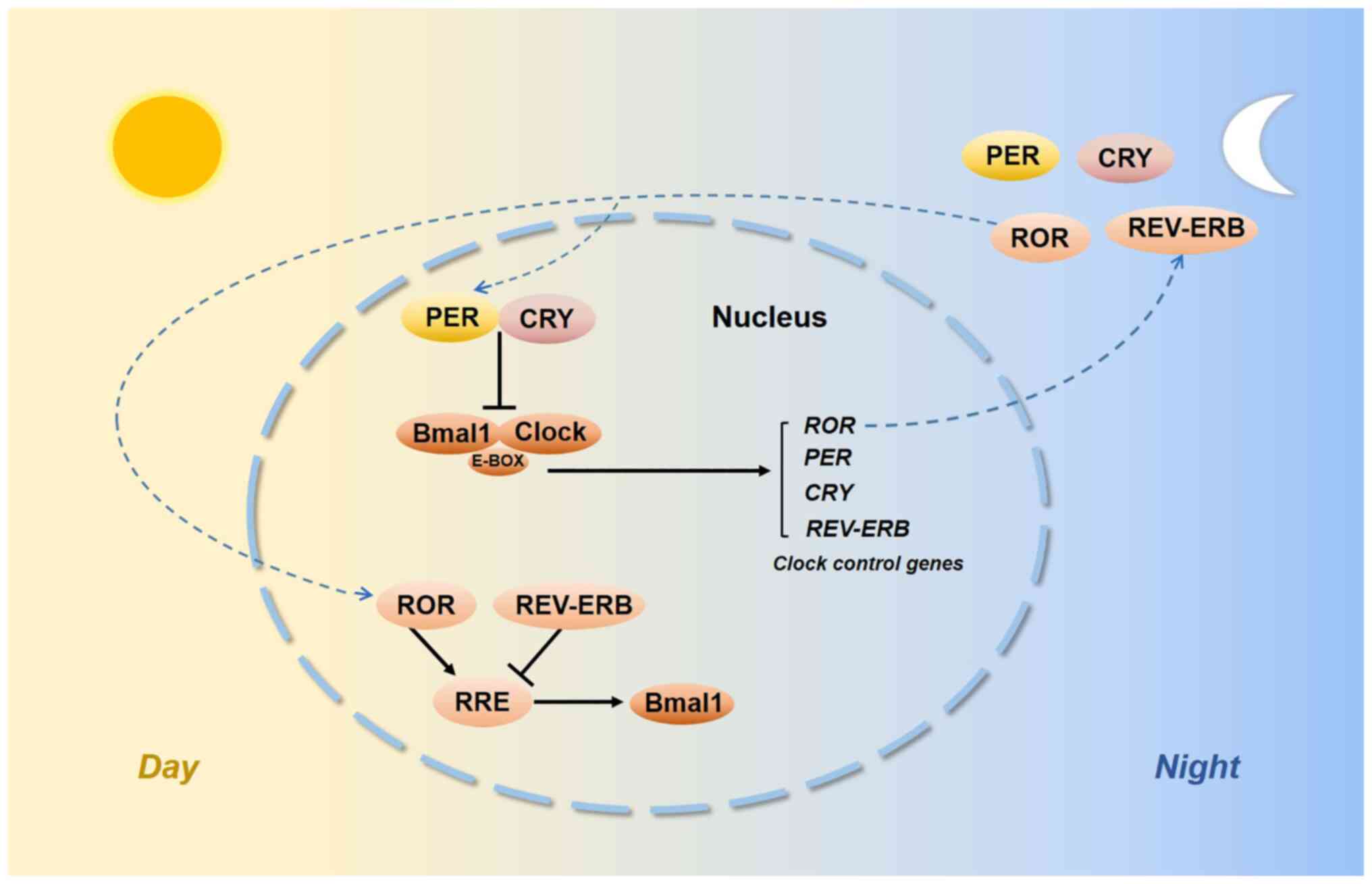
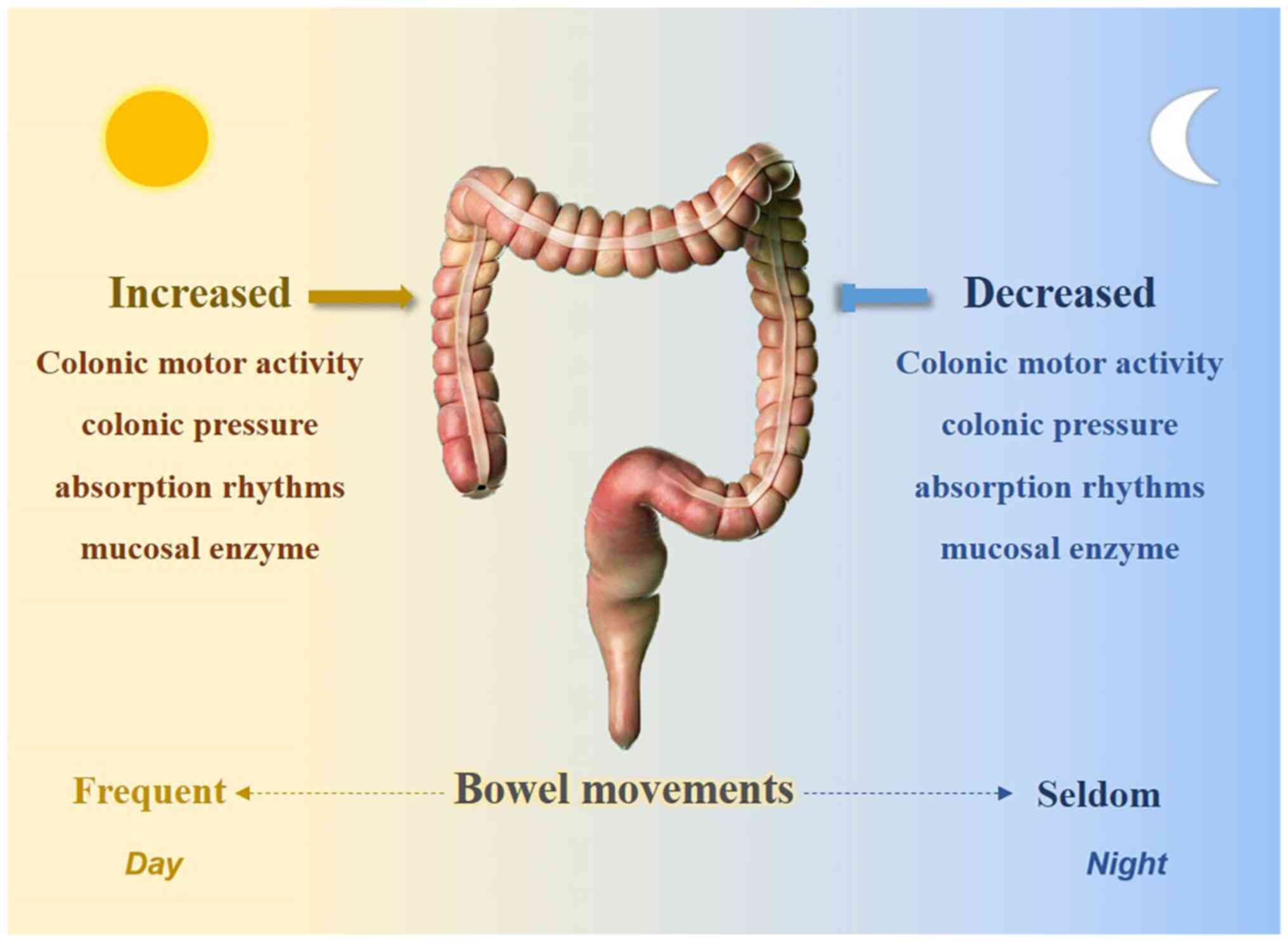
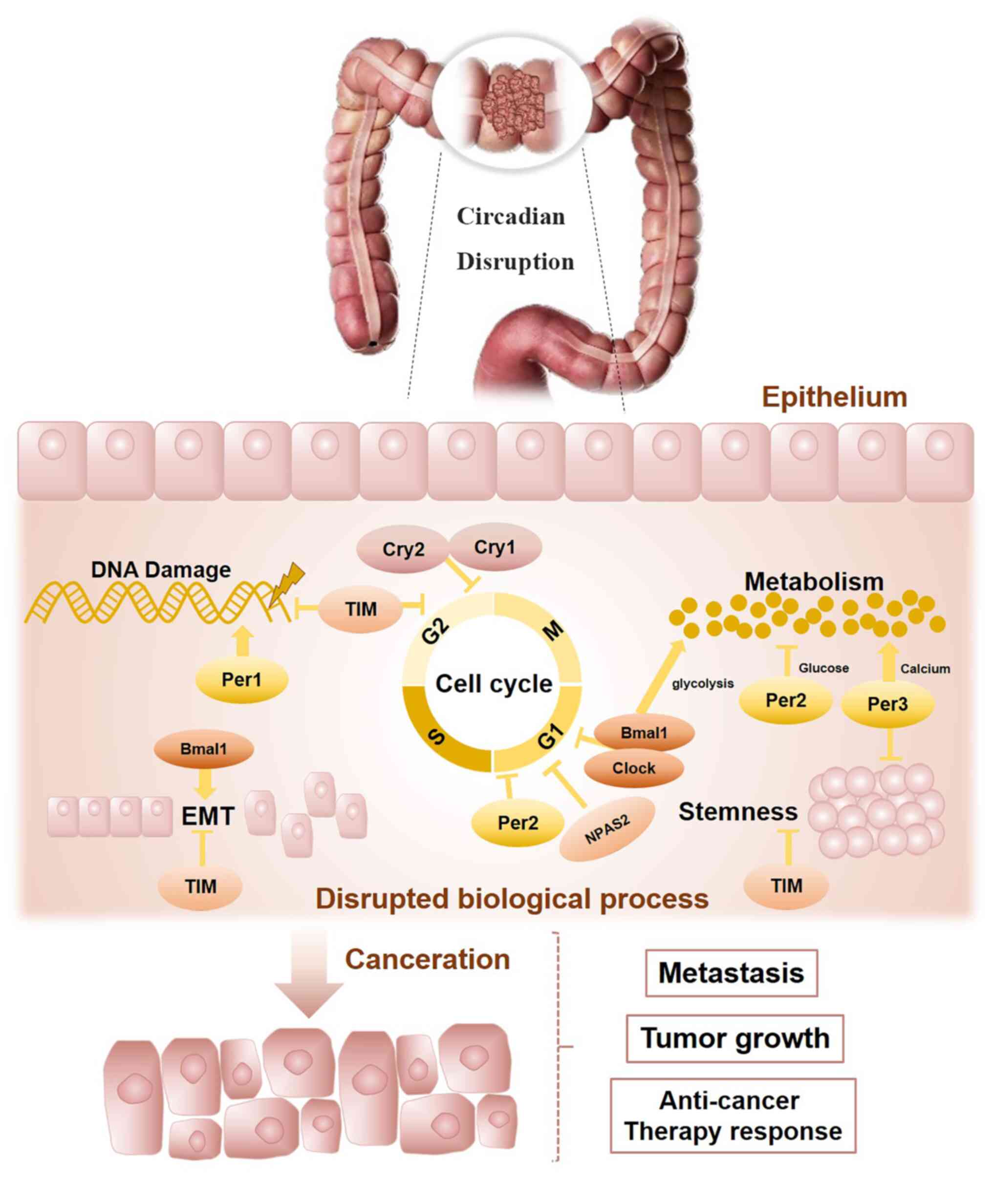
|
1
|
Shafer OT, Levine JD, Truman JW and Hall
JC: Flies by night: Effects of changing day length on Drosophila's
circadian clock. Curr Biol. 14:424–432. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rusak B and Zucker I: Neural regulation of
circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev. 59:449–526. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dibner C, Schibler U and Albrecht U: The
mammalian circadian timing system: Organization and coordination of
central and peripheral clocks. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:517–549. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gekakis N, Staknis D, Nguyen HB, Davis FC,
Wilsbacher LD, King DP, Takahashi JS and Weitz CJ: Role of the
CLOCK protein in the mammalian circadian mechanism. Science.
280:1564–1569. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antoch MP, Song EJ, Chang AM, Vitaterna
MH, Zhao Y, Wilsbacher LD, Sangoram AM, King DP, Pinto LH and
Takahashi JS: Functional identification of the mouse circadian
Clock gene by transgenic BAC rescue. Cell. 89:655–667. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Preitner N, Damiola F, Lopez-Molina L,
Zakany J, Duboule D, Albrecht U and Schibler U: The orphan nuclear
receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the
positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell.
110:251–260. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho H, Zhao X, Hatori M, Yu RT, Barish GD,
Lam MT, Chong LW, DiTacchio L, Atkins AR, Glass CK, et al:
Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and
REV-ERB-β. Nature. 485:123–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grunstein M: Histone acetylation in
chromatin structure and transcription. Nature. 389:349–352. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doi M, Hirayama J and Sassone-Corsi P:
Circadian regulator CLOCK is a histone acetyltransferase. Cell.
125:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hirayama J, Sahar S, Grimaldi B, Tamaru T,
Takamatsu K, Nakahata Y and Sassone-Corsi P: CLOCK-mediated
acetylation of BMAL1 controls circadian function. Nature.
450:1086–1090. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakahata Y, Kaluzova M, Grimaldi B, Sahar
S, Hirayama J, Chen D, Guarente LP and Sassone-Corsi P: The
NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 modulates CLOCK-mediated chromatin
remodeling and circadian control. Cell. 134:329–340. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asher G, Gatfield D, Stratmann M, Reinke
H, Dibner C, Kreppel F, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW and Schibler U:
SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2
deacetylation. Cell. 134:317–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sulli G, Lam MTY and Panda S: Interplay
between circadian clock and cancer: New frontiers for cancer
treatment. Trends Cancer. 5:475–494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erren TC, Morfeld P, Foster RG, Reiter RJ,
Groß JV and Westermann IK: Sleep and cancer: Synthesis of
experimental data and meta-analyses of cancer incidence among some
1,500,000 study individuals in 13 countries. Chronobiol Int.
33:325–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papantoniou K, Devore EE, Massa J,
Strohmaier S, Vetter C, Yang L, Shi Y, Giovannucci E, Speizer F and
Schernhammer ES: Rotating night shift work and colorectal cancer
risk in the nurses' health studies. Int J Cancer. 143:2709–2717.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Liu L, Hamada T, Nowak JA,
Giannakis M, Ma Y, Song M, Nevo D, Kosumi K, Gu M, et al:
Night-shift work duration and risk of colorectal cancer according
to IRS1 and IRS2 expression. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
29:133–140. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Bishehsari F, Engen PA, Voigt RM, Swanson
G, Shaikh M, Wilber S, Naqib A, Green SJ, Shetuni B, Forsyth CB, et
al: Abnormal eating patterns cause circadian disruption and promote
alcohol-associated colon carcinogenesis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 9:219–237. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pelullo M, Nardozza F, Zema S, Quaranta R,
Nicoletti C, Besharat ZM, Felli MP, Cerbelli B, d'Amati G, Palermo
R, et al: Kras/ADAM17-dependent Jag1-ICD reverse signaling sustains
colorectal cancer progression and chemoresistance. Cancer Res.
79:5575–5586. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Afrăsânie VA, Marinca MV, Alexa-Stratulat
T, Gafton B, Păduraru M, Adavidoaiei AM, Miron L and Rusu C: KRAS,
NRAS, BRAF, HER2 and microsatellite instability in metastatic
colorectal cancer-practical implications for the clinician. Radiol
Oncol. 53:265–274. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Slik K, Turkki R, Carpén O, Kurki S,
Korkeila E, Sundström J and Pellinen T: CDX2 loss with
microsatellite stable phenotype predicts poor clinical outcome in
stage II colorectal carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 43:1473–1482.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wolpin BM and Mayer RJ: Systemic treatment
of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 134:1296–1310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Narducci F, Bassotti G, Gaburri M and
Morelli A: Twenty four hour manometric recording of colonic motor
activity in healthy man. Gut. 28:17–25. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rao SS, Sadeghi P, Beaty J, Kavlock R and
Ackerson K: Ambulatory 24-h colonic manometry in healthy humans. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 280:G629–G639. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clench J, Reinberg A, Dziewanowska Z,
Ghata J and Smolensky M: Circadian changes in the bioavailability
and effects of indomethacin in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin
Pharmacol. 20:359–369. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Markiewicz A, Kamiński M, Chocilowski W,
Gomoluch T, Bołdys H and Skrzypek B: Circadian rhythms of four
marker enzymes activity of the jejunal villi in man. Acta
Histochem. 72:91–99. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hoogerwerf WA, Shahinian VB, Cornélissen
G, Halberg F, Bostwick J, Timm J, Bartell PA and Cassone VM:
Rhythmic changes in colonic motility are regulated by period genes.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G143–G150. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Thaiss CA, Zeevi D, Levy M,
Zilberman-Schapira G, Suez J, Tengeler AC, Abramson L, Katz MN,
Korem T, Zmora N, et al: Transkingdom control of microbiota diurnal
oscillations promotes metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 159:514–529.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sládek M, Rybová M, Jindráková Z, Zemanová
Z, Polidarová L, Mrnka L, O'Neill J, Pácha J and Sumová A: Insight
into the circadian clock within rat colonic epithelial cells.
Gastroenterology. 133:1240–1249. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hoogerwerf WA, Hellmich HL, Cornélissen G,
Halberg F, Shahinian VB, Bostwick J, Savidge TC and Cassone VM:
Clock gene expression in the murine gastrointestinal tract:
Endogenous rhythmicity and effects of a feeding regimen.
Gastroenterology. 133:1250–1260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brandi G, Calabrese C, Pantaleo MA,
Morselli Labate A, Di Febo G, Hakim R, De Vivo A, Di Marco MC and
Biasco G: Circadian variations of rectal cell proliferation in
patients affected by advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett.
208:193–196. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu F, Zhang T, Zhou C, Xu H, Guo L, Chen M
and Wu B: The circadian clock gene Bmal1 controls intestinal
exporter MRP2 and drug disposition. Theranostics. 9:2754–2767.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Lévi F, Dugué PA, Innominato P, Karaboué
A, Dispersyn G, Parganiha A, Giacchetti S, Moreau T, Focan C,
Waterhouse J, et al: Wrist actimetry circadian rhythm as a robust
predictor of colorectal cancer patients survival. Chronobiol Int.
31:891–900. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Innominato PF, Focan C, Gorlia T, Moreau
T, Garufi C, Waterhouse J, Giacchetti S, Coudert B, Iacobelli S,
Genet D, et al: Circadian rhythm in rest and activity: A biological
correlate of quality of life and a predictor of survival in
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
69:4700–4707. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stokes K, Nunes M, Trombley C, Flôres
DEFL, Wu G, Taleb Z, Alkhateeb A, Banskota S, Harris C, Love OP, et
al: The circadian clock gene, Bmal1, regulates intestinal stem cell
signaling and represses tumor initiation. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:1847–1872.e0. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
He A, Huang Z, Zhang R, Lu H, Wang J, Cao
J and Feng Q: Circadian clock genes are correlated with prognosis
and immune cell infiltration in colon adenocarcinoma. Comput Math
Methods Med. 2022:17099182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karantanos T, Theodoropoulos G, Gazouli M,
Vaiopoulou A, Karantanou C, Lymberi M and Pektasides D: Expression
of clock genes in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Biol
Markers. 28:280–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mazzoccoli G, Panza A, Valvano MR, Palumbo
O, Carella M, Pazienza V, Biscaglia G, Tavano F, Di Sebastiano P,
Andriulli A and Piepoli A: Clock gene expression levels and
relationship with clinical and pathological features in colorectal
cancer patients. Chronobiol Int. 28:841–851. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mostafaie N, Kállay E, Sauerzapf E, Bonner
E, Kriwanek S, Cross HS, Huber KR and Krugluger W: Correlated
downregulation of estrogen receptor beta and the circadian clock
gene Per1 in human colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 48:642–647.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Orhan T, Nielsen PB, Hviid TVF, Rosen AW
and Gögenür I: Expression of circadian clock genes in human
colorectal cancer tissues using droplet digital PCR. Cancer Invest.
37:90–98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oshima T, Takenoshita S, Akaike M,
Kunisaki C, Fujii S, Nozaki A, Numata K, Shiozawa M, Rino Y, Tanaka
K, et al: Expression of circadian genes correlates with liver
metastasis and outcomes in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep.
25:1439–1446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu S, Fesler A and Ju J: Implications of
circadian rhythm regulation by microRNAs in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Transl Med. 2:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
No authors listed. Expression of PER, CRY,
and TIM genes for the pathological features of colorectal cancer
patients [Retraction]. Onco Targets Ther. 9:56992016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Krugluger W, Brandstaetter A, Kállay E,
Schueller J, Krexner E, Kriwanek S, Bonner E and Cross HS:
Regulation of genes of the circadian clock in human colon cancer:
Reduced period-1 and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase transcription
correlates in high-grade tumors. Cancer Res. 67:7917–7922. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu H, Chu Q, Xie G, Han H, Chen Z, Xu B
and Yue Z: Circadian gene expression predicts patient response to
neoadjuvant chemo-radiation therapy for rectal cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:10985–10994. 2015.
|
|
47
|
Nemeth C, Humpeler S, Kallay E, Mesteri I,
Svoboda M, Rögelsperger O, Klammer N, Thalhammer T and Ekmekcioglu
C: Decreased expression of the melatonin receptor 1 in human
colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
25:531–542. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Hua L, Lu C and Chen Z: Expression
of circadian clock gene human Period2 (hPer2) in human colorectal
carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 9:1662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Aroca-Siendones MI, Moreno-SanJuan S,
Puentes-Pardo JD, Verbeni M, Arnedo J, Escudero-Feliu J,
García-Costela M, García-Robles A, Carazo Á and León J: Core
circadian clock proteins as biomarkers of progression in colorectal
cancer. Biomedicines. 9:9672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hasakova K, Vician M, Reis R, Zeman M and
Herichova I: Sex-dependent correlation between survival and
expression of genes related to the circadian oscillator in patients
with colorectal cancer. Chronobiol Int. 35:1423–1434. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang Y, Cheng Y, Yu G, Jia B, Hu Z and
Zhang L: Expression of PER, CRY, and TIM genes for the pathological
features of colorectal cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther.
9:1997–2005. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xiong Y, Zhuang Y, Zhong M, Qin W, Huang
B, Zhao J, Gao Z, Ma J, Wu Z, Hong X, et al: Period 2 suppresses
the malignant cellular behaviors of colorectal cancer through the
epithelial-mesenchymal transformation process. Cancer Control.
29:107327482210813692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hasakova K, Reis R, Vician M, Zeman M and
Herichova I: Expression of miR-34a-5p is up-regulated in human
colorectal cancer and correlates with survival and clock gene PER2
expression. PLoS One. 14:e02243962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang X, Yan D, Teng M, Fan J, Zhou C, Li
D, Qiu G, Sun X, Li T, Xing T, et al: Reduced expression of PER3 is
associated with incidence and development of colon cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19:3081–3088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Alexander M, Burch JB, Steck SE, Chen CF,
Hurley TG, Cavicchia P, Ray M, Shivappa N, Guess J, Zhang H, et al:
Case-control study of the PERIOD3 clock gene length polymorphism
and colorectal adenoma formation. Oncol Rep. 33:935–941. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Momma T, Okayama H, Saitou M, Sugeno H,
Yoshimoto N, Takebayashi Y, Ohki S and Takenoshita S: Expression of
circadian clock genes in human colorectal adenoma and carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 14:5319–5325. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Štorcelová M, Vicián M, Reis R, Zeman M
and Herichová I: Expression of cell cycle regulatory factors hus1,
gadd45a, rb1, cdkn2a and mre11a correlates with expression of clock
gene per2 in human colorectal carcinoma tissue. Mol Biol Rep.
40:6351–6361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Soták M, Polidarová L, Ergang P, Sumová A
and Pácha J: An association between clock genes and
clock-controlled cell cycle genes in murine colorectal tumors. Int
J Cancer. 132:1032–1041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Bednarski JJ and Sleckman BP: At the
intersection of DNA damage and immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol.
19:231–242. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ciccia A and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 40:179–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gery S, Komatsu N, Baldjyan L, Yu A, Koo D
and Koeffler HP: The circadian gene per1 plays an important role in
cell growth and DNA damage control in human cancer cells. Mol Cell.
22:375–382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Arango D, Mariadason JM, Wilson AJ, Yang
W, Corner GA, Nicholas C, Aranes MJ and Augenlicht LH: c-Myc
overexpression sensitises colon cancer cells to
camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 89:1757–1765. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Borgs L, Beukelaers P, Vandenbosch R,
Belachew S, Nguyen L and Malgrange B: Cell 'circadian' cycle: New
role for mammalian core clock genes. Cell Cycle. 8:832–837. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wood PA, Yang X, Taber A, Oh EY, Ansell C,
Ayers SE, Al-Assaad Z, Carnevale K, Berger FG, Peña MM and
Hrushesky WJ: Period 2 mutation accelerates ApcMin/+ tumorigenesis.
Mol Cancer Res. 6:1786–1793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fu L, Pelicano H, Liu J, Huang P and Lee
C: The circadian gene Period2 plays an important role in tumor
suppression and DNA damage response in vivo. Cell. 111:41–50. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shen P, Pichler M, Chen M, Calin GA and
Ling H: To Wnt or lose: The missing non-coding linc in colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:20032017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Filipovich A, Gehrke I, Poll-Wolbeck SJ
and Kreuzer KA: Physiological inhibitors of Wnt signaling. Eur J
Haematol. 86:453–465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yang X, Wood PA, Ansell CM, Ohmori M, Oh
EY, Xiong Y, Berger FG, Peña MM and Hrushesky WJ: Beta-catenin
induces beta-TrCP-mediated PER2 degradation altering circadian
clock gene expression in intestinal mucosa of ApcMin/+ mice. J
Biochem. 145:289–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Schroll MM, LaBonia GJ, Ludwig KR and
Hummon AB: Glucose restriction combined with autophagy inhibition
and chemotherapy in HCT 116 spheroids decreases cell clonogenicity
and viability regulated by tumor suppressor genes. J Proteome Res.
16:3009–3018. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang F, Sun H, Zhang S, Yang X, Zhang G
and Su T: Overexpression of PER3 inhibits self-renewal capability
and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer stem-like cells via
inhibition of notch and β-catenin signaling. Oncol Res. 25:709–719.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wang JL, Lin YW, Chen HM, Kong X, Xiong H,
Shen N, Hong J and Fang JY: Calcium prevents tumorigenesis in a
mouse model of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 6:e225662011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hasakova K, Vician M, Reis R, Zeman M and
Herichova I: The expression of clock genes cry1 and cry2 in human
colorectal cancer and tumor adjacent tissues correlates differently
dependent on tumor location. Neoplasma. 65:986–992. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yu H, Meng X, Wu J, Pan C, Ying X, Zhou Y,
Liu R and Huang W: Cryptochrome 1 overexpression correlates with
tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e616792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mazzoccoli G, Colangelo T, Panza A, Rubino
R, De Cata A, Tiberio C, Valvano MR, Pazienza V, Merla G, Augello
B, et al: Deregulated expression of cryptochrome genes in human
colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 15:62016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Heald R, McLoughlin M and McKeon F: Human
wee1 maintains mitotic timing by protecting the nucleus from
cytoplasmically activated Cdc2 kinase. Cell. 74:463–474. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Backert S, Gelos M, Kobalz U, Hanski ML,
Böhm C, Mann B, Lövin N, Gratchev A, Mansmann U, Moyer MP, et al:
Differential gene expression in colon carcinoma cells and tissues
detected with a cDNA array. Int J Cancer. 82:868–874. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
van der Horst GT, Muijtjens M, Kobayashi
K, Takano R, Kanno S, Takao M, de Wit J, Verkerk A, Eker AP, van
Leenen D, et al: Mammalian Cry1 and Cry2 are essential for
maintenance of circadian rhythms. Nature. 398:627–630. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Burgermeister E, Battaglin F, Eladly F, Wu
W, Herweck F, Schulte N, Betge J, Härtel N, Kather JN, Weis CA, et
al: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like
(ARNTL/BMAL1) is associated with bevacizumab resistance in
colorectal cancer via regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor A. EBioMedicine. 45:139–154. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang Y, Devocelle A, Desterke C, de Souza
LEB, Hadadi É, Acloque H, Foudi A, Xiang Y, Ballesta A, Chang Y and
Giron-Michel J: BMAL1 knockdown leans epithelial-mesenchymal
balance toward epithelial properties and decreases the
chemoresistance of colon carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci.
22:52472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang L, Chen B, Wang Y, Sun N, Lu C, Qian
R and Hua L: hClock gene expression in human colorectal carcinoma.
Mol Med Rep. 8:1017–1022. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Sun N, Lu C, Bei Y, Qian R and Hua
L: Upregulation of circadian gene 'hClock' contribution to
metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 50:2191–2199. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Karantanos T, Theodoropoulos G, Gazouli M,
Vaiopoulou A, Karantanou C, Stravopodis DJ, Bramis K, Lymperi M and
Pektasidis D: Association of the clock genes polymorphisms with
colorectal cancer susceptibility. J Surg Oncol. 108:563–567. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kurzawski G, Suchy J, Debniak T, Kładny J
and Lubiński J: Importance of microsatellite instability (MSI) in
colorectal cancer: MSI as a diagnostic tool. Ann Oncol. 15(Suppl
4): iv283–iv284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Alhopuro P, Björklund M, Sammalkorpi H,
Turunen M, Tuupanen S, Biström M, Niittymäki I, Lehtonen HJ,
Kivioja T, Launonen V, et al: Mutations in the circadian gene CLOCK
in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 8:952–960. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fuhr L, El-Athman R, Scrima R, Cela O,
Carbone A, Knoop H, Li Y, Hoffmann K, Laukkanen MO, Corcione F, et
al: The circadian clock regulates metabolic phenotype rewiring via
HKDC1 and modulates tumor progression and drug response in
colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine. 33:105–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Nelson RL: Iron and colorectal cancer
risk: Human studies. Nutr Rev. 59:140–148. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Osborne NJ, Gurrin LC, Allen KJ,
Constantine CC, Delatycki MB, McLaren CE, Gertig DM, Anderson GJ,
Southey MC, Olynyk JK, et al: HFE C282Y homozygotes are at
increased risk of breast and colorectal cancer. Hepatology.
51:1311–1318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Okazaki F, Matsunaga N, Okazaki H, Azuma
H, Hamamura K, Tsuruta A, Tsurudome Y, Ogino T, Hara Y, Suzuki T,
et al: Circadian clock in a mouse colon tumor regulates
intracellular iron levels to promote tumor progression. J Biol
Chem. 291:7017–7028. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sakamoto W and Takenoshita S:
Overexpression of both clock and BMAL1 inhibits entry to S phase in
human colon cancer cells. Fukushima J Med Sci. 61:111–124. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zeng ZL, Wu MW, Sun J, Sun YL, Cai YC,
Huang YJ and Xian LJ: Effects of the biological clock gene Bmal1 on
tumour growth and anti-cancer drug activity. J Biochem.
148:319–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang Y, Devocelle A, Souza L, Foudi A,
Tenreira Bento S, Desterke C, Sherrard R, Ballesta A, Adam R,
Giron-Michel J and Chang Y: BMAL1 knockdown triggers different
colon carcinoma cell fates by altering the delicate equilibrium
between AKT/mTOR and P53/P21 pathways. Aging (Albany NY).
12:8067–8083. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Dong P, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhu C, Lin J, Qian
R, Hua L and Lu C: BMAL1 induces colorectal cancer metastasis by
stimulating exosome secretion. Mol Biol Rep. 49:373–384. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Gu D, Li S, Ben S, Du M, Chu H, Zhang Z,
Wang M, Zhang ZF and Chen J: Circadian clock pathway genes
associated with colorectal cancer risk and prognosis. Arch Toxicol.
92:2681–2689. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Pazienza V, Piepoli A, Panza A, Valvano
MR, Benegiamo G, Vinciguerra M, Andriulli A and Mazzoccoli G: SIRT1
and the clock gene machinery in colorectal cancer. Cancer Invest.
30:98–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Colangelo T, Carbone A, Mazzarelli F,
Cuttano R, Dama E, Nittoli T, Albanesi J, Barisciano G, Forte N,
Palumbo O, et al: Loss of circadian gene timeless induces EMT and
tumor progression in colorectal cancer via Zeb1-dependent
mechanism. Cell Death Differ. 29:1552–1568. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Xue X, Liu F, Han Y, Li P, Yuan B, Wang X,
Chen Y, Kuang Y, Zhi Q and Zhao H: Silencing NPAS2 promotes cell
growth and invasion in DLD-1 cells and correlated with poor
prognosis of colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
450:1058–1062. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yang X, Wood PA and Hrushesky WJ:
Mammalian TIMELESS is required for ATM-dependent CHK2 activation
and G2/M checkpoint control. J Biol Chem. 285:3030–3034. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
98
|
Neilsen BK, Frodyma DE, McCall JL, Fisher
KW and Lewis RE: ERK-mediated TIMELESS expression suppresses G2/M
arrest in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 14. pp. e2092242019,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Pruitt K, Zinn RL, Ohm JE, McGarvey KM,
Kang SH, Watkins DN, Herman JG and Baylin SB: Inhibition of SIRT1
reactivates silenced cancer genes without loss of promoter DNA
hypermethylation. PLoS Genet. 2:e402006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Levi F, Perpoint B, Garufi C, Focan C,
Chollet P, Depres-Brummer P, Zidani R, ienza S, Itzhaki M,
Iacobelli S, et al: Oxaliplatin activity against metastatic
colorectal cancer. A phase II study of 5-day continuous venous
infusion at circadian rhythm modulated rate. Eur J Cancer.
29A:1280–1284. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lévi FA, Zidani R, Vannetzel JM, Perpoint
B, Focan C, Faggiuolo R, Chollet P, Garufi C, Itzhaki M, Dogliotti
L, et al: Chronomodulated versus fixed-infusion-rate delivery of
ambulatory chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic
acid (leucovorin) in patients with colorectal cancer metastases: A
randomized multi-institutional trial. J Natl Cancer Inst.
86:1608–1617. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Lévi F, Karaboué A, Gorden L, Innominato
PF, Saffroy R, Giacchetti S, Hauteville D, Guettier C, Adam R and
Bouchahda M: Cetuximab and circadian chronomodulated chemotherapy
as salvage treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC):
Safety, efficacy and improved secondary surgical resectability.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:339–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Innominato PF, Giacchetti S, Moreau T,
Smaaland R, Focan C, Bjarnason GA, Garufi C, Iacobelli S,
Tampellini M, Tumolo S, et al: Prediction of survival by
neutropenia according to delivery schedule of
oxaliplatin-5-fluorouracil-leucovorin for metastatic colorectal
cancer in a randomized international trial (EORTC 05963).
Chronobiol Int. 28:586–600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Innominato PF, Karaboué A, Focan C,
Chollet P, Giacchetti S, Bouchahda M, Ulusakarya A, Torsello A,
Adam R, Lévi FA and Garufi C: Efficacy and safety of
chronomodulated irinotecan, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and
leucovorin combination as first- or second-line treatment against
metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from the international EORTC
05011 trial. Int J Cancer. 148:2512–2521. 2020.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Innominato PF, Ballesta A, Huang Q, Focan
C, Chollet P, Karaboué A, Giacchetti S, Bouchahda M, Adam R, Garufi
C and Lévi FA: Sex-dependent least toxic timing of irinotecan
combined with chronomodulated chemotherapy for metastatic
colorectal cancer: Randomized multicenter EORTC 05011 trial. Cancer
Med. 9:4148–4159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Henricks LM, Opdam FL, Beijnen JH, Cats A
and Schellens JHM: DPYD genotype-guided dose individualization to
improve patient safety of fluoropyrimidine therapy: Call for a drug
label update. Ann Oncol. 28:2915–2922. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Fang L, Yang Z, Zhou J, Tung JY, Hsiao CD,
Wang L, Deng Y, Wang P, Wang J and Lee MH: Circadian clock gene
CRY2 degradation is involved in chemoresistance of colorectal
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1476–1487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Ballesta A, Dulong S, Abbara C, Cohen B,
Okyar A, Clairambault J and Levi F: A combined experimental and
mathematical approach for molecular-based optimization of
irinotecan circadian delivery. PLoS Comput Biol. 7:e10021432011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Hesse J, Martinelli J, Aboumanify O,
Ballesta A and Relógio A: A mathematical model of the circadian
clock and drug pharmacology to optimize irinotecan administration
timing in colorectal cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
19:5170–5183. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|