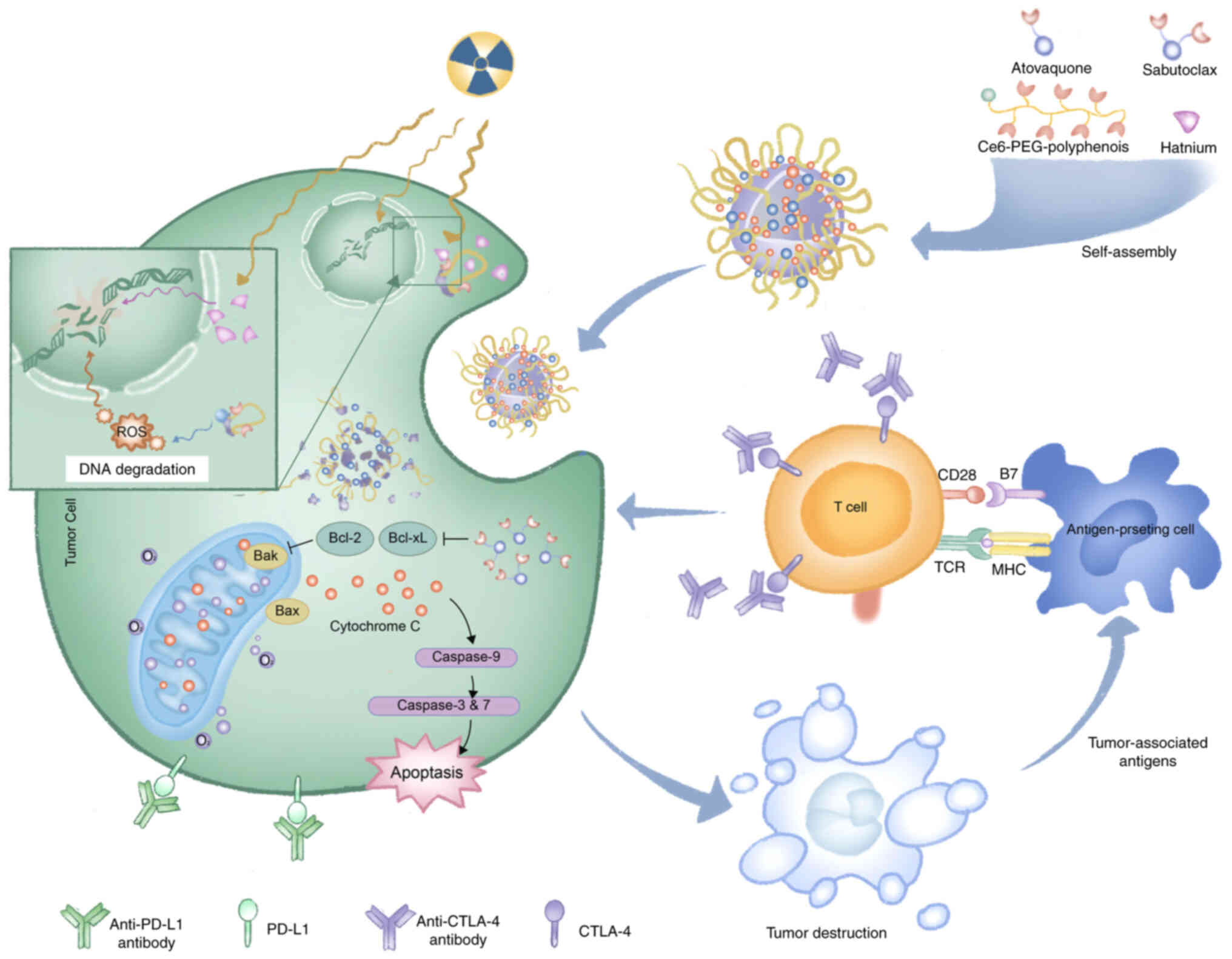
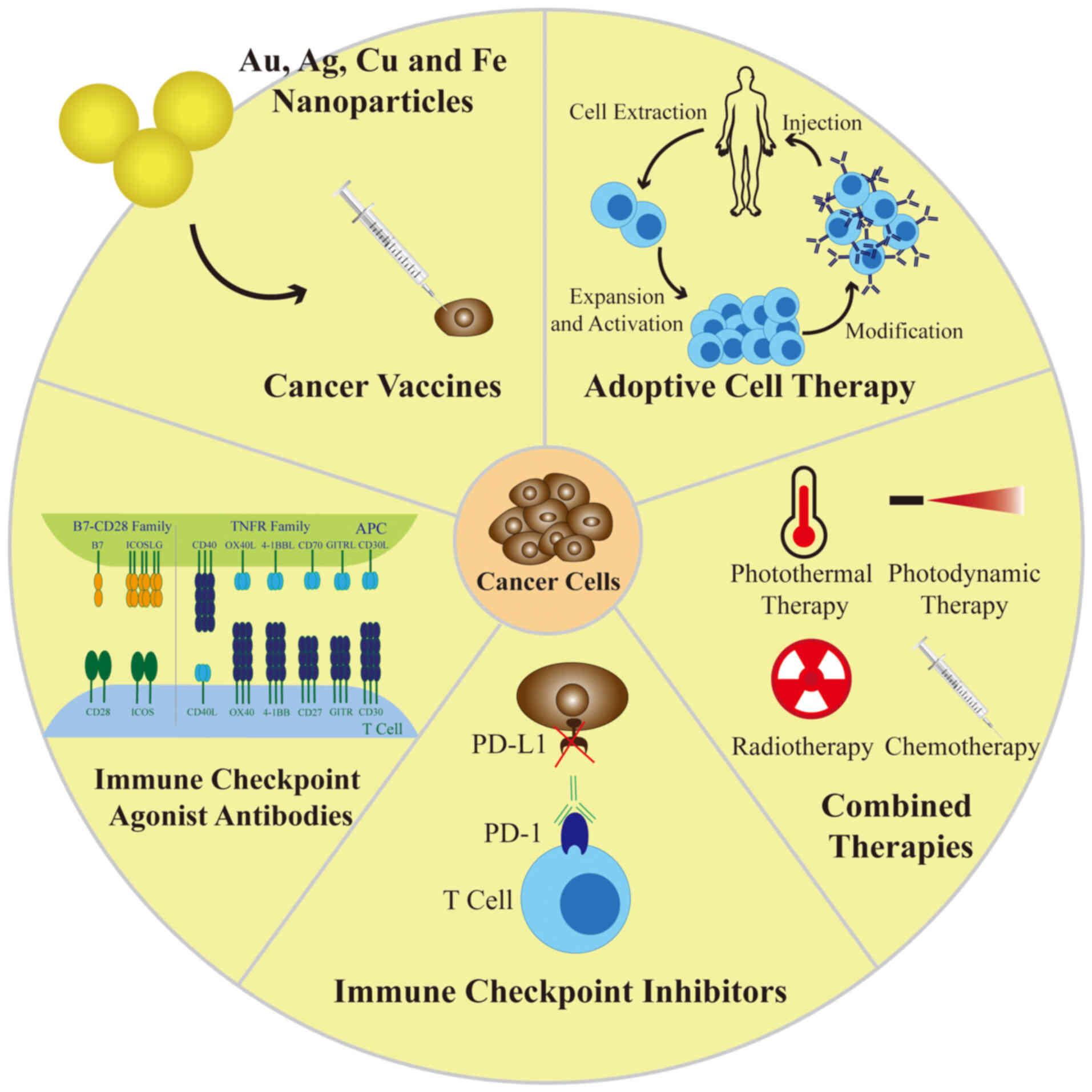
|
1
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Z: The history and
advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic
implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:807–821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parreno V, Loubiere V, Schuettengruber B,
Fritsch L, Rawal CC, Erokhin M, Győrffy B, Normanno D, Di Stefano
M, Moreaux J, et al: Transient loss of Polycomb components induces
an epigenetic cancer fate. Nature. 629:688–696. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chong G, Zang J, Han Y, Su R,
Weeranoppanant N, Dong H and Li Y: Bioengineering of nano
metal-organic frameworks for cancer immunotherapy. Nano Res.
14:1244–1259. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Surendran SP, Moon MJ, Park R and Jeong
YY: Bioactive Nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:38772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bertrand N, Wu J, Xu X, Kamaly N and
Farokhzad OC: Cancer nanotechnology: The impact of passive and
active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 66:2–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R and Farokhzad
OC: Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 17:20–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Zheng X, Wu Y, Zuo H, Chen W and Wang K:
Metal nanoparticles as novel agents for lung cancer diagnosis and
therapy. Small. 19:e22066242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao W, Li A, Zhang A, Zheng Y and Liu J:
Recent advances in functional-polymer-decorated transition-metal
nanomaterials for bioimaging and cancer therapy. ChemMedChem.
13:2134–2149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang J and Zhang C: Regulation of
cancer-immunity cycle and tumor microenvironment by
nanobiomaterials to enhance tumor immunotherapy. Wiley Interdiscip
Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 12:e16122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu W, Song X, Jiang Q, Guo W, Liu J, Chu
X and Lei Z: Transition metal oxide nanomaterials: New weapons to
boost anti-tumor immunity cycle. Nanomaterials (Basel).
14:10642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Daniel MC and Astruc D: Gold
nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry,
quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology,
catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev. 104:293–346. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee KX, Shameli K, Yew YP, Teow SY,
Jahangirian H, Rafiee-Moghaddam R and Webster TJ: Recent
developments in the facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles
(AuNPs) and their biomedical applications. Int J Nanomed.
15:275–300. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hemalatha T, Prabu P, Gunadharini DN and
Gowthaman MK: Fabrication and characterization of dual acting oleyl
chitosan functionalised iron oxide/gold hybrid nanoparticles for
MRI and CT imaging. Int J Biol Macromol. 112:250–257. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh P, Pandit S, Mokkapati VRSS, Garg A,
Ravikumar V and Mijakovic I: Gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and
therapeutics for human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:19792018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang R, Deng J, He D, Yang E, Yang W, Shi
D, Jiang Y, Qiu Z, Webster TJ and Shen Y: PEGylated hollow gold
nanoparticles for combined X-ray radiation and photothermal therapy
in vitro and enhanced CT imaging in vivo. Nanomedicine. 16:195–205.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Karthika V, Arumugam A, Gopinath K,
Kaleeswarran P, Govindarajan M, Alharbi NS, Kadaikunnan S, Khaled
JM and Benelli G: Guazuma ulmifolia bark-synthesized Ag, Au and
Ag/Au alloy nanoparticles: Photocatalytic potential, DNA/protein
interactions, anticancer activity and toxicity against 14 species
of microbial pathogens. J Photochem Photobiol, B. 167:189–199.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bankar A, Joshi B, Kumar AR and Zinjarde
S: Banana peel extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles.
Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces. 80:45–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumar CG, Poornachandra Y and Mamidyala
SK: Green synthesis of bacterial gold nanoparticles conjugated to
resveratrol as delivery vehicles. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces.
123:311–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng J, Gu YJ, Cheng SH and Wong WT:
Surface functionalized gold nanoparticles for drug delivery. J
Biomed Nanotechnol. 9:1362–1369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Cao Z, Liu R, Liu L, Li H, Li X,
Chen Y, Lu C and Liu Y: AuNPs as an important inorganic
nanoparticle applied in drug carrier systems. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 47:4222–4233. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim DY, Kim M, Shinde S, Sung JS and
Ghodake G: Cytotoxicity and antibacterial assessment of gallic acid
capped gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf, B Biointerfaces.
149:162–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee KD, Nagajyothi PC, Sreekanth TVM and
Park S: Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using
Inonotus obliquus and their antibacterial, antioxidant and
cytotoxic activities. J Ind Eng Chem. 26:67–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Naraginti S and Li Y: Preliminary
investigation of catalytic, antioxidant, anticancer and
bactericidal activity of green synthesized silver and gold
nanoparticles using Actinidia deliciosa. J Photochem Photobiol, B.
170:225–234. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vijayakumar S, Vaseeharan B,
Malaikozhundan B, Gopi N, Ekambaram P, Pachaiappan R, Velusamy P,
Murugan K, Benelli G, Suresh Kumar R and Suriyanarayanamoorthy M:
Therapeutic effects of gold nanoparticles synthesized using Musa
paradisiaca peel extract against multiple antibiotic resistant
Enterococcus faecalis biofilms and human lung cancer cells (A549).
Microb Pathogen. 102:173–183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mironava T, Hadjiargyrou M, Simon M,
Jurukovski V and Rafailovich MH: Gold nanoparticles cellular
toxicity and recovery: Effect of size, concentration and exposure
time. Nanotoxicology. 4:120–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ziyu P and Haodong J: Controlled synthesis
of silver nanomaterials and their environmental applications. Prog
Chem. 35:1229–1257. 2023.
|
|
27
|
Huy TQ, Huyen PTM, Le AT and Tonezzer M:
Recent advances of silver nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and
treatment. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 20:1276–1287. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mohamed AF, Nasr M, Amer ME, Abuamara TMM,
Abd-Elhay WM, Kaabo HF, Matar EER, El Moselhy LE, Gomah TA, Deban
MAE and Shebl RI: Anticancer and antibacterial potentials induced
post short-term exposure to electromagnetic field and silver
nanoparticles and related pathological and genetic alterations: In
vitro study. Infect Agent Cancer. 17:42022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan YG, Zhang S, Hwang JY and Kong IK:
Silver Nanoparticles potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptotic
potential of camptothecin in human cervical cancer cells. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2018:61213282018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jeong JK, Gurunathan S, Kang MH, Han JW,
Das J, Choi YJ, Kwon DN, Cho SG, Park C, Seo HG, et al:
Hypoxia-mediated autophagic flux inhibits silver
nanoparticle-triggered apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Sci
Rep. 6:216882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin M, Xu X, Han H, Dai J, Sun R, Yang L,
Xie J and Wang Y: Preparation of triangular silver nanoparticles
and their biological effects in the treatment of ovarian cancer. J
Ovarian Res. 15:1212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Noorbazargan H, Amintehrani S, Dolatabadi
A, Mashayekhi A, Khayam N, Moulavi P, Naghizadeh M, Mirzaie A,
Mirzaei Rad F and Kavousi M: Anti-cancer & anti-metastasis
properties of bioorganic-capped silver nanoparticles fabricated
from Juniperus chinensis extract against lung cancer cells. AMB
Express. 11:612021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lu W and Kang Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell.
49:361–374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meenakshisundaram S, Krishnamoorthy V,
Jagadeesan Y, Vilwanathan R and Balaiah A: Annona muricata assisted
biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles regulates cell cycle
arrest in NSCLC cell lines. Bioorg Chem. 95:1034512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miranda RR, Sampaio I and Zucolotto V:
Exploring silver nanoparticles for cancer therapy and diagnosis.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 210:1122542022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jia B, Mei Y, Cheng L, Zhou J and Zhang L:
Preparation of copper nanoparticles coated cellulose films with
antibacterial properties through one-step reduction. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 4:2897–2902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luque-Jacobo CM, Cespedes-Loayza AL,
Echegaray-Ugarte TS, Cruz-Loayza JL, Cruz I, de Carvalho JC and
Goyzueta-Mamani LD: Biogenic synthesis of copper nanoparticles: A
systematic review of their features and main applications.
Molecules. 28:48382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smith AM, Duan H, Rhyner MN, Ruan G and
Nie S: A systematic examination of surface coatings on the optical
and chemical properties of semiconductor quantum dots. Phys Chem
Chem Phys. 8:3895–3903. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Letchumanan D, Sok SPM, Ibrahim S, Nagoor
NH and Arshad NM: Plant-based biosynthesis of copper/copper oxide
nanoparticles: An update on their applications in biomedicine,
mechanisms, and toxicity. Biomolecules. 11:5642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS and
Rahiman AK: Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of
copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important
plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1067–1077. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mahmood RI, Kadhim AA, Ibraheem S,
Albukhaty S, Mohammed-Salih HS, Abbas RH, Jabir MS, Mohammed MKA,
Nayef UM, AlMalki FA, et al: Biosynthesis of copper oxide
nanoparticles mediated Annona muricata as cytotoxic and apoptosis
inducer factor in breast cancer cell lines. Sci Rep. 12:161652022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Woźniak-Budych MJ, Przysiecka Ł,
Maciejewska BM, Wieczorek D, Staszak K, Jarek M, Jesionowski T and
Jurga S: Facile synthesis of sulfobetaine-stabilized Cu2O
nanoparticles and their biomedical potential. ACS Biomater Sci Eng.
3:3183–3194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wozniak-Budych MJ, Langer K, Peplinska B,
Przysiecka L, Jarek M, Jarzebski M and Jurga S: Copper-gold
nanoparticles: Fabrication, characteristic and application as drug
carriers. Mater Chem Phys. 179:242–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tortella GR, Pieretti JC, Rubilar O,
Fernández-Baldo M, Benavides-Mendoza A, Diez MC and Seabra AB:
Silver, copper and copper oxide nanoparticles in the fight against
human viruses: progress and perspectives. Crit Rev Biotechnol.
42:431–449. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yuan Z, Qu S, He Y, Xu Y, Liang L, Zhou X,
Gui L, Gu Y and Chen H: Thermosensitive drug-loading system based
on copper sulfide nanoparticles for combined photothermal therapy
and chemotherapy in vivo. Biomater Sci. 6:3219–3230. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang M, Wang W, Cui Y, Chu X, Sun B, Zhou
N and Shen J: Magnetofluorescent Fe3O4/carbon quantum dots coated
single-walled carbon nanotubes as dual-modal targeted imaging and
chemo/photodynamic/photothermal triple-modal therapeutic agents.
Chem Eng J. 338:526–538. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Frtús A, Smolková B, Uzhytchak M, Lunova
M, Jirsa M, Kubinová Š, Dejneka A and Lunov O: Analyzing the
mechanisms of iron oxide nanoparticles interactions with cells: A
road from failure to success in clinical applications. J Control
Release. 328:59–77. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xuan S, Wang F, Lai JM, Sham KW, Wang YX,
Lee SF, Yu JC, Cheng CH and Leung KC: Synthesis of biocompatible,
mesoporous Fe(3)O(4) nano/microspheres with large surface area for
magnetic resonance imaging and therapeutic applications. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 3:237–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang L, Wang Z, Li X, Zhang Y, Yin M, Li
J, Song H, Shi J, Ling D, Wang L, et al: Deciphering active
biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles from their intrinsic
antagonism. Nano Res. 11:2746–2755. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jin R, Lin B, Li D and Ai H:
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging and
therapy: Design considerations and clinical applications. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 18:18–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Latunde-Dada GO: Ferroptosis: Role of
lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys
Acta-Gen Subj. 1861:1893–1900. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen S, Yang J, Liang Z, Li Z, Xiong W,
Fan Q, Shen Z, Liu J and Xu Y: Synergistic functional nanomedicine
enhances ferroptosis therapy for breast tumors by a blocking
defensive redox system. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 15:2705–2713.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cormode DP, Gao L and Koo H: Emerging
biomedical applications of enzyme-like catalytic nanomaterials.
Trends Biotechnol. 36:15–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhou C, Wang C, Xu K, Niu Z, Zou S, Zhang
D, Qian Z, Liao J and Xie J: Hydrogel platform with tunable
stiffness based on magnetic nanoparticles cross-linked GelMA for
cartilage regeneration and its intrinsic biomechanism. Bioact
Mater. 25:615–628. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ashraf N, Ahmad F, Da-Wei L, Zhou RB,
Feng-Li H and Yin DC: Iron/iron oxide nanoparticles: Advances in
microbial fabrication, mechanism study, biomedical, and
environmental applications. Crit Rev Microbiol. 45:278–300. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou Z, Sun Y, Shen J, Wei J, Yu C, Kong
B, Liu W, Yang H, Yang S and Wang W: Iron/iron oxide core/shell
nanoparticles for magnetic targeting MRI and near-infrared
photothermal therapy. Biomaterials. 35:7470–7478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang X, Liu Z, Lou Z, Chen F, Chang S,
Miao Y, Zhou Z, Hu X, Feng J, Ding Q, et al: Radiosensitivity
enhancement of Fe3O4@Ag nanoparticles on human glioblastoma cells.
Artif Cell Nanomed Biotechnol. 46(Supp1): 975–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhong D, Zhao J, Li Y, Qiao Y, Wei Q, He
J, Xie T, Li W and Zhou M: Laser-triggered aggregated cubic
α-Fe2O3@Au nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and
photothermal/enhanced radiation synergistic therapy. Biomaterials.
219:1193692019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dennis CL and Ivkov R: Physics of heat
generation using magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. Int J
Hyperthermia. 29:715–729. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Grauer O, Jaber M, Hess K, Weckesser M,
Schwindt W, Maring S, Wölfer J and Stummer W: Combined
intracavitary thermotherapy with iron oxide nanoparticles and
radiotherapy as local treatment modality in recurrent glioblastoma
patients. J Neurooncol. 141:83–94. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Toraya-Brown S and Fiering S: Local tumour
hyperthermia as immunotherapy for metastatic cancer. Int J
Hyperthermia. 30:531–539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Goldberg MS: Immunoengineering: How
nanotechnology can enhance cancer immunotherapy. Cell. 161:201–204.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zanganeh S, Hutter G, Spitler R, Lenkov O,
Mahmoudi M, Shaw A, Pajarinen JS, Nejadnik H, Goodman S, Moseley M,
et al: Iron oxide nanoparticles inhibit tumour growth by inducing
pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization in tumour tissues. Nat
Nanotechnol. 11:986–994. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ge X, Wong R, Anisa A and Ma S: Recent
development of metal-organic framework nanocomposites for
biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 281:1213222022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Auer B, Telfer SG and Gross AJ: Metal
organic frameworks for bioelectrochemical applications.
Electroanalysis. 35:e2022001452023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kim SN, Park CG, Huh BK, Lee SH, Min CH,
Lee YY, Kim YK, Park KH and Choy YB: Metal-organic frameworks,
NH(2)-MIL-88(Fe), as carriers for ophthalmic delivery of
brimonidine. Acta Biomater. 79:344–353. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yang B, Ding L, Yao H, Chen Y and Shi J: A
metal-organic framework (MOF) fenton nanoagent-enabled
nanocatalytic cancer therapy in synergy with autophagy inhibition.
Adv Mater. 32:e19071522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu P, Shi X, Zhong S, Peng Y, Qi Y, Ding
J and Zhou W: Metal-phenolic networks for cancer theranostics.
Biomater Sci. 9:2825–2849. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Luo S, Ma D, Wei R, Yao W, Pang X, Wang Y,
Xu X, Wei X, Guo Y, Jiang X, et al: A tumor microenvironment
responsive nanoplatform with oxidative stress amplification for
effective MRI-based visual tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater.
138:518–527. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Farhood B, Najafi M and Mortezaee K: CD8+
cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: A review. J Cell
Physiol. 234:8509–8521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lin MJ, Svensson-Arvelund J, Lubitz GS,
Marabelle A, Melero I, Brown BD and Brody JD: Cancer vaccines: the
next immunotherapy frontier. Nat Cancer. 3:911–926. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gupta M, Wahi A, Sharma P, Nagpal R, Raina
N, Kaurav M, Bhattacharya J, Rodrigues Oliveira SM, Dolma KG, Paul
AK, et al: Recent advances in cancer vaccines: Challenges,
achievements, and futuristic prospects. Vaccines (Basel).
10:20112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Musetti S and Huang L:
Nanoparticle-mediated remodeling of the tumor microenvironment to
enhance immunotherapy. ACS Nano. 12:11740–11755. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li J, Ren H and Zhang Y: Metal-based
nano-vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Coord Chem Rev.
454:2143452022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Pradeu T and Vivier E: The discontinuity
theory of immunity. Sci Immunol. 1:AAG04792016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Duan X, Chan C and Lin W:
Nanoparticle-mediated immunogenic cell death enables and
potentiates cancer immunotherapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
58:670–680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yang Y, Huang CT, Huang X and Pardoll DM:
Persistent Toll-like receptor signals are required for reversal of
regulatory T cell-mediated CD8 tolerance. Nat Immunol. 5:508–515.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hanson MC, Crespo MP, Abraham W, Moynihan
KD, Szeto GL, Chen SH, Melo MB, Mueller S and Irvine DJ:
Nanoparticulate STING agonists are potent lymph node-targeted
vaccine adjuvants. J Clin Invest. 125:2532–2546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kaur A, Baldwin J, Brar D, Salunke DB and
Petrovsky N: Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists as a driving force
behind next-generation vaccine adjuvants and cancer therapeutics.
Curr Opin Chem Biol. 70:1021722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shinchi H, Yamaguchi T, Moroishi T, Yuki
M, Wakao M, Cottam HB, Hayashi T, Carson DA and Suda Y: Gold
nanoparticles coimmobilized with small molecule toll-like receptor
7 ligand and α-mannose as adjuvants. Bioconjugate Chem.
30:2811–2821. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ishikawa H and Barber GN: STING is an
endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune
signalling. Nature. 455:674–678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Motedayen Aval L, Pease JE, Sharma R and
Pinato DJ: Challenges and opportunities in the clinical development
of STING agonists for cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Med. 9:33232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ding B, Zheng P, Jiang F, Zhao Y, Wang M,
Chang M, Ma P and Lin J: MnOx nanospikes as nanoadjuvants and
immunogenic cell death drugs with enhanced antitumor immunity and
antimetastatic effect. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 59:16381–16384.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Slingluff CL Jr, Petroni GR, Olson WC,
Smolkin ME, Ross MI, Haas NB, Grosh WW, Boisvert ME, Kirkwood JM
and Chianese-Bullock KA: Effect of granulocyte/macrophage
colony-stimulating factor on circulating CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell
responses to a multipeptide melanoma vaccine: Outcome of a
multicenter randomized trial. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7036–7044. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Serafini P, Carbley R, Noonan KA, Tan G,
Bronte V and Borrello I: High-dose granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor-producing vaccines impair the immune
response through the recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells.
Cancer Res. 64:6337–6343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Behzadi M, Vakili B, Ebrahiminezhad A and
Nezafat N: Iron nanoparticles as novel vaccine adjuvants. Eur J
Pharm Sci. 159:1057182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang X, Li X, Onuma K, Sogo Y, Ohno T and
Ito A: Zn- and Mg- containing tricalcium phosphates-based adjuvants
for cancer immunotherapy. Sci Rep. 3:22032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shukla R, Bansal V, Chaudhary M, Basu A,
Bhonde RR and Sastry M: Biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles and
their endocytotic fate inside the cellular compartment: A
microscopic overview. Langmuir. 21:10644–10654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Dobrovolskaia MA and McNeil SE:
Immunological properties of engineered nanomaterials. Nat
Nanotechnol. 2:469–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Tao Y, Ju E, Li Z, Ren J and Qu X:
Engineered CpG- antigen conjugates protected gold nanoclusters as
smart self-vaccines for enhanced immune response and cell imaging.
Adv Funct Mater. 24:1004–1010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhang P, Chiu YC, Tostanoski LH and Jewell
CM: Polyelectrolyte multilayers assembled entirely from immune
signals on gold nanoparticle templates promote antigen-specific T
cell response. ACS Nano. 9:6465–6477. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhao H, Xu J, Li Y, Guan X, Han X, Xu Y,
Zhou H, Peng R, Wang J and Liu Z: Nanoscale coordination polymer
based nanovaccine for tumor immunotherapy. ACS Nano.
13:13127–13135. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jin C, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Wang B and Hua P:
Combination of GNRs-PEI/cGAMP-laden macrophages-based photothermal
induced in situ tumor vaccines and immune checkpoint blockade for
synergistic anti-tumor immunotherapy. Biomater Adv. 133:1126032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chen F, Li T, Zhang H, Saeed M, Liu X,
Huang L, Wang X, Gao J, Hou B, Lai Y, et al: Acid-ionizable iron
nanoadjuvant augments STING activation for personalized vaccination
immunotherapy of cancer. Adv Mater. 35:e22099102023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Ljunggren HG, Jonsson R and Höglund P:
Seminal immunologic discoveries with direct clinical implications:
The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine honours discoveries
in cancer immunotherapy. Scand J Immunol. 88:e127312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Xie L, Wang G, Sang W, Li J, Zhang Z, Li
W, Yan J, Zhao Q and Dai Y: Phenolic immunogenic cell death
nanoinducer for sensitizing tumor to PD-1 checkpoint blockade
immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 269:1206382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Sang W, Zhang Z, Wang G, Xie L, Li J, Li
W, Tian H and Dai L: A triple-kill strategy for tumor eradication
reinforced by metal-phenolic network nanopumps. Adv Funct Mater.
32:21131682022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Mayes PA, Hance KW and Hoos A: The promise
and challenges of immune agonist antibody development in cancer.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 17:509–527. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lim SH, Beers SA, Al-Shamkhani A and Cragg
MS: Agonist antibodies for cancer immunotherapy: History, hopes and
challenges. Clin Cancer Res. 30:1712–1723. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Boomer JS and Green JM: An enigmatic tail
of CD28 signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2:a0024362010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang Q and Vignali DA: Co-stimulatory and
co-inhibitory pathways in autoimmunity. Immunity. 44:1034–1051.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yoshinaga SK, Whoriskey JS, Khare SD,
Sarmiento U, Guo J, Horan T, Shih G, Zhang M, Coccia MA, Kohno T,
et al: T-cell co-stimulation through B7RP-1 and ICOS. Nature.
402:827–832. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Chiang CS, Lin YJ, Lee R, Lai YH, Cheng
HW, Hsieh CH, Shyu WC and Chen SY: Combination of fucoidan-based
magnetic nanoparticles and immunomodulators enhances
tumour-localized immunotherapy. Nat Nanotechnol. 13:746–754. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Locksley RM, Killeen N and Lenardo MJ: The
TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology.
Cell. 104:487–501. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Vonderheide RH and Glennie MJ: Agonistic
CD40 antibodies and cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1035–1043.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang Y, Zhao G, Chen YF, Zhou SK, Wang Y,
Sun YQ, Shen S, Xu CF and Wang J: Engineering nano-clustered
multivalent agonists to cross-link TNF receptors for cancer
therapy. Aggregate. 4:e3932023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Gupta J, Safdari HA and Hoque M:
Nanoparticle mediated cancer immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol.
69:307–324. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
June CH, Riddell SR and Schumacher TN:
Adoptive cellular therapy: A race to the finish line. Sci Transl
Med. 7:280ps72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Krishna S, Lowery FJ, Copeland AR,
Bahadiroglu E, Mukherjee R, Jia L, Anibal JT, Sachs A, Adebola SO,
Gurusamy D, et al: Stem-like CD8 T cells mediate response of
adoptive cell immunotherapy against human cancer. Science.
370:1328–1334. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
June CH, O'Connor RS, Kawalekar OU,
Ghassemi S and Milone MC: CAR T cell immunotherapy for human
cancer. Science. 359:1361–1365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Met Ö, Jensen KM, Chamberlain CA, Donia M
and Svane IM: Principles of adoptive T cell therapy in cancer.
Semin Immunopathol. 41:49–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Wang C, Sun W, Ye Y, Bomba HN and Gu Z:
Bioengineering of artificial antigen presenting cells and lymphoid
organs. Theranostics. 7:3504–3516. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ichikawa J, Yoshida T, Isser A, Laino AS,
Vassallo M, Woods D, Kim S, Oelke M, Jones K, Schneck JP and Weber
JS: Rapid expansion of highly functional antigen-specific T cells
from patients with melanoma by nanoscale artificial
antigen-presenting cells. Clin Cancer Res. 26:3384–3396. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zheng C, Zhang J, Chan HF, Hu H, Lv S, Na
N, Tao Y and Li M: Engineering nano-therapeutics to boost adoptive
cell therapy for cancer treatment. Small Methods. 5:e20011912021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Youn W, Ko EH, Kim MH, Park M, Hong D,
Seisenbaeva GA, Kessler VG and Choi IS: Cytoprotective
encapsulation of individual jurkat T cells within durable TiO2
Shells for T-cell therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 56:10702–10706.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Nie W, Wei W, Zuo L, Lv C, Zhang F, Lu GH,
Li F, Wu G, Huang LL, Xi X and Xie HY: Magnetic nanoclusters armed
with responsive PD-1 antibody synergistically improved adoptive
T-cell therapy for solid tumors. ACS Nano. 13:1469–1478. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Parkhurst MR, Riley JP, Dudley ME and
Rosenberg SA: Adoptive transfer of autologous natural killer cells
leads to high levels of circulating natural killer cells but does
not mediate tumor regression. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6287–6297. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Baruch EN, Berg AL, Besser MJ, Schachter J
and Markel G: Adoptive T cell therapy: An overview of obstacles and
opportunities. Cancer. 123:2154–2162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lin X, Li F, Gu Q, Wang X, Zheng Y, Li J,
Guan J, Yao C and Liu X: Gold-seaurchin based immunomodulator
enabling photothermal intervention and αCD16 transfection to boost
NK cell adoptive immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 146:406–420. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Kong C and Chen X: Combined photodynamic
and photothermal therapy and immunotherapy for cancer treatment: A
review. Int J Nanomedicine. 17:6427–6446. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Xiong Y, Rao Y, Hu J, Luo Z and Chen C:
Nanoparticle-based photothermal therapy for breast cancer
noninvasive treatment. Adv Mater. 37:e23051402025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Paholak HJ, Stevers NO, Chen H, Burnett
JP, He M, Korkaya H, McDermott SP, Deol Y, Clouthier SG, Luther T,
et al: Elimination of epithelial-like and mesenchymal-like breast
cancer stem cells to inhibit metastasis following
nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy. Biomaterials.
104:145–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Song G, Shao X, Qu C, Shi D, Jia R, Chen
Y, Wang J and An H: A large-pore mesoporous Au@Pt@Rh trimetallic
nanostructure with hyperthermia-enhanced enzyme-mimic activities
for immunomodulation-improved tumor catalytic therapy. Chem Eng J.
477:1471612023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Duan X, Chan C, Guo N, Han W, Weichselbaum
RR and Lin W: Photodynamic therapy mediated by nontoxic core-shell
nanoparticles synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade to elicit
antitumor immunity and antimetastatic effect on breast cancer. J Am
Chem Soc. 138:16686–16695. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Thariat J, Hannoun-Levi JM, Sun Myint A,
Vuong T and Gérard JP: Past, present, and future of radiotherapy
for the benefit of patients. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:52–60. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Wardman P: Chemical radiosensitizers for
use in radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 19:397–417. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Ni K, Lan G, Chan C, Quigley B, Lu K, Aung
T, Guo N, La Riviere P, Weichselbaum RR and Lin W: Nanoscale
metal-organic frameworks enhance radiotherapy to potentiate
checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 9:23512018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xu CF, Yu YL, Sun Y, Kong L, Yang CL, Hu
M, Yang T, Zhang J, Hu Q and Zhang Z: Transformable
nanoparticle-enabled synergistic elicitation and promotion of
immunogenic cell death for triple-negative breast cancer
immunotherapy. Adv Funct Mater. 29:19052132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Liu Y, Qiao L, Zhang S, Wan G, Chen B,
Zhou P, Zhang N and Wang Y: Dual pH-responsive multifunctional
nanoparticles for targeted treatment of breast cancer by combining
immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Acta Biomater. 66:310–324. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Bobo D, Robinson KJ, Islam J, Thurecht KJ
and Corrie SR: Nanoparticle-based medicines: A Review of
FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm Res.
33:2373–2387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Fenton OS, Olafson KN, Pillai PS, Mitchell
MJ and Langer R: Advances in biomaterials for drug delivery. Adv
Mater. May 7–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Anselmo AC and Mitragotri S: Nanoparticles
in the clinic: An update. Bioeng Transl Med. 4:e101432019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Huang Y, Hsu JC, Koo H and Cormode DP:
Repurposing ferumoxytol: Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of
an FDA-approved nanoparticle. Theranostics. 12:796–816. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Khoobchandani M, Katti KK, Karikachery AR,
Thipe VC, Srisrimal D, Dhurvas Mohandoss DK, Darshakumar RD, Joshi
CM and Katti KV: New approaches in breast cancer therapy through
green nanotechnology and nano-ayurvedic medicine - pre-clinical and
pilot human clinical investigations. Int J Nanomedicine.
15:181–197. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Kumthekar P, Ko CH, Paunesku T, Dixit K,
Sonabend AM, Bloch O, Tate M, Schwartz M, Zuckerman L, Lezon R, et
al: A first-in-human phase 0 clinical study of RNA
interference-based spherical nucleic acids in patients with
recurrent glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 13:eabb39452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Rojas LA, Sethna Z, Soares KC, Olcese C,
Pang N, Patterson E, Lihm J, Ceglia N, Guasp P, Chu A, et al:
Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 618:144–150. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Alonso JCC, de Souza BR, Reis IB, de
Arruda Camargo GC, de Oliveira G, de Barros Frazão Salmazo MI,
Gonçalves JM, de Castro Roston JR, Caria PHF, da Silva Santos A, et
al: OncoTherad() (MRB-CFI-1) Nanoimmunotherapy: A promising
strategy to treat bacillus calmette-guérin-unresponsive
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Crosstalk among T-Cell CX3CR1,
immune checkpoints, and the toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:175352023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Zhang G, Yuan J, Pan C, Xu Q, Cui X, Zhang
J, Liu M, Song Z, Wu L, Wu D, et al: Multi-omics analysis uncovers
tumor ecosystem dynamics during neoadjuvant toripalimab plus
nab-paclitaxel and S-1 for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A
single-center, open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial. EBioMedicine.
90:1045152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Blanco E, Shen H and Ferrari M: Principles
of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug
delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 33:941–951. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM,
Wechsler ME, Peppas NA and Langer R: Engineering precision
nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:101–124.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Hosta-Rigau L and Städler B: Shear stress
and its effect on the interaction of myoblast cells with nanosized
drug delivery vehicles. Mol Pharmaceut. 10:2707–2712. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Moghimi SM and Szebeni J: Stealth
liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: Critical issues in
pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog
Lipid Res. 42:463–478. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Nizzero S, Ziemys A and Ferrari M:
Transport barriers and oncophysics in cancer treatment. Trends
Cancer. 4:277–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Wagner AM, Gran MP and Peppas NA:
Designing the new generation of intelligent biocompatible carriers
for protein and peptide delivery. Acta Pharm Sin B. 8:147–164.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Hirai T, Yoshioka Y, Izumi N, Ichihashi K,
Handa T, Nishijima N, Uemura E, Sagami K, Takahashi H, Yamaguchi M,
et al: Metal nanoparticles in the presence of lipopolysaccharides
trigger the onset of metal allergy in mice. Nat Nanotechnol.
11:808–816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Radulescu DM, Surdu VA, Ficai A, Ficai D,
Grumezescu AM and Andronescu E: Green synthesis of metal and metal
oxide nanoparticles: A review of the principles and biomedical
applications. Int J Mol Sci. 24:153972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA and Chan WC:
Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle
uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 6:662–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wills JW, Summers HD, Hondow N, Sooresh A,
Meissner KE, White PA, Rees P, Brown A and Doak SH: Characterizing
nanoparticles in biological matrices: Tipping points in
agglomeration state and cellular delivery in vitro. ACS Nano.
11:11986–12000. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Agarwal R, Jurney P, Raythatha M, Singh V,
Sreenivasan SV, Shi L and Roy K: Effect of shape, size, and aspect
ratio on nanoparticle penetration and distribution inside solid
tissues using 3D spheroid models. Adv Healthc Mater. 4:2269–2280.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Kou L, Bhutia YD, Yao Q, He Z, Sun J and
Ganapathy V: Transporter-guided delivery of nanoparticles to
improve drug permeation across cellular barriers and drug exposure
to selective cell types. Front Pharmacol. 9:272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Li W, Jiang Y and Lu J:
Nanotechnology-enabled immunogenic cell death for improved cancer
immunotherapy. Int J Pharm. 634:1226552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Mulens-Arias V, Rojas JM and Barber DF:
The use of iron oxide nanoparticles to reprogram macrophage
responses and the immunological tumor microenvironment. Front
Immunol. 12:6937092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Younis MA, Tawfeek HM, Abdellatif AAH,
Abdel-Aleem JA and Harashima H: Clinical translation of
nanomedicines: Challenges, opportunities, and keys. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 181:1140832022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Almeida JPM, Lin AY, Figueroa ER, Foster
AE and Drezek RA: In vivo gold nanoparticle delivery of peptide
vaccine induces anti-tumor immune response in prophylactic and
therapeutic tumor models. Small. 11:1453–1459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
155
|
Johannsen M, Gneveckow U, Thiesen B,
Taymoorian K, Cho CH, Waldöfner N, Scholz R, Jordan A, Loening SA
and Wust P: Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic
nanoparticles: Feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional
temperature distribution. Eur Urol. 52:1653–1661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Maier-Hauff K, Ulrich F, Nestler D,
Niehoff H, Wust P, Thiesen B, Orawa H, Budach V and Jordan A:
Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic
iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy
on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol.
103:317–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
157
|
Coyne DW: Ferumoxytol for treatment of
iron deficiency anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 10:2563–2568. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Shah A and Dobrovolskaia MA: Immunological
effects of iron oxide nanoparticles and iron-based complex drug
formulations: Therapeutic benefits, toxicity, mechanistic insights,
and translational considerations. Nanomedicine. 14:977–990. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|