|
1
|
Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, Sung
H and Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J Clin. 75:10–45.
2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Caruso G, Weroha SJ and Cliby W: Ovarian
cancer: A review. JAMA. 334:1278–1291. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rodolakis I, Pergialiotis V, Liontos M,
Haidopoulos D, Loutradis D, Rodolakis A, Bamias A and Thomakos N:
Chemotherapy response score in ovarian cancer patients: An overview
of its clinical utility. J Clin Med. 12:21552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kampan NC, Madondo MT, McNally OM, Quinn M
and Plebanski M: Paclitaxel and its evolving role in the management
of ovarian cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2015:4130762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Olawaiye AB, Kim JW, Bagameri A, Bishop E,
Chudecka-Głaz A, Devaux A, Gladieff L, Gordinier ME, Korach J,
McCollum ME, et al: Clinical trial protocol for ROSELLA: A phase 3
study of relacorilant in combination with nab-paclitaxel versus
nab-paclitaxel monotherapy in advanced platinum-resistant ovarian
cancer. J Gynecol Oncol. 35:e1112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vaidyanathan A, Sawers L, Gannon AL,
Chakravarty P, Scott AL, Bray SE, Ferguson MJ and Smith G: ABCB1
(MDR1) induction defines a common resistance mechanism in
paclitaxel- and olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 115:431–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pei Y, Yang Z, Li B, Chen X, Mao Y and
Ding Y: Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of paclitaxel in
high-grade serous ovarian cancer through network pharmacology. Sci
Rep. 15:164452025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanahan D: Hallmarks of cancer: New
dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12:31–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Qiu JG, Wang W, Sun FL, Wang X,
Liu WJ, Jia XY, Ji H, Wang L and Jiang BH: Suppression of CYLD by
HER3 confers ovarian cancer platinum resistance via inhibiting
apoptosis and by inducing drug efflux. Exp Hematol Oncol.
14:212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mosadegh M, Noori Goodarzi N and Erfani Y:
A comprehensive insight into apoptosis: Molecular mechanisms,
signaling pathways, and modulating therapeutics. Cancer Invest.
43:33–58. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bertheloot D, Latz E and Franklin BS:
Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell
death. Cell Mol Immunol. 18:1106–1121. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cai W, Rong D, Ding J, Zhang X, Wang Y,
Fang Y, Xiao J, Yang S and Wang H: Activation of the PERK/eIF2α
axis is a pivotal prerequisite of taxanes to cancer cell apoptosis
and renders synergism to overcome paclitaxel resistance in breast
cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 24:2492024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McFadden M, Singh SK, Kinnel B, Varambally
S and Singh R: The effect of paclitaxel- and fisetin-loaded PBM
nanoparticles on apoptosis and reversal of drug resistance gene
ABCG2 in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 16:2202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Souto EP, Gong P, Landua JD, Rajaram
Srinivasan R, Ganesan A, Dobrolecki LE, Purdy SC, Pan X, Zeosky M,
Chung A, et al: Lineage tracing and single-cell RNA sequencing
reveal a common transcriptional state in breast cancer
tumor-initiating cells characterized by IFN/STAT1 activity. Cancer
Res. 85:1390–1409. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han H, Gong C, Zhang Y, Liu C, Wang Y,
Zhao D, Huang J and Gong Z: RBM30 recruits DOT1L to activate STAT1
transcription and drive immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncogene. 44:3955–3973. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Wang F, Xu X, Zhang J and Xu G: The
dual role of STAT1 in ovarian cancer: Insight into molecular
mechanisms and application potentials. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6365952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, Shenmen
CM, Grouse LH, Schuler G, Klein SL, Old S, Rasooly R, Good P, et
al: The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA
project: The mammalian gene collection (MGC). Genome Res.
14:2121–2127. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian X, Guan W, Zhang L, Sun W, Zhou D,
Lin Q, Ren W, Nadeem L and Xu G: Physical interaction of STAT1
isoforms with TGF-β receptors leads to functional crosstalk between
two signaling pathways in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37:1032018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Xu X, Li X, Yuan J, Gao X, Wang C,
Guan W and Xu G: Target finder of transcription factor (TFoTF): A
novel tool to predict transcription factor-targeted genes in
cancer. Mol Oncol. 17:1246–1262. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang J, Guan W, Xu X, Wang F, Li X and Xu
G: A novel homeostatic loop of sorcin drives paclitaxel-resistance
and malignant progression via Smad4/ZEB1/miR-142-5p in human
ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 40:4906–4918. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Das AT, Tenenbaum L and Berkhout B: Tet-on
systems for doxycycline-inducible gene expression. Curr Gene Ther.
16:156–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tönjes M, Barbus S, Park YJ, Wang W,
Schlotter M, Lindroth AM, Pleier SV, Bai AHC, Karra D, Piro RM, et
al: BCAT1 promotes cell proliferation through amino acid catabolism
in gliomas carrying wild-type IDH1. Nat Med. 19:901–908. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xu X, Wang C, Guan W, Wang F, Li X, Yuan J
and Xu G: Protoporphyrin IX-loaded albumin nanoparticles reverse
cancer chemoresistance by enhancing intracellular reactive oxygen
species. Nanomedicine. 51:1026882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z,
Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L, et al: clusterProfiler 4.0: A
universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation
(Camb). 2:1001412021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Walter W, Sánchez-Cabo F and Ricote M:
GOplot: An R package for visually combining expression data with
functional analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:2912–2914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H,
Ghandi M, Mesirov JP and Tamayo P: The molecular signatures
database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst.
1:417–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Davidson-Pilon C: lifelines: survival
analysis in Python. J Open Source Softw. 4:13172019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rozowsky J, Euskirchen G, Auerbach RK,
Zhang ZD, Gibson T, Bjornson R, Carriero N, Snyder M and Gerstein
MB: PeakSeq enables systematic scoring of ChIP-seq experiments
relative to controls. Nat Biotechnol. 27:66–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Auerbach RK, Euskirchen G, Rozowsky J,
Lamarre-Vincent N, Moqtaderi Z, Lefrançois P, Struhl K, Gerstein M
and Snyder M: Mapping accessible chromatin regions using Sono-Seq.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14926–14931. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu G, Wang LG and He QY: ChIPseeker: An
R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and
visualization. Bioinformatics. 31:2382–2383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lawrence M, Huber W, Pagès H, Aboyoun P,
Carlson M, Gentleman R, Morgan MT and Carey VJ: Software for
computing and annotating genomic ranges. PLoS Comput Biol.
9:e10031182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koti M, Gooding RJ, Nuin P, Haslehurst A,
Crane C, Weberpals J, Childs T, Bryson P, Dharsee M, Evans K, et
al: Identification of the IGF1/PI3K/NF κB/ERK gene signalling
networks associated with chemotherapy resistance and treatment
response in high-grade serous epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC
Cancer. 13:5492013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Virtanen P, Gommers R, Oliphant TE,
Haberland M, Reddy T, Cournapeau D, Burovski E, Peterson P,
Weckesser W, Bright J, et al: SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for
scientific computing in python. Nat Methods. 17:261–272. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y and Liu Z: STAT1 in cancer: Friend
or foe? Discov Med. 24:19–29. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meissl K, Macho-Maschler S, Müller M and
Strobl B: The good and the bad faces of STAT1 in solid tumours.
Cytokine. 89:12–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu F, Liu J, Zhang J, Shi J, Gui L and Xu
G: Expression of STAT1 is positively correlated with PD-L1 in human
ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 21:963–971. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen G, Wang H, Xie S, Ma J and Wang G:
STAT1 negatively regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation. Oncol Rep. 29:2303–2310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gordziel C, Bratsch J, Moriggl R, Knösel T
and Friedrich K: Both STAT1 and STAT3 are favourable prognostic
determinants in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 109:138–146.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hix LM, Karavitis J, Khan MW, Shi YH,
Khazaie K and Zhang M: Tumor STAT1 transcription factor activity
enhances breast tumor growth and immune suppression mediated by
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Biol Chem. 288:11676–11688.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kovacic B, Stoiber D, Moriggl R, Weisz E,
Ott RG, Kreibich R, Levy DE, Beug H, Freissmuth M and Sexl V: STAT1
acts as a tumor promoter for leukemia development. Cancer Cell.
10:77–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Wang F, Liu F and Xu G:
Predicting STAT1 as a prognostic marker in patients with solid
cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 12:17588359209175582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Darnell JE Jr: Transcription factors as
targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:740–749. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee TI and Young RA: Transcriptional
regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell. 152:1237–1251.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lambert SA, Jolma A, Campitelli LF, Das
PK, Yin Y, Albu M, Chen X, Taipale J, Hughes TR and Weirauch MT:
The human transcription factors. Cell. 175:598–599. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Spitz F and Furlong EE: Transcription
factors: From enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat Rev
Genet. 13:613–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bushweller JH: Targeting transcription
factors in cancer-from undruggable to reality. Nat Rev Cancer.
19:611–624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lambert M, Jambon S, Depauw S and
David-Cordonnier MH: Targeting transcription factors for cancer
treatment. Molecules. 23:14792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Blagosklonny MV, Robey R, Sheikh MS and
Fojo T: Paclitaxel-induced FasL-independent apoptosis and slow
(non-apoptotic) cell death. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:113–117. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang TH, Wang HS and Soong YK:
Paclitaxel-induced cell death: Where the cell cycle and apoptosis
come together. Cancer. 88:2619–2628. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Oda K, Matoba Y, Irie T, Kawabata R,
Fukushi M, Sugiyama M and Sakaguchi T: Structural basis of the
inhibition of STAT1 activity by sendai virus C protein. J Virol.
89:11487–11499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Parrini M, Meissl K, Ola MJ, Lederer T,
Puga A, Wienerroither S, Kovarik P, Decker T, Müller M and Strobl
B: The C-terminal transactivation domain of STAT1 has a
gene-specific role in transactivation and cofactor recruitment.
Front Immunol. 9:28792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wojciak JM, Martinez-Yamout MA, Dyson HJ
and Wright PE: Structural basis for recruitment of CBP/p300
coactivators by STAT1 and STAT2 transactivation domains. EMBO J.
28:948–958. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















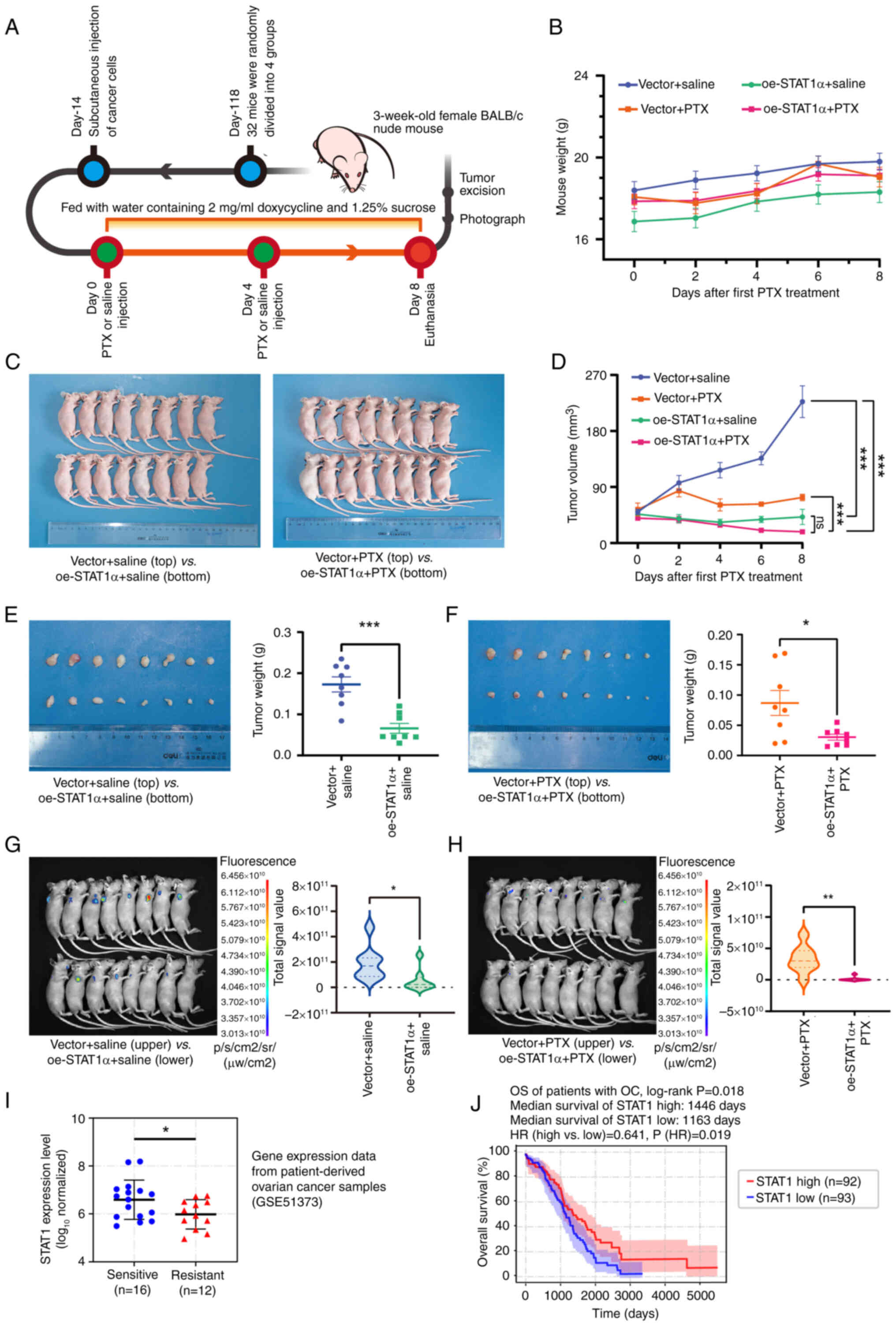
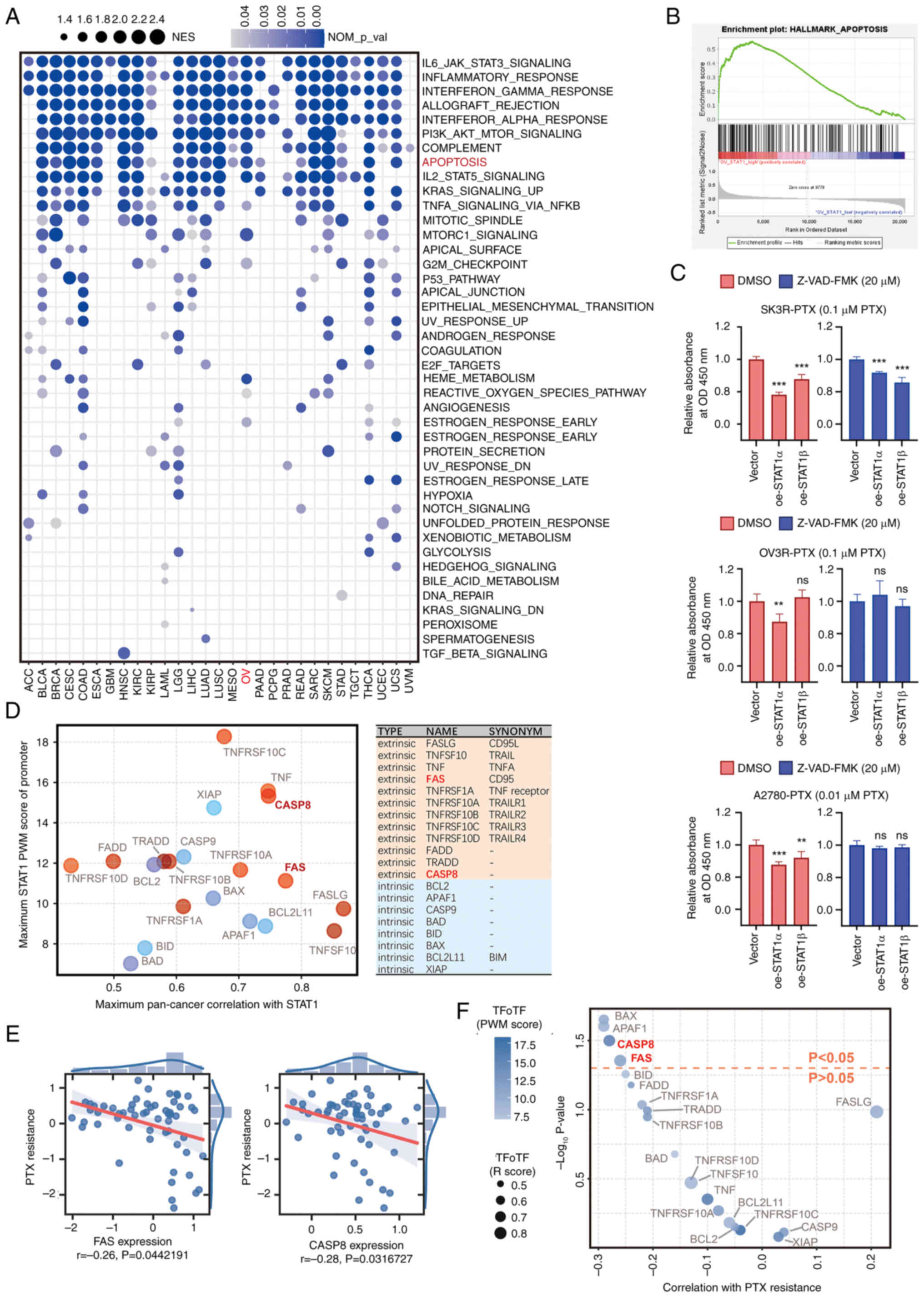
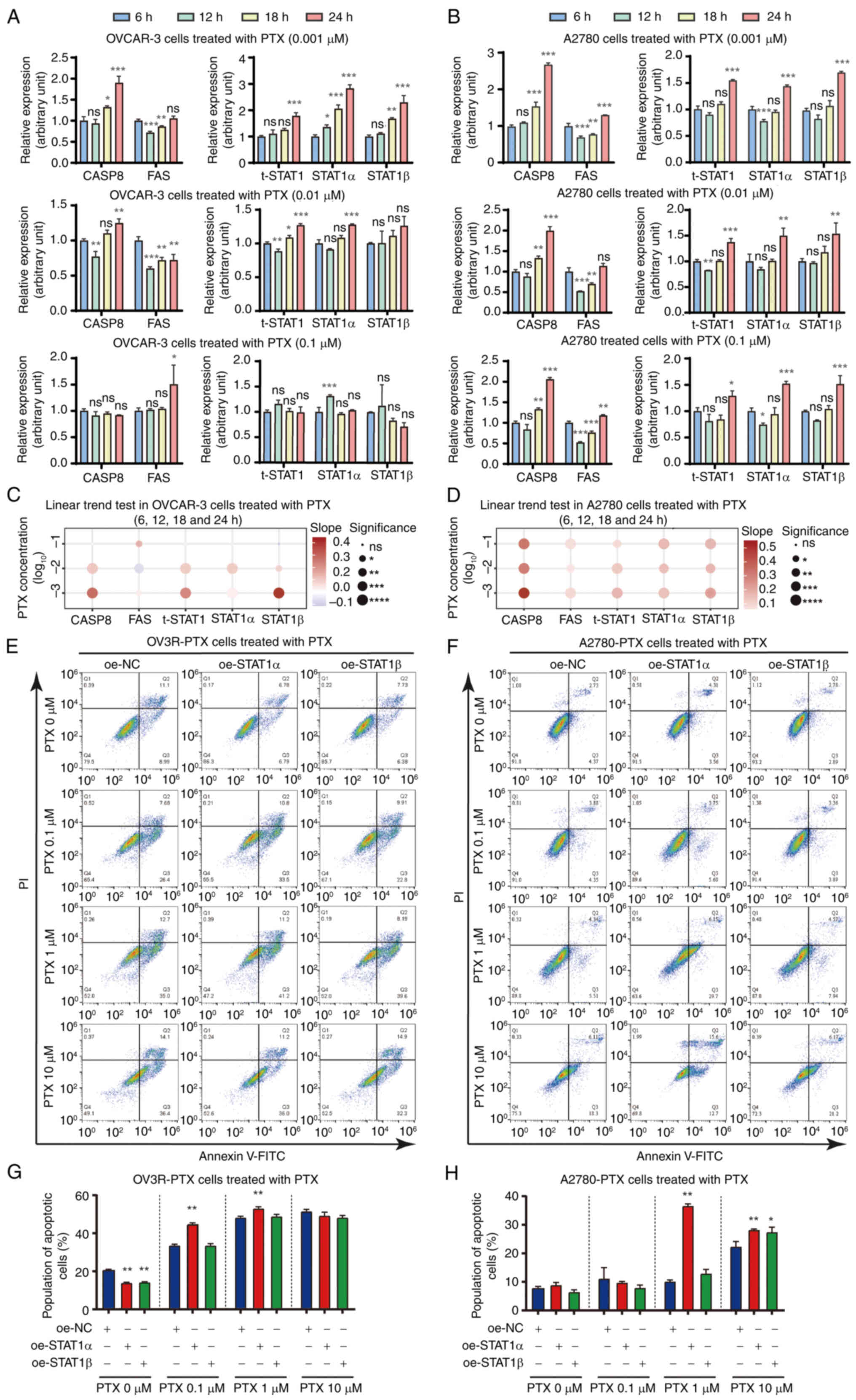
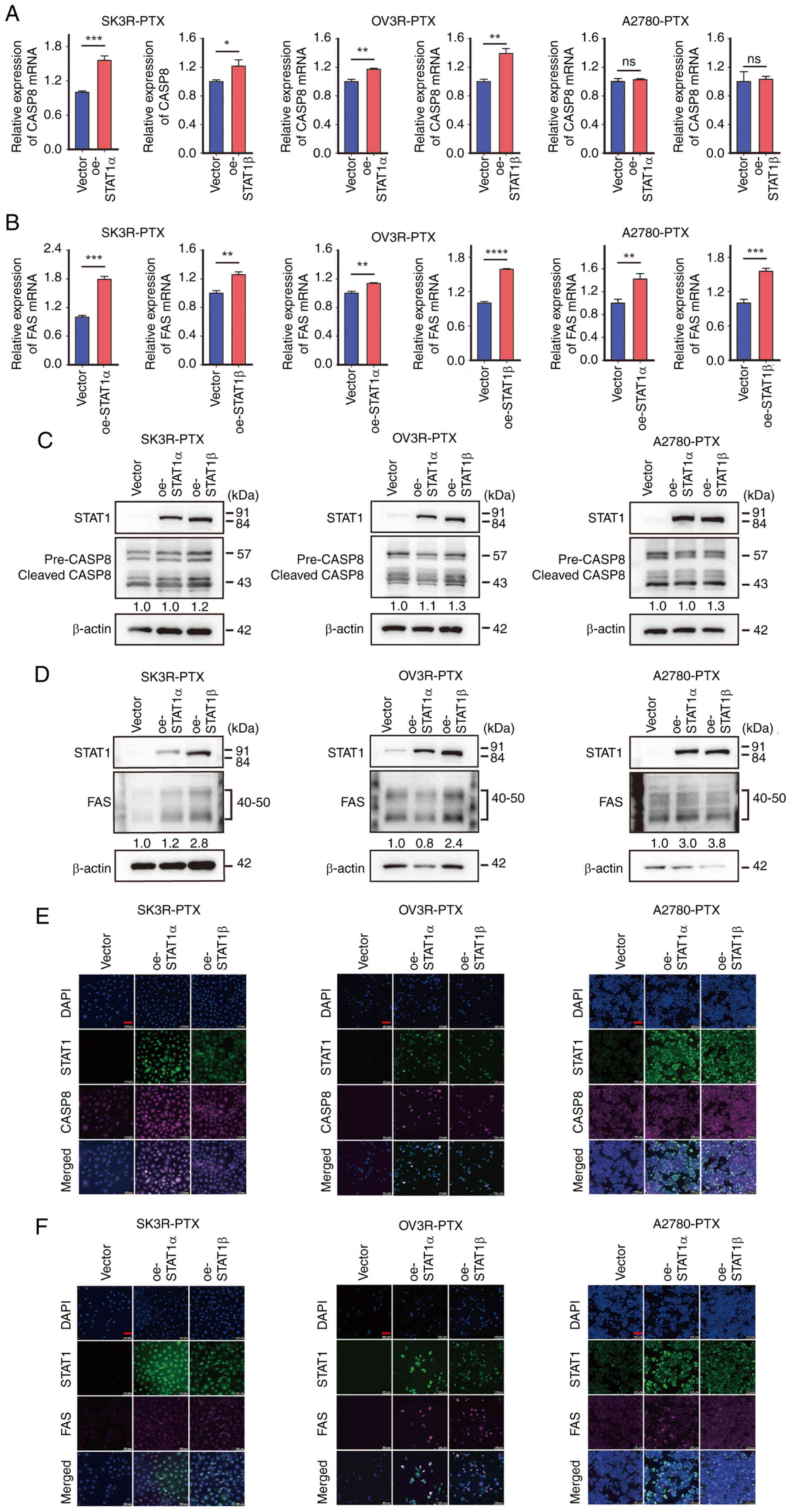
![Detection of STAT1 expression, and
effect of STAT1 on PTX sensitivity and viability in PTX-resistant
OC cells (SK3R-PTX, OV3R-PTX and A2780-PTX cells) and their
sensitive counterpart cells (SK-OV-3, OVCAR-3 and A2780 cells). (A)
Validation of PTX resistance in OC cells. The dots and curves in
the graphs indicate the relative cell viability at the
corresponding PTX concentrations and non-linear regression fitting
curves. Differences between sensitive cells and resistant cells
were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's HSD test.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n=3). (B) Differentially
expressed TF genes in PTX-sensitive and PTX-resistant OC cells. The
pie chart on the left represents the percentage of TF genes that
were differentially expressed at a significant level (expression FC
>2.5 and P<0.05). The pie chart on the right represents the
percentage of upregulated and downregulated TF genes. (C) Volcano
plot showing the alteration of TF gene expression between A2780 and
A2780-PTX cells based on the mRNA-sequencing results (n=3). The
gray horizontal line represents the P-value of 0.05, and the two
gray vertical lines represent the locations of FC >2 in gene
expression (A2780-PTX vs. A2780 cells). TF genes with significantly
altered expression (defined as FC <0.4 or >2.5 and P<0.05)
were marked with red dots. The red star indicates STAT1. (D)
Detection of total STAT1, STAT1α and STAT1β mRNA expression in
three paired cells [PTX-sensitive cells (SK-OV-3, OVCAR-3 and
A2780) vs. counterpart resistant cells (SK3R-PTX, OV3R-PTX and
A2780-PTX)] by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. Expression
values for each group were normalized using β-actin as an internal
reference. Differences between PTX-sensitive cells and
PTX-resistant cells were analyzed using unpaired Student's t-test.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n=3). (E) Detection of STAT1
protein expression in three paired cells by western blotting.
Detection of PTX sensitivity in (F) SK3R-PTX, (G) OV3R-PTX and (H)
A2780-PTX cells after overexpression of STAT1α or STAT1β in the
presence of 8 μg/ml Dox and different doses of PTX. The dots
and curves in the graphs indicate the relative cell viability based
on the Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Blue, red and green vertical
dotted lines in each panel indicated the absolute IC50.
Differences among groups were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by
Tukey's HSD test. Data are presented as the mean ± SD [n=4 for (F
and G); n=3 for (H)]. Determination of growth inhibitory effect of
PTX in (I) SK3R-PTX, (J) OV3R-PTX and (K) A2780-PTX cells after
induction of STAT1 overexpression by Dox. A cell viability assay
was performed. Differences among multiple groups were analyzed by
one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD test. Data are presented as
the mean ± SD (n=3). *P<0.05; **P<0.01;
***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001 resistant
cells vs. sensitive cells in each pair in (A) and (D) or
oe-STAT1α/β vs. oe-NC in (F-K). Dox, doxycycline; FC, fold change;
HSD, Honestly Significant Difference; NC, negative control; ns, not
significant; OC, ovarian cancer; OD, optical density; oe,
overexpression vector; PTX, paclitaxel; TF, transcription
factor.](/article_images/ijo/68/2/ijo-68-02-05832-g00.jpg)