|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crosbie EJ, Kitson SJ, McAlpine JN,
Mukhopadhyay A, Powell ME and Singh N: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
399:1412–1428. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
MacKay HJ, Freixinos VR and Fleming GF:
Therapeutic targets and opportunities in endometrial cancer: Update
on endocrine therapy and nonimmunotherapy targeted options. Am Soc
Clin Oncol Educ Book. 40:1–11. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang J, Chen J, Fei X, Wang X and Wang K:
N6-methyladenine RNA modification and cancer. Oncol Lett.
20:1504–1512. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou Z, Lv J, Yu H, Han J, Yang X, Feng D,
Wu Q, Yuan B, Lu Q and Yang H: Mechanism of RNA modification
N6-methyladenosine in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:1042020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang G, Sun Z and Zhang N: Reshaping the
role of m6A modification in cancer transcriptome: A review. Cancer
Cell Int. 20:3532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han X, Wang M, Zhao YL, Yang Y and Yang
YG: RNA methylations in human cancers. Semin Cancer Biol.
75:97–115. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shen S, Zhang R, Jiang Y, Li Y, Lin L, Liu
Z, Zhao Y, Shen H, Hu Z, Wei Y and Chen F: Comprehensive analyses
of m6A regulators and interactive coding and non-coding RNAs across
32 cancer types. Mol Cancer. 20:672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu AM, Jian C, Yu AH and Tu MJ: RNA
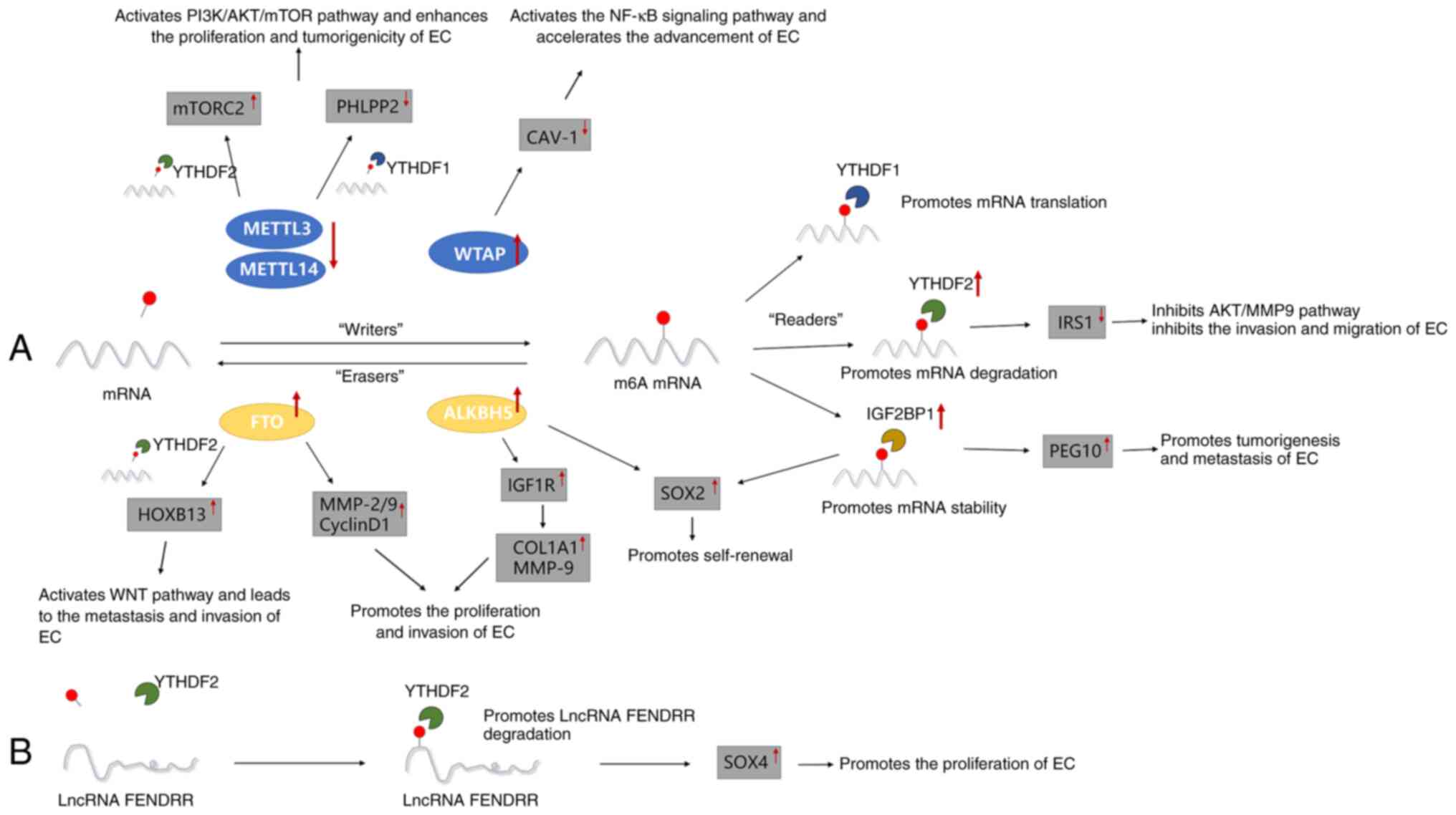
therapy: Are we using the right molecules? Pharmacol Ther.
196:91–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
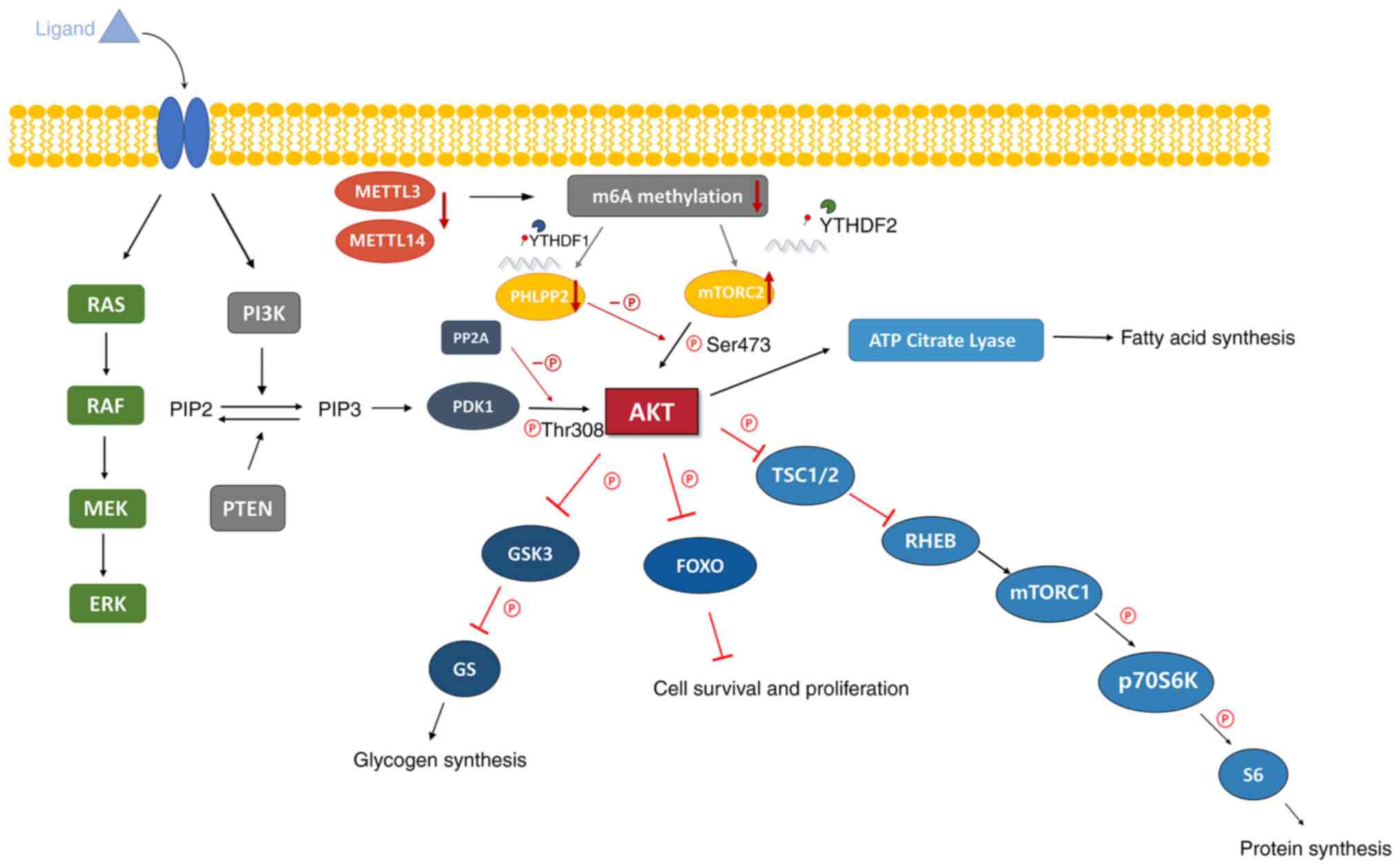
10
|
Arend RC, Jones BA, Martinez A and
Goodfellow P: Endometrial cancer: Molecular markers and management
of advanced stage disease. Gynecol Oncol. 150:569–580. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu B, Shang X, Yan M, Li X, Wang W, Wang Q
and Zhang C: Variations in incidence and mortality rates of
endometrial cancer at the global, regional, and national levels,
1990-2019. Gynecol Oncol. 161:573–580. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ryan NAJ, Glaire MA, Blake D,
Cabrera-Dandy M, Evans DG and Crosbie EJ: The proportion of
endometrial cancers associated with Lynch syndrome: A systematic
review of the literature and meta-analysis. Genet Med.
21:2167–2180. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Onstad MA, Schmandt RE and Lu KH:
Addressing the role of obesity in endometrial cancer risk,
prevention, and treatment. J Clin Oncol. 34:4225–4230. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
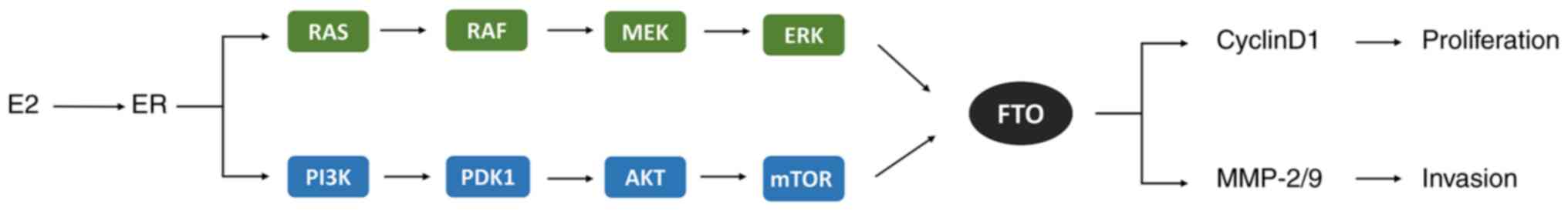
|
14
|
Hecht JL and Mutter GL: Molecular and
pathologic aspects of endometrial carcinogenesis. J Clin Oncol.
24:4783–4791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bansal N, Yendluri V and Wenham RM: The
molecular biology of endometrial cancers and the implications for
pathogenesis, classification, and targeted therapies. Cancer
Control. 16:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Brooks RA, Fleming GF, Lastra RR, Lee NK,
Moroney JW, Son CH, Tatebe K and Veneris JL: Current
recommendations and recent progress in endometrial cancer. CA
Cancer J Clin. 69:258–279. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
León-Castillo A, Gilvazquez E, Nout R,
Smit VT, McAlpine JN, McConechy M, Kommoss S, Brucker SY, Carlson
JW, Epstein E, et al: Clinicopathological and molecular
characterisation of 'multiple-classifier' endometrial carcinomas. J
Pathol. 250:312–322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bell DW and Ellenson LH: Molecular
genetics of endometrial carcinoma. Annu Rev Pathol. 14:339–367.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang M and Hui P: A timely update of
immunohistochemistry and molecular classification in the diagnosis
and risk assessment of endometrial carcinomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
145:1367–1378. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network;
Kandoth C, Schultz N, Cherniack AD, Akbani R, Liu Y, Shen H,
Robertson AG, Pashtan I, Shen R, et al: Integrated genomic
characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 497:67–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murali R, Soslow RA and Weigelt B:
Classification of endometrial carcinoma: more than two types.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e268–e278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Winterhoff B, Thomaier L, Mullany S and
Powell MA: Molecular characterization of endometrial cancer and
therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 32:76–83. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Dyba T, Randi G, Bettio M, Gavin A, Visser O and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality patterns in Europe Estimates for 40
countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur J Cancer. 103:356–387.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McAlpine JN, Temkin SM and Mackay HJ:
Endometrial cancer: Not your grandmother's cancer. Cancer.
122:2787–2798. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hazelwood E, Sanderson E, Tan VY, Ruth KS,
Frayling TM, Dimou N, Gunter MJ, Dossus L, Newton C, Ryan N, et al:
Identifying molecular mediators of the relationship between body
mass index and endometrial cancer risk: A mendelian randomization
analysis. BMC Med. 20:1252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Merritt MA, Strickler HD, Hutson AD,
Einstein MH, Rohan TE, Xue X, Sherma ME, Brinton LA, Yu H, Miller
DS, et al: Sex hormones, insulin, and insulin-like growth factors
in recurrence of high-stage endometrial cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 30:719–726. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O,
Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation
reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.
149:1635–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: m6A
modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: Roles and therapeutic
implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 37:270–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: The biogenesis
and precise control of RNA m6A methylation. Trends
Genet. 36:44–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M and Ju S: The
potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 19:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He L, Li H, Wu A, Peng Y, Shu G and Yin G:
Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer. Mol Cancer.
18:1762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu Y, Wang S, Liu J, Huang Y, Gong C, Liu
J, Xiao Y and Yang S: New sights in cancer: Component and function
of N6-methyladenosine modification. Biomed Pharmacother.
122:1096942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He PC and He C: m6 A RNA methylation: From
mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J. 40:e1059772021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R and
Gregory RI: The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes translation
in human cancer cells. Mol Cell. 62:335–345. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang
L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, et al: A METTL3-METTL14 complex
mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem
Biol. 10:93–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Huang J, Dong X, Gong Z, Qin LY, Yang S,
Zhu YL, Wang X, Zhang D, Zou T, Yin P and Tang C: Solution
structure of the RNA recognition domain of METTL3-METTL14
N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Protein Cell.
10:272–284. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X,
Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS, et al: Mammalian WTAP is
a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine
methyltransferase. Cell Res. 24:177–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yue Y, Liu J, Cui X, Cao J, Luo G, Zhang
Z, Cheng T, Gao M, Shu X, Ma H, et al: VIRMA mediates preferential
m6A mRNA methylation in 3'UTR and near stop codon and
associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov. 4:102018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A,
Jackson C, Guttman M and Jaffrey SR: m(6)A RNA methylation promotes
XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 537:369–373.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu D, Zhou J, Zhao J, Jiang G, Zhang X,
Zhang Y and Dong M: ZC3H13 suppresses colorectal cancer
proliferation and invasion via inactivating Ras-ERK signaling. J
Cell Physiol. 234:8899–8907. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wen J, Lv R, Ma H, Shen H, He C, Wang J,
Jiao F, Liu H, Yang P, Tan L, et al: Zc3h13 regulates nuclear RNA
m6A methylation and mouse embryonic stem cell
self-renewal. Mol Cell. 69:1028–1038.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shen D, Wang B, Gao Y, Zhao L, Bi Y, Zhang
J, Wang N, Kang H, Pang J, Liu Y, et al: Detailed resume of RNA
m6A demethylases. Acta Pharm Sin B. 12:2193–2205. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang
Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG and He C: N6-methyladenosine in
nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat
Chem Biol. 7:885–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wei J, Liu F, Lu Z, Fei Q, Ai Y, He PC,
Shi H, Cui X, Su R, Klungland A, et al: Differential
m6A, m6Am m, and m1A
demethylation mediated by FTO in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
Mol Cell. 71:973–985.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bartosovic M, Molares HC, Gregorova P,
Hrossova D, Kudla G and Vanacova S: N6-methyladenosine demethylase
FTO targets pre-mRNAs and regulates alternative splicing and 3'-end
processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:11356–11370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao S, Li X, Zhang M, Zhang N, Wang R and
Chang J: Structural characteristics of small-molecule inhibitors
targeting FTO demethylase. Future Med Chem. 13:1475–1489. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P,
Huang CM, Li CJ, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH, et al: ALKBH5
is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and
mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 49:18–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Qu J, Yan H, Hou Y, Cao W, Liu Y, Zhang E,
He J and Cai Z: RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: From mechanisms
to therapeutic potential. J Hematol Oncol. 15:82022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H and Xie W:
m6A-binding proteins: The emerging crucial performers in
epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol. 13:352020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M,
Ma J and Wu L: YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through
direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun.
7:126262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu J, Gao M, Xu S, Chen Y, Wu K, Liu H,
Wang J, Yang X, Wang J, Liu W, et al: YTHDF2/3 are required for
somatic reprogramming through different RNA deadenylation pathways.
Cell Rep. 32:1081202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR
and Qian SB: Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational
control of heat shock response. Nature. 526:591–594. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han
D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H and He C: N(6)-methyladenosine
modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell.
161:1388–1399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen Z, Zhong X, Xia M and Zhong J: The
roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor
biology and human diseases. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 26:1270–1279.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi H, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhao BS, Ma H, Hsu
PJ, Liu C and He C: YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of
N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 27:315–328.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W,
Yang Y, Sun HY, Zhu Q, Baidya P, Wang X, et al: Cytoplasmic
m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res.
27:444–447. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li S, Qi Y, Yu J, Hao Y, He B, Zhang M,
Dai Z, Jiang T, Li S, Huang F, et al: Nuclear Aurora kinase A
switches m6A reader YTHDC1 to enhance an oncogenic RNA
splicing of tumor suppressor RBM4. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7:972022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim GW, Imam H and Siddiqui A: The RNA
binding proteins YTHDC1 and FMRP regulate the nuclear export of
N6-methyladenosine-modified hepatitis B virus
transcripts and affect the viral life cycle. J Virol.
95:e00097212021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Shima H, Matsumoto M, Ishigami Y, Ebina M,
Muto A, Sato Y, Kumagai S, Ochiai K, Suzuki T and Igarashi K:
S-adenosylmethionine synthesis is regulated by selective
N6-adenosine methylation and mRNA degradation involving
METTL16 and YTHDC1. Cell Rep. 21:3354–3363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hsu PJ, Zhu Y, Ma H, Guo Y, Shi X, Liu Y,
Qi M, Lu Z, Shi H, Wang J, et al: Ythdc2 is an
N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates
mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 27:1115–1127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X,
Tavazoie S and Tavazoie SF: HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of
m(6)A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 162:1299–1308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Parisien M
and Pan T: N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches
regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 518:560–564. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu N, Zhou KI, Parisien M, Dai Q,
Diatchenko L and Pan T: N6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to
regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:6051–6063. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu
H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, et al: Recognition of RNA
N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA
stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 20:285–295. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Song K, Xu H and Wang C: The role of
N6-methyladenosine methylation in the progression of endometrial
cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. Oct 14–2020.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lan Q, Liu PY, Haase J, Bell JL,
Hüttelmaier S and Liu T: The critical role of RNA m6A
methylation in cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1285–1292. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xue T, Liu X, Zhang M, E Q, Liu S, Zou M,
Li Y, Ma Z, Han Y, Thompson P and Zhang X: PADI2-catalyzed MEK1
citrullination activates ERK1/2 and promotes IGF2BP1-mediated SOX2
mRNA stability in endometrial cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh).
8:20028312021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Liu A, Zhang D, Yang X and Song Y:
Estrogen receptor alpha activates MAPK signaling pathway to promote
the development of endometrial cancer. J Cell Biochem.
120:17593–17601. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Barra F, Evangelisti G, Ferro Desideri L,
Di Domenico S, Ferraioli D, Vellone VG, De Cian F and Ferrero S:
Investigational PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in development for
endometrial cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 28:131–142. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Wang Y, Yin L and Sun X: CircRNA
hsa_circ_0002577 accelerates endometrial cancer progression through
activating IGF1R/PI3K/Akt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:1692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA and He C:
Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:31–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Hu C, Liu J, Li Y, Jiang W, Ji D, Liu W
and Ma T: Multifaceted roles of the N6-methyladenosine
RNA methyltransferase METTL3 in cancer and immune microenvironment.
Biomolecules. 12:10422022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zheng W, Dong X, Zhao Y, Wang S, Jiang H,
Zhang M, Zheng X and Gu M: Multiple functions and mechanisms
underlying the role of METTL3 in human cancers. Front Oncol.
9:14032019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wei W, Huo B and Shi X: miR-600 inhibits
lung cancer via downregulating the expression of METTL3. Cancer
Manag Res. 11:1177–1187. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S,
Nguyen D, Minuesa G, Chou T, Chow A, Saletore Y, MacKay M, et al:
The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme
METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and
leukemia cells. Nat Med. 23:1369–1376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi
J, Millán-Zambrano G, Robson SC, Aspris D, Migliori V, Bannister
AJ, Han N, et al: Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia
by m6A-dependent translation control. Nature.
552:126–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu T, Yang S, Sui J, Xu SY, Cheng YP,
Shen B, Zhang Y, Zhang XM, Yin LH, Pu YP and Liang GY: Dysregulated
N6-methyladenosine methylation writer METTL3 contributes to the
proliferation and migration of gastric cancer. J Cell Physiol.
235:548–562. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yue B, Song C, Yang L, Cui R, Cheng X,
Zhang Z and Zhao G: METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification
is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of
gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:1422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hua W, Zhao Y, Jin X, Yu D, He J, Xie D
and Duan P: METTL3 promotes ovarian carcinoma growth and invasion
through the regulation of AXL translation and epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. Gynecol Oncol. 151:356–365. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Li X, Tang J, Huang W, Wang F, Li P, Qin
C, Qin Z, Zou Q, Wei J, Hua L, et al: The M6A methyltransferase
METTL3: Acting as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:96103–96116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cheng M, Sheng L, Gao Q, Xiong Q, Zhang H,
Wu M, Liang Y, Zhu F, Zhang Y, Zhang X, et al: The m6A
methyltransferase METTL3 promotes bladder cancer progression via
AFF4/NF-κB/MYC signaling network. Oncogene. 38:3667–3680. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu
HC, Yuan WB, Lu JC, Zhou ZJ, Lu Q, et al: METTL3 promote tumor
proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222
maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 18:1102019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao S, Liu J, Nanga P, Liu Y, Cicek AE,
Knoblauch N, He C, Stephens M and He X: Detailed modeling of
positive selection improves detection of cancer driver genes. Nat
Commun. 10:33992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang
Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang W and Ye L: HBXIP-elevated
methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer
via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. 415:–19. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Wu L, Wu D, Ning J, Liu W and Zhang D:
Changes of N6-methyladenosine modulators promote breast cancer
progression. BMC Cancer. 19:3262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu J, Eckert MA, Harada BT, Liu SM, Lu Z,
Yu K, Tienda SM, Chryplewicz A, Zhu AC, Yang Y, et al:
m6A mRNA methylation regulates AKT activity to promote
the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer. Nat
Cell Biol. 20:1074–1083. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB signaling:
Navigating the network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Xue C, Li G, Lu J and Li L: Crosstalk
between circRNAs and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer
progression. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:4002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Engelman JA, Luo J and Cantley LC: The
evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth
and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 7:606–619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ralser DJ, Condic M, Klümper N, Ellinger
J, Staerk C, Egger EK, Kristiansen G, Mustea A and Thiesler T:
Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of N6-methyladenosine
(m6A) writers, erasers, and readers in endometrial cancer. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. Jun 22–2022.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yu HL, Ma XD, Tong JF, Li JQ, Guan XJ and
Yang JH: WTAP is a prognostic marker of high-grade serous ovarian
cancer and regulates the progression of ovarian cancer cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:6191–6201. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kuai Y, Gong X, Ding L, Li F, Lei L, Gong
Y, Liu Q, Tan H, Zhang X, Liu D, et al: Wilms' tumor 1-associating
protein plays an aggressive role in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
and forms a complex with BCL6 via Hsp90. Cell Commun Signal.
16:502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tang J, Wang F, Cheng G, Si S, Sun X, Han
J, Yu H, Zhang W, Lv Q, Wei JF and Yang H: Wilms' tumor
1-associating protein promotes renal cell carcinoma proliferation
by regulating CDK2 mRNA stability. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen Y, Peng C, Chen J, Chen D, Yang B, He
B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Liu H, Dai L, et al: WTAP facilitates progression
of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic
silencing of ETS1. Mol Cancer. 18:1272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yu H, Zhao K, Zeng H, Li Z, Chen K, Zhang
Z, Li E and Wu Z: N6-methyladenosine (m6A)
methyltransferase WTAP accelerates the Warburg effect of gastric
cancer through regulating HK2 stability. Biomed Pharmacother.
133:1110752021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Li Q, Wang C, Dong W, Su Y and Ma Z: WTAP
facilitates progression of endometrial cancer via CAV-1/NF-κB axis.
Cell Biol Int. 45:1269–1277. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Azzam SK, Alsafar H and Sajini AA: FTO m6A
demethylase in obesity and cancer: Implications and underlying
molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 23:38002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Deng X, Su R, Stanford S and Chen J:
Critical enzymatic functions of FTO in obesity and cancer. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:3962018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Tao L, Mu X, Chen H, Jin D, Zhang R, Zhao
Y, Fan J, Cao M and Zhou Z: FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and
promotes bladder cancer progression. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3102021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Su R, Dong L, Li Y, Gao M, Han L,
Wunderlich M, Deng X, Li H, Huang Y, Gao L, et al: Targeting FTO
suppresses cancer stem cell maintenance and immune evasion. Cancer
Cell. 38:79–96.e11. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang Z, Zhou D, Lai Y, Liu Y, Tao X, Wang
Q, Zhao G, Gu H, Liao H, Zhu Y, et al: Estrogen induces endometrial
cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating the fat mass
and obesity-associated gene via PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling
pathways. Cancer Lett. 319:89–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhang L, Wan Y, Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Lang J,
Cheng W and Zhu L: FTO demethylates m6A modifications in HOXB13
mRNA and promotes endometrial cancer metastasis by activating the
WNT signalling pathway. RNA Biol. 18:1265–1278. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Lewczuk Ł, Pryczynicz A and
Guzińska-Ustymowicz K: Cell adhesion molecules in endometrial
cancer-a systematic review. Adv Med Sci. 64:423–429. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Delaunay S and Frye M: RNA modifications
regulating cell fate in cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 21:552–559. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhu Y, Shen J, Gao L and Feng Y: Estrogen
promotes fat mass and obesity-associated protein nuclear
localization and enhances endometrial cancer cell proliferation via
the mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:2391–2397. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S,
Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, et al: m6A
demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma
stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell
proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 31:591–606.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Chao Y, Shang J and Ji W:
ALKBH5-m6A-FOXM1 signaling axis promotes proliferation
and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells under intermittent
hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 521:499–506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Shen C, Sheng Y, Zhu AC, Robinson S, Jiang
X, Dong L, Chen H, Su R, Yin Z, Li W, et al: RNA demethylase ALKBH5
selectively promotes tumorigenesis and cancer stem cell
self-renewal in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Stem Cell.
27:64–80.e9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Thalhammer A, Bencokova Z, Poole R,
Loenarz C, Adam J, O'Flaherty L, Schödel J, Mole D, Giaslakiotis K,
Schofield CJ, et al: Human AlkB homologue 5 is a nuclear
2-oxoglutarate dependent oxygenase and a direct target of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α). PLoS One. 6:e162102011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang
H, Chen I, He X and Semenza GL: Hypoxia induces the breast cancer
stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated
m6A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E2047–E2056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Guo X, Li K, Jiang W, Hu Y, Xiao W, Huang
Y, Feng Y, Pan Q and Wan R: RNA demethylase ALKBH5 prevents
pancreatic cancer progression by posttranscriptional activation of
PER1 in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 19:912020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Pu X and Gu Z and Gu Z: ALKBH5 regulates
IGF1R expression to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of
endometrial cancer. J Cancer. 11:5612–5622. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chen G, Liu B, Yin S, Li S, Guo Y, Wang M,
Wang K and Wan X: Hypoxia induces an endometrial cancer stem-like
cell phenotype via HIF-dependent demethylation of SOX2 mRNA.
Oncogenesis. 9:812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li J, Wu L, Pei M and Zhang Y: YTHDF2, a
protein repressed by miR-145, regulates proliferation, apoptosis,
and migration in ovarian cancer cells. J Ovarian Res. 13:1112020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Xu F, Li J, Ni M, Cheng J, Zhao H, Wang S,
Zhou X and Wu X: FBW7 suppresses ovarian cancer development by
targeting the N6-methyladenosine binding protein YTHDF2.
Mol Cancer. 20:452021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Li Z, Luo Q, Wang H, Liu Y, Feng X, Li Z
and Yi P: Knockdown of YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA
binding protein 2 (YTHDF2) inhibits cell proliferation and promotes
apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 36:255–263. 2020.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Shen X, Zhao K, Xu L, Cheng G, Zhu J, Gan
L, Wu Y and Zhuang Z: YTHDF2 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth by
regulating FOXC2 signaling pathway. Front Genet. 11:5920422021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Zhong L, Liao D, Zhang M, Zeng C, Li X,
Zhang R, Ma H and Kang T: YTHDF2 suppresses cell proliferation and
growth via destabilizing the EGFR mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 442:252–261. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Hong L, Pu X, Gan H, Weng L and Zheng Q:
YTHDF2 inhibit the tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer via
downregulating the expression of IRS1 methylated with
m6A. J Cancer. 12:3809–3818. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
120
|
Reuveni H, Flashner-Abramson E, Steiner L,
Makedonski K, Song R, Shir A, Herlyn M, Bar-Eli M and Levitzki A:
Therapeutic destruction of insulin receptor substrates for cancer
treatment. Cancer Res. 73:4383–4394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ganeff C, Chatel G, Munaut C, Frankenne F,
Foidart JM and Winkler R: The IGF system in in-vitro human
decidualization. Mol Hum Reprod. 15:27–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Hopkins BD, Goncalves MD and Cantley LC:
Insulin-PI3K signalling: An evolutionarily insulated metabolic
driver of cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 16:276–283. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Shen J, Feng XP, Hu RB, Wang H, Wang YL,
Qian JH and Zhou YX: N-methyladenosine reader YTHDF2-mediated long
noncoding RNA FENDRR degradation promotes cell proliferation in
endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Lab Invest. 101:775–784. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Luo L, Zhen Y, Peng D, Wei C, Zhang X, Liu
X, Han L and Zhang Z: The role of N6-methyladenosine-modified
non-coding RNAs in the pathological process of human cancer. Cell
Death Discov. 8:3252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Li Y, Zhang W, Liu P, Xu Y, Tang L, Chen W
and Guan X: Long non-coding RNA FENDRR inhibits cell proliferation
and is associated with good prognosis in breast cancer. Onco
Targets Ther. 11:1403–1412. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Liu J and Du W: LncRNA FENDRR attenuates
colon cancer progression by repression of SOX4 protein. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:4287–4295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhang YQ, Chen X, Fu CL, Zhang W, Zhang
DL, Pang C, Liu M and Wang JY: FENDRR reduces tumor invasiveness in
prostate cancer PC-3 cells by targeting CSNK1E. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:7327–7337. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Bian PP, Liu SY, Luo QP and Xiong ZT:
YTHDF2 is a novel diagnostic marker of endometrial adenocarcinoma
and endometrial atypical hyperplasia/intraepithelial neoplasia.
Pathol Res Pract. 234:1539192022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Müller S, Bley N, Glaß M, Busch B,
Rousseau V, Misiak D, Fuchs T, Lederer M and Hüttelmaier S: IGF2BP1
enhances an aggressive tumor cell phenotype by impairing
miRNA-directed downregulation of oncogenic factors. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:6285–6303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Sun CY, Cao D, Du BB, Chen CW and Liu D:
The role of Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins
(IGF2BPs) as m6A readers in cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
18:2744–2758. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
131
|
Ma J, Yang D and Ma XX: Immune
infiltration-related N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation regulators
influence the malignancy and prognosis of endometrial cancer. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:16287–16315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Zhang L, Wan Y, Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Gu Z, Ma
X, Nie S, Yang J, Lang J, Cheng W and Zhu L: IGF2BP1 overexpression
stabilizes PEG10 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner and promotes
endometrial cancer progression. Theranostics. 11:1100–1114. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Nicholson AL and Pasquinelli AE: Tales of
detailed poly(A) tails. Trends Cell Biol. 29:191–200. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Xie T, Pan S, Zheng H, Luo Z, Tembo KM,
Jamal M, Yu Z, Yu Y, Xia J, Yin Q, et al: PEG10 as an oncogene:
Expression regulatory mechanisms and role in tumor progression.
Cancer Cell Int. 18:1122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Peng YP, Zhu Y, Yin LD, Zhang JJ, Wei JS,
Liu X, Liu XC, Gao WT, Jiang KR and Miao Y: PEG10 overexpression
induced by E2F-1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:302017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Li Y, Guo D, Lu G, Mohiuddin Chowdhury
ATM, Zhang D, Ren M, Chen Y, Wang R and He S: LncRNA SNAI3-AS1
promotes PEG10-mediated proliferation and metastasis via decoying
of miR-27a-3p and miR-34a-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 11:6852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kawai Y, Imada K, Akamatsu S, Zhang F,
Seiler R, Hayashi T, Leong J, Beraldi E, Saxena N, Kretschmer A, et
al: Paternally expressed gene 10 (PEG10) promotes growth, invasion,
and survival of bladder cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 19:2210–2220.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Chang X, Han J, Pang L, Zhao Y, Yang Y and
Shen Z: Increased PADI4 expression in blood and tissues of patients
with malignant tumors. BMC Cancer. 9:402009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Pang X, Zhang X, Huang Y and Qian S:
Development and validation of m6A regulators' prognostic
significance for endometrial cancer. Medicine (Baltimore).
100:e265512021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Wang Y, Ren F, Song Z, Wang X and Ma X:
Multiomics profile and prognostic gene signature of m6A regulators
in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. J Cancer. 11:6390–6401.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Han Y, Liu D and Li L: PD-1/PD-L1 pathway:
Current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 10:727–742.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhai J, Li S, Li Y and Du Y: Data mining
analysis of the prognostic impact of N6-methyladenosine
regulators in patients with endometrial adenocarcinoma. J Cancer.
12:4729–4738. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
143
|
Huisman B, Manske G, Carney S and Kalantry
S: Functional dissection of the m6A RNA modification. Trends
Biochem Sci. 42:85–86. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS and Yang YG:
Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers,
readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 28:616–624.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Xu Z, Peng B, Cai Y, Wu G, Huang J, Gao M,
Guo G, Zeng S, Gong Z and Yan Y: N6-methyladenosine RNA
modification in cancer therapeutic resistance: Current status and
perspectives. Biochem Pharmacol. 182:1142582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Su R, Dong L, Li C, Nachtergaele S,
Wunderlich M, Qing Y, Deng X, Wang Y, Weng X, Hu C, et al: R-2HG
exhibits anti-tumor activity by targeting
FTO/m6A/MYC/CEBPA signaling. Cell. 172:90–105.e23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Zhang J, Tsoi H, Li X, Wang H, Gao J, Wang
K, Go MY, Ng SC, Chan FK, Sung JJ and Yu J: Carbonic anhydrase IV
inhibits colon cancer development by inhibiting the Wnt signalling
pathway through targeting the WTAP-WT1-TBL1 axis. Gut.
65:1482–1493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|