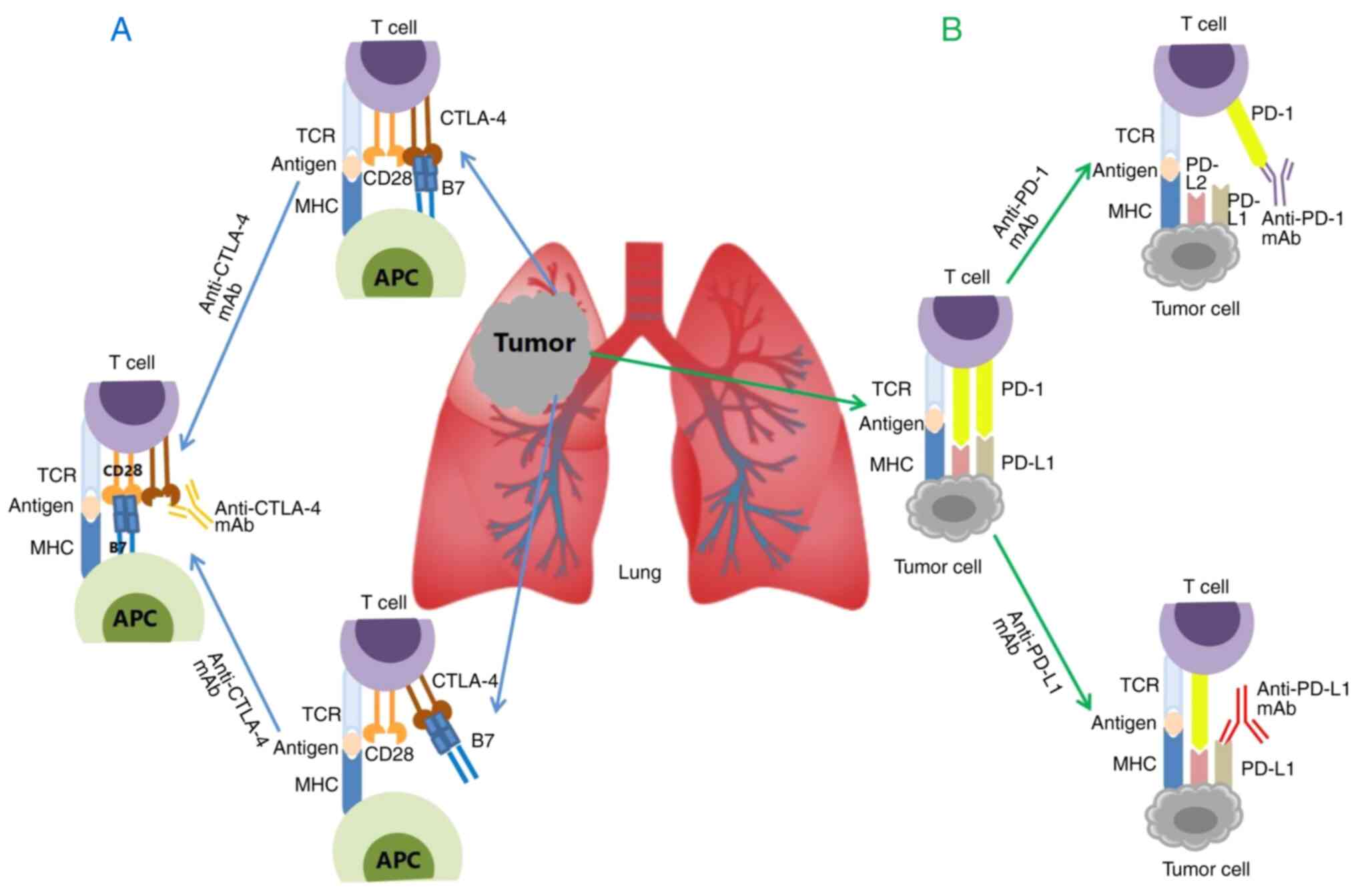
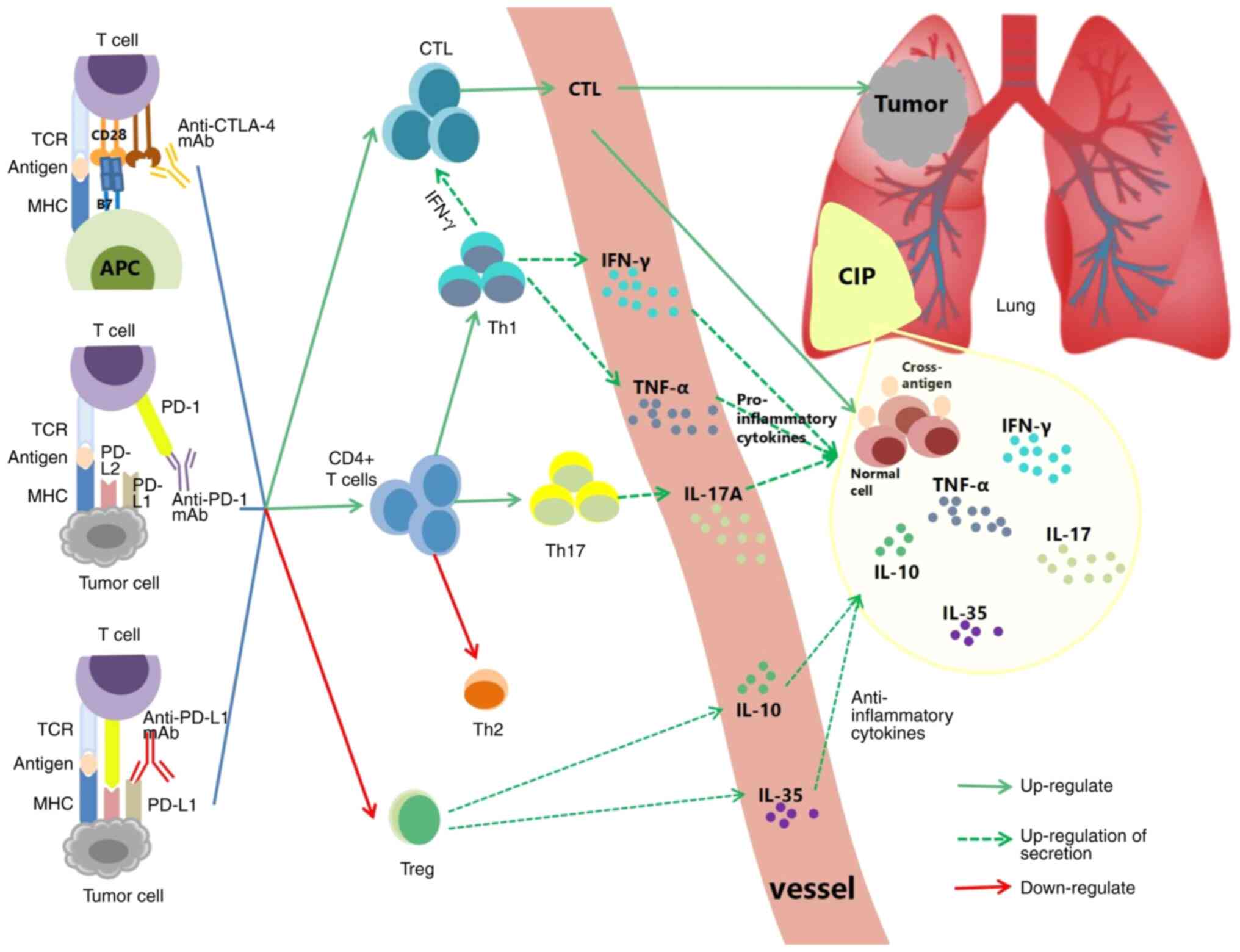
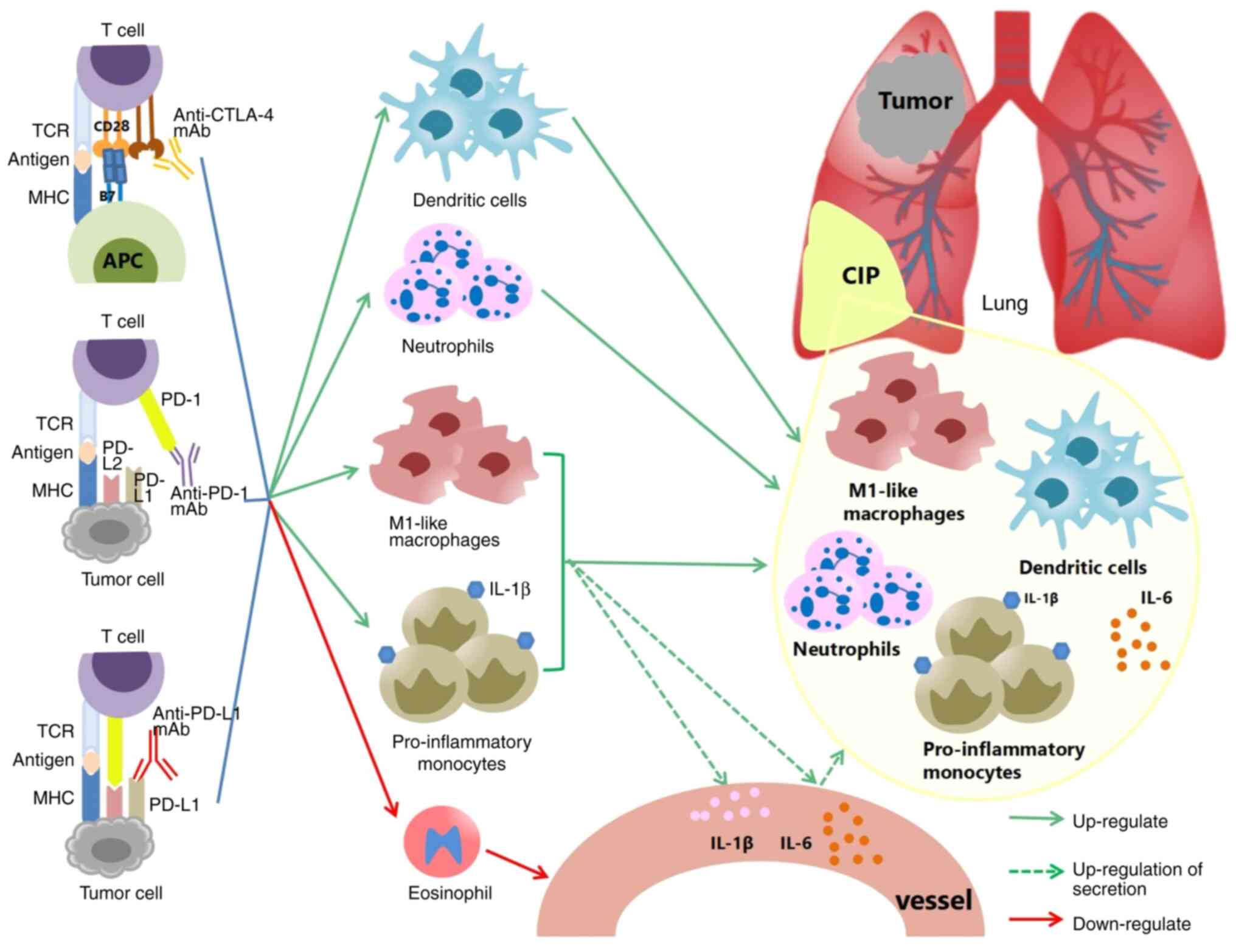
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Toi Y, Sugawara S, Kawashima Y, Aiba T,
Kawana S, Saito R, Tsurumi K, Suzuki K, Shimizu H, Sugisaka J, et
al: Association of immune-related adverse events with clinical
benefit in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
treated with nivolumab. Oncologist. 23:1358–1365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ozkaya S, Findik S, Dirican A and Atici
AG: Long-term survival rates of patients with stage IIIB and IV
non-small cell lung cancer treated with cisplatin plus vinorelbine
or gemcitabine. Exp Ther Med. 4:1035–1038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, Carcereny
E, Leighl NB, Ahn MJ, Eder JP, Balmanoukian AS, Aggarwal C, Horn L,
et al: Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: Results from
the phase I KEYNOTE-001 study. J Clin Oncol. 37:2518–2527. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente
D, Murakami S, Hui R, Yokoi T, Chiappori A, Lee KH, de Wit M, et
al: Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 377:1919–1929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Naidoo J, Wang X, Woo KM, Iyriboz T,
Halpenny D, Cunningham J, Chaft JE, Segal NH, Callahan MK, Lesokhin
AM, et al: Pneumonitis in patients treated with anti-programmed
death-1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J Clin Oncol.
35:709–717. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park
K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, Gadgeel SM, Hida T, Kowalski DM, Dols
MC, et al: Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with
previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3,
open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
389:255–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gettinger SN, Redman MW, Bazhenova L,
Hirsch FR, Mack PC, Schwartz LH, Bradley JD, Stinchcombe TE, Leighl
NB, Ramalingam SS, et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs nivolumab
for previously treated patients with stage IV squamous cell lung
cancer: The lung-MAP S1400I phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA
Oncol. 7:1368–1377. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hellmann MD, Ciuleanu TE, Pluzanski A, Lee
JS, Otterson GA, Audigier-Valette C, Minenza E, Linardou H, Burgers
S, Salman P, et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a
high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med. 378:2093–2104. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boyer M, Şendur MAN, Rodríguez-Abreu D,
Park K, Lee DH, Çiçin I, Yumuk PF, Orlandi FJ, Leal TA, Molinier O,
et al: Pembrolizumab plus ipilimumab or placebo for metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score ≥50%:
Randomized, double-blind phase III KEYNOTE-598 study. J Clin Oncol.
39:2327–2338. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rizvi NA, Cho BC, Reinmuth N, Lee KH, Luft
A, Ahn MJ, van den Heuvel MM, Cobo M, Vicente D, Smolin A, et al:
Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab vs standard chemotherapy in
first-line treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: The
MYSTIC phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:661–674.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cascone T, William WN Jr, Weissferdt A,
Leung CH, Lin HY, Pataer A, Godoy MCB, Carter BW, Federico L,
Reuben A, et al: Neoadjuvant nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab
in operable non-small cell lung cancer: The phase 2 randomized
NEOSTAR trial. Nat Med. 27:504–514. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khoja L, Day D, Wei-Wu Chen T, Siu LL and
Hansen AR: Tumour- and class-specific patterns of immune-related
adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic
review. Ann Oncol. 28:2377–2385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen K and Sun B: Incidence and risk of
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-associated pneumonia in advance cancer
patients: A meta-analysis. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 23:927–940.
2020.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu J, Hasegawa T, Horio
Y, Inaba Y, Hanai N, Muro K and Hida T: Pre-existing interstitial
lung disease is associated with onset of nivolumab-induced
pneumonitis in patients with solid tumors: A retrospective
analysis. BMC Cancer. 21:9242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV, Chandra S,
Menzer C, Ye F, Zhao S, Das S, Beckermann KE, Ha L, et al: Fatal
toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 4:1721–1728. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishino M, Giobbie-Hurder A, Hatabu H,
Ramaiya NH and Hodi FS: Incidence of programmed cell death 1
inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with advanced cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2:1607–1616. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hahn AW, Gill DM, Agarwal N and Maughan
BL: PD-1 checkpoint inhibition: Toxicities and management. Urol
Oncol. 35:701–707. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Cancer Institute: Common
Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v 5.0. Available
from: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applica-tions/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf.
|
|
20
|
Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, Provencio M,
Mitsudomi T, Awad MM, Felip E, Broderick SR, Brahmer JR, Swanson
SJ, et al: Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 386:1973–1985. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao S, Li N, Gao S, Xue Q, Ying J, Wang S,
Tao X, Zhao J, Mao Y, Wang B, et al: Neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor
(Sintilimab) in NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 15:816–826. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Zhang T, Huang Y, Li W, Zhao J,
Yang Y, Li C, Wang L and Bi N: Real-world safety and efficacy of
consolidation durvalumab after chemoradiation therapy for stage III
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 112:1154–1164. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fukihara J, Sakamoto K, Koyama J, Ito T,
Iwano S, Morise M, Ogawa M, Kondoh Y, Kimura T, Hashimoto N and
Hasegawa Y: Prognostic impact and risk factors of immune-related
pneumonitis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who
received programmed death 1 inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer.
20:442–450.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shibaki R, Murakami S, Matsumoto Y,
Yoshida T, Goto Y, Kanda S, Horinouchi H, Fujiwara Y, Yamamoto N,
Kusumoto M, et al: Association of immune-related pneumonitis with
the presence of preexisting interstitial lung disease in patients
with non-small lung cancer receiving anti-programmed cell death 1
antibody. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 69:15–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fujimoto D, Miura S, Yoshimura K, Wakuda
K, Oya Y, Yokoyama T, Yokoi T, Asao T, Tamiya M, Nakamura A, et al:
Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy-induced pneumonitis in chemo-naïve
patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A
multicentre, retrospective cohort study. Eur J Cancer. 150:63–72.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ono K, Ono H, Toi Y, Sugisaka J, Aso M,
Saito R, Kawana S, Aiba T, Odaka T, Matsuda S, et al: Association
of immune-related pneumonitis with clinical benefit of
anti-programmed cell death-1 monotherapy in advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Med. 10:4796–4804. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chu X, Zhao J, Zhou J, Zhou F, Jiang T,
Jiang S, Sun X, You X, Wu F, Ren S, et al: Association of baseline
peripheral-blood eosinophil count with immune checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis and clinical outcomes in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint
inhibitors. Lung Cancer. 150:76–82. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cui P, Huang D, Wu Z, Tao H, Zhang S, Ma
J, Liu Z, Wang J, Huang Z, Chen S, et al: Association of
immune-related pneumonitis with the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
12:17588359209220332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang A, Xu Y, Zang X, Wu C, Gao J, Sun X,
Xie M, Ma X, Deng H, Song J, et al: Radiographic features and
prognosis of early- and late-onset non-small cell lung cancer
immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. BMC Cancer.
21:6342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamagata A, Yokoyama T, Fukuda Y and
Ishida T: Impact of interstitial lung disease associated with
immune checkpoint inhibitors on prognosis in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 87:251–258.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chao Y, Zhou J, Hsu S, Ding N, Li J, Zhang
Y, Xu X, Tang X, Wei T, Zhu Z, et al: Risk factors for immune
checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in non-small cell lung
cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 11:295–306. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crinò L,
Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE,
Holgado E, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced
squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
373:123–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Suresh K, Voong KR, Shankar B, Forde PM,
Ettinger DS, Marrone KA, Kelly RJ, Hann CL, Levy B, Feliciano JL,
et al: Pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving
immune checkpoint immunotherapy: incidence and risk factors. J
Thorac Oncol. 13:1930–1939. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho JY, Kim J, Lee JS, Kim YJ, Kim SH, Lee
YJ, Cho YJ, Yoon HI, Lee JH, Lee CT and Park JS: Characteristics,
incidence, and risk factors of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related
pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 125:150–156. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Y, Shao C, Li S, Xu Y, Xu K, Zhang Y,
Huang H, Wang M and Xu Z: Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)/PD-ligand
1(PD-L1) inhibitors-related pneumonitis in patients with advanced
non-small cell lung cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 16:299–304.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Q, Tang L, Zhou Y, He W and Li W:
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated pneumonitis in non-small
cell lung cancer: Current understanding in characteristics,
diagnosis, and management. Front Immunol. 12:6639862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Gao F, Jin S, Gao W, Chen S and
Guo R: Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in Chinese lung cancer
patients: Clinical characteristics and risk factors. Ann Palliat
Med. 9:3957–3965. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim ST, Sheshadri A, Shannon V,
Kontoyiannis DP, Kantarjian H, Garcia-Manero G, Ravandi F, Im JS,
Boddu P, Bashoura L, et al: Distinct immunophenotypes of T cells in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from leukemia patients with immune
checkpoint inhibitors-related pulmonary complications. Front
Immunol. 11:5904942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Si X, Song P,
Xiao Y, Yang X, Song L, Shi J, Zhao H and Zhang L: Clinical
characteristics and management of immune checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis: A single-institution retrospective
study. Cancer Med. 10:188–198. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nishino M, Ramaiya NH, Awad MM, Sholl LM,
Maattala JA, Taibi M, Hatabu H, Ott PA, Armand PF and Hodi FS: PD-1
inhibitor-related pneumonitis in advanced cancer patients:
Radiographic patterns and clinical course. Clin Cancer Res.
22:6051–6060. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tone M, Izumo T, Awano N, Kuse N, Inomata
M, Jo T, Yoshimura H, Minami J, Takada K, Miyamoto S and Kunitoh H:
High mortality and poor treatment efficacy of immune checkpoint
inhibitors in patients with severe grade checkpoint inhibitor
pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer.
10:2006–2012. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Suresh K, Naidoo J, Lin CT and Danoff S:
Immune checkpoint immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer:
Benefits and pulmonary toxicities. Chest. 154:1416–1423. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ribas A and Wolchok JD: Cancer
immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 359:1350–1355.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schildberg FA, Klein SR, Freeman GJ and
Sharpe AH: Coinhibitory pathways in the B7‑CD28 ligand‑receptor
family. Immunity. 44:955–972. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qureshi OS, Zheng Y, Nakamura K, Attridge
K, Manzotti C, Schmidt EM, Baker J, Jeffery LE, Kaur S, Briggs Z,
et al: Trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86: A molecular basis for
the cell-extrinsic function of CTLA-4. Science. 332:600–603. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Baumeister SH, Freeman GJ, Dranoff G and
Sharpe AH: Coinhibitory pathways in immunotherapy for cancer. Annu
Rev Immunol. 34:539–573. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kang SP, Gergich K, Lubiniecki GM, de
Alwis DP, Chen C, Tice MAB and Rubin EH: Pembrolizumab KEYNOTE-001:
An adaptive study leading to accelerated approval for two
indications and a companion diagnostic. Ann Oncol. 28:1388–1398.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Suresh K, Naidoo J, Zhong Q, Xiong Y,
Mammen J, de Flores MV, Cappelli L, Balaji A, Palmer T, Forde PM,
et al: The alveolar immune cell landscape is dysregulated in
checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 129:4305–4315.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Läubli H, Koelzer VH, Matter MS, Herzig P,
Dolder Schlienger B, Wiese MN, Lardinois D, Mertz KD and Zippelius
A: The T cell repertoire in tumors overlaps with pulmonary
inflammatory lesions in patients treated with checkpoint
inhibitors. Oncoimmunology. 7:e13863622017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Rowshanravan B, Halliday N and Sansom DM:
CTLA-4: A moving target in immunotherapy. Blood. 131:58–67. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Naidoo J, Cottrell TR, Lipson EJ, Forde
PM, Illei PB, Yarmus LB, Voong KR, Feller-Kopman D, Lee H, Riemer
J, et al: Chronic immune checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. J
Immunother Cancer. 8:e0008402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Subudhi SK, Aparicio A, Gao J, Zurita AJ,
Araujo JC, Logothetis CJ, Tahir SA, Korivi BR, Slack RS, Vence L,
et al: Clonal expansion of CD8 T cells in the systemic circulation
precedes development of ipilimumab-induced toxicities. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 113:11919–11924. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ivanova EA and Orekhov AN: T helper
lymphocyte subsets and plasticity in autoimmunity and cancer: An
overview. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3274702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lee J, Lozano-Ruiz B, Yang FM, Fan DD,
Shen L and González-Navajas JM: The multifaceted role of Th1, Th9,
and Th17 cells in immune checkpoint inhibition therapy. Front
Immunol. 12:6256672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dejima H, Hu X, Chen R, Zhang J, Fujimoto
J, Parra ER, Haymaker C, Hubert SM, Duose D, Solis LM, et al:
Immune evolution from preneoplasia to invasive lung adenocarcinomas
and underlying molecular features. Nat Commun. 12:27222021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dulos J, Carven GJ, van Boxtel SJ, Evers
S, Driessen-Engels LJ, Hobo W, Gorecka MA, de Haan AF, Mulders P,
Punt CJ, et al: PD-1 blockade augments Th1 and Th17 and suppresses
Th2 responses in peripheral blood from patients with prostate and
advanced melanoma cancer. J Immunother. 35:169–178. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yoshino K, Nakayama T, Ito A, Sato E and
Kitano S: Severe colitis after PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in
advanced melanoma patients: potential role of Th1-dominant immune
response in immune-related adverse events: Two case reports. BMC
Cancer. 19:10192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang YN, Lou DF, Li DY, Jiang W, Dong JY,
Gao W and Chen HC: Elevated levels of IL-17A and IL-35 in plasma
and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid are associated with checkpoint
inhibitor pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Lett. 20:611–622. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Passat T, Touchefeu Y, Gervois N, Jarry A,
Bossard C and Bennouna J: Physiopathological mechanisms of
immune-related adverse events induced by anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1 and
anti-PD-L1 antibodies in cancer treatment. Bull Cancer.
105:1033–1041. 2018.In French. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Martin-Orozco N, Muranski P, Chung Y, Yang
XO, Yamazaki T, Lu S, Hwu P, Restifo NP, Overwijk WW and Dong C: T
helper 17 cells promote cytotoxic T cell activation in tumor
immunity. Immunity. 31:787–798. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Franken A, Van Mol P, Vanmassenhove S,
Donders E, Schepers R, Van Brussel T, Dooms C, Yserbyt J, De Crem
N, Testelmans D, et al: Single-cell transcriptomics identifies
pathogenic T-helper 17.1 cells and pro-inflammatory monocytes in
immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. J Immunother
Cancer. 10:e0053232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gianchecchi E and Fierabracci A:
Inhibitory receptors and pathways of lymphocytes: The role of PD-1
in treg development and their involvement in autoimmunity onset and
cancer progression. Front Immunol. 9:23742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
D'Alessio FR, Tsushima K, Aggarwal NR,
West EE, Willett MH, Britos MF, Pipeling MR, Brower RG, Tuder RM,
McDyer JF and King LS: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental
lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung
injury. J Clin Invest. 119:2898–2913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lin X, Deng J, Deng H, Yang Y, Sun N, Zhou
M, Qin Y, Xie X, Li S, Zhong N, et al: Comprehensive analysis of
the immune microenvironment in checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis.
Front Immunol. 12:8184922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Y, Jia X, Du Y, Mao Z, Zhang Y, Shen Y,
Sun H, Liu M, Niu G, Wang J, et al: Eosinophil as a biomarker for
diagnosis, prediction, and prognosis evaluation of severe
checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. Front Oncol. 12:8271992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kowalski B, Valaperti A, Bezel P, Steiner
UC, Scholtze D, Wieser S, Vonow-Eisenring M, Widmer A, Kohler M and
Franzen D: Analysis of cytokines in serum and bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid in patients with immune-checkpoint
inhibitor-associated pneumonitis: A cross-sectional case-control
study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 148:1711–1720. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhou Q, Chen M, Jiang O, Pan Y, Hu D, Lin
Q, Wu G, Cui J, Chang J, Cheng Y, et al: Sugemalimab versus placebo
after concurrent or sequential chemoradiotherapy in patients with
locally advanced, unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung
cancer in China (GEMSTONE-301): Interim results of a randomised,
double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:209–219.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lim SY, Lee JH, Gide TN, Menzies AM,
Guminski A, Carlino MS, Breen EJ, Yang JYH, Ghazanfar S, Kefford
RF, et al: Circulating cytokines predict immune-related toxicity in
melanoma patients receiving anti-PD-1-based immunotherapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 25:1557–1563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Martins F, Sykiotis GP, Maillard M, Fraga
M, Ribi C, Kuntzer T, Michielin O, Peters S, Coukos G, Spertini F,
et al: New therapeutic perspectives to manage refractory immune
checkpoint-related toxicities. Lancet Oncol. 20:e54–e64. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hunter CA and Jones SA: IL-6 as a keystone
cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol. 16:448–457. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D
and Rose-John S: The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the
cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:878–888. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lin X, Deng H, Yang Y, Wu J, Qiu G, Li S,
Xie X, Liu M, Xie Z, Qin Y, et al: Peripheral blood biomarkers for
early diagnosis, severity, and prognosis of checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer. Front
Oncol. 11:6988322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou C, Yang Y, Lin X, Fang N, Chen L,
Jiang J, Deng H, Deng Y, Wan M, Qiu G, et al: Proposed clinical
phases for the improvement of personalized treatment of checkpoint
inhibitor-related pneumonitis. Front Immunol. 13:9357792022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Iwanaga N and Kolls JK: Updates on T
helper type 17 immunity in respiratory disease. Immunology.
156:3–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Mi S, Li Z, Yang HZ, Liu H, Wang JP, Ma
YG, Wang XX, Liu HZ, Sun W and Hu ZW: Blocking IL-17A promotes the
resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via
TGF-beta1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol.
187:3003–3014. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Miossec P and Kolls JK: Targeting IL-17
and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
11:763–776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
McAlees JW, Lajoie S, Dienger K, Sproles
AA, Richgels PK, Yang Y, Khodoun M, Azuma M, Yagita H, Fulkerson
PC, et al: Differential control of CD4(+) T-cell subsets by the
PD-1/PD-L1 axis in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol.
45:1019–1029. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tarhini AA, Zahoor H, Lin Y, Malhotra U,
Sander C, Butterfield LH and Kirkwood JM: Baseline circulating
IL-17 predicts toxicity while TGF-β1 and IL-10 are prognostic of
relapse in ipilimumab neoadjuvant therapy of melanoma. J Immunother
Cancer. 3:392015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Kolb M, Margetts PJ, Anthony DC, Pitossi F
and Gauldie J: Transient expression of IL-1beta induces acute lung
injury and chronic repair leading to pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin
Invest. 107:1529–1536. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen Z and He J: Infliximab in the
treatment of tislelizumab-induced steroid-refractory immune
checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonia: Case report and literature
review. Transl Cancer Res. 11:3309–3314. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Shamskhou EA, Kratochvil MJ, Orcholski ME,
Nagy N, Kaber G, Steen E, Balaji S, Yuan K, Keswani S, Danielson B,
et al: Hydrogel-based delivery of Il-10 improves treatment of
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Biomaterials. 203:52–62.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Osuna-Gómez R, Barril S, Mulet M, Zamora
Atenza C, Millan-Billi P, Pardessus A, Brough DE, Sabzevari H,
Semnani RT, Castillo D and Vidal S: The immunoregulatory role of
IL-35 in patients with interstitial lung disease. Immunology.
168:610–621. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
de Waal Malefyt R, Haanen J, Spits H,
Roncarolo MG, te Velde A, Figdor C, Johnson K, Kastelein R, Yssel H
and de Vries JE: Interleukin 10 (IL-10) and viral IL-10 strongly
reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing
the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of
class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med.
174:915–924. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Okada K, Fujimura T, Kikuchi T, Aino M,
Kamiya Y, Izawa A, Iwamura Y, Goto H, Okabe I, Miyake E, et al:
Effect of interleukin (IL)-35 on IL-17 expression and production by
human CD4+ T cells. PeerJ. 5:e29992017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Wang HM, Zhang XH, Feng MM, Qiao YJ, Ye
LQ, Chen J, Fan FF and Guo LL: Interleukin-35 suppresses the
antitumor activity of T cells in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:2407–2419. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Castellani ML, Anogeianaki A, Felaco P,
Toniato E, De Lutiis MA, Shaik B, Fulcheri M, Vecchiet J, Tetè S,
Salini V, et al: IL-35, an anti-inflammatory cytokine which expands
CD4+CD25+ Treg cells. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 24:131–135.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang H, Zhou F, Zhao C, Cheng L, Zhou C,
Qiao M, Li X and Chen X: Interleukin-10 is a promising marker for
immune-related adverse events in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer receiving immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 13:8403132022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Toi Y, Sugawara S, Sugisaka J, Ono H,
Kawashima Y, Aiba T, Kawana S, Saito R, Aso M, Tsurumi K, et al:
Profiling preexisting antibodies in patients treated with anti-PD-1
therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol.
5:376–383. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhou J, Zhao J, Jia Q, Chu Q, Zhou F, Chu
X, Zhao W, Ren S, Zhou C and Su C: Peripheral blood autoantibodies
against to tumor-associated antigen predict clinical outcome to
immune checkpoint inhibitor-based treatment in advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 11:6255782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Tahir SA, Gao J, Miura Y, Blando J,
Tidwell RSS, Zhao H, Subudhi SK, Tawbi H, Keung E, Wargo J, et al:
Autoimmune antibodies correlate with immune checkpoint
therapy-induced toxicities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:22246–22251. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chaput N, Lepage P, Coutzac C, Soularue E,
Le Roux K, Monot C, Boselli L, Routier E, Cassard L, Collins M, et
al: Baseline gut microbiota predicts clinical response and colitis
in metastatic melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Ann Oncol.
28:1368–1379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu J, Hasegawa T, Horio
Y, Inaba Y, Yatabe Y and Hida T: Pre-existing pulmonary fibrosis is
a risk factor for anti-PD-1-related pneumonitis in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lung Cancer.
125:212–217. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kanai O, Kim YH, Demura Y, Kanai M, Ito T,
Fujita K, Yoshida H, Akai M, Mio T and Hirai T: Efficacy and safety
of nivolumab in non-small cell lung cancer with preexisting
interstitial lung disease. Thorac Cancer. 9:847–855. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhang M, Fan Y, Nie L, Wang G, Sun K and
Cheng Y: Clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy
in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and
preexisting interstitial lung diseases: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Chest. 161:1675–1686. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Tasaka Y, Honda T, Nishiyama N, Tsutsui T,
Saito H, Watabe H, Shimaya K, Mochizuki A, Tsuyuki S, Kawahara T,
et al: Non-inferior clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial
lung disease. Lung Cancer. 155:120–126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Fujimoto D, Yomota M, Sekine A, Morita M,
Morimoto T, Hosomi Y, Ogura T, Tomioka H and Tomii K: Nivolumab for
advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with mild idiopathic
interstitial pneumonia: A multicenter, open-label single-arm phase
II trial. Lung Cancer. 134:274–278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yamaguchi O, Kaira K, Shinomiya S, Mouri
A, Hashimoto K, Shiono A, Miura Y, Akagami T, Imai H, Kobayashi K
and Kagamu H: Pre-existing interstitial lung disease does not
affect prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with PD-L1
expression ≥50% on first-line pembrolizumab. Thorac Cancer.
12:304–313. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Lu Y, Zhong W, Liu Y, Chen W, Zhang J,
Zeng Z, Huang H, Qiao Y, Wan X, Meng X, et al: Anti-PD-L1 antibody
alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inducing autophagy via inhibition
of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 104:1085042022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Sul J, Blumenthal GM, Jiang X, He K,
Keegan P and Pazdur R: FDA approval summary: Pembrolizumab for the
treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
whose tumors express programmed death-ligand 1. Oncologist.
21:643–650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhai X, Zhang J, Tian Y, Li J, Jing W, Guo
H and Zhu H: The mechanism and risk factors for immune checkpoint
inhibitor pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Cancer Biol Med. 17:599–611. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Galant-Swafford J, Troesch A, Tran L,
Weaver A, Doherty TA and Patel SP: Landscape of immune-related
pneumonitis in cancer patients with asthma being treated with
immune checkpoint blockade. Oncology. 98:123–130. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Barrón F, Sánchez R, Arroyo-Hernández M,
Blanco C, Zatarain-Barrón ZL, Catalán R, Ramos-Ramírez M, Cardona
AF, Flores-Estrada D and Arrieta O: Risk of developing checkpoint
immune pneumonitis and its effect on overall survival in non-small
cell lung cancer patients previously treated with radiotherapy.
Front Oncol. 10:5702332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Cui P, Liu Z, Wang G, Ma J, Qian Y, Zhang
F, Han C, Long Y, Li Y, Zheng X, et al: Risk factors for
pneumonitis in patients treated with anti-programmed death-1
therapy: A case-control study. Cancer Med. 7:4115–4120. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K,
Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC, Garon EB and Lee P:
Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of
pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: A
secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:895–903. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Voong KR, Hazell SZ, Fu W, Hu C, Lin CT,
Ding K, Suresh K, Hayman J, Hales RK, Alfaifi S, et al:
Relationship between prior radiotherapy and checkpoint-inhibitor
pneumonitis in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
Clin Lung Cancer. 20:e470–e479. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Lin GF, Xu Y, Lin H, Yang DY, Chen L,
Huang LL, Su XS, Xu YX and Zeng YM: The association between the
incidence risk of pneumonitis and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced
NSCLC: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int
Immunopharmacol. 99:1080112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wang M, Liang H, Wang W, Zhao S, Cai X,
Zhao Y, Li C, Cheng B, Xiong S, Li J, et al: Immune-related adverse
events of a PD-L1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy versus a PD-L1
inhibitor alone in first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell
lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Cancer.
127:777–786. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Matsuo N, Azuma K, Kojima T, Ishii H,
Tokito T, Yamada K and Hoshino T: Comparative incidence of
immune-related adverse events and hyperprogressive disease in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune
checkpoint inhibitors with and without chemotherapy. Invest New
Drugs. 39:1150–1158. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Oshima Y, Tanimoto T, Yuji K and Tojo A:
EGFR-TKI-associated interstitial pneumonitis in nivolumab-treated
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 4:1112–1115.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Oxnard GR, Yang JCH, Yu H, Kim SW, Saka H,
Horn L, Goto K, Ohe Y, Mann H, Thress KS, et al: TATTON: A
multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib,
savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
31:507–516. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Khunger M, Rakshit S, Pasupuleti V,
Hernandez AV, Mazzone P, Stevenson J, Pennell NA and Velcheti V:
Incidence of pneumonitis with use of programmed death 1 and
programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of trials. Chest.
152:271–281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Balasubramanian A, Onggo J, Gunjur A, John
T and Parakh S: Immune checkpoint inhibition with chemoradiotherapy
in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of safety results. Clin Lung Cancer. 22:74–82. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gomatou G, Tzilas V, Kotteas E, Syrigos K
and Bouros D: Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis.
Respiration. 99:932–942. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Li M, Spakowicz D, Zhao S, Patel SH, Johns
A, Grogan M, Miah A, Husain M, He K, Bertino EM, et al: Brief
report: inhaled corticosteroid use and the risk of checkpoint
inhibitor pneumonitis in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 69:2403–2408. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhou P, Zhao X and Wang G: Risk factors
for immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in cancer
patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Respiration.
101:1035–1050. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Sawa K, Sato I, Takeuchi M and Kawakami K:
Risk of pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with
preexisting interstitial lung diseases treated with immune
checkpoint inhibitors: A nationwide retrospective cohort study.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:591–598. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Suresh K, Psoter KJ, Voong KR, Shankar B,
Forde PM, Ettinger DS, Marrone KA, Kelly RJ, Hann CL, Levy B, et
al: Impact of checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis on survival in NSCLC
patients receiving immune checkpoint immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol.
14:494–502. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Reuss JE, Brigham E, Psoter KJ, Voong KR,
Shankar B, Ettinger DS, Marrone KA, Hann CL, Levy B, Feliciano JL,
et al: Pretreatment lung function and checkpoint inhibitor
pneumonitis in NSCLC. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2:1002202021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ,
Atkins MB, Brassil KJ, Caterino JM, Chau I, Ernstoff MS, Gardner
JM, Ginex P, et al: Management of immune-related adverse events in
patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American
society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin
Oncol. 36:1714–1768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Haanen JBAG, Carbonnel F, Robert C, Kerr
KM, Peters S and Larkin J: Management of toxicities from
immunotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 28(Suppl 4): iv119–iv142. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, Bingham CO
III, Brogdon C, Dadu R, Hamad L, Kim S, Lacouture ME, LeBoeuf NR,
et al: Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint
inhibitors: Consensus recommendations from the Society for
Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) toxicity management working group. J
Immunother Cancer. 5:952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Stroud CR, Hegde A, Cherry C, Naqash AR,
Sharma N, Addepalli S, Cherukuri S, Parent T, Hardin J and Walker
P: Tocilizumab for the management of immune mediated adverse events
secondary to PD-1 blockade. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 25:551–557. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Karayama M, Inui N, Inoue Y, Yasui H,
Hozumi H, Suzuki Y, Furuhashi K, Fujisawa T, Enomoto N, Asada K, et
al: Six-week oral prednisolone therapy for immune-related
pneumonitis: A single-arm phase II study. J Immunother Cancer.
11:e0070562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Luo J, Beattie JA, Fuentes P, Rizvi H,
Egger JV, Kern JA, Leung DYM, Lacouture ME, Kris MG, Gambarin M, et
al: Beyond steroids: Immunosuppressants in steroid-refractory or
resistant immune-related adverse events. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1759–1764. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Balaji A, Hsu M, Lin CT, Feliciano J,
Marrone K, Brahmer JR, Forde PM, Hann C, Zheng L, Lee V, et al:
Steroid-refractory PD-(L)1 pneumonitis: Incidence, clinical
features, treatment, and outcomes. J Immunother Cancer.
9:e0017312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Beattie J, Rizvi H, Fuentes P, Luo J,
Schoenfeld A, Lin IH, Postow M, Callahan M, Voss MH, Shah NJ, et
al: Success and failure of additional immune modulators in
steroid-refractory/resistant pneumonitis related to immune
checkpoint blockade. J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0018842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Camard M, Besse B, Cariou PL, Massayke S,
Laparra A, Noel N, Michot JM, Ammari S, Pavec JL and Lambotte O:
Prevalence and outcome of steroid-resistant/refractory pneumonitis
induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Respir Med Res.
82:1009692022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Xie XH, Deng HY, Lin XQ, Wu JH, Liu M, Xie
ZH, Qin YY and Zhou CZ: Case report: Nintedanib for
pembrolizumab-related pneumonitis in a patient with non-small cell
lung cancer. Front Oncol. 11:6738772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Gu J, Shi L, Jiang X, Wen J, Zheng X, Cai
H and Zhang W: Severe immune-related adverse events of immune
checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A
network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 71:2239–2254. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Hailemichael Y, Johnson DH, Abdel-Wahab N,
Foo WC, Bentebibel SE, Daher M, Haymaker C, Wani K, Saberian C,
Ogata D, et al: Interleukin-6 blockade abrogates immunotherapy
toxicity and promotes tumor immunity. Cancer Cell. 40:509–523.e6.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Renga G, Bellet MM, Pariano M, Gargaro M,
Stincardini C, D'Onofrio F, Mosci P, Brancorsini S, Bartoli A,
Goldstein AL, et al: Thymosin α1 protects from CTLA-4 intestinal
immunopathology. Life Sci Alliance. 3:e2020006622020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:1823–1833. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Carbone DP, Reck M, Paz-Ares L, Creelan B,
Horn L, Steins M, Felip E, van den Heuvel MM, Ciuleanu TE, Badin F,
et al: First-line nivolumab in stage IV or recurrent non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:2415–2426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S,
Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ,
Powell SF, et al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:2078–2092. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Paz-Ares L, Luft A, Vicente D, Tafreshi A,
Gümüş M, Mazières J, Hermes B, Çay Şenler F, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, et
al: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 379:2040–2051. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, Kowalski DM, Cho
BC, Turna HZ, Castro G Jr, Srimuninnimit V, Laktionov KK,
Bondarenko I, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for
previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or
metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised,
open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 393:1819–1830. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Yang Y, Wang Z, Fang J, Yu Q, Han B, Cang
S, Chen G, Mei X, Yang Z, Ma R, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum as first-line treatment for
locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: A randomized,
double-blind, phase 3 study (Oncology pRogram by InnovENT
anti-PD-1-11). J Thorac Oncol. 15:1636–1646. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Zhou C, Wu L, Fan Y, Wang Z, Liu L, Chen
G, Zhang L, Huang D, Cang S, Yang Z, et al: Sintilimab plus
platinum and gemcitabine as first-line treatment for advanced or
metastatic squamous NSCLC: Results from a randomized, double-blind,
phase 3 trial (ORIENT-12). J Thorac Oncol. 16:1501–1511. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhou C, Chen G, Huang Y, Zhou J, Lin L,
Feng J, Wang Z, Shu Y, Shi J, Hu Y, et al: Camrelizumab plus
carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in
chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous
non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): A randomised, open-label,
multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 9:305–314. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Sezer A, Kilickap S, Gümüş M, Bondarenko
I, Özgüroğlu M, Gogishvili M, Turk HM, Cicin I, Bentsion D, Gladkov
O, et al: Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: A
multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled
trial. Lancet. 397:592–604. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Socinski MA, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi
F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Moro-Sibilot D,
Thomas CA, Barlesi F, et al: Atezolizumab for first-line treatment
of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 378:2288–2301. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, de Marinis F,
Reinmuth N, Vergnenegre A, Barrios CH, Morise M, Felip E, Andric Z,
Geater S, et al: Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of
PD-L1-selected patients with NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 383:1328–1339.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Nishio M, Barlesi F, West H, Ball S,
Bordoni R, Cobo M, Longeras PD, Goldschmidt J Jr, Novello S,
Orlandi F, et al: Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy for first-line
treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC: Results From the randomized phase 3
IMpower132 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 16:653–664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Zhou C, Wang Z, Sun Y, Cao L, Ma Z, Wu R,
Yu Y, Yao W, Chang J, Chen J, et al: Sugemalimab versus placebo, in
combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, as first-line
treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (GEMSTONE-302):
Interim and final analyses of a double-blind, randomised, phase 3
clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:220–233. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E,
Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY, Molina J, Kim JH, Arvis CD, Ahn MJ, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated,
PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010):
A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 387:1540–1550. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Wu YL, Lu S, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Wang J, Mok
T, Zhang L, Tu HY, Wu L, Feng J, et al: Nivolumab versus docetaxel
in a predominantly Chinese patient population with previously
treated advanced NSCLC: CheckMate 078 randomized phase III clinical
trial. J Thorac Oncol. 14:867–875. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|