li MY, Yang P, Liu YW, Zhang CB, Wang KY,
Wang YY, Yao K, Zhang W, Qiu XG, Li WB, et al: Low c-Met expression
levels are prognostic for and predict the benefits of temozolomide
chemotherapy in malignant gliomas. Sci Rep. 6:211412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu P, Cai J, Chen Q, Han B, Meng X, Li Y,
Li Z, Wang R, Lin L, Duan C, et al: Lnc-TALC promotes
O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression via regulating
the c-Met pathway by competitively binding with miR-20b-3p. Nat
Commun. 10:20452019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Wesolowska A, Kwiatkowska A, Slomnicki L,
Dembinski M, Master A, Sliwa M, Franciszkiewicz K, Chouaib S and
Kaminska B: Microglia-derived TGF-beta as an important regulator of
glioblastoma invasion-an inhibition of TGF-beta-dependent effects
by shRNA against human TGF-beta type II receptor. Oncogene.
27:918–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Han J, Alvarez-Breckenridge CA, Wang QE
and Yu J: TGF-β signaling and its targeting for glioma treatment.
Am J Cancer Res. 5:945–955. 2015.
|
|
58
|
Miyazawa K and Miyazono K: Regulation of
TGF-β family signaling by inhibitory smads. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 9:a0220952017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Brunen D, Willems SM, Kellner U, Midgley
R, Simon I and Bernards R: TGF-β: An emerging player in drug
resistance. Cell Cycle. 12:2960–2968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Oshimori N, Oristian D and Fuchs E: TGF-β
promotes heterogeneity and drug resistance in squamous cell
carcinoma. Cell. 160:963–976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nie E, Jin X, Miao F, Yu T, Zhi T, Shi Z,
Wang Y, Zhang J, Xie M and You Y: TGF-β1 modulates temozolomide
resistance in glioblastoma via altered microRNA processing and
elevated MGMT. Neuro Oncol. 23:435–446. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
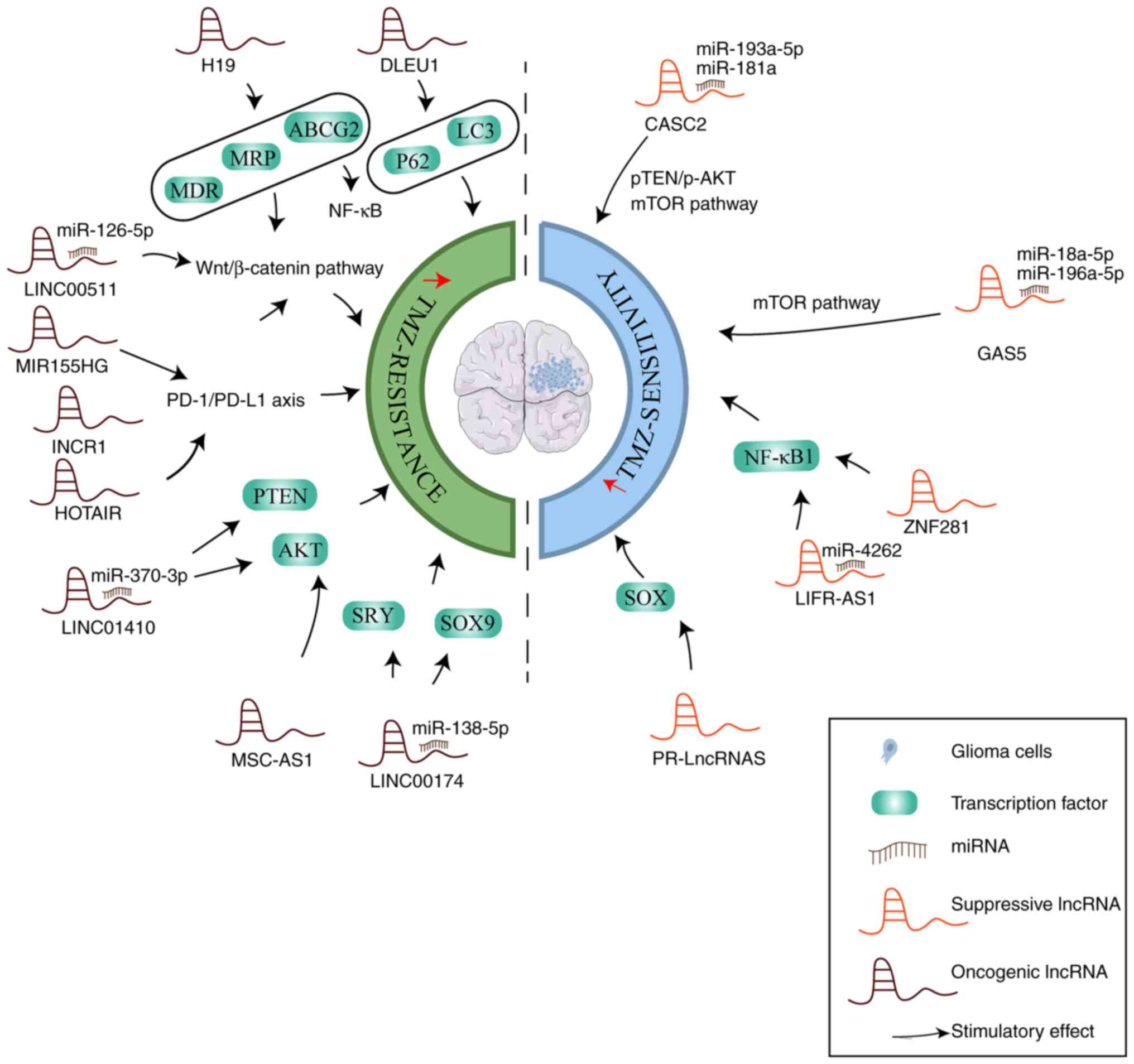
Fu T, Yang Y, Mu Z, Sun R, Li X and Dong
J: Silencing lncRNA LINC01410 suppresses cell viability yet
promotes apoptosis and sensitivity to temozolomide in glioblastoma
cells by inactivating PTEN/AKT pathway via targeting miR-370-3p.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 43:680–692. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Peng L, Chen Z, Chen Y, Wang X and Tang N:
MIR155HG is a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune
infiltration and immune checkpoint molecules expression in multiple
cancers. Cancer Med. 8:7161–7173. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
He X, Sheng J, Yu W, Wang K, Zhu S and Liu
Q: LncRNA MIR155HG promotes temozolomide resistance by activating
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via binding to PTBP1 in glioma. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 41:1271–1284. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Li C, Feng S and Chen L: MSC-AS1 knockdown
inhibits cell growth and temozolomide resistance by regulating
miR-373-3p/CPEB4 axis in glioma through PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Cell
Biochem. 476:699–713. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Boustani MR, Mehrabi F, Yahaghi E,
Khoshnood RJ, Shahmohammadi M, Darian EK and Goudarzi PK: Somatic
CPEB4 and CPEB1 genes mutations spectrum on the prognostic
predictive accuracy in patients with high-grade glioma and their
clinical significance. J Neurol Sci. 363:80–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gu N, Wang X, Di Z, Xiong J, Ma Y, Yan Y,
Qian Y, Zhang Q and Yu J: Silencing lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 inhibits
proliferation, migration, invasion and drug resistance of
drug-resistant glioma cells and promotes their apoptosis via
microRNA-98-5p/CPEB4 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 11:10266–10283. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Su YK, Lin JW, Shih JW, Chuang HY, Fong
IH, Yeh CT and Lin CM: Targeting BC200/miR218-5p signaling axis for
overcoming temozolomide resistance and suppressing glioma stemness.
Cells. 9:18592020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Ding J, Zhang L, Chen S, Cao H, Xu C and
Wang X: lncRNA CCAT2 enhanced resistance of glioma cells against
chemodrugs by disturbing the normal function of miR-424. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:1431–1445. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li Z, Meng X, Wu P, Zha C, Han B, Li L,
Sun N, Qi T, Qin J, Zhang Y, et al: Glioblastoma cell-derived
lncRNA-containing exosomes induce microglia to produce complement
C5, promoting chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Immunol Res.
9:1383–1399. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li B, Zhao H, Song J, Wang F and Chen M:
LINC00174 down-regulation decreases chemoresistance to temozolomide
in human glioma cells by regulating miR-138-5p/SOX9 axis. Hum Cell.
33:159–174. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jia L, Tian Y, Chen Y and Zhang G: The
silencing of LncRNA-H19 decreases chemoresistance of human glioma
cells to temozolomide by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Onco Targets Ther.
11:313–321. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Jiang P, Wang P, Sun X, Yuan Z, Zhan R, Ma
X and Li W: Knockdown of long noncoding RNA H19 sensitizes human
glioma cells to temozolomide therapy. Onco Targets Ther.
9:3501–3509. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou L, Huang X, Zhang Y, Wang L, Li H and
Huang H: PSMG3-AS1 enhances glioma resistance to temozolomide via
stabilizing c-Myc in the nucleus. Brain Behav. 12:e25312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang S, Guo S, Liang C and Lian M: Long
intergenic noncoding RNA 00021 promotes glioblastoma temozolomide
resistance by epigenetically silencing p21 through Notch pathway.
IUBMB Life. 72:1747–1756. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cui B, Li B, Liu Q and Cui Y: lncRNA CCAT1
promotes glioma tumorigenesis by sponging miR-181b. J Cell Biochem.
118:4548–4557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang Y, Yi K, Liu X, Tan Y, Jin W, Li Y,
Zhou J, Wang F and Kang C: HOTAIR up-regulation activates NF-κB to
induce immunoescape in gliomas. Front Immunol. 12:7854632021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Wang W, Han S, Gao W, Feng Y, Li K and Wu
D: Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 confers gliomas resistance to
temozolomide and enhances cell growth by retrieving PIM1 from
miR-761. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 42:695–708. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Wang Y, Shan A, Zhou Z, Li W, Xie L, Du B
and Lei B: LncRNA TCONS_00004099-derived microRNA regulates
oncogenesis through PTPRF in gliomas. Ann Transl Med. 9:10232021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dong ZQ, Guo ZY and Xie J: The lncRNA
EGFR-AS1 is linked to migration, invasion and apoptosis in glioma
cells by targeting miR-133b/RACK1. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1092922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen M, Cheng Y, Yuan Z, Wang F, Yang L
and Zhao H: NCK1-AS1 increases drug resistance of glioma cells to
temozolomide by modulating miR-137/TRIM24. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 35:101–108. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Lu Y, Tian M, Liu J and Wang K: LINC00511
facilitates temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma cells via
sponging miR-126-5p and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J
Biochem Mol Toxicol. 35:e228482021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Tomar VS, Patil V and Somasundaram K:
Temozolomide induces activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
glioma cells via PI3K/Akt pathway: Implications in glioma therapy.
Cell Biol Toxicol. 36:273–278. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Liu H, Liu Z, Jiang B, Peng R, Ma Z and Lu
J: SOX9 overexpression promotes glioma metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:205–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos
B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ,
Berman SH, et al: The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma.
Cell. 155:462–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chen Q, Cai J, Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu M, Yang
J, Zhou J, Kang C, Li M and Jiang C: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1,
regulated by the EGFR pathway, contributes to glioblastoma
progression through the WNT/β-catenin pathway by scaffolding EZH2.
Clin Cancer Res. 24:684–695. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Knizhnik AV, Roos WP, Nikolova T, Quiros
S, Tomaszowski KH, Christmann M and Kaina B: Survival and death
strategies in glioma cells: Autophagy, senescence and apoptosis
triggered by a single type of temozolomide-induced DNA damage. PLoS
One. 8:e556652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Linder S, Wiesner C and Himmel M:
Degrading devices: Invadosomes in proteolytic cell invasion. Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:185–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ulasov IV, Mijanovic O, Savchuk S,
Gonzalez-Buendia E, Sonabend A, Xiao T, Timashev P and Lesniak MS:
TMZ regulates GBM stemness via MMP14-DLL4-Notch3 pathway. Int J
Cancer. 146:2218–2228. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wen Q, Chen Z, Chen Z, Chen J, Wang R,
Huang C and Yuan W: EphA2 affects the sensitivity of oxaliplatin by
inducing EMT in oxaliplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 8:47998–48011. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gaianigo N, Melisi D and Carbone C: EMT
and treatment resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel).
9:1222017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Peng F, Fan H, Li S, Peng C and Pan X:
MicroRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition process of cancer:
potential targets for chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 22:75262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li Z, Li M, Xia P and Lu Z: HOTTIP
mediated therapy resistance in glioma cells involves regulation of
EMT-related miR-10b. Front Oncol. 12:8735612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Loilome W, Joshi AD, ap Rhys CM,
Piccirillo S, Vescovi AL, Gallia GL and Riggins GJ: Glioblastoma
cell growth is suppressed by disruption of fibroblast growth factor
pathway signaling. J Neurooncol. 94:359–366. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Snuderl M, Fazlollahi L, Le LP, Nitta M,
Zhelyazkova BH, Davidson CJ, Akhavanfard S, Cahill DP, Aldape KD,
Betensky RA, et al: Mosaic amplification of multiple receptor
tyrosine kinase genes in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 20:810–817.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Raoof S, Ruddy D, Timonia D, Damon L,
Engelman J and Hata A: Abstract A142: Targeting FGFR to overcome
EMT-related resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.
Mol Cancer Ther. 17(1 Suppl): A1422018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zhang L, Zhang W, Li Y, Alvarez A, Li Z,
Wang Y, Song L, Lv D, Nakano I, Hu B, et al: SHP-2-upregulated ZEB1
is important for PDGFRα-driven glioma epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion in mice and humans. Oncogene. 35:5641–5652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Brichkina A, Nguyen NT, Baskar R, Wee S,
Gunaratne J, Robinson RC and Bulavin DV: Proline isomerisation as a
novel regulatory mechanism for p38MAPK activation and functions.
Cell Death Differ. 23:1592–1601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Park CM, Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Lee HC, Kim MS,
Lee SH, Park IC, Rhee CH and Hong SI: Ionizing radiation enhances
matrix metalloproteinase-2 secretion and invasion of glioma cells
through Src/epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated p38/Akt and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. Cancer Res.
66:8511–8519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Cong ZX, Wang HD, Zhou Y, Wang JW, Pan H,
Zhang DD, Zhang L and Zhu L: Temozolomide and irradiation combined
treatment-induced Nrf2 activation increases chemoradiation
sensitivity in human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol. 116:41–48.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Ma L, Liu J, Zhang X, Qi J, Yu W and Gu Y:
p38 MAPK-dependent Nrf2 induction enhances the resistance of glioma
cells against TMZ. Med Oncol. 32:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O,
Link W and Leal JF: The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer,
therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:187–198.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Harder BG, Peng S, Sereduk CP, Sodoma AM,
Kitange GJ, Loftus JC, Sarkaria JN and Tran NL: Inhibition of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by PX-866 suppresses
temozolomide-induced autophagy and promotes apoptosis in
glioblastoma cells. Mol Med. 25:492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Pridham KJ, Shah F, Hutchings KR, Sheng
KL, Guo S, Liu M, Kanabur P, Lamouille S, Lewis G, Morales M, et
al: Connexin 43 confers chemoresistance through activating PI3K.
Oncogenesis. 11:22022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zając A, Sumorek-Wiadro J, Langner E,
Wertel I, Maciejczyk A, Pawlikowska-Pawlęga B, Pawelec J, Wasiak M,
Hułas-Stasiak M, Bądziul D, et al: Involvement of PI3K pathway in
glioma cell resistance to temozolomide treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
22:51552021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Zhang LH, Yin AA, Cheng JX, Huang HY, Li
XM, Zhang YQ, Han N and Zhang X: TRIM24 promotes glioma progression
and enhances chemoresistance through activation of the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Oncogene. 34:600–610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Cao X, Hou J, An Q, Assaraf YG and Wang X:
Towards the overcoming of anticancer drug resistance mediated by
p53 mutations. Drug Resist Updat. 49:1006712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Hientz K, Mohr A, Bhakta-Guha D and
Efferth T: The role of p53 in cancer drug resistance and targeted
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 8:8921–8946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
109
|
Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO:
Abrogation of the Chk1-mediated G(2) checkpoint pathway potentiates
temozolomide-induced toxicity in a p53-independent manner in human
glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 61:5843–5849. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Holder SL and Abdulkadir SA: PIM1 kinase
as a target in prostate cancer: Roles in tumorigenesis, castration
resistance, and docetaxel resistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
14:105–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Wang BW, Huang CH, Liu LC, Cheng FJ, Wei
YL, Lin YM, Wang YF, Wei CT, Chen Y, Chen YJ and Huang WC: Pim1
kinase inhibitors exert anti-cancer activity against HER2-positive
breast cancer cells through downregulation of HER2. Front
Pharmacol. 12:6146732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Trigg RM, Lee LC, Prokoph N, Jahangiri L,
Reynolds CP, Amos Burke GA, Probst NA, Han M, Matthews JD, Lim HK,
et al: The targetable kinase PIM1 drives ALK inhibitor resistance
in high-risk neuroblastoma independent of MYCN status. Nat Commun.
10:54282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wein L and Loi S: Mechanisms of resistance
of chemotherapy in early-stage triple negative breast cancer
(TNBC). Breast. 34(Suppl 1): S27–S30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Bobustuc GC, Kassam AB, Rovin RA, Jeudy S,
Smith JS, Isley B, Singh M, Paranjpe A, Srivenugopal KS and Konduri
SD: MGMT inhibition in ER positive breast cancer leads to CDC2,
TOP2A, AURKB, CDC20, KIF20A, Cyclin A2, cyclin B2, cyclin D1, ERα
and survivin inhibition and enhances response to temozolomide.
Oncotarget. 9:29727–29742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Song Z, Pan Y, Ling G, Wang S, Huang M,
Jiang X and Ke Y: Escape of U251 glioma cells from
temozolomide-induced senescence was modulated by CDK1/survivin
signaling. Am J Transl Res. 9:2163–2180. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Reich TR, Schwarzenbach C, Vilar JB, Unger
S, Mühlhäusler F, Nikolova T, Poplawski A, Baymaz HI, Beli P,
Christmann M and Tomicic MT: Localization matters: Nuclear-trapped
survivin sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by elevating
cellular senescence and impairing homologous recombination. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 78:5587–5604. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Li Z, Wu X, Zhao Y, Xiao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang
T, Li H, Sha F, Wang Y, Deng L and Ma X: Clinical benefit of
neoadjuvant anti-PD-1/PD-L1 utilization among different tumors.
MedComm (2020). 2:60–68. 2021.
|
|
118
|
Zhou Y, Miao J, Wu H, Tang H, Kuang J,
Zhou X, Peng Y, Hu D, Shi D, Deng W, et al: PD-1 and PD-L1
expression in 132 recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: The
correlation with anemia and outcomes. Oncotarget. 8:51210–51223.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Qin T, Zeng YD, Qin G, Xu F, Lu JB, Fang
WF, Xue C, Zhan JH, Zhang XK, Zheng QF, et al: High PD-L1
expression was associated with poor prognosis in 870 Chinese
patients with breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:33972–33981. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Ge J,
Xiang B, Wu X, Ma J, Zhou M, Li X, et al: Role of the tumor
microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol
Cancer. 18:102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Kathuria H, Millien G, McNally L, Gower
AC, Tagne JB, Cao Y and Ramirez MI: NKX21-AS1 negatively regulates
CD274/PD-L1, cell-cell interaction genes, and limits human lung
carcinoma cell migration. Sci Rep. 8:144182018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Tian Y, Li L, Lin G, Wang Y, Wang L, Zhao
Q, Hu Y, Yong H, Wan Y and Zhang Y: lncRNA SNHG14 promotes
oncogenesis and immune evasion in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma by
sequestering miR-152-3p. Leuk Lymphoma. 62:1574–1584. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Dang S, Malik A, Chen J, Qu J, Yin K, Cui
L and Gu M: LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to immuno-escape of gastric
cancer through targeting miR141/PD-L1. Onco Targets Ther.
13:8547–8556. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
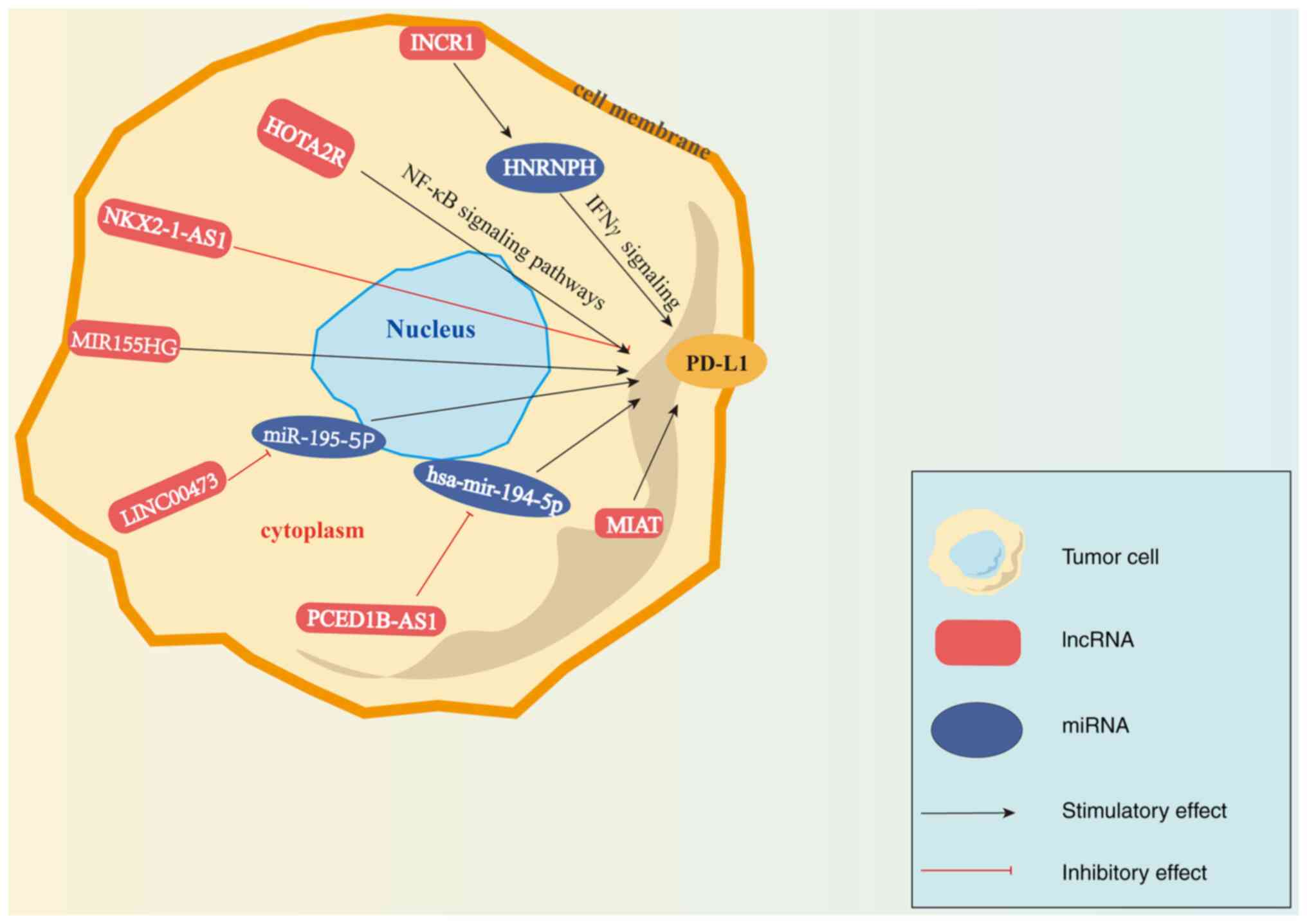
|
Zhou WY, Zhang MM, Liu C, Kang Y, Wang JO
and Yang XH: Long noncoding RNA LINC00473 drives the progression of
pancreatic cancer via upregulating programmed death-ligand 1 by
sponging microRNA-195-5p. J Cell Physiol. 234:23176–23189. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Fan F, Chen K, Lu X, Li A, Liu C and Wu B:
Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1 via sponging
hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 15:444–458. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Peng L, Chen Y, Ou Q, Wang X and Tang N:
LncRNA MIAT correlates with immune infiltrates and drug reactions
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 89:1070712020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Mineo M, Lyons SM, Zdioruk M, von
Spreckelsen N, Ferrer-Luna R, Ito H, Alayo QA, Kharel P, Giantini
Larsen A, Fan WY, et al: Tumor interferon signaling is regulated by
a lncRNA INCR1 transcribed from the PD-L1 locus. Mol Cell.
78:1207–1223.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Wagle N, Nguyen M, Carrillo J, Truong J,
Dobrawa L and Kesari S: Characterization of molecular pathways for
targeting therapy in glioblastoma. Chin Clin Oncol. 9:772020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Miyazaki T, Ishikawa E, Matsuda M, Sugii
N, Kohzuki H, Akutsu H, Sakamoto N, Takano S and Matsumura A:
Infiltration of CD163-positive macrophages in glioma tissues after
treatment with anti-PD-L1 antibody and role of PI3Kγ inhibitor as a
combination therapy with anti-PD-L1 antibody in in vivo model using
temozolomide-resistant murine glioma-initiating cells. Brain Tumor
Pathol. 37:41–49. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Roth P, Valavanis A and Weller M:
Long-term control and partial remission after initial
pseudoprogression of glioblastoma by anti-PD-1 treatment with
nivolumab. Neuro Oncol. 19:454–456. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zeng J, See AP, Phallen J, Jackson CM,
Belcaid Z, Ruzevick J, Durham N, Meyer C, Harris TJ, Albesiano E,
et al: Anti-PD-1 blockade and stereotactic radiation produce
long-term survival in mice with intracranial gliomas. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 86:343–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Jan CI, Tsai WC, Harn HJ, Shyu WC, Liu MC,
Lu HM, Chiu SC and Cho DY: Predictors of response to autologous
dendritic cell therapy in glioblastoma multiforme. Front Immunol.
9:7272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H, Wang J, Luo T and
Jiang Y: Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol.
12:712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Vargas-Toscano A, Nickel AC, Li G, Kamp
MA, Muhammad S, Leprivier G, Fritsche E, Barker RA, Sabel M,
Steiger HJ, et al: Rapalink-1 targets glioblastoma stem cells and
acts synergistically with tumor treating fields to reduce
resistance against temozolomide. Cancers (Basel). 12:38592020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Zou Y, Chen M, Zhang S, Miao Z, Wang J, Lu
X and Zhao X: TRPC5-induced autophagy promotes the TMZ-resistance
of glioma cells via the CAMMKβ/AMPKα/mTOR pathway. Oncol Rep.
41:3413–3423. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Jiang C, Shen F, Du J, Fang X, Li X, Su J,
Wang X, Huang X and Liu Z: Upregulation of CASC2 sensitized glioma
to temozolomide cytotoxicity through autophagy inhibition by
sponging miR-193a-5p and regulating mTOR expression. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:844–850. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Liu Q, Yu W, Zhu S, Cheng K, Xu H, Lv Y,
Long X, Ma L, Huang J, Sun S and Wang K: Long noncoding RNA GAS5
regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma
cells by negatively regulating miR-18a-5p. J Cell Physiol.
234:757–768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhao X, Liu Y, Zheng J, Liu X, Chen J, Liu
L, Wang P and Xue Y: GAS5 suppresses malignancy of human glioma
stem cells via a miR-196a-5p/FOXO1 feedback loop. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1864:1605–1617. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Huo JF and Chen XB: Long noncoding RNA
growth arrest-specific 5 facilitates glioma cell sensitivity to
cisplatin by suppressing excessive autophagy in an mTOR-dependent
manner. J Cell Biochem. 120:6127–6136. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Li G, Cai Y, Wang C, Huang M and Chen J:
LncRNA GAS5 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and
apoptosis of brain glioma cells through targeting GSTM3 expression.
The effect of LncRNA GAS5 on glioma cells. J Neurooncol.
143:525–536. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Yan Y, Xu Z, Dai S, Qian L, Sun L and Gong
Z: Targeting autophagy to sensitive glioma to temozolomide
treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Liao Y, Shen L, Zhao H, Liu Q, Fu J, Guo
Y, Peng R and Cheng L: LncRNA CASC2 interacts with miR-181a to
modulate glioma growth and resistance to TMZ through PTEN pathway.
J Cell Biochem. 118:1889–1899. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Jing H and Lee S: NF-κB in cellular
senescence and cancer treatment. Mol Cells. 37:189–195. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Sánchez Y, Segura V, Marín-Béjar O, Athie
A, Marchese FP, González J, Bujanda L, Guo S, Matheu A and Huarte
M: Genome-wide analysis of the human p53 transcriptional network
unveils a lncRNA tumour suppressor signature. Nat Commun.
5:58122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Torres-Bayona S, Aldaz P, Auzmendi-Iriarte
J, Saenz-Antoñanzas A, Garcia I, Arrazola M, Gerovska D, Undabeitia
J, Querejeta A, Egaña L, et al: PR-LncRNA signature regulates
glioma cell activity through expression of SOX factors. Sci Rep.
8:127462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Ding H, Cui L and Wang C: Long noncoding
RNA LIFR-AS1 suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion and
promotes apoptosis through modulating miR-4262/NF-κB pathway in
glioma. Neurol Res. 43:210–219. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Li XT, Li JC, Feng M, Zhou YX and Du ZW:
Novel lncRNA-ZNF281 regulates cell growth, stemness and invasion of
glioma stem-like U251s cells. Neoplasma. 66:118–127. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K, Brada M,
Berger M, Pfister SM, Nishikawa R, Rosenthal M, Wen PY, Stupp R and
Reifenberger G: Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150172015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Yang W and Gao Y: Translesion and repair
DNA polymerases: Diverse structure and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem.
87:239–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Bailly V, Lamb J, Sung P, Prakash S and
Prakash L: Specific complex formation between yeast RAD6 and RAD18
proteins: A potential mechanism for targeting RAD6
ubiquitin-conjugating activity to DNA damage sites. Genes Dev.
8:811–820. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Wojtaszek JL, Chatterjee N, Najeeb J,
Ramos A, Lee M, Bian K, Xue JY, Fenton BA, Park H, Li D, et al: A
small molecule targeting mutagenic translesion synthesis improves
chemotherapy. Cell. 178:152–159.e11. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Peng C, Chen Z, Wang S, Wang HW, Qiu W,
Zhao L, Xu R, Luo H, Chen Y, Chen D, et al: The error-prone DNA
polymerase κ promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma
through Rad17-dependent activation of ATR-Chk1 signaling. Cancer
Res. 76:2340–2353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Vassel FM, Bian K, Walker GC and Hemann
MT: Rev7 loss alters cisplatin response and increases drug efficacy
in chemotherapy-resistant lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:28922–28924. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Wu B, Wang H, Zhang L, Sun C, Li H, Jiang
C and Liu X: High expression of RAD18 in glioma induces
radiotherapy resistance via down-regulating P53 expression. Biomed
Pharmacother. 112:1085552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Rezaei O, Tamizkar KH, Sharifi G, Taheri M
and Ghafouri-Fard S: Emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in the
pathobiology of glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 10:6258842021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Luo J, Bai R, Liu Y, Bi H, Shi X and Qu C:
Long non-coding RNA ATXN8OS promotes ferroptosis and inhibits the
temozolomide-resistance of gliomas through the ADAR/GLS2 pathway.
Brain Res Bull. 186:27–37. 2022.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Gao XY, Zang J, Zheng MH, Zhang YF, Yue
KY, Cao XL, Cao Y, Li XX, Han H, Jiang XF and Liang L: Temozolomide
treatment induces HMGB1 to promote the formation of glioma stem
cells via the TLR2/NEAT1/Wnt pathway in glioblastoma. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 9:6208832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Wang C, Chen Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Liu Y, Li
Y, Chen H, Fan C, Wu D and Yang J: Inhibition of COX-2, mPGES-1 and
CYP4A by isoliquiritigenin blocks the angiogenic Akt signaling in
glioma through ceRNA effect of miR-194-5p and lncRNA NEAT1. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 38:3712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|