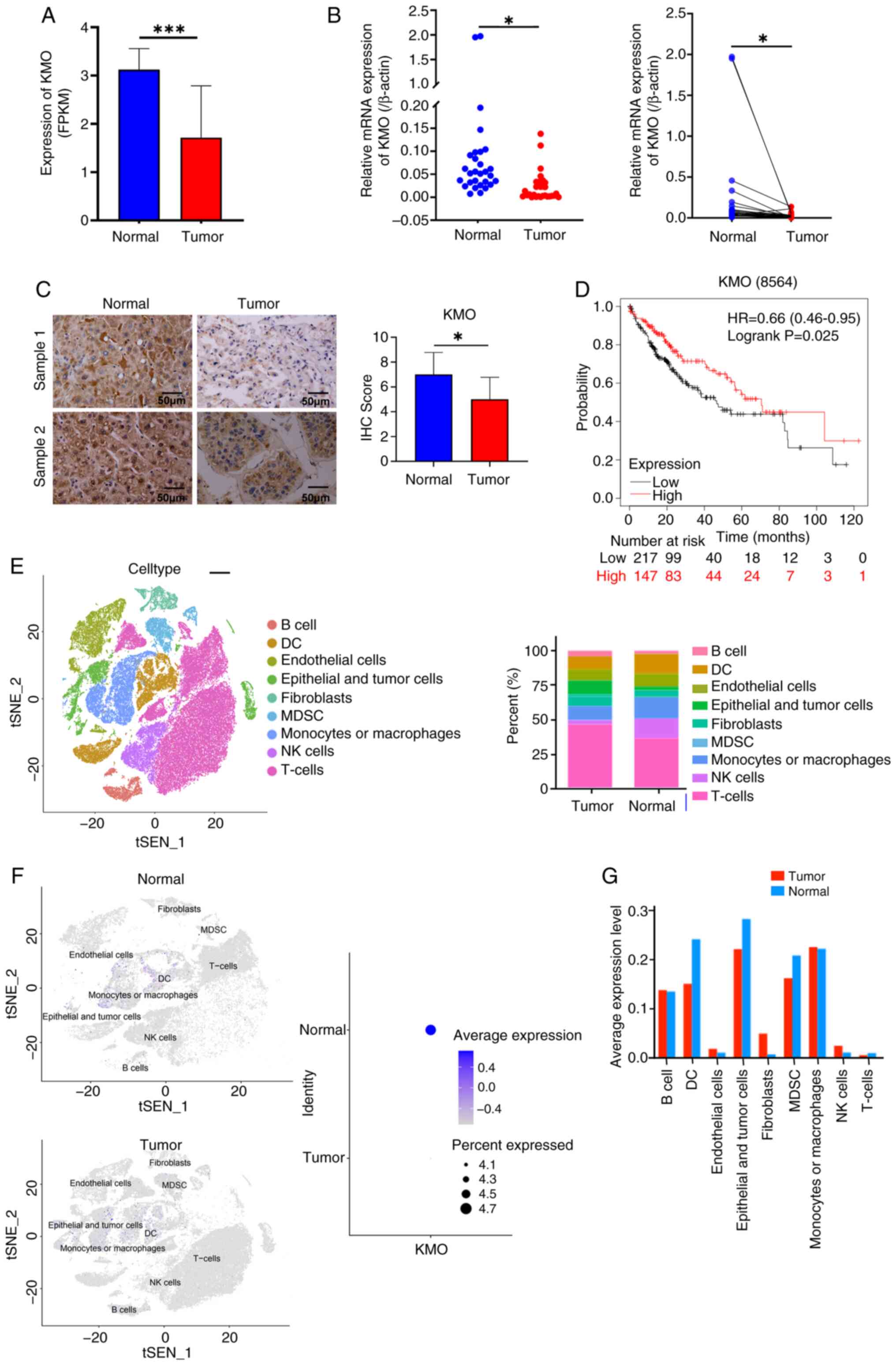
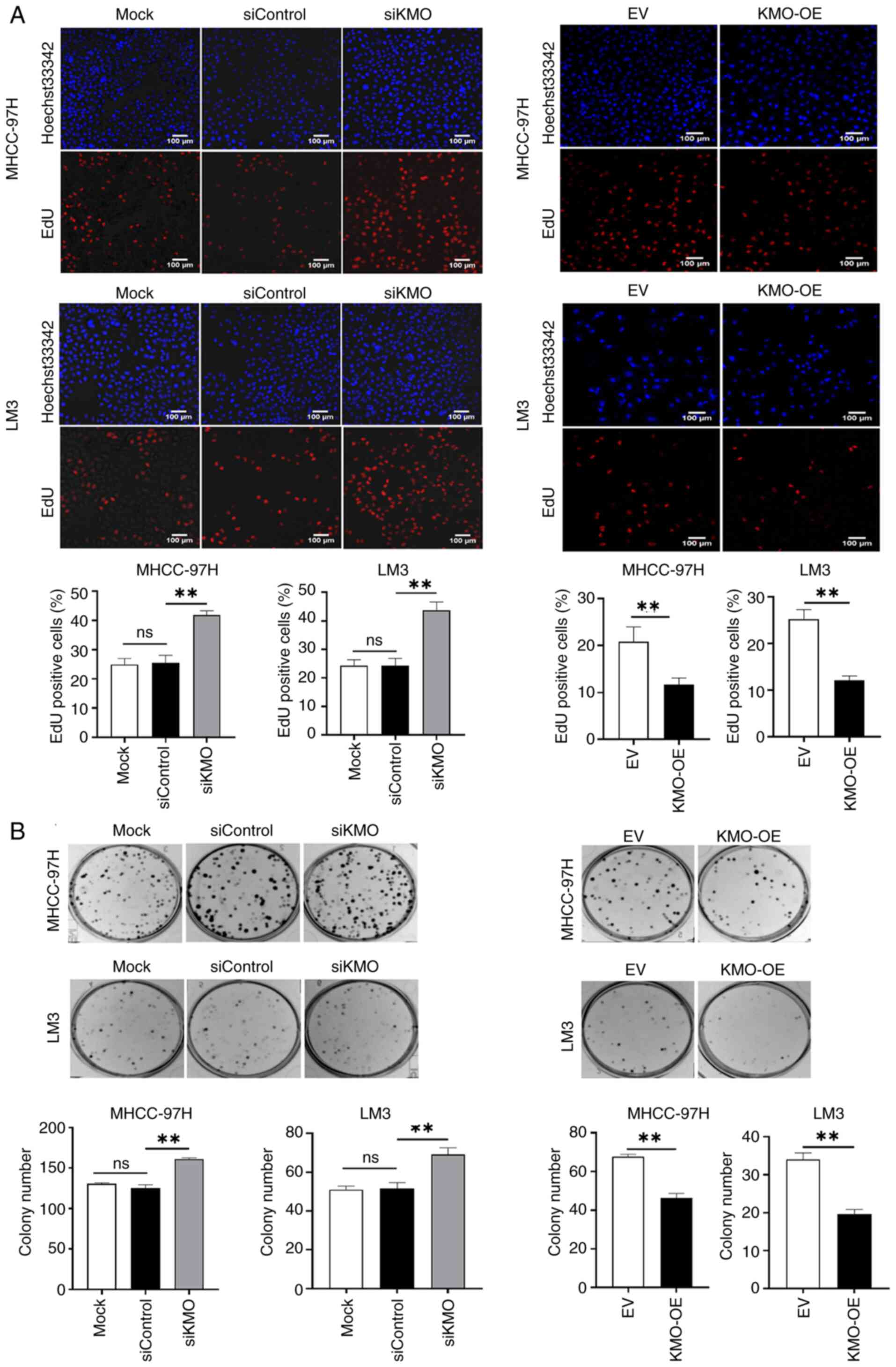
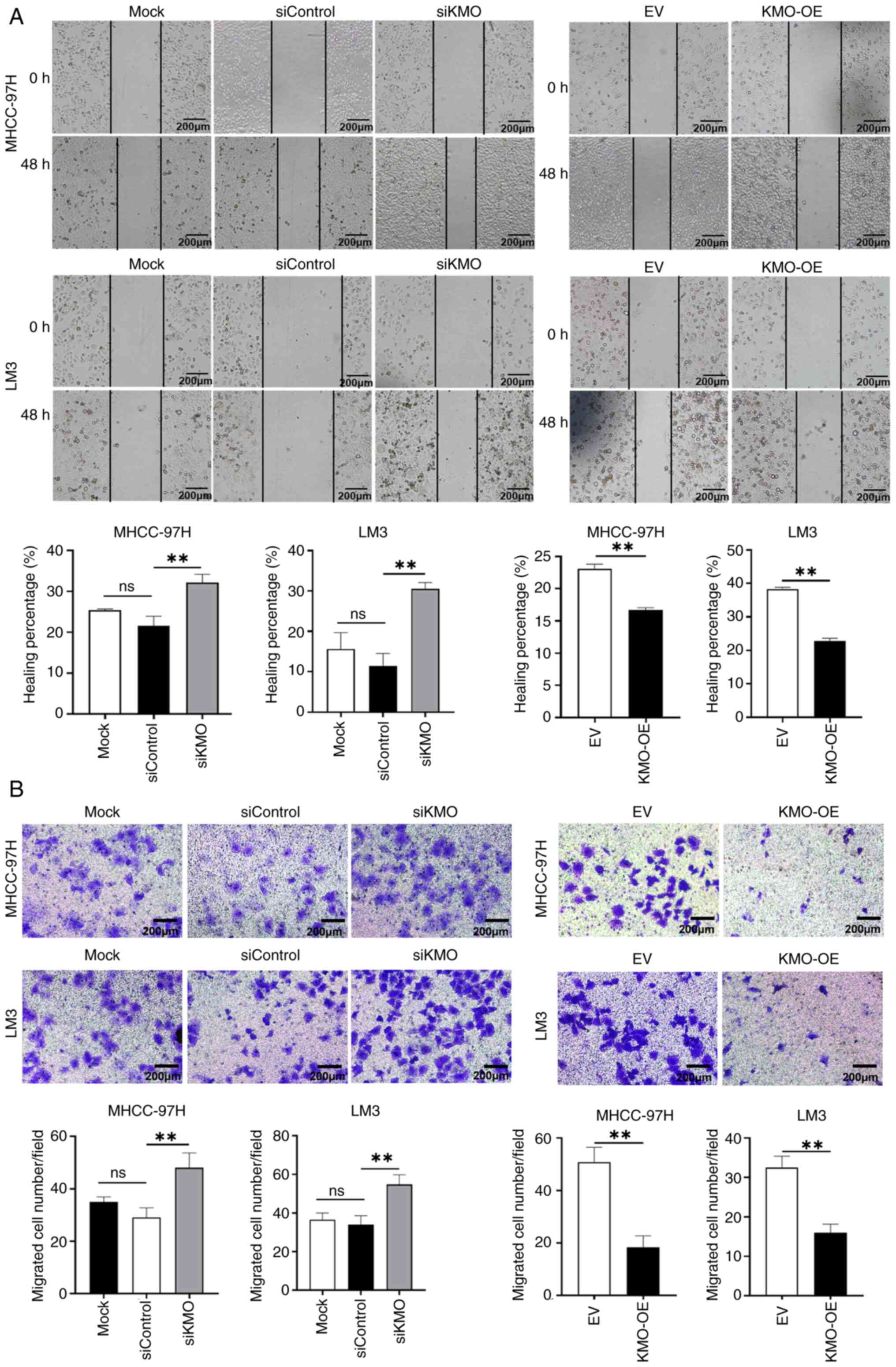
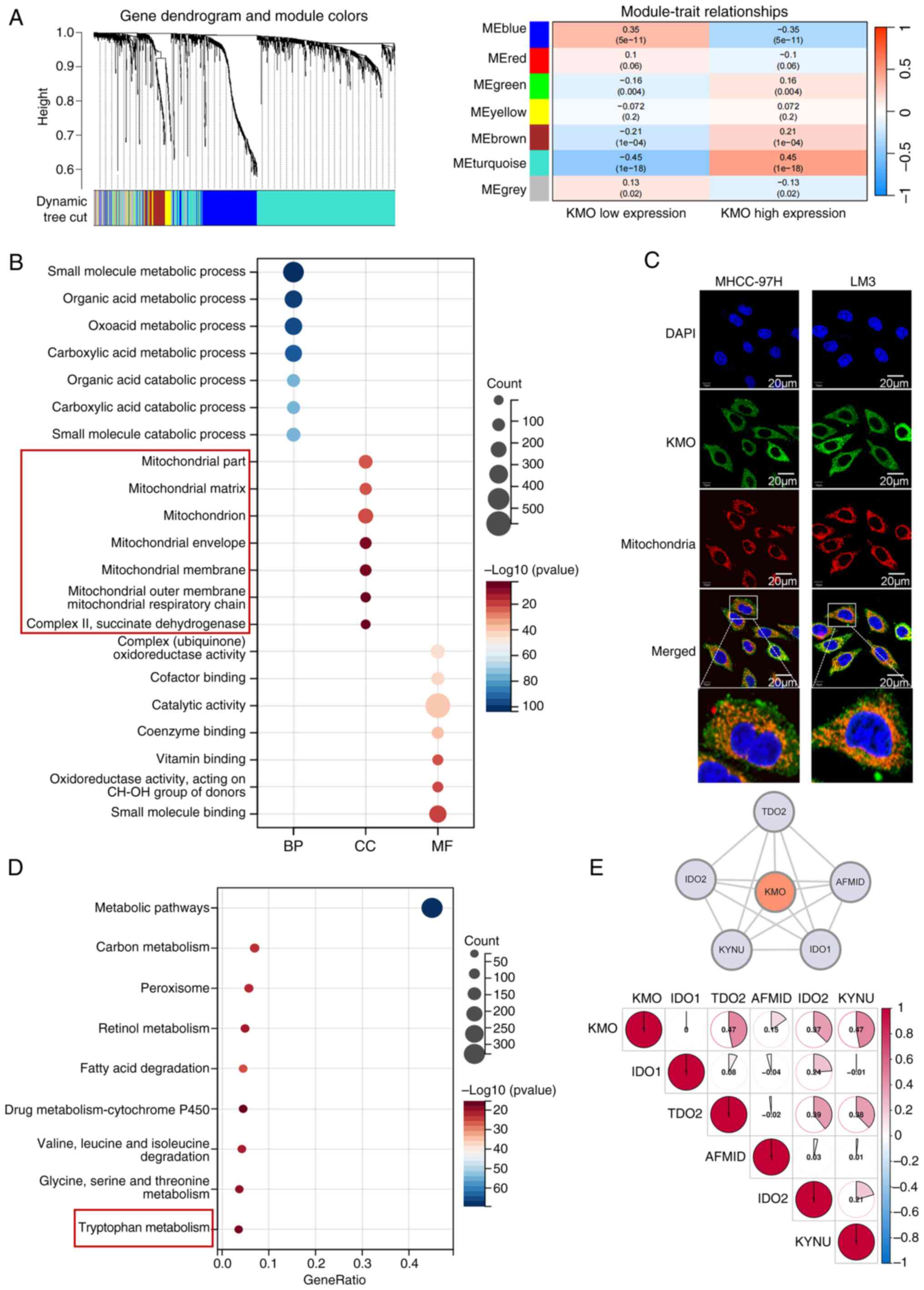
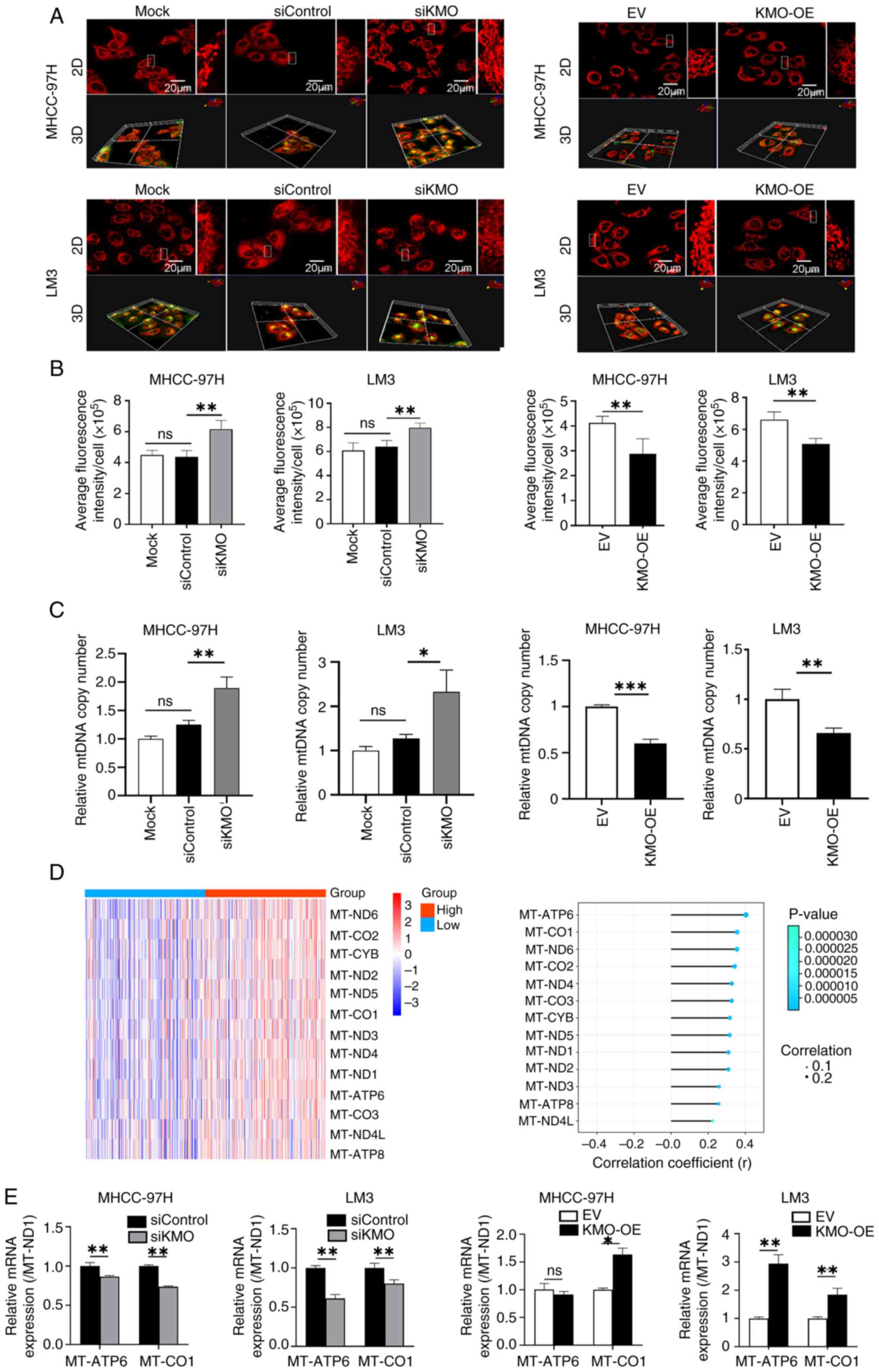
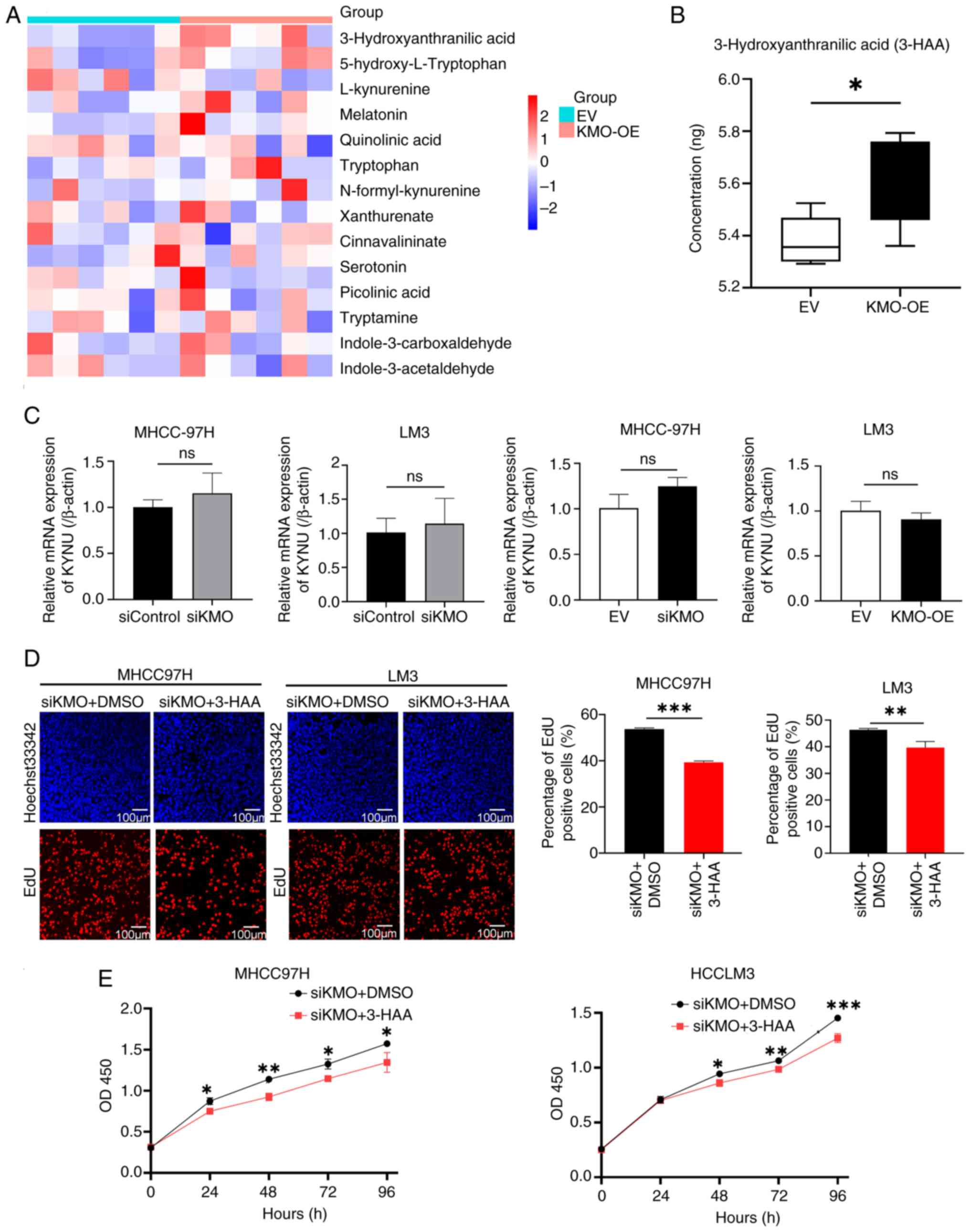
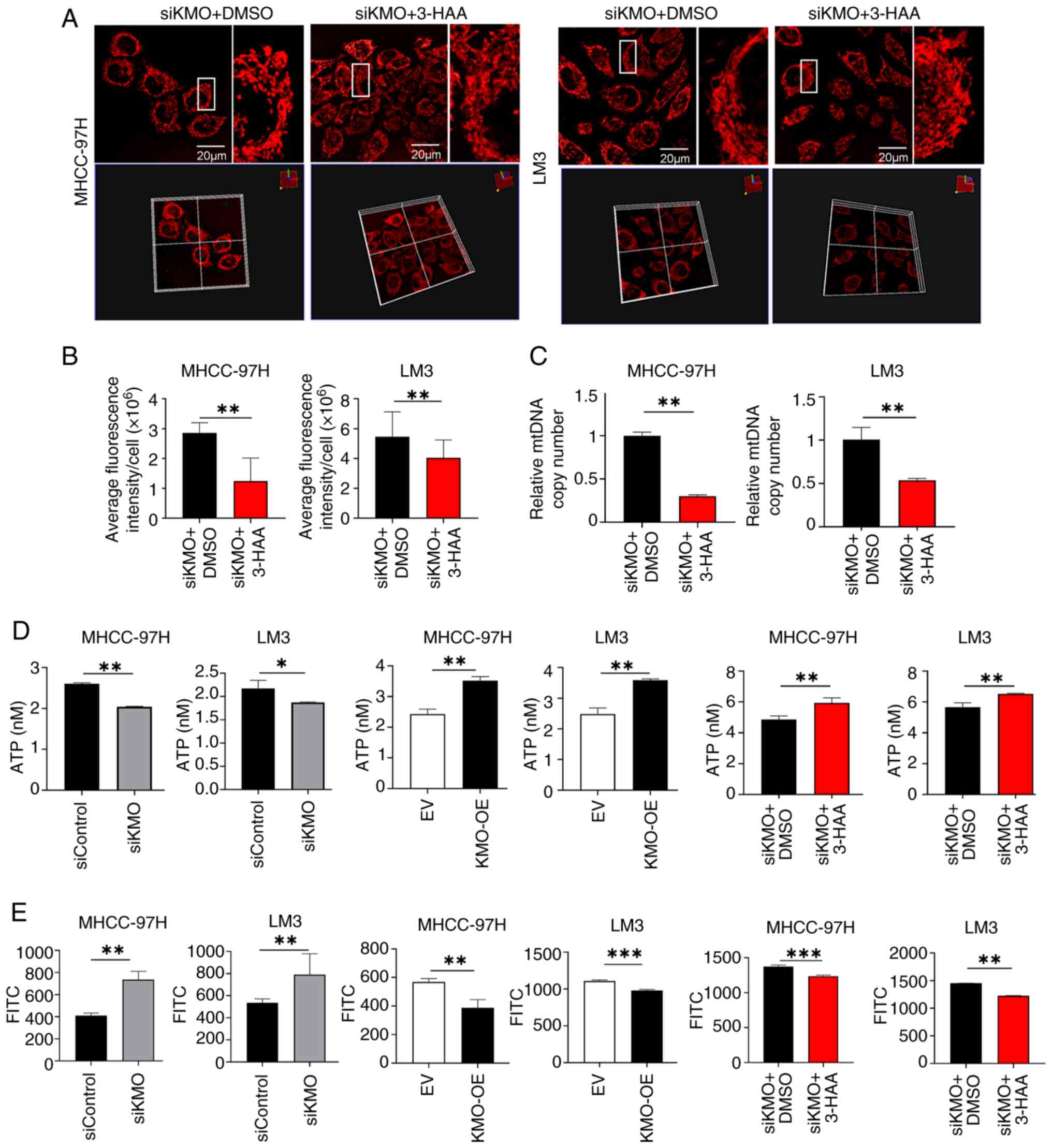
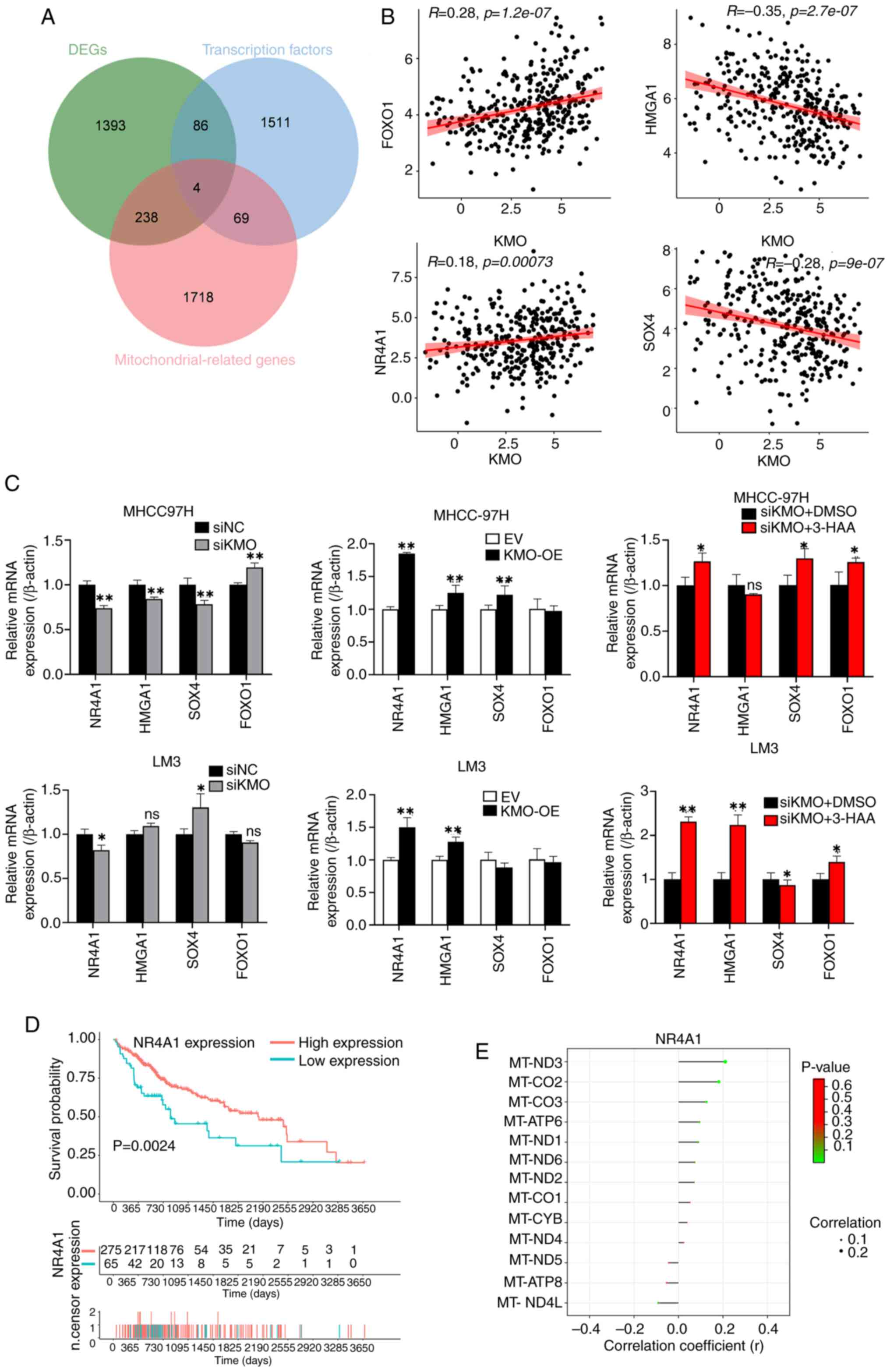
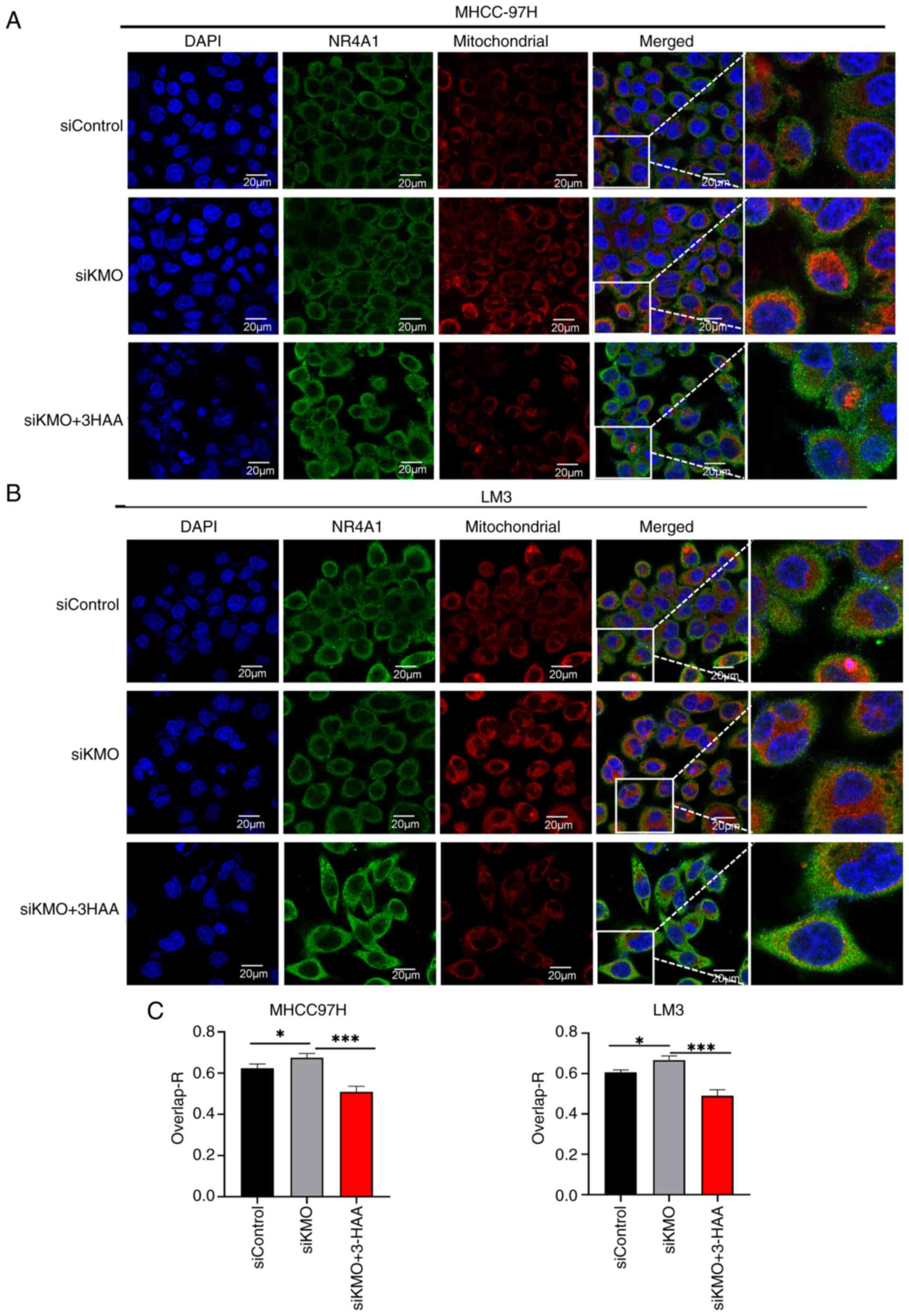
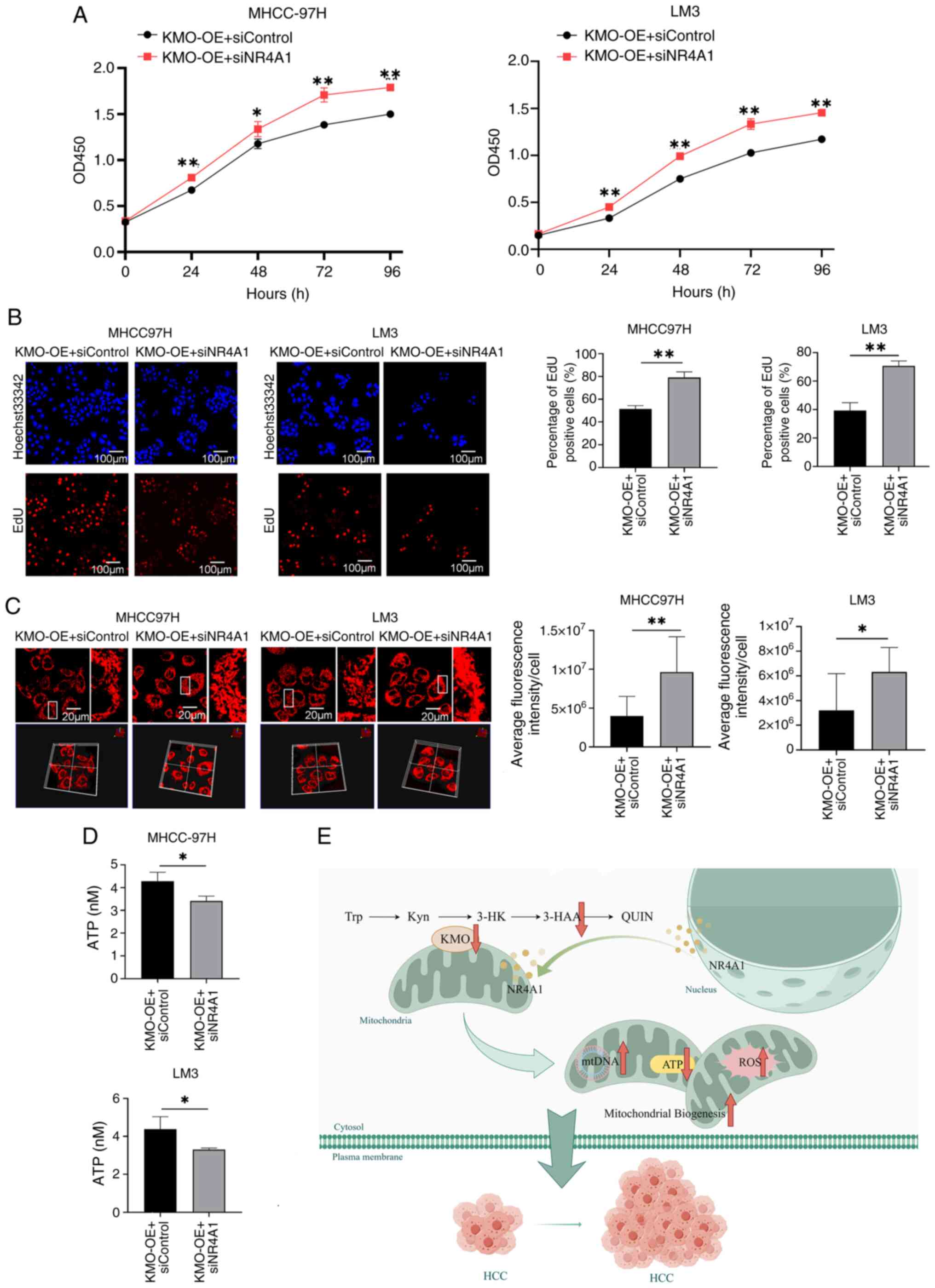
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C, Georges
D, Ibrahim AS, Zheng R, Wei W, Lemmens VEPP and Soerjomataram I:
Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by
subtype. Eur J Cancer. 161:108–118. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
de Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J
and Clifford GM: Global burden of cancer attributable to infections
in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob Health.
8:e180–e90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Marques HP, Gomes da Silva S, De Martin E,
Agopian VG and Martins PN: Emerging biomarkers in HCC patients:
Current status. Int J Surg. 82S:70–76. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R
and Saborowski A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 400:1345–1362.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo Y, Ma J and Lu W: The significance of
mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:55982020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu BH, Xu CZ, Liu Y, Lu ZL, Fu TL, Li GR,
Deng Y, Luo GQ, Ding S, Li N and Geng Q: Mitochondrial quality
control in human health and disease. Mil Med Res.
11:322024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Swaih AM, Breda C, Sathyasaikumar KV,
Allcock N, Collier MEW, Mason RP, Feasby A, Herrera F, Outeiro TF,
Schwarcz R, et al: Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase interacts with
huntingtin at the outer mitochondrial membrane. Biomedicines.
10:22942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uemura T and Hirai K: L-kynurenine
3-monooxygenase from mitochondrial outer membrane of pig liver:
Purification, some properties and monoclonal antibodies directed to
the enzyme. J Biochem. 123:253–262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maddison DC, Alfonso-Nunez M, Swaih AM,
Breda C, Campesan S, Allcock N, Straatman-Iwanowska A, Kyriacou CP
and Giorgini F: A novel role for kynurenine 3-monooxygenase in
mitochondrial dynamics. PLoS Genet. 16:e10091292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Zhao H and Li Y: Mitochondrial
dynamics in health and disease: Mechanisms and potential targets.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang TT, Tseng LM, Chen JL, Chu PY, Lee
CH, Huang CT, Wang WL, Lau KY, Tseng MF, Chang YY, et al:
Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase upregulates pluripotent genes through
β-catenin and promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression.
EBioMedicine. 54:1027172020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu CY, Huang TT, Chen JL, Chu PY, Lee CH,
Lee HC, Lee YH, Chang YY, Yang SH, Jiang JK, et al: Significance of
kynurenine 3-monooxygenase expression in colorectal cancer. Front
Oncol. 11:6203612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hornigold N, Dunn KR, Craven RA, Zougman
A, Trainor S, Shreeve R, Brown J, Sewell H, Shires M, Knowles M, et
al: Dysregulation at multiple points of the kynurenine pathway is a
ubiquitous feature of renal cancer: Implications for tumour immune
evasion. Br J Cancer. 123:137–147. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang H, Cheung LW, Li J, Ju Z, Yu S,
Stemke-Hale K, Dogruluk T, Lu Y, Liu X, Gu C, et al: Whole-exome
sequencing combined with functional genomics reveals novel
candidate driver cancer genes in endometrial cancer. Genome Res.
22:2120–2129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen N, Zong Y, Yang C, Li L, Yi Y, Zhao
J, Zhao X, Xie X, Sun X, Li N and Jiang L: KMO-driven metabolic
reconfiguration and its impact on immune cell infiltration in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A new avenue for immunotherapy. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 74:752025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SY and Nam JS: Kynurenine pathway
enzyme KMO in cancer progression: A tip of the Iceberg.
EBioMedicine. 55:1027622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan J, Chen D, Ye Z, Zhu X, Li X, Jiao H,
Duan M, Zhang C, Cheng J, Xu L, et al: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic significance of tryptophan metabolism and signaling in
cancer. Mol Cancer. 23:2412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin H, Zhang Y, You H, Tao X, Wang C, Jin
G, Wang N, Ruan H, Gu D, Huo X, et al: Prognostic significance of
kynurenine 3-monooxygenase and effects on proliferation, migration
and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep.
5:104662015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shi Z, Gan G, Gao X, Chen F and Mi J:
Kynurenine catabolic enzyme KMO regulates HCC growth. Clin Transl
Med. 12:e6972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang D, Chen M, Huang X, Zhang G, Zeng L,
Zhang G, Wu S and Wang Y: SRplot: A free online platform for data
visualization and graphing. PLoS One. 18:e02942362023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu J, Ru NY, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wei D, Ren Z,
Huang XF, Chen ZN and Bian H: HAb18G/CD147 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through TGF-β signaling and is
transcriptionally regulated by Slug. Oncogene. 30:4410–4427. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shi Z, Gan G, Xu X, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Bi B,
Gao X, Xu P, Zeng W, Li J, et al: Kynurenine derivative 3-HAA is an
agonist ligand for transcription factor YY1. J Hematol Oncol.
14:1532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong Q, Liang Q, Tan Y, Luo X, Ling Y, Li
X, Cai Y and Chen H: Induction of ferroptosis by SIRT1 knockdown
alleviates cytarabine resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by
activating the HMGB1/ACSL4 pathway. Int J Oncol. 66:22025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Wu H, Niu J, Hu Y, Zhang W, Chang
J, Li L, Zhu J, Zhang C and Liu M: A novel mitochondria-related
gene signature in esophageal carcinoma: Prognostic, immune and
therapeutic features. Funct Integr Genomics. 23:1092023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Trezeguet V, Fatrouni H and Merched AJ:
Immuno-metabolic modulation of liver oncogenesis by the tryptophan
metabolism. Cells. 10:34692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fiore A and Murray PJ: Tryptophan and
indole metabolism in immune regulation. Curr Opin Immunol. 70:7–14.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ and Ruas JL:
Kynurenines: Tryptophan's metabolites in exercise, inflammation and
mental health. Science. 357:eaaf97942017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Krishnamurthy S, Gilot D, Ahn SB, Lam V,
Shin JS, Guillemin GJ and Heng B: Involvement of kynurenine pathway
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 13:51802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai Q, Wu L, Dong S, Zhu X, Fan Z, Kou J,
Liu F, Yu B and Li F: Inhibition of KMO ameliorates myocardial
ischemia injury via maintaining mitochondrial fusion and fission
balance. Int J Biol Sci. 19:3077–3098. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen B, Xie K, Zhang J, Yang L, Zhou H,
Zhang L and Peng R: Comprehensive analysis of mitochondrial
dysfunction and necroptosis in intracranial aneurysms from the
perspective of predictive, preventative and personalized medicine.
Apoptosis. 28:1452–1468. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Bai Y, Cai Y, Zhang Y, Shen L, Xi
W, Zhou Z, Xu L, Liu X, Han B and Yao H: Circular RNA SCMH1
suppresses KMO expression to inhibit mitophagy and promote
functional recovery following stroke. Theranostics. 14:7292–7308.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu ZQ, Ciudad MT and McGaha TL: New
insights into tryptophan metabolism in cancer. Trends Cancer.
11:629–641. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xue C, Gu X, Zheng Q, Shi Q, Yuan X, Chu
Q, Jia J, Su Y, Bao Z, Lu J and Li L: Effects of 3-HAA on HCC by
regulating the heterogeneous macrophages-A scRNA-Seq analysis. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 10:e22070742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gan G, Shi Z, Shangguan C, Zhang J, Yuan
Y, Chen L, Liu W, Li B, Meng S, Xiong W and Mi J: The kynurenine
derivative 3-HAA sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib
by upregulating phosphatases. Theranostics. 11:6006–6018. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gan G, Shi Z, Liu D, Zhang S, Zhu H, Wang
Y and Mi J: 3-hydroxyanthranic acid increases the sensitivity of
hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib by decreasing tumor cell
stemness. Cell Death Discov. 7:1732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pan X, Wang W, Wang Y, Gu J and Ma X: M2
macrophage-secreted KYNU promotes stemness remodeling and malignant
behavior in endometrial cancer via the SOD2-mtROS-ERO1alpha-UPR(ER)
axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44:1932025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ruan Q, Peng Y, Yi X, Yang J, Ai Q, Liu X,
He Y and Shi Y: The tryptophan metabolite 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid
alleviates hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia via
inhibiting ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 82:1035792025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SO, Li X, Khan S and Safe S: Targeting
NR4A1 (TR3) in cancer cells and tumors. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
15:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, Li N, Guan W and Wang D:
Controversy and multiple roles of the solitary nucleus receptor
Nur77 in disease and physiology. FASEB J. 39:e704682025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen QT, Zhang ZY, Huang QL, Chen HZ, Hong
WB, Lin T, Zhao WX, Wang XM, Ju CY, Wu LZ, et al: HK1 from hepatic
stellate cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes progression
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Metab. 4:1306–1321. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bian XL, Chen HZ, Yang PB, Li YP, Zhang
FN, Zhang JY, Wang WJ, Zhao WX, Zhang S, Chen QT, et al: Nur77
suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via switching glucose
metabolism toward gluconeogenesis through attenuating
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase sumoylation. Nat Commun.
8:144202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang H, Nie Y, Li Y and Wan YJ: ERK1/2
deactivation enhances cytoplasmic Nur77 expression level and
improves the apoptotic effect of fenretinide in human liver cancer
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 81:910–916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fu R, Ling D, Zhang Q, Jiang A and Pang H:
Harnessing Nur77's mitochondrial apoptotic pathway: A promising
therapeutic strategy for targeted disease intervention. Biomed
Pharmacother. 187:1180912025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ye H, Lin J, Zhang H, Wang J, Fu Y, Zeng
Z, Zheng J, Tao J and Qiu J: Nuclear receptor 4A1 regulates
mitochondrial homeostasis in cardiac post-ischemic injury by
controlling mitochondrial fission 1 protein-mediated fragmentation
and parkin-dependent mitophagy. Int J Biol Sci. 21:400–414. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Koenis DS, Evers-van Gogh IJA, van Loenen
PB, Zwart W, Kalkhoven E and de Vries CJM: Nuclear receptor Nur77
and Yin-Yang 1 synergistically increase mitochondrial abundance and
activity in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 598:1715–1729. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yin S, Zhai Y, Song R, Wu J, Zhang Y, Yu
M, Ma H, Shen M, Lai X, Jin W, et al: PARL stabilizes mitochondrial
Bcl-2 via Nur77-mediated scaffolding as a therapeutic strategy for
Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis. 16:7002025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|