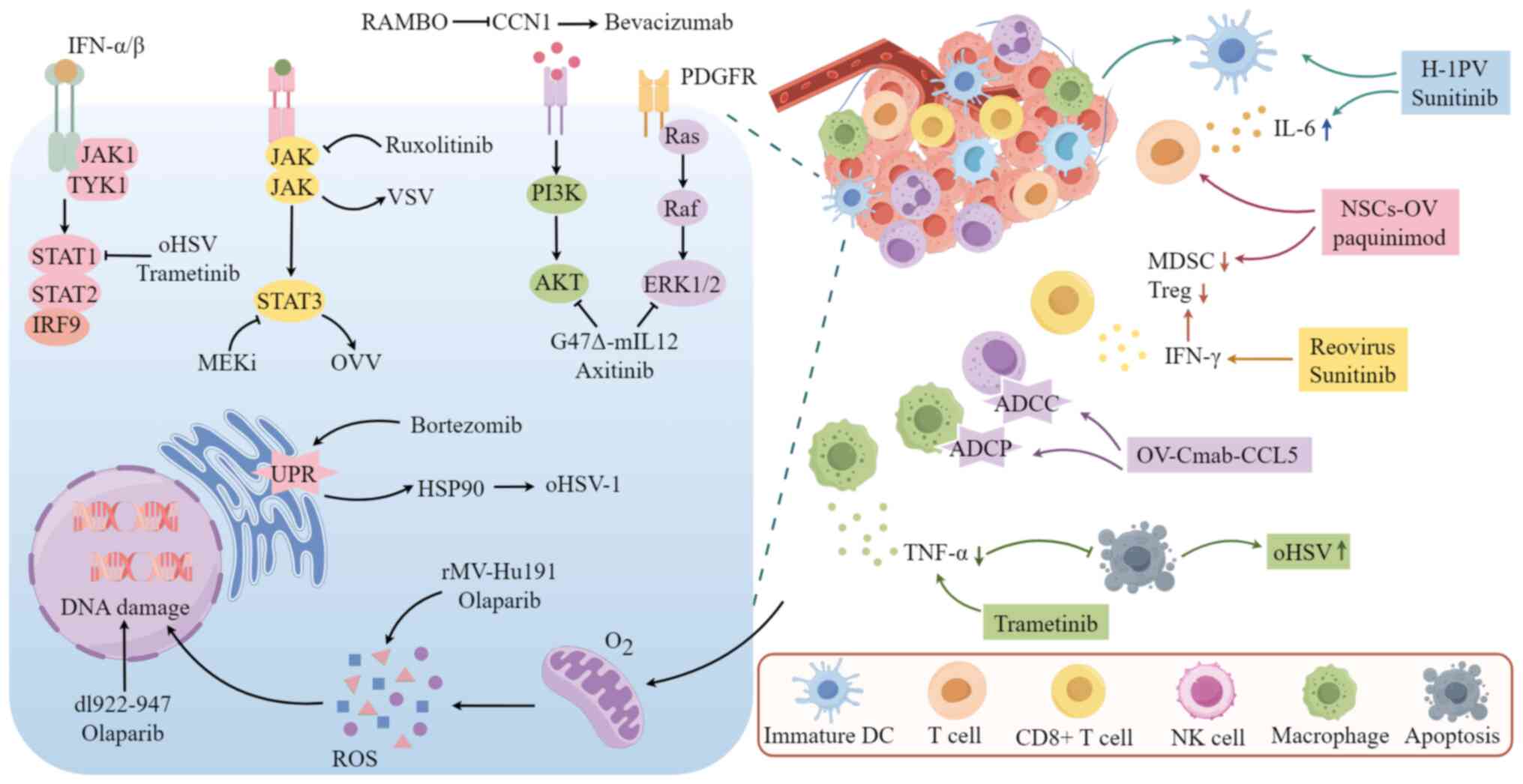
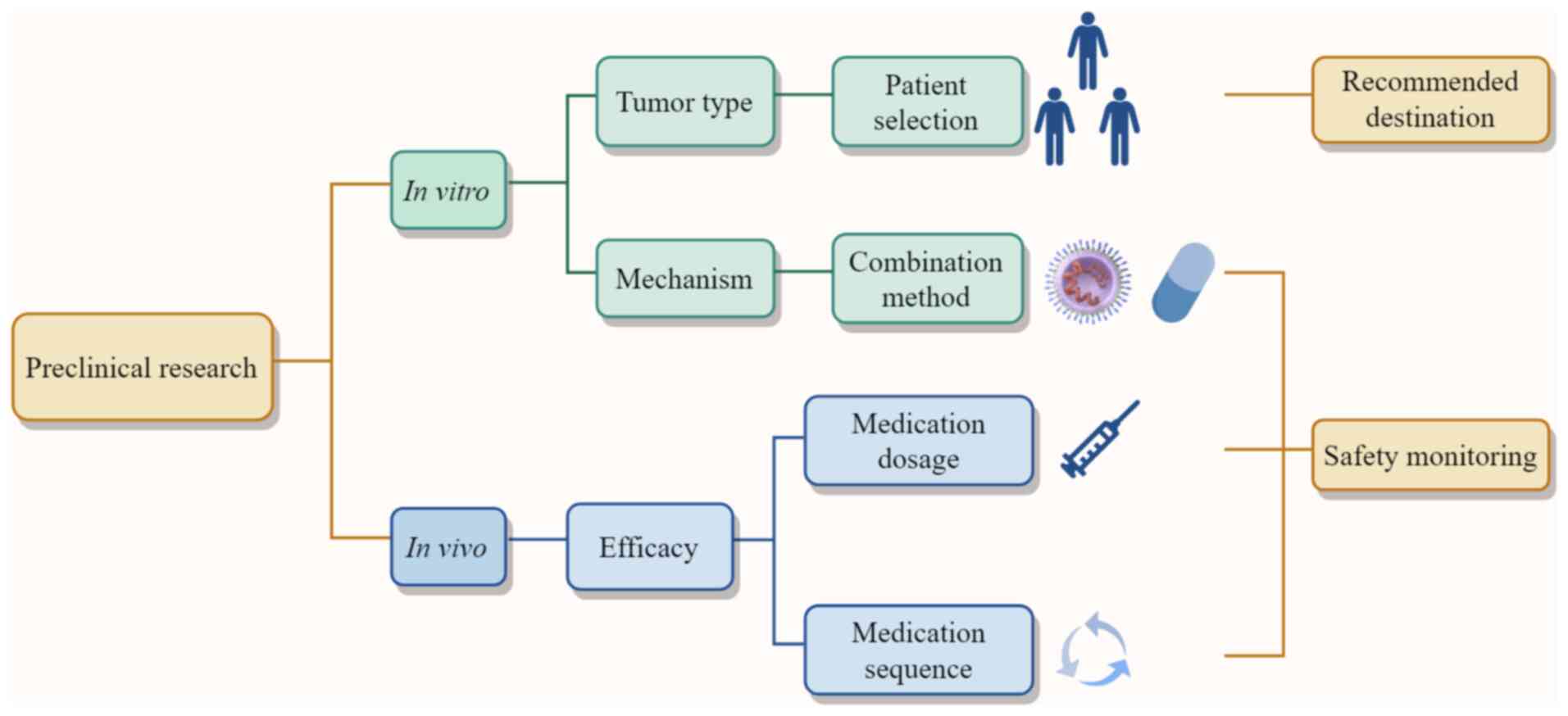
|
1
|
Ma R, Li Z, Chiocca EA, Caligiuri MA and
Yu J: The emerging field of oncolytic virus-based cancer
immunotherapy. Trends Cancer. 9:122–139. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Rasa A and Alberts P: Oncolytic virus
preclinical toxicology studies. J Appl Toxicol. 43:620–648. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shalhout SZ, Miller DM, Emerick KS and
Kaufman HL: Therapy with oncolytic viruses: Progress and
challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 20:160–177. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Todo T, Ito H, Ino Y, Ohtsu H, Ota Y,
Shibahara J and Tanaka M: Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47
for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: A phase 2 trial. Nat Med.
28:1630–1639. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gazal S, Gazal S, Kaur P, Bhan A and
Olagnier D: Breaking barriers: Animal viruses as oncolytic and
immunotherapeutic agents for human cancers. Virology.
600:1102382024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kaufman HL, Shalhout SZ and Iodice G:
Talimogene laherparepvec: Moving from first-in-class to
best-in-class. Front Mol Biosci. 9:8348412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xi P, Zeng D, Chen M, Jiang L, Zhang Y,
Qin D, Yao Z and He C: Enhancing pancreatic cancer treatment: The
role of H101 oncolytic virus in irreversible electroporation. Front
Immunol. 16:15462422025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee T, Gianchandani A, Boorjian SA, Shore
ND, Narayan VM, Dinney CPN and Kamat AM: Intravesical
interferon-α2b gene therapy with nadofaragene firadenovec-vncg: A
contemporary review. Future Oncol. 21:2429–2438. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen L, Zuo M, Zhou Q and Wang Y:
Oncolytic virotherapy in cancer treatment: Challenges and
optimization prospects. Front Immunol. 14:13088902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin D, Shen Y and Liang T: Oncolytic
virotherapy: Basic principles, recent advances and future
directions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:1562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ and Oon CE: Molecular
targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur J
Pharmacol. 834:188–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aldea M, Andre F, Marabelle A, Dogan S,
Barlesi F and Soria JC: Overcoming resistance to tumor-targeted and
immune-targeted therapies. Cancer Discov. 11:874–899. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu Z, McGray AJR, Jiang W, Lu B, Kalinski
P and Guo ZS: Improving cancer immunotherapy by rationally
combining oncolytic virus with modulators targeting key signaling
pathways. Mol Cancer. 21:1962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou X, Hu S and Wang X: Recent advances
in oncolytic virus combined immunotherapy in tumor treatment. Genes
Dis. 12:1015992025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Cillis J, Deshpande S, Park AK,
Valencia H, Kim SI, Lu J, Vashi Y, Yang A, Zhang Z, et al:
Oncolytic virotherapy in solid tumors: A current review. BioDrugs.
39:857–876. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ullah R, Yin Q, Snell AH and Wan L:
RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer evolution and treatment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 85:123–154. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee S, Yang W, Kim DK, Kim H, Shin M, Choi
KU, Suh DS, Kim YH, Hwang TH and Kim JH: Inhibition of MEK-ERK
pathway enhances oncolytic vaccinia virus replication in
doxorubicin-resistant ovarian cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
25:211–224. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Okemoto K, Wagner B, Meisen H, Haseley A,
Kaur B and Chiocca EA: STAT3 activation promotes oncolytic HSV1
replication in glioma cells. PLoS One. 8:e719322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Q, Zhang R, Qiao C, Miao Y, Yuan Y
and Zheng H: Ubiquitination network in the type I IFN-induced
antiviral signaling pathway. Eur J Immunol. 53:e23503842023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schneider W M, Chevillotte M D and Rice
CM: Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses.
Annu Rev Immunol. 32:513–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou X, Zhao J, Zhang JV, Wu Y, Wang L,
Chen X, Ji D and Zhou GG: Enhancing therapeutic efficacy of
oncolytic herpes simplex virus with MEK inhibitor trametinib in
some BRAF or KRAS-Mutated colorectal or lung carcinoma models.
Viruses. 13:17582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nguyen TT, Ramsay L, Ahanfeshar-Adams M,
Lajoie M, Schadendorf D, Alain T and Watson IR: Mutations in the
IFNγ-JAK-STAT pathway causing resistance to immune checkpoint
inhibitors in melanoma increase sensitivity to oncolytic virus
treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 27:3432–3442. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Patel MR, Dash A, Jacobson BA, Ji Y,
Baumann D, Ismail K and Kratzke RA: JAK/STAT inhibition with
ruxolitinib enhances oncolytic virotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer models. Cancer Gene Ther. 26:411–418. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Otani Y, Ishida J, Kurozumi K, Oka T,
Shimizu T, Tomita Y, Hattori Y, Uneda A, Matsumoto Y, Michiue H, et
al: PIK3R1Met326Ile germline mutation correlates with cysteine-rich
protein 61 expression and poor prognosis in glioblastoma. Sci Rep.
7:73912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Long QZ, Zhou M, Liu XG, Du YF, Fan JH, Li
X and He DL: Interaction of CCN1 with αvβ3 integrin induces
P-glycoprotein and confers vinblastine resistance in renal cell
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 24:810–817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin BR, Chang CC, Chen LR, Wu MH, Wang MY,
Kuo IH, Chu CY, Chang KJ, Lee PH, Chen WJ, et al: Cysteine-rich 61
(CCN1) enhances chemotactic migration, transendothelial cell
migration, and intravasation by concomitantly up-regulating
chemokine receptor 1 and 2. Mol Cancer Res. 5:1111–1123. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Di Y, Zhang Y, Nie Q and Chen X:
CCN1/Cyr61-PI3K/AKT signaling promotes retinal neovascularization
in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Mol Med. 36:1507–1518. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomita Y, Kurozumi K, Yoo JY, Fujii K,
Ichikawa T, Matsumoto Y, Uneda A, Hattori Y, Shimizu T, Otani Y, et
al: Oncolytic herpes virus armed with vasculostatin in combination
with bevacizumab abrogates glioma invasion via the CCN1 and AKT
signaling pathways. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:1418–1429. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sugawara K, Iwai M, Ito H, Tanaka M, Seto
Y and Todo T: Oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ works synergistically
with CTLA-4 inhibition via dynamic intratumoral immune modulation.
Mol Ther Oncolytics. 22:129–142. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma W, He H and Wang H: Oncolytic herpes
simplex virus and immunotherapy. BMC Immunol. 19:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saha D, Wakimoto H, Peters CW, Antoszczyk
SJ, Rabkin SD and Martuza RL: Combinatorial effects of VEGFR kinase
inhibitor axitinib and oncolytic virotherapy in mouse and human
glioblastoma stem-like cell models. Clin Cancer Res. 24:3409–3422.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jha BK, Dong B, Nguyen CT, Polyakova I and
Silverman RH: Suppression of antiviral innate immunity by sunitinib
enhances oncolytic virotherapy. Mol Ther. 21:1749–1757. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khoury R, Saleh K, Khalife N, Saleh M,
Chahine C, Ibrahim R and Lecesne A: Mechanisms of resistance to
antibody-drug conjugates. Int J Mol Sci. 24:96742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arulanandam R, Taha Z, Garcia V, Selman M,
Chen A, Varette O, Jirovec A, Sutherland K, Macdonald E, Tzelepis
F, et al: The strategic combination of trastuzumab emtansine with
oncolytic rhabdoviruses leads to therapeutic synergy. Commun Biol.
3:2542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du Z, Whitt MA, Baumann J, Garner JM,
Morton CL, Davidoff AM and Pfeffer LM: Inhibition of type I
interferon-mediated antiviral action in human glioma cells by the
IKK inhibitors BMS-345541 and TPCA-1. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
32:368–377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dolcetti L, Marigo I, Mantelli B,
Peranzoni E, Zanovello P and Bronte V: Myeloid-derived suppressor
cell role in tumor-related inflammation. Cancer Lett. 267:216–225.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lawson KA, Mostafa AA, Shi ZQ, Spurrell J,
Chen W, Kawakami J, Gratton K, Thakur S and Morris DG: Repurposing
sunitinib with oncolytic reovirus as a novel immunotherapeutic
strategy for renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5839–5850.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moehler M, Sieben M, Roth S, Springsguth
F, Leuchs B, Zeidler M, Dinsart C, Rommelaere J and Galle PR:
Activation of the human immune system by chemotherapeutic or
targeted agents combined with the oncolytic parvovirus H-1. BMC
Cancer. 11:4642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ichikawa M, Williams R, Wang L, Vogl T and
Srikrishna G: S100A8/A9 activate key genes and pathways in colon
tumor progression. Mol Cancer Res. 9:133–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chai H, Xu H, Jiang S, Zhang T, Chen J,
Zhu R, Wang Y, Sun M, Liu B, Wang X, et al: Neural stem
cell-delivered oncolytic virus via intracerebroventricular
administration enhances glioblastoma therapy and immune modulation.
J Immunother Cancer. 13:e0129342025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu Z, Chen H, Feng C, Chen L, Ma C, Liu
Z, Qu Z, Bartlett DL, Lu B, Li K and Guo ZS: Specific inhibitor to
KRASG12C induces tumor-specific immunity and synergizes
with oncolytic virus for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. J
Immunother Cancer. 13:e0105142025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Herman ML, Geanes ES, McLennan R, Greening
GJ, Mwitanti H and Bradley T: ICAM-1 autoantibodies detected in
healthy individuals and cross-react with functional epitopes.
Immunohorizons. 9:vlaf0252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shin J, Lim J, Han D, Lee S, Sung NS, Kim
JS, Kim DK, Lee HY, Lee SK, Shin J, et al: TBK1 inhibitor amlexanox
exerts anti-cancer effects against endometrial cancer by regulating
AKT/NF-κB signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 21:143–159. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Guo X, Feng H, Xi Z, Zhou J, Huang Z, Guo
J, Zheng J, Lyu Z, Liu Y, Zhou J, et al: Targeting TBK1 potentiates
oncolytic virotherapy via amplifying ICAM1-mediated NK cell
immunity in chemo-resistant colorectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer.
13:e0114552025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meisen WH, Wohleb ES, Jaime-Ramirez AC,
Bolyard C, Yoo JY, Russell L, Hardcastle J, Dubin S, Muili K, Yu J,
et al: The impact of macrophage- and microglia-secreted TNFα on
Oncolytic HSV-1 therapy in the glioblastoma tumor microenvironment.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:3274–3285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yoo JY, Swanner J, Otani Y, Nair M, Park
F, Banasavadi-Siddegowda Y, Liu J, Jaime-Ramirez AC, Hong B, Geng
F, et al: Oncolytic HSV therapy increases trametinib access to
brain tumors and sensitizes them in vivo. Neuro Oncol.
21:1131–1140. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Burch AD and Weller SK: Herpes simplex
virus type 1 DNA polymerase requires the mammalian chaperone hsp90
for proper localization to the nucleus. J Virol. 79:10740–10749.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yoo JY, Hurwitz BS, Bolyard C, Yu JG,
Zhang J, Selvendiran K, Rath KS, He S, Bailey Z, Eaves D, et al:
Bortezomib-induced unfolded protein response increases oncolytic
HSV-1 replication resulting in synergistic antitumor effects. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:3787–3798. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tian L, Xu B, Chen Y, Li Z, Wang J, Zhang
J, Ma R, Cao S, Hu W, Chiocca EA, et al: Specific targeting of
glioblastoma with an oncolytic virus expressing a cetuximab-CCL5
fusion protein via innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Cancer.
3:1318–1335. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Napolitano F, Di Somma S, Castellano G,
Amato J, Pagano B, Randazzo A, Portella G and Malfitano AM:
Combination of dl922-947 oncolytic adenovirus and G-quadruplex
binders uncovers improved antitumor activity in breast cancer.
Cells. 11:24822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Passaro C, Volpe M, Botta G, Scamardella
E, Perruolo G, Gillespie D, Libertini S and Portella G: PARP
inhibitor olaparib increases the oncolytic activity of dl922-947 in
in vitro and in vivo model of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Mol
Oncol. 9:78–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kyula-Currie J, Roulstone V, Wright J,
Butera F, Legrand A, Elliott R, McLaughlin M, Bozhanova G, Krastev
D, Pettitt S, et al: The PARP inhibitor talazoparib synergizes with
reovirus to induce cancer killing and tumour control in vivo in
mouse models. Nat Commun. 16:62992025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhong Y, Le H, Zhang X, Dai Y, Guo F, Ran
X, Hu G, Xie Q, Wang D and Cai Y: Identification of restrictive
molecules involved in oncolytic virotherapy using genome-wide
CRISPR screening. J Hematol Oncol. 17:362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tapeinos C and Pandit A: Physical,
chemical, and biological structures based on ROS-Sensitive moieties
that are able to respond to oxidative microenvironments. Adv Mater.
28:5553–5585. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L, Wang D, Sonzogni O, Ke S, Wang Q,
Thavamani A, Batalini F, Stopka SA, Regan MS, Vandal S, et al:
PARP-inhibition reprograms macrophages toward an anti-tumor
phenotype. Cell Rep. 41:1114622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tubbs A and Nussenzweig A: Endogenous DNA
damage as a source of genomic instability in cancer. Cell.
168:644–656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Packiriswamy N, Upreti D, Zhou Y, Khan R,
Miller A, Diaz RM, Rooney CM, Dispenzieri A, Peng KW and Russell
SJ: Oncolytic measles virus therapy enhances tumor antigen-specific
T-cell responses in patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia.
34:3310–3322. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhou S, Li Y, Huang F, Zhang B, Yi T, Li
Z, Luo H, He X, Zhong Q, Bian C, et al: Live-attenuated measles
virus vaccine confers cell contact loss and apoptosis of ovarian
cancer cells via ROS-induced silencing of E-cadherin by
methylation. Cancer Lett. 318:14–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang CD, Jiang LH, Zhou X, He YP, Liu Y,
Zhou DM, Lv Y, Wu BQ and Zhao ZY: Synergistic antitumor efficacy of
rMV-Hu191 and Olaparib in pancreatic cancer by generating oxidative
DNA damage and ROS-dependent apoptosis. Transl Oncol.
39:1018122024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Meikrantz W and Schlegel R: Apoptosis and
the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem. 58:160–174. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lee B, Min JA, Nashed A, Lee SO, Yoo JC,
Chi SW and Yi GS: A novel mechanism of irinotecan targeting MDM2
and Bcl-xL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 514:518–523. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hubbard JM and Grothey A: Napabucasin: An
update on the first-in-class cancer stemness inhibitor. Drugs.
77:1091–1103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Babaei A, Soleimanjahi H, Soleimani M and
Arefian E: The synergistic anticancer effects of ReoT3D, CPT-11,
and BBI608 on murine colorectal cancer cells. Daru. 28:555–565.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen Y and Zhou X: Research progress of
mTOR inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 208:1128202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang Y and Zhang H: Regulation of
autophagy by mTOR signaling pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1206:67–83.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yoshida GJ: Therapeutic strategies of drug
repositioning targeting autophagy to induce cancer cell death: From
pathophysiology to treatment. J Hematol Oncol. 10:672017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Saran U, Foti M and Dufour JF: Cellular
and molecular effects of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus. Clin Sci
(Lond). 129:895–914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Alonso MM, Jiang H, Yokoyama T, Xu J,
Bekele NB, Lang FF, Kondo S, Gomez-Manzano C and Fueyo J:
Delta-24-RGD in combination with RAD001 induces enhanced
anti-glioma effect via autophagic cell death. Mol Ther. 16:487–493.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lang FF, Conrad C, Gomez-Manzano C, Yung
WKA, Sawaya R, Weinberg JS, Prabhu SS, Rao G, Fuller GN, Aldape KD,
et al: Phase I study of DNX-2401 (Delta-24-RGD) oncolytic
adenovirus: Replication and immunotherapeutic effects in recurrent
malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 36:1419–1427. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xue C, Chu Q, Shi Q, Zeng Y, Lu J and Li
L: Wnt signaling pathways in biology and disease: Mechanisms and
therapeutic advances. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:1062025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang H, Hang W, Jing Z, Liu B, Wang X, Li
Y, Luo H, Lv H, Tao X, Timashev P, et al: The role of notch
signaling pathway in cancer: Mechanistic insights, therapeutic
potential, and clinical progress. Front Immunol. 16:15675242025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang H, Yang J, Zheng X, Chen T, Zhang R,
Chen R, Cao T, Zeng F and Liu Q: The hippo pathway in breast
cancer: The extracellular matrix and hypoxia. Int J Mol Sci.
25:128682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ushijima Y, Luo C, Goshima F, Yamauchi Y,
Kimura H and Nishiyama Y: Determination and analysis of the DNA
sequence of highly attenuated herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant
HF10, a potential oncolytic virus. Microbes Infect. 9:142–149.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yamamura K, Kasuya H, Sahin TT, Tan G,
Hotta Y, Tsurumaru N, Fukuda S, Kanda M, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, et
al: Combination treatment of human pancreatic cancer xenograft
models with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor erlotinib and oncolytic herpes simplex virus HF10. Ann
Surg Oncol. 21:691–698. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Tan G, Kasuya H, Sahin TT, Yamamura K, Wu
Z, Koide Y, Hotta Y, Shikano T, Yamada S, Kanzaki A, et al:
Combination therapy of oncolytic herpes simplex virus HF10 and
bevacizumab against experimental model of human breast carcinoma
xenograft. Int J Cancer. 136:1718–1730. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Libertini S, Iacuzzo I, Perruolo G, Scala
S, Ieranò C, Franco R, Hallden G and Portella G: Bevacizumab
increases viral distribution in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
xenografts and enhances the effects of E1A-defective adenovirus
dl922-947. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6505–6514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Mahller YY, Vaikunth SS, Currier MA,
Miller SJ, Ripberger MC, Hsu YH, Mehrian-Shai R, Collins MH,
Crombleholme TM, Ratner N and Cripe TP: Oncolytic HSV and erlotinib
inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis in a novel malignant
peripheral nerve sheath tumor xenograft model. Mol Ther.
15:279–286. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bin Y, Ren J and Zhang H, Zhang T, Liu P,
Xin Z, Yang H, Feng Z, Chen Z and Zhang H: Against all odds: The
road to success in the development of human immune reconstitution
mice. Animal Model Exp Med. 7:460–470. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen J, Liao S, Xiao Z and Pan Q, Wang X,
Shen K, Wang S, Yang L, Guo F, Liu HF and Pan Q: The development
and improvement of immunodeficient mice and humanized immune system
mouse models. Front Immunol. 13:10075792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Reeh M, Bockhorn M, Görgens D, Vieth M,
Hoffmann T, Simon R, Izbicki JR, Sauter G, Schumacher U and Anders
M: Presence of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) in
human neoplasms: A multitumour array analysis. Br J Cancer.
109:1848–1858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cohen CJ, Shieh JT, Pickles RJ, Okegawa T,
Hsieh JT and Bergelson JM: The coxsackievirus and adenovirus
receptor is a transmembrane component of the tight junction. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:15191–15196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Su Y, Liu Y, Behrens CR, Bidlingmaier S,
Lee NK, Aggarwal R, Sherbenou DW, Burlingame AL, Hann BC, Simko JP,
et al: Targeting CD46 for both adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine
prostate cancer. JCI Insight. 3:e1214972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Do MH, To PK, Cho YS, Kwon SY, Hwang EC,
Choi C, Cho SH, Lee SJ, Hemmi S and Jung C: Targeting CD46 enhances
anti-tumoral activity of adenovirus type 5 for bladder cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 19:26942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Trinh HV, Lesage G, Chennamparampil V,
Vollenweider B, Burckhardt CJ, Schauer S, Havenga M, Greber UF and
Hemmi S: Avidity binding of human adenovirus serotypes 3 and 7 to
the membrane cofactor CD46 triggers infection. J Virol.
86:1623–1637. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Dhiman N, Jacobson RM and Poland GA:
Measles virus receptors: SLAM and CD46. Rev Med Virol. 14:217–229.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nestić D, Uil TG, Ma J, Roy S, Vellinga J,
Baker AH, Custers J and Majhen D: αvβ3 integrin is required for
efficient infection of epithelial cells with human adenovirus type
26. J Virol. 93:e01474–18. 2018.
|
|
88
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: αV integrins in
angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
1:a0064782011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lyle C and McCormick F: Integrin
alphavbeta5 is a primary receptor for adenovirus in CAR-negative
cells. Virol J. 7:1482010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Koehler M, Petitjean SJL, Yang J,
Aravamudhan P, Somoulay X, Lo Giudice C, Poncin MA, Dumitru AC,
Dermody TS and Alsteens D: Reovirus directly engages integrin to
recruit clathrin for entry into host cells. Nat Commun.
12:21492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ioannou M and Stanway G: Tropism of
Coxsackie virus A9 depends on the +1 position of the RGD
(arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) motif found at the C' terminus of
its VP1 capsid protein. Virus Res. 294:1982922021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Stern PL and Harrop R: 5T4 oncofoetal
antigen: An attractive target for immune intervention in cancer.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:415–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Scurr M, Pembroke T, Bloom A, Roberts D,
Thomson A, Smart K, Bridgeman H, Adams R, Brewster A, Jones R, et
al: Effect of modified vaccinia ankara-5T4 and low-dose
cyclophosphamide on antitumor immunity in metastatic colorectal
cancer: A Randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 3:e1725792017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jian C, Jing Z, Yinhang W, Jinlong D,
Yuefen P, Quan Q and Shuwen H: Colorectal cancer and gut viruses: A
visualized analysis based on CiteSpace knowledge graph. Front
Microbiol. 14:12398182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yi J, Quji S, Guo L, Chai Z, Kong X and
Meng J: Exploring novel strategies of oncolytic viruses and gut
microbiota to enhance CAR-T cell therapy for colorectal cancer.
Cell Immunol. 417:1050262025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Boixareu C, Taha T, Venkadakrishnan VB, de
Bono J and Beltran H: Targeting the tumour cell surface in advanced
prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 22:569–589. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Vannini A, Parenti F, Bressanin D, Barboni
C, Zaghini A, Campadelli-Fiume G and Gianni T: Towards a precision
medicine approach and in situ vaccination against prostate cancer
by PSMA-Retargeted oHSV. Viruses. 13:20852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li Y, Shen Y, Tang T, Tang Z, Song W, Yang
Z, Zhang X, Wang M, Bai X and Liang T: Oncolytic virus combined
with traditional treatment versus traditional treatment alone in
patients with cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Oncol.
25:1901–1913. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Hirooka Y, Kasuya H, Ishikawa T, Kawashima
H, Ohno E, Villalobos IB, Naoe Y, Ichinose T, Koyama N, Tanaka M,
et al: A Phase I clinical trial of EUS-guided intratumoral
injection of the oncolytic virus, HF10 for unresectable locally
advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:5962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kim JH, Oh JY, Park BH, Lee DE, Kim JS,
Park HE, Roh MS, Je JE, Yoon JH, Thorne SH, et al: Systemic armed
oncolytic and immunologic therapy for cancer with JX-594, a
targeted poxvirus expressing GM-CSF. Mol Ther. 14:361–370. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Breitbach CJ, Parato K, Burke J, Hwang TH,
Bell JC and Kirn DH: Pexa-Vec double agent engineered vaccinia:
Oncolytic and active immunotherapeutic. Curr Opin Virol. 13:49–54.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Heo J, Breitbach CJ, Moon A, Kim CW, Patt
R, Kim MK, Lee YK, Oh SY, Woo HY, Parato K, et al: Sequential
therapy with JX-594, a targeted oncolytic poxvirus, followed by
sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: Preclinical and clinical
demonstration of combination efficacy. Mol Ther. 19:1170–1179.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Moehler M, Heo J, Lee HC, Tak WY, Chao Y,
Paik SW, Yim HJ, Byun KS, Baron A, Ungerechts G, et al:
Vaccinia-based oncolytic immunotherapy Pexastimogene Devacirepvec
in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after sorafenib
failure: A randomized multicenter Phase IIb trial (TRAVERSE).
Oncoimmunology. 8:16158172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Galle PR, Chao Y, Erinjeri
J, Heo J, Borad MJ, Luca A, Burke J, Pelusio A, Agathon D, et al:
PHOCUS: A phase 3, Randomized, open-label study of sequential
treatment with pexa-vec (JX-594) and sorafenib in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 13:248–264. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chaurasiya S, Yang A, Zhang Z, Lu J,
Valencia H, Kim SI, Woo Y, Warner SG, Olafsen T, Zhao Y, et al: A
comprehensive preclinical study supporting clinical trial of
oncolytic chimeric poxvirus CF33-hNIS-anti-PD-L1 to treat breast
cancer. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 24:102–116. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Yuan Y, Egelston C, Colunga Flores O,
Chaurasiya S, Lin D, Chang H, Chong LMO, Seiz A, Shah M, Meisen WH,
et al: CF33-hNIS-anti-PD-L1 oncolytic virus followed by
trastuzumab-deruxtecan in a patient with metastatic triple negative
breast cancer: A case study. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
15:175883592312106752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Tilgase A, Olmane E, Nazarovs J, Brokāne
L, Erdmanis R, Rasa A and Alberts P: Multimodality treatment of a
colorectal cancer stage IV patient with FOLFOX-4, bevacizumab,
rigvir oncolytic virus, and surgery. Case Rep Gastroenterol.
12:457–465. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Filho AM, Laversanne M, Ferlay J, Colombet
M, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Parkin DM, Soerjomataram I and Bray F: The
GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: Data sources, methods, and a
snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide. Int J Cancer.
156:1336–1346. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Liu S, Jiang W, Sheng J, Wang L and Cui M:
Adoptive cell therapy for cancer: Combination strategies and
biomarkers. Front Immunol. 16:16037922025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Goswami S, Pauken KE, Wang L and Sharma P:
Next-generation combination approaches for immune checkpoint
therapy. Nat Immunol. 25:2186–2199. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Xie B, Zhang L, Hu W, Fan M, Jiang N, Duan
Y, Jing D, Xiao W, Fragoso RC, Lam KS, et al: Dual blockage of
STAT3 and ERK1/2 eliminates radioresistant GBM cells. Redox Biol.
24:1011892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Nagathihalli NS, Castellanos JA,
Lamichhane P, Messaggio F, Shi C, Dai X, Rai P, Chen X, VanSaun MN
and Merchant NB: Inverse correlation of STAT3 and MEK signaling
mediates resistance to RAS pathway inhibition in pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Res. 78:6235–6246. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Vultur A, Villanueva J, Krepler C, Rajan
G, Chen Q, Xiao M, Li L, Gimotty PA, Wilson M, Hayden J, et al: MEK
inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma
cell lines. Oncogene. 33:1850–1861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Appleton E, Chiocca EA, Ungerechts G,
Melcher A and Vile R: Oncolytic viruses as anticancer agents:
clinical progress and remaining challenges. Lancet. 406:1295–1312.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Hossain MA: Targeting the RAS upstream and
downstream signaling pathway for cancer treatment. Eur J Pharmacol.
979:1767272024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zou J, Han W, Hu Y, Zeng C, Li J, Lei W,
Cao J, Fei Q, Shao M, Yi J, et al: Gene mutation, clinical
characteristics and pathology in resectable lung adenocarcinoma.
World J Surg Oncol. 23:162025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Yang T, Li W, Huang T and Zhou J: Genetic
testing enhances the precision diagnosis and treatment of breast
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:166072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Chaudagar K, Hieromnimon HM, Khurana R,
Labadie B, Hirz T, Mei S, Hasan R, Shafran J, Kelley A, Apostolov
E, et al: Reversal of lactate and PD-1-mediated macrophage
immunosuppression controls growth of PTEN/p53-deficient prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 29:1952–1968. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhao F, Jiang X, Li Y, Huang T, Xiahou Z,
Nie W and Li Q: Characterizing tumor biology and immune
microenvironment in high-grade serous ovarian cancer via
single-cell RNA sequencing: Insights for targeted and personalized
immunotherapy strategies. Front Immunol. 15:15001532025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Cooper AJ, Sequist LV and Lin JJ:
Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: Mechanisms of resistance
and management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:499–514. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Taverna JA, Hung CN, DeArmond DT, Chen M,
Lin CL, Osmulski PA, Gaczynska ME, Wang CM, Lucio ND, Chou CW, et
al: Single-cell proteomic profiling identifies combined AXL and
JAK1 inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy for lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 80:1551–1563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Yadav M, Sharma A, Patne K, Tabasum S,
Suryavanshi J, Rawat L, Machaalani M, Eid M, Singh RP, Choueiri TK,
et al: AXL signaling in cancer: From molecular insights to targeted
therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:372025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Shen M, Jiang X, Peng Q, Oyang L, Ren Z,
Wang J, Peng M, Zhou Y, Deng X and Liao Q: The cGAS-STING pathway
in cancer immunity: mechanisms, challenges, and therapeutic
implications. J Hematol Oncol. 18:402025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Xia T, Konno H, Ahn J and Barber GN:
Deregulation of STING signaling in colorectal carcinoma constrains
DNA damage responses and correlates with tumorigenesis. Cell Rep.
14:282–297. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Xia T, Konno H and Barber GN: Recurrent
loss of STING signaling in melanoma correlates with susceptibility
to viral oncolysis. Cancer Res. 76:6747–6759. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
de Queiroz N, Xia T, Konno H and Barber
GN: Ovarian cancer cells commonly exhibit defective STING signaling
which affects sensitivity to viral oncolysis. Mol Cancer Res.
17:974–986. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
127
|
Meric-Bernstam F, Sweis RF, Hodi FS,
Messersmith WA, Andtbacka RHI, Ingham M, Lewis N, Chen X, Pelletier
M, Chen X, et al: Phase I dose-escalation trial of MIW815
(ADU-S100), an intratumoral STING agonist, in patients with
advanced/metastatic solid tumors or lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res.
28:677–688. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Chang W, Altman MD, Lesburg CA, Perera SA,
Piesvaux JA, Schroeder GK, Wyss DF, Cemerski S, Chen Y, DiNunzio E,
et al: Discovery of MK-1454: A potent cyclic dinucleotide
stimulator of interferon genes agonist for the treatment of cancer.
J Med Chem. 65:5675–5689. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Song Z, Wang X, Zhang Y, Gu W, Shen A,
Ding C, Li H, Xiao R, Geng M, Xie Z and Zhang A: Structure-activity
relationship study of amidobenzimidazole analogues leading to
potent and systemically administrable stimulator of interferon gene
(STING) agonists. J Med Chem. 64:1649–1669. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Sibal PA, Matsumura S, Ichinose T,
Bustos-Villalobos I, Morimoto D, Eissa IR, Abdelmoneim M, Aboalela
MAM, Mukoyama N, Tanaka M, et al: STING activator 2'3'-cGAMP
enhanced HSV-1-based oncolytic viral therapy. Mol Oncol.
18:1259–1277. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Thoresen D, Wang W, Galls D, Guo R, Xu L
and Pyle AM: The molecular mechanism of RIG-I activation and
signaling. Immunol Rev. 304:154–168. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Berry N, Suspène R, Caval V, Khalfi P,
Beauclair G, Rigaud S, Blanc H, Vignuzzi M, Wain-Hobson S and
Vartanian JP: Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection disturbs the
mitochondrial network, leading to type I interferon production
through the RNA polymerase III/RIG-I pathway. mBio.
12:e02557212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Farhangnia P, Khorramdelazad H, Nickho H
and Delbandi AA: Current and future immunotherapeutic approaches in
pancreatic cancer treatment. J Hematol Oncol. 17:402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Dan J, Cai J, Zhong Y, Wang C, Huang S,
Zeng Y, Fan Z, Xu C, Hu L, Zhang J, et al: Oncolytic virus M1
functions as a bifunctional checkpoint inhibitor to enhance the
antitumor activity of DC vaccine. Cell Rep Med. 4:1012292023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Shen KY, Zhu Y, Xie SZ and Qin LX:
Immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and prospectives. J
Hematol Oncol. 17:252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wang JW, Feng Q, Liu JH and Xun JJ:
Opportunities, challenges, and future perspectives of oncolytic
virus therapy for malignant melanoma. Front Immunol.
16:16536832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Wang JW, Liu JH, Liu YL, Xu WZ and Zhang
ZB: Oncolytic virus therapy in the elderly: Immune frailty,
challenges, and perspectives. Front Immunol. 16:16866592025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Lang SI, Giese NA, Rommelaere J, Dinsart C
and Cornelis JJ: Humoral immune responses against minute virus of
mice vectors. J Gene Med. 8:1141–1150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Hirasawa K, Nishikawa SG, Norman KL,
Coffey MC, Thompson BG, Yoon CS, Waisman DM and Lee PW: Systemic
reovirus therapy of metastatic cancer in immune-competent mice.
Cancer Res. 63:348–353. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Chen G, Yuan Y, Li Y, He Q, Qin Z, Hu H,
Gao C, Xu Z, Xu Q, Gao Q and Li F: Enhancing oncolytic virus
efficiency with methionine and N-(3-aminoprolil)methacrylamide
modified acrylamide cationic block polymer. J Mater Chem B.
12:3741–3750. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Perera AS and Coppens MO: Re-designing
materials for biomedical applications: From biomimicry to
nature-inspired chemical engineering. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng
Sci. 377:201802682019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Pang L, Zhang C, Qin J, Han L, Li R, Hong
C, He H and Wang J: A novel strategy to achieve effective drug
delivery: Exploit cells as carrier combined with nanoparticles.
Drug Deliv. 24:83–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zhang Z, Yang N, Xu L, Lu H, Chen Y, Wang
Z, Lu Q, Zhong K, Zhu Z, Wang G, et al: Systemic delivery of
oncolytic herpes virus using CAR-T cells enhances targeting of
antitumor immuno-virotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
73:1732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Reale A, Calistri A and Altomonte J:
Giving oncolytic viruses a free ride: Carrier cells for oncolytic
virotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 13:21922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ghasemi Darestani N, Gilmanova AI,
Al-Gazally ME, Zekiy AO, Ansari MJ, Zabibah RS, Jawad MA, Al-Shalah
SAJ, Rizaev JA, Alnassar YS, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell-released
oncolytic virus: An innovative strategy for cancer treatment. Cell
Commun Signal. 21:432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Collet G, Grillon C, Nadim M and Kieda C:
Trojan horse at cellular level for tumor gene therapies. Gene.
525:208–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Mader EK, Maeyama Y, Lin Y, Butler GW,
Russell HM, Galanis E, Russell SJ, Dietz AB and Peng KW:
Mesenchymal stem cell carriers protect oncolytic measles viruses
from antibody neutralization in an orthotopic ovarian cancer
therapy model. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7246–7255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Hakkarainen T, Särkioja M, Lehenkari P,
Miettinen S, Ylikomi T, Suuronen R, Desmond RA, Kanerva A and
Hemminki A: Human mesenchymal stem cells lack tumor tropism but
enhance the antitumor activity of oncolytic adenoviruses in
orthotopic lung and breast tumors. Hum Gene Ther. 18:627–641. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Cook M and Chauhan A: Clinical application
of oncolytic viruses: A systematic review. Int J Mol Sci.
21:75052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Rathod LS, Sakle NS and Mokale SN: KRAS
inhibitors in drug resistance and potential for combination
therapy. Tumori. 111:20–40. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Rahimi A, Baghernejadan Z, Hazrati A,
Malekpour K, Samimi LN, Najafi A, Falak R and Khorramdelazad H:
Combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal
cancer: Challenges, resistance mechanisms, and the role of
microbiota. Biomed Pharmacother. 186:1180142025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
He X, Deng H, Liu W, Hu L and Tan X:
Advances in understanding drug resistance mechanisms and innovative
clinical treatments for melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol.
25:1615–1633. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Xuan Y, Yan W, Wang R, Wang X, Guo Y, Dun
H, Huan Z, Xu L, Han R, Sun X, et al: GM-CSF and IL-21-armed
oncolytic vaccinia virus significantly enhances anti-tumor activity
and synergizes with anti-PD1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer.
Front Immunol. 15:15066322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ottolino-Perry K, Tang N, Head R, Ng C,
Arulanandam R, Angarita FA, Acuna SA, Chen Y, Bell J, Dacosta RS
and McCart JA: Tumor vascularization is critical for oncolytic
vaccinia virus treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Int J
Cancer. 134:717–730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Arulanandam R, Batenchuk C, Angarita FA,
Ottolino-Perry K, Cousineau S, Mottashed A, Burgess E, Falls TJ, De
Silva N, Tsang J, et al: VEGF-mediated induction of PRD1-BF1/Blimp1
expression sensitizes tumor vasculature to oncolytic virus
infection. Cancer Cell. 28:210–224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Kurozumi K, Hardcastle J, Thakur R, Yang
M, Christoforidis G, Fulci G, Hochberg FH, Weissleder R, Carson W,
Chiocca EA and Kaur B: Effect of tumor microenvironment modulation
on the efficacy of oncolytic virus therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst.
99:1768–1781. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Maliepaard M, Faber YS and van Bussel MTJ:
Reported hepatotoxicity and hepatotoxicity guidance in the product
information of protein kinase inhibitors in oncology registered at
the European medicines agency. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
11:e010672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Godoy P, Hewitt NJ, Albrecht U, Andersen
ME, Ansari N, Bhattacharya S, Bode JG, Bolleyn J, Borner C, Böttger
J, et al: Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using
primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and
non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating
mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch
Toxicol. 87:1315–1530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Rock EP, Goodman V, Jiang JX, Mahjoob K,
Verbois SL, Morse D, Dagher R, Justice R and Pazdur R: Food and
drug administration drug approval summary: Sunitinib malate for the
treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor and advanced renal cell
carcinoma. Oncologist. 12:107–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Fukuhara H, Ino Y and Todo T: Oncolytic
virus therapy: A new era of cancer treatment at dawn. Cancer Sci.
107:1373–1379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
LaFargue CJ, Dal Molin GZ, Sood AK and
Coleman RL: Exploring and comparing adverse events between PARP
inhibitors. Lancet Oncol. 20:e15–e28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Arrillaga-Romany I, Gardner SL, Odia Y,
Aguilera D, Allen JE, Batchelor T, Butowski N, Chen C, Cloughesy T,
Cluster A, et al: ONC201 (Dordaviprone) in recurrent H3 K27M-Mutant
diffuse midline glioma. J Clin Oncol. 42:1542–1552. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Peters C, Paget M, Tshilenge KT, Saha D,
Antoszczyk S, Baars A, Frost T, Martuza RL, Wakimoto H and Rabkin
SD: Restriction of replication of oncolytic herpes simplex virus
with a deletion of γ34.5 in glioblastoma stem-like cells. J Virol.
92:e00246–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
164
|
Nakashima H, Nguyen T, Kasai K, Passaro C,
Ito H, Goins WF, Shaikh I, Erdelyi R, Nishihara R, Nakano I, et al:
Toxicity and efficacy of a novel GADD34-expressing oncolytic HSV-1
for the treatment of experimental glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
24:2574–2584. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Balathasan L, Tang VA, Yadollahi B, Brun
J, Labelle M, Lefebvre C, Swift SL and Stojdl DF: Activating
peripheral innate immunity enables safe and effective oncolytic
virotherapy in the brain. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 7:45–56. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Takata F, Nakagawa S, Matsumoto J and
Dohgu S: Blood-Brain barrier dysfunction amplifies the development
of neuroinflammation: Understanding of cellular events in brain
microvascular endothelial cells for prevention and treatment of BBB
Dysfunction. Front Cell Neurosci. 15:6618382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Zhuang H, Shi S, Yuan Z and Chang JY:
Bevacizumab treatment for radiation brain necrosis: mechanism,
efficacy and issues. Mol Cancer. 18:212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Seet RC, Rabinstein AA, Lindell PE, Uhm JH
and Wijdicks EF: Cerebrovascular events after bevacizumab
treatment: an early and severe complication. Neurocrit Care.
15:421–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zhou BX and Li Y: Significance of
desmoglein-2 on cell malignant behaviors via mediating MAPK
signaling in cervical cancer. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 36:336–343.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Sun R, Ma C, Wang W and Yang S:
Upregulation of desmoglein 2 and its clinical value in lung
adenocarcinoma: A comprehensive analysis by multiple bioinformatics
methods. PeerJ. 8:e84202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Han CP, Yu YH, Wang AG, Tian Y, Zhang HT,
Zheng ZM and Liu YS: Desmoglein-2 overexpression predicts poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:5481–5489. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Cai F, Zhu Q, Miao Y, Shen S, Su X and Shi
Y: Desmoglein-2 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer
tissues and its knockdown suppresses NSCLC growth by regulation of
p27 and CDK2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:59–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Tan LY, Mintoff C, Johan MZ, Ebert BW,
Fedele C, Zhang YF, Szeto P, Sheppard KE, McArthur GA, Foster-Smith
E, et al: Desmoglein 2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry in melanoma
and is associated with poor clinical outcome. Oncotarget.
7:46492–46508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Kamekura R, Kolegraff KN, Nava P, Hilgarth
RS, Feng M, Parkos CA and Nusrat A: Loss of the desmosomal cadherin
desmoglein-2 suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation through
EGFR signaling. Oncogene. 33:4531–4536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
175
|
Brennan D and Mahoney MG: Increased
expression of Dsg2 in malignant skin carcinomas: A
tissue-microarray based study. Cell Adh Migr. 3:148–154. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Chen L, Liu X, Zhang J and Liu Y, Gao A,
Xu Y, Lin Y, Du Q, Zhu Z, Hu Y and Liu Y: Characterization of
desmoglein 2 expression in ovarian serous tumors and its prognostic
significance in high-grade serous carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
11:4977–4986. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Ramani VC, Hennings L and Haun RS:
Desmoglein 2 is a substrate of kallikrein 7 in pancreatic cancer.
BMC Cancer. 8:3732008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Biedermann K, Vogelsang H, Becker I,
Plaschke S, Siewert JR, Höfler H and Keller G: Desmoglein 2 is
expressed abnormally rather than mutated in familial and sporadic
gastric cancer. J Pathol. 207:199–206. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Mundy RM, Baker AT, Bates EA, Cunliffe TG,
Teijeira-Crespo A, Moses E, Rizkallah PJ and Parker AL: Broad
sialic acid usage amongst species D human adenovirus. Npj Viruses.
1:12023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Rodrigues E and Macauley MS:
Hypersialylation in cancer: Modulation of inflammation and
therapeutic opportunities. Cancers (Basel). 10:2072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Hu K, He S, Xiao J, Li M, Luo S, Zhang M
and Hu Q: Interaction between herpesvirus entry mediator and HSV-2
glycoproteins mediates HIV-1 entry of HSV-2-infected epithelial
cells. J Gen Virol. 98:2351–2361. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Montgomery RI, Warner MS, Lum BJ and Spear
PG: Herpes simplex virus-1 entry into cells mediated by a novel
member of the TNF/NGF receptor family. Cell. 87:427–436. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Ren S, Tian Q, Amar N, Yu H, Rivard CJ,
Caldwell C, Ng TL, Tu M, Liu Y, Gao D, et al: The immune
checkpoint, HVEM may contribute to immune escape in non-small cell
lung cancer lacking PD-L1 expression. Lung Cancer. 125:115–120.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Tsang JYS, Chan KW, Ni YB, Hlaing T, Hu J,
Chan SK, Cheung SY and Tse GM: Expression and clinical significance
of herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) in breast cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 24:4042–4050. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Lan X, Li S, Gao H, Nanding A, Quan L,
Yang C, Ding S and Xue Y: Increased BTLA and HVEM in gastric cancer
are associated with progression and poor prognosis. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:919–926. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Migita K, Sho M, Shimada K, Yasuda S,
Yamato I, Takayama T, Matsumoto S, Wakatsuki K, Hotta K, Tanaka T,
et al: Significant involvement of herpesvirus entry mediator in
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 120:808–817.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Ahn AR, Noh SJ, Hussein UK, Park HS, Chung
MJ, Lee H, Moon WS, Kang MJ, Kim HJ, Lee NR, et al: FAM83H and
Nectin1 expression are related with survival and relapse of bladder
urothelial carcinoma patients. BMC Urol. 21:1432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Tampakis A, Tampaki EC, Nonni A, Droeser
R, Posabella A, Tsourouflis G, Kontzoglou K, Patsouris E, von Flüe
M and Kouraklis G: Nectin-1 expression in colorectal cancer: Is
there a group of patients with high risk for early disease
recurrence? Oncology. 96:318–325. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Cocchi F, Menotti L, Dubreuil P, Lopez M
and Campadelli-Fiume G: Cell-to-cell spread of wild-type herpes
simplex virus type 1, but not of syncytial strains, is mediated by
the immunoglobulin-like receptors that mediate virion entry,
nectin1 (PRR1/HveC/HIgR) and nectin2 (PRR2/HveB). J Virol.
74:3909–3917. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Girgis NM, Dehaven BC, Fan X, Viner KM,
Shamim M and Isaacs SN: Cell surface expression of the vaccinia
virus complement control protein is mediated by interaction with
the viral A56 protein and protects infected cells from complement
attack. J Virol. 82:4205–4214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Marques C, Reis CA, Vivès RR and Magalhães
A: Heparan sulfate biosynthesis and sulfation profiles as
modulators of cancer signalling and progression. Front Oncol.
11:7787522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Li C, Luo P, Guo F, Jia X, Shen M, Zhang
T, Wang S and Du T: Identification of HSPG2 as a bladder pro-tumor
protein through NID1/AKT signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 24:3452024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Lambrecht V, Le Bourhis X, Toillon RA,
Boilly B and Hondermarck H: Alterations in both heparan sulfate
proteoglycans and mitogenic activity of fibroblast growth factor-2
are triggered by inhibitors of proliferation in normal and breast
cancer epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 245:239–244. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Yi B, Qiu Y, Ji W, Wei M, Liu C, Peng Z,
Zhang Y, Quan Z, Tang Z and Su C: Desulfation of cell surface HSPG
is an effective strategy for the treatment of gallbladder
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 381:349–358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Xiong R, Long Q, Zhang X, Xu J, Liu Y,
Xiong L, Yang S, Feng G, Song G and Liu K: HOXD11 upregulates JAM-A
and exerts oncogenic properties via NF-κB signaling pathway in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Cell. 36:244–257. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Aravamudhan P, Guzman-Cardozo C, Urbanek
K, Welsh OL, Konopka-Anstadt JL, Sutherland DM and Dermody TS: The
murine neuronal receptor NgR1 is dispensable for reovirus
pathogenesis. J Virol. 96:e00055222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Rosager AM, Sørensen MD, Dahlrot RH, Boldt
HB, Hansen S, Lathia JD and Kristensen BW: Expression and
prognostic value of JAM-A in gliomas. J Neurooncol. 135:107–117.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Ikeo K, Oshima T, Shan J, Matsui H, Tomita
T, Fukui H, Watari J and Miwa H: Junctional adhesion molecule-A
promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of gastric cancer.
Hepatogastroenterology. 62:540–545. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
McSherry EA, McGee SF, Jirstrom K, Doyle
EM, Brennan DJ, Landberg G, Dervan PA, Hopkins AM and Gallagher WM:
JAM-A expression positively correlates with poor prognosis in
breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 125:1343–1351. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Marcq I, Nyga R, Cartier F, Amrathlal RS,
Ossart C, Ouled-Haddou H, Ghamlouch H, Galmiche A, Chatelain D,
Lamotte L, et al: Identification of SLAMF3 (CD229) as an inhibitor
of hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and tumour
progression. PLoS One. 8:e829182013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
201
|
Agresta L, Lehn M, Lampe K, Cantrell R,
Hennies C, Szabo S, Wise-Draper T, Conforti L, Hoebe K and Janssen
EM: CD244 represents a new therapeutic target in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0002452020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Zhang J, Zhu Y, Wang Q, Kong Y, Sheng H,
Guo J, Xu J and Dai B: Poliovirus receptor CD155 is up-regulated in
muscle-invasive bladder cancer and predicts poor prognosis. Urol
Oncol. 38:41.e11–41.e18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Nishiwada S, Sho M, Yasuda S, Shimada K,
Yamato I, Akahori T, Kinoshita S, Nagai M, Konishi N and Nakajima
Y: Clinical significance of CD155 expression in human pancreatic
cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:2287–2297. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Li YC, Zhou Q, Song QK, Wang RB, Lyu S,
Guan X, Zhao YJ and Wu JP: Overexpression of an immune checkpoint
(CD155) in breast cancer associated with prognostic significance
and exhausted tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: A cohort study. J
Immunol Res. 2020:39489282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Zhuo B, Li Y, Gu F, Li Z, Sun Q, Shi Y,
Shen Y, Zhang F, Wang R and Wang X: Overexpression of CD155 relates
to metastasis and invasion in osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett.
15:7312–7318. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Murakami D, Matsuda K, Iwamoto H, Mitani
Y, Mizumoto Y, Nakamura Y, Matsuzaki I, Iwamoto R, Takahashi Y,
Kojima F, et al: Prognostic value of CD155/TIGIT expression in
patients with colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 17:e02659082022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Finkelshtein D, Werman A, Novick D, Barak
S and Rubinstein M: LDL receptor and its family members serve as
the cellular receptors for vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:7306–7311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Behrouj H, Erfani M and Mokarram P:
Examining the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR)
and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) genes
in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Res Commun. 13:85–88.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Zhang GM, Chen W, Yao Y, Luo L and Sun LJ:
LDLR promotes growth and invasion in renal cell carcinoma and
activates the EGFR pathway. Neoplasma. 69:113–122. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Tang S, Chen K, Zheng F, Fu Z, Niu Y, Liu
X, Ni H, Yuan X, Cui Z, Lu W, et al: High serum LDL promotes EMT
and stemness through LDLR/FOXQ1/NF-κB1 pathway in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 44:4587–4600. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Örbom A, Evans-Axelsson S, Jansson B,
Vilhelmsson Timmermand O, Tran TA, Bjartell A and Strand SE:
Intratumoral distribution and pharmacokinetics of the radiolabeled
ICAM-1 targeting monoclonal antibody R6.5 in a prostate cancer
mouse model. Nuklearmedizin. 64:163–169. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Gultekin O, Gonzalez-Molina J, Sarhan D,
Groes-Kofoed N, Hassan MU, Lehti K and Salehi S: Systemic and
tumor-specific inflammatory markers VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 as indicators
of extent of surgery and oncologic outcome in advanced ovarian
cancer. Transl Oncol. 59:1024622025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Chen YH, Chu CC, Liu JF, Lai HS and Chen
YT: C-X-C motif ligand 1 induces cell migration by upregulating
ICAM-1 expression by activating PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling
pathway in liver cancer. Adv Biol (Weinh). 9:e24002952025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Annels NE, Mansfield D, Arif M,
Ballesteros-Merino C, Simpson GR, Denyer M, Sandhu SS, Melcher AA,
Harrington KJ, Davies B, et al: Phase I trial of an ICAM-1-targeted
immunotherapeutic-coxsackievirus A21 (CVA21) as an oncolytic agent
against non muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
25:5818–5831. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Tempia-Caliera AA, Horvath LZ, Zimmermann
A, Tihanyi TT, Korc M, Friess H and Büchler MW: Adhesion molecules
in human pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 79:93–100. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Wang Q, Yang Q, Liu C, Wang G, Song H,
Shang G, Peng R, Qu X, Liu S, Cui Y, et al: Molecular basis of
differential receptor usage for naturally occurring CD55-binding
and -nonbinding coxsackievirus B3 strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
119:e21185901192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Koretz K, Brüderlein S, Henne C and Möller
P: Decay-accelerating factor (DAF, CD55) in normal colorectal
mucosa, adenomas and carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 66:810–814. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Madjd Z, Durrant LG, Bradley R, Spendlove
I, Ellis IO and Pinder SE: Loss of CD55 is associated with
aggressive breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2797–2803. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Mäenpää A, Junnikkala S, Hakulinen J,
Timonen T and Meri S: Expression of complement membrane regulators
membrane cofactor protein (CD46), decay accelerating factor (CD55),
and protectin (CD59) in human malignant gliomas. Am J Pathol.
148:1139–1152. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Mustafa T, Klonisch T, Hombach-Klonisch S,
Kehlen A, Schmutzler C, Koehrle J, Gimm O, Dralle H and Hoang-Vu C:
Expression of CD97 and CD55 in human medullary thyroid carcinomas.
Int J Oncol. 24:285–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Yamayoshi S, Iizuka S, Yamashita T,
Minagawa H, Mizuta K, Okamoto M, Nishimura H, Sanjoh K, Katsushima
N, Itagaki T, et al: Human SCARB2-dependent infection by
coxsackievirus A7, A14, and A16 and enterovirus 71. J Virol.
86:5686–5696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Zhang D, Fang J, Shan J, Xu L, Wu Y, Lu B,
Zhang X, Wang C, Sun P and Wang Q: SCARB2 associates with
tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and predicts poor prognosis in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 207:15–24. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Wang F, Gao Y, Xue S, Zhao L, Jiang H,
Zhang T, Li Y, Zhao C, Wu F, Siqin T, et al: SCARB2 drives
hepatocellular carcinoma tumor initiating cells via enhanced MYC
transcriptional activity. Nat Commun. 14:59172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Hance KW, Rogers CJ, Zaharoff DA, Canter
D, Schlom J and Greiner JW: The antitumor and immunoadjuvant
effects of IFN-alpha in combination with recombinant poxvirus
vaccines. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2387–2396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Duggan MC, Jochems C, Donahue RN, Richards
J, Karpa V, Foust E, Paul B, Brooks T, Tridandapani S, Olencki T,
et al: A phase I study of recombinant (r) vaccinia-CEA(6D)-TRICOM
and rFowlpox-CEA(6D)-TRICOM vaccines with GM-CSF and IFN-α-2b in
patients with CEA-expressing carcinomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
65:1353–1364. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Qi C, Liu C, Peng Z, Zhang Y, Wei J, Qiu
W, Zhang X, Pan H, Niu Z, Qiu M, et al: Claudin-18 isoform
2-specific CAR T-cell therapy (satri-cel) versus treatment of
physician's choice for previously treated advanced gastric or
gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (CT041-ST-01): A randomised,
open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 405:2049–2060. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Liu S, Li F, Deng L, Ma Q, Lu W, Zhao Z,
Liu H, Zhou Y, Hu M, Wang H, et al: Claudin18.2 bispecific T cell
engager armed oncolytic virus enhances antitumor effects against
pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 30:275–285. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Yoon AR, Hong J, Kim M and Yun CO:
Hepatocellular carcinoma-targeting oncolytic adenovirus overcomes
hypoxic tumor microenvironment and effectively disperses through
both central and peripheral tumor regions. Sci Rep. 8:22332018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Cordeiro R, Oliveira D, Santo D, Coelho J
and Faneca H: Mesoporous silica-glycopolymer hybrid nanoparticles
for dual targeted chemotherapy and gene therapy to liver cancer
cells. Int J Pharm. 675:1255532025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Deng Y, Yang B, Yang Z, Xiao H, Zou Y, Zou
C, Yang S, Sun X, Wang Y, Bai J, et al: Engineered E. coli OMVs
carrying the membrane-binding hGC33 fragment precisely target liver
cancer and effectively treat tumor. Int J Nanomedicine.
20:6573–6590. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
West CE, Mirshahi UL, Ruth KS, Sharp LN,
Arni AM, Turnbull C, Wright CF, Vaidya B, Owens MM, Carey DJ and
Patel KA: Medullary thyroid cancer risk and mortality in carriers
of incidentally identified MEN2A RET variants. JAMA Netw Open.
8:e25179372025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Cañizo CG, Guerrero-Ramos F, Perez Escavy
M, Lodewijk I, Suárez-Cabrera C, Morales L, Nunes SP,
Munera-Maravilla E, Rubio C, Sánchez R, et al: Characterisation of
the tumour microenvironment and PD-L1 granularity reveals the
prognostic value of cancer-associated myofibroblasts in
non-invasive bladder cancer. Oncoimmunology. 14:24382912025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Okato A, Utsumi T, Ranieri M, Zheng X,
Zhou M, Pereira LD, Chen T, Kita Y, Wu D, Hyun H, et al: FGFR
inhibition augments anti-PD-1 efficacy in murine FGFR3-mutant
bladder cancer by abrogating immunosuppression. J Clin Invest.
134:e1692412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Cheng L, Lopez-Beltran A, Massari F,
MacLennan GT and Montironi R: Molecular testing for BRAF mutations
to inform melanoma treatment decisions: A move toward precision
medicine. Mod Pathol. 31:24–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
235
|
Rosenkrans ZT, Erbe AK, Clemons NB, Feils
AS, Medina-Guevara Y, Jeffery JJ, Barnhart TE, Engle JW, Sondel PM
and Hernandez R: ImmunoPET demonstrates that Co-Targeting GD2 and
B7-H3 with bispecific antibodies enhances tumor selectivity in
preclinical melanoma models. Bioconjug Chem. 36:1595–1603. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Krug C, Birkholz K, Paulus A, Schwenkert
M, Schmidt P, Hoffmann N, Hombach A, Fey G, Abken H, Schuler G, et
al: Stability and activity of MCSP-specific chimeric antigen
receptors (CARs) depend on the scFv antigen-binding domain and the
protein backbone. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 64:1623–1635. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|