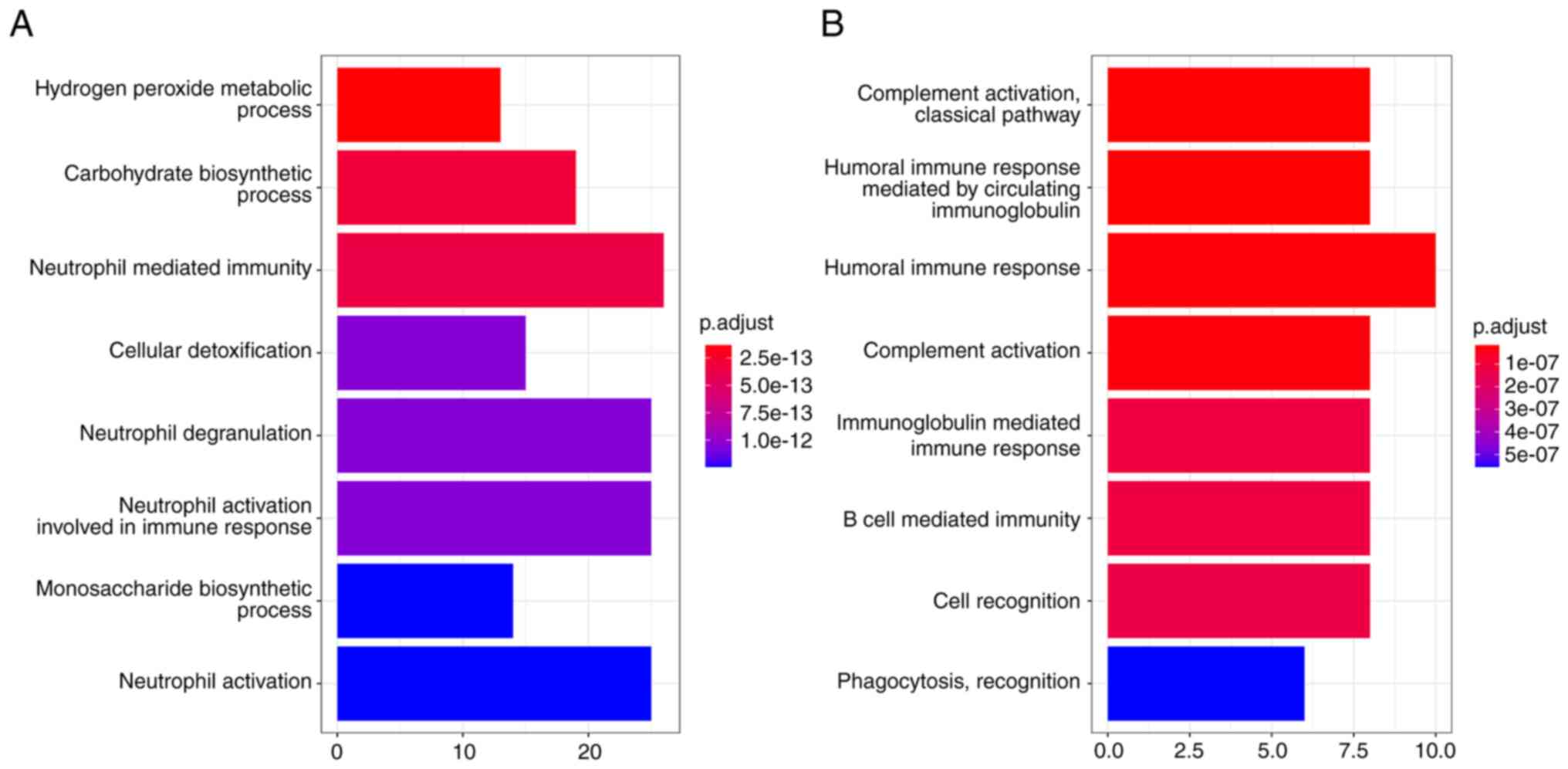
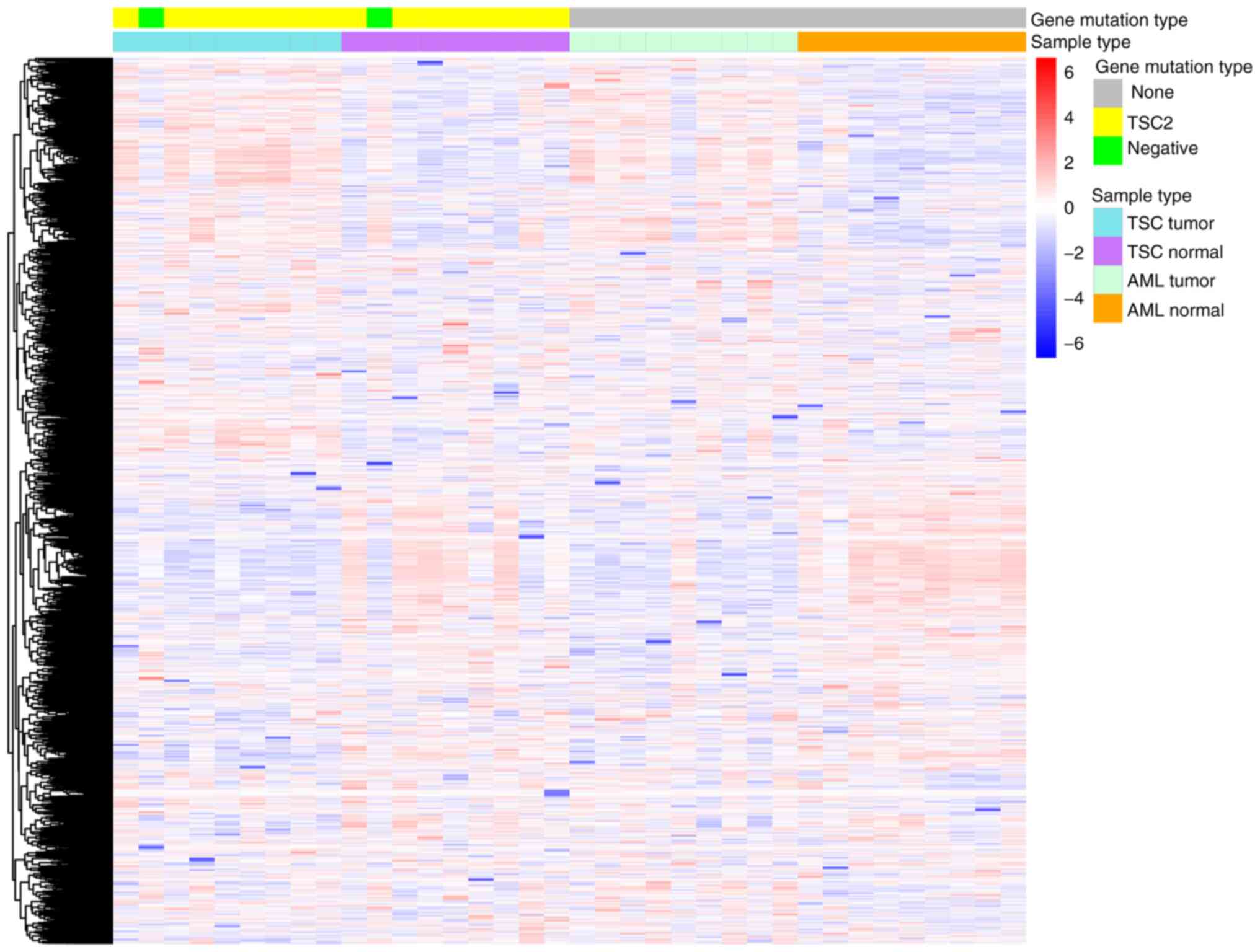
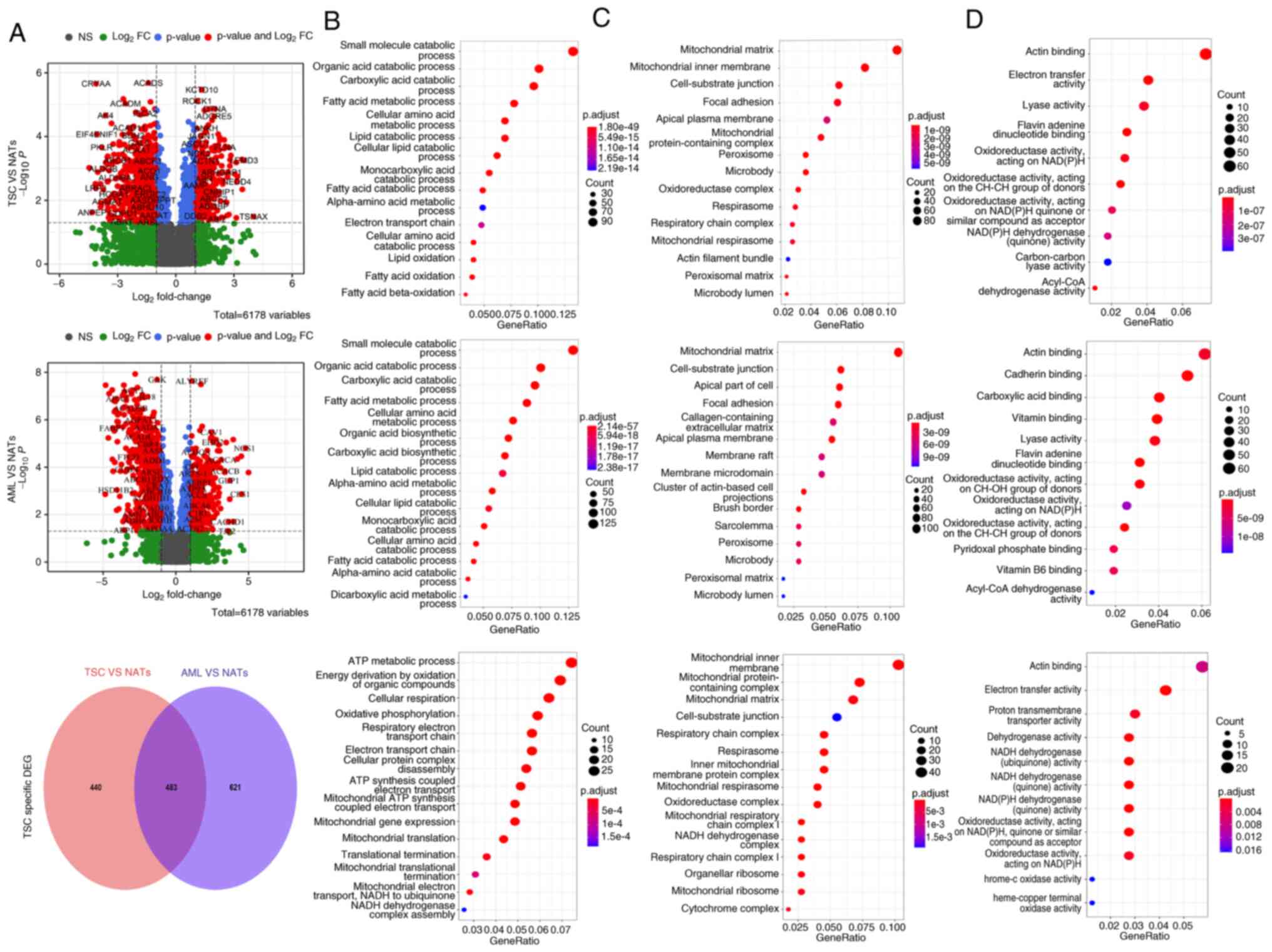
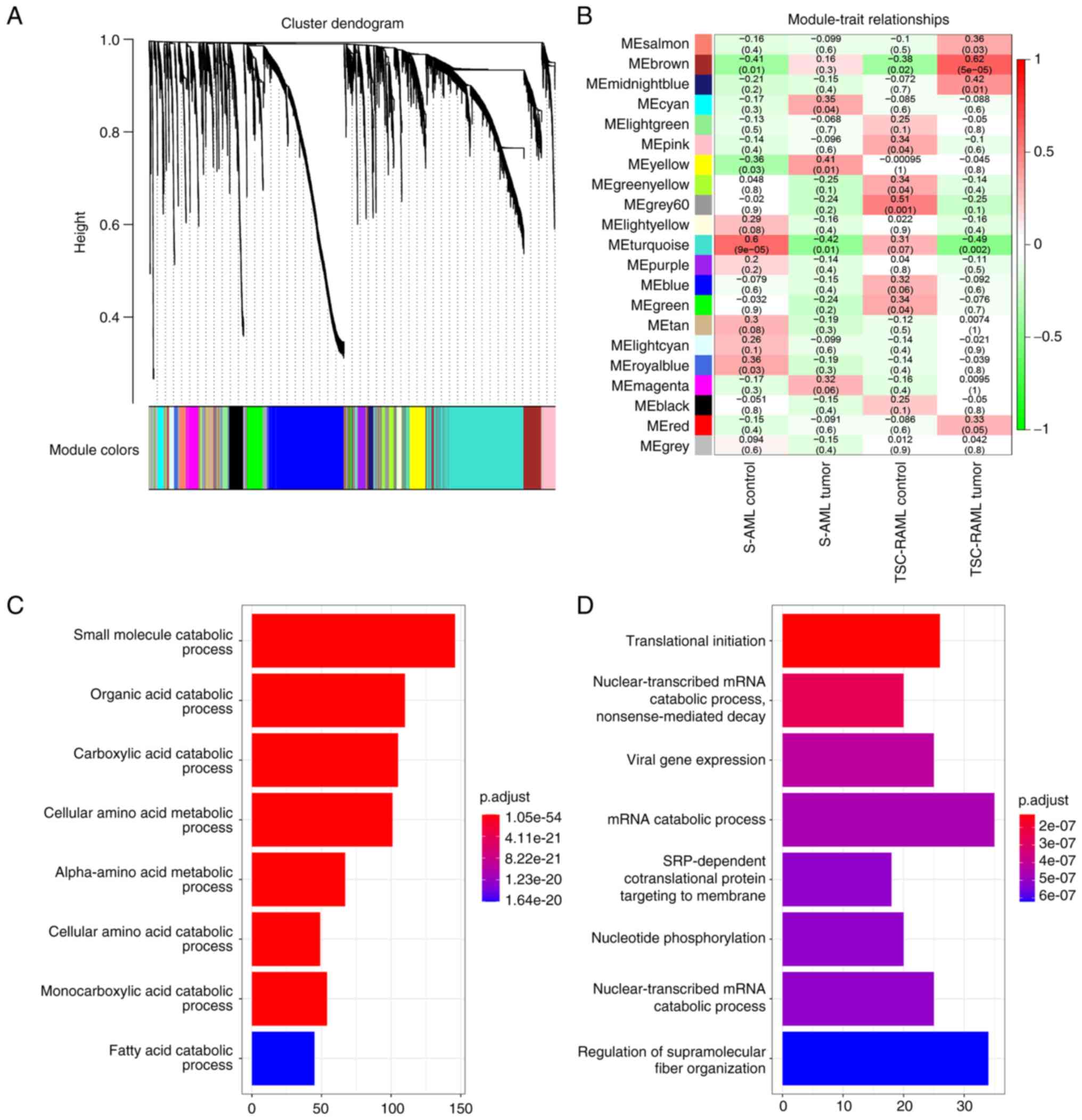
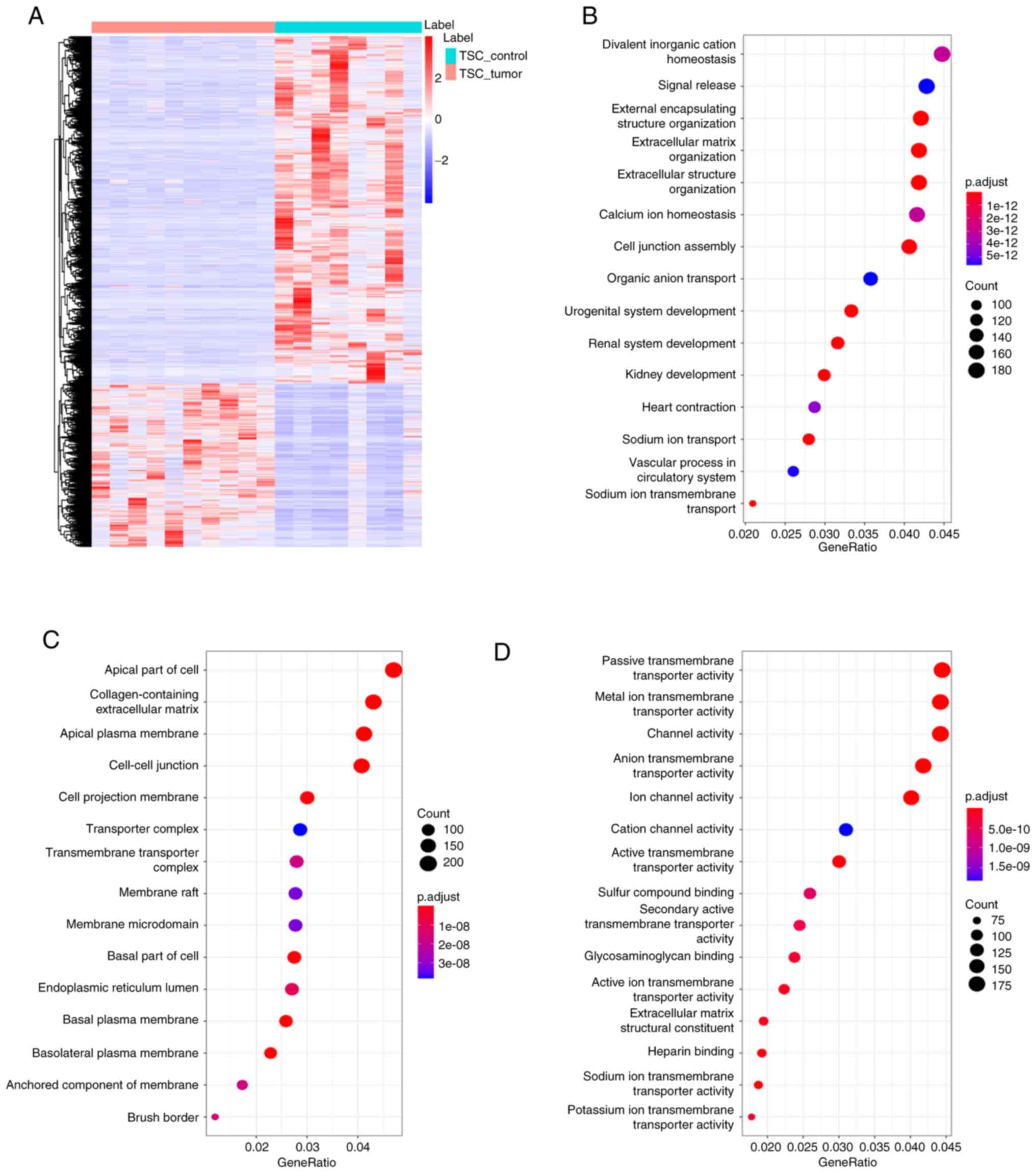
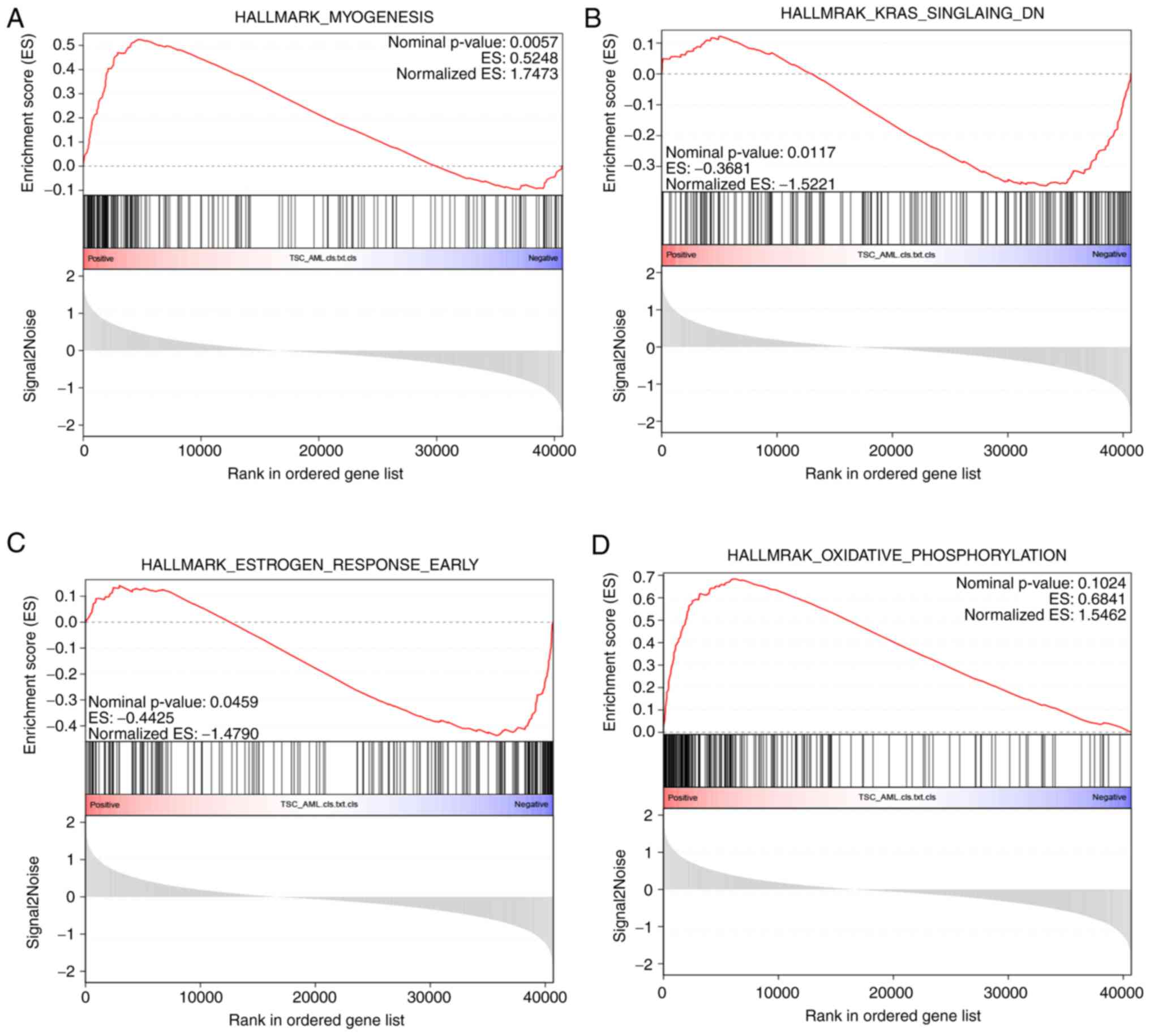
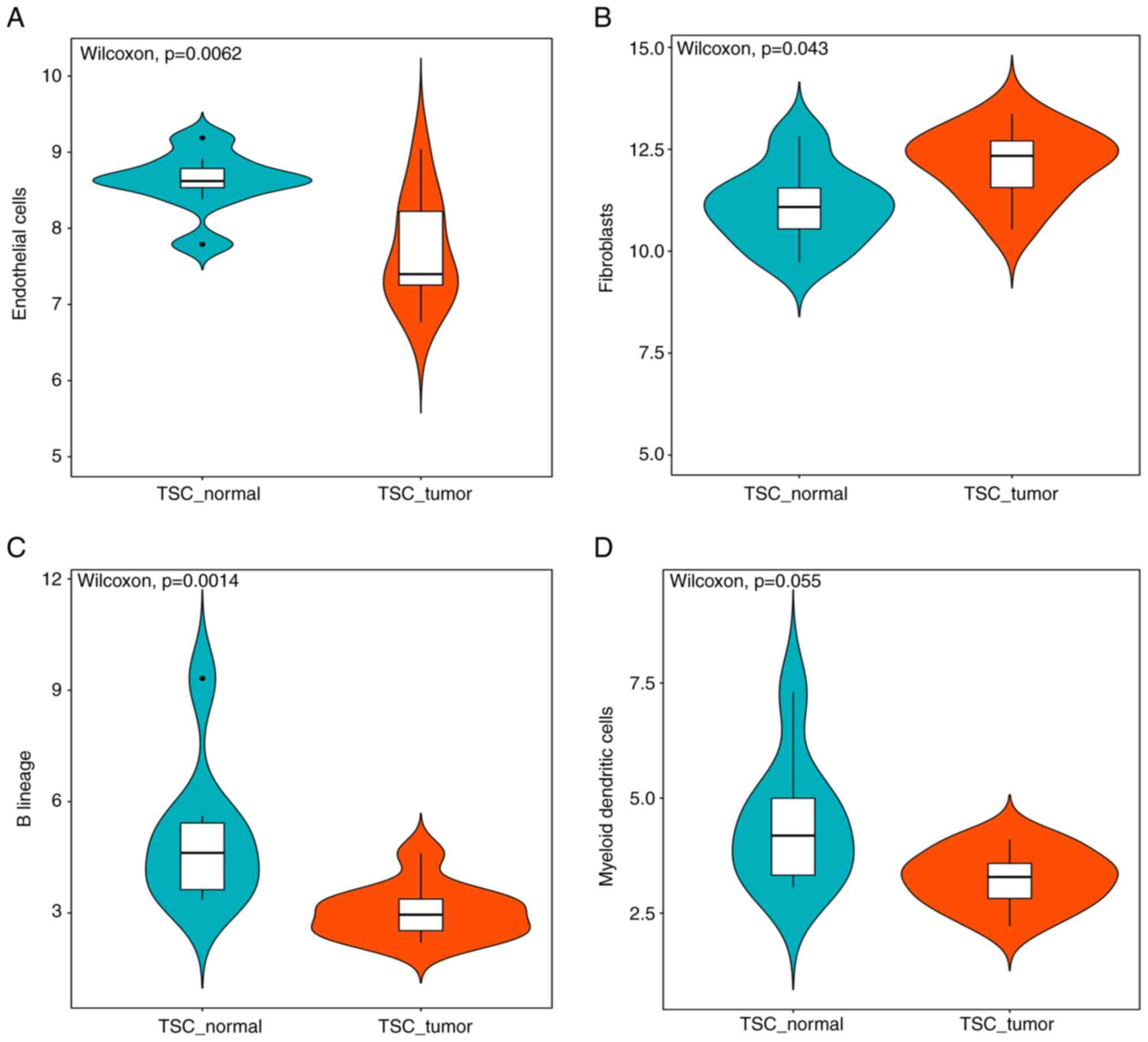
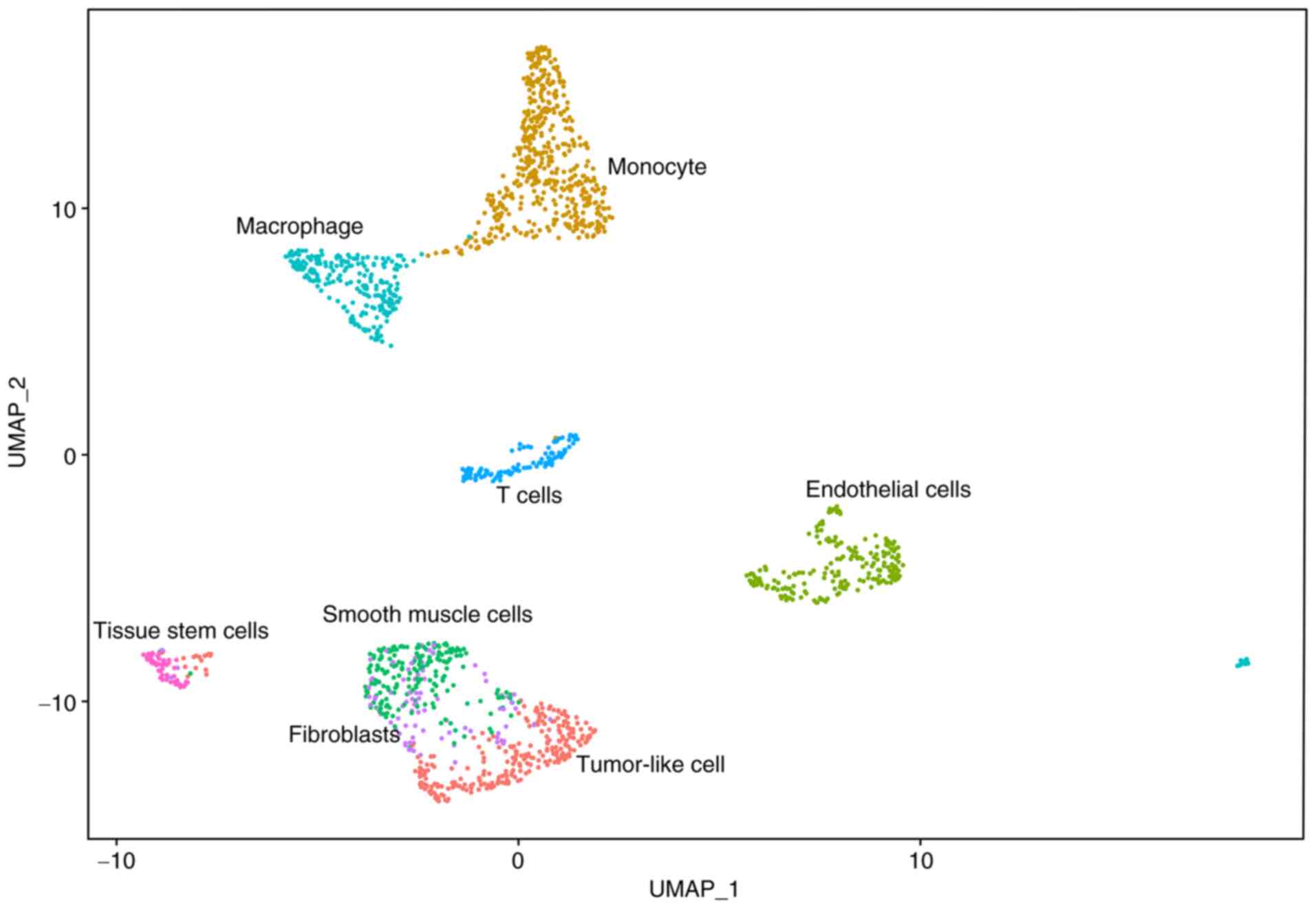
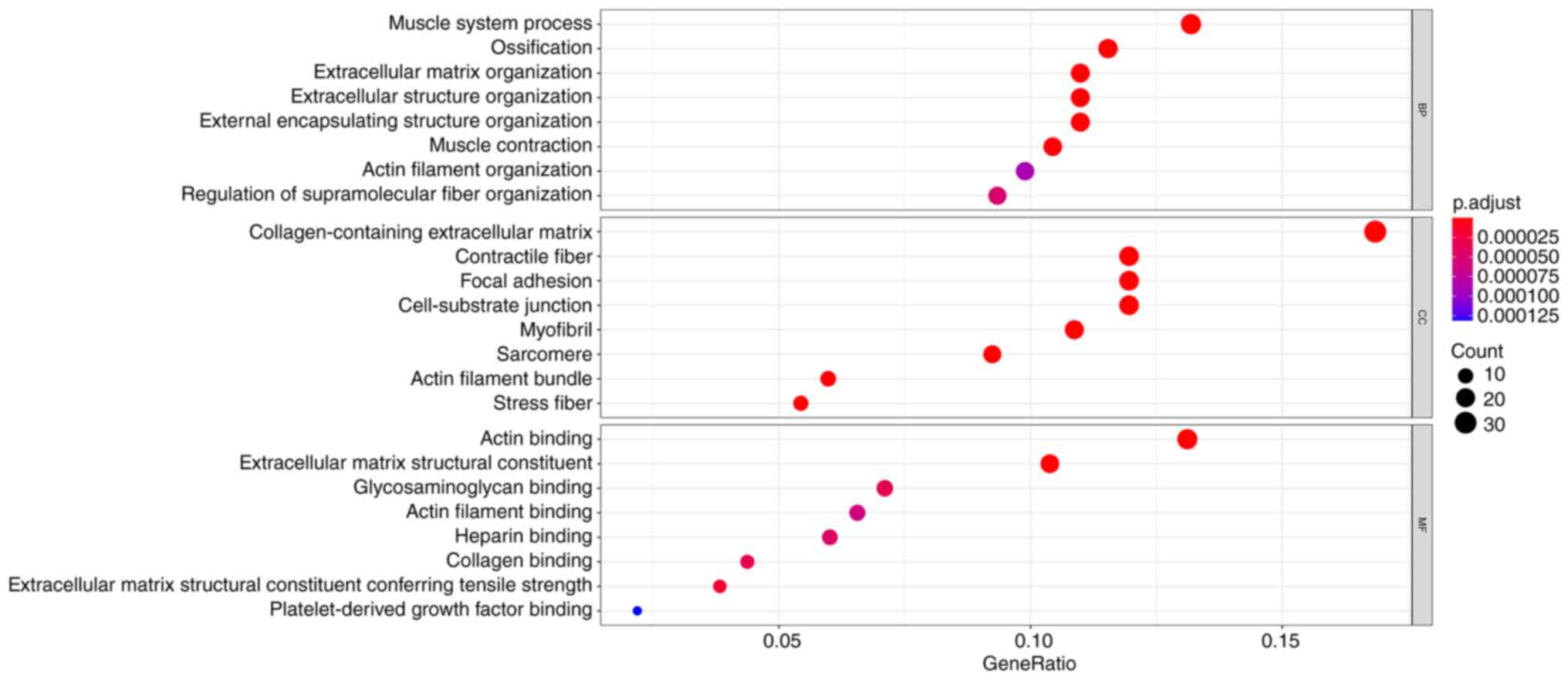
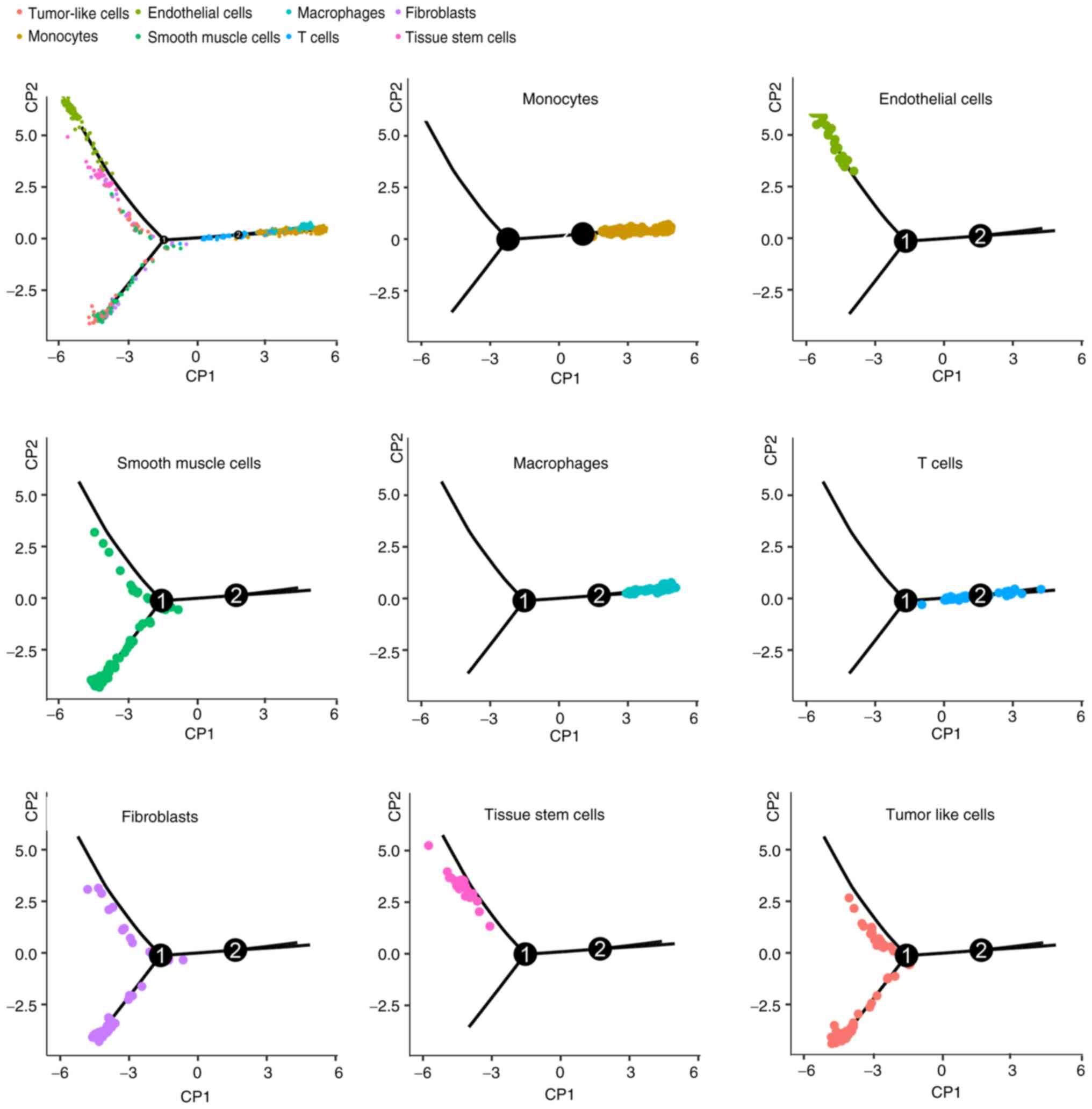
|
1
|
Curatolo P, Bombardieri R and Jozwiak S:
Tuberous sclerosis. Lancet. 372:657–668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Henske EP, Jóźwiak S, Kingswood JC,
Sampson JR and Thiele EA: Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 2:160352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rebaine Y, Nasser M, Girerd B, Leroux C
and Cottin V: Tuberous sclerosis complex for the pulmonologist. Eur
Respir Rev. 30:2003482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crino PB, Nathanson KL and Henske EP: The
tuberous sclerosis complex. N Eng J Med. 355:1345–1356. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Amin S, Lux A, Calder N, Laugharne M,
Osborne J and O'callaghan F: Causes of mortality in individuals
with tuberous sclerosis complex. Dev Med Child Neurol. 59:612–617.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shepherd CW, Gomez MR, Lie JT and Crowson
CS: Causes of death in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Mayo Clin
Proc. 66:792–796. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saffari A, Brösse I, Wiemer-Kruel A,
Wilken B, Kreuzaler P, Hahn A, Bernhard MK, van Tilburg CM,
Hoffmann GF, Gorenflo M, et al: Safety and efficacy of mTOR
inhibitor treatment in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex
under 2 years of age-a multicenter retrospective study. Orphanet J
Rare Dis. 14:962019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bissler JJ, Kingswood JC, Radzikowska E,
Zonnenberg BA, Frost M, Belousova E, Sauter M, Nonomura N,
Brakemeier S, de Vries PJ, et al: Everolimus for angiomyolipoma
associated with tuberous sclerosis complex or sporadic
lymphangi-oleiomyomatosis (EXIST-2): A multicentre, randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 381:817–824. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hatano T and Egawa S: Renal angiomyolipoma
with tuberous sclerosis complex: How it differs from sporadic
angiomyolipoma in both management and care. Asian J Surg.
43:967–972. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Northrup H and Krueger DA; International
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Consensus Group: Tuberous sclerosis
complex diagnostic criteria update: Recommendations of the 2012
iinternational tuberous sclerosis complex consensus conference.
Pediatr Neurol. 49:243–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eijkemans MJ, van der Wal W, Reijnders LJ,
Roes KC, van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani SB, Pelletier C,
Magestro M and Zonnenberg B: Long-term follow-up assessing renal
angiomyolipoma treatment patterns, morbidity, and mortality: An
observational study in tuberous sclerosis complex patients in the
Netherlands. Am J Kidney Dis. 66:638–645. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao F, Kataoka M, Liu N, Liang T, Huang
ZP, Gu F, Ding J, Liu J, Zhang F, Ma Q, et al: Therapeutic role of
miR-19a/19b in cardiac regeneration and protection from myocardial
infarction. Nat Commun. 10:18022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo M, Yu JJ, Perl AK, Wikenheiser-Brokamp
KA, Riccetti M, Zhang EY, Sudha P, Adam M, Potter A, Kopras EJ, et
al: Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a unique
pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis cell. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
202:1373–1387. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hao Y, Hao S, Andersen-Nissen E, Mauck WM
III, Zheng S, Butler A, Lee MJ, Wilk AJ, Darby C, Zager M, et al:
Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell.
184:3573–3587.e29. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stuart T, Butler A, Hoffman P, Hafemeister
C, Papalexi E, Mauck WM III, Hao Y, Stoeckius M, Smibert P and
Satija R: Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell.
177:1888–1902.e21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aran D, Looney AP, Liu L, Wu E, Fong V,
Hsu A, Chak S, Naikawadi RP, Wolters PJ, Abate AR, et al:
Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a
transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nat Immunol. 20:163–172. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2:1001412021.
|
|
19
|
Trapnell C, Cacchiarelli D, Grimsby J,
Pokharel P, Li S, Morse M, Lennon NJ and Livak KJ: The dynamics and
regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal
ordering of single cells. Nat Biotechnol. 32:381–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: Fast R
functions for robust correlations and hierarchical clustering. J
Statis Softw. 46:i112012.
|
|
22
|
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B,
Elarouci N, Petitprez F, Selves J, Laurent-Puig P, Sautès-Fridman
C, Fridman WH and de Reyniès A: Estimating the population abundance
of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using
gene expression. Genome Biol. 17:2182016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bongaarts A, de Jong JM, Broekaart DW, van
Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Mijnsbergen C, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, den
Dunnen WFA, Gruber VE, et al: Dysregulation of the MMP/TIMP
proteolytic system in subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in
patients with tuberous sclerosis complex: Modulation of MMP by
MicroRNA-320d in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 79:777–790. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Broekaart DW, van Scheppingen J, Anink JJ,
Wierts L, van Het Hof B, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC,
Kamphuis WW, de Vries HE, et al: Increased matrix
metalloproteinases expression in tuberous sclerosis complex:
Modulation by microRNA 146a and 147b in vitro. Neuropathol Appl
Neurobiol. 46:142–159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Zeng Z, Lan T, Wei Y and Wei X: CCL5/CCR5
axis in human diseases and related treatments. Genes Dis. 9:12–27.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
McCormack FX, Inoue Y, Moss J, Singer LG,
Strange C, Nakata K, Barker AF, Chapman JT, Brantly ML, Stocks JM,
et al: Efficacy and safety of sirolimus in
lymphangioleiomyomatosis. N Eng J Med. 364:1595–1606. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Muto Y, Sasaki H, Sumitomo M, Inagaki H,
Kato M, Kato T, Miyai S, Kurahashi H and Shiroki R:
Genotype-phenotype correlation of renal lesions in the tuberous
sclerosis complex. Hum Genome Var. 9:52022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang N, Wang X, Tang Z, Qiu X, Guo Z,
Huang D, Xiong H and Guo Q: The correlation between tuberous
sclerosis complex genotype and renal angiomyolipoma phenotype.
Front Genet. 11:5757502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng JB, Sedgewick AJ, Finnegan AI,
Harirchian P, Lee J, Kwon S, Fassett MS, Golovato J, Gray M,
Ghadially R, et al: Transcriptional programming of normal and
inflamed human epidermis at single-cell resolution. Cell Rep.
25:871–883. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Holzinger D, Foell D and Kessel C: The
role of S100 proteins in the pathogenesis and monitoring of
autoinflammatory diseases. Mol Cell Pediatr. 5:72018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pruenster M, Vogl T, Roth J and Sperandio
M: S100A8/A9: From basic science to clinical application. Pharmacol
Ther. 167:120–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spiekerkoetter E, Guignabert C, de Jesus
Perez V, Alastalo TP, Powers JM, Wang L, Lawrie A, Ambartsumian N,
Schmidt AM, Berryman M, et al: S100A4 and bone morphogenetic
protein-2 codependently induce vascular smooth muscle cell
migration via phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase and
chloride intracellular channel 4. Circ Res. 105:639–647. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lam HC, Siroky BJ and Henske EP: Renal
disease in tuberous sclerosis complex: Pathogenesis and therapy.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:704–716. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1α-responsive genes involved
in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in
human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ng HY, Oliver BG, Burgess JK, Krymskaya
VP, Black JL and Moir LM: Doxycycline reduces the migration of
tuberous sclerosis complex-2 null cells-effects on RhoA-GTPase and
focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2633–2646. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pollizzi K, Malinowska-Kolodziej I,
Doughty C, Betz C, Ma J, Goto J and Kwiatkowski DJ: A hypomorphic
allele of Tsc2 highlights the role of TSC1/TSC2 in signaling to AKT
and models mild human TSC2 alleles. Hum Mol Genet. 18:2378–2387.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Terraneo S, Lesma E, Ancona S, Imeri G,
Palumbo G, Torre O, Giuliani L, Centanni S, Peron A, Tresoldi S, et
al: Exploring the role of matrix metalloproteinases as biomarkers
in sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis and tuberous sclerosis
complex. A pilot study. Front Med (Lausanne). 8:6059092021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li S, Yu S, Zhang C, Shu H, Liu S, An N,
Yang M, Yin Q and Yang H: Increased expression of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 in cortical lesions from patients with focal
cortical dysplasia type IIb and tuberous sclerosis complex. Brain
Res. 1453:46–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ancona S, Orpianesi E, Bernardelli C,
Chiaramonte E, Chiaramonte R, Terraneo S, Di Marco F and Lesma E:
Differential modulation of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -7 in
LAM/TSC cells. Biomedicines. 9:17602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tyryshkin A, Bhattacharya A and Eissa NT:
SRC kinase is a novel therapeutic target in
lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Cancer Res. 74:1996–2005. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
William M, Leroux LP, Chaparro V, Graber
TE, Alain T and Jaramillo M: Translational repression of Ccl5 and
Cxcl10 by 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2 restrains the ability of mouse
macrophages to induce migration of activated T cells. Eur J
Immunol. 49:1200–1212. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Walens A, DiMarco AV, Lupo R, Kroger BR,
Damrauer JS and Alvarez JV: CCL5 promotes breast cancer recurrence
through macrophage recruitment in residual tumors. eLife.
8:e436532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Soria G and Ben-Baruch A: The inflammatory
chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
267:271–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rabe DC, Walker ND, Rustandy FD, Wallace
J, Lee J, Stott SL and Rosner MR: Tumor extracellular vesicles
regulate macrophage-driven metastasis through CCL5. Cancers
(Basel). 13:34592021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Farach LS, Pearson DA, Woodhouse JP,
Schraw JM, Sahin M, Krueger DA, Wu JY, Bebin EM, Lupo PJ, Au KS, et
al: Tuberous sclerosis complex genotypes and developmental
phenotype. Pediatr Neurol. 96:58–63. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ogórek B, Hamieh L, Hulshof HM, Lasseter
K, Klonowska K, Kuijf H, Moavero R, Hertzberg C, Weschke B, Riney
K, et al: TSC2 pathogenic variants are predictive of severe
clinical manifestations in TSC infants: Results of the EPISTOP
study. Genet Med. 22:1489–1497. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bottolo L, Miller S and Johnson SR:
Sphingolipid, fatty acid and phospholipid metabolites are
associated with disease severity and mTOR inhibition in
lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Thorax. 75:679–688. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Feng Y, Mischler WJ, Gurung AC, Kavanagh
TR, Androsov G, Sadow PM, Herbert ZT and Priolo C: Therapeutic
targeting of the secreted lysophospholipase D autotaxin suppresses
tuberous sclerosis complex-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
80:2751–2763. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li S, Thangapazham RL, Wang JA, Rajesh S,
Kao TC, Sperling L, Moss J and Darling TN: Human TSC2-null
fibroblast-like cells induce hair follicle neogenesis and hamartoma
morphogenesis. Nat Commun. 2:2352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
García-Aguilar A, Guillén C, Nellist M,
Bartolomé A and Benito M: TSC2 N-terminal lysine acetylation status
affects to its stability modulating mTORC1 signaling and autophagy.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2658–2667. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu Z, Wu H, Md S, Yu G, Habib SL, Li B and
Li J: Tsc1 ablation in Prx1 and Osterix lineages causes renal
cystogenesis in mouse. Sci Rep. 9:8372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu K, Lin K, Li X, Yuan X, Xu P, Ni P and
Xu D: Redefining tumor-associated macrophage subpopulations and
functions in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol.
11:17312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li S, Takeuchi F, Wang JA, Fuller C,
Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Moss J and Darling TN: MCP-1 overexpressed in
tuberous sclerosis lesions acts as a paracrine factor for tumor
development. J Exp Med. 202:617–624. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Byles V, Covarrubias AJ, Ben-Sahra I,
Lamming DW, Sabatini DM, Manning BD and Horng T: The TSC-mTOR
pathway regulates macrophage polarization. Nat Commun. 4:28342013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|