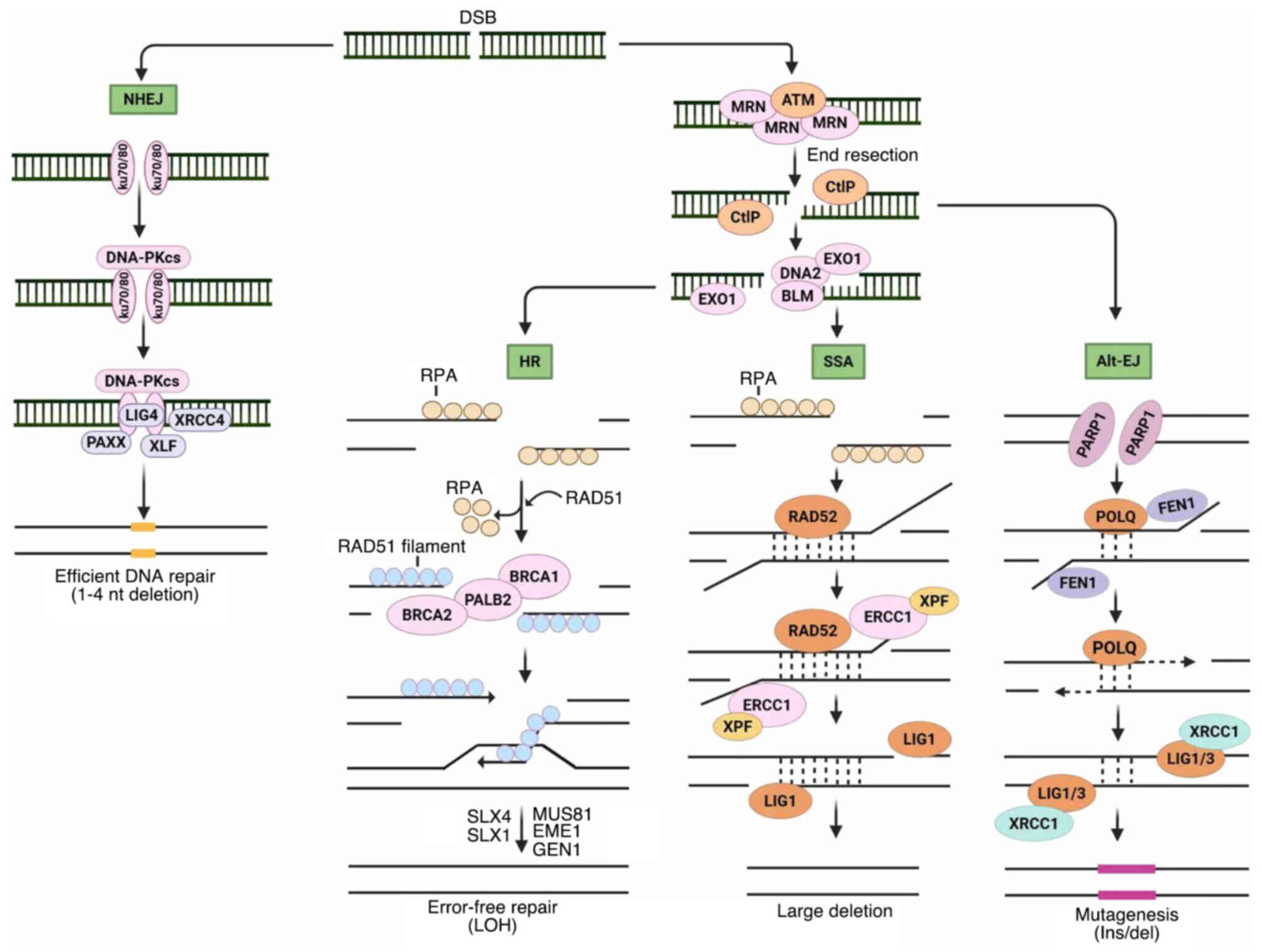
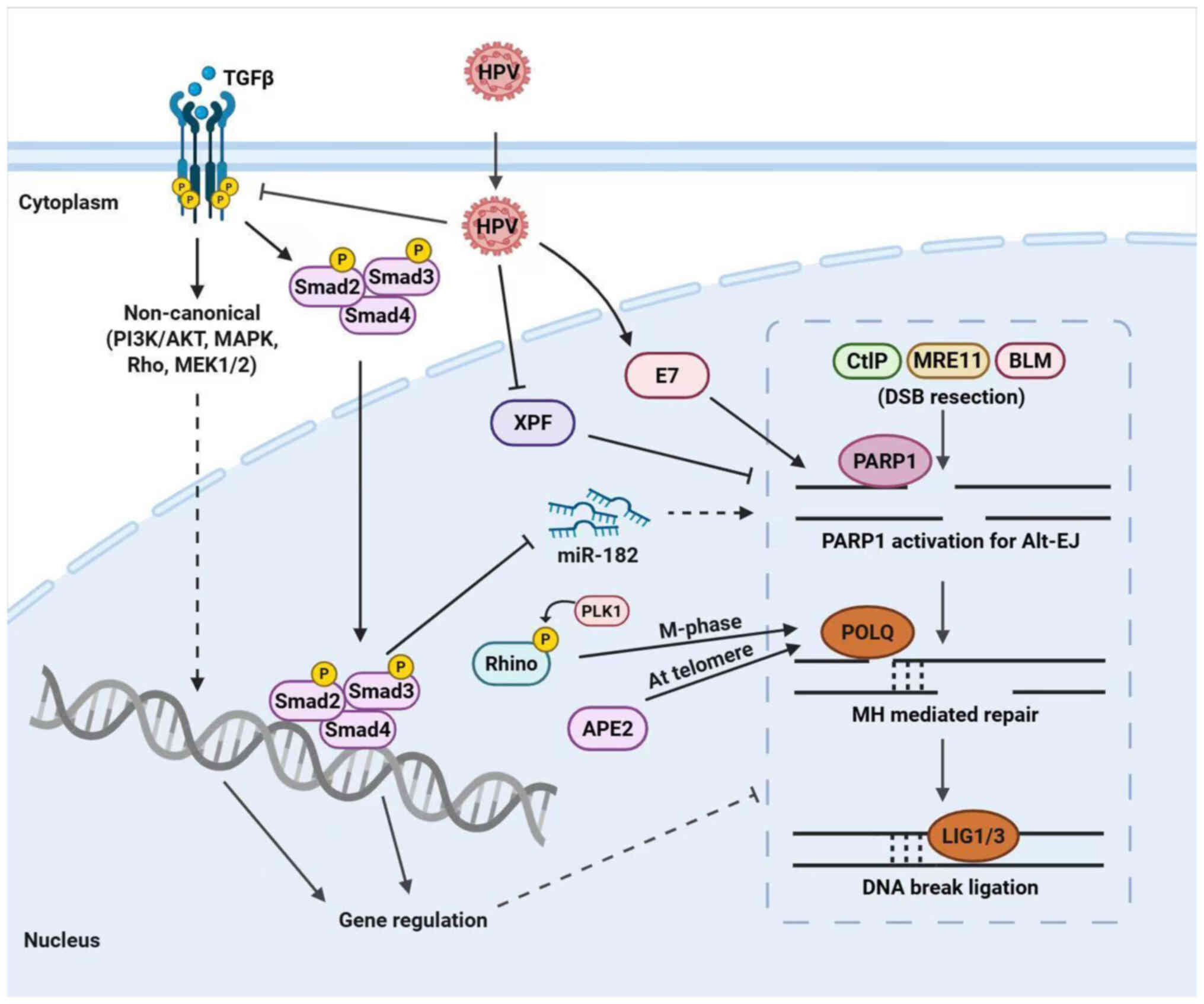
|
1
|
Liu Q, Lopez K, Murnane J, Humphrey T and
Barcellos-Hoff MH: Misrepair in context: TGFβ regulation of DNA
repair. Front Oncol. 9:7992019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Negrini S, Gorgoulis VG and Halazonetis
TD: Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:220–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Driscoll M: Diseases associated with
defective responses to DNA damage. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:a0127732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taylor AMR, Rothblum-Oviatt C, Ellis NA,
Hickson ID, Meyer S, Crawford TO, Smogorzewska A, Pietrucha B,
Weemaes C and Stewart GS: Chromosome instability syndromes. Nat Rev
Dis Primers. 5:642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chae YK, Anker JF, Carneiro BA, Chandra S,
Kaplan J, Kalyan A, Santa-Maria CA, Platanias LC and Giles FJ:
Genomic landscape of DNA repair genes in cancer. Oncotarget.
7:23312–23321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma J, Setton J, Lee NY, Riaz N and Powell
SN: The therapeutic significance of mutational signatures from DNA
repair deficiency in cancer. Nat Commun. 9:32922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vilenchik MM and Knudson AG: Endogenous
DNA Double-strand breaks: Production, fidelity of repair, and
induction of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:12871–12876. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trenner A and Sartori AA: Harnessing DNA
double-strand break repair for cancer treatment. Front Oncol.
9:13882019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Linders AN, Dias IB, López Fernández T,
Tocchetti CG, Bomer N and Van der Meer P: A review of the
pathophysiological mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
and aging. NPJ Aging. 10:92024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qian J, Liao G, Chen M, Peng RW, Yan X, Du
J, Huang R, Pan M, Lin Y, Gong X, et al: Advancing cancer therapy:
New frontiers in targeting DNA damage response. Front Pharmacol.
15:14743372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: The DNA damage
response and cancer therapy. Nature. 481:287–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jasin M and Rothstein R: Repair of strand
breaks by homologous recombination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0127402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Q, Zuo N, Li X, Deng Y, Wei L and Ma
L: Novel insights into DNA damage repair defects in HPV-positive
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: From the molecular basis to
therapeutic opportunities. Genome Instability Dis. 4:255–265. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kang X, Li X, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Qiu L, Tian
C, Deng Z, Liang X, Zhang Z, Du S, et al: Extrachromosomal DNA
replication and maintenance couple with DNA damage pathway in
tumors. Cell. 188:3405–3421.e27. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ramsden DA, Carvajal-Garcia J and Gupta
GP: Mechanism, cellular functions and cancer roles of
polymerase-theta-mediated DNA end joining. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
23:125–140. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Newman JA, Cooper CD, Aitkenhead H and
Gileadi O: Structure of the helicase domain of DNA polymerase theta
reveals a possible role in the microhomology-mediated end-joining
pathway. Structure. 23:2319–2330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kent T, Chandramouly G, McDevitt SM,
Ozdemir AY and Pomerantz RT: Mechanism of microhomology-mediated
end-joining promoted by human DNA polymerase θ. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 22:230–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dueva R and Iliakis G: Alternative
pathways of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in genomic
instability and cancer. Transl Cancer Res. 2:163–177. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Daley JM and Wilson TE: Rejoining of DNA
double-strand breaks as a function of overhang length. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:896–906. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang HH, Pannunzio NR, Adachi N and
Lieber MR: Non-homologous DNA end joining and alternative pathways
to double-strand break repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 18:495–506.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Patterson-Fortin J and D'Andrea AD:
Exploiting the microhomology-mediated end-joining pathway in cancer
therapy. Cancer Res. 80:4593–4600. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Howard SM, Yanez DA and Stark JM: DNA
damage response factors from diverse pathways, including DNA
crosslink repair, mediate alternative end joining. PLoS Genetics.
11:e10049432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Q, Ma L, Jones T, Palomero L, Pujana
MA, Martinez-Ruiz H, Ha PK, Murnane J, Cuartas I, Seoane J, et al:
Subjugation of TGFβ signaling by human papilloma virus in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma shifts DNA repair from homologous
recombination to alternative end joining. Clin Cancer Res.
24:6001–6014. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Palomero L, Moore J, Guix I, Espín
R, Aytés A, Mao JH, Paulovich AG, Whiteaker JR, Ivey RG, et al:
Loss of TGFβ signaling increases alternative end-joining DNA repair
that sensitizes to genotoxic therapies across cancer types. Sci
Transl Med. 13:eabc44652021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu Z, Zan H, Pone EJ, Mai T and Casali P:
Immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination: Induction, targeting
and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. 12:517–531. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zan H, Tat C, Qiu Z, Taylor JR, Guerrero
JA, Shen T and Casali P: Rad52 competes with Ku70/Ku86 for binding
to S-region DSB ends to modulate antibody class-switch DNA
recombination. Nat Commun. 8:142442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boboila C, Yan C, Wesemann DR, Jankovic M,
Wang JH, Manis J, Nussenzweig A, Nussenzweig M and Alt FW:
Alternative end-joining catalyzes class switch recombination in the
absence of both Ku70 and DNA ligase 4. J Exp Med. 207:417–427.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Robert I, Dantzer F and Reina-San-Martin
B: Parp1 facilitates alternative NHEJ, whereas Parp2 suppresses
IgH/c-myc translocations during immunoglobulin class switch
recombination. J Exp Med. 206:1047–1056. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ortega R, Bitler BG and Arnoult N:
Multiple functions of PARP1 in the repair of DNA double strand
breaks. DNA Repair (Amst). 152:1038732025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boboila C, Oksenych V, Gostissa M, Wang
JH, Zha S, Zhang Y, Chai H, Lee CS, Jankovic M, Saez LM, et al:
Robust chromosomal DNA repair via alternative end-joining in the
absence of X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1). Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2473–2478. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saha T, Sundaravinayagam D and Di Virgilio
M: Charting a DNA repair roadmap for immunoglobulin class switch
recombination. Trends Biochem Sci. 46:184–199. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Espín R, Medina-Jover F, Sigüenza-Andrade
J, Farran-Matas S, Mateo F, Figueras A, Sanz RT, Vicent GP, Shabbir
A, Ruiz-Auladell L, et al: Harnessing transcriptional regulation of
alternative end-joining to predict cancer treatment. NAR Cancer.
7:zcaf0072025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng B, Ding Z, Hong Y, Wang Y, Zhou Y,
Chen J, Peng X and Zeng C: Research progress in DNA damage response
(DDR)-Targeting modulators: From hits to clinical candidates. Eur J
Med Chem. 287:1173472025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wright WD, Shah SS and Heyer WD:
Homologous recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand
breaks. J Biol Chem. 293:10524–10535. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ranjha L, Howard SM and Cejka P: Main
steps in DNA Double-strand break repair: An introduction to
homologous recombination and related processes. Chromosoma.
127:187–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lieber MR: The mechanism of double-strand
DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Annu
Rev Biochem. 79:181–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bhargava R, Onyango DO and Stark JM:
Regulation of single-strand annealing and its role in genome
maintenance. Trends Genet. 32:566–575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zha S, Guo C, Boboila C, Oksenych V, Cheng
HL, Zhang Y, Wesemann DR, Yuen G, Patel H, Goff PH, et al: ATM
damage response and XLF repair factor are functionally redundant in
joining DNA breaks. Nature. 469:250–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Ochi T, Blackford AN, Coates J, Jhujh S,
Mehmood S, Tamura N, Travers J, Wu Q, Draviam VM, Robinson CV, et
al: PAXX, a paralog of XRCC4 and XLF, interacts with Ku to promote
DNA double-strand break repair. Science. 347:185–188. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Shao Z, Jiang W, Lee BJ and Zha S:
PAXX promotes KU accumulation at DNA breaks and is essential for
end-joining in XLF-deficient mice. Nat Commun. 8:138162017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Voutsadakis IA and Stravodimou A:
Homologous recombination defects and mutations in DNA damage
response (DDR) genes besides BRCA1 and BRCA2 as breast cancer
biomarkers for PARP inhibitors and other DDR targeting therapies.
Anticancer Res. 43:967–981. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wen H, Feng Z, Ma Y, Liu R, Ou Q, Guo Q,
Shen Y and Wu X, Shao Y, Bao H and Wu X: Homologous recombination
deficiency in diverse cancer types and its correlation with
platinum chemotherapy efficiency in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer.
22:5502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Takamatsu S, Murakami K and Matsumura N:
Homologous recombination deficiency unrelated to platinum and PARP
inhibitor response in cell line libraries. Sci Data. 11:1712024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vu TV, Das S, Nguyen CC, Kim J and Kim JY:
Single-strand annealing: Molecular mechanisms and potential
applications in CRISPR-Cas-based precision genome editing.
Biotechnol J. 17:21004132022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liang CC, Greenhough LA, Masino L, Maslen
S, Bajrami I, Tuppi M, Skehel M, Taylor IA and West SC: Mechanism
of single-stranded DNA annealing by RAD52-RPA complex. Nature.
629:697–703. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wyatt DW, Feng W, Conlin MP, Yousefzadeh
MJ, Roberts SA, Mieczkowski P, Wood RD, Gupta GP and Ramsden DA:
Essential roles for polymerase θ-mediated end joining in the repair
of chromosome breaks. Mol Cell. 63:662–673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Truong LN, Li Y, Shi LZ, Hwang PY, He J,
Wang H, Razavian N, Berns MW and Wu X: Microhomology-mediated End
Joining and Homologous Recombination share the initial end
resection step to repair DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:7720–7725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saito S, Maeda R and Adachi N: Dual loss
of human POLQ and LIG4 abolishes random integration. Nat Commun.
8:161122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wood RD and Doublié S: DNA polymerase θ
(POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer. DNA Repair (Amst).
44:22–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chatterjee N and Walker GC: Mechanisms of
DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen.
58:235–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Suskiewicz MJ, Zobel F, Ogden TEH, Fontana
P, Ariza A, Yang JC, Zhu K, Bracken L, Hawthorne WJ, Ahel D, et al:
HPF1 completes the PARP active site for DNA damage-induced
ADP-ribosylation. Nature. 579:598–602. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao F, Kim W, Kloeber JA and Lou Z: DNA
end resection and its role in DNA replication and DSB repair choice
in mammalian cells. Exp Mol Med. 52:1705–1714. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Daley JM, Jimenez-Sainz J, Wang W, Miller
AS, Xue X, Nguyen KA, Jensen RB and Sung P: Enhancement of
BLM-DNA2-mediated long-range DNA end resection by CtIP. Cell Rep.
21:324–332. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Carvajal-Garcia J, Cho JE, Carvajal-Garcia
P, Feng W, Wood RD, Sekelsky J, Gupta GP, Roberts SA and Ramsden
DA: Mechanistic basis for microhomology identification and genome
scarring by polymerase theta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:8476–8485. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mateos-Gomez PA, Gong F, Nair N, Miller
KM, Lazzerini-Denchi E and Sfeir A: Mammalian polymerase θ promotes
alternative NHEJ and suppresses recombination. Nature. 518:254–257.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Black SJ, Kashkina E, Kent T and Pomerantz
RT: DNA polymerase θ: A unique multifunctional end-joining machine.
Genes. 7:672016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Li C, Maksoud LM and Gao Y: Structural
basis of error-prone DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase θ. Nat Commun.
16:20632025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Masani S, Han L, Meek K and Yu K:
Redundant function of DNA ligase 1 and 3 in alternative end-joining
during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 113:1261–1266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Audebert M, Salles B and Calsou P:
Involvement of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase
III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining.
J Biol Chem. 279:55117–55126. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Soni A, Siemann M, Grabos M, Murmann T,
Pantelias GE and Iliakis G: Requirement for Parp-1 and DNA ligases
1 or 3 but not of Xrcc1 in chromosomal translocation formation by
backup end joining. Nucl Acids Res. 42:6380–6392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chandramouly G, Jamsen J, Borisonnik N,
Tyagi M, Calbert ML, Tredinnick T, Ozdemir AY, Kent T, Demidova EV,
Arora S, et al: Polλ promotes microhomology-mediated end-joining.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 30:107–114. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Fleury H, MacEachern MK, Stiefel CM, Anand
R, Sempeck C, Nebenfuehr B, Maurer-Alcalá K, Ball K, Proctor B III,
Belan O, et al: The APE2 nuclease is essential for DNA
double-strand break repair by microhomology-mediated end joining.
Mol Cell. 83:1429–1445.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lin Y, McMahon A, Driscoll G, Bullock S,
Zhao J and Yan S: Function and molecular mechanisms of APE2 in
genome and epigenome integrity. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res.
787:1083472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kumar S, Talluri S, Pal J, Yuan X, Lu R,
Nanjappa P, Samur MK, Munshi NC and Shammas MA: Role of
apurinic/apyrimidinic nucleases in the regulation of homologous
recombination in myeloma: Mechanisms and translational
significance. Blood Cancer J. 8:922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chan SH, Yu AM and McVey M: Dual roles for
DNA polymerase theta in alternative end-joining repair of
double-strand breaks in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 6:e10010052010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yousefzadeh MJ, Wyatt DW, Takata K, Mu Y,
Hensley SC, Tomida J, Bylund GO, Doublié S, Johansson E, Ramsden
DA, et al: Mechanism of suppression of chromosomal instability by
DNA polymerase POLQ. PLoS Genet. 10:e10046542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ceccaldi R, Liu JC, Amunugama R, Hajdu I,
Primack B, Petalcorin MI, O'Connor KW, Konstantinopoulos PA,
Elledge SJ, Boulton SJ, et al: Homologous-recombination-deficient
tumours are dependent on Polθ-mediated repair. Nature. 518:258–262.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Brambati A, Sacco O, Porcella S, Heyza J,
Kareh M, Schmidt JC and Sfeir A: RHINO directs MMEJ to repair DNA
breaks in mitosis. Science. 381:653–660. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang Y and Jasin M: An essential role for
CtIP in chromosomal translocation formation through an alternative
end-joining pathway. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 18:80–84. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Seki M, Masutani C, Yang LW, Schuffert A,
Iwai S, Bahar I and Wood RD: High-efficiency bypass of DNA damage
by human DNA polymerase Q. EMBO J. 23:4484–4494. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ceccaldi R and Cejka P: Mechanisms and
regulation of DNA end resection in the maintenance of genome
stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 26:586–599. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Deng SK, Gibb B, De Almeida MJ, Greene EC
and Symington LS: RPA antagonizes microhomology-mediated repair of
DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 21:405–412. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zimmermann M, Lottersberger F, Buonomo SB,
Sfeir A and de Lange T: 53BP1 regulates DSB repair using Rif1 to
control 5' end resection. Science. 339:700–704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen C, Umezu K and Kolodner RD:
Chromosomal rearrangements occur in S. cerevisiae rfa1 mutator
mutants due to mutagenic lesions processed by double-strand-break
repair. Mol Cell. 2:9–22. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zuo N, Ma L, Liu T, Hu W, Luo Y, Meng H,
Ren Q, Deng Y, Wei L and Liu Q: Human papillomavirus associated XPF
deficiency increases alternative end joining and cisplatin
sensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
140:1063672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shahid M, Azfaralariff A, Zubair M,
Abdulkareem Najm A, Khalili N, Law D, Firasat S and Fazry S: In
silico study of missense variants of FANCA, FANCC and FANCG genes
reveals high risk deleterious alleles predisposing to Fanconi
anemia pathogenesis. Gene. 812:1461042022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Barcellos-Hoff MH and Yom SS: Revisiting
the TGFβ paradox: Insights from HPV-driven cancer and the DNA
damage response. Nat Rev Cancer. 25:534–544. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Guix I, Liu Q, Pujana MA, Ha P, Piulats J,
Linares I, Guedea F, Mao JH, Lazar A, Chapman J, et al: Validation
of anticorrelated TGFβ signaling and alternative end-joining DNA
repair signatures that predict response to genotoxic cancer
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 28:1372–1382. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kirshner J, Jobling MF, Pajares MJ, Ravani
SA, Glick AB, Lavin MJ, Koslov S, Shiloh Y and Barcellos-Hoff MH:
Inhibition of TGFbeta1 signaling attenutates ATM activity in
response to genotoxic stress. Cancer Res. 66:10861–10869. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chowdhury S, Kennedy JJ, Ivey RG, Murillo
OD, Hosseini N, Song X, Petralia F, Calinawan A, Savage SR, Berry
AB, et al: Proteogenomic analysis of chemo-refractory high-grade
serous ovarian cancer. Cell. 187:10162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Parfenov M, Pedamallu CS, Gehlenborg N,
Freeman SS, Danilova L, Bristow CA, Lee S, Hadjipanayis AG, Ivanova
EV, Wilkerson MD, et al: Characterization of HPV and host genome
interactions in primary head and neck cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:15544–15549. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Leeman JE, Li Y, Bell A, Hussain SS,
Majumdar R, Rong-Mullins X, Blecua P, Damerla R, Narang H,
Ravindran PT, et al: Human papillomavirus 16 promotes
microhomology-mediated end-joining. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:21573–21579. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Eccleston J, Schrader CE, Yuan K,
Stavnezer J and Selsing E: Class switch recombination efficiency
and junction microhomology patterns in Msh2-, Mlh1-, and
Exo1-deficient mice depend on the presence of mu switch region
tandem repeats. J Immunol. 183:1222–1228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Mann A, Ramirez-Otero MA, De Antoni A,
Hanthi YW, Sannino V, Baldi G, Falbo L, Schrempf A, Bernardo S,
Loizou J and Costanzo V: POLθ prevents MRE11-NBS1-CtIP-dependent
fork breakage in the absence of BRCA2/RAD51 by filling
lagging-strand gaps. Mol Cell. 82:4218–4231.e8. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ceccaldi R, Rondinelli B and D'Andrea AD:
Repair pathway choices and consequences at the double-strand break.
Trends Cell Biol. 26:52–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
87
|
Sfeir A and Symington LS:
Microhomology-mediated end joining: A back-up survival mechanism or
dedicated pathway? Trends Biochem Sci. 40:701–714. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Brambati A, Barry RM and Sfeir A: DNA
polymerase theta (Polθ)-an error-prone polymerase necessary for
genome stability. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 60:119–126. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
McVey M and Lee SE: MMEJ repair of
double-strand breaks (director's cut): Deleted sequences and
alternative endings. Trends Genet. 24:529–538. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wang Z, Song Y, Li S, Kurian S, Xiang R,
Chiba T and Wu X: DNA polymerase θ (POLQ) is important for repair
of DNA double-strand breaks caused by fork collapse. J Biol Chem.
294:3909–3919. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Belan O, Sebald M, Adamowicz M, Anand R,
Vancevska A, Neves J, Grinkevich V, Hewitt G, Segura-Bayona S,
Bellelli R, et al: POLQ seals post-replicative ssDNA gaps to
maintain genome stability in BRCA-deficient cancer cells. Mol Cell.
82:4664–4680.e9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Schrempf A, Bernardo S, Verge E, Ramirez
Otero MA, Wilson J, Kirchhofer D, Timelthaler G, Ambros AM, Kaya A,
Wieder M, et al: POLθ processes ssDNA gaps and promotes replication
fork progression in BRCA1-deficient cells. Cell Rep. 41:1117162022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Chanut P, Britton S, Coates J, Jackson SP
and Calsou P: Coordinated nuclease activities counteract Ku at
single-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Commun. 7:128892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Britton S, Chanut P, Delteil C, Barboule
N, Frit P and Calsou P: ATM antagonizes NHEJ proteins assembly and
DNA-ends synapsis at single-ended DNA double strand breaks. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48:9710–9723. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
van Schendel R, van Heteren J, Welten R
and Tijsterman M: Genomic scars generated by polymerase theta
reveal the versatile mechanism of alternative end-joining. PLoS
Genet. 12:e10063682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gou R, Dong H and Lin B: Application and
reflection of genomic scar assays in evaluating the efficacy of
platinum salts and PARP inhibitors in cancer therapy. Life Sci.
261:1184342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hanscom T, Woodward N, Batorsky R, Brown
AJ, Roberts SA and McVey M: Characterization of sequence contexts
that favor alternative end joining at Cas9-induced double-strand
breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:7465–7478. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Rempel E, Kluck K, Beck S, Ourailidis I,
Kazdal D, Neumann O, Volckmar AL, Kirchner M, Goldschmid H, Pfarr
N, et al: Pan-cancer analysis of genomic scar patterns caused by
homologous repair deficiency (HRD). NPJ Precis Oncol. 6:362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yu AM and McVey M: Synthesis-dependent
microhomology-mediated end joining accounts for multiple types of
repair junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:5706–5717. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sinha S, Li F, Villarreal D, Shim JH, Yoon
S, Myung K, Shim EY and Lee SE: Microhomology-mediated end joining
induces hypermutagenesis at breakpoint junctions. PLoS Genet.
13:e10067142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Villarreal DD, Lee K, Deem A, Shim EY,
Malkova A and Lee SE: Microhomology directs diverse DNA break
repair pathways and chromosomal translocations. PLoS Genet.
8:e10030262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chiarle R, Zhang Y, Frock RL, Lewis SM,
Molinie B, Ho YJ, Myers DR, Choi VW, Compagno M, Malkin DJ, et al:
Genome-wide translocation sequencing reveals mechanisms of
chromosome breaks and rearrangements in B cells. Cell. 147:107–119.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Brunet E, Simsek D, Tomishima M, DeKelver
R, Choi VM, Gregory P, Urnov F, Weinstock DM and Jasin M:
Chromosomal translocations induced at specified loci in human stem
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:10620–10625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ghezraoui H, Piganeau M, Renouf B, Renaud
JB, Sallmyr A, Ruis B, Oh S, Tomkinson AE, Hendrickson EA,
Giovannangeli C, et al: Chromosomal translocations in human cells
are generated by canonical nonhomologous end-joining. Mol Cell.
55:829–842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Simsek D and Jasin M: Alternative
end-joining is suppressed by the canonical NHEJ component
Xrcc4-ligase IV during chromosomal translocation formation. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 17:410–416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Simsek D, Brunet E, Wong SY, Katyal S, Gao
Y, McKinnon PJ, Lou J, Zhang L, Li J, Rebar EJ, et al: DNA ligase
III promotes alternative nonhomologous end-joining during
chromosomal translocation formation. PLoS Genet. 7:e10020802011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Cesare AJ, Hayashi MT, Crabbe L and
Karlseder J: The telomere deprotection response is functionally
distinct from the genomic DNA damage response. Mol Cell.
51:141–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gu L, Liu M, Zhang Y, Zhou H, Wang Y and
Xu ZX: Telomere-related DNA damage response pathways in cancer
therapy: Prospective targets. Front Pharmacol. 15:13791662024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Maciejowski J and de Lange T: Telomeres in
cancer: Tumour suppression and genome instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 18:175–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Bai Y, Wang W and Wang J: Targeting DNA
repair pathways: Mechanisms and potential applications in cancer
therapy. Genome Instability Dis. 1:318–338. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Xu X, Nowsheen S and Deng M: Exploring the
DNA damage response pathway for synthetic lethality. Genome
Instability Dis. 4:98–120. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Choi W and Lee ES: Therapeutic targeting
of DNA damage response in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 23:17012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gourley C, Balmaña J, Ledermann JA, Serra
V, Dent R, Loibl S, Pujade-Lauraine E and Boulton SJ: Moving from
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition to targeting DNA repair and
DNA damage response in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 37:2257–2269.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Guo Y, Fan B and Li M: PARP molecular
functions and applications of PARP inhibitors in cancer treatment.
Genome Instability Dis. 4:137–153. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Neeb A, Herranz N, Arce-Gallego S, Miranda
S, Buroni L, Yuan W, Athie A, Casals T, Carmichael J, Rodrigues DN,
et al: Advanced prostate cancer with ATM loss: PARP and ATR
inhibitors. Eur Urol. 79:200–211. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Liu Q, Gheorghiu L, Drumm M, Clayman R,
Eidelman A, Wszolek MF, Olumi A, Feldman A, Wang M, Marcar L, et
al: PARP-1 inhibition with or without ionizing radiation confers
reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity preferentially to
cancer cells with mutant TP53. Oncogene. 37:2793–2805. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Weaver AN, Cooper TS, Rodriguez M,
Trummell HQ, Bonner JA, Rosenthal EL and Yang ES: DNA double strand
break repair defect and sensitivity to poly ADP-ribose polymerase
(PARP) inhibition in human papillomavirus 16-positive head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:26995–27007. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Staniszewska M, Iking J, Lueckerath K,
Hadaschik B, Herrmann K, Ferdinandus J and Fendler WP: Drug and
molecular radiotherapy combinations for metastatic castration
resistant prostate cancer. Nucl Med Biol. 96:101–111. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Nonnekens J, van Kranenburg M, Beerens CE,
Suker M, Doukas M, van Eijck CH, de Jong M and van Gent DC:
Potentiation of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy by the PARP
inhibitor olaparib. Theranostics. 6:1821–1832. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
De Haan R, Van Werkhoven E, Van Den Heuvel
MM, Peulen HMU, Sonke GS, Elkhuizen P, van den Brekel MWM,
Tesselaar MET, Vens C, Schellens JHM, et al: Study protocols of
three parallel phase 1 trials combining radical radiotherapy with
the PARP inhibitor olaparib. BMC Cancer. 19:9012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Jagsi R, Griffith KA, Bellon JR, Woodward
WA, Horton JK, Ho A, Feng FY, Speers C, Overmoyer B, Sabel M, et
al: Concurrent veliparib with chest wall and nodal radiotherapy in
patients with inflammatory or locoregionally recurrent breast
cancer: The TBCRC 024 phase I multicenter study. J Clin Oncol.
36:1317–1322. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Hou Z, Yu T, Yi Q, Du Y, Zhou L, Zhao Y,
Wu Y, Wu L, Wang T and Bian P: High-complexity of DNA double-strand
breaks is key for alternative end-joining choice. Commun Biol.
7:9362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Carter R, Nickson C, Thompson J, Kacperek
A, Hill M and Parsons J: Complex DNA damage induced by high linear
energy transfer Alpha-particles and protons triggers a specific
cellular DNA damage response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
100:776–784. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Hirai T, Shirai H, Fujimori H, Okayasu R,
Sasai K and Masutani M: Radiosensitization effect of poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition in cells exposed to low and high
liner energy transfer radiation. Cancer Sci. 103:1045–1050. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Césaire M, Ghosh U, Austry JB, Muller E,
Cammarata FP, Guillamin M, Caruso M, Castéra L, Petringa G, Cirrone
GAP and Chevalier F: Sensitization of chondrosarcoma cells with
PARP inhibitor and high-LET radiation. J Bone Oncol. 17:1002462019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Dong M, Luo H, Liu R, Zhang J, Yang Z,
Wang D, Wang Y, Chen J, Ou Y, Zhang Q and Wang X:
Radiosensitization of osteosarcoma cells using the PARP inhibitor
olaparib combined with X-rays or carbon ions. J Cancer. 15:6992024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Molkentine JM, Molkentine DP, Bridges KA,
Xie T, Yang L, Sheth A, Heffernan TP, Clump DA, Faust AZ, Ferris
RL, et al: Targeting DNA damage response in head and neck cancers
through abrogation of cell cycle checkpoints. Int J Radiat Biol.
97:1121–1128. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Machacova Z, Chroma K, Lukac D,
Protivankova I and Moudry P: DNA polymerase α-primase facilitates
PARP inhibitor-induced fork acceleration and protects
BRCA1-deficient cells against ssDNA gaps. Nat Commun. 15:73752024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Russo TDB, Mujacic C, Di Giovanni E,
Vitale MC, Ferrante Bannera C, Randazzo U, Contino S, Bono M,
Gristina V, Galvano A, et al: Polθ: Emerging synthetic lethal
partner in homologous recombination-deficient tumors. Cancer Gene
Ther. 31:1619–1631. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Rodriguez-Berriguete G, Ranzani M, Prevo
R, Puliyadi R, Machado N, Bolland HR, Millar V, Ebner D, Boursier
M, Cerutti A, et al: Small-molecule Polθ inhibitors provide safe
and effective tumor radiosensitization in preclinical models. Clin
Cancer Res. 29:1631–1642. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhou J, Gelot C, Pantelidou C, Li A, Yücel
H, Davis RE, Färkkilä A, Kochupurakkal B, Syed A, Shapiro GI, et
al: A first-in-class polymerase theta inhibitor selectively targets
homologous-recombination-deficient tumors. Nat Cancer. 2:598–610.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zatreanu D, Robinson HM, Alkhatib O,
Boursier M, Finch H, Geo L, Grande D, Grinkevich V, Heald RA and
Langdon S: Polθ inhibitors elicit BRCA-gene synthetic lethality and
target PARP inhibitor resistance. Nat Commun. 12:36362021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Fried W, Tyagi M, Minakhin L, Chandramouly
G, Tredinnick T, Ramanjulu M, Auerbacher W, Calbert M, Rusanov T
and Hoang T: Discovery of a small-molecule inhibitor that traps
Polθ on DNA and synergizes with PARP inhibitors. Nat Commun.
15:28622024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Higgins GS, Prevo R, Lee YF, Helleday T,
Muschel RJ, Taylor S, Yoshimura M, Hickson ID, Bernhard EJ and
McKenna WG: A small interfering RNA screen of genes involved in DNA
repair identifies tumor-specific radiosensitization by POLQ
knockdown. Cancer Res. 70:2984–2993. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Shima N, Munroe RJ and Schimenti JC: The
mouse genomic instability mutation chaos1 is an allele of Polq that
exhibits genetic interaction with Atm. Mol Cell Biol.
24:10381–10389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Mengwasser KE, Adeyemi RO, Leng Y, Choi
MY, Clairmont C, D'Andrea AD and Elledge SJ: Genetic screens reveal
FEN1 and APEX2 as BRCA2 synthetic lethal targets. Mol Cell.
73:885–899.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Sharma S, Javadekar S, Pandey M,
Srivastava M, Kumari R and Raghavan S: Homology and enzymatic
requirements of microhomology-dependent alternative end joining.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e1697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Li J, Ko JMY, Dai W, Yu VZ, Ng HY,
Hoffmann JS and Lung ML: Depletion of DNA polymerase theta inhibits
tumor growth and promotes genome instability through the
cGAS-STING-ISG pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 13:32042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Dai C-H, Chen P, Li J, Lan T, Chen YC,
Qian H, Chen K and Li MY: Co-inhibition of pol θ and HR genes
efficiently synergize with cisplatin to suppress
cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells survival. Oncotarget.
7:65157–65170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Chen X, Zhong S, Zhu X, Dziegielewska B,
Ellenberger T, Wilson GM, MacKerell AD Jr and Tomkinson AE:
Rational design of human DNA ligase inhibitors that target cellular
DNA replication and repair. Cancer Res. 68:3169–3177. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Martires LCM, Ahronian LG, Pratt CB, Das
NM, Zhang X, Whittington DA, Zhang H, Shen B, Come J, McCarren P,
et al: LIG1 is a synthetic lethal target in BRCA1 mutant cancers.
Mol Cancer Ther. 24:618–627. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Tobin LA, Robert C, Nagaria P, Chumsri S,
Twaddell W, Ioffe OB, Greco GE, Brodie AH, Tomkinson AE and Rassool
FV: Targeting abnormal DNA repair in therapy-resistant breast
cancers. Mol Cancer Res. 10:96–107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
143
|
Tobin LA, Robert C, Rapoport AP, Gojo I,
Baer MR, Tomkinson AE and Rassool FV: Targeting abnormal DNA
double-strand break repair in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant
chronic myeloid leukemias. Oncogene. 32:1784–1793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Álvarez-Quilón A, Wojtaszek JL, Mathieu
MC, Patel T, Appel CD, Hustedt N, Rossi SE, Wallace BD, Setiaputra
D, Adam S, et al: Endogenous DNA 3' blocks are vulnerabilities for
BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficiency and are reversed by the APE2 nuclease.
Mol Cell. 78:1152–1165.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Hossain MA, Lin Y, Driscoll G, Li J,
McMahon A, Matos J, Zhao H, Tsuchimoto D, Nakabeppu Y, Zhao J and
Yan S: APE2 is a general regulator of the ATR-Chk1 DNA damage
response pathway to maintain genome integrity in pancreatic cancer
cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7385022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Barcellos-Hoff MH and Gulley JL: Molecular
pathways and mechanisms of TGFβ in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
29:2025–2033. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
de Bono J, Mateo J, Fizazi K, Saad F,
Shore N, Sandhu S, Chi KN, Sartor O, Agarwal N, Olmos D, et al:
Olaparib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N
Engl J Med. 382:2091–2102. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wang L, Cao J, Wang X, Lin E, Wang Z, Li
Y, Li Y, Chen M, Wang X, Jiang B, et al: Proton and photon
radiosensitization effects of niraparib, a PARP-1/-2 inhibitor, on
human head and neck cancer cells. Head Neck. 42:2244–2256. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Hintelmann K, Berenz T, Kriegs M,
Christiansen S, Gatzemeier F, Struve N, Petersen C, Betz C,
Rothkamm K, Oetting A and Rieckmann T: Dual inhibition of PARP and
the intra-S/G2 cell cycle checkpoints results in highly effective
radiosensitization of HPV-positive HNSCC cells. Front Oncol.
11:6836882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|